Abstract
The delivery of proteins and peptides via an oral route poses numerous challenges to improve the oral bioavailability and patient compliance. To overcome these challenges, as well as to improve the permeation of proteins and peptides via intestinal mucosa, several chemicals have been studied such as surfactants, fatty acids, bile salts, pH modifiers, and chelating agents, amongst these medium chain fatty acid like C10 (sodium caprate) and Sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] caprylate (SNAC) and its derivatives that have been well studied from a clinical perspective. This current review enumerates the challenges involved in protein and peptide delivery via the oral route, i.e., non-invasive routes of protein and peptide administration. This review also covers the chemistry behind SNAC and toxicity as well as mechanisms to enhance the oral delivery of clinically proven molecules like simaglutide and other small molecules under clinical development, as well as other permeation enhancers for efficient delivery of proteins and peptides.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whitehead K, Karr N, Mitragotri S. Safe and effective permeation enhancers for oral drug delivery. Pharm Res. 2008;25(8):1782–8.
Fuhrmann G, Leroux J-C. Improving the stability and activity of oral therapeutic enzymes—Recent advances and perspectives. Pharm Res. 2014;31(5):1099–105.
Gupta V, Hwang BH, Doshi N, Mitragotri S. A permeation enhancer for increasing transport of therapeutic macromolecules across the intestine. J Control Release. 2013;172(2):541–9.
Renukuntla J, Vadlapudi AD, Patel A, Boddu SH, Mitra AK. Approaches for enhancing oral bioavailability of peptides and proteins. Int J Pharm. 2013;447(1–2):75–93.
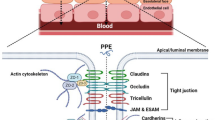
Salama NN, Eddington ND, Fasano A. Tight junction modulation and its relationship to drug delivery. Tight junctions. 2006:206–219.
Jain S, Rathi VV, Jain AK, Das M, Godugu C. Folate-decorated PLGA nanoparticles as a rationally designed vehicle for the oral delivery of insulin. Nanomedicine. 2012;7(9):1311–37.
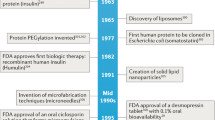
Bulbake U, Doppalapudi S, Kommineni N, Khan W. Liposomal formulations in clinical use: an updated review. Pharmaceutics. 2017;9(2):12.
Déat-Lainé E, Hoffart V, Garrait G, Jarrige J-F, Cardot J-M, Subirade M, Beyssac E. Efficacy of mucoadhesive hydrogel microparticles of whey protein and alginate for oral insulin delivery. Pharm Res. 2013;30(3):721–34.
Salamat-Miller N, Johnston TP. Current strategies used to enhance the paracellular transport of therapeutic polypeptides across the intestinal epithelium. Int J Pharm. 2005;294(1–2):201–16.
Drucker DJ, Habener JF, Holst JJ. Discovery, characterization, and clinical development of the glucagon-like peptides. J Clin Investig. 2017;127(12):4217–27.
Al-Hilal TA, Alam F, Byun Y. Oral drug delivery systems using chemical conjugates or physical complexes. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(6):845–64.
Maher S, Ryan B, Duffy A, Brayden DJ. Formulation strategies to improve oral peptide delivery. Pharmaceutical patent analyst. 2014;3(3):313–36.
Rosenthal R, Heydt MS, Amasheh M, Stein C, Fromm M, Amasheh S. Analysis of absorption enhancers in epithelial cell models. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012;1258(1):86–92.
Kondoh M, Yoshida T, Kakutani H, Yagi K. Targeting tight junction proteins-significance for drug development. Drug Discovery Today. 2008;13(3–4):180–6.
Maher S, Brayden DJ, Casettari L, Illum L. Application of permeation enhancers in oral delivery of macromolecules: an update. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(1):41.
Maher S, Mrsny RJ, Brayden DJ. Intestinal permeation enhancers for oral peptide delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;106:277–319.
Zupančič O, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Lipophilic peptide character–What oral barriers fear the most. J Control Release. 2017;255:242–57.
