Abstract
Czech cardiovascular disease (CVD) morbidity and mortality rates are among the highest in the world. A 2-year community-based project was designed to increase CVD awareness and knowledge and behavior change skills, thus stimulating change in CVD-related behaviors. Dubec, a Czech town located just outside Prague, was the study community. Risk-factor surveys were conducted before and after the intervention (1992 and 1994). The intervention combined communitywide health education and intensive medical treatment of individuals at high risk for CVD.
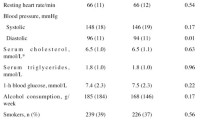
At baseline, 55% of the eligible population (n = 1,119) participated in the survey; however, the dropout rate in 1994 was high (46%). After taking those factors associated with dropout into consideration, regression analyses revealed significant increases in CVD knowledge, reductions in blood pressure, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C), and dietary intake of fat in both the high-risk CVD group and the community sample. In addition, the community sample had significant reductions in total cholesterol and a positive shift in their attitudes about changing CVD risk. There were no significant changes in percentage of smokers, body mass index (BMI), or dietary intake of high-fiber foods.
This study demonstrates the feasibility of addressing CVD risk-related behaviors in Central Europe and supports additional efforts to address this significant public health problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright, C. L. (1996). Nutritional epidemiology: Methods and innovations used in a Central European community-based program. Guest Editorial. International Journal of Applied and Basic Nutritional Sciences, 12, 386–387.
Albright, C. L., Farquhar, J. W., Havel, R., Frost, P., Palmer, S., Komárek, L., Lhotská, L., Osancová, K., Janovská, J., Okénková, J., Kebzam, V., Roth, Z., Vignerová, J., Poledne, R., Andel, M., Málková, J., Herman, D., Kraml, P. (1997). Program to reduce cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in the Czech Republic: Design and methods of the Healthy Dubec Project. International Quarterly of Community Health Education, 16, 315–331.
Albright, C. L., Komarek, L., Kebza, K., Oscancova, K., Janovská, J., Okénková, J., Roth, Z., Vignerová, J. Potocková, J., Havel, R. L., Albright, C. L., Farquhar, J. W., Poledne, R., Andel, M., Málková, J., Kraml, P., Bartáková, H., Herman, D., Palmer, S., & Stanková, I. (1997). Reducing cardiovascular risk in the Czech Republic: Healthy Dubec. Canadian Journal of Cardiology, 13 (suppl B), 129.
Bobak, M., & Feachem, R. G. A. (1992). Health status in the Czech and Slovak Federal Republic. Health Policy and Planning, 7, 234–242.
Bobak, M., Skodova, Z., Pisa, Z., Poledne, R., Marmot, M. (1997). Political changes and trends in CVD risk factors in the Czech Republic 1985–1992. Canadian Journal of Cardiology, 13 (suppl B), 266B.
Catalonia declaration: Investing in heart health. (1996). Advisory Board of the Second International Heart Health Conference. Barcelona, Spain, June 1, 1995. Declaration published by the Autonomous Government of Catalonia, Department of Health and Social Security.
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. (1993). Summary of the Second Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel II). Journal of the American Medical Association, 269, 3015–3023.
Farquhar, J. W., Maccoby, N., Wood, P. D., Alexander, J. K., Breitrose, H., Brown, B. W., Jr., Haskell, I. L., McAlister, A. L., Meyer, A. J., Nash, J. D., & Stern, M.P. (1977). Community education for cardiovascular health. Lancet, 1, 1192–1195.
Farquhar, J. W., Fortmann, S. P., Flora, J. A., Maccoby, N. (1991). Methods of communication to influence behavior. In W. W. Holland, R. Detels, & G. Knox (Eds.), Oxford textbook of public health: Vol. 2 (2nd ed., pp. 331–344). Oxford, U.K.: Oxford University Press.
Farquhar, J. W., Fortmann, S. P., Flora, J. A., Taylor, C. B., Haskell, W. L., Williams, P. T., Maccoby, N., Wood, P. D. (1990). Effects of communitywide education on cardiovascular disease risk factors: The Stanford Five-City Project. Journal of the American Medical Association, 264, 359–365.
