Abstract
Introduction
The acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), affects up to 150,000 patients per year in the United States. We and other groups have demonstrated that bone marrow derived mesenchymal stromal stem cells prevent ARDS induced by systemic and local administration of endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide (LPS)) in mice.
Methods
A study was undertaken to determine the effects of the diverse populations of bone marrow derived cells on the pathophysiology of ARDS, using a unique ex-vivo swine preparation, in which only the ventilated lung and the liver are perfused with autologous blood. Six experimental groups were designated as: 1) endotoxin alone, 2) endotoxin + total fresh whole bone marrow nuclear cells (BMC), 3) endotoxin + non-hematopoietic bone marrow cells (CD45 neg), 4) endotoxin + hematopoietic bone marrow cells (CD45 positive), 5) endotoxin + buffy coat and 6) endotoxin + in vitro expanded swine CD45 negative adherent allogeneic bone marrow cells (cultured CD45neg). We measured at different levels the biological consequences of the infusion of the different subsets of cells. The measured parameters were: pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), gas exchange (PO2), lung edema (lung wet/dry weight), gene expression and serum concentrations of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6.
Results
Infusion of freshly purified autologous total BMCs, as well as non-hematopoietic CD45(-) bone marrow cells significantly reduced endotoxin-induced pulmonary hypertension and hypoxemia and reduced the lung edema. Also, in the groups that received BMCs and cultured CD45neg we observed a decrease in the levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in plasma. Infusion of hematopoietic CD45(+) bone marrow cells or peripheral blood buffy coat cells did not protect against LPS-induced lung injury.
Conclusions
We conclude that infusion of freshly isolated autologous whole bone marrow cells and the subset of non-hematopoietic cells can suppress the acute humoral and physiologic responses induced by endotoxemia by modulating the inflammatory response, mechanisms that do not involve engraftment or trans-differentiation of the cells. These observations may have important implications for the design of future cell therapies for ARDS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Respiratory diseases kill more than 400,000 Americans each year and significantly reduce the quality of life for millions more. The National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) estimated that in 2009 the annual cost of providing healthcare related to all respiratory conditions, excluding lung cancer, was $113 billion [1]. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a very common clinical entity and a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the critical care setting. Historically, ARDS has been associated with mortality ranging from 40% to 60%, with worse outcomes in the older population. In the US alone, 150,000 new cases of ARDS occur every year [2]. Moreover, ARDS has a significant impact on long-term disability and adverse psycho-social outcomes in survivors [3]. According to the Berlin definition of ARDS, the diagnostic criteria for ARDS rely on four categories: (i) timing: within one week of a known clinical insult or new or worsening respiratory symptoms; (ii) radiographic: bilateral opacities not fully explained by effusions, lobar/lung collapse, or nodule; (iii) origin of lung edema: respiratory failure not fully explained by cardiac failure or fluid overload; and (iv) oxygenation impairment. Consequently, ARDS was divided into three categories according to the degree of hypoxemia: mild, moderate and severe. Thus, the Berlin definition eliminated the concept of acute lung injury (ALI), which now falls into the category of mild ARDS. ARDS always results from another severe underlying disease. The range of diseases causing ARDS is broad, and they may also damage organs other than the lungs, but the lung injury invariably dominates the clinical picture. Sepsis is the most common condition leading to ARDS. In mammals, ARDS is initiated by an acute inflammatory response to a physical trauma or infection [4–9] followed by sequestration of neutrophils in the lung, lung edema, and up-regulation of inflammatory mediators both locally and systemically.
Bone marrow derived stem cells can be divided in two groups: hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) and mesenchymal stromal stem cells (MSC). Bone marrow derived MSC were first described in the early 1970s by Friedenstein and collaborators [10–13]. They are defined as clonal, plastic adherent cells capable of differentiating into cells of mesenchymal origin. These cells are also able to support hematopoiesis in culture providing extracellular matrix, cytokines, and growth factors to the HSC. The ultimate characterization of mesenchymal stem cells has been a complicated issue since there are no specific cell surface markers. Enrichment of mesenchymal stem cells from crude bone marrow suspensions is achieved by selecting a plastic-adherent population that expresses neither hematopoietic nor endothelial cell surface markers but is positive for the expression of adhesion and stromal markers [14]. The criterion for establishing MSC phenotype is to use adherent cells that: (i) express CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105; (ii) lack the expression of hematopoietic markers, such as CD45, CD34 and CD31; and (iii) confirm their plasticity by the ability of the cells to differentiate into adipocytes, osteocytes, and chondrocytes in a multilineage differentiation assay [15]. Cells used in the present work are non-hematopoietic bone marrow adherent cells. However, because the cells were not completely characterized, mainly because of the lack of specific antibodies to all the markers required, we limit the denomination to in vitro expanded swine CD45 negative adherent allogeneic bone marrow cells (cultured CD45neg)
Cell-based therapy in experimental models of ARDS and sepsis has been the focus of intense investigation since the publication of our original work in 2007 [16]. In our initial observation, we defined the beneficial effects of the systemic administration of mesenchymal stem cells to control ARDS mainly by their anti-inflammatory properties. Multiple groups have reported similar observations where the protective effect has been demonstrated in different animal models and human ex-vivo lungs [17–22]. The protective effects of mesenchymal stem cells are attributed to several mechanisms including secretion of the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and TGF-β, and Keratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF) and elaboration of antibacterial peptides. As a result of these most recent studies, mesenchymal stem cells are increasingly recognized for having complex interactions with the host immune system and share properties with cells of the innate immune system. Given the pleiotropic effects of these stem cells in the setting of ARDS and sepsis, there has been considerable interest in initiating translational studies in this field.
