Abstract
Background
Callosobruchus maculatus and C. chinensis (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) are dangerous insects to stored grains. They are controlled by chemical insecticides, which cause a lot of harmful diseases and pollute the environment. Essential oils are a new trend for controlling of storage pests.
Methods
The nano-encapsulation process was carried out by polymerization technology. The tested nano-oils were experimented at tested concentration (0.5%) for their insecticidal activities against the third-instar larvae of tested insects. After 7 days of exposure, accumulative mortality percentages were calculated in the treated and untreated control. Also, the tested nano-oils were sprayed to the foam granules and were mixed with 2 g foam/100 g cow pea for testing the oviposition inhibitory effects of the tested oils. Additionally, the experiment was designed to test the latent effect of the tested oils against C. maculatus and C. chinensis on foam as surface protectant after 90-day intervals.
Results
After 7 days of treatments, the accumulations of C. maculatus were 61.2, 42.0, 46.6, and 35.5% after being treated with rosemary, catnip, garlic, and citronella oil, respectively, as compared to 0.3% in the control. When C. chinensis were treated with corresponding oils, the accumulations obtained 68.9, 44.1, 49.9, and 37.9% as compared to 0.1% in the control. When both the target insect pests, C. maculatus and C. chinensis, were treated with the tested nano-oils, results showed that the accumulations of C. maculatus recorded 82.2, 55.8, 66.3, and 46.3% when treated with nano-rosemary, nano-anis, nano-garlic, and nano-citronella as compared to 0.1 in the control. When the corresponding nano-oils were applied against C. chinensis, the accumulations obtained 89.7, 42.8, 70.9, and 48.9% as compared to 0.1% in the control. When the tested oils and their nano were tested against C. maculatus life cycle, the number of eggs laid/female were significantly decreased to 6.4 ± 9.89 eggs/female after nano-rosemary treatments as compared to 299.9 ± 9299 eggs/female in the control. The adult emergence decreased to 1% after nano-rosemary treatments as compared to 100% in the control. The malformations of the insect significantly increased after nano-rosemary and nano-anis to 100% as compared to 0% in the control. The same results obtained when C. chinensis were treated with different tested oils. The number of eggs C. chinensis laid/female was 8.3 ± 1.0 eggs/female as compared to 298.9 ± 7.89 eggs/female in the control.
Conclusion
This work research indicate that some essential oils might be useful for managing C. maculatus and C. chinensis in enclosed spaces because of their fumigant harmful action. Plant essential oils and their active ingredient have potentially high bioactivity against a range of the target insect pests. Furthermore, they are highly selective to C. maculatus and C. chinensis. Incorporation of essential oils into a controlled release nano-formulation prevents rapid vaporization and degradation, increases constancy, and preserves the lower effective dosage/application. Treated foam with nano-rosemary and nano-garlic oils and covering gunny bags provided many efficient effects against tested insects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introductions
Many researches study the potential use of botanical applications in biological control of different insect pests since some are selective, biodegrade to nontoxic products, and have few effects on non-target organisms and the environment (Singh and Upadhyay 1993; Isman 2000; Kim et al. 2010). The essential oils may be more rapidly degraded in the environment than synthetic compounds, and some have increased specificity that favors beneficial insects. Their action against stored-product insects has been extensively studied (Negahban et al. 2007; Sahaf and Moharramipour 2008). In spite of the fact that essential oils have most promising properties, problems related to their volatility, poor water solubility, and potential for oxidation have to be resolved before used as alternative pest control means (Moretti et al. 2002). In this endeavor, the use of encapsulated formulations seem to be a useful tool to answer those problems (Clancy et al. 1992; Passino et al. 2004). The propagation of poly urea-formaldehyde (PUF) nanoencapsulation techniques would supply insecticide formulations of essential oils without widespread destruction effects on their major compounds. Urea formaldehyde is used in agriculture as a controlled release source of nitrogen fertilizer. Urea formaldehyde’s rate of decomposition into CO2 and NH3 is determined by the action of microbes found naturally in most soils (Martin and Trenkel 1997). Studies relating to the activity of PUF nano-capsules of Artemisia sieberi as an insecticide have not been carried out.
The purpose of this study is to test the toxicity and persistence of produced oils and nano-encapsulated essential oil against Callosobruchus maculatus and Callosobruchus chinensis (the most economically important pests of stored grain).
