Abstract
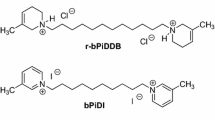
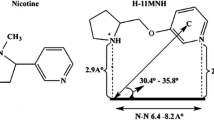
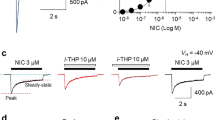
PyridineN-n-alkylation of S(-)-nicotine (NIC) affordsN-n-alkylnicotinium analogs, previously shown to competitively inhibit [3H]NIC binding and interact with α4β2* nicotinic receptors (nAChRs). The present study determined the ability of the analogs to inhibit NIC-evoked86Rb+ efflux from rat thalamic synaptosomes to assess functional interaction with α4β2* nAChRs. In a concentration-dependent manner, NIC evoked86Rb+ efflux (EC50=170 nmol/L). Analoginduced inhibition of NIC-evoked86Rb+ efflux varied over a ≈450-fold range. Analogs with longn-alkyl chain lengths (C9−C12) inhibited efflux in the low nmol/L range (IC50=9–20 nmol/L), similar to dihydro-β-erythroidine (IC50=19 nmol/L). Compounds with shortern-alkyl chain lengths (C1−C8) produced inhibition in the low μmol/L range (IC50 =3–12 μmol/L). C10 and C12 analogs completely inhibited NIC-evoked efflux, whereas C1–9 analogs produced maximal inhibition of only 10% to 60%. While the C10 analogN-n-decylnicotiniumiodide (NDNI) did not produce significant inhibition of NIC-evoked dopamine release in previously reported studies, NDNI possesses high affinity for [3H]NIC binding sites (Ki=90 nmol/L) and is a potent and efficacious inhibitor of NIC-evoked86Rb+ efflux as demonstrated in the current studies. Thus, NDNI is a competitive, selective antagonist at α4β2* nAChRs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Itier V, Bertrand D. Neuronal nicotinic receptors: from protein structure to function.FEBS Lett. 2001;504:118–125.
Whiting P, Lindstrom J. Pharmacological properties of immunoisolated neuronal nicotinic receptors.J Neurosci. 1986;6:3061–3069.
Whiting P, Lindstrom J. Purification and characterization of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor from rat brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987;84:595–599.
Flores CM, Rogers SW, Pabreza LA, Wolfe BB, Kellar KJ. A subtype of nicotinic cholinergic receptor in brain is composed of alpha 4 and beta 2 subunits and is up-regulated by chronic nicotine treatment.Mol Pharmacol. 1992;41:31–37.
Picciotto MR, Zoli M, Lena C, et al. Abnormal avoidance learning in mice lacking functional high-affinity nicotine receptor in the brain.Nature. 1995;374:65–67.
Zoli M, Lena C, Picciotto MR, Changeux J-P. Identification of 4 classes of brain nicotinic receptors using beta2 mutant mice.J Neurosci. 1998;18:4461–4472.
Marks MJ, Stitzel JA, Grady SR, Picciotto MR, Changeux JP, Collins AC. Nicotinic-agonist stimulated86Rb+ efflux and [3H]epibatidine binding of mice differing in β2 genotype.Neuropharmacology. 2000;39:2632–2645.
Marks MJ, Whiteaker P, Grady SR, Picciotto MR, McIntosh JM, Collins AC. Characterization of [(125)I]epibatidine binding and nicotinic agonist-mediated (86)Rb(+) efflux in interpeduncular nucleus and inferior colliculus of beta2 null mutant mice.J Neurochem. 2002;81:1102–1115.
Marks MJ, Farnham DA, Grady SR, Collins AC. Nicotinic receptor function determined by stimulation of rubidium efflux from mouse brain synaptosomes.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;264:542–552.
Marks MJ, Whiteaker P, Calcaterra J, et al. Two pharmacologically distinct components of nicotinic receptor-mediated rubidium efflux in mouse brain require the beta2 subunit.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;289:1090–1103.
Nguyen HN, Rasmussen BA, Perry DC. Binding and functional activity of nicotinic cholinergic receptors in selected rat brain regions are increased following long-term but not short-term nicotine treatment.J Neurochem. 2004;90:40–49.
Eaton JB, Peng JH, Schroeder KM, et al. Characterization of human α4β2-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors stably and heterologously expressed in native nicotinic receptor-null SH-EP1 human epithelial cells.Mol Pharmacol. 2003;64:1283–1294.
Karadsheh MS, Shah MS, Tang X, Macdonald RL, Stitzel JA. Functional characterization of mouse α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors stably expressed in HEK293T cells.J Neurochem. 2004;91:1138–1150.
Decker MW, Anderson DJ, Brioni JD, et al. Erysodine, a competitive antagonist at neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;280:79–89.
Puttfarcken PS, Manelli AM, Arneric SP, Donnelly-Roberts DL. Evidence for nicotinic receptors potentially modulating nociceptive transmission at the level of the primary sensory neuron: studies with F11 cells.J Neurochem. 1997;69:930–938.