In the present pre-clinical model, we found that infusion of freshly purified autologous nuclear bone marrow cell preparations or non-hematopoietic CD45 (-) bone marrow cells has similar protective characteristics to in vitro expanded CD45neg by moderating the very early pathophysiological events in endotoxin-induced lung injury. They also were able to moderate pulmonary hypertension and hypoxemia and, in the case of bone marrow cells and cultured CD45neg, attenuated the increase in serum levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β.Neither autologous buffy coat cells nor hematopoietic CD45 (+) cells had those effects. We conclude that similar to cultured CD45neg, freshly isolated nucleated bone marrow cells and the subpopulation of non-hematopoietic bone marrow cells can interact with the immune system to modulate inflammation and control lung injury resulting from severe endotoxemia.
Methods
The in situ piglet preparation
We have previously described an ex-vivo perfusing piglet preparation, which permits perfusion restricted to the lung and the liver using autologous blood [23]. Piglets were anesthetized, a tracheostomy was performed, and cannulas were placed in a carotid artery and a jugular vein. After heparinization, the animals were ex-sanguinated and the blood was used to fill the blood reservoir and the perfusion circuit. The lungs were perfused at a constant flow rate of 40 ml/kg/minute (up to 400 ml/min); half of the blood in the efferent circuit transverses the liver before perfusing the lung. In all the preparations, lungs were ventilated under the same conditions with a piston ventilator (Harvard Apparatus, Dover, MA, USA) with room air and 5% CO2. The minute ventilation was adjusted to maintain perfusate pH between 7.35 and 7.45. Throughout the experiments, pressures in the pulmonary artery, left atrium and portal vein and flow in and out of both organs was monitored continuously and the data were stored in a computer for later analysis.
The study adhered to National Institute of Health guidelines on the use of experimental animals and was approved by the institutional animal care and use committee of Emory University. Animals were maintained in the Emory University Division of Animal Resources, an AAALAC approved facility.
Experimental protocols and data collection
Six groups of experiments were performed with four to six animals in each group. The groups were designated as: 1) endotoxin alone, 2) endotoxin + freshly isolated autologous bone marrow nuclear cells, 3) endotoxin + non-hematopoietic bone marrow autologous cells CD45(-), 4) endotoxin + hematopoietic bone marrow cells CD45(+), 5) endotoxin + buffy coat and 6) endotoxin + in vitro expanded swine CD45 negative adherent allogeneic bone marrow cells (cultured CD45neg). For all the groups, 5 μg/kg body weight of endotoxin was used (Serotype O55:B5 Difco, Detroit, MI, USA), directly into the blood reservoir fifteen minutes after endotoxin cells were added to the blood reservoir. A total of 100 x106 whole bone marrow cells were used. In the case of the subpopulations, CD45 (-), CD45(+), buffy coat and cultured CD45neg, 50 x106 purified cells were perfused in each preparation. Blood samples were collected before and after endotoxin administration. Blood gas analysis was performed every 15 minutes for the duration of the experiment using a portable blood gas analyzer (Rapidlab 248, Diamond Diagnostics, East Walpole, MA, USA). Serum samples were separated and stored at -80o for measurement of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β. Automated cell count and differential counts were performed every 15 minutes using a device which is specifically designed for use in laboratory animals (Hemevet, CDC Technologies, Oxford, CT, USA). At each time point, we recorded pressures and flows in and out of the lungs and flow to the liver. Pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) was calculated as in-flow pressure (pulmonary artery pressure) minus out-flow pressures (left atrial pressure) divided by total blood flow through the lungs and expressed in cm H2O/ml/min. Temperature was measured continuously and kept between 38°C and 40°C by adjusting the temperature of the water in the water-jacket surrounding the reservoir.
Lung and liver tissue specimens were obtained at three time points (30 minutes before endotoxin and 45 minutes and 135 minutes after endotoxin) for the determination of histology, cell engraftment and gene expression in a microarray system. The study was terminated two and a half hours after endotoxin administration and both lungs were taken for determination of wet-to-dry weight ratio.
Generation and administration of cells
Briefly, fresh swine bone marrow derived cells were isolated by mechanically extracting bone marrow from both femurs of the animal while the preparation was being set up. The harvested bone marrow was cut in small fragments and cells detached by continuous vortex for 30 seconds followed by 1X trypsin-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for 2 minutes. Cell suspensions were centrifuged for 2 minutes at 700 RPM to separate insoluble material. Supernatant was collected and cells transferred to a 50 ml conical tube where cells were washed twice with PBS containing penicillin-streptomycin. Red blood cells were lysed by re-suspending the cell pellet with 3 ml of sterile water. After 15 seconds lysis was stopped by adding 27 ml of 10X PBS for a final concentration of 1X PBS. Cells were washed twice with sterile PBS and counted in a hemocytometer. To isolate CD45 (+) and CD45 (-) cells, 300 × 106 bone marrow cells were transferred into a 15 ml conical tube and incubated with 35 μg of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) conjugated mouse anti-porcine CD45 (ABD Serotec, Oxford, UK) for 10 minutes at 4#176;C. Cells were washed twice with cold MACS buffer (PBS +0.5% BSA+2mM EDTA). After washing, cells were re-suspended in 1.5 ml MACS buffer and incubated with 300 μl of anti-FITC microbeads (Myltenyi Biotec, Auburn, CA, USA) for 15 minutes at 4#176;C. CD45 (-) cells were sorted using LD columns (Myltenyi Biotec, Auburn, CA, USA). Cell sorting was repeated once to ensure the purity of the cells. Cells that were retained in the column were used as CD45 (+) cells. After the final elution, cells were washed twice with sterile saline solution. Before infusion, cells were counted in a hemocytometer with Trypan blue to determine cell numbers and viability.