Materials and methods
Experimental insects
Larvae of C. maculatus and C. chinensis were used in the experiments. The target insects were reared under laboratory conditions on semi-artificial diet (fine cow pea seeds with some adherent endosperm) with 20% glycin and 5% yeast powder. All cultures and experiments were held at 26 ± 2 °C and 70–80% relative humidity (RH), with 16 h light and 8 h dark.
Tested oils
Three essential oils were used in the bioassay, rosemary, citronella, garlic, and catnip. The essential oils were obtained by steam distillation methods of dried plants (Guenther 1961). The tested oil emulsions were prepared according to Sabbour and Shadia Abd El-Aziz (2016a, 2016b).
The nano-encapsulation
The process was carried out by polymerization technology. The tested oils were used as a core material, and urea (U) and formaldehyde (F) as shell materials. Sulfuric acid solution (10% w/w) was prepared in our laboratory to control the pH of emulsion, and tween 80 (Polysorbate 80) was used as emulsifier (Merck, Germany). The obtained suspension of nano-capsules was cooled down to ambient temperature, rinsed with deionized water, filtered, and finally dehydrated by freeze-drying using a LIO-5P apparatus (CinquePascal, Trezzano SN, Milan, Italy). Scanning and transmission electron microscopy were used to observe surface morphology of the nano-capsules.
Larvicidal activity of tested oils (bulk and nano)
The insecticidal activities of tested oils (bulk and nano) were experimented at tested concentrations against the third-instar larvae of C. maculatus and C. chinensis. The foam granules sprayed with the tested oils (bulk and nano) were (2 g foam/100 g cow pea) according to Abd El-Aziziz (2001). For each tested concentration, four glass jars as replicates were used. Subsequently, ten third-instar larvae were introduced into each glass jar which were covered with muslin for appropriate ventilation. Twelve replicates as control larvae were kept under the same conditions without any essential oil treatments. Mortality was evaluated after 7 days of exposure in the treated and untreated control. All tests were carried at 27 ± 2 °C and 65 ± 5% relative humidity (RH). The number of dead larvae in each jar was assessed, and the percentages of mortality were calculated. The experiment was repeated four times.
The ovipositional deterrent effects of the tested oils
The foam granules sprayed with the tested oils (bulk and nano) were mixed with 2 g foam/100 g cow pea) according to Abd El-Aziz (2001). The ovipositional deterrent of the tested oils was experimented by placing two pairs of mixed sex of C. maculatus and C. chinensis (2–3 days old) with treated or untreated grains with foam particles in glass jars (250 cc capacity) covered with muslin (no-choice). The moths were left to lay eggs, and then, the numbers of deposited eggs on treated or untreated grains/female were counted in the tested jars. For each tested concentration, four glass jars as replicates were used and the test was repeated four times.
The latent effect of tested oils in the store
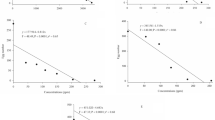
The latent effect of tested oils (bulk and nano) on foam as surface protectant was evaluated during storage intervals (25 over 125 days) against C. maculatus and C. chinensis moths’ infestation. 100 grams of heat sterilized cow pea grains was introduced to the gunny sacks (10 × 10 cm each) closed each with a string. The foam granules (about 1 cm in diameter) were sprayed with treatments, dried and provided as a layer between sacks. Then, two pairs of newly emerged moths were placed in a jar (2 L capacity with two gunny sacks). After egg laying, the dead moths were removed. The emerged adult moths were counted after tested intervals. After 90 days, the percentage of grain weight lost was calculated from the differences between the original and the final weight in each jar using the following formula:
% WL (% Weight Loss) = [(OW–FW)/OW] × 100.
where OW = original weight and FW = final weight.
Each experiment was repeated five times (Abd El-Aziz and Abd El-Ghany 2018).
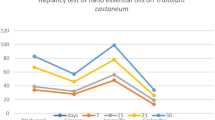
Repellency test
The experiments were conducted in an arena based on the choice test (Abd El-Aziz and Ismail 2000). Disc of filter paper (Whatman No. 1) was treated with the tested oil at 1% concentration and placed in the cell A. While filter paper treated with distilled water and emulsifier only as control was placed in the cell B. Twenty newly emerged beetles were introduced into each arena. After 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 days, the number of beetles present in the cells A and B were recorded. The percentages of repellency values were calculated using the equation: D = [1 − (T/C)] × 100 (Lwande et al. 1985) where T and C represent the mean number of beetles in cells A and B treated and untreated, respectively.
