Abstract
This study investigates the provenance of sedimentary rocks in Bogda Mountains, NW China, and reconstructs the lithology and unroofing history of the Eastern North Tianshan Suture. Petrographic point counting data of sandstones and compositions of conglomerates of upper Permian-lowermost Triassic Wutonggou low-order cycle from Zhaobishan, North Tarlong, Taodonggou, and Dalongkou sections in the southern and northern foothills of Bogda Mountains were used to interpret the temporal and spatial variations of lithology of the Eastern North Tianshan Suture, which is the sediment source area. Three compositional trends were identified. A trend of upward-increasing quartz content and granitic pebbles in Zhaobishan section suggests a change from the undissected volcanic arc, accretionary wedge and trench setting to predominantly transitional volcanic arc and subordinate accretionary wedge and trench, in the eastern part of the Eastern North Tianshan Suture. In North Tarlong and Taodonggou sections, however, the lithic content decreases and the contents of quartz and granitic pebbles increase up sections. These trends indicate that the western part of the Eastern North Tianshan Suture changed from an undissected volcanic arc to the transitional volcanic arc, accretionary wedge and trench. No clear trend in the lithic-rich sandstones of the Dalongkou section indicates that sediments were derived from the undissected volcanic arc in the Eastern North Tianshan Suture and local rift shoulders. Compositional variations of studied rocks suggest that the Eastern North Tianshan Suture was an amalgamated complex with great spatial and temporal heterogeneities in lithology and experienced persistent unroofing during late Permian-earliest Triassic. This study reconstructs a key element of the Chinese Tianshan Suture and serves as an example to understand the unroofing processes of ancient sutures.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
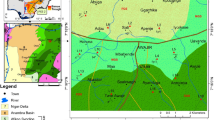
The Central Asian Orogenic Belt is one of the accretionary orogens that were the main sites of continental growth since the Phanerozoic, and resulted from the accretion and collision of magmatic arcs, accretionary complexes, trapped oceanic plates, and trailing continental plates (Şengör et al. 1993; Sengör and Natal'in 1996; Windley et al. 2007; Xiao et al. 2013). The Eastern North Tianshan Suture (ENTS) is located in the southern part of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt (Fig. 1). It marks the closure of the North Tianshan Ocean, which was the major southern segment of the Paleo-Asian Ocean (e.g., Xiao et al., 2009, Xiao et al. 2013). Detailed studies of the ENTS can provide critical information on the final assembly of the southern parts of Central Tianshan Orogenic Belt (e.g., Charvet et al. 2007; Han et al. 2010). Most studies of the ENTS focus on its tectonic evolution based on regional tectonics, structures, and geochemical and geochronological data of the rocks exposed in the ENTS (e.g., Allen et al. 1993; Gao et al., 1998; Xiao et al. 2004, 2013; Wang et al. 2007; Han et al. 2010; Charvet et al. 2011). However, the eroded rocks in the ENTS during late Permian-earliest Triassic are not well understood.
Provenance studies of sandstones are useful to reconstruct the eroded parts of adjacent orogens (e.g., Dickinson and Suczek 1979; Ingersoll and Suczek 1979; Dickinson 1985; Dorsey 1988; Garzanti et al. 1996, 2007; Trop and Ridgway 1997; Ingersoll 2012; Chaudhuri et al. 2018). However, detailed reconstruction of rocks in the ENTS during the late Permian-earliest Triassic cannot be achieved by previous petrographic studies due to out-of-date chronostratigraphy or limited samples (Carroll et al. 1995; Shao et al. 2001; Greene et al. 2005; Guan 2011). This study focuses on the sandstones of upper Permian-lowermost Triassic Wutonggou low-order cycle (WTG-LC) exposed in the northern and southern foothills of Bogda Mountains, the greater Turpan-Junggar intracontinental rift basin (Yang et al. 2010). The main goals are to document the high-resolution temporal and spatial variations of sandstone compositions, to interpret the provenance of these sandstones, and to reconstruct the unroofing history of the ENTS.
2 Geological background
This study focuses on the upper Permian-lowermost Triassic fluvial-lacustrine sandstones of WTG-LC in Zhaobishan, North Tarlong, and Taodonggou sections in the southern and Dalongkou section in the northern foothills of Bogda Mountains, NW China (Figs. 2, 3). The Bogda Mountains is an E-W striking giant anticline with exposures of Devonian to Quaternary sedimentary and igneous rocks. This anticline is located between the Junggar Basin to the north and Turpan-Hami Basin to the south (Fig. 2). It was a part of the greater Turpan-Junggar basin during the late Carboniferous-Jurassic (Shao et al. 1999, 2001; Greene et al. 2001, 2005; Yang et al. 2007, 2010). The greater Turpan-Junggar basin is speculated to be a back-arc basin (Hsü 1988), a transitional basin from rift to foreland basin (Carroll et al. 1990; Hendrix et al. 1992; Shao et al. 1999, 2001; Greene et al. 2001, 2005), or a rift basin (Allen et al. 1991; Allen et al. 1993; Shu et al. 2005, 2011; Yang et al. 2010, 2013). The seismic profiles (Yang et al. 2010), mixed tholeiitic volcanism and marine sedimentation in the uppermost basement (Yang et al. 2013), the bimodal volcanic rocks (Shu et al. 2005, 2011), continental rift-type geochemical signatures (Allen et al. 1991; Shu et al. 2005, 2011), and regional scale strike-slip shear zones (Laurent-Charvet et al. 2002, 2003; Shu et al. 2005, 2011) support that the greater Turpan-Junggar basin was an intracontinental rift basin over a Carboniferous volcanic arc or back-arc basement (Shu et al. 2005; Yang et al. 2010; Yang et al. 2013). Regional dextral strike-slip movement triggered the rifting that starting in the latest Carboniferous (Laurent-Charvet et al. 2002, 2003; Yang et al. 2010, 2013; Shu et al. 2011). The rifting formed a series of grabens and half-grabens in the greater Turpan-Junggar basin, which resemble the Basin and Range Province in the western United States (Yang et al. 2010).
Tectonic map of eastern Xinjiang, showing the locations of the Eastern North Tianshan Suture, Central Tianshan Suture, Bogda Mountains, and measured sections. Modified from Xia et al. (2004)
The Chinese Tianshan separates the Junggar Basin to the north from the Tarim Basin to the south and has been created since the Cenozoic collision between the Indian and Asian plates (e.g., Windley et al. 1990; Hendrix et al. 1994; Yin et al. 1998). Before the Cenozoic collision, a series of suture zones were formed in the Chinese Tianshan area during the Paleozoic, one of which is the North Tianshan Suture. The North Tianshan Suture is further divided into the western and eastern segments in terms of their relative locations to the city of Urumqi (Fig. 2). This study focuses on the eastern segment of the North Tianshan Suture, which is situated about 100 km south of Bogda Mountains and north of the Central Tianshan Suture. The origin of the ENTS is not fully understood, but the southward subduction of North Tianshan Ocean beneath the Central Tianshan Suture, and the collision between the Central Tianshan Suture and the trailing Junggar Plate are widely accepted (Windley et al. 1990; Gao et al., 1998; Xiao et al. 2004, 2013; Charvet et al. 2011). The timing of the collision is in debate, varying from Middle Ordovician (Gao et al., 1998), Devonian-early Carboniferous (Xiao et al. 2004, 2013) to Late Devonian-Carboniferous (Charvet et al. 2011). Similarly, the proposed closure time varies from the end of Early Carboniferous (Gao et al., 1998), Late Carboniferous (Windley et al. 1990; Xiao et al. 2004, 2013; Han et al. 2010), to Late Carboniferous-Early Permian (Allen et al. 1993; Carroll et al. 1995). The current ENTS consists of Ordovician to Devonian-Carboniferous volcanic-arc rocks and associated submarine volcanic-sedimentary rocks (Allen et al. 1993; Xiao et al. 2004). Fragmental ophiolites, radiolarian chert, turbidites, and high-pressure schists mark the subduction of the oceanic crust between the Junggar Plate and Central Tianshan Suture (Carroll et al. 1990; Gao et al., 1998; Shu et al. 1999; Xiao et al. 2004; Charvet et al. 2007).
