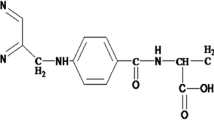
Abstract
Nanotechnology has been utilized in developing novel drug formulations with minimal adverse effects. Nanoparticles in a lower size range with great surface area, increased potency, and easy permeability could be an approach for the treatment of cancer and other diseases. Unlike other nanoparticles, quantum dots have specific functional groups, have charges over their surface, and are extremely small in size (2–10nm), which makes them more permeable through tight junctions. Quantum dots are interesting materials that offer diagnosis and treatment concurrently. Quantum dots are reported to have several applications in pharmaceuticals as well as drug delivery, diagnosis, immunolabeling, and cell labeling tools. However, the existence of heavy metals in quantum dots such as cadmium poses a potential challenge for future medical applications, where quantum dots may be deliberately injected into the body. In this review, we are focusing on various pharmaceutical applications of quantum dots.

Graphical Abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- QDs:
-
Quantum dots
- CQDs:
-
Carbon quantum dots
- NPs:
-
Nanoparticles
- CdSe:
-
Cadmium and selenium
- GSH–TGA:
-
Glutathione-thioglycolic acid
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- MR:
-
Magnetic resonance
- MoS2QDs:
-
Molybdenum disulfide quantum dots
- Mal-PEG-NHS:
-
Maleimide-polyethylene glycol-aminosuccinyl imine succinate
- NIR:
-
Near infrared
- siRNA–QDs:
-
Small interfering RNA quantum dots
- Cds:
-
Cadmium sulfide
- CMC:
-
Carboxy methyl cellulose
References
Gour A, Jain NK. Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):844–51.
Oroojalian F, Charbgoo F, Hashemi M, Amani A, Yazdian-Robati R, Mokhtarzadeh A, Ramezani M, Hamblin MR. Recent advances in nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the kidney. J Control Release. 2020;321:442–62.
Misra RDK. Quantum dots for tumor-targeted drug delivery and cell imaging. Nanomedicine. 2008;3:271–4.
Delcassian D, Patel AK. Nanotechnology and drug delivery. Bioeng Innov Solut Cancer. 2020:197–219.
Sonkar R, Jha A, Viswanadh MK, Burande AS, Pawde DM, Patel KK, et al. Gold liposomes for brain-targeted drug delivery: formulation and brain distribution kinetics. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;10:111652.
Henna TK, Pramod K. Graphene quantum dots redefine nanobiomedicine. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;110:110651.
Matea CT, Mocan T, Tabaran F, Pop T, Mosteanu O, Puia C, Iancu C, Mocan L. Quantum dots in imaging, drug delivery and sensor applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:5421–31.
Henna TK, Raphey VR, Sankar R, Shirin VKA, Gangadharappa H V, Pramod K. Carbon nanostructures: the drug and the delivery system for brain disorders. Int J Pharm. 2020;119701.
Almourani R, Chinnakotla B, Patel R, Kurukulasuriya LR, Sowers J. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: an update. Curr Diab Rep. 2019;19:161.
Zhang J, Yu S-H. Carbon dots: large-scale synthesis, sensing and bioimaging. Mater Today. 2016;19:382–93.
Obonyo O, Fisher E, Edwards M, Douroumis D. Quantum dots synthesis and biological applications as imaging and drug delivery systems. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2010;30:283–301.
Yuan Q, Hein S, Misra RDK. New generation of chitosan-encapsulated ZnO quantum dots loaded with drug: synthesis, characterization and in vitro drug delivery response. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:2732–9.
Yan C, Hu X, Guan P, Hou T, Chen P, Wan D, Zhang X, Wang J, Wang C. Highly biocompatible graphene quantum dots: green synthesis, toxicity comparison and fluorescence imaging. J Mater Sci. 2020;55:1198–215.
Jha S, Mathur P, Ramteke S, Jain NK. Pharmaceutical potential of quantum dots. Artif Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnol. 2018;46:57–65.
Han H-S, Niemeyer E, Huang Y, Kamoun WS, Martin JD, Bhaumik J, Chen Y, Roberge S, Cui J, Martin MR, Fukumura D, Jain RK, Bawendi MG, Duda DG. Quantum dot/antibody conjugates for in vivo cytometric imaging in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112:1350–5.
