Abstract
Background
Euphorbia resinifera is a melliferous, medicinal, and endemic plant to Morocco. Nevertheless, its ecological and genetic diversity still unknown. The objective of this study is to analyze the diversity and genetic structure of Moroccan wild populations of E. resinifera using ISSR markers. Twelve natural populations collected from its geographical range in Morocco were analyzed using 14 ISSR primers.
Results
A total of 125 bands were obtained, with polymorphism of 74.81%. The polymorphic information content (PIC), resolving power (Rp), Shannon’s information index (I), and total genetic diversity (Ht) were 0.33, 2.8, 0.35, and 0.21, respectively. The analysis of molecular variance showed that 75.56% of the total variability is present within populations and that 24.44% exists among populations. Also, the analysis showed a very low genetic differentiation between groups of mountain range type (FCT = 0.066), mountain versant type groups (FCT = −0.024), and altitude groups (FCT = −0.022). Moreover, the geographical distances between populations are correlated with their corresponding genetic distances according to the Mantel test (r = 0.507; P < 0.0001).
Conclusion
These results suggest that the population structuring follows a model of isolation by geographical distance. Indeed, the genetic structuring of populations into two groups obtained from PCoA and structure analysis revealed a dependence on the geographical origin of the populations. By contrast, the genetic distances are not correlated with the altitude.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
With nearly 2000 species, the genus Euphorbia is the largest of the Euphorbiaceae family and the second largest genus of flowering plants in the world [1, 2]. Despite its great vegetative diversity [3], the genus is united morphologically by the possession of a cyathium, a highly reduced inflorescence that resembles a single flower [4]. In Morocco, few species exist, with a notable proportion of them being endemic [5]. Euphorbia resinifera O. berg is one among them, growing naturally in the Atlas Mountains, particularly in Beni Mellal and Azilal provinces [5]. The plant covers the mountain in a very discontinuous way from the High Atlas Mountain (Demnat) to the Middle Atlas Mountain (El Ksiba) [6]. It presents a cushioned physiognomy constituted by a bush of juxtaposed stems. On average, the growth in height does not exceed one meter; however, their lateral growth is more important ranging from 0.5 to 2 m, which contributes to the decrease of the soil erosion. The mating system of species is primarily allogamous. Indeed, the Cyathes are arranged by 3 in axillary cyme stalks, towards the end of stems and branches; Cyathes are lateral hermaphroditic, stalked with thick peduncle; the median subsessile and male usually develop first and fall before the maturity of the capsules of the lateral cyathiums. E. resinifera employs both sexual and vegetative means of reproduction to ensure the survival and expansion of its population [7]. The yellow flowers of this wild species attract and feed the bees. The beekeepers came from all regions of Morocco for take place near of the E. resinifera populations during the flowering season. Thus, with an annual honey production of about 300 tons, it is an important plant of the solidary agriculture in the region. It is well known as a melliferous plant for its high therapeutic and nutritional quality honey [8, 9], which has been recognized as a local product of the region and has been labeled Protected Geographical Indication (PGI) [10].
Additionally, E. resinifera was recognized as having a vast therapeutic properties and benefits. In folk medicine, it is used to treat some types of complicated dermatoses, cancer treatment and control glycaemia in type II diabetics [11,12,13]. In 1975, the resiniferatoxin major element in the latex of E. resinifera was identified [14]. This molecule has many potential medical applications, analog to capsaicin but 1000 more potent than it [15]. Moreover, many compounds of the latex of this species are endowed with biological activities as an anticancer [16, 17], antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal [18, 19], an anti-pain and anti-tuberculosis [20, 21].
Nevertheless, the genetic resources of this species underwent important genetic erosion caused by various factors including the overgrazing, the deforestation provoked by a demographic pressure, voluntary or natural fires, and some fungal diseases attacking the plant. Consequently, emergency measures should be taken to safeguard this wild species. Thus, the safeguard and valorization of these local plant genetic resources constitute not only an imperative but also a major component of the stability of natural ecosystems and their valorization in agro-economic, therapeutic, and environmental perspectives. For that, the description of Moroccan E. resinifera populations may help to identify different genotypes and rationalize conservative treatments. Therefore, it has become imperative to establish a research program aiming at the evaluation of the genetic diversity of this species. Our first study on morphological characters showed high phenotypic diversity in twelve Moroccan populations [3]. However, no information is available on its genetic diversity. For this, it becomes necessary to find more discriminating markers, which could provide information about the variability within and among populations of this species and investigate new resources of variation which might be used for specific conservation programs.