Autologous buffy coat cells were obtained by separating leukocytes from fresh heparinized peripheral blood by osmotic gradient using HISTOPAQUE® 1083 (Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA). Twenty ml of fresh blood was centrifuged and red blood cells lysed. Cells were re-suspended in 20 ml of PBS and placed on top of 20 ml of Histopaque 1083. The opaque interface, containing the mononuclear cell band, was collected using a Pasteur pipet and transferred into a 50 ml conical centrifuge tube. Cells were washed twice with PBS. After the last wash, cells were counted to determine viability and cell numbers.
Swine CD45 negative adherent allogeneic bone marrow cells (cultured CD45neg) were isolated by negative selection of CD45(+) cells, using an anti-CD45-FITC antibody, followed by anti-FITC-conjugated magnetic beads (Miltenyi Biotec). Cultured CD45neg cells were expanded in vitro in 175 cm2 flasks in Iscove's modified Dulbeccos's medium (IMDM) containing 9% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Atlanta, Biologicals, Norcross, GA, USA), 9% horse serum, and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. Cells were harvested at 70% confluence using 0.25% trypsin. For in vivo infusion, cells were detached using 0.25% trypsin at 37°C for 5 minutes. Trypsin was neutralized by adding IMDM with 10% serum. The cell suspension was centrifuged and suspended in sterile PBS (without Ca and Mg). After two additional washes with PBS, cells were counted in a hemocytometer with trypan blue and were re-suspended in PBS at 5 × 106 cells per ml final concentration.
To track the cells in the swine preparation, BMCs were surface-labeled using PKH (Sigma. St Louis MO, USA). Prior to infusion, 10 × 107 cells were re-suspended in 5 ml of staining buffer and 50 μl of PKH solution were added. After incubating for 5 minutes at room temperature, the reaction was stopped by adding 10 ml of complete FBS. Cells were washed twice with 50 ml of sterile saline solution. Before infusion, cells were counted to determine viability and cell numbers.
FACS analysis
Blood samples obtained from preparations were collected at different time points. Red blood cells were lysed by hypotonic shock and samples analyzed for PKH-26 staining on a fluorescence-assisted cell sorting (FACS) Excalibur (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA, USA), using CellQuest software (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA, USA) and analyzed using FlowJo software (Tree Star, San Carlos, CA, USA).
Immunohistochemistry
Pig lungs were placed in 2% paraformaldehyde and processed for paraffin embedding. Sections (5 mm) were cut, mounted on the slides, and subjected to antigen retrieval in a decloaking chamber (BioCare Medical, Gaithersburg, MD, USA). Endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with 3% peroxide for 5 minutes. Slides were incubated with anti-myeloperoxidase antibody (MPO) (Abcam Cambridge, MA, USA) overnight at 4#176;C. Immune complexes were visualized with biotinylated secondary antibody and 3,3'-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride using the streptavidin-biotin complex method.
Cytokine measurements
Plasma concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β were measured separately using Quantikine® ELISA kits (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, samples were dispensed into 96-well micro-titer plates that are precoated with porcine monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies specific to the above cytokines. After washing away any unbound substances, an enzyme (horseradish peroxidase)-linked monoclonal (TNF-α) or polyclonal (IL-6 and IL-1β) antibody specific to the above cytokines was added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound antibody-enzyme reagent, a substrate solution (hydrogen peroxide/tetramethylbenzidine) was added to the wells. The reaction was terminated with a stop buffer and absorbance read at 450 nm using an MRX Revelation (Dynex Technologies, Chantilly, VA, USA) multi-well plate reader. Values of IL-6, TNF-α and IL-1β were determined by reference to a standard curve constructed using the porcine proteins and computer software capable of generating a four parameter logistic curve-fit.
Measurements of lung water
At the completion of each experiment, both lungs were harvested and homogenized. The homogenate was weighed (wet weight), then dried to constant weight in a microwave oven and reweighed (dry weight). The ratio of wet/dry lung weight was calculated as a measure of the amount of lung water (edema) that was present.
Liver RNA isolation and Affymetrix GeneChip array
We used a swine specific microarray chip from Affymetrix with 27,000 genes represented. RNA was isolated from liver tissue samples taken 30 minutes after endotoxin in a liver-lung perfused preparation or after 30 minutes of perfusion without addition of endotoxin as a control. We performed microarray analyses of these samples and calculated the ratio of expression in the sample from the endotoxin-treated preparation to the control sample. Liver tissue samples from both endotoxin and endotoxin-bone marrow cell groups were homogenized in TRIzol reagent (Gibco BRL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA), and RNA was extracted according to the instructions of the manufacturer. RNA precipitates were briefly air-dried then subjected to an RNeasy protect mini kit and DNAse I treatment (Qiagen, Miami, FL, USA). Total RNA concentration was measured spectrophotometrically at 260 and 280 nm and dissolved in RNAse-free water to 1 µg/µL and stored at -80°C. For control of concentration and integrity, 1 µg of each RNA sample was subjected to formaldehyde-agarose electrophoresis.