The WTG-LC is an informal cyclostratigraphic unit defined by Yang et al. (2007, see also Yang et al., 2010) and approximately correlates with the Wutonggou and Guodikeng formations (Fig. 4; XBGMR 1993; Yang et al. 2007, 2010). A low-order cycle formed during a period of long-term stable tectonic and/or climatic conditions and contains high and intermediate-order cycles. The high-order cycle is the smallest unit that records the environmental changes caused by the transgression and regression of lakes or erosion and deposition of rivers. The intermediate-order cycle includes several high-order cycles, representing longer trends of transgression and regression or erosion and deposition than the high-order cycles. The WTG-LC records an overall persistently uplifting history of the source areas and humid to sub-humid climate conditions (Yang et al. 2007, 2010; Thomas et al. 2011).
Chrono-, litho-, and cyclostratigraphy of Upper Carboniferous-Middle Triassic strata in Bogda Mountains. Wavy lines are major unconformities; dashed lines are disconformities; and hachured areas missing strata. The studied Wutonggou low-order cycle is shown in the shaded box. Modified from Yang et al. (2010, 2013) and Obrist-Farner and Yang (2015)
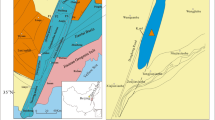
Stratigraphic correlations have been largely based on lithostratigraphy, biostratigraphy, and cyclostratigraphy (Zhang 1981; Liao et al. 1987; Wartes et al. 2002; Yang et al. 2007, 2010). The chronostratigraphy in the greater Turpan-Junggar basin is not well constrained. Yang et al. (2010) placed the Permo-Triassic boundary in a 90 m-thick interval in North Tarlong section. Based on stratigraphic correlation and petrographic studies, the strata in Tarlong and Taodonggou areas were interpreted as being deposited within one half-graben, termed the Tarlong-Taodonggou half-graben (Yang et al. 2010; see also Guan 2011; Peng 2016; Obrist-Farner and Yang 2017; Fredericks 2017). The basin geometry of the Zhaobishan and Dalongkou areas is not clear due to a limited number of measured sections and is speculated to be similar to that of Tarlong-Taodonggou half-graben.
Sandstones of WTG-LC can be divided into fluvial, deltaic, and littoral-lakeplain facies (Yang et al. 2010; Fig. 5). The fluvial facies includes meandering stream and braided stream deposits. The former is characterized by a high-relief erosional base with upward-fining succession of channel-fill conglomerate, point bar sandstone, and overbank siltstone and shale; and the latter by a low-relief erosional base with upward-fining association of channel-fill conglomerate, bar sandstone and absence of overbank deposit. The deltaic facies includes the upward-coarsening and thickening successions of prodeltaic shale and siltstone, delta front sandstone and/or conglomerate in the lower part, and distributary channel-fill and interdistributary delta plain mudrock, sandstone, conglomerate, and paleosol in the upper part. The littoral-lakeplain facies is characterized by the upward-coarsening succession of sublittoral shale and littoral well-washed sandstone and conglomerate in the lower part, and muddy to sandy paleosol in the upper part.
Field photos and litho-columns showing the lithology, sedimentary structure, and stratal successions of major environmental facies, from which sandstones samples were collected in this study. a Littoral-lakeplain facies showing a high-angle beach accretionary set; b Deltaic facies showing coarsening-upward successions from shale to sandstone; c Fluvial facies showing a fining-upward succession from channel-fill conglomerate to cross-bedded bar sandstone. See text and Yang et al. (2007, 2010) for detailed descriptions
3 Data and methodology
Sixty sandstones from four sections were studied to observe their compositional and textural characteristics (Fig. 6; see Yang et al. 2007, 2010 for detailed measured sections). Three hundred framework grains in each thin section were counted using both Suttner’s (Suttner 1974) and Gazzi-Dickinson’s methods (Gazzi 1966; Dickinson 1970). The Gazzi-Dickinson method counts sand-size (0.063 mm) mineral crystals within large rock fragments as individual grains, whereas the Suttner’s method does not count the mineral crystals, only as the rock fragments (Ingersoll et al. 1984). As most of the counted lithic grains in the studied sandstones contain minerals smaller than sand, the results of these two methods are similar. Definitions of raw and recalculated parameters of point counting categories are tabulated in Table 1. The interpretations of volcanic lithic fragments follow the descriptions of Dickinson (1970) and Marsaglia and Ingersoll (1992). The interpretation of polycrystalline quartz grains follows those of Basu et al. (1975), Young (1976), and Blatt et al. (2006). Point counting data in recalculated parameters are presented in Table 2 in terms of Gazzi-Dickinson method so that petrofacies can be defined by composition and compared with the tectonic fields in templates from previous studies (Dickinson and Suczek 1979; Dickinson et al. 1983; Dickinson 1985; Marsaglia and Ingersoll 1992; Critelli and Ingersoll 1995).
One thousand nine hundred fourteen gravels in 17 conglomeratic beds were counted and described in the field to obtain the spatial and temporal trends of clast composition. Fresh surfaces were used to identify lithologies. A rectangular grid on the outcrop surface was laid out as a guide for counting. About 100 clasts were counted in each location. In addition, 168 attitudes of nine tabular cross beds of fluvial sandstones were measured in the field. They were later corrected using the method of Davis et al. (2011), pp. 710–714). The correction, rose diagrams, and mean vectors were performed using the software StereoNet of Allmendinger (2005).
4 Results
Sandstone compositions are used to classify petrofacies, from which the lithology and tectonic settings of the source areas can be interpreted. Clast composition of conglomerates and paleocurrent directions supplement the classification of petrofacies and provenance interpretation. The stratigraphic distribution of petrofacies, clast composition, and paleocurrent directions in individual sections show the temporal changes of sandstone composition. Finally, the spatial variations of sandstone composition are interpreted on the basis of correlations among sections in the study areas.
4.1 Framework grains
The major framework grains in sandstones of WTG-LC include quartz, feldspar, and lithic fragment. They are further differentiated on the basis of optical mineralogic characteristics, such as extinction, twinning, and relict textures (Tables 1, 2). Accessory minerals, including micas and heavy and opaque minerals, are scarce.
4.1.1 Quartz
Quartz occurs as monocrystalline crystals (Qm) and polycrystalline (Qp) and microcrystalline aggregates (Cht). Qm grains are clear, inclusion-free, and subangular-angular, and are subdivided into nonundulatory (Qnu; Fig. 7a) and undulatory types (Qu). Qnu grains exhibit straight extinctions, whereas Qu grains are strained with undulose extinction at an angle between 5 and 10 degrees. Qp grains are subdivided into polycrystalline ones with metamorphic deformed texture (Qpt; Fig. 7b) and polycrystalline ones without such texture (Qpw). Qpt grains contain more than five sutured, elongate quartz crystals. In contrast, Qpw grains contain two to five monocrystalline quartz grains without sutured contacts. Cht grains are aggregates of microcrystalline quartz and interpreted as fragments of chert (Fig. 7c).
Photomicrographs of sandstones in the Wutonggou low-order cycle. a A nonundulatory monocrystalline quartz grain (Qnu) with embayment, a potassium feldspar with Carlsbad twinning, and a plagioclase with albite twinning. Sample TD110, lower Taodonggou section; b A polycrystalline quartz grain with sutured quartz crystals, indicating its metamorphic origin. The blue arrow points to an elongate muscovite grain. S15–36, lower Zhaobishan section; c A slightly clay coated chert grain. NTR39–17, upper North Tarlong section; d A volcanic lithic fragment with felsic texture. The phenocrysts are mainly feldspar grains. TD110, lower Taodonggou section; e A volcanic lithic fragment with microlitic texture, an angular mudrock fragment, and a volcanic lithic with lathwork texture showing large feldspar laths. These grains suggest sedimentary and volcanic origins. TD108, lower Taodonggou section; f A volcanic lithic fragment with microlitic texture and a volcanic lithic with vitric texture, suggesting a volcanic origin. TD168, upper Taodonggou section. All micrographs are taken under cross-polarized light. Scale bar is 1 mm long in all photos. See Table 1 for the abbreviations of grain categories
4.1.2 Feldspars
This group includes plagioclase (P; Fig. 7a) and potassium feldspar (K; Fig. 7a). Plagioclase grains usually exhibit polysynthetic twinning. The plagioclase grains in North Tarlong and Taodonggou sections are common with albite twinning. They occur as discrete angular-subangular grains and lath or mosaic phenocrysts in volcanic lithic fragments. Potassium feldspar includes microcline and orthoclase. The microclines exhibit tartan twinning and only occur in Zhaobishan and Taodonggou sections. The orthoclase is usually Carlsbad twinned or untwinned. Clear, inclusion-free orthoclase is common in the studied thin sections.