Several types of molecular markers are employed for assessment of genetic diversity and relationships in plant species, including RFLPs (restriction fragment length polymorphisms) [22], RAPDs (randomly amplified polymorphic DNAs) [23,24,25], AFLP (amplified fragment length polymorphisms) [26, 27], SNPs (single-nucleotide polymorphic) [28], SSRs (simple sequence repeats) [29,30,31], and ISSRs (inter simple sequence repeats) [32,33,34,35]. However, RAPDs have low reproducibility, RFLPs are time-consuming and labor-intensive, SSRs require the knowledge of the flanking regions for the development of species-specific primers, and AFLPs and SNPs have high cost [36], while the ISSR markers are hypervariable, highly reproducible, fast, inexpensive, and do not require any prior sequence information of amplified locus [36, 37]. ISSR is a kind of DNA sequences confined by two inverted SSR composed of the same motives, which are amplified by a unique PCR primer. ISSR-PCR detects the levels of variation in microsatellite regions and gives multi-locus schemes, which are very iterative, plentiful, and polymorphic in plant genomes [38, 39].
The present work provides the first data on the genetic diversity of Moroccan E. resinifera based on molecular markers. Our objectives were to give a preliminary estimation of the genetic diversity and structure of this species. Then, twelve natural populations of E. resinifera originating from diverse altitudes and geographical area were analyzed using fourteen ISSR primers.
Materials and methods
Plant material and DNA extraction
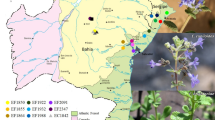
The plant material used in this study included twelve natural populations representing the distribution area of E. resinifera in Morocco (Fig. 1). Six populations are originating from High Atlas Mountain and six belonging to the Middle Atlas Mountain. The geographic characteristics and meteorological conditions such as altitude slice, central latitude and longitude as well as the mean precipitation and temperature average of these populations are provided in Table 1. From each population, five bush of similar age were randomly sampled and the collected young stems were stored at −20 °C until DNA extractions.
The DNA was extracted following the method described by Doyle and Doyle [40] slightly modified [41]. The quality of extracted DNA was examined by electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel, and DNA quantity was determined spectrophotometrically. Later, the samples were brought to a working concentration of 10 ng/μl.
ISSR analyses
A total of 14 ISSR primers previously displayed reliable and polymorphic band profiles [42, 43] were used in this work (Table 2). The amplification reactions were performed in a volume of 12.5 μl, which contained 6.25 μL 2 × Green Taq Mix (Vazyme, Nanjing, China), 0.5 μL of each primer (0.4 μM), 5 μL of template genomic DNA (4 ng/μL), and 0.75 μL of distilled deionized water. PCRs were conducted in a DNA thermocycler (Multigene gradient, Labnet, NJ. USA). The PCR program consisted of an initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles according to the following procedure: denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at determined temperature for 30 s, extension at 72 °C for 1 min, the last cycle was followed by a final extension for 7 min at 72 °C. Gradient PCR was used to determine the annealing temperature of each primer (Table 2). PCR products were separated by electrophoresis on 1.7% agarose gel submerged in 0.5 × TBE buffer and stained with 1 μg/μl of ethidium bromide. The DNAs were visualized under UV light using the Gel Doc system (EnduroTM GDS, Labnet). The fragment size was estimated by using a DNA marker (100 bp plus II DNA ladder, TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd).
Data analyses
The band profiles of each gel were scored visually and recorded as presence (1) or absence (0) of bands leading to the construction of data binary matrix (1,0). For each primer, the percentage of polymorphic band (PPB), the polymorphic information content (PIC), and resolving power (Rp) were determined. Also, the POPGENE software was used to measure the following parameters: numbers of alleles (Na), effective number of alleles (Ne), genetic diversity within populations (Hs), total gene diversity (Ht), coefficient of gene differentiation (Gst), and Shannon’s information index (I). Partition of the observed genetic variation and calculation of the corresponding F values were carried out using different hierarchical analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA). Firstly, global analysis of AMOVA was done to apportion the total genetic variation into two hierarchical levels: among populations (FST) and within populations. Secondly, hierarchical AMOVA analysis was used to partition the variation among:
-
Two mountain range groups of populations: Middle Atlas (populations: KSB, TAG, AAS, OAY, AFO, and MOD) and High Atlas (populations: BIN, BZO, FMJ, IMI, WAW, and OUZ)
-
Three mountain versant groups of populations: North versant (populations: BIN, AAS, OAY, and AFO), Southwest versant (populations: OUZ, TAG, FMJ, and IMI), and South versant (populations: BZO, MOD, WAW, and KSB)
-
Two altitude groups of populations: very low (populations: BZO, OAY, TAG, AAS, FMJ, BIN, OUZ, and AFO) and low (populations: KSB, MOD, IMI, and WAW) (Table 1)
Population’s specific FST indices were also calculated to investigate which population is more divergent from the remaining. The average gene diversity over loci was calculated to estimate intra-population variability. These evaluations were performed using the package ARLEQUIN version 3.01 [44]. The pairwise genetic differentiations (FST) between the twelve populations were also generated by AMOVA and the gene flow (Nem) was approximated estimated through Wright’s island model: Nem = 0.25 (1/FST - 1) [45]. A Mantel test was used to test whether matrix of genetic distances (FST) between populations was significantly correlated with their corresponding matrices of geographic distances and difference of altitude (1000 permutations; routine MXCOMP of the NTSYS-pc; package). A Bayesian structure analysis was executed using the STRUCTURE v.2.3.4 software to deduce the population genetic structure and define the number of groups within the studied populations [46]. To identify the number of K clusters explaining the observed genetic structure, we used the STRUCTURE Harvester website [47], which implements the Evanno method [48]. Furthermore, to elucidate the populations’ relationships, principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) was carried out using the DARwin software version 6.0.02 [49].
