Abstract
Background
The three known subtypes of the retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor (ROR) have been implicated in the control of immunity, brain function, and circadian rhythm in mammals. Here, we demonstrate by phylogenetic analysis that there were originally four subtypes of RORs in vertebrates. One of the novel ror paralogs, rord1 (rorca in the Ensembl database), is conserved among teleosts, but absent in mammals. Using medaka (Oryzias latipes) as a model teleost, we evaluated the expression pattern of this gene, its transactivational properties for endogenic chemicals, and its ability to activate the promoters of putative target genes.
Results
In eyes, the transcript of rord1 was expressed at higher levels during the day than at night. Interestingly, cholesterol derivatives, which are well-known ligands for mammalian RORs, did not efficiently promote transcriptional activity via RORd1. Thus we sought to identify the ligands that regulate the transcriptional activity of RORd1 using a luciferase reporter cell-based screening system. Using this system, we identified two metabolites of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), 4OH-ATRA and 4-keto ATRA, as potential ligands of RORd1. Moreover, RORd1 activated the promoter of cyp26a1 in a 4OH-ATRA -dependent manner.
Conclusions
A novel ror subtype, rord has two paralogs, rord1 and rord2, in teleost. Rord1 mRNA is highly abundant in the eyes of medaka during light periods, suggesting that rord1 expression is involved in the regulation of circadian rhythm. We identified two ATRA metabolites, 4OH-ATRA and 4 K–ATRA, as endogenous candidate ligands of RORd1. We also show that 4-oxygenated ATRA metabolites have the potential to activate cyp26a1, the metabolic enzyme of ATRA. Our results support the notion that RORd1 is involved in the metabolism of ATRA in medaka.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The retinoic acid receptor (RAR)-related orphan receptors alpha, beta and gamma (RORα-γ, NR1F1–3 or RORa-c) constitute a subfamily of nuclear receptors that appear to function as ligand-dependent transcription factors [1]. Thus, although RORs may function as constitutively active receptors, several endogenous substances have been identified as agonists; for example, melatonin [2], cholesterol [3] and cholesterol sulfate [4] can activate RORa, whereas 20α-hydroxycholesterol (20α-OHC), 22(R)-hydroxycholesterol, 25-hydroxycholesterol [5] and 7β, 27-dihydroxycholesterol [6] have the ability to activate RORc. All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) was not reported as an agonist, but rather as an inverse agonist of RORb [7], despite the view that this receptor is a ‘retinoic acid’ receptor-related receptor.
The RORs have been implicated in the regulation of immunity, brain function, retinal development, glucose and lipid metabolism, and circadian rhythm [8]. They exert these effects by modulating gene transcription after binding as monomers to ROR response elements (ROREs) consisting of the consensus sequence WAWNTRGGTCA in the regulatory regions of target genes [9, 10]. As opposed to the breadth of detail obtained from mammals, very little is known about RORs in basal vertebrates. Interestingly, five subtypes of ROR—RORa, RORb, RORc, RORca, and RORcb—are found in the genome database of medaka, Oryzias latipes.
Many gene families in vertebrates were generated during two rounds of whole-genome duplication that occurred early in the evolution of Chordata [11,12,13]. An additional whole genome duplication event occurred in the fish lineage [14]. For example, four ROR paralogs are expected in humans, such as types a, b, c and d. In the case of teleost fish, there may be as many as eight paralogs, types a1, a2, b1, b2, c1, c2, d1, and d2. However, medaka clearly does not fit this scenario, highlighting the need for a review of ROR classification.
In the present study, we sought to categorize the ROR paralogs in vertebrates, and identified the novel ROR paralogs, RORd1 and RORd2. Subsequently, we investigated the time- and tissue-dependent expression profiles of these genes, and identified potential ligands for RORd1 as a representative subtype of the RORds. We also demonstrate RORd1-dependent regulation of the bmal1a and cyp26a1 genes.
Methods
Phylogenetic analysis
ROR protein sequences were retrieved from the Ensembl database. Amino acid sequence IDs were as follows: human (Homo sapiens) RORa: BAH02285.1, RORb: BAH02286.1, RORg: BAH02287.1; mouse (Mus musculus) RORa2: NP_001276845.1, RORb2: ABG77270.1, RORg: AAC53501.1, chicken (Gallus gallus) RORa: NP_001276816.1, RORb: NP_990424.1, RORg: XP_015135499.1, RORblike: XP_003642912.2; sea turtle (Chelonia mydas) RORb: XP_007065615.1, RORblike: XP_007068624.1; soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) RORa: XP_014435946.1, RORbX1: XP_006137881.1, RORg: XP_014427156.1, RORblike: XP_006129037.1; frog (Xenopus tropicalis) RORaX1: XP_012822203.1, RORb: XP_002940077.1, RORblike: XP_002938868.1; medaka (Oryzias latipes) RORaX1: XP_004069686.1, RORb: ENSORLT00000015579.1, RORgX1: XP_011483568.1, RORblike: XP_004067713.1, RORcb: ENSORLT00000018666.1, RARb: ENSORLT00000010680.1; Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) RORaX2: XP_005470779.1, RORbX1: XP_005473204.1, RORgX1: XP_013130314.1, RORblike: XP_005478800.1, RORblikeX2: XP_005476199.1; zebrafish (Danio rerio) RORa2: BAF76726.1, RORb: ABO15413.1, RORc: ENSDART00000149097.2, RORca: NP_001076288.1, RORcb: NP_001264023.1; grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) RORg1: AFC34773.1, RORg2: AFC34774.1; fugu (Takifugu rubripes) RORaX2: XP_011605662.1, RORca: ENSTRUT00000007520.1, RORcb: ENSTRUT00000013484.1; spotted gar (Lepisosteus oculatus) RORaX2: XP_015199181.1, RORbX1: XP_006627046.2, RORblikeX1: XP_015221273.1. Amino acid sequences of RORs were aligned using ClustalW displayed in MEGA 7.0.14 (Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis, ver. 7.0.14), and manually adjusted. Phylogenetic trees were constructed with MEGA 7.0.14 software using the neighbor-joining method [15] with branch support values estimated using bootstrap with 1000 replications.
Experimental animals
All of the animal experiments described below were conduct in compliance with institutional guidelines and approved by the Animal Experiment Committee of Nagahama Institute of Bio-Science and Technology. Mature fish of the orange-red variety of medaka were acclimated to conditions of 24 °C on a 14-h light, 10-h dark cycle for at least 2 weeks prior to sampling. All fish were anaesthetized in aqueous solution of 0.01% ethyl p-aminobenzoate buffered with 0.01% sodium hydrogen carbonate before euthanasia. For expression analysis, brains and peripheral tissues from three fish from both sexes (body length = 22–31 mm) were collected every fourth hour [Zeitgeber time (ZT); 3, 7, 11, 15, 19, 23 h after “light on”]. Samples were immersed in Sepasol RNA I Super G (Nacalai Tesque) and kept at −80 °C until use.
Quantitative Real-time (RT)-PCR
Total RNA from each tissue was extracted using Sepasol RNA I Super G (Nacalai Tesque) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Total RNA was reverse-transcribed and genomic DNA was removed using ReverTra Ace qPCR RT Master Mix with gDNA Remover (TOYOBO). Quantitative Real-time (RT)-PCR was conducted with SsoAdvanced Universal SYBR Green Supermix (BIO-RAD) using the MiniOpticon real-time PCR system (BIO-RAD). The primer set for rord1 (XM_004067665.2) was 5′-TGACGTCCAGAAGGTTCAAAAGT-3′ (forward) and 5′-TCTCCTCAGACGCTCCTTTATTCT-3′ (reverse). The primer set for bmal1a (scaffold212: 822,689–822,960) was 5′-CTCCTTCTACGAGTACTTCCATCAG-3′ (forward) and 5′-ATGGTGTTGGTAGAGACGATGTACT-3′ (reverse). The primer set for cyp26a1 (ENSORLG00000014516) was 5′- CCCAGCACAGGACGAAGAA-3′ (forward) and 5′- CTGGATGACGGGGATGTAGAG-3′ (reverse). These primers were designed using Primer3 ver. 0.4.0 (1, 2). The conditions for PCR were as follows: initial denaturation at 98 °C for 2 min, 40 amplification cycles including denaturation at 98 °C for 2 s, annealing at 60 °C for 5 s. Measured values were normalized over the amount of total RNA and presented as copy/μg-total RNA.
Development of medaka ror1d expression construct, transfection into HEK293 and ligand screening by luciferase assay
A chimera expression construct for Gal4-RORd1, which contains the cDNA of the hinge domain and the ligand-binding domain (from Glu-Lys-His to C terminus; amino acids 98–473) of medaka RORd1 (the same amino acid sequence used in phylogenetic analysis) fused to the DNA binding domain (amino acids 1–161) of the yeast Gal4 transcription factor in the pBIND vector (CheckMate mammalian two-hybrid system, Promega) was made by the following process. The amplicon of the pBIND vector, amplified with T7 and T3 primers, was cloned into a pGEM-T Easy vector (Promega), and the vector was treated with NotI. The fragment was subcloned into the NotI site of a pcDNA3.1(+) plasmid vector. The resulting plasmid construct was named pcDNA3.1(+)-GAL4DBD vector. The PCR fragment of the RORd1 ligand-binding domain, amplified with the primer set: 5′-GTTGATATCATCTAGCCAGAAACACCGGCA-3′ (forward) and 5′-AATAGGGCCCTCTAGTTAGCCCTCTGTGGA-3′ (reverse), was cloned into a pcDNA3.1(+)-GAL4DBD vector treated with XbaI.
A Gal4-regulated reporter vector which contains the luciferase gene under the control of five GAL4 binding sites upstream of a minimal TATA box, named pG5luc, was from the CheckMate mammalian two-hybrid system (Promega). Human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells were seeded in 9 cm dishes before transfection. Both plasmids, i.e., the expression vector for Gal4- RORd1 (1500 ng) and pG5luc (1500 ng), were transfected with X-tremeGENE 9 DNA Transfection Reagent (Roche), following the manufacturer’s instructions. Stably transfected cells were selected with G418 (Nacalai Tesque). Cells derived from the chosen clone were seeded in 96-well luminometer plates with phenol red-free Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium supplemented with 5% dextran-charcoal-treated fetal bovine serum and the test compound (Additional file 1: Table S1); as a preliminary test, each reagent was applied at 10, 1, or 0.1 μM. If significant transactivity was detected in this pre-test, treatment of cells was pursued at four-fold serial dilution from 1 × 10−5 M to 6.1 × 10−10 M or 3.8 × 10−11 M. Cultures were again run; negative control wells were dosed with media containing 0.1% ethanol. After 24 h, the luciferase activities of the cells were measured by a luminescence assay using Steady-Glo Assay System Kit (Promega) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Concentration-response curves were fitted and the EC50 or IC50 values were calculated using the sigmoidal fit in GraphPad Prism5 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). The efficacy of each reagent is expressed as a percentage of the reporter induction of EtOH treatment.
Luciferase reporter assay for medaka bmal1a or cyp26a1
The entire protein-encoding region (corresponding to amino acids 1–473) and stop codon of the medaka rord1 (the same amino acid sequence used in phylogenetic analysis) was amplified by PCR and cloned into pcDNA3.1(+) (Invitrogen) at the XbaI site by using In-Fusion HD cloning kit (Takara). We named the resulting DNA construct pcDNA-RORd1. A 271-bp fragment of the medaka bmal1a promoter region (scaffold212: 822,689–822,960) containing one RORE (AAAGTGGGTCA, consensus sequence: WAWNTRGGTCA) and one RORE-like sequence (TCCACGGGTCA) was isolated by PCR and cloned into the luciferase reporter pGL4.20 vector (Promega) at the EcoRV site by using In-Fusion HD cloning kit (Takara). We designated the resulting DNA construct bmal1ap-luc. A 1213-bp fragment of the medaka cyp26a1 promoter region (chromosome19: 21,523,225–21,524,438) containing two RORE-like sequences (GAGGAAGGTCA and TGGCGCGGTCA) was isolated by PCR and cloned into the luciferase reporter pGL4.20 vector (Promega) at the EcoRV site using the In-Fusion HD cloning kit (Takara). We named the resulting DNA construct cyp26a1p-luc. HEK293 cells in 24-well plates were transfected with 500 ng luciferase reporter plasmid (bmal1ap-luc or cyp26a1p-luc) and 50 ng expression vector (pcDNA-RORd1 or pcDNA). Cells were dosed with vehicle (EtOH) or 10−5 M 4-hydroxy-ATRA (4OH-ATRA). Cell culture conditions and measurements of luciferase activity were as described above for the pG5luc assays.
Results
Phylogenetic analysis
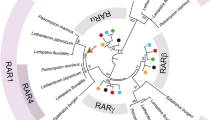
Using phylogenetic analysis, four groups of rors formed monophyletic clades, supported by bootstrap values >98% (Fig. 1). These clades correspond with nr1f1 (rora), nr1f2 (rorb), nr1f3 (rorc) and a new subtype, named nr1f4 (rord). It is conceivable that they are ohnologs. Most non-mammalian species used for our analysis have four ror ohnologs. In contrast, mammalian species were not represented in the branch for nr1f4/rord, although it is represented among the other three groups, nr1f1–3. Other tetrapods (birds, reptiles and amphibians) had one ortholog belonging to the nr1f4/rord subtype, while nr1f4/rord was clearly subdivided into two distinctive clades, rord1 and rord2, in teleost fishes (zebrafish, grass carp, medaka, Nile tilapia, and fugu).
Phylogenetic tree based on the protein sequences of the RORs in vertebrates. Amino acid sequences were aligned and a phylogenetic tree was constructed with the MEGA 7.0.14 software, using the neighbor-joining method. Branch support values estimated using bootstrap tests with 1000 replications are shown next to the branches. A new branch against conventional RORs was described as NR1F4 (RORd)
Spatial distribution for rord1 mRNA
Significantly higher expression of rord1 was observed in the eye than in other tissues at ZT7 (Fig. 2a). Employing time-course analysis, rord1 expression in the eye showed clear diurnal oscillations, increasing during the day to reach a peak at ZT7, before decreasing towards night (Fig. 2b). Since no differences in expression of rord1 were detected between sexes by t-test (P values >0.01) (Additional file 2: Figure S1), male and female data were pooled for this analysis.
Tissue-specific distribution and time course of expression of medaka rord1 assessed by quantitative Real-time (RT)-PCR. a expression of rord1 mRNA in various tissues from adult medaka raised under 14 L:10D and sampled at Zeitgeber time ZT7 (7 h after “lights on”). B: brain; E: eye; G: gill; H: heart; K: kidney; L: liver; S: spleen; I: intestine; T: testis; O: ovary. b temporal changes in expression of rord1 in eyes. The sample collection time is indicated as ZT. White and black bars above each graph represent light and dark periods. Y-axes represent rord1 expression as copies/μg-total RNA. Data are expressed as means ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M.) (n = 6). Different letters on the columns indicate group means that are statistically different when analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test (P < 0.001)
Efficacy of typical mammalian ROR ligands for medaka RORd1
In medaka, 20α-OHC was the most potent agonist of RORd1 among the natural cholesterol-related reagents containing well-known ligands for mammalian RORs we tested (Fig. 3a, Table 1). However, the concentration-response curve of 20α-OHC was not sigmoidal and its EC50 value could thus not be calculated (Fig. 3b). Other cholesterols yielding significantly increased reporter activity compared to control incubations were 7α-hydroxycholesterol (7α-OHC), 7β-hydroxycholesterol (7β-OHC), 7- ketocholesterol (7 K–C) and 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-OHC); no significant effect was detected in response to treatment with cholesterol or 22R–hydroxycholesterol. The RORdl-dependent transcription was increased slightly in cells treated with 7α-OHC, 7β-OHC, 7 K–C or 25-OHC compared with that in cells treated with EtOH, amounting to 125%, 122%, 127% and 155%, respectively.
Effects of cholesterols on medaka RORd1. a Effects of cholesterols on medaka RORd1 transcriptional activity, assessed by luciferase reporter assay; stably transfected cells were treated with vehicle (control) or 10 μM of cholesterol derivatives. The white column is vehicle (ethanol), and the hatched and black columns represent ROR inverse agonists and agonists in mammals, respectively. Longitudinal axis shows relative luminescence units (RLU). Statistical differences between vehicle and ligands are indicated by asterisks (**: P < 0.01; ***: P < 0.001). 7α-hydroxycholesterol (7αOHC); 7β-hydroxycholesterol (7βOHC); 7-ketocholesterol (7ketoC); 22(R)-hydroxycholesterol (22RHC); 20α-hydroxycholesterol (20αHC); 25-hydroxycholesterol (25HC). b Concentration-response curve of 20αHC. Broken line shows the luminescence of ethanol-treated cells. Each point represents the mean of triplicate determinations, and vertical bars represent the S.E.M (a, b)
Screening for endogenous ligands of medaka RORd1
To identify potential ligands regulating medaka the transcriptional activity of RORd1, we used a stable cell line expressing a Gal4-RORd1 fusion protein for a reporter gene assay. Fifteen compounds yielded agonistic effects on the medaka RORd1 (Table 2). 4OH-ATRA and 4-keto ATRA (4 K–ATRA), both belonging to the retinoids, showed the highest potency, with EC50 values in the order of 100 nM (Fig. 4). The reporter activity of 4OH-ATRA was 3.1-fold higher than that of EtOH, whereas luminescence after addition of 4 K–ATRA was 3.3 times that seen in response to adding EtOH. However, 5,6-epoxy-ATRA (5,6E–ATRA) had lower potency (EC50 > 10 μM); administration of 10−5 M 5,6E–ATRA showed a 2.8-fold higher reporter-induced luminescence than that observed in controls. Low potency (EC50 > 10 μM) was also detected in response to supplementation with other reagents, i.e., three steroids (estradiol, 17-hydroxyprogesterone, and androstenedione), one amino acid derivative (melatonin), and eight retinoids [retinol, retinal, all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), 11-cis retinol, 11-cis retinal, 11-cis retinoic acid, 9-cis retinoic acid, 13-cis retinoic acid]. ATRA, 11-cis retinoic acid, 9-cis retinoic acid, and 11-cis retinal enhanced luciferase activity in a dose-dependent manner; the fold-induction of these ligands compared to that of EtOH was 2.90, 2.84, 2.39 and 2.37, respectively. By comparison, retinal, 13-cis retinoic acid induced approximately twice the luminescence to that of controls. The agonistic activity of estradiol, 17-hydroxyprogesterone and 11-cis retinol were higher than that of EtOH (1.73-, 1.62- and 1.67-fold, respectively), whereas androstenedione, melatonin and retinol yielded fold-values of 1.26, 1.37 and 1.29, respectively, lower than the fold-induction observed in response to the mammalian ligand for ROR, 20α-OHC.
Concentration-response curve of all-trans retinoic acid metabolites. Y-axis shows relative luminescent units (RLU). The dashed line represents the average value of controls, the gray solid line signifies the average value of 10−5 M 20α-hydroxycholesterol (20α-OHC) and the black solid line that of 10−5 M all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA). Each point represents the mean of triplicate determinations, and vertical bars represent the S.E.M. 4OH-ATRA: 4-hydroxy ATRA; 4 K–ATRA: 4-keto ATRA; 5,6E–ATRA: 5,6-epoxy ATRA
Not all tested ligands displayed agonistic activity. The amino acid derivative 3,3′,5-triiodo-L-thyronine (T3), a thyroid hormone, presented with an inverse agonistic effect on RORd1 in this study (Table 2). The luciferase activity was decreased by 15.4% compared to that in EtOH-supplemented incubations, and the EC50 of T3 was higher than 10 μM. Other compounds tested had no effect on medaka RORd1.
Luciferase reporter assay for medaka bmal1a or cyp26a1 and these expression rhythms
We tested a full-length RORd1 in transient transactivation assay to rule out possibility that differences in ROR activity were due to interaction between Gal4 DBD and ROR LBD. Using the bmal1ap-luc reporter, 4OH-ATRA significantly induced luciferase activity relative to EtOH, irrespective of the presence or absence of RORd1 (Fig. 5a). However, with RORd1, luciferase activity was significantly increased compared to without RORd1 for both doses. In contrast, when using the cyp26a1p-luc reporter, a significant increase in luminescence was detected in cells expressed RORd1 and exposed to 4OH-ATRA relative to in other cells, which are exposed to EtOH, not expressed RORd1 and both (Fig. 5b). Time-course analysis indicated that bmal1a and cyp26a1 mRNA expression were similar to that of rord1 in that a peak showed at ZT7 in the eyes (Fig. 5c, d). Since no differences in expression of rord1 were detected between sexes by t-test (P values >0.01) (Additional file 2: Figure S1), male and female data were pooled for this analysis.
Reporter gene assay using consensus RRE in bmal1a or cyp26a1 promoter of medaka and these expression rhythms. HEK293 cells transfected with (a) bmal1ap-luc or (b) cyp26a1p-luc and pcDNA-RORd1 or pcDNA were dosed with EtOH (open) or 10−5 M 4OH-ATRA (closed). Longitudinal axis shows relative luminescent units (RLU). The temporal change in expression of (c) bmal1a and (d) cyp26a1 in eyes. The sample collection time is indicated as ZT. White and black bars above each graph represent light and dark periods. Y-axes represent gene expression as copies/μg-total RNA. Data are expressed as means ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M.) (n = 6). Different letters on the columns indicate group means that are statistically different when analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test (P < 0.001)
Discussion
The relationships between the different paralogs of RORs in vertebrates have remained unclear, in part due to the abundance of products for this gene family in teleost fish. We therefore set out to first clarify the ROR family relationships. In our phylogenetic analysis, rors were classified into four main groups, a new fourth group being created against the conventional ror subtypes, nr1f1–3. This additional subtype consists of rorca, rorcb, and rorb-like homologs. We propose to name this group rord or nr1f4.
On the basis of the phylogenetic tree, we propose that a proto-ortholog of ror in the cephalochordate ancestral genome gave rise to two paralogs, the common ancestor for both rora and rorc and its counterpart (rorb + rord), after an initial round of duplication. A total of four orthologs were generated thereafter following a second genome duplication event. Interestingly, orthologs belonging to nr1f4/rord were not found in mammalian taxa in any databases. Nr1f4/rord thus appears to have been lost in the mammalian lineage during evolution, as these orthologs were present in other tetrapods and in fish. In the latter group, the fourth ror subtype gave rise to two daughters, rord1 and rord2, after yet another round of genome duplication; this third duplication is a teleost-specific whole genome-duplication (TWGD) and is believed to have occurred around 320 million years ago [16]. Indeed, the presence of only a single nr1f4/rord1 ortholog in taxa including chicken, turtle, and the holostean (non-teleost) spotted gar reinforces the notion that rord1 and rord2 paralogs appeared as a consequence of TWGD. Although nr1f1, nr1f2 and nr1f3 could be expected to also have two paralogs after TWGD, just like nr1f4, there was no evidence to support this; two functional NR1F4s are seemingly needed in teleosts, while this subtype appears to be dispensable in mammals.
Among the tissues we examined, the eye showed the highest expression of rord1 mRNA in adult medaka at ZT7. Expression of ror subtypes in various organs, including the eye, has been documented in different species; for example, Rora mRNA was detected in moderate quantities in muscle and skin in mouse, but its principal expression site is the brain, particularly the thalamus and Purkinje cell layer of the cerebellum [17]. The Rorb gene is highly expressed in the pineal gland, the thalamus and the hypothalamus in the rat. In situ hybridization analysis revealed that the suprachiasmatic nucleus and the inner nuclear layer of the retina in particular are high-expression Rorb sites [18]. Similarly, Rorc expression has been reported in muscle and the thymus in mammals. In mouse, Rorγt, which is an alternative splicing form of Rorc in the thymus, was shown to be an essential factor for differentiation of naïve CD4+T (Th0) cells into Th17 cells, indicating an immunologically relevant function [19].
Unlike their mammalian counterparts, in non-mammalian species only a few studies on localization and function of rors/RORs have been reported. Using whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis, rora, rorb and rorc expression were detected in diencephalon, eyes, pineal gland, pharynx, heart, liver, gut, and somites of the zebrafish embryo [20]. The rora and rorc were strongly expressed in pituitary, brain and immune-related tissues in grass carp, suggesting that these subtypes are associated with the endocrine and immune systems [21]. In rainbow trout, rorc was reportedly highly expressed in muscle, other sites of expression being brain, heart, and skin [22]. In keeping with these findings on rors in fish, medaka rord1 was also detected in the brain. It is unclear whether rord1 is expressed universally in the eye, as there are no studies of tissue localization of this subtype in other species. In any case, its conspicuous expression in the eyes suggests that RORd1 may relate to visual functions; indeed, there are two earlier reports that implicate RORa and RORb in the regulation of the expression of opsins, suggestive of a photoreceptor function, in cone cells [23, 24]. Furthermore, RORd1 could be involved in yet-unknown physiological responses characteristic to teleost fish.
Rord1 mRNA abundance peaked during the middle of the light phase in eyes of medaka in the present study. It is thus tempting to speculate that RORd1 may be involved in synchronizing the circadian clock, or that it plays a role in regulation of rhythmicity. An example of the latter, via RORE, RORs are likely to control the expression level of bmal1 whose products constitute a core loop of the circadian rhythm [25, 26]. In a promoter assay performed using bmal1a-luc in this study, although 4OH-ATRA stimulated the expression of luciferase without RORd1, significantly higher expression of luciferase was detected in the presence of RORd1 than in the absence of RORd1. This suggest two possibilities: (1) the endogenous 4OH-ATRA receptor binding to bmal1a promoter domain is expressed in HEK293; and (2) the sequence that acts as a RORE resides in the bmal1a promoter domain of transfected bmal1a-luc. Thus, RORd1 can enhance bmal1a promoter activity. Given the periodic expression of RORd1, this receptor could therefore be involved in the regulation of circadian clocks, at least in the eyes. The finding that the mRNA expression pattern of medaka bmal1a is similar to that of rord1 in eyes supports this notion.
In the present study, we used a heterogeneous system consisting of a mammalian host cell and a Gal4-fusion receptor, which we believe properly represents the transactivational ability of medaka RORd1. It has been suggested that mammalian RORs can function as constitutively active receptors [27], and indeed, constitutive luminescence was observed in the absence of any ligand in the present study. However, forcing the cell line to express the medaka RORd1 resulted in threefold increases in luciferase activity in the presence of a suitable ligand – therefore, RORd1 is likely to act as a bona fide nuclear receptor.
Natural cholesterol-related compounds, which are known ligands for RORs in mammals [27], had varying effects on activity of the medaka RORd1. Among the cholesterol derivatives, 20α-OHC displayed the highest agonist activity for medaka RORd1 in this system. However, the potency of 20α-OHC for medaka RORd1 (EC50; > 1 μM) was substantially lower than that for human RORC (EC50; 20-40 nM) [5]. Interestingly, 7α-hydroxycholesterol, 7β-hydroxycholesterol and 7-ketocholesterol all showed agonistic activity for medaka RORd1. These findings contrast with their natural inverse agonistic effects on RORa and RORc in mammals, as assessed by decreased transactivation activity [28]. This prompts us to suggest a physiological function for RORd1 in medaka that is distinct from the ROR-mediated role in glucose metabolism in response to binding 7-oxygenated cholesterol in mammals; ROR subtypes other than RORd may perform this function in medaka.
Putative natural agonists for medaka RORd1 were identified in this study as retinoids, rather than cholesterols. A previous study documented that ATRA induced the expression of a Purkinje cell-specific gene ‘synergistically’ with RORa via RAR/RXR [29]. ATRA was further reported as an ‘antagonist’ for RORb [7], in contrast with our results which, for the first time, assign an agonistic effect to a retinoid for ROR. Among all-trans retinoids, the more oxidized it was, the higher its efficacy, reflected by ATRA > retinal > retinol. Meanwhile, the stereoisomers 9-cis retinoic acid and 13-cis retinoic acid affected RORd1 in comparable manner to ATRA, but induced higher reporter activity than did 20α-OHC.
We were particularly interested in the ligand activity of 11-cis-retinoid species, as these are generated only in the retina, which is relevant, as rord1 expression was highest in the eyes. However, 11-cis-isomers were no more effective in elevating reporter activity than ATRA. Admittedly, ATRA yielded high transactivation activity mediated by RORd1 but its effective concentration was not calculable (EC50 value >1 μM). Therefore, ATRA is too weak to act as a ligand for RORd1 in vivo. In contrast, 4OH-ATRA and 4 K–ATRA yielded EC50 values in the sub-μM range, while that of 5,6E–ATRA was not calculable. It is widely held that the predominant route of elimination of ATRA is through its oxidation in the 4-position of the β-ionone ring to generate 4OH-RA [30, 31]. Here, we show that ATRA metabolites may serve as bona fide ligands for RORd1, reflecting their high potency for this receptor.
Retinoic acid plays an important role as a morphogen during embryonic development [32]. However, catabolism of retinoic acid is also essential. The concentration of retinoic acid is regulated by Cyp26, a hydroxylase that degrades ATRA into 4OH-ATRA [33,34,35], highlighting the importance of this enzyme for proper development [36]. A recent study revealed the existence of a retinoic acid concentration gradient in the zebrafish embryo by 14 h after fertilization; retinoic acid levels were low in the head and tail, which was due to local expression of cyp26s (cyp26a1, cyp26b1 and cyp26c1) responsible for retinoic acid conversion into its metabolites [37]. In one previous study, rora, rorb and rorc message RNAs were detected in the head and other areas of the zebrafish embryo [19]; these ROR subtypes conceivably receive ATRA metabolites, as shown for medaka RORd1. It appears likely that RORs function as a key regulator in a positive feedback loop resulting in the rapid degradation of ATRA, as RORs serve as sensors for ATRA metabolites and upregulate the expression of these enzymes for catabolism. Further studies of the distribution of RORd1 in the medaka embryo are necessary to define the role of this receptor during development. Aside from its role in development, RORd1 may also be required for hematopoiesis or immunity, as our results indicate that this subtype is expressed at around 107 copies/μg-RNA in a suite of tissues in adult medaka. Our finding, obtained by qPCR, that cyp26a1 mRNA levels increase at nearly the same time with rord1 expression suggests that medaka RORd1 may primarily regulate the transactivation of cyp26a1 gene, and consequently induce ATRA metabolism, at least in the eye, at ZT7. The results of our luciferase reporter assay using cyp26a1p-luc support this possibility.
A promoter assay using cyp26a1p-luc demonstrated that one of the four ROR subtypes, RORd1, is activated by 4-oxygenated ATRA’s metabolites. It is unclear whether these metabolites also act as agonists for other ROR subtypes, prompting the need for further study to compare and define ligand selectivity and physiological function. In any case, a suit of endogenous compounds, including 17-hydroxyprogesterone, melatonin, estradiol, androstenedione, and T3, stimulated or inhibited the transcriptional activity in HEK293 cells expressing Gal4-RORd1 LBD. Despite modulation of transcriptional activity, however, we suggest that these compounds do not normally interact with RORd1 in vivo, given the significantly lower ED50 for RORd1 compared to that of ATRA metabolites.
Conclusions
We have characterized a new member of the ROR family, rord1, in medaka by analyzing molecular phylogeny, tissue-dependent expression patterns, pharmacological profile, and transactivational activity of the promoters of putative target genes. Phylogenetic tree analysis showed that rord1 is a novel ror subtype that differs from the previously reported subtypes: rora, rorb and rorc. Two paralogs, rord1 and rord2, are thought to have diverged after the TWGD. Rord1 mRNA was highly abundant in the eyes of medaka during the light period, suggesting that rord1 expression is regulated by circadian rhythm. Using a stable cell line expressing a Gal4DBD-RORd1 fusion protein, two ATRA metabolites, 4OH-ATRA and 4 K–ATRA, were found as endogenous candidate ligands for RORd1. Furthermore, we demonstrated that 4-oxygenated ATRA metabolites have the potential to activate the promoter of cyp26a1, the metabolic enzyme of ATRA, through RORd1. Our results support the notion that RORd1 is involved in the metabolism of ATRA in medaka.
References
Jetten AM. Retinoid-related orphan receptors (RORs): critical roles in development, immunity, circadian rhythm, and cellular metabolism. Nucl Recept Signal. 2009;7:e003.
Wiesenberg I, Missbach M, Kahlen JP, Schräder M, Carlberg C. Transcriptional activation of the nuclear receptor RZR alpha by the pineal gland hormone melatonin and identification of CGP 52608 as a synthetic ligand. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995;23:327–33.
Kallen JA, Schlaeppi JM, Bitsch F, Geisse S, Geiser M, Delhon I, et al. X-ray structure of the hRORα LBD at 1.63 A: structural and functional data that cholesterol or a cholesterol derivative is the natural ligand of RORα. Structure. 2002;10:1697–707.
Kallen J, Schlaeppi JM, Bitsch F, Delhon I, Fournier B. Crystal structure of the human RORα Ligand binding domain in complex with cholesterol sulfate at 2.2 A. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:14033–8.
Jin L, Martynowski D, Zheng S, Wada T, Xie W, Li Y. Structural basis for hydroxycholesterols as natural ligands of orphan nuclear receptor RORγ. Mol Endocrinol. 2010;24:923–9.
Soroosh P, Wu J, Xue X, Song J, Sutton SW, Sablad M, et al. Oxysterols are agonist ligands of RORγt and drive Th17 cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:12163–8.
Stehlin-Gaon C, Willmann D, Zeyer D, Sanglier S, Van Dorsselaer A, Renaud JP, et al. All-trans retinoic acid is a ligand for the orphan nuclear receptor ROR beta. Nat Struct Biol. 2003;10:820–5.
Cook DN, Kang HS, Jetten AM. Retinoic Acid-Related Orphan Receptors (RORs): Regulatory Functions in Immunity, Development, Circadian Rhythm, and Metabolism. Nucl Receptor Res. 2015;2:101185.
Giguère V, McBroom LD, Flock G. Determinants of target gene specificity for ROR α 1: monomeric DNA binding by an orphan nuclear receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15:2517–26.
Medvedev A, Yan ZH, Hirose T, Giguère V, Jetten AM. Cloning of a cDNA encoding the murine orphan receptor RZR/ROR γ and characterization of its response element. Gene. 1996;181:199–206.
Ohno S. Evolution by Gene Duplication. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1970.
Abi-Rached L, Gilles A, Shiina T, Pontarotti P, Inoko H. Evidence of enbloc duplication in vertebrate genomes. Nat Genet. 2002;31:100–5.
Dehal P, Boore JL. Two rounds of whole genome duplication in the ancestral vertebrate. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:e314.
Meyer A, Schartl M. Gene and genome duplications in verterbrates: the one-to-four (−to-eight in fish) rule and the evolution of novel gene functions. Curr Op Cell Biol. 1999;11:699–704.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33:1870–4.
Vandepoele K, De Vos W, Taylor JS, Meyer A, Van de Peer Y. Major events in the genome evolution of vertebrates: paranome age and size differ considerably between ray-finned fishes and land vertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:1638–43.
Matsui T, Sashihara S, Oh Y, Waxman SG. An orphan nuclear receptor, mROR alpha, and its spatial expression in adult mouse brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1995;33:217–26.
Becker-André M, Wiesenberg I, Schaeren-Wiemers N, André E, Missbach M, Saurat JH, et al. Pineal gland hormone melatonin binds and activates an orphan of the nuclear receptor superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:28531–4.
Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell. 2006;126:1121–33.
Flores MV, Hall C, Jury A, Crosier K, Crosier P. The zebrafish retinoid-related orphan receptor (ror) gene family. Gene Expr Patterns. 2007;7:535–43.
Du L, Yang X, Yang L, Wang X, Zhang A, Zhou H. Molecular evidence for the involvement of RORα and RORγ in immune response in teleost. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012;33:418–26.
Monte MM, Wang T, Costa MM, Harun NO, Secombes CJ. Cloning and expression analysis of two ROR-γ homologues (ROR-γa1 and ROR-γa2) in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012;33:365–74.
Fujieda H, Bremner R, Mears AJ, Sasaki H. Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor alpha regulates a subset of cone genes during mouse retinal development. J Neurochem. 2009;108:91–101.
Srinivas M, Ng L, Liu H, Jia L, Forrest D. Activation of the blue opsin gene in cone photoreceptor development by retinoid-related orphan receptor beta. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:1728–41.
Ueda HR, Chen W, Adachi A, Wakamatsu H, Hayashi S, Takasugi T, et al. A transcription factor response element for gene expression during circadian night. Nature. 2002;418:534–9.
Wang M, Zhong Z, Zhong Y, Zhang W, Wang H. The zebrafish period2 protein positively regulates the circadian clock through mediation of retinoic acid receptor (RAR)-related orphan receptor α (Rorα). J Biol Chem. 2015;290:4367–82.
Solt LA, Burris TP. Action of RORs and their ligands in (patho)physiology. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012;23:619–27.
Wang Y, Kumar N, Solt LA, Richardson TI, Helvering LM, Crumbley C, et al. Modulation of retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor alpha and gamma activity by 7-oxygenated sterol ligands. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:5013–25.
Matsui T. Transcriptional regulation of a Purkinje cell-specific gene through a functional interaction between ROR alpha and RAR. Genes Cells. 1997;2:263–72.
Ross AC, Zolfaghari R. Cytochrome P450s in the regulation of cellular retinoic acid metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 2011;31:65–87.
Stevison F, Jing J, Tripathy S, Isoherranen N. Role of retinoic acid metabolizing cytochrome P450s, CYP26, in inflammation and cancer. Adv Pharmacol. 2015;74:373–412.
Ross SA, McCaffery PJ, Drager UC, De Luca LM. Retinoids in embryonal development. Physiol Rev. 2000;80:1021–54.
White JA, Guo YD, Baetz K, Beckett-Jones B, Bonasoro J, Hsu KE, et al. Identification of the retinoic acid-inducible all-trans-retinoic acid 4-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:29922–7.
Fujii H, Sato T, Kaneko S, Gotoh O, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Osawa K, et al. Metabolic inactivation of retinoic acid by a novel P450 differentially expressed in developing mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1997;16:4163–73.
Samokyszyn VM, Gall WE, Zawada G, Freyaldenhoven MA, Chen G, Mackenzie PI, et al. 4-hydroxyretinoic acid, a novel substrate for human liver microsomal UDP-glucuronosyltransferase(s) and recombinant UGT2B7. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:6908–14.
Hernandez RE, Putzke AP, Myers JP, Margaretha L, Moens CB. Cyp26 enzymes generate the retinoic acid response pattern necessary for hindbrain development. Development. 2007;134:177–87.
Shimozono S, Iimura T, Kitaguchi T, Higashijima S, Miyawaki A. Visualization of an endogenous retinoic acid gradient across embryonic development. Nature. 2013;496:363–6.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Mark Lokman, Department of Zoology, University of Otago, for critically reading this manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Availability of data and materials
The data supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.S. and T.I. designed experiment. K.S., H.F., Y.Y. and T.I. performed experiment. K.S. and T.I. wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No applicable.
Consent for publication
No applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional files
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Tested compounds. (XLSX 11 kb)
Additional file 2: Figure S1.
No sex difference was shown in tissue-specific distribution and time course of expression of medaka genes assessed by quantitative Real-time (RT)-PCR (A) Expression of rord1 mRNA in various tissues from adult medaka raised under 14L10D and sampled at Zeitgeber time ZT7 (7 h after “lights on”). B: brain; E: eye; G: gill; H: heart; K: kidney; L: liver; S: spleen; I: intestine; T: testis; O: ovary. Time course of expression of medaka rord1 (B), bmal1a (C), and cyp26a1 (D). The sample collection time is indicated as ZT. White and black bars above each graph represent light and dark periods. Y-axes represent gene expression as copies/ μg-total RNA. Male is shown in black column, and female is shown in white column. Data are expressed as means ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M.) (n = 3). Different letters on the columns indicate group means that are statistically different when analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test (P < 0.001). (JPEG 67 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, K., Fukushima, H., Yamamoto, Y. et al. A fourth subtype of retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptors is activated by oxidized all-trans retinoic acid in medaka (Oryzias latipes). Zoological Lett 3, 11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40851-017-0074-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40851-017-0074-7