Abstract
Background
Consumption of medicinal plants has diverse therapeutic benefits and could also have toxic effect. Justicia carnea is a medicinal plant that is used conventionally as blood tonic from time immemorial in Nigeria. The aim of this study is to evaluate the safety of ethanol extract of J. carnea leaf assessing the hematology indices, organ antioxidant system and histology in healthy male wistar rats.
Methods
Powdered sample was extracted using absolute ethanol and concentrated to obtain a slurry paste of J. carnea ethanol extracts. Acute toxicity was determined in two phases using Lorke method. In subacute study, rats were randomized into six groups of five rats per group: Group 1 (control) received distilled water, group 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 received 50, 100, 500, 800 and 1200 mg/kg body weight of J. carnea ethanol extract once daily using oral gavage. At the end of 14th day of administration, rats were allowed to fast overnight, sacrificed to collect samples for biochemical analysis and histopathological examination.
Results
The LD50 of extract was greater than 5000 mg/kg body weight. Higher doses (> 500 mg/kg) of extract significantly (p < 0.05) increased RBC, hemoglobin and platelet compared to the control. Liver superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was significantly (p < 0.05) increased at 1200 mg/kg while other tested doses caused no detrimental effect on glutathione, catalase, SOD and malondialdehyde level in liver and kidney. Histopathological examination of liver and kidney showed mild to severe pathological lesion in a dose dependent manner.
Conclusions
The results of this study suggests that ethanol extract of J. carnea leaf is relatively safe, could be beneficial in alleviating hematology related abnormalities without causing adverse effects on endogenous antioxidant system. However, caution should be taken as higher dose at 1200 mg/kg could cause noticeable tissue injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In recent time, copious attention has been focused on the use of medicinal plants in the management and treatment of ailments such as anemia, diabetes and malaria. Due to the local availability, easy access and relatively low cost, medicinal plants are gaining attentions in health care programmes. Based on estimation by World Health Organization (WHO), larger percentage (between 80 and 90%) of the world’s population especially in developing countries depends on traditional system of medicine [1, 2]. Despite the therapeutic importance of medicinal plants, toxic substances have been shown to be present in large numbers of plants investigated [3]. Contamination of medicinal plant could be as a result of contaminants (such as heavy metals, aflatoxin and pathogenic microbes) from soil and manner of herbal preparations [4].
Consumption of medicinal plants without scrutinizing its efficacy and safety can result in unexpected toxic effects resulting in physiology changes of different organs in the body. Liver and kidney are the main targets of toxicants because they are respectively involved in biotransformation and excretion of xenobiotics. Hepatic and renal damage has been recently linked with the use of medicinal plants in the treatment of various diseases [5, 6].
Justicia carnea (belonging to Acanthaceae family) is a flowering plant consisting ~ 600 species that are widely distributed in the tropics and subtropics [7]. In various parts of Africa, several species of Justicia are used in traditional medicine for the treatment of anemia, inflammation, fever, diarrhea, liver diseases and arthritis respiratory and gastrointestinal disorder [8, 9]. Recently, it has also been reported that the species possess cardioprotective properties, antioxidant and are generally rich in vitamins and minerals [10,11,12].
In Nigeria, the leaf of Justicia carnea is usually prepared with edible vegetables to make soup, boiled separately in water to make tea or prepared by cooking with other medicinal plants for therapeutic purposes. Despite the avalanche use of medicinal plant, preliminary toxicity studies remain essential tools to ensure safe consumption and prevent unexpected toxicity that could arise from long term exposure. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effects of J. carnea leaf extract on hematology indices and organ antioxidant system in healthy wistar rats.
Methods
Plant sample
Fresh leaves of Justicia carnea were collected from Okitipupa area Ondo State. The fresh leaves were thoroughly washed under running tap, air dried under shade, pulverized and extracted with ethanol. Extraction was carried out by maceration (72 h) following the method of Onoagbe et al., [13]. Powdered sample (1000 g) was soaked in absolute ethanol (3000 mL) with constant stirring. After 72 h of soaking, the wine (dark purplish red) colored filtrate was filtered using a double cheese cloth, concentrated under reduced pressure using rotary evaporator and subsequently water bath at 40 °C to obtain a slurry (dark purple) extract termed Justicia carnea ethanol extract (JCEE).
