Abstract
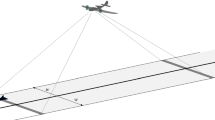
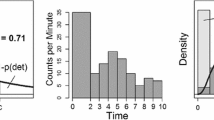
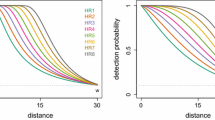
We have developed a procedure for estimating animal population size from aerial survey data collected simultaneously by two observers on the same sighting platform. We used a line transect sample design where transects follow elevation contours in mountainous terrain. Because our 10 data sets from aerial line transect surveys, conducted over a terrestrial environment, consistently show unimodal detection shapes, we chose a gamma-shaped detection function that is unimodal and admits covariates. We fit models separately to data from each observer, and then used all of the data to estimate the probabilities at the apex of the detection curves. We used a Horvitz-Thompson estimator to estimate the population size. We illustrate our procedure on a recently collected brown bear data set.
The programs and data set used in this work are available in the online supplements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike, H. (1985), “Prediction and Entrophy,” in A Celebration of Statistics, eds. A. C. Atkinson and S. E. Finberg, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, pp. 1–24.
Aldredge, J. R., and Gates, C. E. (1985), “Line Transect Estimators for Left-Truncated Distributions,” Biometrics, 41, 273–280.
Alpiza-Jara, R., and Pollock, K. H. (1996), “A Combination of Line Transect and Capture-Recapture Sampling Model for Multiple Observers in Aerial Surveys,” Journal of Ecological and Environmental Statistics, 3, 311–327.
Borchers, D. L., and Burnham, K. P. (2004), “General Formulation for Distance Sampling,” in Advanced Distance Sampling, Estimating Abundance of Biological Populations, eds. S. T. Buckland, D. R. Anderson, K. P. Burnham, J. L. Laake, D. L. Borchers, and L. Thomas, Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 6–30.
Borchers, D. L., Buckland, S. T., Goedhart, P. W., Clarke, E. D., and Hedley, S. L. (1998a), “Horwitz-Thompson Estimators for Double Platform Line Transect Surveys,” Biometrics, 54, 1221–1237.
Borchers, D. L., Laake, J. L., Southwell, C., and Paxton, C. G. M. (2006), “Accommodating Unmodeled Heterogeneity in Double-Observer Distance Sampling Surveys,” Biometrics, 62, 372–378.
Borchers, D. L., Zucchini, W., and Fewster, R. M. (1998b), “Mark Recapture Models for Line Transect Surveys,” Biometrics, 54, 1207–1220.
Buckland, S. T., and Turnock, B. J. (1992), “A Robust Line Transect Method,” Biometrics, 48, 901–909.
Buckland, S. T., Anderson, D. R., Burnham, K. P., Laake, J. L., Borchers, D. L., and Thomas, L. (2001), Introduction to Distance Sampling, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Burnham, K. P., Anderson, D. R., and Laake, J. L. (1980), “Estimation of Density From Line Transect Sampling of Biological Populations,” Wildlife Monograph 72, supplement to Journal of Wildlife Management, 44.
Burnham, K. P., Buckland, S. T., Laake, J. L., Borchers, D. L., Marques, T. A., Bishop, J. R. B., and Thomas, L. (2004), “Further Topics in Distance Sampling,” in Advanced Distance Sampling, Estimating Abundance of Biological Populations, eds. S. T. Buckland, D. R. Anderson, K. P. Burnham, J. L. Laake, D. L. Borchers, and L. Thomas, Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 307–392.
Chen, S. X. (1999), “Estimation in Independent Observer Line Transect Surveys for Clustered Populations,” Biometrics, 55, 754–759.
Conover, W. J. (1999), Practical Nonparametric Statistics (3rd ed.), New York: Wiley.
Drummer, T. D., and McDonald, L. L. (1987), “Size Bias in Line Transect Sampling,” Biometrics, 43, 13–21.
Drummer, T. D., DeGrange, A. R., Pank, L. L., and McDonald, L. L. (1990), “Adjusting for Group Size Influence in Line Transect Sampling,” Journal of Wildlife Management, 54, 511–514.
Efron, B., and Tibshirani, R. J. (1993), An Introduction to the Bootstrap, New York: Chapman & Hall.
Hiby, A. R., and Lovell, P. (1998), “Using Aircraft in Tandem Formation to Estimate the Abundance of Harbour Porpoise,” Biometrics, 54, 1280–1289.
Hiby, L. (1999), “The Objective Identification of Duplicate Sightings in Aerial Survey for Porpoise,” in Marine Mammal Survey and Assessment Methods, eds. G. W. Garner, S. C. Amstrup, J. L. Laake, B. F. J. Manly, L. L. McDonald, and D. G. Robertson, Rotterdam: A. A. Balkema, pp. 179–189.