Results
ISSR polymorphism
The 14 ISSR primers amplified a total of 125 bands in the set of twelve E. resinifera populations, of which 101 band were polymorphic. The number of bands ranged from 4 (UBC810, UBC834, UBC84, and UBC845) to 13 (UBC840), with an average of 7.21 (Table 2). The percentage of polymorphic bands (PPB) oscillated from 33.33% (UBC84) to 100% (UBC811, UBC814, and UBC840), with an average of 74.81%. The PIC value varied from 0.14 (UBC853) to 0.48 (UBC834) with mean of 0.33. Regarding, the resolving power (Rp), which present an interesting tool to determine the efficiency of primer to differentiate between populations, varied from 2.07 (UBC815) to 4.87 (UBC811), with an average of 4.91.
Genetic diversity
Estimates of genetic diversity of studied populations are summarized in Table 3. The results showed that the number of observed alleles (Na) was fixed in the value of 2 for all primers. The highest effective number of alleles (Ne) varied from 1.09 (UBC853) to 1.56 (UC834) with a general mean of 1.34 allele per primer, while Shannon’s Information index (I) showed a lowest value (0.17) for UBC853 and the highest value (0.54) for UBC834, with an average of 0.35. In addition, the total genetic diversity (Ht) oscillated from 0.08 for UBC853 to 0.33 for UBC834 with an average of 0.21. The genetic diversity within species (Hs) ranged from 0.06 for UBC853 to 0.31 for UBC834 (mean 0.15). Moreover, Nei’s coefficient of genetic differentiation between populations (GST) varied from 0.12 (UBC834) to 0.44 (UBC836) with an average of 0.32, indicating that 32% of total genetic variability was distributed among populations and the remaining (68%) accounted for within populations. These results were congruent with that revealed by FST value, accounting for 0. 244 (Table 4). The great level of genetic differentiation among population of this wild plant is in accordance with the low value of gene flow estimated (Nem = 0.77) which provides information on amount of number of exchanged individuals between populations studied.
When AMOVA was performed, at three hierarchical levels, with two mountain range type, very low genetic differentiation was observed between groups (FCT = 0.066) even though that it is slightly significant (Table 4). This indicates that mountain range type has had little effect on populations’ structuration which implies that there is no local adaptation of studied populations. Also, a very low genetic differentiation was obtained between mountain versant type groups of populations (FCT = −0.244) and among altitude groups (FCT = −0.222).
Genetic relationship
The pairwise FST values and geographic distances between the 12 populations are presented in Table 5. According to the Mantel test (r = 0.507; P < 0.0001), the geographical distances between populations are correlated with their corresponding genetic distances. These results suggest that the populations’ structure follows a model of isolation by geographical distance. By contrast, no significant association was obtained between the genetic distance and difference of altitude between populations (r = −0.16, P = 0.19). Thus, the populations “AAS” and “FMJ” with a low difference of altitude (2 m) have a high value of genetic distance (0.376), and the populations “BZO” and “WAW” with a high difference of altitude (743 m) have obtained the low value of genetic distance (0.195). Between 66 pairwise FST values, 54 values are significant, meaning that the populations are widely different from each other. The significant values varied from 0.084 (FMJ/BZO; 12) to 0.466 (OUZ/KSB; 87), which mean that populations FMJ/BZO are the most genetically similar and OUZ/KSB are the most divergent. The result indicated that the Bin El Ouidane (BIN) and Bzou (BZO) populations have the lowest value of specific FST index (respectively 0.209 and 0.212), and Elksiba (KSB) population has the highest value of this index (FST = 0.289), implying that this latter population is the most divergent from the others studied. Regarding the intrapopulation variability assessed by gene diversity over loci (data not shown) which oscillated from 0.148 for Elksiba (KSB) to 0.261 for Bin El Ouidane (BIN) and 0.257 for Bzou (BZO), reflecting consequently for any in situ and/or ex situ conservation strategy should aim to include those later populations.