Galanis D. J., Harris, T., Sharp, D. S., Petrovitch, H. (1998). Relative weight, weight change, and risk of CHD in the Honolulu Heart Program. American Journal of Epidemiology, 147, 379–86.
Ginter, E. (1995). Cardiovascular risk factors in the former communist countries: Analysis of 40 European MONICA populations. European Journal of Epidemiology, 11, 119–205.
Goodman, R. M., Wheeler, F. C., Lee, P. R. (1995). Evaluation of the Heart to Heart Project: Lessons from a community-based chronic disease prevention project. American Journal of Health Promotion, 9, 443–445.
Grabowsky, T. A., Farquhar, J. W., Sunnarborg, K. R., Bales, V. S. (1997, June). Worldwide efforts to improve heart health: A follow-up to the Catalonia Declaration-A selected program descriptions. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Center for Disease Control, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Atlanta, GA.
Herman, D., & Kebza, V. (1995, May 28-June 1). Program for reduction of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in Czech Republic-Quit smoking activities. Poster presented at Second International Heart Health Conference, Barcelona, Spain.
Huang, Z., Willett, W. C., Manson, J. E., Rosner, B., Stampfer, M. J., Speizer, F. E., Colditz, G. A. (1998). Body weight, weight change, and risk for hypertension in women. Annals Internal Medicine, 128, 81–88.
Kebza, V. (1995, May 28-June 1). Program for reduction of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in Czech Republic-Coping with stress. Poster presented at Second International Heart Health Conference, Barcelona, Spain.
Kebza, V. (1997) Coping with stress in cardiovascular disease prevention. Work Congress of the World Federation for Mental Health. July 6–11, Lahti, Finland.
Keil, V., & Kuulasmaa, K. (1989). WHO MONICA Project: Risk factors. International Journal of Epidemiology, 18 (Suppl. 1), S46-S55.
Komarek, L. (1997, June). The countrywide integrated noncommunicable disease intervention programme in the Czech Republic. In T. A. Grabowsky, J. W. Farquhar, K. R. Sunnarborg, & V. S. Bales (Eds.), Worldwide efforts to improve heart health: a follow-up to the Catalonia Declaration—Selected program descriptions. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Center for Disease Control, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Atlanta, GA.
Komárek, L., Kebza, V., Lhotská, L., Osancová, K., Janovská, J., Okénková, J., Roth, Z., Vignerová, J., Potocková, J., Havel, R. L., Albright, C. L., Farquhar, J. W., Poledne, R., Andel, M., Málková, J., Kraml, P., Bartáková, H., Herman, D., Palmer, S., & Stanková, I. (1995a). “Healthy Dubec”—Design of ajoint Czech-American community project for the reduction of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease. Central European Journal of Public Health, 3, 230–233.
Komarek, L., Janovská, J., Kebza, V., Lhotská, L., Okénková, J., Osancová, K. (1995, May 28-June 1). Programfor reduction of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in Czech Republic—community cardiovascular disease prevention. Paper presented at Second International Heart Health Conference, Barcelona, Spain.
Mensink, R. P., & Katan, M. B. (1992). Effect of dietary fatty acids on serum lipids and lipoproteins. A meta-analysis of 27 trials. Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis, 12, 911–919.
Neaton, J. D., & Wentworth, D. (for Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial Research Group). (1992). Serum cholesterol, blood pressure, cigarette smoking, and death from coronary heart disease. Archives of Internal Medicine, 152, 44–56.
Okenkova, J. (1995, May 28-June 1). Program for reduction of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in Czech Republic—Health education of children. Poster presented at 2nd International Heart Health Conference, Barcelona, Spain.
Osancova, K., & Janovska, J. (1995, May 28-June 1). Program for reduction of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in Czech Republic—Dietary intervention. Poster presented at Second International Heart Health Conference, Barcelona, Spain.