Experimental animals
A total number of forty two (42) male albino rats weighing between 120 and 170 g were used in this study. These animals were obtained from the animal house of the Department of Chemical Sciences, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology Ogbomoso Oyo State, Nigeria. The animals were randomly distributed into cages and allowed to acclimatize for 2 weeks in a well ventilated room under natural lighting condition. The animals were allowed free access to rat chow and water ad libitum. Treatments of experimental animals were in accordance with the Principle of Laboratory Animal Care manual guide of National Institute of Health [14] as approved by the Institution Research Ethics committee.
Toxicity study
Oral acute toxicity study on J. carnea ethanol extract (JCEE) was carried out according to Lorke [15] method using the total of twelve (12) albino rats in two phases. In phase I, rats were randomized into 3 groups of 3 rats per group. Rats in the 3 different groups received 10, 100 and 1000 mg/kg body weight of JCEE orally using oral gavage. The animals were initially examined for any signs of toxicity after 60 min of administration and further observed for a period of 24 h. The absence of rat mortality in phase I necessitated the conduct of the second phase. In phase two, three rats were separated into 3 groups of one rat per group. Each of the rats received 1500, 2900 and 5000 mg/kg body weight of JCEE respectively and examined within 24 h for manifestation of toxicity. Rats were further observed for extended hours of 48 h to see if mortality would occur. In sub-acute toxicity study, total of thirty (30) rats were randomized into six groups of five rats per group: Group 1 served as control and was administered with 1 ml of distilled water (dH2O). Group 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 were respectively administered orally with 50, 100, 500, 800 and 1200 mg/kg body weight of JCEE once daily for 14 days using an oral gavage. Rats were routinely observed for signs of toxicity.
Experiment termination and biochemical analysis
At the end of the 14th day of administration, the rats were allowed to fast overnight and sacrificed the following morning by anesthetizing each rat in a closed chamber containing drops of chloroform. Each rat was dissected and blood samples were collected by cardiac puncture using 5 mL into tubes containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for hematological analysis. The liver and kidneys were excised and rinsed immediately in a normal saline (0.9% Nacl) to remove blood stain, dried between layers of Whatman filter paper, weighed and homogenized to obtain the supernatant for biochemical analysis. Section of livers and kidneys were excised and fixed in 10% formalin for histopathology examination.
Hematological analysis
The haematological indices of the blood samples were determined using an automated URIT – 2900 Plus 3 Differential Haematological Analyzer. Parameter that were determined include total haemoglobin concentration (HGB), packed cell volume (PCV), red blood cell count (RBC), mean corpuscular haemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration (MCHC), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), white blood cell count (WBC), Lymphocyte count (LYM), MID – sized cell (MID), Granulocyte Count (GRM) and platelet count (PLT).
Total protein
Total protein concentration in tissue homogenates were determined using biuret method Tietz [16]. The principle is based on the formation of coloured complex when protein peptide interacts with cupric ions in an alkaline medium. Sample (or standard solution) (0.01 ml) was mixed with diluted (1:4 v/v distilled water) biuret reagent (100 mM sodium hydroxide, 16 mM sodium-potassium tartrate, 15 mM potassium iodide and 6 mM copper sulphate). The mixture was incubated at 28 °C for 30 min and the absorbance read at 550 nm against the reagent blank.
Oxidative stress markers
Catalase activity
Catalase activity (U/ml) was measured following the method of Sinha [17]. The principle is based on the reduction of dichromate in a weak acid medium (acetic acid) to chromic acetate which is further heated in the presence of hydrogen peroxide to form an unstable intermediate (perchromic acid) that can be monitored spectrophotometrically at 620 nm. In a reaction mixture containing 0.01 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), 0.5 ml of 0.2 M H2O2 and 0.4 ml distilled water, 0.5 ml of sample was added. The reaction is terminated by the addition of 2 ml of dichromoacetic acid mixture (potassium dichromate (5%) and glacial acetic acid; 1:3 v/v) and heated at 60 °C for 10 min. Absorbance reading was taken at 620 nm regularly at an interval of 1 min against reagent blank. The catalase activity was calculated using the expression:
Note: ΔA = change in absorbance, TV = total volume, TP = total protein, SV = sample volume, ɛ = molar extinction = 40 M− 1 cm− 1.