Hiby, L., and Krishna, M. B. (2001), “Line Transect Sampling From a Curved Path,” Biometrics, 57, 727–731.
Horvitz, D. G., and Thompson, D. J. (1952), “A Generalization of Sampling Without Replacement From a Finite Universe,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 47, 663–685.
Innes, S., Heide-Jorgensen, M. P., Laake, J. L., Laidre, K. L., Cleator, H. P., Richard, P., and Stewart, R. E. A. (2002), “Surveys of Belugas and Narwhals in the Canadian High Arctic in 1996,” NAMMCO Scientific Publications, 4, 169–190.
Johnson, B. K., Lindzey, F. G., and Guenzel, R. J. (1991), “Use of Aerial Line Transect Surveys to Estimate Pronghorn Populations in Wyoming,” Wildlife Society Bulletin, 19, 315–321.
Laake, J. L. (1999), “Distance Sampling With Independent Observers: Reducing Bias From Heterogeneity by Weakening the Conditional Independence Assumption,” in Marine Mammal Survey and Assessment Methods, eds. G. W. Garner, S. C. Amstrup, J. L. Laake, B. F. J. Manly, L. L. McDonald, and D. G. Robertson, Rotterdam: Balkema Press, pp. 137–148.
Laake, J. L., and Borchers, D. L. (2004), “Methods for Incomplete Detection at Distance Zero,” in Advanced Distance Sampling, Estimating Abundance of Biological Populations, eds. S. T. Buckland, D. R. Anderson, K. P. Burnham, J. L. Laake, D. L. Borchers, and L. Thomas, Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 108–189.
Manly, B. F., McDonald, L. L., and Garner, G. W. (1996), “The Double Count Method With Two Independent Observers,” Journal of Ecological and Environmental Statistics, 1, 170–189.
Marques, F. F. C., and Buckland, S. T. (2003), “Incorporating Covariates Into Standard Line Transect Analyses,” Biometrics, 35, 597–604.
Patil, G. P., Taillie, C., and Wigley, R. L. (1979a), “Transect Sampling Methods and Their Application to Deep-Sea Red Crab,” in Environmental Biomonitoring, Assessment, Prediction, and Management#x2014;Certain Case Studies and Related Quantitative Issues, eds. J. Cairns, Jr., G. P. Patil, and W. E. Waters, Fairland, MD: International Co-Operative Publishing House, pp. 51–75.
Patil, S. A., Burnham, K. P., and Kovner, J. L. (1979b), “Nonparametric Estimation of Plant Density by the Distance Method,” Biometrics, 35, 597–604.
Quang, P. X. (1991), “A Nonparametric Approach to Size-Biased Line Transect Sampling,” Biometrics, 47, 269–279.
Quang, P. X., and Becker, E. F. (1996), “Line Transect Sampling Under Varying Conditions With Application to Aerial Surveys,” Ecology, 77, 1297–1302.
— (1997), “Combining Line Transect and Double Count Sampling Techniques for Aerial Surveys,” Journal of Agricultural, Biological, and Environmental Statistics, 2, 230–242.
— (1999), “Aerial Survey Sampling of Contour Transects Using Double-Count and Covariate Data,” in Marine Mammal Survey and Assessment Methods, eds. G. W. Garner, S. C. Amstrup, J. L. Laake, B. F. J. Manly, L. L. McDonald, and D. G. Robertson, Rotterdam: Balkema Press, pp. 87–97.
Quang, P. X., and Lanctot, R. B. (1991), “A Line Transect Model for Aerial Surveys,” Biometrics, 47, 1089–1102.
R Development Core Team (2008), R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. ISBN 3-900051-07-0. Available at http://www.R-project.org.
Ramsey, F. L., Wildman, V., and Engbring, J. (1987), “Covariate Adjustments to Effective Area in Variable-Area Wildlife Surveys,” Biometrics, 43, 1–11.
S-PLUS Version 6.2 (2003), Insightful Corporation, Seattle, WA.
Schwartz, C. C., Miller, S. D., and Haroldson, M. A. (2003), “Grizzly Bear (Ursus arctos),” in Wild Mammals of North America; Biology, Management, and Conservation, eds. G. A. Feldmamer, B. C. Thompson, and J. A. Chapman, Baltimore, MD: John Hopkins University Press, pp. 556–586.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, E.F., Quang, P.X. A gamma-shaped detection function for line-transect surveys with mark-recapture and covariate data. JABES 14, 207–223 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1198/jabes.2009.0013
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1198/jabes.2009.0013