Statistical analysis
The data was analyzed using analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA), where significant differences between the treatments were observed. Mean values were significantly separated by using the least significant difference (LSD) test at 5% level (Sokal and Rohlf 1981).
Results
Under laboratory conditions, the accumulation mortality of C. maculatus obtained significantly increased to 61.2 and 46.6% in rosemary and garlic treatments after 7 days as compared to 0.1% in control. When C. chinensis larvae were treated with the same last oils, the accumulations mortality recorded 44.1and 49.9% as compared to 0.1% in the control (Table 1).
Under laboratory conditions, when both the target pests C. maculatus and C. chinensis were treated with the tested oils, results showed that the accumulations of C. maculatus recorded 82.2, 55.8, 66.3, and 43.3% when treated with nano-rosemary, nano-anis, nano-garlic, and nano-citronella as compared to 0.1 in the control. When the corresponding nano-oils were applied against C. chinensis, the accumulations obtained 89.7, 42.8, 70.9, and 48.9% as compared to 0.1% in the control (Table 2).
In all treatments, percentage of larval mortality of tested insects (Tables 3 and 4) increased with increase of concentrations. Larvae of C. maculatus were more susceptible to the treatments than C. chinensis larvae. Nano-oils were more effective than natural oils. The larval mortality percentage of C. maculatus recorded 45.4, 23.3, and 21.3% after rosemary 1.0–0.5 and 0.25% treatments, respectively. The larval percentages mortality were 24.2, 30.3, and 19.8% in case of C. chinensis (Table 3).
Table 4 shows that after nano-oil treatments the percentages of larval mortality of C. maculatus significantly increased to 61.3 and 59.8% after rosemary and garlic nano-oil treatments. Also C. chinensis mortality significantly increased to 59.8 and 50.7% for corresponding oils as compared to control (Table 4).
When the tested oils and its nano were tested against C. maculatus life cycle, the number of eggs laid/female were significantly decreased to 6.4 ± 9.89 eggs/female after nano-rosemary treatments as compared to 299.9 ± 9.89 eggs/female in the control. The adult emergence decreased to 1% after nano-rosemary treatments as compared to 100% in the control. The malformations of the insect significantly increased after nano-rosemary and nano-anis to 100% as compared to zero in the control (Table 5). When C. chinensis treated with the nano-oils were tested, the number of eggs laid/female significantly decreased to 8.3 ± 1.0 after nano-rosemary treatments as compared to 298.9 ± 7.89 eggs/female. The percentages of adult emergence significantly decreased to 0.1% as compared to 100% in the control. The percentages of malformed between adults 99% after nano-rosemary treatments as compared to 0% in the control (Table 6). Figures 1 and 2 show the weight loss of seeds was significantly decreased after nano-oil treatments for both two pests. Figures 3 and 4 show the repellency test of nano-oils, in which nano-rosemary and nano-garlic are the highest repellant oils.
Discussions
Natural oils affected on the pests show some repellant, antifeedant, and toxic effects (Lee et al. 2002), which were reported in monoterpenoids that are typically volatile and rather lipophilic compounds that can penetrate into insect pests rapidly and interfere their physiological functions. Sabbour et al. (2012) found that the modified diatomaceous earth with calcium hydroxide (Ca-DE) and modified diatoms with sodium hydroxide (Na-DE) were the highlight treatments against tested pests and had the highest mortality percentages found among C. maculatus. Sabbour and Abd-El-Raheem (2013) showed that Jatropha curcas oil not only acted as oviposition deterrents but also adversely influence fecundity. Moths oviposited eggs on treated seeds with jatropha oil, but the numbers of eggs is always lower in treated seeds than in the control. Also, it was found that the accumulative mortality (%) of Ephestia cautella and Plodia interpunctella larvae increased gradually by increasing the period of exposure in case of treated foam with different tested oils, the same as that obtained by Sabbour et al. (2013). Sabbour (2013) found that Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana when combined with some extract oils could decrease the infestations of wheat and flour pests under laboratory and store conditions.