Krug SM, Amasheh M, Dittmann I, Christoffel I, Fromm M, Amasheh S. Sodium caprate as an enhancer of macromolecule permeation across tricellular tight junctions of intestinal cells. Biomaterials. 2013;34(1):275–82.
Rosenthal R, Günzel D, Finger C, Krug SM, Richter JF, Schulzke J-D, Fromm M, Amasheh S. The effect of chitosan on transcellular and paracellular mechanisms in the intestinal epithelial barrier. Biomaterials. 2012;33(9):2791–800.
Twarog C, McCartney F, Harrison SM, Illel B, Fattal E, Brayden DJ. Comparison of the effects of the intestinal permeation enhancers, SNAC and sodium caprate (C10): Isolated rat intestinal mucosae and sacs. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021;158: 105685.
Castelli MC, Friedman K, Sherry J, Brazzillo K, Genoble L, Bhargava P, Riley MGI. Comparing the efficacy and tolerability of a new daily oral vitamin B12 formulation and intermittent intramuscular vitamin B12 in normalizing low cobalamin levels: a randomized, open-label, parallel-group study. Clinical therapeutics. 2011;33(3):358–371. e352.
Davies M, Pieber TR, Hartoft-Nielsen M-L, Hansen OK, Jabbour S, Rosenstock J. Effect of oral semaglutide compared with placebo and subcutaneous semaglutide on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318(15):1460–70.
Sastry SV, Nyshadham JR, Fix JA. Recent technological advances in oral drug delivery–a review. Pharm Sci Technol Today. 2000;3(4):138–45.
Brown DG, Wobst HJ. A decade of FDA-approved drugs (2010–2019): trends and future directions. J Med Chem. 2021;64(5):2312–38.
Soltero R, Soltero R. Oral protein and peptide drug delivery. In.: Wiley Online Library; 2005. p. 189–200.
Liu NF, Brown AS, Folias AE, Younge MF, Guzman SJ, Close KL, Wood R. Stigma in people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Clinical Diabetes. 2017;35(1):27–34.
Shaji J, Patole V. Protein and peptide drug delivery: oral approaches. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2008;70(3):269.
Brown TD, Whitehead KA, Mitragotri S. Materials for oral delivery of proteins and peptides. Nat Rev Mater. 2020;5(2):127–48.
Zhou X, Po ALW. Peptide and protein drugs: II. Non-parenteral routes of delivery. International journal of pharmaceutics. 1991;75(2–3):117–130.
Fjellestad-Paulsen A, Höglund P, Lundin S, Paulsen O. Pharmacokinetics of 1-deamino-8-d-arginine vasopressin after various routes of administration in healthy volunteers. Clin Endocrinol. 1993;38(2):177–82.
Lee VH, Satish D, George M, Werner R. Oral route of protein and peptide drug delivery. Peptide and protein drug delivery New York: Marcel Dekker; 1991. p. 691–738.
Sayani AP, Chien YW. Systemic delivery of peptides and proteins across absorptive mucosae. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 1996;13(1–2):85–184.
Mahato RI, Narang AS, Thoma L, Miller DD. Emerging trends in oral delivery of peptide and protein drugs. Critical Reviews™ in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems. 2003;20(2&3).
Pauletti GM, Gangwar S, Knipp GT, Nerurkar MM, Okumu FW, Tamura K, Siahaan TJ, Borchardt RT. Structural requirements for intestinal absorption of peptide drugs. J Control Release. 1996;41(1–2):3–17.
Pauletti GM, Gangwar S, Siahaan TJ, Aubé J, Borchardt RT. Improvement of oral peptide bioavailability: Peptidomimetics and prodrug strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997;27(2–3):235–56.
Kahns AH, Friis GJ, Bundgaard H. Protection of the peptide bond against α-chymotrypsin by the prodrug approach. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1993;3(5):809–12.
Gangwar S, Pauletti GM, Wang B, Siahaan TJ, Stella VJ, Borchardt RT. Prodrug strategies to enhance the intestinal absorption of peptides. Drug Discovery Today. 1997;2(4):148–55.