The structure analysis based on the ΔK method showed that the best number of genetic clusters (K) was 2, suggesting that all individuals fell into two clusters (Fig. 2). Moreover, based on the permuted average Q-matrix generated by Clumpak, the highest H′ was observed for K = 2 (H′ = 0.947), indicating the stability of the result for this model. Considering the genotypes as pure when the membership coefficient was greater than 0.80 and as a hybrid or admixture when the membership coefficient was lower than 0.80, 41 individuals among the 60 analyzed (68.33%) were assigned to one of the model’s defined groups. The first group (red) was formed by the individuals from High Atlas Mountain populations, namely Bzou (BZO4), Ouled Ayyad (OAY2, OAY3, and OAY5), Bin El Ouidane (BO3 and BO4), all individuals from populations of Ouzoud (OUZ1, 2, 3, 4, and 5), Imi n’Ifri (IMI5), and four from Wawla (WAW1, WAW2, WAW4, and WAW5), with a membership coefficient oscillated between 0.815 to 0.990, while the rest of this group were originating from Middle Atlas Mountain populations: Afourer (AFO2 and AFO4), Modj (MOD1), with a membership coefficient ranging from 0.953 to 0.980. Nevertheless, the other seven individuals, namely (TAG3, TAG5) from Tagzirt population, (AFO3, AFO5) coming from Afourer population, MOD3 from Modj population, IMI1 belonging to Imi n’Ifri population, and WAW3 from Wawla population could be considered as admixed (coefficients ranged from 0.507 to 0.644). The second group (green) contained individuals coming from High Atlas Mountain populations: (BO1, BO2, and BO5) of North versant, with a membership coefficient ranging from 0.954 to 0.975, all individuals of Foum Jemaa population (FMJ1, 2, 3, 4, and 5), and one individual (IMI2) from Imi n’Ifri population belonging to Southwest versant (coefficients between 0.840 and 0.959) and (BZO1, BZO2, and BZO3) collected from South versant having a membership coefficient between 0.922 and 0.986, while the rest of group include bushes coming from Middle Atlas Mountain populations: (AAS3 and AAS4) of North versant with an assignment coefficient of 0.888 and 0.86 respectively, (TAG1, TAG2 and TAG4) of Southwest versant with a membership coefficient from 0.932 to 0.969, and all bushes of Elksiba population (KSB1, 2, 3, 4, and 5) from South versant mountain, having a coefficient of assignment oscillating between 0.929 and 0.976. Finally, 12 remaining bushes which could be considered as admixture belonged to the OAY, AAS, AFO, MOD, IMI, and BZO populations (coefficients between 0.508 and 0.775).
The genetic structure of Moroccan E. resinifera populations was further reconstructed by using the PCoA. Indeed, about 24% of total variance was explained by the first two components and the plot of PCoA divided studied populations in two groups (I and II, Fig. 3), which corroborates the populations’ structure obtained by Bayesian analysis (Fig. 2). Consequently, the genetic structure of all studied populations bushes in two main groups was operated independently of altitude and mountain versant type.