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity
Superoxide dismutase was carried out using the method of Sun and Zigma [18]. SOD activity was determined by its ability to inhibit the auto-oxidation of epinephrine determined by the increase in absorbance at 480 nm. Total reaction mixture of 3 ml contained 2.95 ml of 0.05 M sodium carbonate buffer (pH 10.2), 0.02 ml tissue sample and 0.03 ml of epinephrine (2 mM) in 0.005 N HCl was used to initiate the reaction. The reference cuvette contained 2.95 ml buffer, 0.03 ml of substrate (epinephrine) and 0.02 ml of water. The absorbance was taken at interval of 1 min for 3 min at 480 nm.
Note: ΔA = change in absorbance, TV = total volume, SV = sample volume, ɛ = molar extinction = 4020 M− 1 cm− 1, TP = total protein.
Reduced glutathione (GSH)
The concentration of reduced glutathione content of the tissues was estimated according to Sedlak and Lindsay [19] method. Exactly 1.0 ml of tissues (liver and kidney) was deproteinised using 0.1 ml of 10% TCA and centrifuged at 650×g for 5 min to obtain supernatant. Further, 0.5 ml of supernatant was treated with 0.5 ml of Ellmans reagent (containing 19.8 mg of 5′,5′ – dithiobis - (2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) in 100 ml of 0.1% sodium nitrate) and 3.0 ml of phosphate buffer (0.2 M, pH 8.0). The absorbance was read at 412 nm against the reagent blank.
Note: ΔA = change in absorbance, TV = total volume, SV = sample volume, TP = total protein, ɛ = molar extinction =1.34 × 104 M− 1 cm− 1.
Malondialdehyde
Lipid peroxidation was determined by measuring the formation of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) according to the method described by Buege and Aust [20]. Briefly, 1.0 ml of the sample was mixed with 2 ml of TCA-TBA-HCl reagent (0.37% thiobarbituric acid, 15% trichloroacetic acid and 0.24 N HCl in 1:1:1) and boiled at 100 °C in a water bath for 15 min. The mixture was allowed to cool and centrifuged at 650×g for 10 min to obtain the supernatant. The absorbance of the supernatant was measured against reagent blank at 532 nm.
Extinction coefficient (ε) of MDA – TBA complex = 1.56 × 105 M− 1 cm− 1.
Where, A = absorbance, TV = total volume, SV = sample volume, ɛ = extinction coefficient, TP = total protein.
Histopathological examination
The liver and kidneys excised from all the experimental rats were fixed in a labeled sample bottles containing 10% formalin and processed for histological examination. Tissues were processed automatically using automatic tissue processor (Leica TP 1020) and allowed to pass through varying percentage of alcohol and absolute alcohol for the purpose of dehydration following dewaxing in Xylene for 15 mins. Tissues were stained with haematoxylin and eosin, mounted on glass slides and examined under a standard light microscope.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) version 17.0 and results were expressed as mean ± SEM. Differences between means were considered to be significant at (p < 0.05) using LSD (Least Square Difference) post hoc test.
Results
Acute toxicity result
Results obtained from the acute oral toxicity study revealed tolerance of experimental rat to acute administration of J. carnea ethanol extracts since no mortality and signs of toxicity were observed after 24 h (Table 1). Mean lethal dose of the extract was found to be above 5000 mg/kg body weight (bw).
Organ weights
The weight of liver and kidney of rats were measured immediately after excising the organs and is presented in Table 2. Rats that received 50 and 100 mg/kg body weight JCEE showed significant (p < 0.05) increase in liver weight while other doses showed no significant difference compared to the control. Kidney weight of rats treated with JCEE showed no significant difference with exception in 800 mg/kg JCEE that demonstrated significant reduction.
Hematology indices
The result of hematology indices is presented in Table 3. Ethanol extracts of J. carnea leaf increased RBC, hemoglobin and platelet with significant increase (p < 0.05) in groups that received higher dose (> 500 mg/kg b.w) of extract compared to the control. WBC reduced in rats treated with doses of J. carnea with significant decrease (p < 0.05) in rats that received 50, 100 and 1200 mg/kg body weight. Relative to control, lymphocyte and granulocyte exhibited no significant difference in all doses while MID was elevated in treated groups with significant increase in rats administered with 500 and 800 mg/kg body weight. Packed cell volume (PCV) and mean corpuscular volume (MCV) in treated rats with JCEE were statistically unperturbed compared to the control. Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) showed significant (p < 0.05) increased at 50 mg/kg while doses greater than 100 mg/kg showed no significant difference compared to the control.
