Abstract
Background
Whether Smad7 acts as a tumor proliferation promoting factor or as a metastatic suppressor in human pancreatic cancer remains unclear. This study aims to determine the prognostic value of Smad7 in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Methods
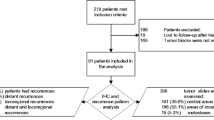
Surgical specimens obtained from 71 patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma were immunohistochemically assessed for Smad7, Ki-67, MMP2, CD34, and Smad4 expression. The relationship between Smad7 expression and the clinicopathological characteristics of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma were also evaluated.
Results
Fifty-one of 71 specimens (71.8%) were Smad7 positive and 20 specimens were Smad7 negative. Negative expression of Smad7 correlated with lymph node metastasis, liver metastasis after surgery, and a poor survival rate (P = 0.0004, 0.0044, and 0.0003, respectively). We also found an inverse correlation between the expression of Smad7 and MMP2 (P = 0.0189). Multivariate analysis revealed that Smad7 expression was an independent prognostic factor [hazard ratio (HR) 0.3902; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.1839–0.8277; P = 0.0142]. Furthermore, in both Smad4-negative and Smad4-positive groups, survival of patients with Smad7-positive tumors was significantly better than those with Smad7-negative tumors (both P < 0.0001).
Conclusions
We conclude that low-level expression of Smad7 in pancreatic cancer is significantly associated with lymph node metastasis, high MMP2 expression, and poor prognosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goggins M, Shekher M, Turnacioglu K, et al. Genetic alterations of the transforming growth factor beta receptor genes in pancreatic and biliary adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5329–32.
Jonson T, Gorunova L, Dawiskiba S, et al. Molecular analyses of the 15q and 18q SMAD genes in pancreatic cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1999;24:62–71.
Villanueva A, Garcia C, Paules AB, et al. Disruption of the antiproliferative TGF-beta signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene. 1998;17:1969–78.
Markowitz S, Wang J, Myeroff L, et al. Inactivation of the type II TGF-beta receptor in colon cancer cells with microsatellite instability. Science. 1995;268:1336–8.
Hahn SA, Schutte M, Hoque AT, et al. DPC4, a candidate tumor suppressor gene at human chromosome 18q21.1. Science. 1996;271:350–3.
Schutte M, Hruban RH, Hedrick L, et al. DPC4 gene in various tumor types. Cancer Res. 1996;56:2527–30.
Togo G, Toda N, Kanai F, et al. A transforming growth factor beta type II receptor gene mutation common in sporadic cecum cancer with microsatellite instability. Cancer Res. 1996;56:5620–3.
Miyaki M, Iijima T, Konishi M, et al. Higher frequency of Smad4 gene mutation in human colorectal cancer with distant metastasis. Oncogene. 1999;18:3098–103.
Wang D, Kanuma T, Mizunuma H, et al. Analysis of specific gene mutations in the transforming growth factor-beta signal transduction pathway in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2000;60:4507–12.
Boulay JL, Mild G, Lowy A, et al. SMAD7 is a prognostic marker in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2003;104:446–9.
Cerutti JM, Ebina KN, Matsuo SE, et al. Expression of Smad4 and Smad7 in human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines. J Endocrinol Invest. 2003;26:516–21.
Kim YH, Lee HS, Lee HJ, et al. Prognostic significance of the expression of Smad4 and Smad7 in human gastric carcinomas. Ann Oncol. 2004;15:574–80.
Monteleone G, Del Vecchio Blanco G, Palmieri G, et al. Induction and regulation of Smad7 in the gastric mucosa of patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:674–82.
Dowdy SC, Mariani A, Reinholz MM, et al. Overexpression of the TGF-beta antagonist Smad7 in endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;96:368–73.
Kuang C, Xiao Y, Liu X, et al. In vivo disruption of TGF-beta signaling by Smad7 leads to premalignant ductal lesions in the pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:1858–63.
Kleeff J, Maruyama H, Friess H, et al. Smad6 suppresses TGF-beta-induced growth inhibition in COLO–357 pancreatic cancer cells and is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;255:268–73.
Halder SK, Beauchamp RD, Datta PK. Smad7 induces tumorigenicity by blocking TGF-beta-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 2005;307:231–46.
Akhurst RJ, Derynck R. TGF-beta signaling in cancer—a double-edged sword. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:S44–51.
Wakefield LM, Roberts AB. TGF-beta signaling: positive and negative effects on tumorigenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002;12:22–9.
Azuma H, Ehata S, Miyazaki H, et al. Effect of Smad7 expression on metastasis of mouse mammary carcinoma JygMC(A) cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:1734–46.
Javelaud D, Mohammad KS, McKenna CR, et al. Stable overexpression of Smad7 in human melanoma cells impairs bone metastasis. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2317–24.
Sobin LH, Wittekind CH. International Union Against Cancer. TNM classification of malignant tumours (6th ed.). New York: Wiley-Liss; 2002.
Fukuchi M, Fukai Y, Masuda N, et al. High-level expression of the Smad ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 correlates with poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:7162–5.
Takahashi H, Oda T, Hasebe T, et al. Biologically different subgroups of invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas: Dpc4 status according to the ratio of intraductal carcinoma components. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:3772–9.