Borchardt RT. Optimizing oral absorption of peptides using prodrug strategies. J Control Release. 1999;62(1–2):231–8.
Roberts M, Bentley M, Harris J. Chemistry for peptide and protein PEGylation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:116–27.
Hinds KD, Kim SW. Effects of PEG conjugation on insulin properties. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002;54(4):505–30.
Cefalu WT. Concept, strategies, and feasibility of noninvasive insulin delivery. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(1):239–46.
Wang J, Chow D, Heiati H, Shen W-C. Reversible lipidization for the oral delivery of salmon calcitonin. J Control Release. 2003;88(3):369–80.
Qvit N, Rubin SJ, Urban TJ, Mochly-Rosen D, Gross ER. Peptidomimetic therapeutics: scientific approaches and opportunities. Drug Discovery Today. 2017;22(2):454–62.
Jones RM, Boatman PD, Semple G, Shin YJ, Tamura SY. Clinically validated peptides as templates for de novo peptidomimetic drug design at G-protein-coupled receptors. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003;3(5):530–43.
Friedrichsen GM, Nielsen CU, Steffansen B, Begtrup M. Model prodrugs designed for the intestinal peptide transporter. A synthetic approach for coupling of hydroxy-containing compounds to dipeptides. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2001;14(1):13–19.
Daugherty AL, Mrsny RJ. Transcellular uptake mechanisms of the intestinal epithelial barrier Part one. Pharm Sci Technol Today. 1999;4(2):144–51.
Russell-Jones GJ, Arthur L, Walker H. Vitamin B12-mediated transport of nanoparticles across Caco-2 cells. Int J Pharm. 1999;179(2):247–55.
Baird AW, Campion DP, O’Brien L, Brayden DJ. Oral delivery of pathogens from the intestine to the nervous system. J Drug Target. 2004;12(2):71–8.
Langguth P, Bohner V, Heizmann J, Merkle H, Wolffram S, Amidon G, Yamashita S. The challenge of proteolytic enzymes in intestinal peptide delivery. J Control Release. 1997;46(1–2):39–57.
Bernkop-Schnürch A. The use of inhibitory agents to overcome the enzymatic barrier to perorally administered therapeutic peptides and proteins. J Control Release. 1998;52(1–2):1–16.
Brahmbhatt D. Bioadhesive drug delivery systems: Overview and recent advances. Int J Chem Life Sci. 2017;6(3):2016–24.
Boddupalli BM, Mohammed ZN, Nath RA, Banji D. Mucoadhesive drug delivery system: An overview. Journal of advanced pharmaceutical technology & research. 2010;1(4):381.
Junginger H. Mucoadhesive hydrogels. Pharmazeutische Industrie. 1991;53(11):1056–65.
Hejazi R, Amiji M. Chitosan-based gastrointestinal delivery systems. J Control Release. 2003;89(2):151–65.
Lehr C-M. Lectin-mediated drug delivery: The second generation of bioadhesives. J Control Release. 2000;65(1–2):19–29.
Hamman JH, Enslin GM, Kotzé AF. Oral delivery of peptide drugs. BioDrugs. 2005;19(3):165–77.
Leichner C, Jelkmann M, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Thiolated polymers: Bioinspired polymers utilizing one of the most important bridging structures in nature. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;151:191–221.
Marschütz MK, Caliceti P, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Design and in vivo evaluation of an oral delivery system for insulin. Pharm Res. 2000;17(12):1468–74.
Marschütz MK, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Thiolated polymers: self-crosslinking properties of thiolated 450 kDa poly(acrylic acid) and their influence on mucoadhesion. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2002;15(4):387–94.
Fischer KE, Nagaraj G, Daniels RH, Li E, Cowles VE, Miller JL, Bunger MD, Desai TA. Hierarchical nanoengineered surfaces for enhanced cytoadhesion and drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2011;32(13):3499–506.