4.1.3 Lithic fragments
Lithic fragments include volcanic (Lv), sedimentary (Ls), and metamorphic (Lm). Lv and Ls grains dominate and account for over 99% of the total lithics. Lm grains are rare.
The Lv grains are subdivided into four types based on their textures, including felsic (Lvf; Fig. 7d), microlitic (Lvmi; Fig. 7e, f), lathwork (Lvl; Fig. 7e), and vitric (Lvv; Fig. 7f). Lvf, Lvmi, Lvl, and Lvv grains are interpreted to be derived from felsic (Lvf), intermediate (Lvmi), and mafic (Lvl) igneous rocks and volcanic glass (Lvv), respectively (Dickinson 1970). The Ls grains are subdivided into three types based on their textures, including mudrock (Lmd; Fig. 7e), siltstone (Lslt), and sandstone fragments (Lsd). The Lmd grains account for more than 95% of the total sedimentary lithics. Finally, a trace amount of Lm grains, mainly schist fragments, are identified on the basis of their foliations.
4.1.4 Accessory minerals
Accessory mineral grains are the minor framework grains in WTG-LC sandstones and account for 2% of the total detrital grains. Muscovite, biotite, zircon, tourmaline, amphibole, and opaque minerals are observed.
4.2 Matrix, cement, and sandstone classification
WTG-LC sandstones contain 1% of matrix. Based on the sandstone classification of Dott (1964) 46 litharenites, 11 feldspathic arenites, and three lithic wackes (Table 2) were recognized. The cements in the sandstones are predominately calcite, clays, and iron oxides and sulfides. Zeolite and silica are rare. As the matrix is not further studied and cements are largely controlled by diagenesis rather than provenance lithology (Dickinson and Suczek 1979), they are not included in the classification of petrofacies.
4.3 Composition of gravels and paleocurrent measurements
Conglomerates in the WTG-LC are typically polymictic, either clast- or matrix-supported. The composition of individual conglomeratic beds is summarized in Section 5 to facilitate the interpretations of source lithology.
Gravels are igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic in composition (Fig. 6; Table 3). Igneous gravels are volcanic and plutonic clasts, including white or gray rhyolite, dark green or dark purple andesite, and dark green, dark purple or black basalt, and reddish granite. Sedimentary gravels are mudrock and chert, including green, purple, and brown soft clasts of mudrock and massive or laminated gray chert. Metamorphic gravels include white quartzite, of which the boundaries of single quartz crystals are interlocking with each other.
The paleocurrent directions were only measured from cross-beddings of a decimeter scale within point bar sandstones, in order to remove the possible errors induced by bed-form hierarchies (Allen 1968; Miall 1974). The mean vectors of paleocurrent directions provide qualitative estimates of the locations of the surrounding highs. These results are further discussed in Section 4.5 to aid the interpretations of source locations (Fig. 6).
4.4 Petrofacies and implications on lithology and tectonic settings of source areas
Three petrofacies were recognized in sandstones of the WTG-LC on the basis of relative abundance of quartz, feldspar, and lithic fragment. The distributions of these petrofacies are shown in the QFL and QmFLt ternary diagrams (Fig. 8; Table 2). All quartz grains are grouped together in the QFL diagram to emphasize the variations of grain stability among quartz, feldspar, and lithic fragments. In contrast, polycrystalline and microcrystalline quartz grains are counted as lithic fragments in the QmFLt diagram to emphasize the grain size of the source rocks, because fine-grained source rocks produce more lithic fragments than monocrystalline grains (Dickinson and Suczek 1979). Moreover, ternary diagrams of QmPK, QpLvLs, LmtLvLst, and LvfLvmiLvl use subgroups of QFL to show the characteristics of monocrystalline, polycrystalline, lithic, and volcanic lithic grains, respectively (Fig. 8; Dickinson and Suczek 1979; Dickinson et al. 1983). These diagrams are used to further classify the petrofacies for detailed interpretation of source lithology. Finally, ternary diagrams of QFL, QmFLt, and QpLvLs are used to interpret the tectonic settings of source areas using the templates of Dickinson and Suczek (1979) and Dickinson et al. (1983).
Ternary diagrams showing mean compositions and classifications of petrofacies of Wutonggou low-order cycle sandstones. Sandstones of Petrofacies 1 (n = 21), Petrofacies 2 (n = 9), and Petrofacies 3 (n = 30) are shown as orange, blue, and gray symbols, respectively. See Table 1 for definitions of grain categories and end-members. Fields of tectonic settings are adapted from Dickinson and Suczek (1979) and Dickinson et al. (1983). CI-craton interior; TC-transitional continent; BU-basement uplift; RO-recycled orogeny; DA-dissected arc; TA-transitional arc; UA-undissected arc; QR-quartzose recycled; TR-transitional recycled; LR-lithic recycled; SC-subduction complex; CO-collision orogen; AO-arc orogen
4.4.1 Petrofacies 1
Petrofacies 1 has a mean composition of Q51F30L19 and Qm21F30Lt49 and occurs in 11 lithic arenites, nine feldspathic arenites, and one lithic wacke (Fig. 8; Table 2). Quartz grains dominate and consist of monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and chert grains, which account for 21%, 13%, and 17% of the total grains, respectively. Feldspars account for 30% of the total grains and are slightly more enriched with plagioclase than potassium feldspars, with an average plagioclase/feldspar (P/F) ratio of 0.55 and a mean composition of Qm43P33K24 (Fig. 8). Polycrystalline and lithic grains are mainly composed of polycrystalline quartz and chert with mean compositions of Qp61Lv25Ls14 and Lmt19Lv29Lst52 (Fig. 8). Other lithic fragments include volcanic and mudrock, which account for 12% and 7% of the total grains, respectively. Volcanic lithic fragments are the minor component and are mainly composed of felsic volcanic lithics with a mean composition of Lvf66Lvmi25Lvl9 (Fig. 8).
The mean composition of Petrofacies 1 suggests that its source rocks were probably a suite of felsic igneous rocks, quartzite, chert, and mudrocks. The common monocrystalline quartz and feldspar grains and the occurrence of felsic volcanic lithic sandy and gravelly clasts (see also Section 5) indicate a felsic plutonic and volcanic origin for this petrofacies. The undulatory quartz grains and polycrystalline quartz with deformed texture indicate a metamorphic origin. Finally, chert and mudrock fragments were originated from sedimentary rocks.
The mean composition of Petrofacies 1 also provides clues to understand the tectonic setting of source areas. The mean compositions of QFL, QmFLt, QpLvLs groups fall within the tectonic fields of the recycled orogen, transitional arc, and subduction complex (Fig. 8; Dickinson and Suczek 1979; Dickinson et al. 1983). The tectonic settings interpreted from QFL and QmFLt distributions are different, because polycrystalline quartz and chert grains are incorporated as quartz in QFL diagram but as lithic fragments in QmFLt diagram. The chert-rich sandstones from Klamath Mountains within the North American Cordillera with known magmatic arc and associated accretionary wedge and trench sources fall in the recycled orogen in QFL and lithic recycled field in QmFLt (Dickinson and Suczek 1979; Dickinson et al. 1983). Similarly, Petrofacies 1 of WTG-LC sandstones is also enriched in polycrystalline quartz and chert and falls in the recycled orogen in QFL and transitional arc in QmFLt plots. Hence, Petrofacies 1 was likely derived from transitional arc sources and associated accretionary wedge and trench, which, as a whole, is termed as a subduction complex by Dickinson and Suczek (1979). The QpLvLs plot substantiates the interpretation that Petrofacies 1 falls in the subduction complex field (Fig. 8). Overall, these three diagrams indicate that the sources of Petrofacies 1 include felsic volcanic and plutonic rocks from a transitional volcanic arc, and quartzite, chert and mudrock from the associated accretionary wedge and trench.