Esteves da Silva JCG and Gonçalves HMR. Analytical and bioanalytical applications of carbon dots. Trends Anal Chem. 2011;30:1327–36.
Xi J, Xie C, Zhang Y, Wang L, Xiao J, Duan X, Ren J, Xiao F, Wang S. Pd nanoparticles decorated N-doped graphene quantum dots@ N-doped carbon hollow nanospheres with high electrochemical sensing performance in cancer detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8:22563–73.
Cui L, Ren X, Wang J, Sun M. Synthesis of homogeneous carbon quantum dots by ultrafast dual-beam pulsed laser ablation for bioimaging. Mater Today Nano. 2020;12:100091.
Wang Y, Chen T, Huang C, Wang Y, Wu J, Sun B. Electrochemically switchable electrochemiluminescent sensor constructed based on inorganic perovskite quantum dots synthesized with microwave irradiation. J Electroanal Chem. 2020;114181.
Calabro RL, Yang D-S, Kim DY. Liquid-phase laser ablation synthesis of graphene quantum dots from carbon nano-onions: comparison with chemical oxidation. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;527:132–40.
Shen L, Zhang L, Chen M, Chen X, Wang J. The production of pH-sensitive photoluminescent carbon nanoparticles by the carbonization of polyethylenimine and their use for bioimaging. Carbon. 2013;55:343–9.
Iravani S, Varma RS. Green synthesis, biomedical and biotechnological applications of carbon and graphene quantum dots. A review. Environ Chem Lett. 2020;18:703–27. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-00984-0.
Amaral PEM, Hall DC Jr, Pai R, Król JE, Kalra V, Ehrlich GD, Ji HF. Fibrous phosphorus quantum dots for cell imaging. Nanostruct Mater. 2020;3(1):752–9.
Guo Y, Li J. MoS2 quantum dots: synthesis, properties and biological applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;109:110511.
Abbasi E, Kafshdooz T, Bakhtiary M, Nikzamir N, Nikzamir N, Nikzamir M, et al. Biomedical and biological applications of quantum dots. Artif Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnol. 2016;44:885–91.
Smith AM, Duan H, Mohs AM, Nie S. Bioconjugated quantum dots for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:1226–40.
Cai W, Shin D-W, Chen K, Gheysens O, Cao Q, Wang SX, et al. Peptide-labeled near-infrared quantum dots for imaging tumor vasculature in living subjects. Nano Lett. American Chemical Society. 2006;6:669–76. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/nl052405t
Shamsipour M, Mansouri AM, Moradipour P. Temozolomide conjugated carbon quantum dots embedded in core/shell nanofibers prepared by coaxial electrospinning as an implantable delivery system for cell imaging and sustained drug release. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019;20:259. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1466-0
Lai C-Y, Trewyn BG, Jeftinija DM, Jeftinija K, Xu S, Jeftinija S, Lin VSY. A mesoporous silica nanosphere-based carrier system with chemically removable CdS nanoparticle caps for stimuli-responsive controlled release of neurotransmitters and drug molecules. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:4451–9.
Azzazy HME, Mansour MMH, Kazmierczak SC. From diagnostics to therapy: prospects of quantum dots. Clin Biochem. 2007;40:917–27.
Cheki M, Moslehi M, Assadi M. Marvelous applications of quantum dots. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17:1141–8.
Field LD, Chen YC, Delehanty JB. Semiconductor quantum dots for visualization and sensing in neuronal cell systems - basic neurobiology techniques. In: Wright NJD, editor. New York, NY: US; 2020;1–18. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9944-6_1, 2020.
Nair A, Haponiuk JT, Thomas S, Gopi S. Natural carbon-based quantum dots and their applications in drug delivery: a review. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2020; 1:132:110834.
Sun L, Qu L, Yang R, Yin L, Zeng H. Cysteamine functionalized MoS2 quantum dots inhibit amyloid aggregation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;128:870–6 Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S014181301833887X.
