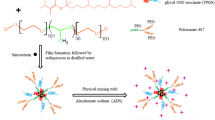
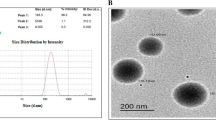
Abstract
Lung cancer patients develop acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors including erlotinib (ERL) after few months of primary treatment. Evidently, new chemotherapy strategies to delay or overcome the resistance are urgently needed to improve the clinical outcome in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. In this paper, we have investigated the cytotoxic interaction of ERL and valproic acid (VA) in ERL-resistant NSCLC cells and developed a liquisolid formulation of ERL-VA for improving oral bioavailability of ERL. ERL is weakly basic, biopharmaceutical classification system (BCS) class II drug with extremely poor aqueous solubility while VA is a branched chain fatty acid. Ionic interaction between ERL and VA (1:2 M ratio) resulted in significant enhancement in saturation solubility of ERL at different pH range. Liquisolid formulation of ERL-VA (EVLF) developed using PEG 400 and mesoporous calcium silicate was characterized for solid state and in vitro dissolution in biorelevant dissolution medium (FaSSIF and FeSSIF). Cytotoxicity of ERL was enhanced by 2–5 folds on co-incubation with VA in HCC827/ERL cell line. Flow cytometry analysis using AnnexinV-FITC assay demonstrated that VA and ERL alone have poor apoptotic effect on HCC827/ERL cells while combination showed around 69% apoptotic cells. Western blot analysis confirmed the role of survivin in overcoming resistance. In vivo pharmacokinetic studies of EVLF in rats demonstrated a 199% relative bioavailability compared to ERL suspension. Thus, EVLF could be a promising alternative to current ERL formulations in the treatment of NSCLC.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brückl W, Tufman A, Huber RM. Advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with activating EGFR mutations: first-line treatment with afatinib and other EGFR TKIs. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017;17(2):143–55.
Chan BA, Hughes BG. Targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: current standards and the promise of the future. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4(1):36.
Patel K, Doddapaneni R, Chowdhury N, Boakye CH, Behl G, Singh M. Tumor stromal disrupting agent enhances the anticancer efficacy of docetaxel loaded PEGylated liposomes in lung cancer. Nanomed (Lond). 2016;11(11):1377–92.
Sullivan I, Planchard D. Next-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for treating EGFR-mutant lung cancer beyond first line. Front Med. 2017;3:76.
Goss GD, Spaans JN. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in the management of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Oncologist. 2016;21:205–13.
Wu S-G, Shih J-Y. Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI–targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):38.
Biran A, Brownstein M, Haklai R, Kloog Y. Downregulation of survivin and aurora A by histone deacetylase and RAS inhibitors: a new drug combination for cancer therapy. Int J Cancer. 2011;128(3):691–701.
Okamoto K, Okamoto I, Hatashita E, Kuwata K, Yamaguchi H, Kita A, et al. Overcoming erlotinib resistance in EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting survivin. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011.
Edwards R, Andan C, Lalla R, Lacouture M, O'Brien D, Sequist L. Afatinib therapy: practical management of adverse events with an oral agent for non-small cell lung cancer treatment. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2018;22(5):542–8.
Ruess DA, Probst M, Marjanovic G, Wittel UA, Hopt UT, Keck T, et al. HDACi valproic acid (VPA) and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) delay but fail to protect against warm hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 2016;11(8):e0161233.
Zhang L, Wang G, Wang L, Song C, Leng Y, Wang X, et al. VPA inhibits breast cancer cell migration by specifically targeting HDAC2 and down-regulating survivin. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;361(1–2):39–45.
Dora CP, Trotta F, Kushwah V, Devasari N, Singh C, Suresh S, et al. Potential of erlotinib cyclodextrin nanosponge complex to enhance solubility, dissolution rate, in vitro cytotoxicity and oral bioavailability. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;137:339–49.
Yang KM, Shin IC, Park JW, Kim K-S, Kim DK, Park K, et al. Nanoparticulation improves bioavailability of Erlotinib. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2017;43(9):1557–65.
