Abstract
Background
Concussion in sports has received a great deal of media attention and may result in short and longer-lasting symptoms, especially in adolescents. Although significant strides have been made in the identification and management of concussion, less is known about the primary prevention of this condition. The aims of this scoping review are to (1) summarize the current research of physical conditioning strategies to reduce or prevent concussion incidence in individuals participating in sport, especially adolescents, and (2) to identify gaps in the knowledge base. Our research question was what is known from the existing literature about physical preparation strategies to reduce or prevent concussion in adult and adolescent sports?
Methods
Three literature searches were conducted by information officers at two universities at six-month intervals, using five electronic databases (PubMed; WorldCat.org; Mendeley; EBSCOHost and Ovid MEDLINE). To increase the search range, subject experts were consulted and articles and reference lists were hand searched. A scoping review methodology identified eligible studies that analyzed physical preparation techniques on modifiable physical risk factors in athletes to reduce the incidence of concussion. The PRISMA-ScR checklist guided the reporting of the findings.
Results
A total of 1414 possible articles were identified, after duplicates removed, and articles analyzed against the inclusion and exclusion criteria, only 9 articles qualified for analysis. Two articles were found from studying reference lists. Thus, a total of 11 articles were included in the final evaluation for the purposes of this study. Data are reported from mostly adolescent subjects participating in nine different sports from three countries. Findings are presented with specific reference to previously recognized modifiable risk factors of concussion which include neck strength, neck size, cervical stiffness, type of sport, and pre-activity exercises.
Conclusions
There is limited research examining the physical preparation of athletes, especially in adolescents, to reduce or prevent concussion, and conflicting evidence in the few small sample studies that were identified. This scoping review identifies the research gap for a potentially vital modifiable risk factor, notably in the physical preparation of children and adolescents to reduce or prevent sports-related concussion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Key Points
-
Physical conditioning strategies may have beneficial effects on some modifiable risk factors for sustaining a sport-related concussion, although existing evidence is limited and conflicting.
-
It is unclear which modes or dosage of physical conditioning strategies reduce the incidence or effects of sport-related concussion.
-
Future studies to specifically assess the effects of both proprioceptive and dynamic strengthening of the neck musculature to reduce forces transmitted to the brain are recommended.
Background
Sport-related concussion (SRC) has a high incidence affecting approximately four million people in the USA every year, mainly persons aged 7 to 19 years [1, 2], with potentially long-lasting adverse effects [3]. The incidence of concussion is highest in athletes participating in contact sports such as Rugby Union, American Football, basketball, wrestling, ice hockey, and soccer [4, 5]. In some sports, concussion is the most common injury, with the reported incidence increasing [6]. There is a heightened concern during important neurodevelopmental years as adolescents may demonstrate larger post-concussion neuropsychological deficits and symptoms compared to adults [7]. The negative symptoms of concussion may persist for a few days to several weeks, although in a small number of cases, symptoms may persist for longer than 3 months [8]. Public awareness of the potential adverse effects of repeated concussive exposures on the brain is increasing [3] and news reporting agencies in many countries have recently emphasized the need for improved interventions to reduce concussion incidence and improve player welfare [9,10,11,12,13]. International collaborative efforts have improved the understanding of SRC and the appropriate identification and management of children who have sustained an injury to the brain [14], but strategies for the primary prevention of concussion need further exploration to help ensure the health and safety of populations most at risk.
Trauma to the brain can result from direct and indirect contact events. Player-to-player contact (especially the tackle) is the most common scenario that results in concussion in many sports [4, 5, 15, 16], although contact with the ground [15] and equipment is also common [17, 18]. Due to the nature of contact and collision sports, physical contest between players is inevitable. Thus, research into making collision events safer is vital. Rule changes may have the greatest potential population health effect in lowering concussion in youth sport [19]. In soccer, head injuries were reduced following a single rule change for intentional elbow-head contact [20]. In Rugby Union (“rugby”), some law changes and educational initiatives have shown positive impacts in reducing the incidence of concussion and improving awareness [21]. Other law changes did not seem to reduce the incidence of concussion and increased the risk of sustaining a SRC to the tackler [22]; this research raised ethical concerns regarding participants’ informed consent and their right to withdraw. As a result, recommendations for substantiated research evidence and dialog should precede changes to the professional game [23]. Similarly in youth ice hockey, law changes have identified mixed results for injury risk [24, 25]. Current research which examines primary concussion prevention strategies in sport is, however, very limited [26].
The ability to minimize or modify identified risk factors may reduce the effect or incidence of concussions in children. Previously identified risk factors for concussion include: a history of concussions, level of education, age, level of competition, behavior, sex, unanticipated contact, neck stiffness, predisposing psychological factors, neck strength, and neck girth [4, 7, 15, 16, 18, 27,28,29,30,31,32]. Children are at greater risk for sustaining a concussion, for having increased severity of symptoms and for experiencing longer recovery times compared to adults, which may be attributable to muscular (especially neck) characteristics [7]. The ability to withstand forces indirectly or directly applied to the head has been proposed as a possible mechanism to reduce traumatic brain injury and concussion [33,34,35,36,37]. As a result, adults may be more resilient to the effects of head trauma as they have greater neck strength and neck girth to control the inertia of the head during potentially traumatic events.