4.4.2 Petrofacies 2
Petrofacies 2 has a mean composition of Q28F36L36 and Qm14F36Lt50 and consists of seven litharenites and two feldspathic arenites (Fig. 8; Table 2). Quartz is still the major component but less enriched than Petrofacies 1. The monocrystalline and polycrystalline quartz and chert account for 14%, 7%, and 7% of the total grains, respectively. Feldspars are slightly enriched than Petrofacies 1 and account for 36% of the total grains. Plagioclase is dominant with an average P/F ratio of 0.65 and a mean composition of Qm29P47K24 (Fig. 8). The polycrystalline grains and lithic fragments include mainly volcanic lithic fragments and subordinate polycrystalline quartz, chert and mudrock fragments with mean compositions of Qp28Lv65Ls7 and Lmt9Lv68Lst23. Similar to Petrofacies 1, the felsic volcanic lithic fragments are the major components of volcanic lithic fragments with a mean composition of Lvf78Lvmi15Lvl7.
The composition of Petrofacies 2 suggests that the sources include predominant felsic volcanic and plutonic rocks and subordinate quartzite, chert, and mudrocks. The occurrence of large amounts of volcanic lithic fragments, especially felsic volcanic ones, is indicative of felsic volcanic and plutonic source rocks. The common occurrence of monocrystalline quartz and feldspar grains and rhyolitic and granitic gravels (see Section 5) support this interpretation. The content of polycrystalline quartz, chert, and mudrock fragments is markedly lower than that of volcanic lithic fragments, suggesting that metamorphic and sedimentary rocks are subordinate sources.
The mean compositions of samples of Petrofacies 2 on the QFL, QmFLt, and QpLvLs ternary diagrams fall within the tectonic fields of transitional arc and the mixed zone between subduction complex and arc orogen (Fig. 8). Mean composition falls in the field of transitional arc in both QFL and QmFLt diagrams, indicating the transitional volcanic arc origin of these sandstones. In addition, mean composition falls in the mixed zone rather than the arc orogen field in the QpLvLs diagram, which indicates that the sources are mixed rocks from volcanic arc, accretionary wedge, and trench. The sources of accretionary wedge and trench are not reflected in the QFL and QmFLt diagrams due to the relatively low content of chert and polycrystalline quartz grains. Overall, the three diagrams indicate that the transitional or dissected volcanic arc rocks are the major sources, and the accretionary wedge and trench metamorphic and sedimentary rocks are the secondary sources.
4.4.3 Petrofacies 3
Petrofacies 3 has a mean composition of Q8F13L79 and Qm2F13Lt85 and occurs in 28 litharenites and two lithic wackes (Fig. 8; Table 2). Quartz is no longer the major component. Monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and chert grains only account for 2%, 1%, and 5% of the total grains, respectively. Similarly, feldspars decrease significantly and only account for 13% of the total grains. Plagioclase is still more than K-feldspars, with an average P/F ratio of 0.69 and a mean composition of Qm16P64K20 (Fig. 8). In contrast to Petrofacies 1 and Petrofacies 2, polycrystalline grains and lithic fragments are the major components and largely consist of volcanic and sedimentary fragments with mean compositions of Qp6Lv60Ls34 and Lmt0Lv60Lst40 (Fig. 8d, e). Finally, although felsic volcanic lithic fragments still dominate in Petrofacies 3, the proportion of microlitic volcanic lithic fragments increases significantly, as indicated by the mean composition of volcanic lithic fragments Lvf46Lvmi39Lvl15 (Fig. 8).
The mean composition of Petrofacies 3 indicates that the sources are rhyolites, andesites, and mudrocks. Moreover, the mean compositions of Petrofacies 3 fall within the fields of undissected volcanic arc in QFL and QmFLt diagrams and arc orogen in the QpLvLs diagram, indicating the presence of undissected volcanic arc rocks in the sources. However, although the mean composition is in the undissected arc field in QmFLt diagram, 15 sandstones of Petrofacies 3 fall within the lithic recycled field (Fig. 8). The recycled lithics may be derived from uplifted older sedimentary strata (Dickinson et al. 1983; Dickinson 1985). Thus, these sandstones may have mixed sources of sedimentary and volcanic rocks. The sedimentary sources are unlikely the trench-fill sedimentary rocks, because the mudrocks fragments of Petrofacies 3 include abundant angular rip-up clasts and the concurrent chert fragments are rare. As a result, mudrock fragments were more likely derived from a nearby source area, such as the rift shoulders, the uplifted hanging wall of the graben (Yang et al. 2010; Guan 2011; Obrist-Farner and Yang 2017).
4.5 Provenance of sedimentary rocks in Bogda Mountains
The stratigraphic distribution of petrofacies along each section provides clues to understand the evolution of provenance through time. Clast composition of conglomerates and paleocurrent directions are used to substantiate provenance interpretations. Finally, the correlation of the four studied sections demonstrates the spatial variations of sandstone composition and source areas.
4.5.1 Provenance of sedimentary rocks in the Zhaobishan section
Petrofacies of sandstones of the WTG-LC in Zhaobishan section change upsection, suggesting that the lithology and tectonic setting of the source areas of the lower and upper WTG-LC sandstones are different. Petrofacies 1 occurs in 14 sandstones in the lower 420 m, whereas Petrofacies 2 occurs in nine sandstones in the upper 350 m of Zhaobishan section (Figs. 6, 9; Table 2). The occurrence of Petrofacies 1 suggests that the sandstones in the lower WTG-LC were derived from a transitional volcanic arc and associated accretionary wedge and trench. As the ENTS was the collisional product of oceanic plate, volcanic arc, and continental plates (Allen et al. 1991; Gao et al., 1998; Xiao et al. 2004, 2013; Charvet et al. 2011), it should contain volcanic, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. Rhyolites, fragmental radiolarian chert and high-pressure metamorphic rocks are still exposed in current ENTS (Xiao et al. 2004; Wang et al. 2006), indicating that the ENTS was the available source area of Zhaobishan section during late Permian-earliest Triassic.
Correlation of petrofacies distribution of Wutonggou low-order cycle sandstones in five sections in the study area. The correlation assumes that the changes of petrofacies in the sections are approximately coeval. The correlation with Dalongkou section is uncertain because there is no compositional change in the section. PF1-Petrofacies 1; PF2-Petrofacies 2; PF3-Petrofacies 3; m-mudstone; s-sandstone; g-conglomerate
Clast composition of WTG-LC conglomerates and paleocurrent directions support the provenance interpretation. Two conglomeratic beds at the 26 and 204 m thickness points in the lower Zhaobishan section consist of abundant volcanic and a few quartzite and chert gravels (Fig. 6; Table 3). The paleocurrent direction is northward at the bottom of Zhaobishan section (Fig. 6). These data indicate that the ENTS, located ~ 100 km south of the section, served as the volcanic, metamorphic, and sedimentary sources to the lower WTG-LC sandstones in Zhaobishan section. Finally, the absence of plutonic gravels in the conglomerates suggests that the volcanic arc might be undissected or slightly dissected without major exposure of plutons.
In contrast, the occurrence of Petrofacies 2 in the upper WTG-LC sandstones indicates that the sources are mainly transitional volcanic arc and subordinately accretionary wedge and trench. The ENTS is still interpreted as the available source areas containing igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. The northward paleocurrent direction identified in the bed at 450 m in the upper half of the section, supports the interpretation (Fig. 6). The significant decrease of polycrystalline quartz and chert fragments and the occurrence of granitic gravels in conglomeratic beds at the thickness levels of 501 and 765 m (Fig. 6; Table 3) indicate that the source lithology contains a significant amount of granites along with rhyolites from the transitional volcanic arc and diminishing quartzite and chert from the accretionary wedge and trench.
4.5.2 Provenance of sedimentary rocks in the North Tarlong section
The distribution of petrofacies in sandstones of the WTG-LC in North Tarlong section also indicates different provenances for lower and upper WTG-LC sandstones. Petrofacies 3 occurs in 11 sandstones in the lower 600 m, whereas Petrofacies 1 occurs in four sandstones in the upper 220 m of North Tarlong section. The occurrence of Petrofacies 3 in the lower WTG-LC sandstones indicates that the sources were an undissected volcanic arc and rift shoulders. The overall northward paleocurrent directions documented in the beds at 5, 29, and 38 m suggest the presence of a highland to the south, likely the ENTS (Fig. 6; Table 3). Abundant volcanic clasts are present in the lower five conglomeratic beds (Fig. 6). Thus, rhyolites and andesites probably covered a large area in the ENTS as the main source. In addition, the large number of mudrock fragments in the lower sandstones may have been derived from local rift shoulders.