Peters, J. R., Quiter, E. S., Brekke, M. L., Admire, J., Brekke, M. J., Mullis, R. M., Hunninghake, D. B. (1994). The Eating Pattern Assessment Tool: A simple instrument for assessing dietary fat and cholesterol intake. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 94, 1008–1013.
Report of the Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC-V). (1993). Archives of’Internal Medicine, 153, 154–183.
Schooler, C., Farquhar, J. W., Fortmann, S. P., & Flora, J. A. (1997). Synthesis of findings and issues from community prevention trials. Annals of Epidemiology, S7, S54-S68.
Skodová, Z., Pisa, Z., Emrová, R., Vorlicek, J., Vojtisek, P., Berka, L., Pikhartová, J., Cicha, Z.,Wiesner, E., Grafnetter, D., Paclt, M., & Valenta, Z. (1991). Cardiovascular risk factors in the Czech Population. Cor Vasa, 33, 114–122.
Skodová, Z., Pisa, Z., Poledne, R., Berka, L., Cicha, Z., Emrova, R., Hoke, M., Pikhartová, J., Vojtisek, P., Graffietter, D., Wiesner, E., Hrdlickova, K., Havlikova, A., Bobak, M., Vorlicek, J., Paclt, M., Lanska, V. (1997). Disease in the cardiovascular mortality rate in the Czech Republic in 1984-1993 and its possible causes. Casopis Lekaru Ceskych [Journal of Czech Physicians], 136, 373–379.
Stachenko, S., Glasunov, I., Bischof, H. P., (1995, December). Processes of policy development and implementation: The CINDI approach. In P. Harrington & A. Ritsatakis (Eds.), Proceedings of the European Health Policy Conference: Opportunities for the future (Vol. 3, pp. 187–196). World Health Organization, Copenhagen, Denmark.
Statisticka rocenka [Statistical Yearbook]. (1993). Prague: SCU (Czech Statistical Office).
Tunstall-Pedoe, H., Kuulasmaa, K., Amouyel, P., Arveiler, D., Rajakangas, A. M., & Pajak, A. (1994). Myocardial infarction and coronary deaths in the World Health Organization MONICA Project: Registration procedures, event rates, and case-fatality rates in 38 populations from 21 countries in four continents. Circulation, 90, 583–612.
United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). (1994). Crisis in mortality, health, and nutrition. Central and Eastern Europe in transition, public policy and social conditions. Florence, Italy: UNICEF, International Child Development Centre.
U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare. (1979). Smoking and health. A report of the Surgeon General. Washington, DC: USDHEW, Public Health Service, Office on Smoking and Health. PHS pub. 79–50066.
WHO-MONICA Project. (1987). WHO-MONICA project: Geographic variation in mortality from cardiovascular diseases: Baseline data on selected population characteristics and cardiovascular mortality. World Health Statistics Quarterly, 40, 171–84.
WHO-MONICA Project. (1988a). Geographical variation in the major risk factors of coronary heart disease in men and women aged 35–64 years. World Health Statistics Quarterly, 41, 115–139.
WHO-MONICA. (1988b). The World Health Organization MONICA Project (Monitoring trends and determinants in Cardiovascular Disease): A major international collaboration. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 41, 105–114.
Zatonski, W. A., McMichael, A. J., Powles, J. W. (1998). Ecological study of reasons for sharp decline in mortality from Ischaemic heart disease in Poland since 1991. British Medical Journal, 316, 1047–1051.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This program was supported by the U.S. Agency for International Development (US AID) under the Partnerships in Health Care Program (EUR 00037-G-00-2026-00).
The authors wish to acknowledge the considerable support of Julia Terry, US AID program officer for the Central and Eastern European Partnerships.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albright, C.L., Komárek, L., Osancová, K. et al. Results of a multifactor cardiovascular risk reduction program in the czech republic: The healthy dubec project. Int. J. Behav. Med. 7, 44–61 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327558IJBM0701_4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327558IJBM0701_4