Abstract
Background
Cerebral fat embolism (CFE) syndrome at high altitude was rare complicated with paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity (PSH) syndrome and septic shock. It is a challenge to differential diagnosis and treatment at high altitude.
Case presentation
This case presents a CFE with PSH and septic shock of a 23-year-old man occurred at high altitude of 3800 m above sea level, transferred by airplane successfully and cured in the department of neurosurgery, Xi’an Tangdu Hospital.
Conclusions
It is key that CFE with PSH can be rapid diagnosed and treatment bundles of septic shock should be initiated as soon as possible. Early neurological rehabilitation played an important role for good outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Cerebral fat embolism (CFE) usually occurs after trauma or during surgical procedures and it occurs in 0.5–3.5% of cases [1, 2]. A limited case CFE with paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity (PSH) has been reported [3]. We presented a complicated young case of CFE complicated with PSH and septic shock at high altitude.
Case presentation
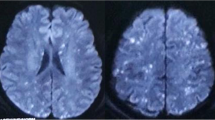
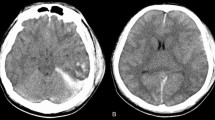
A 23-year-old man had a right closed femoral midshaft femur, tibia, and fibula fracture (Fig. 1) from a motor vehicle accident on a height of 3800 m above sea level. He was rescued 1 h later and conscious (GCS 15). Four hours later, he was transferred to local hospital and place a proximal tibial traction pin. Eleven hours after the accident, the patient was agitated and lost consciousness with convulsions. GCS was reduced to 6. The head CT scan showed normal (Fig. 2A). Three days later, he had a fever over 39 °C and the convulsions were more frequently than before. The convulsion was controlled by propofol and sodium valproate, but consciousness was not improved (GCS 6) after suspending sedatives. Then, we did the neuroimaging examination for consciousness disorder. The head CT scan indicated brain swelling (Fig. 2B). MRI showed innumerable foci of hyperintense lesions in a “starfield” pattern on T2, FLAIR and DWI sequence images, located at the periventricular, subcortical, basal ganglia, cerebellum, and deep white matter predominantly (Fig. 3). The diagnosis maybe difficult to differentiate diffused axion injury (DAI) and CFE if only based on neuroimaging evidence. Finally, CFE was diagnosed based on clinical features and neuroimaging. The reason was illuminated in the discussion section.
His core temperature was over 39 °C after 3 days post trauma. The chest CT scan indicated pneumonia (Fig. 4A) and antibiotics was administrated. More seriously, hypotension was presented (85/50 mmHg) and respirate rate was 30/min, indicating that the patient got to be septic shock caused by pneumonia. The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score was 12. As to be more critical than before, he was transferred to Tang Du Hospital by air.
When arrived, he was comatose and convulsive with ictus from 8 to 10 times daily. The manifestation was the intermittent hypertension (blood pressure up to 175/90 mmHg), tachycardia (pulse up to 155/min), febrile (up to 39 °C), tachypnea (respire rate up to 45/min), and diaphoresis. Flexor posturing was existed at the same time. The duration of episodes was within 5 min. Moreover, continuous electroencephalogram (cEEG) suggested a moderate inhibition of cortex function without epileptiform discharges. PSH was diagnosed based on clinical features, imaging, and cEEG. The treatment included propranolol and midazolam. To better control the episodes, fentanyl, dexmedetomidine, and bromocriptine were administered. The episode of PSH was gradually improved, no more than 2 times per day.