Physical preparation exercises have proven successful in reducing the effects of less common and less serious injuries [38,39,40,41,42] and recent evidence highlights exercise as a treatment of SRC [43, 44]. However, little is known about how physical preparation exercises improve the primary prevention of concussion in populations at most risk. The primary aim of this scoping review is to achieve an in-depth and broad understanding of the current literature on physical preparation strategies specifically designed to reduce or prevent SRC, especially in adolescents. Secondary aims included identifying gaps in the existing evidence base and recommending areas for future research with a focus on physical conditioning to reduce the incidence of sport-related concussion.
Methods
The methodological framework to identify literature for the current scoping review was developed by Arksey and O’Malley [45, 46]. This framework includes the following steps:
-
1.
Identifying the research question
-
2.
Identifying relevant studies
-
3.
Study selection
-
4.
Charting the data
-
5.
Collating, summarizing and reporting the results
-
6.
Optional consultation.
Finally, for reporting guidance of the results, the PRISMA-ScR checklist was used [47].
Identifying the Research Question
The research question for this scoping review was what is known from the existing literature about physical preparation strategies to reduce or prevent concussion in adult and adolescent sports? The wide approach to this review was maintained to generate a breadth of coverage.
Identifying Relevant Studies
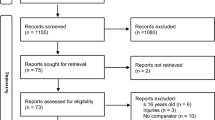
To comprehensively identify applicable search results of this scoping review, a three-round strategy involved searching for research evidence via different sources, including electronic databases, reference lists, and hand-searching journals (Fig. 1).
Electronic Databases, the Internet and Research Registers
The first electronic search was conducted on 9 September 2019 using keywords selected by the author team assisted by an Information Officer from University of KwaZulu Natal (UKZN) who guided the search strategy. The search strategy of UKZN’s electronic databases (PubMed; WorldCat.org and Mendeley) used the keywords and combinations of keywords as described in Additional file 1. Titles and abstracts were screened for inclusion after each consecutive search (Table 1), similarly, articles were excluded. Before submission on 30 April 2020, a second electronic search was conducted, using the same methods. Full articles were reviewed for a final decision on inclusion in this review. Following the peer-review process, a further electronic search was performed, to include the most recent research, on 1 December 2020 by an Information Officer from the University of Pretoria. This search was performed using the WorldCat.org, EBSCOHost and Ovid MEDLINE Databases using keywords as described in Additional file 2. The results were ranked by relevance and screened by title and abstract and retrieved 109 possible articles. This search was limited to English-only articles with publication dates between 1 January 2005 and 1 December 2020. The articles included in this review have been sourced by two information officers using five databases and reflect the current literature. The EndNote X9 online library was used for managing records and keeping track of articles. The EndNote Word Plugin is compatible with MS Word that the author used for the transcription of this manuscript.
Reference List and Hand-Searching of Journals
To encompass a broader search, bibliographies, and reference lists of studies found in the electronic database were checked to discover further studies that match the inclusion criteria to be incorporated in this scoping review. Journals were hand-searched to identify articles that may have been overlooked in the electronic database and reference list searches.
Study Selection
The information officers provided comprehensive lists of possible articles based on relevance and ranking. The lead author applied the inclusion and exclusion criteria to all these citations. All authors had an input on the analysis of the findings. Reflecting on the global advancement in the understanding of concussion in recent years, the preliminary search included articles less than ten years old. Due to the scarcity of results, this timeline was extended to 15 years. Thus, only those studies published between 1 January 2005 and 1 December 2020 were included. The search was limited to English language articles only, due to nearly all high impact and highly cited SRC articles being published in English and the cost and time involved in translating foreign material. However, there is a strong possibility that resources in other languages could have added to the information in this scoping review. Copies of the full articles were obtained. All articles that matched the exclusion criteria or did not match the inclusion criteria were removed (Table 1).
Study Exclusion Criteria
Articles were omitted if they were older than 15 years, not peer-reviewed, not in the English language, and were considered expert opinion only.
Charting the Data
The data were interpreted by sorting material according to key issues and themes using Microsoft Excel. Together, these data formed the basis of the analysis. The information was recorded as follows:
-
Author(s), year of data collection, study location, sport
-
Intervention type, and comparator (if any); duration of the intervention
-
Study populations (carer group; care recipient group)
-
Aims of the study
-
Methodology
-
Outcome measures
-
Important results
Results
Framework Stage 5: Collating, Summarizing, and Reporting the Results
The results of this search were summarized and combined in the data extraction table (Table 2). The authors interpreted and analyzed the results within the broader context of participant health in sports activities.