Total RNA (5 µg) was used for microarray analysis on swine Affymetrix chips. Preparation of complementary RNA, hybridization, scanning and image analysis of the microarrays were each performed according to the manufacturer's protocol (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA, USA) at the Emory Bio-Core facility with a final ArrayExpress accession: E-MTAB-1436
Statistical analysis
Statistically significant differences were determined by using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey-Kramer for post hoc test. P <0.05 was considered significant. In most cases the physiological data are presented as change from baseline, with the baseline calculated as the mean of values at thirty minutes prior and immediately prior to administering endotoxin.
Results
Infusion of autologous bone marrow cells prevented lung inflammation induced by systemic administration of endotoxin
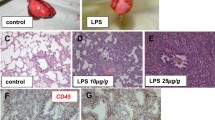
As one measure of the inflammatory response, we analyzed the influx of neutrophils into lungs by MPO immunostaining of histologic sections. As shown in Figure 1, lungs from animals receiving endotoxin had extensive infiltration of MPO-positive cells, most prominently at 45 minutes after administering endotoxin [23]. The marked alteration in lung architecture was largely resolved by 135 min after endotoxin. To investigate whether infusion of freshly isolated total BMCs into the lung reduced the lung inflammatory response, we added 100 × 106 cells of fresh isolated autologous BMCs to the reservoir 15 minutes after endotoxin. Histopathological analyses and MPO staining of lungs treated with BMCs showed reduced inflammatory infiltrates and tissue edema at the 45-minute time point (Figure 1) compared to animals receiving endotoxin alone.
Systemic administration of freshly isolated autologous whole bone marrow nuclear cells (BMC) modifies endotoxin (LPS) induced lung inflammation. A. Lung biopsies were obtained at the indicated time points after endotoxin and stained with an anti-myeloperoxidase (MPO) antibody to detect neutrophils. Samples from two independent animals treated with endotoxin (Endo1 and 2) are shown. Note the significant alteration of lung architecture with increased inflammatory infiltrates and edema at 15 and 45 minutes after endotoxin. B. Histological lung sections stained with MPO from swine preparations infused with total BMCs 15 minutes after endotoxin. Three independent animals are shown (BMC 1, 2 and 3). Tissue samples were collected at the indicated time points after endotoxin. Notice reduction in the severity of inflammation and edema compared to endotoxin alone treated swine. LPS, lipopolysaccharide.
Trafficking of infused bone marrow cells in the lung after endotoxin-induced lung injury
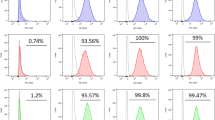
To determine the homing of whole bone marrow cells to the lung in response to endotoxin, BMCs were labeled with a fluorescent membrane dye, PKH26. Fifteen minutes after adding endotoxin to the reservoir, 100 × 106 labeled cells were added to the reservoir and the cell traffic was followed by collecting 0.5 ml blood samples from the pulmonary vein and pulmonary artery every 5 minutes until the end of the experiment. We detected few PKH labeled cells in histological sections from lungs (Figure 2A); however, a substantial number of labeled cells were detected by FACS analysis in the peripheral blood. Figure 2B shows higher numbers of labeled cells in afferent than in efferent circulation of the lungs during the early time points which is consistent with the retention of the cells in the lung after injury that has been observed in other animal models.
Infused autologous bone marrow nuclear cells are retained in the lungs after endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. To differentiate infused from endogenous cells, isolated cells were surface stained with PKH. To detected engrafted cells in the lung, a sample of lung tissue was collected at the end of the experiment and frozen in Tissue-Tek solution. A. Persistent localization of PKH staining bone marrow cells (red) in the lung following endotoxemia in the swine liver-lung perfused preparation (blue = nuclei). B. To demonstrate trapping of the cells in the lung, 0.5 cc blood sample was collected every 5 minutes from the pulmonary vein and artery, and analyzed by FACS. On B, there is a quantification of the percentage of PKH+ cells collected from blood before and after the lung. FACS, fluorescence-assisted cell sorting.
BMCs infusion protects against endotoxin-induced pulmonary hypertension and hypoxemia
Figure 3A shows attenuation of endotoxin-induced pulmonary hypertension by the infusion of freshly isolated autologous BMCs. Similarly, statistically significant diminution of the pulmonary vascular resistance response to endotoxin was observed when the subpopulations of non-hematopoietic CD45(-) bone marrow cells or swine CD45 negative adherent allogeneic bone marrow cells (cultured CD45neg) were administered. Neither buffy coat nor hematopoietic CD45(+) cells affected the endotoxin-induced pulmonary hypertension significantly (Figure 3B).
Freshly isolated bone marrow nuclear cells moderated the increase in pulmonary vascular resistance induced by endotoxin. A. Comparison of effects of the fresh bone marrow cells and the blood buffy coat cells on the pulmonary vascular resistance response. B. Endotoxin-induced PVR rapidly recovered in preparations in which CD45(-) and cultured CD45neg cells were included but persisted in the presence of CD45(+). (n = 6 in each group, **P <0.01). PVR, pulmonary vascular resistance.