The same were obtained by Sabbour and Abd el-Aziz (2015, 2016a, 2016b, 2017, and 2019). Essential oil contains compounds that show ovicidal, repellent, antifeedant, and toxic effects in insects. The toxicity may act by fumigant action (Negahban et al. 2007). Focus on the insecticidal toxicity of essential oils of plants and their constituents have sharpened since the 1980s specifically on essential oils (Rajendran and Sriranjini 2008). There are many reviews dealing with the use of plant products in general, against insect pests (Isman 2000; Rajendran and Sriranjini 2008). Therefore, it was considered appropriate to look into the status of research on plant’s essential oils and their constituents as insecticides. The present study examines the work conducted and addresses the prospects and problems of the use of plant products as fumigants within these parameters. The nano-capsule of Artemisia oil was shown here to possess fumigant toxicity, as well as its longer persistence compared to Artemisia oil before formulation. In consistence with studies of Moretti et al. (2004) and Passino et al. (2004), our findings showed higher mortality rates in nano-capsule than in pure essential oil due to controlled release formulations allowing smaller quantities of essential oil to be used more effectively over a given time interval. The reasons for nano-encapsulating the essential oil have been to improve its stability to reduce side effects or to reduce dosing frequency and total dosing amount 105 oil release, to obtain better toxicity activity, and for long-lasting release (Huang et al. 2007). Generally, the modifications of nano-capsules prepared by poly (urea-formaldehyde) (PUF) are required in order to improve their insecticidal toxicity stability, strength, or sustained release. The same results obtained by Sabbour and Abd El-Aziz (2010, 2016a, 2016b, 2017), Sabbour et al. (2012), and Sabbour 2013 and 2014.
Conclusion
This study discovered the nano-oils rosemary and garlic are the most effective oils against the tested two serious pests C. maculatus and C. chinensis. These results can be helpful and beneficial for controlling many stored insect pests. These results encourage the extension in the use of nanotechnology for pest control.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Abd El-Aziz SE, Abd El-Ghany N (2018) Impact of diatomaceous earth modifications for controlling the granary weevil, Sitophilus granaries (Linnaeus) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Agric Sci Technol 20:519–531 http://jast.modares.ac.ir/article-23-20116-en.pdf
Abd El-Aziz Shadia E, (2001) Persistence of some plant oils against the Bruchid beetle, Callosobruchus maculates (F.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) during storage. Arab Universities Journal of Agricultural Sciences, Ain Shams , Cairo, 2001, 9 (1): 423–432
Clancy KM, Foust RD, Huntsberger TG, Whtaker JG, Whitaker DM (1992) Technique for using microencapsulated terpenes in lepidopteran artificial diets. J Chem Ecol 18:543–560
Guenther E (1961) The essential oils. D. von Nostrand Co. Inc. New York, vol. 3, 155 pp.
Huang J, Li Q, Sun D, Lu Y, Su Y, Yang X, Wang H, Wang Y, Shao W, He N, Hong J, Chen C (2007) Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by novel sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf. Nanotechnology 18:105104
Isman MB (2000) Plant essential oils for pest and disease management. Crop Prot 19:603–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-2194(00)00079-X
Kim S, Yoon JS, Jung JW, Hong KB, Ahn YJ, Kwon HW (2010) Toxicity and repellency of origanum essential oil and its components against Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) adults. J Asia Pac Entomol 13:369–373
Lee S, Peterson CJ, Coats JR (2002) Fumigation toxicity of monoterpenoids to several stored product insects. J Stored Prod Res 39:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-474X(02)00020-6
Lwande W, Hassanalli A, Njorage PW, Bentley MD, Delle Monache F, Jondiks JI (1985) A new 6a-hydroxy pterocarpan with insect antifeedant and antifungal properties from the root of Tephrosia hildebrandtu. Vatle Insect Sci Appl 6:537–541
Martin DR, Trenkel E (1997) Improving fertilizer use efficiency. Controlled release and stabilized fertilizers in agriculture. IFA, Paris
Moretti MDL, Sanna-Passino G, Demontis S, Bazzoni E (2002) Essential oil formulations useful as a new tool for the insect pest control. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech 3(2):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1208/pt030213
Negahban M, Moharramipour S, Sefidkon F (2007) Chemical composition and insecticidal activity of Artemisia scoparia essential oil against three coleopteran stored-product insects. J Asia-Pac Entomol 9: 381-388. doi.org/10.1016/S1226-8615(08)60318-0