Total protein and antioxidant system in organs
The effects of ethanol extract of J. carnea leaf on total protein concentration and antioxidant system in liver and kidney of normal wistar rat is presented in Table 4. Compared to the control, total protein in liver and kidney were statistically not altered except rats that were administered with 1200 mg/kg JCEE that showed significant (p < 0.05) decrease in the liver. Except the group that received 1200 mg/kg JCEE which showed significant (p < 0.05) elevation of SOD and MDA in the liver, other doses (< 1200 mg/kg) demonstrated no significant difference compared to the control. In the kidney, SOD and MDA level were indistinguishable compared to the control except SOD level in rats that received 800 mg/kg JCEE that reduced significantly (p < 0.05). While graded doses of J. carnea ethanol extract showed no significant difference in the liver and kidney GSH compared to the control, only rats that received 1200 mg/kg body weight JCEE statistically decreased in the kidney. Liver and kidney in all treated groups maintained similar activities of catalase (CAT) compared to the control.
Histopathological studies
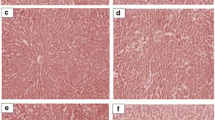
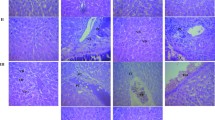
Photomicrograph of liver sections stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H & E) are presented in Fig. 1. Relative to the control, liver of rats treated with doses of J. carnea ethanol extract showed varied degree of hepatic injury in a dose dependent manner. With exception of low doses that showed normal morphology of the hepatocyte and sinusoid that is not infiltrated, high doses of extract greater than 500 mg/kg showed mild fat congestion in the central venules with liver parenchyma showing area of hemorrhage compared to the control. The kidney of rats treated with doses of J. carnea ethanol extract revealed dose dependent degree of renal injury (Fig. 2). From mild to severe order, the graded doses showed distorted renal cortex with collapsed renal glomeruli and dillated capsular spaces. The renal tubules and interstitial spaces appears distorted with presence of red inflammatory cells infiltrating the renal interstitial spaces as well as focal sclerosis of renal glomeruli with associated degeration of the glomerular membrane.
Photomicrograph of a liver sections stained with Haematoxylin and Eosin (Mag. × 400). The Portal triad (blue arrow) composed of the hepatic vein and artery as well as the bile duct (PT), the well distributed hepatocytes (H) (yellow arrow) and hepatic sinusoids (black arrow) are demonstrated across study groups. Control treatment showed normal central venules without congestion, the morphology of the hepatocytes appear normal, the sinusoids appear normal with no observable form of infiltration and no observable pathological lesion seen. 50 mg/kg-1200 mg/kg treatments relative to control showed varied degree of hepatic injury that is dose dependent. In these groups, from mild to severe order; shows observable congested portal vein, the liver parenchyma showed area of harmorrhage, the morphology of the hepatocytes appear pyknotic, some show mild fat infiltration (red arrow) the sinusoids appear fibrotic with infiltration of inflammatory red cells (red arrow). Summarily, experimental group shows some degenerative changes that can be termed as necrosis, some mild fibrosis and hemorrhage characterized by the presences of infiltrated red hemorrhagic and inflammatory cells. Also observed is a distortion in the walls of the blood vessels (red arrow), pyknotic hepatocytes and signs of inflammation (red arrow)
Photomicrographs of kidney sections stained with Haematoxylin and Eosin (Mag. × 400). Control treated group showed normal micromorphological sections. The renal cortex showed normal glomeruli with mesangial cells and capsular spaces appeared normal (white arrow), the renal tubules appear normal (blue arrow) and interstitial spaces also observed normal (black arrow). No observable focal sclerosis of renal glomeruli, capsular spaces around the glomerulus appears normal with distinct layering of renal microcellular structures. 50 mg/kg-1200 mg/kg treatment relative to control treatment showed varied degree of renal injury that is dose dependent. In these groups, from mild to severe order; the renal cortex appears distorted, Renal glomeruli and dillated capsular spaces appeared collapsed with characteristic pyknosis of the mesangial cells, The renal tubules, interstitial spaces, appears distorted with presence of red inflammatory cells, hemorrhagic cells infiltrating the renal interstitial spaces as well as focal sclerosis of renal glomeruli with associated degeration of the glomerular membrane (red arrows)
Discussion
This research focused on the safety and in – vivo antioxidant status of healthy albino rats exposed to J. carnea leaf ethanol extract. In an acute exposure of experimental rats to single oral doses of extract, no mortality and signs of adverse effects were observed. The higher LD50 (> 5000 mg/kg body weight) of J. carnea leaf ethanol extract suggested that the ethanol extract is experimentally safe and not toxic. This is in agreement with study of Anthonia et al., [21] who obtained LD50 above 5000 mg/kg for aqueous extracts of J. carnea leaf. According to acute toxicity grading standards, LD50 of substances greater than 5000 mg/kg is practically considered non-toxic [22, 23].