Systemic administration of endotoxin also resulted in arterial hypoxemia. Those values are shown over the course of the endotoxin reaction in Figure 4. Arterial hypoxemia following endotoxin was attenuated significantly by administration of either total autologous BMCs, non-hematopoietic CD45(-) cells or swine cultured CD45neg cells. Some average effect was also seen with either buffy coat or CD45 (+) cells, but these were not significantly different from endotoxin alone.
Changes of blood oxygenation are abrogated by the infusion of bone marrow derived cells. A. Change from baseline perfusate oxygen tension expressed in mmHg (means ± SE) in six experimental groups over the two-hour experimental period. Perfusate blood pO2 was measured with a blood gas analyzer. From the infused cell, buffy coat and CD45(+) have the weakest protective effect compared to total BMCs and cultured CD45neg cells. Statistical analysis was done by 2-way ANOVA and Tukey-Kramer for post hoc test. ANOVA, analysis of variance.
Infusion of fresh autologous BMC decreased endotoxemia-induced lung edema
As we have reported previously, endotoxin causes a large and significant increase in lung water content [24–30]. Lung wet to dry weight ratios in the experiments reported here are shown in Figure 5. For reference, as has been published by our group, average values in control experiments are approximately 7 [23]. Endotoxin caused pulmonary edema that was significantly attenuated by the infusion of autologous BMCs and swine cultured CD45neg. The lung wet-to-dry weight ratios were not significantly different from the endotoxin group in groups receiving either the subpopulations of CD45(+), CD45(-) or buffy coat.
Infusion of BMC reduces pulmonary edema induced by systemic administration of endotoxin. As a control lung fibroblasts and buffy coat were added instead of BMC. CD45 (-) cells significantly reduced but did not prevent pulmonary edema induced by endotoxin (n = 4 to 5 in each group, P <0.05. **). BMC, bone marrow nuclear cells.
Modification of gene expression in the liver by infusion of bone marrow cells
Since previous studies showed that maximal activation of lung pro-inflammatory responses required the presence of the liver, we analyzed gene expression in liver samples after administration of endotoxin. Table 1 lists all of the identified genes that were at least two fold higher in the post endotoxin sample than in samples from animals that did not receive endotoxin. Potential candidate mediators of liver-dependent lung injury are highlighted in the table. Analysis of the data using the Integrity Systems software which links gene expression patterns to biologic pathways, showed the major association with immune/inflammation pathways. Interestingly, of the genes expression of which was increased by endotoxin, 20 were identified as belonging to the canonical acute phase response pathway.
Figure 6 shows the effects of BMCs on endotoxin-induced hepatic gene expression, both the fold effect (that is, the ratio of expression with BMCs and endotoxin to expression with endotoxin alone) and the network analysis of gene expression. These results of gene expression implicate IL-1β and TNF-α as prime candidates for the liver-induced lung injury seen after endotoxin. To confirm these results we measured levels of these two cytokines, together with IL-6 as the other inflammatory cytokine involved on ARDS, in the perfusate at baseline and at 15-minute intervals following endotoxin administration and infusion of autologus BMCs, buffy coat and swine cultured CD45neg cells (Figure 7). Endotoxin induced progressive increases in all three cytokines, with particularly high levels of TNF-α. Total BMCs significantly attenuated the TNF-α and IL-1β responses whereas expanded cultured CD45neg cells mainly diminished IL-1β levels. Buffy coat cells had no effect on any of these pro-inflammatory responses. Levels of IL-6 were not affected significantly by the infusion of any type of cell.
Immune/inflammation network of genes in the liver whose expression was altered by the infusion of bone marrow derived cells were analyzed using Ingenuity Software. Response to endotoxin in the presence of bone marrow cells relative to responses to endotoxin alone. Red = marked increase, Pink = increase, Green = decrease. Numbers are fold difference from the endotoxin only control sample.
Administration of freshly isolated whole bone marrow nuclear cells (BMC) altered the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Compared to responses with buffy coat cells, sixty minutes after infusion of BMC, there was a significant suppression in endotoxin-induced increased systemic concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines (A) IL-1β and (B) TNF-α. There was no attenuation of endotoxin induced release of IL-6 by any of the cells administrated (C). (n = 6 in each group, **P <0.01, *P <0.05).
Discussion
One reason for the high morbidity and mortality of ARDS is the lack of effective treatment available. Currently, the only existing therapy is limited to supportive care. Since the introduction of ventilation with low tidal volumes there has been a significant decrease in mortality and an increase in the number of days without ventilator use, which often results in further injury to the lungs [31]. Peak end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) is also an essential component of mechanical ventilation that decreases repetitive opening and closing during the respiratory cycle and opens collapsed alveoli decreasing intrapulmonary shunt. Other ventilatory strategies used in ARDS include recruitment maneuvers, prone position and high frequency ventilation, although the role of these strategies is not well defined and improvement in mortality has not been demonstrated [31].
ARDS can be associated with different clinical disorders directly affecting the lungs (pneumonia or pulmonary contusion) or systemic diseases affecting the lung through the bloodstream (sepsis, severe trauma or acute pancreatitis). Regardless of the cause of ARDS, the alveolar epithelium and capillary endothelium are affected, leading to an increase in permeability that allows fluid to accumulate in the alveolar space (alveolar edema). Loss of epithelial integrity also disrupts alveolar clearance and production of surfactant [32–34]. The extensive alveolar and endothelial damage causes an influx of circulating inflammatory cells that secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6.