Characteristics of Included Samples
The 11 articles included in this review comprised of studies conducted only in the Northern Hemisphere, 8 in North America, 1 in Germany, and 2 in the UK [27, 30, 33, 48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55]. One study used non-human neck model simulations [51]. The human participants of the remaining included studies varied significantly in age. One study included only adult males (men aged 25.5 ± 5.6) [48]. Three studies included collegiate participants, (men aged 19.21 ± 0.918; women aged 19.16 ± 0.898 years) [55] (males aged 20.3 ± 3.6) [49] (men aged 21.6 ± 2.8) [54], three studies included high school and collegiate participants (high school 16.6 ± 0.9, collegiate 20.5 ± 1.4 years) [30]; (16.3 ± 5.0 years for males and 15.0 ± 4.4 years for females) [52] (males and females 17.1 ± 3.5) [50], and three studies included only high school participants (intervention 16.0 ± 1.2 years; control 15.9 ± 1.1) [53]; (15.0 ± 1.0 years) [33]; (girls and boys with no age descriptions) [27].
With regard to sports codes discussed in the selected articles [27, 30, 33, 48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55], two studies reported exclusively on Rugby Union (men; sex unspecified) [48, 53], another exclusively ice hockey (sex unspecified) [33], two studies on American Football (sex unspecified) [30] (males only) [54], two studies focused on men’s and women’s soccer [50, 55] and one study on men’s soccer only [49]. Three studies reported on multiple sports codes, namely, boys’ and girls’ soccer, basketball, and lacrosse [27], soccer, ice hockey, American Football, wrestling, lacrosse, and martial arts [52] and baseball and American Football [51].
Mansell et al. (2005) [55] reported on the effect of an 8-week isotonic resistance training program on head-neck segment dynamic stabilization in a small sample of men’s and women’s soccer players [55]. The training program consisted of 3 sets of 10 repetitions of neck flexion and extension at 55% to 70% of their 10-repetition maximum, two times a week. Measurements included anthropometric assessments, head-neck segment kinematics and stiffness, electromyographic activity of the upper trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles during force application to the head, and neck flexor and extensor isometric strength. Although the intervention group showed a 15% improvement in isometric neck flexor strength, no kinematic, electromyographic, or stiffness training effects were seen. In female intervention group participants, isometric neck extensor strength increased by 22.5%, and neck girth increased by 3.4%. Female soccer players demonstrated less head-neck segment length (7%) and less head-neck segment mass (26%) than men. The researchers concluded that regardless of the improvements in neck isometric strength and increases in neck girth, the resistance training protocol used in this study did not increase head-neck segment dynamic stabilization during force application in soccer players [55].
Schmidt et al. (2014) reported on the incidence and nature of head impact biomechanics using the Head Impact Telemetry System in a small sample of American Football players who completed preseason cervical testing of isometric neck strength, electromyography, muscle size, and response to cervical perturbation [30]. The reported findings showed the likelihood of sustaining higher magnitude head impacts was reduced in players with greater cervical stiffness and who experienced a smaller amount of angular displacement after impact. The results of this study showed that players with stronger lateral flexors and composite cervical strength had increased likelihood (1.75×) of receiving moderate head impacts rather than mild impacts, compared with weaker players. Similarly, players who developed faster torque in cervical extension had twice the likelihood of receiving severe head impacts (odds ratio [OR], 2.10; 95% CI, 1.08–4.05) rather than mild head impacts. However, players with greater cervical stiffness had reduced likelihood of sustaining both moderate (OR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.61–0.96) and severe (OR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.46–0.89) head impacts compared with players who demonstrated less cervical stiffness. The authors conclude that the study’s findings showed that greater cervical stiffness reduced the likelihood of sustaining higher degree head impacts. Further, the results of this study do not support that stronger and larger neck muscles reduce the severity of head impacts [30].
Lisman et al. (2012) examined the effects of an 8-week isoinertial cervical resistance training program and the electromyographic (EMG) activity of neck muscles and the kinematics of the head and neck in response to a American Football tackle [54]. The results of the study showed modest increases in isometric strength in cervical extension (7%) and left lateral flexion (10%), but the program had no influence on the EMG responses of neck muscles, peak linear, or angular head accelerations during tackling. This authors conclude that this 8-week isoinertial cervical resistance training program did not increase dynamic stabilization of the head and neck during a American Football tackle [54].
Mihalik et al. (2011) evaluated the effect of cervical muscle strength on the head after an impact by collecting data from accelerometer instrumented ice hockey helmets throughout a playing season [33]. A small sample of players’ cervical isometric strength measurements were recorded using a hand-held dynamometer (Model: 01163; Lafayette Instrument, Co, Lafayette, IN) in the preseason. Muscle strength testing involved two practice trials performed before three test trials (of 3 s duration) for each direction of motion, with a 30 s rest period between trials. The maximum forces for each of the three test trials were averaged and normalized to the player’s body mass. These data were compared with head biomechanics from the collected helmet data (Head Impact Telemetry System). The authors identified significant differences in cervical muscle strength between the participants. However, no differences were recorded in peak linear (PLin) or peak rotational acceleration (PRot) for the anterior neck flexors (PLin = 0.399; PRot = 0.060), anterolateral neck flexors (PLin = 0.987; PRot = 0.579), cervical rotators (PLin = 0.136; PRot = 0.238), posterolateral neck extensors (PLin = 0.883; PRot = 0.101), or upper trapezius (PLin = 0.892; PRot = 0.689). The authors concluded that the findings of this study do not support that cervical muscle strength is a factor in modifying head impact severity [33].
Collins et al. (2014) reported on a large sample of adolescent athletes (n = 6662) over a full academic year in multiple contact sports, namely soccer, basketball, and lacrosse [27]. In this study, the researchers developed and validated a cost-effective tool to measure neck strength in these athletes and found a high correlation (0.83 to 0.94 for the four neck strength measurements—all p values < 0.05) between the hand-held dynamometer and tension scale measurements. High inter-tester reliability was observed between different athletic trainers (ATs). In the second part of the study, AT’s recorded athletic anthropometric measurements, exposure, and injury data on the internet-based data collection tool developed for the National High School Sports-Related Injury Surveillance Study. Athletes were prospectively monitored for sustaining a concussion from 2010 to 2011. The results showed that the rate of concussion in the three contact sports was higher in adolescent girls when compared to adolescent boys (4.9 per 10,000 athlete exposures in girls and 2.5 per 10,000 athlete exposures in boys), with soccer having the highest rate of concussion (5.2 per 10,000 athlete exposures) followed by lacrosse (3.7 per 10,000 athlete exposures) and basketball (2.3 per 10,000 athlete exposures). Girls had an increased likelihood of concussion overall (OR = 1.8, 95 % CI 1.36–2.49) and in basketball (OR = 2.7, 95% CI 1.53–4.71) and soccer (OR = 1.8, 95% CI 1.17–2.69). However, no difference was identified between girl and boy lacrosse players (OR = 1.0, 95% CI 0.44–2.10). The researchers reported that a smaller mean neck circumference, smaller mean neck to head circumference ratio, and weaker mean overall neck strength were significantly associated with concussion. Overall, sex (p < 0.001), sport (p = 0.007), and neck strength (p < 0.001) were found to be significant predictors for sustaining a concussion. Specifically for neck strength, the authors reported that for every 1 lb increase in neck strength, the likelihood of concussion decreased by 5% (OR = 0.95, 95% CI 0.92–0.98) [27].
Hislop et al. (2017) evaluated the effects of a prescribed series of progressive warm-up exercises in a cluster-randomized trial of adolescent rugby players injuries over one season [53]. The specific particulars of the intervention and control group exercises are not described in detail and the reader is directed to a previous study by the author for more information [56]. The intervention group exercises consisted of isometric neck exercises, whole-body resistance training, plyometric training, and landing and cutting running movements. These exercises were to be completed in the initial fifteen minutes of training and before every match, although the authors report that certain exercises were “withdrawn when the program is performed prior to matches” [56]. The control group exercises were structurally indistinct to the intervention program and consisted of exercises that were considered “best practice” in schools’ rugby including a running-based warm-up, dynamic stretching, wrestling, mobility, speed, and agility-related exercises [56]. School coaches recorded training exposure, player injury details, match exposure, and program compliance on paper-based or electronic report forms. School medical staff recorded the injury location and diagnosis. The intention-to-treat analyses indicated unclear effects of the trial arm for overall match injury (incidence rate ratio [RR] = 0.85, burden RR = 0.83) and match contact injury (incidence RR = 0.85; burden RR = 0.88). The researchers conclude that the players in the intervention group reported substantially reduced incidence of upper limb injury and concussion. Further, teams that completed the intervention program three times per week reported substantial reductions (72%) in overall match injury incidence (RR = 0.28, 0.14 to 0.51) and concussion incidence (RR = 0.41, 0.17 to 0.99) compared with the control program [53].
Similarly, Attwood et al. (2018) investigated the effects of a movement control program to reduce injury risk in rugby union players [48]. The intervention program involved proprioceptive, mobility, and strengthening exercises targeted at the lower limb, shoulder, head and neck over seven 6-week progressive phases. The control program involved dynamic stretching and non-targeted resistance exercises in a similar progressive structure to the intervention program. Participants were blinded to which program they received. Each participating club nominated an individual who was trained to deliver the program to the players, and a representative to record first team match exposure, exercise program compliance, and match injuries on a weekly basis, using standardized forms. No clear effect was identified for the intervention program using intention-to-treat analysis for overall injury burden, overall injury incidence or severe injury incidence. However, concussion incidence (1.2 vs 3.4 injuries/1000 player match-hours) and concussion burden (38 vs 102 days/1000 player match-hours) was 60% lower in the intervention group compared with the control group. Lower-limb injury incidence was also 40% lower for the intervention group over control group (3.3 vs 5.2 injuries/1000 player match-hours) although shoulder injury incidence (1.7 vs 1.0 injuries/1000 player match-hours) and injury burden (68 vs 45 days/1000 player match-hours) were higher for the intervention group. Further, clubs in the intervention group that had a greater compliance (≥ 85% to < 85% of possible sessions) indicated a likely beneficial 50% reduction in targeted injury burden [48].
Eckner et al. (2014) assessed the influence of neck size, neck strength, rate of force development, and muscle activation on head kinematics following loading in multiple planes [52]. The participants in this cohort comprised of a broad range of ages, competitive levels, and sporting codes. The results of this study showed greater isometric neck strength and anticipatory activation to be independently associated with decreased head peak linear velocity and peak angular velocity after impulsive loading across all planes of motion (all p < .001). Further, neck circumference and sternocleidomastoid cross-sectional area were also significant (p < .001) in all planes of motion and remained significant when adjusted for age and sex (p < .001). This study reports that superior neck strength and anticipatory muscle activation are individually associated with a decreased kinematic response to impulsive forces applied to a subject's head [52].
Caccese et al. (2018) aimed to identify factors that contribute to head acceleration during soccer heading. This study utilized anthropometric measurements, isometric strength and electromyography of muscles of the neck and upper torso and kinematics of the head during active soccer heading in seasoned soccer players [50]. The authors reported that the results suggest that greater head and neck size predicted lower peak linear and rotational accelerations. The results further showed that neck strength, specifically of the sternocleidomastoid muscle predict peak linear (β = − 1.544, p = 0.012) and peak rotational (β = − 0.117, p = 0.018) accelerations of the head. Technique-related predictors did not predict the same during soccer heading [50].
Eckersley et al. (2019) reported on the effects of cervical muscle strength on head kinematics using validated neck model simulations [51]. This study examines plausible impacts to the head for different athletic scenarios, namely impact from a ball to the bare head in major league baseball and impacts between opposing player American Football helmets. The authors report that no consistent effect to the injury metrics for sport-related concussion (SRC) can be seen by changing neck muscle force in models. The results did show that tensed muscle activation conditions resulted in higher peak resultant angular acceleration values compared to relaxed muscle activation conditions. The authors conclude that impact location and impact scenario were greater determinants of SRC injury metrics than the protective capacity of cervical muscle activation. The results of this study do not support the hypothesis that greater cervical muscle force influences head kinematics during impact scenarios and neck strengthening programs and exercises will do little to reduce the risk of concussion [51].
In the most recently published study included in this scoping review, Becker et al. (2019) explored the effects of a 6-week strength training program on head acceleration during three different variations of headers on male soccer players [49]. An interesting inclusion in this study design is that the researchers attempted to fatigue the trunk muscles of the participants to decouple the head-neck-torso alignment, thus resulting in an increased acceleration of the head. The results did not show a significant difference between the strength measurements of the control and intervention groups (p = 0.055). Neck flexion strength improved for all the groups, including the control group, who did not perform extra neck exercises. Neck extension strength improved for one of the intervention groups (youth team) but decreased in the other intervention (adult team) group, and in the control (mixed) group. The authors state that these results do not support the hypothesized preventative benefit of neck strengthening [49].
Framework Optional Stage: Consultation Exercise
As an additional stage in scoping review methodology as recommended by Arksey and O’Malley [45], two International Concussion Societies were consulted (International Concussion Society https://www.concussion.org/contact/ and The Center for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services) for further possible information. These organizations were contacted due to their location as most of the studies identified in this review were conducted in North America. The literature sourced from this optional exercise provided insight into the broader discussion of concussion although the provided literature did not satisfy the inclusion criteria for this scoping review.
Discussion
Summary of Evidence
This study aimed to summarize the current research on physical conditioning strategies to address specific modifiable risk factors in the prevention of sports-related concussion. Secondly, this study aimed to identify the gaps in the knowledge base regarding physical conditioning strategies to address these specific modifiable risk factors.
The studies included in this scoping review provide a lack of generalizability to the broader sports-playing populations for several reasons. Firstly, 6 of the 11 studies have small sample sizes (range n = 16–49). Secondly, 3 of the 10 studies do not describe the sex of the sampled participants. Thirdly, the study with the largest sample size does not specify the ages of its participants. Fourthly, there are significant disparities in age when comparing the results of participants (range 10.6–31.1 years) (Table 3), and previous research has identified significant differences in neck strength in adolescent athletes compared to adult athletes. Further, one study incorporated simulated models instead of human participants. Lastly, the studies included in this review only represent populations in North America, England and Germany and may not be representative of the global community.
Neck Strength
This review identified conflicting evidence in a minimal number of studies regarding the effect of neck strength as a risk factor for concussion in adolescent athletes [27, 30, 33, 49,50,51,52, 54, 55] (Table 3). One large study showed that neck strength is a significant predictor of concussion [27]. Further, greater neck strength has been shown to attenuate head kinematics during unanticipated and anticipated loading of the head [52]. Other studies reported on isometric exercises, which have been shown to increase neck strength, especially in women, although this type of exercise does not show improvements in dynamic stabilisation of the head [55] or in modifying head impact severity [33]. This is supported by Eckersley et al. (2019), who state that neck strengthening exercises are not effective in reducing concussion risk and cervical muscle force does not influence head kinematics after impact [51]. Further, Lisman et al. (2012) and Becker et al., (2019) did not find preventative benefits of neck strengthening to reduce head acceleration forces [49, 54]. One study found that players with stronger cervical musculature were at higher risk of receiving more severe impacts to the head, possibly as a result of risk compensation which theorizes that players accept a certain level of risk and adapt their behavior based on perceived risk until their accepted level of risk is reached again [30] Contrastingly in the largest study in this review, isometric neck exercises were shown to significantly reduce the incidence of concussion in Rugby Union players [53]. Caution should be exercised with this finding as the authors do not measure neck strength or girth and only speculate that their exercises preserved neck function and potentially reduced forces to the brain [53].
Due to the dynamic nature of a concussive event, it is unlikely that strengthening a muscle at a fixed length without movement (isometrically) would achieve the desired response of reducing forces to the brain. The methodology of testing isometric strength in these studies is probably due to the difficulty of testing dynamic neck strength. Based on the studies reviewed here and the current understanding of SRC, future research should assess the effects of both proprioceptive and dynamic (especially eccentric, ballistic and plyometric) strengthening of the neck musculature to reduce forces transmitted to the brain. Ideally, isotonic strength testing through an athlete’s available neck range of motion in all available planes, including rotation in a manner to prepare the body to withstand shearing forces, would provide valuable information towards preparing athletes for participation in sport.
Neck Size
Four studies addressed the effect of neck size as a modifiable risk factor for concussion and reported opposing views. The first study assessed a small sample of American Football players and concluded that players with larger cervical musculature might be at a greater risk of sustaining a concussion, possibly as a result of increased risky technique due to their perception of being more protected from injury [30]. The second study reported on multiple contact sports with a large sample of male and female participants and concluded that a smaller average neck circumference and smaller average neck to head circumference ratio were significantly associated with concussion [27]. The third study reported greater neck circumference and sternocleidomastoid muscle cross-sectional area, in particular, reduced peak linear and peak angular velocity of the head during impulsive loading [52]. The fourth study reported on male and female soccer players and the results show that greater neck girth significantly predicted lower peak linear and rotational head acceleration [50].
Cervical Stiffness
Cervical stiffness in this context relates to the ability of the neck musculature and osteoligamentous structures to withstand displacement and has been proposed as a potential preventative strategy for reducing the risk of concussion, as well as the severity of sub-concussive trauma [30]. In this review, players with greater cervical stiffness had reduced likelihood of sustaining both moderate and severe head impacts compared with players who demonstrated less cervical stiffness.
Type of Sport
The limited sporting codes included in the identified studies are considered “contact sports” and were most likely recognized for the increased risk of concussion in the participating athletes [57]. It should be noted that although there is a potential risk of concussion in contact sports, there is also a potential risk of concussion in non-contact sports codes and in non-contact events, such as cheerleading, volleyball, track and field, and softball [4].
Whole-Body Pre-activity Exercises
Two impactful studies reported a substantial reduction in concussion incidence as a result of pre-participation whole body exercises [48, 53]. There are some limitations to these studies which have attracted criticism [58]. In both studies, with similar methods, the researchers did not test for baseline measurements (for example, cervical strength or cervical stiffness) and were only able to speculate as to the reasons for the reported changes. Both sets of authors suggest that the basic isometric neck exercises may have preserved neck function over the playing season and prevented concussion by dissipating forces applied to the brain [48, 53]. However, Attwood et al. cite a study with numerous limitations to support this statement [48, 59, 60]. Further, Hislop describes a progression through the advancing phases which does not allow sufficient time, frequency, or load required to improve strength [61, 62]. The scope of these studies do not allow adequate identification of the specific exercises which may be responsible for the substantial reduction in concussion incidence; however, the findings reported by Hislop et al. and Attwood et al. are substantial using relevant and large sample sizes [48, 53, 56]. These findings encourage future research as they are in stark contrast to previous studies of similar exercises with more focused testing procedures, which showed isometric exercises to be ineffective in reducing the incidence of concussion [30, 33, 48, 53, 55]. The “golden thread” of these findings may be a move away from testing muscles in isolation and towards testing closed kinematic chains (multi-segment force transmission) to dissipate forces to the brain [63,64,65].
The findings of this research come at a time of increased global attention on concussion prevention to improve welfare of participants involved in sport.
Limitations
This scoping review included articles published in English language only, due to resource and budget constraints. In doing so, it is possible that articles in other languages that may have met the study’s inclusion criteria were excluded in the search strategy. A second limitation is that a timeframe of the past 15 years was used, which may have excluded older articles that met the inclusion criteria. Although the available evidence is limited, the use of the scoping review methodology, rather than a systematic review, allowed for discussion and analysis of a broad spectrum of relevant studies with varied methodologies.
Conclusion
The results of this scoping review are presented at a time of an increased global scrutiny of concussion prevention to improve the welfare of participants involved in sport and reveal a dearth of literature addressing physical preparation strategies to reduce or prevent the incidence of concussion. The small amount of research in this area has shown conflicting results for modifiable risk factors relating to neck size, neck strength, and neck stiffness. Future research should assess the effects of both proprioceptive and dynamic strengthening of the neck and surrounding musculature to reduce forces transmitted to the brain or to increase resilience during participation in sports. The potential of effective protective mechanisms to reduce the incidence and the effects of concussion warrants further research.
Availability of Data and Materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- SRC:
-
Sport-related concussion
- IMVC:
-
Isometric maximum voluntary contraction
- IG:
-
Intervention group
- CG:
-
Control group
- DUHNM:
-
Duke University Head Neck Model
- NCAC:
-
National Crash Analysis Center
- EMG:
-
Electromyographic
- SCM:
-
Sternocleidomastoid
- SSC:
-
Semispinalis capitis
- UT:
-
Upper trapezius
- RM:
-
Repetition maximum
References
Langlois JA, Rutland-Brown W, Wald MM. The epidemiology and impact of traumatic brain injury: a brief overview. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 2006;21(5):375–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001199-200609000-00001.
Coronado VG, Haileyesus T, Cheng TA, Bell JM, Haarbauer-Krupa J, Lionbarger MR, Flores-Herrera J, McGuire LC, Gilchrist J. Trends in sports- and recreation-related traumatic brain injuries treated in US Emergency Departments: The National Electronic Injury Surveillance System-All Injury Program (NEISS-AIP) 2001-2012. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 2015;30(3):185–97. https://doi.org/10.1097/HTR.0000000000000156.
Hume PA, Theadom A, Lewis GN, Quarrie KL, Brown SR, Hill R, et al. A comparison of cognitive function in former Rugby Union players compared with former non-contact-sport players and the impact of concussion history. Sports Med. 2017;47(6):1209–1220.
Marar M, McIlvain NM, Fields SK, Comstock RD. Epidemiology of concussions among united states high school athletes in 20 sports. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(4):747–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546511435626.
Buzas D, Jacobson NA, Morawa LG. Concussions from 9 youth organized sports: results from NEISS hospitals over an 11-year time frame, 2002-2012. Orthopaedic J Sports Med. 2014;2(4):2325967114528460. https://doi.org/10.1177/2325967114528460.
Lincoln A, Caswell S, Almquist J, Dunn R, Norris J, Hinton R. Trends in concussion incidence in high school sports: a prospective 11-year study. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(5):958–63. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546510392326.
Dougan BK, Horswill MS, Geffen GM. Athletes’ age, sex, and years of education moderate the acute neuropsychological impact of sports-related concussion: a meta-analysis. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2014;20(1):64–80. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355617712001464.
Rohling ML, Binder LM, Demakis GJ, Larrabee GJ, Ploetz DM, Langhinrichsen-Rohling J. A meta-analysis of neuropsychological outcome after mild traumatic brain injury: re-analyses and reconsiderations of Binder et al., Frencham et al., and Pertab et al. Clin Neuropsychol. 2011;25(4):608–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/13854046.2011.565076.
Los Angeles Times. Defining Stanford volleyball star Hayley Hodson’s post-concussion syndrome diagnosis 2020, December 08 [Available from: https://www.latimes.com/sports/story/2020-12-08/defining-stanford-volleyball-star-hayley-hodsons-post-concussion-syndrome-diagnosis. Accessed 2020, December 10.
The Sydney Morning Herald. 'How many more is too many?': Pucovski concussions spark concern 2020, December 10 [Available from: https://www.smh.com.au/sport/cricket/how-many-more-is-too-many-pucovski-concussions-spark-concern-20201209-p56m3r.html. Accessed 2020, December 10.
The New York Times. She seemed destined for Olympic glory. Brain Injuries Ended That. 2020, November 22 [Available from: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/11/20/sports/olympics/skeleton-concussion-bobsled-head-injuries.html. Accessed 2020, December 10.
The Guardian. Football without headers is unthinkable – or is it? 2020, December 09. [Available from: https://www.theguardian.com/football/commentisfree/2020/dec/09/football-without-headers-is-unthinkable-or-is-it]. Accessed 2020, December 10.
The Guardian. Rugby urged to improve safety quickly to reduce risk of more lawsuits 2020, December 09 [Available from: https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2020/dec/09/rugby-urged-to-improve-safety-measures-lawsuits-concussion-dementia. Accessed 2020, December 10.
McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Dvořák J, Aubry M, Bailes J, Broglio S, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport—the 5th international conference on concussion in sport held in Berlin, October 2016. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(11):838–847.
Lynall RC, Campbell KR, Wasserman EB, Dompier TP, Kerr ZY. Concussion mechanisms and activities in youth, high school, and college football. J Neurotrauma. 2017;34(19):2684–90. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2017.5032.
Lincoln A, Caswell S, Almquist J, Dunn R, Hinton R. Video incident analysis of concussions in boys’ high school lacrosse. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(4):756–61. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546513476265.