Gavrovic-Jankulovic M, Prodanovic R. Drug delivery: plant lectins as bioadhesive drug delivery systems. Journal of Biomaterials and Nanobiotechnology. 2011;2(05):614.
Wirth M, Gerhardt K, Wurm C, Gabor F. Lectin-mediated drug delivery: influence of mucin on cytoadhesion of plant lectins in vitro. J Control Release. 2002;79(1–3):183–91.
Naisbett B, Woodley J. The potential use of tomato lectin for oral drug delivery. 1. Lectin binding to rat small intestine in vitro. International journal of pharmaceutics. 1994;107(3):223–230.
Martins S, Sarmento B, Ferreira DC, Souto EB. Lipid-based colloidal carriers for peptide and protein delivery–liposomes versus lipid nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2007;2(4):595–607.
Jung T, Kamm W, Breitenbach A, Kaiserling E, Xiao JX, Kissel T. Biodegradable nanoparticles for oral delivery of peptides: is there a role for polymers to affect mucosal uptake? Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2000;50(1):147–60.
Jones M, Leroux J. Polymeric micelles - a new generation of colloidal drug carriers. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1999;48(2):101–11.
Daeihamed M, Dadashzadeh S, Haeri A, Akhlaghi MF. Potential of Liposomes for Enhancement of Oral Drug Absorption. Curr Drug Deliv. 2017;14(2):289–303.
Russell-Jones GJ. The potential use of receptor-mediated endocytosis for oral drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;46(1–3):59–73.
Owens DR, Zinman B, Bolli G. Alternative routes of insulin delivery. Diabet Med. 2003;20(11):886–98.
Turnbull T, Douglass M, Paterson D, Bezak E, Thierry B, Kempson I. Relating Intercellular Variability in Nanoparticle Uptake with Biological Consequence: A Quantitative X-ray Fluorescence Study for Radiosensitization of Cells. Anal Chem. 2015;87(21):10693–7.
Drucker DJ. Advances in oral peptide therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19(4):277–89.
Aungst BJ. Intestinal permeation enhancers. J Pharm Sci. 2000;89(4):429–42.
Lecluyse E, Sutton SC. In vitro models for selection of development candidates. Permeability studies to define mechanisms of absorption enhancement. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 1997;23:163–183.
Liu DZ, LeCluyse EL, Thakker DR. Dodecylphosphocholine-mediated enhancement of paracellular permeability and cytotoxicity in Caco-2 cell monolayers. J Pharm Sci. 1999;88(11):1161–8.
Lindmark T, Kimura Y, Artursson P. Absorption enhancement through intracellular regulation of tight junction permeability by medium chain fatty acids in Caco-2 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998;284(1):362–9.
Shaji J, Patole V. Protein and Peptide drug delivery: oral approaches. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2008;70(3):269–77.
Hochman J, Artursson P. Mechanisms of absorption enhancement and tight junction regulation. J Control Release. 1994;29(3):253–67.
Maher S, Brayden DJ. Overcoming poor permeability: translating permeation enhancers for oral peptide delivery. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2012;9(2):e113–9.
Twarog C, Fattah S, Heade J, Maher S, Fattal E, Brayden DJ. Intestinal permeation enhancers for oral delivery of macromolecules: a comparison between salcaprozate sodium (SNAC) and sodium caprate (C10). Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(2):78.
FDA. RYBELSUS FDA Label. 2021 March 4th. Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/213051s000lbl.pdf.
Bay WE, Bernadino JN, Klein GF, Ren Y, Zhang P. Process for the manufacture of SNAC (salcaprozate sodium). In.: Google Patents; 2020.
Leone-Bay A, Paton DR, Variano B, Leipold H, Rivera T, Miura-Fraboni J, Baughman RA, Santiago N. Acylated non-α-amino acids as novel agents for the oral delivery of heparin sodium. USP Journal of Controlled Release. 1998;50(1–3):41–9.
Brayden D, Creed E, O’connell A, Leipold H, Agarwal R, Leone-Bay A. Heparin absorption across the intestine: effects of sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] caprylate in rat in situ intestinal instillations and in Caco-2 monolayers. Pharm Res. 1997;14(12):1772–9.