A novel ex-vivo swine model developed by our group permits the measurement of lung pathophysiology and the simultaneous collection of lung and liver tissue for histologic and molecular comparisons during the early phase of the response to endotoxemia. In this preparation, endotoxemia causes a liver-dependent inflammatory response and severe lung injury and dysfunction [23]. We chose swine as an experimental animal because, like humans, they are especially sensitive to endotoxin and the pathophysiology of the response appears to be similar to that in humans. The model has some limitations as does any acute model, where the physiology can be monitored only for a short period of time before there is a deterioration of the organs.
Here, we find that infusion of freshly isolated suspensions of autologous whole bone marrow nuclear cells, the subpopulation of non-hematopoietic bone marrow cells CD45(-) or in vitro expanded adherent swine CD45neg cells, have a moderating effect on the response to endotoxemia. As we expected, the greatest effects were seen with swine cultured CD45neg cells. We and, later, other groups, reported findings in mice that are consistent with the observations that we report here [3, 16, 35–37]. The ability of the infusion of bone marrow mononuclear cells to prevent organ injury is well known including in the lung [38, 39]. In a recent publication, bone marrow derived nuclear cells were used to prevent chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/pulmonary emphysema in rats [40]. A similar rationale has been used to design a clinical trial for emphysema [41]. The present work, to our knowledge, is the first evidence in a clinically relevant lung injury model in a large animal preparation suggesting that freshly isolated autologous bone marrow nuclear cells might have a possible role in therapies for patients with acute lung injury.
The effects we observed as a consequence of cell infusion are on the very early endotoxin response and do not appear to require transdifferentiation into a lung-type cell. These effects were accompanied by an increase in the endotoxin-induced expression of genes encoding anti-inflammatory cytokines and decreased endotoxin-induced expression of genes encoding several pro-inflammatory cytokines in the liver compared to the effects of endotoxin at thirty minutes after endotoxemia. An analysis of the involved cytokine networks indicated that the principal effects of bone marrow cells on the endotoxin molecular response in the liver were on networks in which TNF-α and IL1-β play pivotal roles.
A transient inflammatory response is critical to the body's defense against infectious and other toxic insults. Injury of the lungs and other organs consequent to sepsis in humans and several other animal species appears to result from a dysregulated inflammatory response so that intense inflammation is generalized and persistent [24, 42, 43]. In cell therapy, several factors appear to contribute to the termination of acute inflammation, including generation of anti-inflammatory cytokines (for example, IL-10) [44–46], cytokine inhibitors [47], antibacterial peptides [48] and growth factors that induce protection of the alveolar epithelial cells [49–51].
In swine, endotoxemia results in increased circulating concentrations of several cytokines and growth factors [23]. Although administration of bone marrow cells did not entirely prevent these responses, they changed the pattern of cytokine responses, significantly decreasing generation of Th1 pro-inflammatory cytokines without decreasing the anti-inflammatory Th2 cytokine IL-6, preventing lung tissue responses to endotoxemia and lung edema. Those responses were temporally coincident with decreased circulating levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β) that are known to affect inflammatory cell trafficking.
Conclusions
In summary, results presented in the present work suggest that fresh, autologous non-cultured bone marrow nuclear cells, including non-hematopoietic bone marrow derived cells, have the ability to suppress the endotoxin-induced systemic inflammatory response at similar levels to what is observed when in vitro expanded heterologous mesenchymal stromal cells are used. Expanded or freshly isolated autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells could prove to be a novel approach to therapy for some acute and chronic lung diseases.
Abbreviations
- ARDS:
-
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- BMC:
-
whole bone marrow cell suspensions
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- Cultured CD45neg cells:
-
in vitro expanded swine CD45 negative adherent allogeneic bone marrow cells
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- FACS:
-
fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- IL:
-
interleukin
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- MPO:
-
myeloperoxidase
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffered saline
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor alpha.
References
Schraufnagel DE: Breathing in America: Diseases, Progress, and Hope. 2010, New York: American Thoracic Society
Johnson ER, Matthay MA: Acute lung injury: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatent. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010, 23: 243-252. 10.1089/jamp.2009.0775.
Hayes M, Curley G, Ansari B, Laffey JG: Clinical review: stem cell therapies for acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome - hope or hype?. Crit Care. 2012, 16: 205-10.1186/cc10570.
Lee JS, Su X, Rackley C, Matthay MA, Gupta N: Priming with endotoxin increases acute lung injury in mice by enhancing the severity of lung endothelial injury. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2011, 294: 165-172. 10.1002/ar.21244.
Matthay MA, Zemans RL: The acute respiratory distress syndrome: pathogenesis and treatment. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011, 6: 147-163. 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130158.
Matthay MA, Jayr C: Acute respiratory distress syndrome after surgery: can the risk be decreased?. Anesth Analg. 2010, 111: 268-269. 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181e75ced.
Matthay MA, Idell S: Update on acute lung injury and critical care medicine 2009. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010, 181: 1027-1032. 10.1164/rccm.201001-0074UP.
Johnson ER, Matthay MA: Acute lung injury: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010, 23: 243-252. 10.1089/jamp.2009.0775.