Tang M, Pi J, Long Y, Huang N, Cheng Y, Zheng H. Quantum dots-based sandwich immunoassay for sensitive detection of Alzheimer’s disease-related Aβ1–42. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2018;201:82–7 Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S138614251830372X.
Seven ES, Zhou Y, Seven YB, Mitchell GS, Leblanc RM. Crossing the blood-brain barrier with carbon quantum dots. FASEB J. 2019;33:785.8–8 Available from: https://www.fasebj.org/doi/abs/10.1096/fasebj.2019.33.1_supplement.785.8.
Kim D, Yoo JM, Hwang H, Lee J, Lee SH, Yun SP, et al. Graphene quantum dots prevent α-synucleinopathy in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Nanotechnol . 2018;13:812–8. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0179-y
Tosic J, Stanojevic Z, Vidicevic S, Isakovic A, Ciric D, Martinovic T, Kravic-Stevovic T, Bumbasirevic V, Paunovic V, Jovanovic S, Todorovic-Markovic B, Markovic Z, Danko M, Micusik M, Spitalsky Z, Trajkovic V. Graphene quantum dots inhibit T cell-mediated neuroinflammation in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2019;146:95–108.
Wang C, Yang F, Tang Y, Yang W, Zhong H, Yu C, et al. Graphene quantum dots nanosensor derived from 3D nanomesh graphene frameworks and its application for fluorescent sensing of Cu2+ in rat brain. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;258:672–81 Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925400517322293.
Gao L, Zhao X, Wang J, Wang Y, Yu L, Peng H, et al. Multiple functionalized carbon quantum dots for targeting glioma and tissue imaging. Opt Mater (Amst). 2018;75:764–9 Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925346717307437.
Li S, Amat D, Peng Z, Vanni S, Raskin S, De Angulo G, et al. Transferrin conjugated nontoxic carbon dots for doxorubicin delivery to target pediatric brain tumor cells. Nanoscale. 2016;8:16662–9.
Jung J, Solanki A, Memoli KA, Kamei K, Kim H, Drahl MA, et al. Selective inhibition of human brain tumor cells through multifunctional quantum-dot-based siRNA delivery. Angew Chemie Int Ed John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. 2010;49:103–7.
Hettiarachchi SD, Graham RM, Mintz KJ, Zhou Y, Vanni S, Peng Z, Leblanc RM. Triple conjugated carbon dots as a nano-drug delivery model for glioblastoma brain tumors. Nanoscale The. 2019;11:6192–205.
Hunt NJ, Lockwood GP, Le Couteur FH, McCourt PAG, Singla N, Kang SWS, et al. Rapid intestinal uptake and targeted delivery to the liver endothelium using orally administered silver sulfide quantum dots. ACS Nano. 2020;14:1492–507. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b06071
Kikkeri R, Lepenies B, Adibekian A, Laurino P, Seeberger PH. In vitro imaging and in vivo liver targeting with carbohydrate capped quantum dots. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:2110–2.
Freeman R, Girsh J, Willner I. Nucleic acid/quantum dots (QDs) hybrid systems for optical and photoelectrochemical sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:2815–34. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/am303189h
He Z-Y, Jin Z-H, Zhan M, Qin Z, Li Z, Xu T. Advances in quantum dot-mediated siRNA delivery. Chin Chem Lett. 2017;28:1851–6 Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1001841717302486.
Derfus AM, Chen AA, Min D-H, Ruoslahti E, Bhatia SN. Targeted quantum dot conjugates for siRNA delivery. Bioconjug Chem ; 2007;18:1391–6. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/bc060367e
Badıllı U, Mollarasouli F, Bakirhan NK, Ozkan Y, Ozkan SA. Role of quantum dots in pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis, and its application in drug delivery. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2020;20:116013.
Su W, Guo R, Yuan F, Li Y, Li X, Zhang Y, Zhou S, Fan L. Red-emissive carbon quantum dots for nuclear drug delivery in cancer stem cells. J Phys Chem Lett. 2020;11:1357–63.
You Y, Xu Z, Chen Y. Doxorubicin conjugated with a trastuzumab epitope and an MMP-2 sensitive peptide linker for the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer. Drug Deliv. 2018;25:448–60.