In contrast, the occurrence of Petrofacies 1 in the upper WTG-LC sandstones suggests that the source changed to the transitional volcanic arc and associated accretionary wedge and trench of the ENTS. This change is also evidenced by the presence of granitic gravels in the uppermost conglomeratic bed in North Tarlong section (Fig. 6; Table 3).
4.5.3 Provenance of sedimentary rocks in the Taodonggou section
Sandstone petrofacies of the WTG-LC also vary in the Taodonggou section, indicating changes of provenance. Petrofacies 3 occurs in six sandstones in the lower 200 m and six sandstones in the upper 90 m of the section, whereas Petrofacies 1 occurs in three sandstones in the middle 50 m of Taodonggou section (Figs. 6, 9). The occurrence of Petrofacies 3 in the lower and upper parts of Taodonggou section suggests volcanic and sedimentary sources. The rift shoulders are likely the sources for mudrock fragments. In addition, the basement in the Taodonggou-Tarlong area contains upper Carboniferous basaltic, andesitic, and sedimentary rocks (Yang et al. 2010; Yang et al. 2013). Thus, the rift shoulders, if the basement rocks were exposed, might also supply basaltic and andesitic fragments. The abundant volcanic clasts in WTG-LC conglomerates and southward paleocurrent directions documented in Taodonggou section (Fig. 6; Table 3) support a rift-shoulder source. However, the rhyolitic fragments might come from some other sources. Therefore, the ENTS might have provided fragments of rhyolites and likely, andesites.
In contrast, the occurrence of Petrofacies 1 in the middle part of Taodonggou section suggests that sediments were derived from rocks in a transitional volcanic arc and the associated accretionary wedge and trench. The ENTS might have been the likely source to supply the felsic volcanic and plutonic, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks in the sandstones of the middle Taodonggou section.
4.5.4 Provenance of sedimentary rocks in the Dalongkou section
Only Petrofacies 3 occurs in the seven sandstones in Dalongkou section, suggesting a persistent provenance. Petrofacies 3 indicates volcanic and sedimentary sources from rift shoulders and the ENTS, as discussed above. In addition, the paleocurrent directions are either northward or southward (Fig. 6), which suggest a complex dispersal pattern, probably originated from surrounding rift shoulders. No basement rocks are exposed in the Dalongkou area at the present time. Thus, the volcanic clasts may have been derived from either ancient rift shoulders and/or undissected volcanic arc in the ENTS. A dominant rift-shoulder source conforms to that for the sandstones of the underlying Quanzijie low-order cycle (Obrist-Farner and Yang 2017).
4.5.5 Spatial correlations of petrofacies
The distribution of petrofacies in the four studied sections was correlated to identify spatial variations of sandstone compositions and provenance. Petrofacies of North Tarlong section is correlative with those of South Tarlong section (Fig. 9; Guan 2011). These sections are located at the northern and southern limbs of a syncline and both converge toward the axis and were deposited in the same graben (Fig. 3; Yang et al. 2010; Guan 2011). Twenty-three WTG-LC sandstones were divided into the lower lithic-rich and upper quartz- and feldspar-rich petrofacies, which resemble the distribution of petrofacies in North Tarlong section (Guan 2011; Figs. 9, 10). The good correlation between these two sections suggests that they shared the same provenance during the deposition of the WTG-LC. .
QFL ternary diagram of upper Permian-lowermost Triassic sandstones in Bogda Mountains and Turpan Basin. Data of South Tarlong section are from Guan (2011); and data of Turpan Basin from Shao et al. (2001). See Figs. 2 and 3 for locations of measured sections, South Tarlong section and Turpan Basin. See Fig. 8 for explanations of grain categories and tectonic fields
Correlation between petrofacies of North Tarlong and South Tarlong sections and those of Taodonggou section shows a slight difference. The petrofacies of the three sections shift from Petrofacies 3 to Petrofacies 1 upsection, suggesting a similar trend of provenance evolution. However, Petrofacies 1 occurs only in a thin interval in the middle part of the Taodonggou section, about one-seventh of the total thickness, and abruptly changes to Petrofacies 3 again. Taodonggou section is 6 km away from the North Tarlong-South Tarlong sections and located in the same half-graben as North Tarlong-South Tarlong sections (Yang et al. 2010). However, the thickness and types of high-order cycles change significantly. The Taodonggou section was at the ramp of the half-graben, while North Tarlong-South Tarlong sections were at the depocenters (Yang et al. 2010). Thus, they do not have the same depositional environments and even might not have the same drainage areas (e.g., Soreghan and Cohen 1993). These factors may have caused the abrupt shift of petrofacies in the upper Taodonggou section.
Additionally, the correlation between petrofacies of Tarlong-Taodonggou areas and that of the northwestern Turpan Basin has variations. The northwestern Turpan Basin is about 30 km south of Tarlong-Taodonggou area (Fig. 2), where two Wutonggou Formation sandstones are lithic-rich, resembling the lower WTG-LC sandstones in North Tarlong, South Tarlong, and Taodonggou sections (Shao et al. 2001; Fig. 10). However, the upper quartz- and feldspar-rich sandstones are not documented in the northwestern Turpan Basin.
The trend of petrofacies evolution of Zhaobishan section cannot be correlated with those of North Tarlong, South Tarlong, and Taodonggou sections, because Petrofacies 3 is absent in Zhaobishan section. On the other hand, the petrofacies shifts in these sections all occur in the middle parts of the sections (Fig. 9), which suggests an approximately coeval tectonic event in both source areas of Zhaobishan and Tarlong-Taodonggou areas in the ENTS. The shift in North Tarlong section occurred at a bed 10 m below a bentonite with an age of 253.11 ± 0.05 Ma (Yang et al. 2010; Fig. 9). Therefore, the petrofacies shift of the studied sections occurred probably during Wuchiapingian-early Changhsingian transition.
Moreover, the petrofacies of Zhaobishan section may be similar to those of sandstones of the Wutonggou Formation in the northeastern part of the Turpan Basin, as documented by Shao et al. (2001). Eleven sandstones of the Wutonggou Formation from Xishan and Kulai sections in northeastern Turpan Basin are quartz- and feldspar-rich, similar to Petrofacies 2 in this study (see Fig. 2 for the section locations; Fig. 10). This suggests that the two areas may share a similar provenance.
The petrofacies trend of Dalongkou section cannot be correlated with those in the other sections, because the section contains only Petrofacies 3. The Dalongkou section was interpreted to be related to a separated drainage system (see above). This interpretation fits the tectonic setting of the greater Turpan-Junggar basin as a highly-partitioned rift basin (Yang et al. 2010), where the abundant rift shoulders might have hampered the transport of sediments from the ENTS. Alternatively, rivers originating from the ENTS might have been persistently draining an area rich in volcanic and sedimentary rocks during the deposition of the entire WTG-LC.
Previous studies suggest the WTG-LC sandstones in the southern Junggar Basin and Northern Turpan Basin are uniformly volcanic-rich with slight variations in compositions based on limited numbers of point-counting data (Carroll et al. 1995; Hendrix 2000; Greene et al. 2005). The petrofacies distribution and correlation among multiple detailed stratigraphic sections present a clear spatial and temporal pattern of provenance evolution during the deposition of WTG-LC sandstones.