Elkadi S, Elsamaligy S, Al-Suwayeh S, Mahmoud H. The development of self-nanoemulsifying liquisolid tablets to improve the dissolution of simvastatin. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017;18(7):2586–97.
Shokri J, Adibkia K, Javadzadeh Y. Liquisolid technology: what it can do for NSAIDs delivery? Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2015;136:185–91.
Cheriyan VT, Alsaab H, Sekhar S, Venkatesh J, Mondal A, Vhora I, et al. A CARP-1 functional mimetic compound is synergistic with BRAF-targeting in non-small cell lung cancers. Oncotarget. 2018;9(51):29680.
Perrier J, Zhou Z, Dunn C, Khadra I, Wilson CG, Halbert G. Statistical investigation of the full concentration range of fasted and fed simulated intestinal fluid on the equilibrium solubility of oral drugs. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018;111:247–56.
Kutlehria S, Behl G, Patel K, Doddapaneni R, Vhora I, Chowdhury N, et al. Cholecalciferol-PEG conjugate based nanomicelles of doxorubicin for treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018;19(2):792–802.
Patel K, Chowdhury N, Doddapaneni R, Boakye CHA, Godugu C, Singh M. Piperlongumine for enhancing oral bioavailability and cytotoxicity of docetaxel in triple-negative breast cancer. J Pharm Sci. 2015;104(12):4417–26.
Boakye CHA, Patel K, Doddapaneni R, Bagde A, Marepally S, Singh M. Novel amphiphilic lipid augments the co-delivery of erlotinib and IL36 siRNA into the skin for psoriasis treatment. J Control Release. 2017;246:120–32.
Truong DH, Tran TH, Ramasamy T, Choi JY, Lee HH, Moon C, et al. Development of solid self-emulsifying formulation for improving the oral bioavailability of erlotinib. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016;17(2):466–73.
Patel K, Sarma V, Vavia P. Design and evaluation of Lumefantrine—oleic acid self nanoemulsifying ionic complex for enhanced dissolution. Daru. 2013;21(1):27.
Brus J, Albrecht W, Lehmann F, Geier J, Czernek J, Urbanova M, et al. Exploring the molecular-level architecture of the active compounds in liquisolid drug delivery systems based on mesoporous silica particles: old tricks for new challenges. Mol Pharm. 2017;14(6):2070–8.
Gumaste SG, Pawlak SA, Dalrymple DM, Nider CJ, Trombetta LD, Serajuddin AT. Development of solid SEDDS, IV: effect of adsorbed lipid and surfactant on tableting properties and surface structures of different silicates. Pharm Res. 2013;30(12):3170–85.
Brouwers J, Brewster ME, Augustijns P. Supersaturating drug delivery systems: the answer to solubility-limited oral bioavailability? J Pharm Sci. 2009;98(8):2549–72.
Liu C, Chen Z, Chen Y, Lu J, Li Y, Wang S, et al. Improving oral bioavailability of Sorafenib by optimizing the “spring” and “parachute” based on molecular interaction mechanisms. Mol Pharm. 2016;13(2):599–608.
Sun DD, Lee PI. Haste makes waste: the interplay between dissolution and precipitation of supersaturating formulations. AAPS J. 2015;17(6):1317–26.
Frohna P, Lu J, Eppler S, Hamilton M, Wolf J, Rakhit A, et al. Evaluation of the absolute oral bioavailability and bioequivalence of erlotinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in a randomized, crossover study in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2006;46(3):282–90.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank BASF and Tomita Pharmaceutical for kindly supplying the samples of excipients used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Guest Editor: Sanyog Jain
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 262 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, K., Doddapaneni, R., Patki, M. et al. Erlotinib-Valproic Acid Liquisolid Formulation: Evaluating Oral Bioavailability and Cytotoxicity in Erlotinib-Resistant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. AAPS PharmSciTech 20, 135 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1332-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1332-0