Shu M, Gao F, Yu C, Zeng M, He G, Wu Y, Su Y, Hu N, Zhou Z, Lin X, Yang Z. Dual targeted therapy in HER2-positive breast cancer cells with the combination of carbon dots/HER3 siRNA and trastuzumab nanotechnology. 2020;31(33):335102.
Savla R, Taratula O, Garbuzenko O, Minko T. Tumor targeted quantum dot-mucin 1 aptamer-doxorubicin conjugate for imaging and treatment of cancer. J Control Release. 2011;153:16–22 Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365911001003.
Sun YH, Liu YS, Vernier PT, Liang CH, Chong SY, Marcu L, Gundersen MA. Photostability and pH sensitivity of CdSe/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots in living cells. Nanotechnology. 2006;17:4469–76. Available from:. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/17/031.
Bannai H, Inoue T, Hirose M, Niwa F, Mikoshiba K. Synaptic function and neuropathological disease revealed by quantum dot-single-particle tracking - single molecule microscopy in neurobiology. In: Yamamoto N, Okada Y, editors. New York, NY: US. 2020.p.131–55. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0532-5_7,
Kulkarni NS, Parvathaneni V, Shukla SK, Barasa L, Perron JC, Yoganathan S, Muth A, Gupta V. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor conjugated quantum dots for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019;133:145–59.
Wolcott A, Gerion D, Visconte M, Sun J, Schwartzberg A, Chen S, Zhang JZ. Silica-coated CdTe quantum dots functionalized with thiols for bioconjugation to IgG proteins. J Phys Chem B. 2006;110:5779–89.
Zdobnova TA, Dorofeev SG, Tananaev PN, Vasiliev RB, Balandin TG, Edelweiss EF, Stremovskiy OA, Balalaeva IV, Turchin IV, Lebedenko EN, Zlomanov VP, Deyev SM. Fluorescent immunolabeling of cancer cells by quantum dots and antibody scFv fragment. J Biomed Opt. 2009;14:21004.
Yu Y, Xu L, Chen J, Gao H, Wang S, Fang J, Xu S. Hydrothermal synthesis of GSH–TGA co-capped CdTe quantum dots and their application in labeling colorectal cancer cells. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2012;95:247–53 Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927776512001816.
Chen M-L, He Y-J, Chen X-W, Wang J-H. Quantum dots conjugated with Fe3O4-filled carbon nanotubes for cancer-targeted imaging and magnetically guided drug delivery. Langmuir . 2012;28:16469–76. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/la303957y
Chowdhuri AR, Singh T, Ghosh SK, Sahu SK. Carbon dots embedded magnetic nanoparticles chitosan metal organic framework as a nanoprobe for pH sensitive targeted anticancer drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8:16573–83. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b03988.
Takkinen K, Žvirblienė A. Recent advances in homogenous immunoassays based on resonance energy transfer. Curr Opin Biotechnol. ; 2019;55:16–22.
Rees K, Tran MV, Massey M, Kim H, Krause KD, Algar WR. Dextran-functionalized semiconductor quantum dot bioconjugates for bioanalysis and imaging. Bioconjug Chem. 2020;31:861–74.
Li X, Zha M, Li Y, Ni J, Min T, Kang T, et al. Sub-10 nm aggregation-induced emission quantum dots assembled by microfluidics for enhanced tumor targeting and reduced retention in the liver. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;1;59(49);21899-903.
Öztürk MA, De M, Cojocaru V, Wade RC. Chromatosome structure and dynamics from molecular simulations. Annu Rev Phys Chem Annual Reviews. 2020;71:101–19.
Iannazzo D, Pistone A, Celesti C, Triolo C, Patané S, Giofré SV, et al. A smart nanovector for cancer targeted drug delivery based on graphene quantum dots. Nanomaterials. 2019;9:282.
Sheng Y, Dai W, Gao J, Li H, Tan W, Wang J, Deng L, Kong Y. pH-sensitive drug delivery based on chitosan wrapped graphene quantum dots with enhanced fluorescent stability. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;112:110888.