His pneumonia was severe and septic shock was present. Chest CT showed multiple lung effusion with pleural effusion 8 days post trauma (Fig. 4B), so thoracic close drainage and mechanical ventilation was performed. The maximum temperature was up to 40 °C, and blood pressure was reduced to 80/55 mmHg. Abnormal laboratory findings included PCT at 8 ng/ml, peripheral leukocyte count of 36 × 109/L (Fig. 5A, B). The patient got received anti-sepsis bundles in NICU. Firstly, fluid resuscitation was done (30 ml/kg) within 3 h and mean blood pressure was increased to 65 mmHg by norepinephrine (10 μg kg−1 min−1). Secondly, sputum culture was done before imipenem was used initially (1 g intravenous (IV), Q8h). Five days later, antibiotics were adjusted to vancomycin (1 g IV, Q12h) because result of sputum culture was MRSA. Thirdly, airway management was performed strictly, including turning over and slapping his back for sputum draining, subglottic aspiration, and to maintain balloon pressure of endotracheal tube up to 25 cm H2O to prevent aspiration of oral secretion. The pneumonia and septic shock were improved remarkably 14 days post anti-sepsis bundles (Fig. 4C).
After the pneumonia was cured and withdraw mechanical ventilation successfully, the fracture of right femoral shaft, tibia, and fibula were surgically fixed by orthopedic surgeon. Then hyperbaric oxygen therapy was supplement to the therapeutic regimen and the patient got conscious gradually.
The patient was awake 90 days post trauma. After 2 months of rehabilitation treatment, motor and language skills are fully restored. Then, he was discharged home to continue ambulatory rehabilitation. At the 1 year of follow-up, his modified Rankin Scale (mRS) was 2.
Discussion
A typical clinical feature of fat embolism syndrome (FES) was a triad of pulmonary, central nervous system (cerebral fat embolism), and cutaneous manifestations several hours post major trauma [1, 4]. Fat emboli can pass through the pulmonary vasculature, resulting in systemic embolization, most commonly in the brain (CFE) [5].
We presented the complicated CFE case with PSH syndrome and septic shock post trauma. He was cured in NICU by intensive care and rehabilitation treatment and got a good outcome (mRS 2) finally.
CFE is highly variable and nonspecific including headache, lethargy, irritability, delirium, stupor, convulsions, or coma [6]. In this case, we spend some time to differentiate CFE with diffuse axion injury (DAI) or seizures post trauma. We conclude the diagnosis of CFE based on the clinical feature and neuroimaging characteristics of CFE. The clinical feature was conscious on admission (GCS 15) and then fall into coma (GCS 6), suggesting the coma was secondary. If he got DAI, coma was immediate and primary. Secondly, he was complicated right closed femoral midshaft femur, tibia, and fibula fracture, which was had risk factor of CFE occurring. Thirdly, characteristics of CFE and DAI were different in terms of MRI. Rutman et al. studied the differences of neuroimaging between CFE and DAI based on MRI analysis according to number, size/shape, and the distribution of microhemorrhages. It is found that CFE had significantly more hemorrhages than DAI, particularly in the frontal, parietal, and occipital lobes; the corpus callosum; and the cerebellum. CFE microhemorrhages were punctate/round, whereas DAI hemorrhages were medium sized and linear. DAI is more likely to demonstrate hemorrhages larger than punctate, which is found in CFE. Diffuse confluent diffusion restriction favors CFE, whereas a few scattered foci favor DAI [7]. Thus, our diagnosis of CFE was mainly based on his clinical feature and the MRI feather. There are no definitive or specific treatments of FES; therefore, management is entirely supportive. Firstly, because FES may quickly progress to respiratory failure, early detection is important so that supportive treatment can be started promptly. In high-risk patients, respiratory status should be monitored closely via continuous pulse oximetry and ABG analysis. Initial or mild FES is treated with supplemental oxygen, titrated to maintain normal PaO2. FES that progresses to respiratory failure requires mechanical ventilation [8, 9]. Secondly, in patients exhibiting neurologic complications, neurologic status should be closely monitored via frequent Glasgow Coma Scale assessments and serial neurologic examinations. Intracranial pressure monitoring may be considered in patients with cerebral edema. Analgesia and sedation should be used judiciously and in conjunction with a sedation/agitation scale to optimize both patient comfort and neurologic exam. Neuromuscular blocking agents should be avoided if possible [10]. Thirdly, intravascular volume should be maintained to limit shock states, because shock may exacerbate lung injury. Albumin has been recommended for volume resuscitation because it binds to fatty acids and, therefore, may decrease the extent of lung. In patients who develop obstructive shock and right ventricular failure, dobutamine, rather than norepinephrine, may be a more effective agent for hemodynamic support due to its increased inotropic properties.