Xiao Y, Meyer EL, Thompson JM, Surin A, Wroblewski J, Kellar KJ. Rat alpha3/beta4 subtype of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor stably expressed in a transfected cell line: pharmacology of ligand binding and function.Mol Pharmacol. 1998;54:322–333.
Hernandez SC, Bertolino M, Xiao Y, Pringle KE, Caruso FS, Kellar KJ. Dextromethorphan and its metabolite dextrorphan block α3β4 neuronal nicotinic receptors.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;293:962–967.
Lukas R, Fryer J, Eaton J, Gentry C. Some methods for studies of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor pharmacology. In: Levin ED, ed.Nicotinic Receptors and the Nervous System. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2002:3–27.
Crooks PA, Ravard A, Wilkins LH, Teng L-H, Buxton ST, Dwoskin LP. Inhibition of nicotine-evoked [3H]dopamine release by pyridineN-substituted nicotine analogues: a new class of nicotinic antagonist.Drug Dev Res. 1995;36:91–102.
Dwoskin LP, Xu R, Ayers JT, Crooks PA. Recent developments in neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists.Curr Opin Ther Patents. 2000;10:1561–1581.
Dwoskin LP, Crooks PA. Competitive neuronal nicotinic receptor antagonists: a new direction for drug discovery.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;298:395–402.
Wilkins LH, Haubner A, Ayers JT, Crooks PA, Dwoskin LP.N-n-Alkylnicotinium analogs, a novel class of nicotinic receptor antagonist: inhibition of S-(-)-nicotine-evoked [3H]dopamine overflow from superfused rat striatal slices.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;301:1088–1096.
Wilkins LH, Grinevich VP, Ayers JT, Crooks PA, Dwoskin LP.N-n-Alkylnicotinium analogs, a novel class of nicotinic receptor antagonists: interaction with α4β2* and α7* neuronal nicotinic receptors.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;304:400–410.
Xu R, Dwoskin LP, Grinevich V, Sumithran SP, Crooks PA. Synthesis and evaluation of conformationally restricted pyridineN-alkylated nicotine analogs as nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists.Drug Dev Res. 2002;55:173–186.
Allen DD, Lockman PR, Roder KE, Dwoskin LP, Crooks PA. Active transport of high affinity choline and nicotine analogs into the central nervous system by the blood-brain barrier choline transporter.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;304:1268–1274.
Crooks PA, Ayers JT, Xu R, et al. Development of subtype selective ligands as antagonists at nicotinic receptors mediating nicotine-evoked dopamine release.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004;14:1869–1874.
Marks MJ, Robinson SF, Collins AC. Nicotinic agonists differ in activation and desensitization of86Rb+ efflux from mouse thalamic synaptosomes.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;277:1383–1396.
Ramirez-Latorre J, Yu CR, Qu X, Perin F, Karlin A, Role L. Functional contributions of alpha5 subunit to neuronal acetylcholine receptor channels.Nature. 1996;380:347–351.
Goldman D, Deneris E, Luyten W, Kochhar A, Patrick J, Heinemann S. Members of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family are expressed in different regions of the mammalian central nervous system.Cell. 1987;48:965–973.
Yu ZJ, Morgan DG, Wecker L. Distribution of 3 nicotinic receptor alpha 4 mRNA transcripts in rat brain: selective regulation by nicotine administration.J Neurochem. 1996;66:1326–1329.
Stitzel JA, Dobelis P, Jimenez M, Collins AC. Long sleep and short sleep mice differ in nicotine-stimulated86Rb+ efflux and α4 nicotinic receptor subunit cDNA sequence.Pharmacogenetics. 2001;11:331–339.
Dobelis P, Marks MJ, Whiteaker P, Balogh SA, Collins AC, Stitzel JA. A polymorphism in the mouse neuronal α4 nicotinic receptor subunit results in an alteration in receptor function.Mol Pharmacol. 2002;62:334–342.
Zwart R, Vijverberg HP. Four pharmacologically distinct subtypes of α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expressed inXenopus laevis oocytes.Mol Pharmacol. 1998;54:1124–1131.
Liu C, Nordberg A, Zhang X. Differential co-expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha 4 and beta 2 subunit genes in various regions of rat brain.Neuroreport. 1996;7:1645–1649.
Katz B, Thesleff S. A study of the “desensitization” produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate.J Physiol. 1957;138:63–80.
Edelstein SJ, Schaad O, Henry E, Bertrand D, Changeux JP. A kinetic mechanism for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors based on multiple allosteric transitions.Biol Cybern. 1996;75:361–379.
Karlin A. Emerging structure of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:102–114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published: January 13, 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkins, L.H., Miller, D.K., Ayers, J.T. et al. N-n-alkylnicotinium analogs, a novel class of antagonists at α4β2* Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: Inhibition of S(-)-nicotine-evoked 86Rb+Efflux from rat thalamic synaptosomes. AAPS J 7, 90 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1208/aapsj070490
Received:
Accepted:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/aapsj070490