5 Discussion: the unroofing history of the Eastern North Tianshan Suture
The interpreted provenance lithology and tectonic setting, and the evolution of WTG-LC sandstones can be used to reconstruct the unroofing history of the ENTS. Overall, the ENTS had been persistently unroofed during late Permian-earliest Triassic to provide a large amount of siliciclastic sediments northward into the greater Turpan-Junggar basin. Uplifting of the ENTS is likely, but the rate of uplifting cannot be confirmed. During approximately the Wuchiapingian Stage when the lower WTG-LC sandstones in Zhaobishan section were deposited, the source area in the eastern part of the ENTS was composed of rocks of the undissected volcanic arc, accretionary wedge, and trench (Fig. 11). During approximately Changhsingian-early Induan stages, when the upper WTG-LC sandstones were deposited, the source area was covered by rocks mainly generated in a transitional volcanic arc and subordinately the accretionary wedge and trench, where deep-seated granitic plutons started to expose (Fig. 11). The unroofing trend indicates the amalgamation of accretionary wedge, trench, and volcanic arc rocks was caused by the collision between the Junggar Plate and Central Tianshan Suture (Allen et al. 1993; Gao et al., 1998; Xiao et al. 2004, 2013; Charvet et al. 2011). The southward subduction of the North Tianshan Ocean formed the accretionary wedge and trench, and the North Tianshan volcanic arc, which were accreted together by later continuous movement. A similar trend was reported from the Eocene-Middle Miocene sandstones in the collisional zone between Izu Arcs and the Honshu Arc in central Japan (Okuzawa and Hisada 2008), where the older sources are volcaniclasts, and the younger sources are accretionary wedge and trench rocks. The unroofing trend of the ENTS continued through the Triassic as indicated by increasingly quartzose compositions of Triassic sandstones in the Turpan-Hami Basin (Shao et al. 2001; Greene et al. 2005), as a consequence of progressive dissection of the volcanic arc in the ENTS.
Unroofing trends of source areas in Eastern North Tianshan Suture, as interpreted from petrofacies of Wutonggou low-order cycle sandstones in Bogda Mountains. The trend for the Zhaobishan section shows that the sources changed from the undissected volcanic arc, accretionary wedge and trench rocks to the transitional volcanic arc rocks. The trend for North Tarlong, South Tarlong, and Taodonggou sections shows that the sources shifted from undissected volcanic arc rocks to transitional volcanic arc, accretionary wedge and trench rocks. See Fig. 8 for the explanations of the tectonic fields
In contrast to the source area of Zhaobishan section in the eastern part of the ENTS, the source areas of Tarlong-Taodonggou sections are located in the western part of the ENTS. These areas are probably 90 km west of the Zhaobishan source area, which is the present-day distance between Zhaobishan and Tarlong-Taodonggou areas. The Tarlong-Taodonoggou source area in the ENTS has a different unroofing history. It was covered by an undissected volcanic arc during the Wuchiapingian at the time of deposition of the lower WTG-LC sandstones. However, the area was covered with complex lithologies of the amalgamated transitional volcanic arc, accretionary wedge, and trench rocks during the Changhsingian-early Induan at the time of deposition of the upper WTG-LC sandstones. This unroofing trend is similar to that of the continental arc within the Turan Plate, Western Turkmenistan (Garzanti and Gaetani 2002) and the Sierra Nevada in North America (Ingersoll 2012), where the contents of quartz and feldspar in the studied sandstones increase at the expense of volcanic lithic fragments. During continuous plate consumption, sandstones may also show an increase of polycrystalline quartz and chert fragments derived from the accretionary wedge and trench (Dickinson and Suczek 1979; Dickinson et al. 1983; Garzanti et al. 2007).
The two different unroofing trends between the source areas for Zhaobishan and Tarlong-Taodonggou sections indicate that the ENTS was an amalgamated complex with spatial and temporal variations in lithology during the late Permian-earliest Triassic. During the Wuchiapingian, the source areas of Zhaobishan section in the eastern part of the ENTS contained amalgamated rocks of the undissected volcanic arc, accretionary wedge and trench, whereas the source areas of Tarlong-Taodonggou areas in the western part of the ENTS contained assemblages of undissected volcanic arcs. During Changhsingian-early Induan times, the eastern part of the ENTS contained mainly rocks of volcanic arcs that were dissected, whereas the western part of the ENTS contained rocks of the transitional volcanic arc, accretionary and trench (Fig. 12).
Schematic maps showing the reconstruction of lithologic distributions in the source areas in the Eastern North Tianshan Suture during late Permian-earliest Triassic. a During Wuchiapingian, most parts of the Eastern North Tianshan Suture were covered by undissected arc volcanic rocks and sedimentary and metamorphic rocks were exposed in the eastern parts of the Eastern North Tianshan Suture; b During Changhsingian to early Induan, the exposure of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks expanded to the western part of the Eastern North Tianshan Suture and the deep-seated granites were initially exposed. See text for details
6 Conclusions
Sandstones from the upper Permian-lowermost Triassic WTG-LC in Bogda Mountains, NW China, provide critical information to understand the provenance and unroofing history of the ENTS. The source of the Zhaobishan section (east part) changed from the rocks of the undissected volcanic arc, accretionary wedge and trench to those of transitional volcanic arc with subordinate accretionary wedge and trench. The source of the North Tarlong and Taodongou sections (west part) shifted from an undissected volcanic arc and sedimentary rocks from the ENTS and rift shoulders to rocks in the transitional volcanic arc, accretionary wedge and trench. The sources of the Dalongkou section, located 70 km north of the North Tarlong and Taodonggou sections, are undissected volcanic arc and sedimentary rocks from the ENTS and rift shoulders. Unroofing history differs between the source areas for Zhaobishan and North Tarlong-Taodonggou sections, indicating that the eastern ENTS changed from the trinity of volcanic arc, accretionary wedge, and trench to the transitional volcanic arc, whereas the western ENTS shifted from the volcanic arc to the trinity of transitional volcanic arc, accretionary wedge and trench. This study provides sedimentological evidence to support that the ENTS was an amalgamated complex of volcanic arc, accretionary wedge, and trench with great spatial and temporal heterogeneity in lithology and experienced persistent unroofing during the late Permian-earliest Triassic. This study reconstructs a key element of the Chinese Tianshan Suture and serves as an analog for future studies to understand the lithology and unroofing processes of ancient sutures.
Availability of data and materials
The data used during this study are included in this article. Additional raw data are available from the corresponding authors.
Abbreviations
- ENTS:
-
Eastern North Tianshan Suture
- WTG-LC:
-
Wutonggou low-order cycle
References
Allen, J. 1968. The nature and origin of bed-form hierarchies. Sedimentology 10 (3): 161–182.
Allen, M., B. Windley, Z. Chi, Y.Z. Zhong, and R.W. Guang. 1991. Basin evolution within and adjacent to the Tien Shan Range, NW China. Journal of the Geological Society 148 (2): 369–378.
Allen, M.B., B.F. Windley, and C. Zhang. 1993. Palaeozoic collisional tectonics and magmatism of the Chinese Tien Shan, Central Asia. Tectonophysics 220 (1): 89–115.
Allmendinger, R. 2005. Stereonet: Program for stereographic projection.
Basu, A., S.W. Young, L.J. Suttner, W.C. James, and G.H. Mack. 1975. Re-evaluation of the use of undulatory extinction and polycrystallinity in detrital quartz for provenance interpretation. Journal of Sedimentary Research 45 (4): 873–882.
Blatt, H., R. Tracy, and B. Owens. 2006. Petrology: Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic, W, 529. New York: H. Freeman.
Carroll, A., S. Graham, M. Hendrix, D. Ying, and D. Zhou. 1995. Late Paleozoic tectonic amalgamation of northwestern China: sedimentary record of the northern Tarim, northwestern Turpan, and southern Junggar basins. Geological Society of America Bulletin 107 (5): 571–594.
Carroll, A.R., L. Yunhai, S.A. Graham, X. Xuchang, M.S. Hendrix, C. Jinchi, and C.L. McKnight. 1990. Junggar basin, Northwest China: trapped Late Paleozoic ocean. Tectonophysics 181 (1–4): 1–14.
Charvet, J., L. Shu, S. Laurent-Charvet, B. Wang, M. Faure, D. Cluzel, Y. Chen, and K. De Jong. 2011. Palaeozoic tectonic evolution of the Tianshan belt, NW China. Science China Earth Sciences 54 (2): 166–184.
Charvet, J., L.S. Shu, and S. Laurent-Charvet. 2007. Paleozoic structural and geodynamic evolution of eastern Tianshan (NW China): welding of the Tarim and Junggar plates. Episodes Journal of International Geosciences 30 (3): 162–186.