Discussion
DNA markers have become a useful tool for evaluating the genetic diversity of many different plant species. In this work, ISSR markers were used to assess the genetic diversity of E. resinifera populations in Morocco. The 14 tested ISSRs primers revealed a high percentage of polymorphism with an average of 74.81%. This high percentage implies that there is an important genetic diversity in this endemic species. This result is higher than that reported with ISSR markers for other Euphorbia species (E. khabrica, E. buhsei, E. osyridea, and E. austro-iranica) in Iran by Pahlevani et al. (13.02%, 20.71%, 24.85%, and 14.20%, respectively) [50], in Saudi Arabia by Moustafa et al. (Euphorbia prostrata Aiton, Euphorbia peplus L., and Euphorbia terracina L.) (20.28%, 14.08%, and 11.44%, respectively) [51], and for 15 Euphorbia species by El-Hawary et al. (total polymorphism = 57.7%) [52]. However, our finding was lower than that observed by Reginaldo et al. for Brazilian Euphorbiaceae (Croton urucurana Baill) (89%) based on ISSR markers [53] and by Dorset et al. for American E. telephioides (80.7%) revealed by allozyme markers [54]. In addition, the high values of PIC (0.33) and Rp (2.8) parameters show that the ISSR markers are very informative and efficient for analyzing the diversity and genetic structure of E. resinifera. These values are comparable with these obtained by Reginaldo et al. for Brazilian Euphorbiaceae (Croton urucurana Baill) using ISSRs markers (PIC = 0.29 and Rp = 3.4) [53]. Moreover, the high multi-locus value of Ht (= 0.21) suggests the presence of a high level of polymorphism of this endemic species. Indeed, this high polymorphism is confirmed by the Shannon index value (I = 0.35). This value is higher than that obtained by Reginaldo et al. (I = 0.26) for Brazilian Euphorbiaceae using ISSRs markers [53]. Besides, the gene diversity within the species (Hs) was 0.15. This high genetic diversity obtained in Moroccan E. resinifera populations is in agreement with the general trend for allogamous and long-lived woody perennial species (Ht = 0.28) and for angiosperm species (Ht = 0.28) [55]. The wild populations of E. resinifera were largely differentiated (Gst = 0.32, FST = 0.244) which could be due to restricted gene flow (Nem = 0.77) between populations. This finding is in concordance with that observed for other herbaceous outcrossing perennial plant species (Gst > 0.20) [56]. The Gst value (0.32) detected in this investigation is higher than that recorded by Dorset et al. for the endemic North American species Euphorbia telephioides (0.10) using allozyme markers [54]. Similar results were revealed by Ki-Ryong for Euphorbia fauriei in Korea (Fst = 0.237; Nem = 0.80) and Euphorbia jolkinii in Taiwan (Fst = 0.245; Nem = 0.77) [41]. The indirect estimate of gene flow on the basis of FST was low (Nem = 0.77) and might be due to the presence of geographical barriers between populations such mountains. Indeed, many factors such as discontinuous distribution of populations, limited pollinator movements, and low rate of seed migration could be an efficient obstacle to the gene flow and the origin of the high value of differentiation among E. resinifera populations.
The analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) showed that 75.56% of the diversity accounted for within population leaving 24.44% for among populations. The existence of high genetic variability within population should help the population to cope with local environmental changes. This result implies that sampling from a small number of populations, particularly those with high intrapopulation variability, is sufficient for species in situ and/or ex situ conservation. Bin El Ouidane (BIN) and Bzou (BZO) populations with high intrapopulation variability are more convenient for this purpose.
Moreover, hierarchical AMOVA revealed a very low genetic differentiation between the two groups of mountain range (FCT = 0.066), even though that it is slightly significant, which suggests that mountain range type have had little influence on structuration’s populations. These findings give choice to sampling from populations of Middle or High Atlas Mountains for conservation and breeding species. Likewise, when assembling the populations according to their mountain versant type and altitude, a very low genetic differentiation was obtained between respective groups (respectively, FCT = −0.024 and FCT = −0.022), indicating that mountain versant type and altitude did not have an effect on population structure of the Moroccan E. resinifera populations. Strangely enough, genetic distances were not correlated to the difference of altitude between the populations (r = −0.16, P = 0.19). A similar result was reported for Moroccan walnut using SSR marker [57]. Also, other studies described no genetic differentiation among populations at low and high altitudes [58, 59], probably due to the overlap of flowering phenology in populations at different altitudes, species’ extensive pollen flow, and long distance seed dispersal among different altitudes by animals especially birds. This result is confirmed by the biased model and PCoA which showed that the twelve populations are gathered in two groups undependably to mountain range, mountain versant type, and altitude. In contrast, geographic distances have explained the genetic differentiation between populations according to the Mantel test (r = 0.507; P < 0.0001). This result suggests that the population structure follows a model of isolation by geographic distance. Consequently, our finding suggests that more closely situated populations tend to be more genetically similar to one another.
