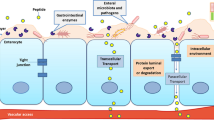
Abstract
To manage early morning symptoms of nocturnal bronchial asthma, a chronotherapeutic drug delivery system (ChrDDS) of montelukast sodium was designed and developed utilizing non-saccharide, fully synthetic Parteck® SRP 80, and hydrophilic cellulose derivative hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Recurrent lag phase, each followed by the release of a fraction of the drug dose, can be achieved by formulating a “tablets in a capsule” system containing more than one compressed coated tablet encapsulated in an enteric-coated capsule. Lag time in this study was controlled by the compressed coating of HPMC K4M and a blend of ethyl cellulose and Carbopol polymer. Assembly of the system includes two compressed coated tablets encapsulated in a capsule which was further proceeded for enteric coating in a conventional, a novel wax-based, and a Eudracap™ enteric-coated capsule. The optimized formulation of directly compressed tablets of Parteck ® SRP 80 showed a hardness of 8.8 kg/cm2 which is 1.25-fold higher than wet granulated tablets of HPMC. In vitro release data of matrix tablets of Parteck® SRP 80 demonstrated controlled release of drug for a duration of up to 10.8–11 h with changing ratio of polymer and filler. Eudracap™ capsule showed a minimum acid uptake value of 1.75%. The current approach can open a path for the time-regulated release of montelukast that may be beneficial for individuals with episodes of asthma attacks mostly in the early morning.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nainwal N. Chronotherapeutics - a chronopharmaceutical approach to drug delivery in the treatment of asthma. J Control Release [Internet]. 2012;163(3):353–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.09.012.
Ramakrishnan S, Zachariah G, Gupta K, Shivkumar Rao J, Mohanan PP, Venugopal K, et al. Prevalence of hypertension among Indian adults: results from the great India blood pressure survey. Indian Heart J. 2019;71(4):309–13.
Li B, Zhu JB, Zheng CL, Gong W. A novel system for three-pulse drug release based on “tablets in capsule” device. Int J Pharm. 2008;352(1–2):159–64.
Reinberg A, Smolensky M, Levi F. Aspects of clinical chronopharmacology. Cephalalgia. 1983;3(Suppl. 1):69–78.
Smolensky MH, Haus E. Circadian rhythms and clinical medicine with applications to hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2001;14(9 II):280–90.
Smolensky MH, Lemmer B, Reinberg AE. Chronobiology and chronotherapy of allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59(9–10):852–82.
Heart N. Nurses: partners in asthma care. National Institutes of Health National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. NIH; 1995 p. 445.
Studies on intermittent corticosteroid dosage regimen. JAMA J Am Med Assoc. 1963;186(3):227.
Dyer MJ, Halpin DMG, Stein K. Inhaled ciclesonide versus inhaled budesonide or inhaled beclomethasone or inhaled fluticasone for chronic asthma in adults: a systematic review. BMC Family Practice. 2006;7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2296-7-34
D’Alonzo GE, Smolensky MH, Feldman S, Gianotti LA, Emerson MB, Staudinger H, et al. Twenty-four hour lung function in adult patients with asthma. Chronoptimized theophylline therapy once-daily dosing in the evening versus conventional twice-daily dosing. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;142(1):84–90.
Munday DL, Fassihi AR. In vitro-in vivo correlation studies on a novel controlled release theophylline delivery system and on Theo-Dur tablets. Int J Pharm. 1995;118(2):251–5.
Hayashi T, Kanbe H, Okada M, Suzuki M, Ikeda Y, Onuki Y, et al. Formulation study and drug release mechanism of a new theophylline sustained-release preparation. Int J Pharm. 2005;304(1–2):91–101.
Dahl R, Harving H, Säwedal L, Anehus S. Terbutaline sustained-release tablets in nocturnal asthma-a placebo-controlled comparison between a high and a low evening dose. Br. J Dis Chest. 1988;82(C):237–41.
Kraft M. Corticosteroids and leukotrienes: chronobiology and chronotherapy. Chronobiol Int. 1999;16(5):683–93.
Kemp JP. Recent advances in the management of asthma using leukotriene modifiers. Am J Respir Med. 2003;2(2):139–56.