Fremont RD, Koyama T, Calfee CS, Wu W, Dossett LA, Bossert FR, Mitchell D, Wickersham N, Bernard GR, Matthay MA, Addison KM, Ware LB: Acute lung injury in patients with traumatic injuries: utility of a panel of biomarkers for diagnosis and pathogenesis. J Trauma. 2010, 68: 1121-1127. 10.1097/TA.0b013e3181c40728.
Friedenstein AJ, Deriglasova UF, Kulagina NN, Panasuk AF, Rudakowa SF, Luria EA, Ruadkow IA: Precursors for fibroblasts in different populations of hematopoietic cells as detected by the in vitro colony assay method. Exp Hematol. 1974, 2: 83-92.
Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK, Latsinik NV, Panasyuk AF, Keiliss-Borok IV: Stromal cells responsible for transferring the microenvironment of the hemopoietic tissues. Cloning in vitro and retransplantation in vivo. Transplantation. 1974, 17: 331-340. 10.1097/00007890-197404000-00001.
Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhjan RK, Lalykina KS: The development of fibroblast colonies in monolayer cultures of guinea-pig bone marrow and spleen cells. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1970, 3: 393-403.
Friedenstein A, Kuralesova AI: Osteogenic precursor cells of bone marrow in radiation chimeras. Transplantation. 1971, 12: 99-108. 10.1097/00007890-197108000-00001.
Singer NG, Caplan AI: Mesenchymal stem cells: mechanisms of inflammation. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011, 6: 457-478. 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130230.
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A, Prockop D, Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006, 8: 315-317. 10.1080/14653240600855905.
Xu J, Woods CR, Mora AL, Joodi R, Brigham KL, Iyer S, Rojas M: Prevention of endotoxin-induced systemic response by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007, 293: L131-141. 10.1152/ajplung.00431.2006.
Gupta N, Su X, Popov B, Lee JW, Serikov V, Matthay MA: Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves survival and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Immunol. 2007, 179: 1855-1863.
Cribbs SK, Matthay MA, Martin GS: Stem cells in sepsis and acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 2010, 38: 2379-2385. 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181f96f5f.
Fang X, Neyrinck AP, Matthay MA, Lee JW: Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cells restore epithelial protein permeability in cultured human alveolar type II cells by secretion of angiopoietin-1. J Biol Chem. 2010, 285: 26211-26222. 10.1074/jbc.M110.119917.
Lee JW, Fang X, Gupta N, Serikov V, Matthay MA: Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of E. coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in the ex vivo perfused human lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009, 106: 16357-16362. 10.1073/pnas.0907996106.
Matthay MA, Goolaerts A, Howard JP, Lee JW: Mesenchymal stem cells for acute lung injury: preclinical evidence. Crit Care Med. 2010, 38: S569-573.
Serikov VB, Mikhaylov VM, Krasnodembskay AD, Matthay MA: Bone marrow-derived cells participate in stromal remodeling of the lung following acute bacterial pneumonia in mice. Lung. 2008, 186: 179-190. 10.1007/s00408-008-9078-6.
Fireman Z, Shabtai F, Lurie B: Chromosome sensitivity to bleomycin-induced mutagenesis in lymphocytes from colorectal cancer patients under 40 years of age. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994, 37: 1317-1320. 10.1007/BF02257804.
Rojas M, Woods CR, Mora AL, Xu J, Brigham KL: Endotoxin-induced lung injury in mice: structural, functional, and biochemical responses. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005, 288: L333-341.
Ohkawa S, Inoue J, Sugiura M: [A clinicopathologic study of dilated cardiomyopathy in the aged]. J Cardiogr Suppl. 1986, 35-47. 9
Davis PB, Del Rio S, Muntz JA, Dieckman L: Sweat chloride concentration in adults with pulmonary diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983, 128: 34-37.
Farrell PM, Mischler EH, Gutcher GR: Evaluation of vitamin E deficiency in children with lung disease. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1982, 393: 96-108. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb31236.x.
Gibson GJ, Pride NB: Lung distensibility. The static pressure-volume curve of the lungs and its use in clinical assessment. Br J Dis Chest. 1976, 70: 143-184.
Jiang ZQ, Yang K, Komaki R, Wei X, Tucker SL, Zhuang Y, Martel MK, Vedam S, Balter P, Zhu G, Gomez D, Lu C, Mohan R, Cox JD, Liao Z: Long-term clinical outcome of intensity-modulated radiotherapy for inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer: the MD Anderson Experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012, 83: 332-329. 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.06.1963.
Nardi A, Brillet PY, Letoumelin P, Girard F, Brauner M, Uzunhan Y, Naccache JM, Valeyre D, Nunes H: Stage IV sarcoidosis comparison of survival with the general population and causes of death. Eur Respir J. 2011, 38: 1368-1373. 10.1183/09031936.00187410.
Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. N Engl J Med. 2000, 342: 1301-1308.
Berger G, Guetta J, Klorin G, Badarneh R, Braun E, Brod V, Saleh NA, Katz A, Bitterman H, Azzam ZS: Sepsis impairs alveolar epithelial function by downregulating Na-K-ATPase pump. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011, 301: L23-30. 10.1152/ajplung.00010.2010.
Vadasz I, Weiss CH, Sznajder JI: Ubiquitination and proteolysis in acute lung injury. Chest. 2012, 141: 763-771. 10.1378/chest.11-1660.