Conclusion
The present study is the first work aiming to evaluate the genetic diversity and structure of E. resinifera populations in Morocco using ISSR markers. The results of this study confirmed that ISSR markers could be powerful tools for detecting genetic diversity among and within E. resinifera populations. The level of genetic diversity was high, and the genetic variation mainly existed within populations. The results led to structure of populations in two gene pools independently of mountain range type, mountain versant type, and altitude. Based on these results, it could be sufficient to sample from a few populations, particularly those most genetically diversified, for any in situ and/or ex situ conservation strategy.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Abbreviations
- ISSR:
-
Inter simple sequence repeat
- PIC:
-
Polymorphic information content
- Rp:
-
Resolving power
- I:
-
Shannon’s information index
- Ht:
-
Total genetic diversity
- Hs:
-
Genetic diversity within populations
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- TBE:
-
Tris-Borate-EDTA
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
- PPB:
-
Percentage of polymorphic band
- Na:
-
Numbers of alleles
- Ne:
-
Effective number of alleles
- Gst:
-
Coefficient of gene differentiation
- AMOVA:
-
Analysis of molecular variance
- Nem:
-
Gene flow
- UPGMA:
-
Unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic mean
- MCMC:
-
Markov chain Monte Carlo
- FST:
-
Pairwise genetic differentiations
- UBC:
-
University of British Columbia
References
Horn JW, Xi Z, Riina R, Peirson JA, Yang Y, Dorsey BL, Berry PE, Davis CC, Wurdack KJ (2014) Evolutionary bursts in Euphorbia (Euphorbiaceae) are linked with photosynthetic pathway. Evolution 68(12):3485–3504. https://doi.org/10.1111/evo.12534
Govaerts R, Frodin DG, Radcliffe-Smith A (2000) World checklist and bibliography of Euphorbiaceae (and Pandaceae). R Bot Gard Kew 1–4:1–1622
Abd-dada H, Bouda S, Ait bella Y, Haddioui A (2023) Phenotypic diversity of natural populations of an endemic Moroccan plant (Euphorbia resinifera O. Berg). Hacquetia 22(1):81–90. https://ojs.zrc-sazu.si/hacquetia/article/view/9573
Steinmann VW, Porter JM (2002) Phylogenetic relationships in Euphorbieae (Euphorbiaceae) based on its and ndhF sequence data. Ann Mo Bot Gard 89:453–490
Jahandiez É, Maire R (1932) Catalogue des Plantes du Maroc: Spermaphytes et Ptéridophytes. Tome deuxième: Dicotylédones Archichlamydées 2, Alger, p 461. https://bibdigital.rjb.csic.es/viewer/13175/?offset=#page=305&viewer=picture&o=bookmark&n=0&q=
Emberger L, Maire R (1941) Catalogue des plantes du Maroc: Spermatophytes et ptéridophytes, Vol. 4
Fennane M, Ibn-Tattou M (2007) Flore pratique du Maroc: Manuel de détermination des plantes vasculaires, Angiospermae (Leguminosae-Lentibulariaceae), Vol 2, Institut Scientifique de rabat, p 635. https://books.google.co.ma/books/about/Flore_pratique_du_Maroc.html?id=9v2UMQEACAAJ&redir_esc=y, https://www.nhbs.com/search?q=Flore+Pratique+du+Maroc+&qtview=205183, https://bibliotheques.mnhn.fr/medias/doc/EXPLOITATION/HORIZON/295259/flore-pratique-dumaroc-manuel-de-determination-des-plantes-
Moujanni A, Essamadi AK, Terrab A (2017) L’apiculture au Maroc: focus sur la production de miel. Int J Innov Appl Stud 20(1):52–78
Bettar I, González-Miret ML, Hernanz D, Marconi A, Heredia FJ, Terrab A (2019) Characterisation of Moroccan Spurge (Euphorbia) honeys by their physicochemical characteristics, mineral contents and colour. Arab J Chem 12(8):2052–2060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.01.003
MMA: Moroccan Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries, Rural Development, Water and Forests (2012). https://www.agriculture.gov.ma/sites/default/files/siam15-produit_terroir-vang.pdf
Bellakhdar J, Claisse R, Fleurentin J, Younos C (1991) Repertory of standard herbal drugs in the Moroccan pharmacopoea. J Ethnopharmacol 35(2):123–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-8741(91)90064-K
Errajraji A, Ouhdouch F, El-Anssari N (2010) Usage des plantes médicinales dans le traitement du diabète de type 2 au Maroc. Méd Des Mal Métab 4(3):301–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1957-2557(10)70064-X
Bourhia M, Shahat AA, Almarfadi OM, Naser FA, Abdelmageed WM, Ait Haj Said A, El Gueddari F, Naamane A, Benbacer L, Khlil N (2019) Ethnopharmacological survey of herbal remedies used for the treatment of cancer in the greater Casablanca-Morocco. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1613457
Hergenhahm M, Adolf W, Hecker E (1975) Resiniferatoxin and other esters of novel polyfunctional diterpenes from Euphorbia resinifera and unispina. Tetrahedron Lett 19:1595–1598
Appendino G, Ech-Chahad A, Minassi A, De Petrocellis L, Di Marzo V (2010) Structure–activity relationships of the ultrapotent vanilloid resiniferatoxin (RTX): the side chain benzylic methylene. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20(1):97–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.11.035