The weight of organs (liver and kidney) reduced steadily in a concentration dependent manner. The gradual decrease in the weight of organs following short-term exposure of J. carnea leaf ethanol extract may be attributed to adaptive response of the organs arising from daily dosage of the extract or its metabolites within their body. The non significant decrease observed in this study is in consonance with the work of Onyeabo et al., [9] who also reported no significant difference in the relative weights of liver and kidney.
The hematopoietic systems represent a sensitive target of toxic compounds and an essential index of physiological and pathological status in experimental animals [24]. Ethanol extract of J. carnea leaf elevated red blood cell, hemoglobin, packed cell volume and platelet count with significant increase at higher doses of extracts compared to the control. This is in agreement with previous work on the reversed effect of J. carnea leaf extract on anaemia – induced experimental rat [9, 21]. The possible anti-anaemic property of the leaf could be linked to the improved hemoglobin, PCV and RBC observed in this study. Several medicinal plants such as Xylopia aethiopica [25], Tectona grandis [26] and extracts of M. indica, A. hybridus and T. occidentalis [27] have also been reported to elevate RBC, hemoglobin and packed cell volume. The blood stimulating effects could be due to the presence of dietary bioactive constituents that stimulate activities of haematopoietic cells and stabilization of blood in circulation [21].
White blood cell counts usually increases following foreign invaders (pathogens) resulting in normal body physiological response which boost the body’s defense mechanisms [28, 29]. Decreased white blood cell count was obtained in this report, the level of lymphocyte and granulocyte was not altered by the extract while MID – sized cell was significantly elevated at 500 and 800 mg/kg dose. The levels of white blood cell count, lymphocyte, granulocyte and MID could indicate that ethanol extract of J. carnea leaf pose no toxicity or sub – acute inflammation to the overall defense mechanism and immunity of the experimental rats. Furthermore, increased MID by the extracts could indicate macrophage formation ability and pathogenic scavenging role.
From this study, the significant increase in platelet counts suggested that the extract could be useful in preventing excessive blood loss (through blood clotting) and resistance of capillary membranes to leakage of red cells when blood vessels are damaged. Macrocytic and hypochromic anemia usually results due to increased mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and decrease in mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration [30]. In this report, MCV, MCH and MCHC in treated group were not altered compared to the control. However, lowest (50 mg/kg) dose of extract significantly elevated MCH and MCHC.
The indistinguishable differences of total protein in the liver and kidney of rats treated with ethanol extract of J. carnea could indicate that the plant extract did not alter protein synthetic function of the organs. Significant (P < 0.05) decrease observed in liver total protein of rat administered with 1200 mg/kg of extract could be due to intrinsic factors in-vivo that might not necessarily indicate adverse reaction of the extracts. The significant decrease in kidney GSH at 1200 mg/kg could be due to ample dietary bioactive constituents in the extract that requires frequent conjugation of GSH in the cell or oxidation to oxidized glutathione (GSSG). Previously, J. carnea leaf has been reported to contain high quantity of phytochemical constituents (such as saponins, alkaloids and terpenoids), vitamins (A, C and E) and minerals [9, 10]. In-vivo studies have revealed that radicals produced from these dietary antioxidants are constantly regenerated back to their active form by GSH in the ascorbate – glutathione cycle. The ability of glutathione to regenerate these dietary antioxidants has been linked to the redox state of glutathione disulphide-glutathione couple (GSSG/GSH) ratio [31]. Paradoxically, oxidation of GSH has been reported to occur when GSH interact with metal ions thereby generating superoxide anions from the transfer of electrons from the metal ions to molecular oxygen [32]. As a consequence, depletion of reduced glutathione (GSH) either by removal from the cell or oxidation to GSSG could eventually lead to mild oxidative stress in cells and tissues [33, 34].