Li Z, Li H, Liu L, You X, Zhang C, Wang Y. A pH-sensitive nanocarrier for co-delivery of doxorubicin and camptothecin to enhance chemotherapeutic efficacy and overcome multidrug resistance in vitro. RSC Adv. 2015;5(94):77097–105.
Ruzycka-Ayoush M, Kowalik P, Kowalczyk A, Bujak P, Nowicka AM, Wojewodzka M, Kruszewski M, Grudzinski IP. Quantum dots as targeted doxorubicin drug delivery nanosystems. Cancer Nanotechnology. 2021 Dec;12(1):1–27.
Bwatanglang IB, Mohammad F, Yusof NA, Mohammed NE, Abu N, Alitheen NB, Abdullah J, Hussein MZ, Abba Y, Nordin N, Zamberi NR. Histological analysis of anti-cancer drug loaded, targeted Mn: ZnS quantum dots in metastatic lesions of 4T1 challenged mice. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017 Sep;28(9):1–3.
Mars A, Hamami M, Bechnak L, Patra D, Raouafi N. Curcumin-graphene quantum dots for dual mode sensing platform: electrochemical and fluorescence detection of APOe4, responsible of Alzheimer’s disease. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1036:141–6.
Sharma S, Singh N, Nepovimova E, Korabecny J, Kuca K, Satnami ML, et al. Interaction of synthesized nitrogen-enriched graphene quantum dots with novel anti-Alzheimer’s drugs: spectroscopic insights. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020;38:1822–37. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2019.1619625
Tak K, Sharma R, Dave V, Jain S, Sharma S. Clitoria ternatea mediated synthesis of graphene quantum dots for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020;11(22): 3741–3748; Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00273
Tabrizi MA, Ferré-Borrull J, Kapruwan P, Marsal LF. A photoelectrochemical sandwich immunoassay for protein S100β, a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease, using an ITO electrode modified with a reduced graphene oxide-gold conjugate and CdS-labeled secondary antibody. Microchim Acta. 2019;186:1–9.
Bwatanglang IB, Mohammad F, Yusof NA, Abdullah J, Alitheen NB, Hussein MZ, Abu N, Mohammed NE, Nordin N, Zamberi NR, Yeap SK. In vivo tumor targeting and anti-tumor effects of 5-fluororacil loaded, folic acid targeted quantum dot system. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016;480:146–58.
Kalaiyarasan G, Veerapandian M, JebaMercy G, Balamurugan K, Joseph J. Amygdalin functionalized carbon quantum dots for probing β-glucosidase activity for cancer diagnosis and therapeutics. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(6):3089–99.
Lian W, Tu D, Hu P, Song X, Gong Z, Chen T, Song J, Chen Z, Chen X. Broadband excitable NIR-II luminescent nano-bioprobes based on CuInSe2 quantum dots for the detection of circulating tumor cells. Nano Today. 2020;35:100943 Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1748013220301122.
Othman HO, Salehnia F, Hosseini M, Hassan R, Faizullah A, Ganjali MR. Fluorescence immunoassay based on nitrogen doped carbon dots for the detection of human nuclear matrix protein NMP22 as biomarker for early stage diagnosis of bladder cancer. Microchem J. 2020;157:104966 Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article.
Park JS, Kim ST, Kim SY, Jo MG, Choi MJ, Kim MO. A novel kit for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using a fluorescent nanoparticle imaging. Sci Rep. 2019;9:1–12.
Barman B, Pientka JM, Murphy JR, Cartwright AN, Chou W-C, Fan W-C, Oszwałdowski R, Petrou A. Circular polarization dynamics during magnetic polaron formation in type II magnetic quantum dots. J Phys Chem C. 2020;124(23):12766–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
• Conception: Aman Gour, Suman Ramteke, and Narendra Kumar Jain
• Design of the work: Aman Gour and Suman Ramteke
• Drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content: Aman Gour, Suman Ramteke, and Narendra Kumar Jain
• Final approval of the version to be published: Narendra Kumar Jain and Suman Ramteke
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gour, A., Ramteke, . & Jain, N.K. Pharmaceutical Applications of Quantum Dots. AAPS PharmSciTech 22, 233 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-021-02103-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-021-02103-w