Chaudhuri, A., S. Banerjee, and E. Le Pera. 2018. Petrography of middle Jurassic to early Cretaceous sandstones in the Kutch Basin, western India: Implications on provenance and basin evolution. Journal of Paleogeography 7 (1): 2–14.
Critelli, S., and R.V. Ingersoll. 1995. Interpretation of neovolcanic versus palaeovolcanic sand grains: an example from Miocene deep-marine sandstone of the Topanga group (Southern California). Sedimentology 42 (5): 783–804.
Davis, G.H., S.J. Reynolds, C.F. Kluth, and C. Kluth. 2011. Structural geology of rocks and regions, 839. New York: Wiley.
Dickinson, W.R. 1985. Interpreting provenance relations from detrital modes of sandstones, 333–361. Provenance of arenites, Netherlands: Springer.
Dickinson, W.R. 1970. Interpreting detrital modes of graywacke and arkose. Journal of Sedimentary Research 40 (2): 695–707.
Dickinson, W.R., L.S. Beard, G.R. Brakenridge, J.L. Erjavec, R.C. Ferguson, K.F. Inman, R.A. Knepp, F.A. Lindberg, and P.T. Ryberg. 1983. Provenance of North American Phanerozoic sandstones in relation to tectonic setting. Geological Society of America Bulletin 94 (2): 222–235.
Dickinson, W.R., and C. Suczek. 1979. Plate tectonics and sandstone composition. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin 63 (12): 2164–2182.
Dorsey, R.J. 1988. Provenance evolution and unroofing history of a modern arc-continent collision; evidence from petrography of Plio-Pleistocene sandstones, eastern Taiwan. Journal of Sedimentary Research 58 (2): 208–218.
Dott, R.H. 1964. Wacke, graywacke and matrix; what approach to immature sandstone classification?. Journal of Sedimentary Research 34 (3): 625–632.
Fredericks, J.G. 2017. Provenance and depositional environments of fluvial-lacustrine deposits in a non-marine rift basin, lower-Triassic Jiucaiyuan and Shaofanggou low-order cycles Bogda Shan, NW China [master thesis]: Missouri University of Science and Technology, 276 p.
Gao, J., M. Li, X. Xiao, Y. Tang, and G. He. 1998. Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Tianshan Orogen, northwestern China. Tectonophysics 287(1): 213–231.
Garzanti, E., S. Critelli, and R.V. Ingersoll. 1996. Paleogeographic and paleotectonic evolution of the Himalayan range as reflected by detrital modes of tertiary sandstones and modern sands (Indus transect, India and Pakistan). Geological Society of America Bulletin 108 (6): 631–642.
Garzanti, E., C. Doglioni, G. Vezzoli, and S. Ando. 2007. Orogenic belts and orogenic sediment provenance. The Journal of Geology 115 (3): 315–334.
Garzanti, E., and M. Gaetani. 2002. Unroofing history of Late Paleozoic magmatic arcs within the “Turan plate”(Tuarkyr, Turkmenistan). Sedimentary Geology 151 (1–2): 67–87.
Gazzi, P. 1966. Le arenarie del flysch sopracretaceo dell’Appennino modenese; correlazioni con il flysch di Monghidoro. Mineralogica et Petrographica Acta 12 (6): 69–97.
Greene, T.J., A.R. Carroll, M.S. Hendrix, S.A. Graham, M.A. Wartes, and O.A. Abbink. 2001. Sedimentary record of Mesozoic deformation and inception of the Turpan-Hami basin, Northwest China. Paleozoic and Mesozoic tectonic evolution of central and eastern Asia. Geological Society of America Memoirs 194: 317–340.
Greene, T.J., A.R. Carroll, M. Wartes, S.A. Graham, and J.L. Wooden. 2005. Integrated provenance analysis of a complex orogenic terrane: Mesozoic uplift of the Bogda Shan and inception of the Turpan-Hami Basin, NW China. Journal of Sedimentary Research 75 (2): 251–267.
Guan, W. 2011. Provenance analysis of upper Permian-basal Triassic fluvial-lacustrine sedimentary rocks in the greater Turpan-Junggar Basin, southern Bogda Mountains, NW China [master thesis]: Wichita State University, 102.
Han, B.F., Z.J. Guo, Z.C. Zhang, L. Zhang, J.F. Chen, and B. Song. 2010. Age, geochemistry, and tectonic implications of a late Paleozoic stitching pluton in the North Tian Shan suture zone, western China. Geological Society of America Bulletin 122 (3–4): 627–640.
Hendrix, M.S. 2000. Evolution of Mesozoic sandstone compositions, southern Junggar, northern Tarim, and western Turpan basins, Northwest China: a detrital record of the ancestral Tian Shan. Journal of Sedimentary Research 70 (3): 520–532.
Hendrix, M.S., T.A. Dumitru, and S.A. Graham. 1994. Late Oligocene-early Miocene unroofing in the Chinese Tian Shan: an early effect of the India-Asia collision. Geology 22 (6): 487–490.
Hendrix, M.S., S.A. Graham, A.R. Carroll, E.R. Sobel, C.L. McKnight, B.J. Schulein, and Z. Wang. 1992. Sedimentary record and climatic implications of recurrent deformation in the Tian Shan: Evidence from Mesozoic strata of the North Tarim, south Junggar, and Turpan basins, Northwest China. Geological Society of America Bulletin 104 (1): 53–79.
Hsü, K.J. 1988. Relict back-arc basins: principles of recognition and possible new examples from China, new perspectives in basin analysis, 245–263. New York: Springer.
Ingersoll, R.V. 2012. Composition of modern sand and Cretaceous sandstone derived from the Sierra Nevada, California, USA, with implications for Cenozoic and Mesozoic uplift and dissection. Sedimentary Geology 280 (1): 195–207.
Ingersoll, R.V., T.F. Bullard, R.L. Ford, J.P. Grimm, J.D. Pickle, and S.W. Sares. 1984. The effect of grain size on detrital modes: a test of the Gazzi-Dickinson point-counting method. Journal of Sedimentary Research 54 (1): 103–116.
Ingersoll, R.V., and C.A. Suczek. 1979. Petrology and provenance of Neogene sand from Nicobar and Bengal fans, DSDP sites 211 and 218. Journal of Sedimentary Research 49 (4): 1217–1228.
Jahn, Bor-ming, Fuyuan Wu, and Bin Chen. 2000. Granitoids of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and continental growth in the Phanerozoic. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh 91 (1–2): 181–193.
Laurent-Charvet, S., J. Charvet, P. Monié, and L. Shu. 2003. Late Paleozoic strike-slip shear zones in eastern Central Asia (NW China): New structural and geochronological data. Tectonics 22 (2): 1099–1101.
Laurent-Charvet, S., J. Charvet, L. Shu, R. Ma, and H. Lu. 2002. Palaeozoic late collisional strike-slip deformations in Tianshan and Altay, Eastern Xinjiang, NW China. Terra Nova 14 (4): 249–256.
Liao, Z., L. Lu, N. Jiang, F. Xia, F. Sung, Y. Zhou, S. Li, and Z. Zhang. 1987. Carboniferous and Permian in the western part of the east Tianshan Mountains: Beijing. In Proceedings Eleventh Congress of Carboniferous Stratigraphy and Geology, Guide Book Excursion, vol. 4, 50.
Marsaglia, K.M., and R.V. Ingersoll. 1992. Compositional trends in arc-related, deep-marine sand and sandstone: a reassessment of magmatic-arc provenance. Geological Society of America Bulletin 104 (12): 1637–1649.
Miall, A.D. 1974. Paleocurrent analysis of alluvial sediments; a discussion of directional variance and vector magnitude. Journal of Sedimentary Research 44 (4): 1174–1185.
Obrist-Farner, J., and W. Yang. 2015. Nonmarine time-stratigraphy in a rift setting: An example from the Mid-Permian lower Quanzijie low-order cycle Bogda Mountains, NW China. Journal of Palaeogeography 4 (1): 27–51.
Obrist-Farner, J., and W. Yang. 2017. Provenance and depositional conditions of fluvial conglomerates and sandstones and their controlling processes in a rift setting, mid-Permian lower and upper Quanzijie low order cycles, Bogda Mountains, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 138: 317–340.