Elevated activity of catalase in liver and kidney across tested doses of J. carnea ethanol extract showed no significant effect compared to the control. This suggested that the extract did not alter tissue function in converting harmful hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities were elevated across all doses in the liver with significant (p < 0.05) difference only observed in the highest dose (1200 mg/kg) while kidney showed no significant difference compared to the control. This could possibly indicate SOD stimulating effects of J. carnea leaf ethanol extract. SOD is involved in the dismutation of the highly reactive superoxide anion to molecular oxygen (O2) and to less reactive hydrogen peroxides (H2O2) species, whereas CAT removes hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and toxic hydroxyl radical into water molecule [35].
The liver and kidney of rats administered with 500 mg/kg JCEE and above demonstrated slight increase in MDA level with significant (P < 0.05) increase only observed in the liver of rats that received 1200 mg/kg of extract. The significant increase in MDA level at 1200 mg/kg might be due to the presence of active secondary metabolites in the extracts that could have acted as prooxidant. Consequently, the effects of the extract on MDA level could indicate damage to cell membrane lipids of the hepatocyte which could result to increased generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). It has been reported previously that under certain conditions, dietary antioxidants such as ascorbic acid, tocopherol and carotenoids could act, occasionally, as pro-oxidants to initiate slight degree of oxidative stress microenvironment. However, the mechanism by which phytochemicals act as prooxidants in-vivo is still under investigation [25].
The liver histopathological examination of the groups treated with J. carnea ethanol extract (JCEE) leaf showed normal liver architecture with slight abnormalities (such as mild fat congestion and hemorrhage) in the central venules of groups that received high doses. Corroborating with the results of the antioxidant system and weight of the liver, continuous exposure to higher dose (1200 mg/kg) of JCEE could result in hepatic damage. While the renal tubules across the tested groups were normal with the interstitial spaces showing moderate congestion and hemorrhage, there appeared some abnormalities in the renal cortex (such as few sclerotic glomeruli with moderately dilated capsular spaces) resulting in fair architectural structure of the kidney (Fig. 2). The result from the kidney histology could be due to the presence of active secondary metabolites and daily dosing of the extract. Further study assessing the kidney indices (urea, creatinine and electrolytes) is however encouraged to ascertain the safety of the plant extract on renal function.
Conclusions
In conclusion, oral acute administration of J. carnea ethanol extract is safe because neither mortality nor any signs of toxicity were observed in experimental rats. The Hematological system and antioxidant status of rats following 14 days of sub-acute exposure tolerated the ethanol extract of J. carnea leaf. While histology of organs showed no adverse pathological lesions in the internal organs of rats, higher dose (1200 mg/kg) over a period of time could cause noticeable liver and kidney injury. This study has confirmed the safety of ethanol extract of J. carnea leaf and validates its conventional use as blood booster. However, serious caution of the dose should be taken into consideration when extrapolating this result for human consumption.
Availability of data and materials
All analyzed dataset to support the conclusions of this article is included as tables in the uploaded supplementary files.
Abbreviations
- JCEE:
-
Justicia carnea ethanol extract
- SEM:
-
Standard error of mean
- HCl:
-
Hydrochloric Acid
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- MID:
-
Mid-sized cell
- LD:
-
Lethal dose
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
References
Kone WM, Koffi AG, Bomisso EL, Tra Bi FH. Ethnomedical study and iron content of some medicinal herbs used in traditional medicine in cote d’ivoire for the treatment of anaemia. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012;9(1):81–7 https://doi.org/10.4314/ajtcam.v9i1.12.
van Andel T., Carvalheiro LG. Why urban citizens in developing countries use traditional medicines: the case of suriname. hindawi publishing corporation evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine. Article ID 687197, 2013; p. 13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/687197.
Mounanga MB, Mewonob L, Angone SA. Toxicity studies of medicinal plants used in sub-Saharan Africa. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;174:618–27 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.06.005.
Olaniyan JM, Hadiza LM, Hussaini AM, Musa BB, Abubakar SA. Acute and sub-acute toxicity studies of aqueous and methanol extracts of Nelsonia campestris in rats. J Acute Disease. 2016;5(1):62–70 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joad.2015.08.006.
Paes-Leme AA, Motta ES, De Mattos JCP. Assessment of Aloe vera (L) genotoxic potential on Escherichia coli and plasmid DNA. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;102(2):197–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2005.06.013.
Mapanga RF, Musabayane CT. The renal effects of blood glucose-lowering plant-derived extracts in diabetes mellitus-an overview. Ren Fail. 2010;32(1):132–8 https://doi.org/10.3109/08860220903367585.
Corrêa, GM., de C. Alcântara, AF. Chemical constituents and biological activities of species of Justicia – a review. Braz. J. Pharmacogn. 2012; 22(1):220–238; https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2011005000196.
Badami S, Aneesh R, Sankar S, Sathishkumar MN, Suresh B, Rajan S. Antifertility activity of Derris brevipes variety coriacea. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003;84:99–104.
Onyeabo C, Achi NK, Ekeleme-Egedigwe CA, Ebere CU, Okoro CK. Haematological and biochemical studies on Justicia carnea leave extract in phenylhydrazine induced-anemia in albino rats. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2017;16(2):217–30 https://doi.org/10.17306/J.AFS.2017.0492.
Faiza R, Waqas KK, Adeel M, Muhammad G. Detection of bioactive fractions of Justicia adhatoda leaves. Canadian J Appl Sci. 2013;1:388–98.
Radhika J, Sathya S, Jothi G, Japasheba JL. Cardioprotective role of Justicia traquebareinsis Linn. Leaf extract in isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction in albino rats. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013;3(4):124–8 https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2013.3422.
Medapa S, Singh GRJ, Ravikumar V. The phytochemical and antioxidant screening of Justicia wynaadensis. African J Plant Sci. 2011;5(9):489–92 https://academicjournals.org/journal/AJPS/article-full-text-pdf/6AA410310867.
Onoagbe IO, Attah V, Luther MM, Esekheigbe A. Hypoglycemic and anti-diabetic effects of Morinda lucida and Tetracera alnifora in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. W Afr J Biol Sci. 1999;9:1–8.
National Research Council. Occupational Health and Safety in the Care and Use of Research Animals. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 1997. https://doi.org/10.17226/4988.
Lorke D. A new approach to practical acute toxicity testing. Arch Toxicol. 1983;53:275–89.
Tietz NW. Clinical Guide to Laboratory tests. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB. Saunders; 1995. p. 268–73.
Sinha AK. Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal Biochem. 1972;47:389–94.
Sun M, Zigma S. An improved spectrophotometer assay of superoxide dismutase based on epinephrine autoxidation. Anal Biochem. 1978;90:81–9.
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH. Estimation of total, protein-bound, and non-protein sulfhydryl groups in tissues with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem. 1958;25(1):192–205.
Buege JA, Aust SD. Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Meth Enzymol. 1978;52:302–10.
Anthonia OC, Ikechukwu UR, Uzoma NO, Sunday ELU. Nutritive properties of aqueous extract Justicia carnea leaves and its effects on haematological and some biochemical indices of anaemia induced male wistar albino rats. Biomed Res. 2019;30(4):645–54. https://doi.org/10.35841/biomedicalresearch.30-18-666.
Duan WL, Liang XM. Technical guidelines assembly of veterinary medicine research. Beijing: Chemical Press; 2011.
Olumese FE, Onoagbe IO, Eze GI, Omoruyi FO. Safety assessment of Uvaria chamae root extract: acute and subchronic toxicity studies. J Afr Ass Physiol Sci. 2016;4(1):53–60.
Mukinda JT, Syce JA. Acute and chronic toxicity of the aqueous extract of Artemisia afra in rodents. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;112(1):138–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2007.02.011.
Oso BJ, Oyewo EB and Oladiji AT. Influence of ethanolic extracts of dried fruit of Xylopia aethiopica (Dunal) A. Rich on haematological and biochemical parameters in healthy Wistar rats. Clin Phytosci 2019; 5:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-019-0104-4.