Drazen JM, Israel E, O'Byrne PM. Drug Therapy. In: Alastair JJ, Wood MD Editors. Treatment of asthma with drugs modifying the Leukotriene pathway. N Engl J Med. 1999;3:197–206.
Wenzel SE, Trudeau JB, Kaminsky DA, Cohn J, Martin RJ, Westcott JAYY. Effect of 5-Lipoxygenase inhibition on bronchoconstrictio and airway inflammation in nocturnal asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152:897–905.
Pajaron-Fernandez M, Garcia-Rubia S, Sanchez-Solis M, Garcia-Marcos L. Montelukast administered in the morning or evening to prevent exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2006;41(3):222–7.
Trial D. Montelukast, a once-daily leukotriene receptor antagonist, in the treatment of chronic asthma. Hispanic. 2012;158:1213–20.
Noonan MJ, Chervinsky P, Brandon M, Zhang J, Kundu S, McBurney J, et al. Montelukast, a potent leukotriene receptor antagonist, causes dose-related improvements in chronic asthma. Eur Respir J. 1998;11(6):1232–9.
Altman LC, Munk Z, Seltzer J, Noonan N, Shingo S, Zhang J, Reiss TF. A placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of montelukast, a cysteinyl leukotriene – receptor antagonist. In Montelukast Asthma Study Group: Seattle Wash, Houston Tex, San Diego Calif, Rahway NJ. J Allergy Clin Immunol ;102(1):50–6.
Bernatoniene J, Civinskiene G, Savickas A. Determination of optimal amount of auxiliary substances required for purple coneflower extract tablets formation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2007;32(1):S22–3.
Duncan QM, Craig MR. Thermal analysis of pharmaceuticals. In: Duncan QM. Craig, Mike Reading, editors, 1st ed. CRC Press; 2006. p. 416. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420014891
Karavas E, Georgarakis E, Bikiaris D. Application of PVP/HPMC miscible blends with enhanced mucoadhesive properties for adjusting drug release in predictable pulsatile chronotherapeutics. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2006;64(1):115–26.
Evonik markets new enteric protected ready-to-fill capsules for fast, high-performance drug development [Internet]. 2021. Available from: https://healthcare.evonik.com/en/evonik-markets-new-enteric-protected-ready-to-fill-capsules-for-fast-high-performance-drug-developme-158686.html.
Habashy R, Khoder M, Zhang S, Pereira B, Bohus M, Tzu-Wen Wang J, et al. An innovative wax-based enteric coating for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical oral products. Int J Pharm. [Internet]. 2020;591(October):119935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119935.
Bohrey S, Chourasiya V, Pandey A. Polymeric nanoparticles containing diazepam: preparation, optimization, characterization, in-vitro drug release and release kinetic study. Nano Converg. 2016;3(1):3–9.
Patil-Gadhe A, Pokharkar V. Montelukast-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: part I oral bioavailability improvement. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. [Internet]. 2014;88(1):160–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2014.05.019.
Dash S, Murthy PN, Nath L, Chowdhury P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol Pharm - Drug Res. 2010;67(3):217–23.
Maroni A, Zema L, Cerea M, Foppoli A, Palugan L, Gazzaniga A. Erodible drug delivery systems for time-controlled release into the gastrointestinal tract. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. [Internet]. 2016;32:229–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2015.10.001.
Singh B, Chakkal SK, Ahuja N. Formulation and optimization of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of atenolol using response surface methodology. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2006;7(1):1–10.
Gyarmati B, Stankovits G, Szilágyi BÁ, Galata DL, Gordon P, Szilágyi A. A robust mucin-containing poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel model for the in vitro characterization of mucoadhesion of solid dosage forms. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces. 2022;213(February):0–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors express gratitude towards Merck Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Mumbai India, Evonik Healthcare, Essen, Germany, and Shin-Etsu Chemical Tylose India Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, for providing Parteck SRP 80, Eudracap™ ready-to-fill capsule, and HPMC phthalate respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Saniya Jawed: methodology, carried out formulation and evaluation, writing the original draft. Satish CS: reviewing, editing, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jawed, S., CS, S. Exploration of Parteck® SRP 80 and Hypromellose for Chronomodulated Release of LTD4 Receptor Antagonist and Statistical Optimization Using Central Composite Design. AAPS PharmSciTech 23, 263 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02415-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02415-5