Okuzawa, K., and K.i. Hisada. 2008. Temporal changes in the composition of Miocene sandstone related to collision between the Honshu and Izu Arcs, Central Japan. Special Papers, Geological Society of America 436: 185.
Peng, X. 2016. Provenance and depositional environments of fluvial-lacustrine sandstones of lower Permian Lucaogou low-order cycle, Bogda Mountains, NW China [master thesis]: Missouri University of Science and Technology, 148.
Sengör, A., and B. Natal'in. 1996. Paleotectonics of Asia: fragments of a synthesis. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 24 (1): 263–337.
Şengör, A., B. Natal'In, and V. Burtman. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia. Nature 364 (6435): 299.
Shao, L., K. Stattegger, and C.D. Garbe-Schoenberg. 2001. Sandstone petrology and geochemistry of the Turpan basin (NW China): Implications for the tectonic evolution of a continental basin. Journal of Sedimentary Research 71 (1): 37–49.
Shao, L., K. Stattegger, W. Li, and B.J. Haupt. 1999. Depositional style and subsidence history of the Turpan Basin (NW China). Sedimentary Geology 128 (1): 155–169.
Shu, L., J. Charvet, L. Guo, H. Lu, and S. Laurent-Charvet. 1999. A large-scale Palaeozoic dextral ductile strike-slip zone: the Aqqikkudug–Weiya Zone along the Northern margin of the Central Tianshan Belt, Xinjiang, NW China. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition) 73 (2): 148–162.
Shu, L., B. Wang, W. Zhu, Z. Guo, J. Charvet, and Y. Zhang. 2011. Timing of initiation of extension in the Tianshan, based on structural, geochemical and geochronological analyses of bimodal volcanism and olistostrome in the Bogda Shan (NW China). International Journal of Earth Sciences 100 (7): 1647–1663.
Shu, L.S., W. Zhu, B. Wang, M. Faure, J. Charvet, and D. Cluzel. 2005. The post-collision intracontinental rifting and olistostrome on the southern slope of Bogda Mountains, Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica 21 (1): 25–36.
Soreghan, M.J., and A.S. Cohen. 1993. The effects of basin asymmetry on sand composition: examples from Lake Tanganyika, Africa. In Special Papers-Geological Society of America, 285–285.
Suttner, L.J. 1974. Sedimentary petrographic provinces: an evaluation. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists. Special Publication 21: 75–84.
Thomas, S.G., N.J. Tabor, W. Yang, T.S. Myers, Y. Yang, and D. Wang. 2011. Palaeosol stratigraphy across the Permian-Triassic boundary, Bogda Mountains, NW China: Implications for palaeoenvironmental transition through Earth's largest mass extinction. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 308 (1–2): 41–64.
Trop, J.M., and K.D. Ridgway. 1997. Petrofacies and provenance of a Late Cretaceous suture zone thrust-top basin, Cantwell Basin, Central Alaska Range. Journal of Sedimentary Research 67 (3): 469–485.
Wang, B., M. Faure, D. Cluzel, L. Shu, J. Charvet, S. Meffre, and Q. Ma. 2006. Late Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the northern West Chinese Tianshan belt. Geodinamica Acta 19 (3–4): 237–247.
Wang, B., L.S. Shu, D. Cluzel, M. Faure, and J. Charvet. 2007. Geochronological and geochemical studies on the Borohoro plutons, north of Yili, NW Tianshan and their tectonic implication. Acta Petrologica Sinica 8: 1885–1900.
Wartes, M.A., A.R. Carroll, and T.J. Greene. 2002. Permian sedimentary record of the Turpan-Hami basin and adjacent regions, Northwest China: Constraints on post-amalgamation tectonic evolution. Geological Society of America Bulletin 114 (2): 131–152.
Windley, B., M. Allen, C. Zhang, Z. Zhao, and G. Wang. 1990. Paleozoic accretion and Cenozoic red formation of the Chinese Tien Shan range, Central Asia. Geology 18 (2): 128–131.
Windley, B.F., D. Alexeiev, W. Xiao, A. Kröner, and G. Badarch. 2007. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Journal of the Geological Society 164 (1): 31–47.
XBGMR. 1993. Regional Geology of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Geological Memoirs, Series 1, No. 32. In Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (In Chinese with English abstract), 762. Beijing: Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources, Geological Publishing House.
Xia, L.Q., X.Y. Xu, Z.C. Xia, X.M. Li, Z.P. Ma, and L.S. Wang. 2004. Petrogenesis of carboniferous rift-related volcanic rocks in the Tianshan, northwestern China. Geological Society of America Bulletin 116 (3–4): 419–433.
Xiao, W.J., B.F. Windley, C. Yuan, M. Sun, C.M. Han, S.F. Lin, H.L. Chen, Q.R. Yan, D.Y. Liu, K.Z. Qin, and J.L. Li. 2009. Paleozoic multiple subduction-accretion processes of the southern Altaids. American Journal of Science 309 (3): 221–270.
Xiao, W., B.F. Windley, M.B. Allen, and C. Han. 2013. Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Chinese Tianshan orogenic collage. Gondwana Research 23 (4): 1316–1341.
Xiao, W.J., L.C. Zhang, K.Z. Qin, S. Sun, and J.L. Li. 2004. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China): implications for the continental growth of Central Asia. American Journal of Science 304 (4): 370–395.
Yang, W., J. Crowley, J. Obrist-Farner, N. Tabor, Q. Feng, and Y. Liu. 2013. A marine back-arc origin for the Upper Carboniferous basement of intracontinental greater Turpan-Junggar basin-Volcanic, sedimentary, and geochronologic evidence from southern Bogda Mountains. In Proceedings NW China. Geological Society of America Annual Meeting, GSA Abstract with Programs, Volume 45.
Yang, W., Q. Feng, Y. Liu, N. Tabor, D. Miggins, J.L. Crowley, J. Lin, and S. Thomas. 2010. Depositional environments and cyclo- and chronostratigraphy of uppermost carboniferous–lower Triassic fluvial–lacustrine deposits, southern Bogda Mountains, NW China — A terrestrial paleoclimatic record of mid-latitude NE Pangea. Global and Planetary Change 73 (1–2): 15–113.
Yang, W., Y. Liu, Q. Feng, J. Lin, D. Zhou, and D. Wang. 2007. Sedimentary evidence of early–late Permian mid-latitude continental climate variability, southern Bogda Mountains, NW China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 252 (1): 239–258.
Yin, A., S. Nie, P. Craig, T. Harrison, F. Ryerson, Q. Xianglin, and Y. Geng. 1998. Late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the southern Chinese Tian Shan. Tectonics 17 (1): 1–27.
Young, S.W. 1976. Petrographic textures of detrital polycrystalline quartz as an aid to interpreting crystalline source rocks. Journal of Sedimentary Research 46 (3): 595–603.
Zhang, X. 1981. Regional Stratigraphic Chart of Northwestern China, Branch of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Beijing: Geological Publishing House.
Acknowledgements
This work is a part of the dissertation research of DYZ at Missouri University of Science and Technology, U.S.A. We would like to thank Drs. J. Wang, M. L. Wan and Mr. S. W. Mei of Nanjing Institute of Geology and Paleontology of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Y. R. Lu, J. Duan, J. Fredericks, Z.Y. Ju, S.X. Wu and J.J. Li for their field assistance. This research was partially supported by the student research grant from Alfred Spreng Graduate Research Grant from Geology and Geophysics Program of Missouri University of Science and Technology to DYZ, and by a research grant (IES-1714749) from National Science Foundation to WY. We are grateful to Professor Zeng-Zhao Feng, Dr. Carlos Zavala, an anonymous reviewer, and the editor for their constructive comments that improved the quality of this contribution.
Funding
This research was partially supported by Alfred Spreng Graduate Research Grant from Geology and Geophysics Program of Missouri University of Science and Technology to DYZ and by a U.S. National Science Foundation grant (IES-1714749) to WY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DYZ performed the data collection, analysis, interpretation, and drafted the manuscript. WY collected data, and revised the manuscript. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, DY., Yang, W. Provenance of upper Permian-lowermost Triassic sandstones, Wutonggou low-order cycle, Bogda Mountains, NW China: implications on the unroofing history of the Eastern North Tianshan Suture. J. Palaeogeogr. 9, 19 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42501-020-00067-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42501-020-00067-9