Malkov D, Angelo R, Wang H-z, Flanders E, Tang H, Gomez-Orellana I. Oral delivery of insulin with the eligen (®) technology: mechanistic studies. Current drug delivery. 2005;2(2):191–197.
Ding X, Rath P, Angelo R, Stringfellow T, Flanders E, Dinh S, Gomez-Orellana I, Robinson JR. Oral absorption enhancement of cromolyn sodium through noncovalent complexation. Pharm Res. 2004;21(12):2196–206.
Serajuddin AT. Salt formation to improve drug solubility. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59(7):603–16.
Pathak K. Effective formulation strategies for poorly water soluble drugs. In. Advances and Challenges in Pharmaceutical Technology: Elsevier; 2021. p. 181–228.
Gupta D, Bhatia D, Dave V, Sutariya V, Varghese GS. Salts of therapeutic agents: Chemical, physicochemical, and biological considerations. Molecules. 2018;23(7):1719.
Saal C, Becker A. Pharmaceutical salts: A summary on doses of salt formers from the Orange Book. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013;49(4):614–23.
Bay WE, Bernadino JN, Klein GF, Ren Y, Zhang P. Process for the manufacture of snac (salcaprozate sodium). In.: Google Patents; 2021.
Mayer RJ, Breugst M, Hampel N, Ofial AR, Mayr H. Ambident reactivity of phenolate anions revisited: a quantitative approach to phenolate reactivities. J Org Chem. 2019;84(14):8837–58.
Riley MGI, Castelli MC, Paehler EA. Subchronic oral toxicity of salcaprozate sodium (SNAC) in Sprague-Dawley and Wistar rats. Int J Toxicol. 2009;28(4):278–93.
Riley MGI, York RG. Peri-and postnatal developmental toxicity of salcaprozate sodium (SNAC) in Sprague-Dawley rats. Int J Toxicol. 2009;28(4):266–77.
Liu C, Kou Y, Zhang X, Cheng H, Chen X, Mao S. Strategies and industrial perspectives to improve oral absorption of biological macromolecules. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2018;15(3):223–33.
Van AJ. ha] lie CM. Physiology and function of the tight junction. 2009;1(2): a002584.
Turner JR. Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation: from basic mechanisms to clinical application. Am J Pathol. 2006;169(6):1901–9.
Odenwald MA, Turner JR. The intestinal epithelial barrier: a therapeutic target? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14(1):9.
Lundquist P, Artursson P. Oral absorption of peptides and nanoparticles across the human intestine: Opportunities, limitations and studies in human tissues. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;106:256–76.
Thuenauer R, Müller SK, Römer W. Pathways of protein and lipid receptor-mediated transcytosis in drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2017;14(3):341–51.
Danielsen EM. Intestinal permeation enhancers: Lessons learned from studies using an organ culture model. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes. 2020:183474.
Brayden DJ, Hill TA, Fairlie DP, Maher S, Mrsny RJ. Systemic delivery of peptides by the oral route: Formulation and medicinal chemistry approaches. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;157:2–36.
Maher S, Geoghegan C, Brayden DJ. Intestinal permeation enhancers to improve oral bioavailability of macromolecules: Reasons for low efficacy in humans. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery. 2020:1–28.
Kidron M, Dinh S, Menachem Y, Abbas R, Variano B, Goldberg M, Arbit E, Bar-On H. A novel per-oral insulin formulation: proof of concept study in non-diabetic subjects. Diabet Med. 2004;21(4):354–7.
Buclin T, Rochat MC, Burckhardt P, Azria M, Attinger M. Bioavailability and biological efficacy of a new oral formulation of salmon calcitonin in healthy volunteers. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(8):1478–85.
Baughman RA, Kapoor SC, Agarwal RK, Kisicki J, Catella-Lawson F, FitzGerald GA. Oral delivery of anticoagulant doses of heparin: a randomized, double-blind, controlled study in humans. Circulation. 1998;98(16):1610–5.