PSH syndrome is similar to seizure post head trauma, sepsis, pulmonary embolism, malignant hyperthermia, overdose of sympathomimetic or anticholinergic agents, or autonomic dysreflexia as seen with acute spinal cord injury. Patient’s medical history, signs, laboratory results (creatine kinase, serial serum lactate, and repeated blood cultures) and cEEG monitoring can facilitate the diagnosis of PSH. Treatment of CFE with PSH is based on supportive and symptomatic therapy. Opioids, β-blockers, α1-agonists, and bromocriptine are some of the options available to manage PSH [3].
Conclusion
This is a complicated case of CFE with PSH and septic shock post trauma at high altitude. It is key that rapid diagnoses and appropriate drug treatment were available as soon as possible. Early neurological rehabilitation played an important role for good outcome.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- CFE:
-
Cerebral fat embolism
- PSH:
-
Paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity
- FES:
-
Fat embolism syndrome
- GCS:
-
Glasgow coma score
- SOFA:
-
Sequential organ failure assessment
- cEEG:
-
Continuous electroencephalogram
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- DAI:
-
Diffuse axion injury
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- mRS:
-
Modified Rankin Scale
- NICU:
-
Neurosurgical intensive care unit
References
Johnson MJ, Lucas GL. Fat embolism syndrome. Orthopedics. 1996;19(1):41–8 discussion 48-49.
Gurd AR. Fat embolism: an aid to diagnosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970;52(4):732–7.
Mittal MK, Burrus TM, Campeau NG, et al. Pearls & oysters: good recovery following cerebral fat embolization with paroxysmal hyperactivity syndrome. Neurology. 2013;81(14):e107–9.
Sevitt S. The significance and pathology of fat embolism. Ann Clin Res. 1977;9(3):173–80.
Richards RR. Fat embolism syndrome. Can J Surg. 1997;40(5):334–9.
Parizel PM, Demey HE, Veeckmans G, et al. Early diagnosis of cerebral fat embolism syndrome by diffusion-weighted MRI (starfield pattern). Stroke. 2001;32(12):2942–4.
Rutman AM, Rapp EJ, Hippe DS, et al. T2*-Weighted and Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Differentiation of Cerebral Fat Embolism From Diffuse Axonal Injury. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2017;41(6):877–83.
Banerjee A, Aggarwal R, Dev Soni K, Tirkha A. Prone positioning in a patient with fat embolism syndrome presenting as diffuse alveolar haemorrhage: new perspective. BMJ Case Rep. 2020;13(3):e233452.
Shaikh N. Emergency management of fat embolism syndrome. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2009;2:29–33.
Habashi NM, Andrews PL, Scalea TM. Therapeutic aspects of fat embolism syndrome. Injury. 2006;37(Suppl 4):S68–73.
Acknowledgements
We thank the medical staff of the Department of Neurosurgery, Xi’an Tangdu Hospital, for their help in the treatment of the case.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ML, GZ, and HG contributed to write the report. ML contributed in clinical treatment of the case. SNG contributed in drafting the manuscript. GDG and YQ contributed in revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
A consent form has been signed by the patient. The original of the signed form is held by the institution and can be made available to the editors upon request.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Zhu, G., Guo, H. et al. Cerebral fat embolization with paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity syndrome and septic shock at high altitude: a case report and literature review. Chin Neurosurg Jl 7, 18 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-021-00232-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-021-00232-6