Passino GS, Bazzoni E, Moretti MDL (2004) Microencapsulated essential oils active against Indianmeal moth. Boi San Veg Plagas 30:125–132
Rajendran S, Sriranjini V (2008) Plant products as fumigant for stored-product insect control. J of Stored Product Res 44:126–135
Sabbour MM (2013) Evaluations of some extracted natural oils against Bruchidius incarnates and Ephestia elutella Global J. of Sci Res Available online at gjsr.blue-ap.org.©2013 GJSR J. Vol. 1(1), pp. 1-7, 5 December, 2013. http://www.blue-ap.org/j/List/2/iss/volume%201%20(2013)/ issue%2001/1.pdf
Sabbour MM, Abd El-Aziz SE (2019) Impact of certain nano oils against Ephestia kuehniella and Ephestia cutella (Lepidoptera-Pyralidae) under laboratory and store conditions. Bulletin of the N R C 43:80. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0129-3
Sabbour MM, Shadia Abd-El-Aziz. (2016a). Roll of three essential oils and their nano against Ephestia cautella Lepidoptera Pyralidae under laboratory and store conditions. International J Pharm Tech Res: 0974-4304 , http://isisn.org/BR_15_3_2018.htm
Sabbour MM, Abd-El-Aziz SE (2010) Efficacy of some bioinsecticides against Bruchidius incarnatus (BOH.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) infestation during storage. J. Plant Prot Rest. 50(1):28–34. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10045-010-16-5
Sabbour MM, Abd-El-Aziz SE (2016b) Efficacy of three essential oils and their nano-particles against Sitophilus granarius under laboratory and store conditions. J ent Res 40(3):229–234. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-4576.2016.00042.6
Sabbour MM, Shadia E Abd-El-Aziz (2017) Screening effect of three natural oils and their nano against Ephestia Kȕehniella (Lepidoptera-Pyralidae) under laboratory and store conditions. Bio.Sci. Res., 14(2): 408–416. http://isisn.org/BR_14_3_2018.htm
Sabbour MM, Shadia El-Sayed Abd-El-Aziz (2015) Efficacy of some nano-diatomaceous earths against red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum and confused flour beetle, Tribolium confusum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) under laboratory and store conditions. Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., 4 [7] June 54–59. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/ 1fc9/4c3276407740f1e9eba5fc42ce4694bbdacf.pdf
Sabbour MM, Abd-El-Aziz S, Sherief M (2012) Efficacy of three entomopathogenic fungi alone or in combination with diatomaceous earth modifications for the control of three pyralid moths in stored grain. J of Plant Pro Res 52(3):359–363 https://www.degruyter.com/downloadpdf/j/jppr.2012.52.issue-3/v10045-012-0059-7/v10045-012-0059-7.pdf
Sabbour MM, MA AbdEl-Raheem (2013) Repellent Effects of Jatropha curcas, canola and Jojoba Seed oil, against Callosobruchus maculates (F.) and Callosobruchus chinensis (L.). J of Appl. Sci. Res. 9(8): 4678–4682, 2013. http://www.aensiweb.com/old/jasr/jasr/2013/4678-4682.pdf
Sabbour MM, AA Abd-El-Rahman , MA Ragei. (2013) Determinations of some extracted oils in controlling two stored product insect pests. Middle East Journal of Agriculture Research, Middle East J. of Agric.Rese. 2(4): 127-132, 2013. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/6339/d63e4f7169df8cc75522c0ce6ebd0f607d3c.pdf
Sahaf BZ, Moharramipour S (2008) Fumigant toxicity of Carum copticum and Vitex pseudonegundo essential oils against eggs, larvae and adults of Callosobruchus maculatus. J Pest Sci 81:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-008-0208-y
Singh G, Upadhyay RK (1993) Essential oils: a potent source of natural pesticides. J Sci Ind Res 52:676–683
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1981) The principles and practice of statistics in biological research. Freeman. San Francisco, p 859
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the National Research Centre for supporting project No 1130139.
Funding
This work was supported and funded by the National Research Centre through the project title “Some strategies for improving weed control efficacy in some export crops,” Project No. 11030139, during in-house project strategy 2016–2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors equally contributed in all the article parts. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
Prof. Dr. Magda Sabbour is a professor at the National Research Centre, Dokki, Giza, Pests and Plant Protection Department, Agricultural and Biological Division.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Sabbour, M.M.A. Efficacy of natural oils against the biological activity on Callosobruchus maculatus and Callosobruchus chinensis (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Bull Natl Res Cent 43, 206 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0252-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0252-1