Diallo A, Gbeassor M, Vovor A, Eklu-Gadegbeku K, Aklikokou K, Agbonon A. Effect of Tectona grandis on phenylhydrazine induced anemia in rats. Fitoterapia. 2008;79:332–6 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2008.02.005.
Ogbe RJ, Adoga GI, Abu AH. Antianaemic potentials of some plant extracts on phenyl hydrazineinduced anemia in rabbits. J Med Plants Res. 2010;4(8):680–4 https://doi.org/10.5897/JMPR09.487.
Eyong EU, Umoh IB, Ebong PE, Eteng MU, Antai AB, Akpa AO. Haematoxic effects following ingestion of Nigerian crude oil and crude oil polluted shellfish by rats. Niger J Physiol Sci. 2004;19(1–2):1–6. https://doi.org/10.4314/njps.v19i1.32627.
Stover PJ, Caudill MA. Generic and epigenetic contributions to human nutrition and health: managing genome-diet interactions. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008;108(9):1480–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2008.06.430.
Chanda S, Parekh J, Vaghasiya Y, Dave R, Baravalia Y, Nair R. Medicinal plants - from traditional use to toxicity assessment: a review. Inter J Pharm Sci Res. 2015;6(7):2652–70. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MTD, Mazur M, Telser J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Inter J Biochem Cell Bio. 2007;39(1):44–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2006.07.001.
Pompella A, Visvikis A, Paolicchi A, De Tata V, Casini AF. The changing faces of glutathione, a cellular protagonist. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;66:1499–503.
Walters DM., Cho Hye-Youn, Kleeberger SR. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Potential Role for Nrf2. Antioxidants & redox signaling Forum Review. 2008; 10:2. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2007.1901.
Oyenihi OR, Brooks NL, Oguntibeju OO. Effects of kolaviron on hepatic oxidative stress in streptozotocin induced diabetes. BMC Complem Altern Med. 2015;15:236. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0760-y.
McCune LM, Johns T. Antioxidant activity in medicinal plants associated with the symptoms of diabetes mellitus used by the indigenous peoples of the north American boreal forest. J Ethnopharmacol. 2002;82:197–205.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Director and staff of Peak – Health Diagnostic and Research Laboratory, Ibadan, Oyo State, Nigeria, for the technical support and interpretation of the histology.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The research work was carried out in collaboration between all authors. ESA conceived and designed the study. Authors TSO, KOK and ESA manage experimental protocols and performed the experiments under the supervision of FOA. Author ESA managed the literature searches and wrote the first draft of the manuscript with the assistant of FOA. Authors KOK and ESA performed the statistical analysis and managed the analyses of study. All authors read and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Authors’ information
Mr. E.S. Akintimehin is a lecturer in the Biochemistry unit of Chemical Sciences Department, Olusegun Agagu University of Science and Technology, Okitipupa, Ondo State, Nigeria. He earned B.Sc. and M.Sc. degree in Biochemistry from Olabisi Onabanjo University, Ago-iwoye, and University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria respectively.
Mr. K.O. Karigidi is a lecturer in the Biochemistry unit of Chemical Sciences Department, Olusegun Agagu University of Science and Technology, Okitipupa, Ondo State, Nigeria. He has B.Sc., and M.Sc. degree in Biochemistry from University of Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria and University of Ibadan, Nigeria respectively.
Mr. T.S. Omogunwa is a graduate of Biochemistry from the Department of Chemical Sciences, Olusegun Agagu University of Science and Technology, Okitipupa, Ondo State, Nigeria. He is a research assistant in the Biochemistry Unit of the same Department.
Prof. F.O. Adetuyi is a Professor of Biochemistry in the Department of Chemical Sciences, Faculty of Sciences, Olusegun Agagu University of Science and Technology, Okitipupa, Ondo State, Nigeria.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Treatments of all experimental animals were performed following Principle of Laboratory Animal Care manual guidebook of National Institute of Health as approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Olusegun Agagu University of Science and Technology, Okitipupa, Ondo State.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
As declared by all authors, no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Akintimehin, E.S., Karigidi, K.O., Omogunwa, T.S. et al. Safety assessment of oral administration of ethanol extract of Justicia carnea leaf in healthy wistar rats: hematology, antioxidative and histology studies. Clin Phytosci 7, 2 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-020-00234-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-020-00234-4