Piantadosi CA, Schwartz DA: The acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 2004, 141: 460-470.
Yamashita CM, Lewis JF: Emerging therapies for treatment of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2012, 17: 1-4.
Lee JW, Fang X, Krasnodembskaya A, Howard JP, Matthay MA: Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells for acute lung injury: role of paracrine soluble factors. Stem Cells. 2011, 29: 913-919. 10.1002/stem.643.
Gotts JE, Matthay MA: Mesenchymal stem cells and acute lung injury. Crit Care Clin. 2011, 27: 719-733. 10.1016/j.ccc.2011.04.004.
Sprengers RW, Moll FL, Teraa M, Verhaar MC: Rationale and design of the JUVENTAS trial for repeated intra-arterial infusion of autologous bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells in patients with critical limb ischemia. J Vasc Surg. 2010, 51: 1564-1568. 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.02.020.
Johnson RF, Gustin J: Acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome requiring tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation in the intensive care unit: impact on managing uncertainty for patient-centered communication. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2012
Starnes-Roubaud M, Bales EA, Williams-Resnick A, Lumb PD, Escudero JA, Chan LS, Garner WL: High frequency percussive ventilation and low FiO(2). Burns. 2012, 38: 984-991. 10.1016/j.burns.2012.05.026.
Ribeiro-Paes JT, Bilaqui A, Greco OT, Ruiz MA, Marcelino MY, Stessuk T, de Faria CA, Lago MR: Unicentric study of cell therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/pulmonary emphysema. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2011, 6: 63-71.
Everhart MB, Han W, Sherrill TP, Arutiunov M, Polosukhin VV, Burke JR, Sadikot RT, Christman JW, Yull FE, Blackwell TS: Duration and intensity of NF-kappaB activity determine the severity of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. J Immunol. 2006, 176: 4995-5005.
Maus UA, Janzen S, Wall G, Srivastava M, Blackwell TS, Christman JW, Seeger W, Welte T, Lohmeyer J: Resident alveolar macrophages are replaced by recruited monocytes in response to endotoxin-induced lung inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006, 35: 227-235. 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0241OC.
Garcia-Yoldi D, Le Fleche P, De Miguel MJ, Munoz PM, Blasco JM, Cvetnic Z, Marin CM, Vergnaud G, Lopez-Goni I: Comparison of multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis with other PCR-based methods for typing Brucella suis isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2007, 45: 4070-4072. 10.1128/JCM.01096-07.
Thomassen MJ, Divis LT, Fisher CJ: Regulation of human alveolar macrophage inflammatory cytokine production by interleukin-10. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1996, 80: 321-324. 10.1006/clin.1996.0130.
Kondoh K, Usui Y, Ohtani Y, Inase N, Miyake S, Yoshizawa Y: Proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Med Dent Sci. 2006, 53: 75-83.
Ortiz LA, Dutreil M, Fattman C, Pandey AC, Torres G, Go K, Phinney DG: Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist mediates the antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect of mesenchymal stem cells during lung injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007, 104: 11002-11007. 10.1073/pnas.0704421104.
Liu L, Bailey SM, Okuka M, Muñoz P, Li C, Zhou L, Wu C, Czerwiec E, Sandler L, Seyfang A, Blasco MA, Keefe DL: Telomere lengthening early in development. Nat Cell Biol. 2007, 9: 1436-1441. 10.1038/ncb1664.
Verdejo B, Blasco S, Garcia-Espana E, Lloret F, Gavina P, Soriano C, Tatay S, Jimenez HR, Domenech A, Latorre J: Imidazolate bridged Cu(II)-Cu(II) and Cu(II)-Zn(II) complexes of a terpyridinophane azamacrocycle: a solution and solid state study. Dalton Trans. 2007, 4726-4737. 41
Murga M, Jaco I, Fan Y, Soria R, Martinez-Pastor B, Cuadrado M, Yang SM, Blasco MA, Skoultchi AI, Fernandez-Capetillo O: Global chromatin compaction limits the strength of the DNA damage response. J Cell Biol. 2007, 178: 1101-1108. 10.1083/jcb.200704140.
Liu F, Liu J, Weng D, Chen Y, Song L, He Q, Chen J: CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells depletion may attenuate the development of silica-induced lung fibrosis in mice. PloS One. 2010, 5: e15404-10.1371/journal.pone.0015404.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grant numbers 5P01 HL0669496-02, 5K01HL084683-02 and 1RO1HL083019-01 from the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, a grant from the American Federation for Aging Research, Emory University URC #2003100 the McKelvey Center for Lung Transplantation at Emory University and the Dorothy P. and Richard P. Simmons Center for Interstitial Lung Diseases at the University of Pittsburgh.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
MR and KLB conceived, interpreted and analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. RP and NT were responsible for swine experiments, collection and assembly of data. CC and SI executed the ELISA and FACS assays and they did the expansion of swine adherent CD45neg and consequent data analysis and interpretation. AS and AM made substantial contributions in the conception and design of the experiments and critically revised the content of the completely revised manuscript. LM, MB and NC were responsible for tissue processing, staining and analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Rojas, M., Parker, R.E., Thorn, N. et al. Infusion of freshly isolated autologous bone marrow derived mononuclear cells prevents endotoxin-induced lung injury in an ex-vivo perfused swine model. Stem Cell Res Ther 4, 26 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt174
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt174