Abstract
Background
Herein, we first time used the gum Moringa oleifera as reducing and capping agent for successful synthesis of silver nitrate and zinc oxide nanoparticles(NPs) through green synthesis approach. This study was aimed to check antibacterial activities of synthesized NPs against multidrug resistant bacteria methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Methods
Aqueous solutions of AgNO3 and purified gum powder were mixed with 1:1 ratio, autoclaved at 120oC for 2 min. NPs pellet collected after centrifugation at 10,000 g for 20 min. ZnO NPs were prepared by mixing purified gum powder and metal salt with1:1 ratio, heated (70oC) and stirred at 100 rpm for 4 h followed by centrifugation at 10,000 g for 20 min. Pellet was washed and calcinated at 400oC for 4 h. Antibacterial potential against E. coli, S. aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was assessed by widely used Kirby-Bauer antibiotic susceptibility test.
Results
Optical observation of colour change from transparent to dark and UV-Visible analysis confirmed the synthesis of NPs. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) of prepared nonmaterial revealed the characteristic AgNPs and ZnO stretch vibrations at wave number of 523 cm− 1 and 471 cm− 1resectively. Crystalline nature of AgNPs and ZnO NPs was confirmed by x-ray diffraction pattern with clear sharp Peaks. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed good surface morphology of AgNPs and ZnO NPs with 50nm and 60nm size respectively. AgNPs and ZnO NPs exhibited excellent antibacterial activity against E. coli (with zone of inhibition of 21 ± 02mm and 22 ± 03mm) and S.aureus ( with zone of inhibition of 20 ± 03mm and 21 ± 02mm) while good activity was observed against “super bug” methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) with 16 ± 03mm ad 17 ± 02mm zone if inhibitions respectively.
Conclusions
This novel addition of Moringa Gum based nanoparticles will open new dimensions in the field of nanomedicine and pharmaceutics especially against MDR bacterial strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Plants gums/ resins due to their properties of non-toxicity, non-polluting, sustainable, recyclable, low costs, eco-friendliness, wide spread availability, biodegradability and biocompatibility have bestowed them unique position in the field of pharmaceuticals, nanoparticles synthesis and food industry[1]. Natural polysaccharides/biopolymers based nanoparticles have a lot of advantages over similar synthetic entities. These plants polymers do double actions i.e. they act as stabilizing as well as reducing agents for metal ions while synthesizing nanoparticles [2].
Moringa oleifera (Moringaceae) is highly important plant from medicinally point of view and is distributed in tropics and subtropics regions of world. Its different parts contain variety of important phenols, amino acids, proteins, vitamins and β-carotene, [3]
Different parts of this plant has amazing medicinal properties like antiulcer, diuretic, antitumor, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic antiepileptic, antihypertensive, anti-diabetic ,cholesterol lowering and antioxidant. This plant is being used in indigenous health system of south Asian region particularly[3].
Over the past few decades, gums from natural sources are widely studies by the researchers due to their valuable physicochemical qualities. During past few years, different researchers have reported synthesis of metal nanoparticles using various plant gum/resins through green synthesis approach such as gum cashew[4], olibanum gum[5], gum karya[6]. Gum ghatti[7]. Gum neem[8], accasia arabica gum[9] and gum kondagogu[10].
The purified gum from Moringa oleifera plant was found to contain number of flavanoids, proteins and carbohydrates such as d-xylose, l-arabinose, d-glucuronic acid, d-galactose,d-mannose, and l-rhamnose[11].
The bio-based ways for silver and zinc oxide NPs synthesis present four major advantages: [1] enhanced biocompatibility (capped with biomolecules such as sugars, proteins, or metabolites); [2] less toxicity [3] trouble-free production (from extracts of plants, bacteria or fungi and silver salt and [4] less cost.
Multidrug-resistant bacteria (MDRB) or “super bugs” are exceptionally treacherous and pose a serious threat to global health systems as they can survive an attack from drug. Adaptive living style of bacteria with antibiotics causes them to modify their genetic makeup to emerge resistance against known antibiotics and their combinations. The appearance of nanoparticles as new antimicrobial agents has boosted up the research for tackling these superbugs. As nanoparticles target the bacterial cell through multiple pathways, it becomes difficult for bacteria to escape from these magical agents.
Zinc oxide NPs have been prepared via leaf extract of Abutilon indicum[12], Aloe barbadensis[13], Indigofera tinctoria[14], Melia azedarach, fungus and bacteria[15]. Recently, ZnO NPs have been synthesized via green approach through leaf extract of Sidium gujava [16], seed extracts of Nigella sativa[17], root extract of Daucus carota, leaf extracts of Monsonia burkeana [18]and Mangifera indica[19], fungus Halomonas elongate and Aspergillus terreus[20]. Considering important characteristic of Moringa Oleifera plant and bio based metal nanoparticles, we developed Gum based novel NPs for their further uses in pharmaceuticals.
Methods
Chemicals
Crude Gum Moringa (GM) was purchased from local market of Gujrat city and purified by ethanol precipitation method. Lab grade AgNO3 (Sigma-Aldrich-204,390) and Zn (NO3)2. 6H2O (Sigma-Aldrich-96,482) was taken from Biochemistry lab, University of Gujrat, Pakistan. Bacterial strains were procured from central lab of University of Veterinary & Animal Sciences – UVAS Lahore, Pakistan.
Preparation of silver and ZnO nanoparticles using gum Moringa oleifera
Silver NPs were prepared by following Venkatesham et al., 2014 [21] with slight modification. Purified gum moringa (0.5 gr) was dissolved in 100 mL of mili-Q water and AgNO3 (0.5 gr) was mixed in 100 mL of milo-Q water. Then, 5 mL from each solution was taken, mixed and kept in autoclave at 15 psi pressure at 120◦Cfor 2 min.
ZnO nanoparticles were prepared with little modification to Ogunyemi et al., 2021 [22]. The procedure carried out by mixing 1:1 ratio (v/v) of zinc nitrate hepta-hydrate and the Gum sample. Solution was heated (70oC) and stirred continuously at 100 rpm for 4 h followed by centrifugation at 10,000 g for 20 min. Nanoparticles pellet obtained, washed with distilled water by discarding the supernatants and calcinated at 400oC for 4 h.
Results
1) Characterization of AgNPs and ZnO NPs synthesized through “green” protocol
a) Optical Observation
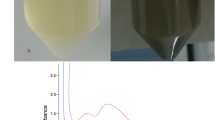
Colour change of developed NPs solutions (Fig. 1) from transparent to dark brown and light brown (for Ag and ZnO NPs respectively) confirmed the formation of nanoparticles. These colours appeared because NPs reflect (scatter) and absorb specific wavelengths of visible light [23].
b) UV-Vis Spectral Study
For characterization of metal nanoparticles, UV-Vis spectrophotometry is one of the most important tools. The absorption behaviour rises from “surface plasmon resonance”, which develops under electromagnetic field. Findings from high performance double beam T80 + UV-Visible spectrophotometer-PG instruments are presented in Fig. 2 reveals absorption pattern of GM, AgNPs and ZnO NPs synthesized through “green” method. It reveals that AgNPs developed comparatively with more efficiency than Zinc Oxide nanoparticles. Hydroxyl groups present in the gum Moringa reduced the silver and zinc. Synthesized nanoparticles exhibited absorption band in the range of 220–300 nm, a good Plasmon resonance band (PRB) of silver and Zinc NPs [24]. Absence of any peak at around 330nm and 550nm confirm the absence of nanoparticles aggregation [25]. No peak observed by gum sample as shown in Fig. 2.
c) Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) of synthesized NPs
The Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra (IRAffinity-SHIZMADZU Japan) revealed the stabilization of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles by GM as shown in Fig. 3. Moringa-AgNPs and Moringa-ZnO NPs have shown characteristic metal nanoparticles bands at 523 cm − 1 and 471 cm − 1 respectively, which was absent in Gum Moringa. The band at 1602 cm − 1 is due to –C = O bending of acid group. Different types of polysaccharides present in gum and synthesized nanoparticles were expressed at 1023 cm − 1, 1027 cm − 1 and 1024 cm − 1. Variations in peak pattern of all three samples were due to process of reduction and stabilization of metals by flavonoids and reducing sugars in GM [26].
d) X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis
To check the crystallinity of synthesized nanoparticles, X-rays diffraction analysis was performed using Rigaku D/max-2400 diffracto-meter with CuKα radiation.
Resulting diffractogram revealed excellent crystalline nature of developed gum based silver and zinc NPs as shown in Fig. 4. Gum powder amorphous nature was confirmed by diffractogram as it didn’t revealed any sharp diffraction pattern while AgNPs and ZnO NPs exhibited strong diffraction peaks.
The surface morphology of the gum powder, gum coated AgNPs and ZnO NPs were investigated using Scanning electron microscope (SEM) TESCAN VEGA3-China with an acceleration voltage of 30Kv and findings are presented in Fig. 5. It is clear from the image that the whole matrix is filled with small ZnO NPs and AgNPs indicating uniform distribution of nanoparticles. It is notable that finely grounded gum powder (purified) is with much higher size as compared to synthesized nanoparticles. Zinc oxide and silver nanoparticles were about size of 60nm and 50nm respectively. From nanomaterials point of view, this is an ideal size range [27].
2) Antibacterial activity against E.coli (gram negative), S. aureus (gram positive) and “super bug” MRSA
The antibacterial activity of AgNPs and ZnO NPs loaded GM polymers against E.coli, S. aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) were investigated by widely used Kirby-Bauer antibiotic susceptibility test[28]. The susceptibility patterns for gum Moringa oleifiera (crude) solution, Moringa olifiera AgNPs, Moringa oleifiera ZnO NPs and Positive control (kanamycin for E.coli and S.aureus and clindamycin for MRSA) are shown in Fig. 6. To perform the test, 6mm filter paper discs were loaded with 20 µl of sample from the stock solution to make 30 µg/disc, 20 µg/disc, 10 µg/disc and 5 µg/disc final concentration of NPs via dilution method (Table 1). Each plate was loaded with positive control with concentration of 30 µg/disc. After that all plates were incubated at 37oC for 24 h[28].
An excellent antibacterial activity was observed against both gram negative and gram positive bacteria (E.coli and S.aureus) while good activity was noted against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) as shown in Table 1; Fig. 6 (a, b, c). No zone of inhibition was observed at 5 µg/ml conc. for both testing samples and hence 10 µg conc. was considered as minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). This indicates that GM-AgNPs and GM-ZnO NPs, due to their multiple mechanisms of action against gram positive, gram negative and multi drug resistant bacteria are good antibiotic agents and can be used further for biomedical applications.
Discussion
Characteristic nature of Gum Moringa based metal NPs synthesized in this study were in line with previous reports of NPs characterization [29, 30].
Increasing popularity of green methods have resulted in different projects to synthesize Silver and ZnO NPs using bio based sources like fungus, bacteria, algae, protein, plants and others [31].
From decades, silver and zinc salts have been used to prevent the growth of different microbes from human. They were used in cuts, catheters, wounds and burns to protect them from infection[32]. Ag and ZnO NPs have been extensively studied for their activity against pathogenic bacteria like Vibrio cholera, E. coli, Syphilis typhus, P. aeruginosa etc.[33]. Thousands of patients died annually across the globe due to infection of resistant bacteria.
Due to emerging bacterial resistance to the available antibiotics, bacterial infections treatment has become alarming issue. There is dire need of new and potent bactericidal agents to cope with this problem. Metallic nanoparticles have shown promising results as antibacterial agents. NPs can targets bacterial cells via multiple routs i.e. by altering cell membrane permeability, protein activation, oxidative stress, enzyme activation and gene expression. Due to these unique properties, it becomes difficult for bacteria to develop resistance against NPs [33]. Our results added that that Gum Moringa based NPs not only worked against normal bacteria but also shown considerable activity against resistant bacteria (MRSA).
Metal NPs, due to their distinctive properties, have not only shown proven applicability in the field of medicine but also in catalysis, textile engineering, Nano biotechnology, bio-engineering sciences, optics, electronics and water treatment [22]. Novel NPs developed in this study can also be tested for said purposes.
However, there is further need of testing these NPs against fungus and other multi drug resistant bacteria. More characterization techniques can be applied to developed NPs. Detail mechanism of action of these NPs against microbes and resistant bacteria should be explored to unleash the underlying principles behind these important properties of NPs.
Conclusions
Moringa oleifera Gum based Silver and Zinc Oxide nanoparticles were successfully prepared through eco-friendly, sustainable, economical and easy to use “green synthesis” process. Characterization with UV-Visible, FTIR, XRD, and SEM confirmed the chemical and physical properties of synthesized nanocomposites. A good antibacterial potential was shown by these nanomaterials against gram positive, gram negative and MDR bacterial strain. These finding encourages the use of these nanoparticles in field of nanomedicine and pharmaceuticals at industrial scale. Further in-depth study on these materials can open new horizon in the nanomedicine areas.
Availability of data and materials
All data incorporated in article.
References
Carnachan SM, Bell TJ, Hinkley SF, Sims IM. Polysaccharides from New Zealand Native Plants: A Review of Their Structure, Properties, and Potential Applications. Plants. 2019;8(6):163.
Kpodo F, Agbenorhevi JK, Alba K, Smith A, Morris G, Kontogiorgos V. Structure and physicochemical properties of Ghanaian grewia gum. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;122:866–72.
Anwar F, Latif S, Ashraf M, Gilani AH. Moringa oleifera: a food plant with multiple medicinal uses. Phytotherapy Research: An International Journal Devoted to Pharmacological Toxicological Evaluation of Natural Product Derivatives. 2007;21(1):17–25.
Quelemes PV, Araruna FB, De Faria BE, Kuckelhaus SA, Da Silva DA, Mendonça RZ, et al. Development and antibacterial activity of cashew gum-based silver nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(3):4969–81.
Kora AJ, Sashidhar R, Arunachalam J. Aqueous extract of gum olibanum (Boswellia serrata): a reductant and stabilizer for the biosynthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles. Process Biochem. 2012;47(10):1516–20.
MP PR. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using water soluble gum of Sterculia foetida and evaluation of its antimicrobial activity. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2013;4:563568Kudle.
Kora AJ, Beedu SR, Jayaraman A. Size-controlled green synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by gum ghatti (Anogeissus latifolia) and its biological activity. Organic medicinal chemistry letters. 2012;2(1):1–10.
Velusamy P, Das J, Pachaiappan R, Vaseeharan B, Pandian K. Greener approach for synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles using aqueous solution of neem gum (Azadirachta indica L.). Ind Crops Prod. 2015;66:103–9.
Ansari MA, Khan HM, Khan AA, Cameotra SS, Saquib Q, Musarrat J. Gum arabic capped-silver nanoparticles inhibit biofilm formation by multi‐drug resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Basic Microbiol. 2014;54(7):688–99.
Kora AJ, Sashidhar R, Arunachalam J. Gum kondagogu (Cochlospermum gossypium): a templatee for the green synthesis and stabilization of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial application. Carbohyd Polym. 2010;82(3):670–9.
Bhattacharya SB, Das AK, Banerji N. Chemical investigations on the gum exudate from sajna (Moringa oleifera). Carbohydr Res. 1982;102(1):253–62.
Jain N, Bhargava A, Tarafdar JC, Singh SK, Panwar J. A biomimetic approach towards synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;97(2):859–69.
Sangeetha G, Rajeshwari S, Venckatesh R. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract: Structure and optical properties. Mater Res Bull. 2011;46(12):2560–6.
Prashanth G, Prashanth P, Nagabhushana B, Ananda S, Krishnaiah G, Nagendra H, et al. Comparison of anticancer activity of biocompatible ZnO nanoparticles prepared by solution combustion synthesis using aqueous leaf extracts of Abutilon indicum, Melia azedarach and Indigofera tinctoria as biofuels. Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology. 2018;46(5):968–79.
Jayaseelan C, Rahuman AA, Kirthi AV, Marimuthu S, Santhoshkumar T, Bagavan A, et al. Novel microbial route to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles using Aeromonas hydrophila and their activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2012;90:78–84.
Saha R, Subramani K, Raju SAKPM, Rangaraj S, Venkatachalam R. Psidium guajava leaf extract-mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles under different processing parameters for hydrophobic and antibacterial finishing over cotton fabrics. Prog Org Coat. 2018;124:80–91.
Alaghemand A, Khaghani S, Bihamta MR, Gomarian M, Ghorbanpour M. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Nigella sativa L. extract: the effect on the height and number of branches. Journal of Nanostructures. 2018;8(1):82–8.
Ngoepe N, Mbita Z, Mathipa M, Mketo N, Ntsendwana B, Hintsho-Mbita N. Biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Monsonia burkeana for use in photocatalytic, antibacterial and anticancer applications. Ceram Int. 2018;44(14):16999–7006.
Rajeshkumar S, Kumar SV, Ramaiah A, Agarwal H, Lakshmi T, Roopan SM. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles usingMangifera indica leaves and evaluation of their antioxidant and cytotoxic properties in lung cancer (A549) cells. Enzym Microb Technol. 2018;117:91–5.
Fouda A, Saad E, Salem SS, Shaheen TI. In-Vitro cytotoxicity, antibacterial, and UV protection properties of the biosynthesized Zinc oxide nanoparticles for medical textile applications. Microb Pathog. 2018;125:252–61.
Venkatesham M, Ayodhya D, Madhusudhan A, Babu NV, Veerabhadram G. A novel green one-step synthesis of silver nanoparticles using chitosan: catalytic activity and antimicrobial studies. Applied Nanoscience. 2014;4(1):113–9.
Ogunyemi SO, Abdallah Y, Zhang M, Fouad H, Hong X, Ibrahim E, et al. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using different plant extracts and their antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology. 2019;47(1):341–52.
Aritonang HF, Koleangan H, Wuntu AD. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of medicinal plants’(Impatiens balsamina and Lantana camara) fresh leaves and analysis of antimicrobial activity. International journal of microbiology. 2019;2019.
Duque JS, Madrigal BM, Riascos H, Avila YP. Colloidal metal oxide nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation technique and their antibacterial test. Colloids Interfaces. 2019;3(1):25.
Venkatesham M, Ayodhya D, Madhusudhan A, Veerabhadram G. Synthesis of stable silver nanoparticles using gum acacia as reducing and stabilizing agent and study of its microbial properties: A novel green approach. International journal of green nanotechnology. 2012;4(3):199–206.
Devaraj P, Kumari P, Aarti C, Renganathan A. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using cannonball leaves and their cytotoxic activity against MCF-7 cell line. Journal of nanotechnology. 2013;2013.
Kora AJ, Arunachalam J. Green fabrication of silver nanoparticles by gum tragacanth (Astragalus gummifer): a dual functional reductant and stabilizer. Journal of Nanomaterials. 2012;2012.
Hudzicki J. Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test protocol. 2009.
Rajeshkumar S, Bharath L. Mechanism of plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles–a review on biomolecules involved, characterisation and antibacterial activity. Chemico-Biol Interact. 2017;273:219–27.
Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A, Kaus NHM, Ann LC, Bakhori SKM, et al. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-micro letters. 2015;7(3):219–42.
Srikar SK, Giri DD, Pal DB, Mishra PK, Upadhyay SN. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: a review. Green Sustainable Chemistry. 2016;6(1):34–56.
Lansdown AB. A review of the use of silver in wound care: facts and fallacies. British journal of nursing. 2004;13(Sup1):6–19.
Van Hengel I, Putra N, Tierolf M, Minneboo M, Fluit A, Fratila-Apachitei L, et al. Biofunctionalization of selective laser melted porous titanium using silver and zinc nanoparticles to prevent infections by antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Acta biomaterialia. 2020;107:325–37.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Mr. Muhammad Tayyab, PhD Scholar East China University of Science and technology, China, for providing support in characterization of developed nanoparticles.
Funding
This study has no funding from any source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MI and HM designed the study. MI screened and purified the Gum sample, prepared the nanoparticles, checked their antibacterial activities and wrote the manuscript. HM guided different protocol of study and proof read the manuscript. HI provided the support in characterization, interpretations and antibacterial assay of Nanoparticles. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable (no human participant, human data or human tissue used in study).
Consent for publication
Not Applicable as no individual person’s data in any form has been used in this study.
Competing interests
Authors declare no conflict in any financial and non-financial competing interests regarding this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Irfan, M., Munir, H. & Ismail, H. Moringa oleifera gum based silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles: green synthesis, characterization and their antibacterial potential against MRSA. Biomater Res 25, 17 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40824-021-00219-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40824-021-00219-5