Zhang K, Fan W, Huang Z, Chen D, Yao Z, Li Y, Yang Y, Qiu D (2019) Transcriptome analysis identifies novel responses and potential regulatory genes involved in 12-deoxyphorbol-13-phenylacetate biosynthesis of Euphorbia resinifera. Ind Crops Prod 135(April):138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.04.030
Talbaoui A, Hamdaoui L (2020) Chemical composition, in vitro cytotoxic, and antibacterial activities of Moroccan medicinal plants Euphorbia resinifera and Marrubium vulgare. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 10(6):7343–7355. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC106.73437355
Glatthaar-Saalmüller B, Fallier-Becker P (2001) Antiviral action of Euphorbium compositum and its components. Forschende Komplementarmedizin Und Klassische Naturheilkunde 8(4):207–212. https://doi.org/10.1159/000057223
Farah H, Ech-chahad A, Lamiri A (2014) In vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activity of the root extract of Euphorbia resinifera. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 2(5):161–163
Szallasi A, Blumberg PM (1989) Resiniferatoxin, a phorbol-related diterpene, acts as an ultrapotent analog of capsaicin, the irritant constituent in red pepper. Neuroscience 30(2):515–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(89)90269-8
Sharma PK, Avula B, Panda A, Wang YH, Khan IA, Murthy SN (2019) A sensitive bioanalytical method for quantitative determination of resiniferatoxin in rat plasma using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry and its application in pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Biomed Anal 165:284–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.12.024
Fjellstrom RG, Parfitt DE (1995) Phylogenetic analysis and evolution of the genus Juglans (Juglandaceae) as determined from nuclear genome RFLPs. Plant Syst Evol 197:19–32
Nicese FP, Hormasa JI, Mc Granaham GH (1998) Molecular characterization and genetic relatedness among walnut (Juglans regia L.) genotypes based on RAPD markers. Euphytica 101:199–206
Fatahi R, Ebrahimi A, Zamani Z (2010) Characterization of some Iranians and foreign walnut genotypes using morphological traits and RAPDs markers. Hort Environ Biotechnol 51:51–60
Li Z, Lanying Z, Qianwen X (2007) Identification of RAPD markers linked to thickness gene of shuck in walnut. Adv Biol Res 1:137–140
Kafkas S, Ozkan H, Sutyemez M (2005) DNA polymorphism and assessment of genetic relationships in walnut genotypes based on AFLP and SAMPL markers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 130:585–590
Bayazit S, Kazan K, Gulbitti S, Çevik V, Ayanoglu H, Ergul A (2007) AFLP analysis of genetic diversity in low chill requiring walnut (Juglans regia L.) genotypes from Hatay, Turkey. Sci Hort 111:394–398
Ciarmiello LF, Piccirillo P, Pontecorvo G, Luca AD, Kafantaris I, Woodrow P (2011) A PCR based SNPs marker for specific characterization of English walnut (Juglans regia L.) cultivars. Mol Biol Rep 38:1237–1249
Ross-Davis A, Woeste K (2008) Microsatellite markers for Juglans cinerea L. and their utility in other Juglandaceae species. Conserv Genet 9:465–469
Pollegioni P, Woeste K, Mugnozza GS, Malvolti ME (2009) Retrospective identification of hybridogenic walnut plants by SSRs fingerprinting and parentage analysis. Mol Breeding 24:321–335
Karimi R, Ershadi A, Vahdati KK, Woeste K (2010) Molecular characterization of Persian walnut populations in Iran with microsatellite markers. Hort Sci 45:1403–1406
Potter D, Gao F, Aiello G, Leslie C, McGranahan G (2002) Intersimple sequence repeat markers for fingerprinting and determining genetic relationships of walnut (Juglans regia) cultivars. J Am Soc Horti Sci 127:75–81
Pollegioni P, Bartoli S, Cannata F, Malvolti ME (2003) Genetic differentiation of four Italian walnut (Juglans regia L.) varieties by inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR). J Genet Breeding 57:231–240
Malvolti ME, Pollegioni P, Bertani A, Mapelli S, Cannata F (2010) Juglans regia provenance research by molecular, morphological and biochemical markers: a case study in Italy. Bioremed Biodiv Bioavailab 4(1):84–92
Miltiadis VC, Dimos R, Eleni T, Penelope JB (2010) Germplasm diversity and genetic relationships among walnut (Juglans regia L.) cultivars and Greek local selections revealed by Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) markers. Sci Hortic 125:584–592
Reddy MP, Sarla N, Siddiq EA (2002) Inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphism and its application in plant breeding. Euphytica 128:9–17
Zietkiwewicz E, Rafalasky JA, Labua D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20:176–183
Agostini G, Echeverrigaray S, Souza-Chies TT (2008) Genetic relationships among South American species of Cunila D. Royen ex L. based on ISSR. Plant Syst Evol 274(3–4):135–141
Yu HH, Yang ZL, Sun B, Liu RN (2011) Genetic diversity and relationship of endangered plant Magnolia officinalis (Magnoliaceae) assessed with ISSR polymorphisms. Biochem Syst Ecol 39(2):71–78