Ebisawa T, Fukuchi M, Murakami G, et al. Smurf1 interacts with transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor through Smad7 and induces receptor degradation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:12477–80.
Shi W, Sun C, He B, et al. GADD34-PP1c recruited by Smad7 dephosphorylates TGFbeta type I receptor. J Cell Biol. 2004;164:291–300.
Hata A, Lagna G, Massague J, et al. Smad6 inhibits BMP/Smad1 signaling by specifically competing with the Smad4 tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 1998;12:186–97.
Bai S, Cao X. A nuclear antagonistic mechanism of inhibitory Smads in transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:4176–82.
Osawa H, Nakajima M, Kato H, et al. Prognostic value of the expression of Smad6 and Smad7, as inhibitory Smads of the TGF-beta superfamily, in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2004;24:3703–9.
Kleeff J, Ishiwata T, Maruyama H, et al. The TGF-beta signaling inhibitor Smad7 enhances tumorigenicity in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. 1999;18:5363–72.
Zhu HJ, Iaria J, Sizeland AM. Smad7 differentially regulates transforming growth factor beta-mediated signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:32258–64.
Dahler AL, Cavanagh LL, Saunders NA. Suppression of keratinocyte growth and differentiation by transforming growth factor beta1 involves multiple signaling pathways. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:266–74.
Blanchette F, Rivard N, Rudd P, et al. Cross-talk between the p42/p44 MAP kinase and Smad pathways in transforming growth factor beta 1-induced furin gene transactivation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:33986–94.
Javelaud D, Delmas V, Moller M, et al. Stable overexpression of Smad7 in human melanoma cells inhibits their tumorigenicity in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 2005;24:7624–9.
Boyer Arnold N, Korc M. Smad7 abrogates transforming growth factor-beta1-mediated growth inhibition in COLO–357 cells through functional inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:21858–66.
Kleeff J, Korc M. Up-regulation of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta receptors by TGF-beta1 in COLO-357 cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:7495–500.
Nicolas FJ, Hill CS. Attenuation of the TGF-beta-Smad signaling pathway in pancreatic tumor cells confers resistance to TGF-beta-induced growth arrest. Oncogene. 2003;22:3698–711.
Subramanian G, Schwarz RE, Higgins L, et al. Targeting endogenous transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling in SMAD4-deficient human pancreatic carcinoma cells inhibits their invasive phenotype1. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5200–11.
Pardali K, Moustakas A. Actions of TGF-beta as tumor suppressor and pro-metastatic factor in human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1775:21–62.
Ijichi H, Ikenoue T, Kato N, et al. Systematic analysis of the TGF-beta-Smad signaling pathway in gastrointestinal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;289:350–7.
Ijichi H, Otsuka M, Tateishi K, et al. Smad4-independent regulation of p21/WAF1 by transforming growth factor-beta. Oncogene. 2004;23:1043–51.
Leivonen SK, Ala-Aho R, Koli K, et al. Activation of Smad signaling enhances collagenase-3 (MMP-13) expression and invasion of head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2006;25:2588–600.
Delcore R, Rodriguez FJ, Forster J, et al. Significance of lymph node metastases in patients with pancreatic cancer undergoing curative resection. Am J Surg. 1996;172:463–8; discussion 8–9
Pedrazzoli S, DiCarlo V, Dionigi R, et al. Standard versus extended lymphadenectomy associated with pancreatoduodenectomy in the surgical treatment of adenocarcinoma of the head of the pancreas: a multicenter, prospective, randomized study. Lymphadenectomy Study Group. Ann Surg. 1998;228:508–17.
Koshiba T, Hosotani R, Wada M, et al. Involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity in invasion and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer. 1998;82:642–50.
Juuti A, Lundin J, Nordling S, et al. Epithelial MMP-2 expression correlates with worse prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Oncology. 2006;71:61–8.
Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;438:932–6.
Enholm B, Paavonen K, Ristimaki A, et al. Comparison of VEGF, VEGF-B, VEGF-C and Ang-1 mRNA regulation by serum, growth factors, oncoproteins and hypoxia. Oncogene. 1997;14:2475–83.
Benckert C, Jonas S, Cramer T, et al. Transforming growth factor beta 1 stimulates vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription in human cholangiocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1083–92.
Dickson MC, Martin JS, Cousins FM, et al. Defective haematopoiesis and vasculogenesis in transforming growth factor-beta 1 knock out mice. Development. 1995;121:1845–54.
Oshima M, Oshima H, Taketo MM. TGF-beta receptor type II deficiency results in defects of yolk sac hematopoiesis and vasculogenesis. Dev Biol. 1996;179:297–302.
Li DY, Sorensen LK, Brooke BS, et al. Defective angiogenesis in mice lacking endoglin. Science. 1999;284:1534–7.
Larsson J, Goumans MJ, Sjostrand LJ, et al. Abnormal angiogenesis but intact hematopoietic potential in TGF-beta type I receptor-deficient mice. EMBO J. 2001;20:1663–73.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the “Climbing Up” Project of Shanghai Municipal Commission for Science and Technology, Shanghai, China, grant number GJ-KW0601.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Peng Wang and Jie Fan contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Fan, J., Chen, Z. et al. Low-Level Expression of Smad7 Correlates with Lymph Node Metastasis and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 16, 826–835 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-0284-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-0284-5