Berkowitz S, Marder V, Kosutic G, Baughman R. Oral heparin administration with a novel drug delivery agent (SNAC) in healthy volunteers and patients undergoing elective total hip arthroplasty. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1(9):1914–9.
Aungst BJ. Absorption enhancers: applications and advances. AAPS J. 2012;14(1):10–8.
Goldberg M, Gomez-Orellana I. Challenges for the oral delivery of macromolecules. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2003;2(4):289–95.
Rivera TM, Leone-Bay A, Paton DR, Leipold HR, Baughman RA. Oral delivery of heparin in combination with sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] caprylate: pharmacological considerations. Pharm Res. 1997;14(12):1830.
Hess S, Rotshild V, Hoffman A. Investigation of the enhancing mechanism of sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] caprylate effect on the intestinal permeability of polar molecules utilizing a voltage clamp method. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005;25(2–3):307–12.
Hossain S, Joyce P, Parrow A, Jõemetsa S, Höök F, Larsson P, Bergström CA. Influence of bile composition on membrane incorporation of transient permeability enhancers. Mol Pharm. 2020;17(11):4226–40.
Buckley ST, Bækdal TA, Vegge A, Maarbjerg SJ, Pyke C, Ahnfelt-Rønne J, Madsen KG, Schéele SG, Alanentalo T, Kirk RK. Transcellular stomach absorption of a derivatized glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist. Science translational medicine. 2018;10(467).
Bucheit JD, Pamulapati LG, Carter N, Malloy K, Dixon DL, Sisson EM. Oral semaglutide: a review of the first oral glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(1):10–8.
Schiller C, Fröhlich CP, Giessmann T, Siegmund W, Mönnikes H, Hosten N, Weitschies W. Intestinal fluid volumes and transit of dosage forms as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22(10):971–9.
Brayden DJ, Walsh E. Efficacious intestinal permeation enhancement induced by the sodium salt of 10-undecylenic acid, a medium chain fatty acid derivative. AAPS J. 2014;16(5):1064–76.
Krishna R, Yu L. Biopharmaceutics applications in drug development: Springer Science & Business Media; 2007.
Alani AW, Robinson JR. Mechanistic understanding of oral drug absorption enhancement of cromolyn sodium by an amino acid derivative. Pharm Res. 2008;25(1):48–54.
Twarog C, Liu K, O’Brien PJ, Dawson KA, Fattal E, Illel B, Brayden DJ. A head-to-head Caco-2 assay comparison of the mechanisms of action of the intestinal permeation enhancers: SNAC and sodium caprate (C10). Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020;152:95–107.
Chiang P-C, Deshmukh G, Liu J, Nagapudi K, Chen JZ, Valle N, Li R, Plise EG, Durk MR. Evaluating the Pharmacokinetics and Systemic Effects of a Permeability Enhancer Sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] Caprylate in Rats. J Pharm Sci. 2020;109(8):2629–36.
Michael Danielsen E, Hansen GH. Lipid raft organization and function in brush borders of epithelial cells. Mol Membr Biol. 2006;23(1):71–9.
Tomita M, Hayashi M, Awazu S. Comparison of absorption-enhancing effect between sodium caprate and disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate in Caco-2 cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 1994;17(5):753–5.
Hussain A, Arnold JJ, Khan MA, Ahsan F. Absorption enhancers in pulmonary protein delivery. J Control Release. 2004;94(1):15–24.
Maher S, Geoghegan C, Brayden DJ. Intestinal permeation enhancers to improve oral bioavailability of macromolecules: Reasons for low efficacy in humans. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021;18(2):273–300.
Maher S, Leonard TW, Jacobsen J, Brayden DJ. Safety and efficacy of sodium caprate in promoting oral drug absorption: from in vitro to the clinic. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61(15):1427–49.
Walsh EG, Adamczyk BE, Chalasani KB, Maher S, O’Toole EB, Fox JS, Leonard TW, Brayden DJ. Oral delivery of macromolecules: rationale underpinning Gastrointestinal Permeation Enhancement Technology (GIPET®). Ther Deliv. 2011;2(12):1595–610.