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Ajal EA, Jbir R, Legua P, Martínez JJ, Martinez R, Salhi-Hannachi A, Haddioui A (2015) Genetic diversity of Moroccan pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) cultivars using AFLP markers. Aust J Crop Sci 9(1):22–29
Kabiri G, Bouda S, Elhansali M, Haddioui A (2019) Genetic diversity and structure of walnut (Juglans regia L.) genotypes from middle and high Atlas Mountains of Morocco a investigated by Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) markers. Aust J Crop Sci 13(12):1983–1991. https://doi.org/10.21475/ajcs.19.13.12.p1932
Ait Bella Y, Bouda S, Khachtib Y, Haddioui A (2021) Genetic variability of cultivated plum (Prunus domestica L. & Prunus salicina Lindl.) in Morocco assessed by ISSR markers. Aust J Crop Sci 15(6):948–954. https://doi.org/10.21475/ajcs.21.15.06.p3217
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin ver 30: an integrated software for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinformatics Online 1(4):47–50
Slatkin M, Barton NH (1989) A comparison of three indirect methods for estimating average levels of gene flow. Evolution 43(7):1349–1368. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1989.tb02587.x
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2):945–959. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/155.2.945
Earl DA, Von Holdt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4(2):359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14(8):2611–2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x
Perrier X, Jacquemoud-Collet JP (2006) Darwin software. Available online: http://darwin.cirad.fr/. Accessed 12 Sept 2022.
Pahlevani AH, Feulner M, Weig A, Liede-Schumann S (2017) Molecular and morphological studies disentangle species complex in Euphorbia sect. Esula (Euphorbiaceae) from Iran, including two new species. Plant Syst Evol 303(2):139–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-016-1358-7
Moustafa M, Mostafa O, Al-Shahrani D, Alrumman S (2016) An application of genetics-chemicals constituents to the relatedness of three Euphorbia species. Biologia 71(11):1240–1249. https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2016-0148
El-Hawary SS, Lithy NM, Amin E (2021) Anti-trypanosomal activity and DNA fingerprinting of fifteen Euphorbia species using ISSR and SCoT markers. Beni-Suef Univ Basic Appl Sci 10(1):54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-021-00140-9
Costa RB, de Moraes PM, Skowronski L, de Oliveira CE, Nogueira ML, dos Santos Yui RM, Lorenz AP, Fava WS (2020) Genetic diversity and population structure of Croton urucurana Baill. (Euphorbiaceae) in Central Brazil by ISSR markers. Braz J Bot 43(4):831–838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-020-00657-w
Trapnell DW, Hamrick JL, Negrón-Ortiz V (2012) Genetic diversity within a threatened, endemic North American species, Euphorbia telephioides (Euphorbiaceae). Conserv Genet 13(3):743–751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-012-0323-4
Hamrick JL, Godt MJW, Sherman-Broyles SL (1992) Factors influencing levels of genetic diversity in woody plant species. In: Adams WT, Strauss SH, Copes DL, Griffin AR (eds) Population genetics of forest trees. Forestry sciences, vol 42. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 95–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2815-5_7
Hamrick JL, Godt MJW (1989) Allozyme diversity in plant species. In: Brown AHD, Clegg MT, Kahler AL, Weir BS (eds) Plant population genetics, breeding and genetic resources. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, pp 46–63
Kabiri G, Bouda S, Haddioui A (2022) Evaluation of genetic diversity and structuration across altitude of walnut (Juglans regia L.) accessions from Morocco using SSR markers. Bulg J Agric Sci 28(3):451–458
Ohsawa T, Ide Y (2008) Global patterns of genetic variation in plant species along vertical and horizontal gradients on mountains. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 17(2):152–163. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2007.00357.x
Hahn T, Kettle CJ, Ghazoul J, Frei ER, Matter P (2012) Patterns of genetic variation across altitude in three plant species of semi-dry grasslands. PLoS One 7(8):e41608. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041608
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H. Abd-dada: performed the experiment, analyzed the data, and contributed in writing—original draft; S. Bouda: designed the study and interpreted the data; Y. Khachtib: performed the experiment and took part in preparing and critical checking this manuscript; Y. AIT Bella: investigation, data analysis; A. Haddioui: supervised and coordinated the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Abd-dada, H., Bouda, S., Khachtib, Y. et al. Use of ISSR markers to assess the genetic diversity of an endemic plant of Morocco (Euphorbia resinifera O. Berg). J Genet Eng Biotechnol 21, 91 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-023-00543-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-023-00543-4