Brayden DJ, Gleeson J, Walsh EG. A head-to-head multi-parametric high content analysis of a series of medium chain fatty acid intestinal permeation enhancers in Caco-2 cells. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014;88(3):830–9.
Ukai H, Kawagoe A, Sato E, Morishita M, Katsumi H, Yamamoto A. Propylene glycol caprylate as a novel potential absorption enhancer for improving the intestinal absorption of insulin: efficacy, safety, and absorption-enhancing mechanisms. J Pharm Sci. 2020;109(4):1483–92.
Maitani Y, Hattori Y. Oligoarginine-PEG-lipid particles for gene delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009;6(10):1065–77.
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM. Claudin interactions in and out of the tight junction. Tissue barriers. 2013;1(3): e25247.
Christiaens B, Grooten J, Reusens M, Joliot A, Goethals M, Vandekerckhove J, Prochiantz A, Rosseneu M. Membrane interaction and cellular internalization of penetratin peptides. Eur J Biochem. 2004;271(6):1187–97.
Khafagy E-S, Morishita M. Oral biodrug delivery using cell-penetrating peptide. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(6):531–9.
Li Y, Yang D, Zhu C. Impact of sodium N-[8-(2-Hydroxybenzoyl) amino]-caprylate on intestinal permeability for notoginsenoside R1 and salvianolic acids in Caco-2 cells transport and rat pharmacokinetics. Molecules. 2018;23(11):2990.
Weng H, Hu L, Hu L, Zhou Y, Wang A, Wang N, Li W, Zhu C, Guo S, Yu M. The complexation of insulin with sodium N‐[8‐(2‐hydroxybenzoyl) amino]‐caprylate for enhanced oral delivery: Effects of concentration, ratio, and pH. Chinese Chemical Letters. 2021.
Li Y, Zhu C. Development and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of microspheres containing sodium n-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] caprylate for the oral delivery of berberine hydrochloride. Molecules. 2020;25(8):1957.
McIntyre C, Schmidt J, Castelli M, Bittner B. Study on the impact of SNAC (sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] caprylate) on the bioavailability of ibandronate (IBN) in postmenopausal women. Journal of drug delivery science and technology. 2011;21(6):521–5.
Buckley S, Scheele S, Kirk R, Knudsen L. SNAC-mediated absorption mechanism of action in an oral formulation of semaglutide. In.DIABETOLOGIA: SPRINGER 233 SPRING ST, NEW YORK, NY 10013 USA; 2017. p. S360-S361.
Hubbard D, Enda M, Bond T, Moghaddam SPH, Conarton J, Scaife C, Volckmann E, Ghandehari H. Transepithelial transport of PAMAM dendrimers across isolated human intestinal tissue. Mol Pharm. 2015;12(11):4099–107.
Ghadiri M, Young PM, Traini D. Strategies to enhance drug absorption via nasal and pulmonary routes. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(3):113.
Ibrahim YHY, Regdon G, Hamedelniel EI, Sovány T. Review of recently used techniques and materials to improve the efficiency of orally administered proteins/peptides. DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2020;28(1):403–16.
Park K, Kwon IC, Park K. Oral protein delivery: Current status and future prospect. React Funct Polym. 2011;71(3):280–7.
Alai MS, Lin WJ, Pingale SS. Application of polymeric nanoparticles and micelles in insulin oral delivery. J Food Drug Anal. 2015;23(3):351–8.
Dvořáčková K, Doležel P, Mašková E, Muselík J, Kejdušová M, Vetchý D. The effect of acid pH modifiers on the release characteristics of weakly basic drug from hydrophlilic–lipophilic matrices. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2013;14(4):1341–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this review paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kommineni, N., Sainaga Jyothi, V.G., Butreddy, A. et al. SNAC for Enhanced Oral Bioavailability: An Updated Review. Pharm Res 40, 633–650 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03459-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03459-9