Collins MW, Kontos AP, Reynolds E, Murawski CD, Fu FH. A comprehensive, targeted approach to the clinical care of athletes following sport-related concussion. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(2):235–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2791-6.
Dick RW. Is there a gender difference in concussion incidence and outcomes? Br J Sports Med. 2009;43:46–51.
Emery CA, Black AM. Are Rule Changes the Low-Hanging Fruit for Concussion Prevention in Youth Sport? JAMA Pediatr. 2019;173(4):309–10. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.5498.
Beaudouin F, Aus der Funten K, Tross T, Reinsberger C, Meyer T. Head injuries in professional male football (soccer) over 13 years: 29% lower incidence rates after a rule change (red card). Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(15):948–52. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2016-097217.
Brown J, Viljoen W, Hendricks S, Abrahams S, Burger N, McFie S, et al. On-field identification and management of concussion in amateur rugby union. South Afr J Sports Med. 2016;28(1):6–10. https://doi.org/10.17159/2078-516X/2016/v28i1a1412.
Stokes KA, Locke D, Roberts S, Henderson L, Tucker R, Ryan D, et al. Does reducing the height of the tackle through law change in elite men's rugby union (The Championship, England) reduce the incidence of concussion? A controlled study in 126 games. Br J Sports Med. 2019;55(4):220–25.
White AJ, Piggin J, Batten J, Turner G, Pearce A, Bullingham R, et al. Ethics and injury risk in World Rugby and England Rugby tackle-height trial. Br J Sports Med. 2020;bjsports-2020-101983. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2020-101983.
Emery CA, Hagel B, Decloe M, Carly M. Risk factors for injury and severe injury in youth ice hockey: a systematic review of the literature. Injury Prev. 2010;16(2):113–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/ip.2009.022764.
Krolikowski MP, Black AM, Palacios-Derflingher L, Blake TA, Schneider KJ, Emery CA. The effect of the “zero tolerance for head contact” rule change on the risk of concussions in youth ice hockey players. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(2):468–73. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546516669701.
Waltzman D, Sarmiento K. What the research says about concussion risk factors and prevention strategies for youth sports: a scoping review of six commonly played sports. J Saf Res. 2019;68:157–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsr.2018.11.005.
Collins FE, Fields S, Kluchurosky L, Rohrkemper MK, Comstock D, et al. Neck Strength: A Protective Factor Reducing Risk for Concussion in High School Sports. J Prim Prev. 2014;35:309–19.
Emery CA, Kang J, Schneider KJ, Meeuwisse WH. Risk of injury and concussion associated with team performance and penalty minutes in competitive youth ice hockey. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45(16):1289–93. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2011-090538.
McGuine TA, Hetzel S, McCrea M, Brooks MA. Protective equipment and player characteristics associated with the incidence of sport-related concussion in high school football players: a multifactorial prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(10):2470–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546514541926.
Schmidt JD, Guskiewicz KM, Blackburn JT, Mihalik JP, Siegmund GP, Marshall SW. The influence of cervical muscle characteristics on head impact biomechanics in football. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(9):2056–66. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546514536685.
Abrahams S, McFie S, Patricios J, Posthumus M, September AV. Risk factors for sports concussion: An evidence-based systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2013;48:91–7.
Broshek DK, De Marco AP, Freeman JR. A review of post-concussion syndrome and psychological factors associated with concussion. Brain Inj. 2015;29(2):228–37. https://doi.org/10.3109/02699052.2014.974674.
Mihalik JP, Guskiewicz KM, Marshall SW, Greenwald RM, Blackburn JT, Cantu RC. Does Cervical Muscle Strength in Youth Ice Hockey Players Affect Head Impact Biomechanics? Clin Sports Med. 2011;21(5):416–21. https://doi.org/10.1097/JSM.0B013E31822C8A5C.
Tierney RT, Higgins M, Caswell SV, Brady J, McHardy K, Driban JB, Darvish K. Sex differences in head acceleration during heading while wearing soccer headgear. J Athl Train. 2008;43(6):578–84. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-43.6.578.
Viano DC, Casson IR, Pellman EJ. Concussion in professional football: Biomechanics of the struck player - Part 14. Neurosurgery. 2007;61(2):313–28. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000279969.02685.D0.
Eckner JT, Goshtasbi A, Curtis K, Kapshai A, Myyra E, Franco LM, Favre M, Jacobson JA, Ashton-Miller JA. Feasibility and effect of cervical resistance training on head kinematics in youth athletes. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;97(4):292–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/PHM.0000000000000843.
Gutierrez GM, Conte C, Lightbourne K. The relationship between impact force, neck strength, and neurocognitive performance in soccer heading in adolescent females. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2014;26(1):33–40. https://doi.org/10.1123/pes.2013-0102.
Silvers-Granelli HJ, Bizzini M, Arundale A, Mandelbaum BR, Snyder-Mackler L. Does the FIFA 11+ Injury Prevention Program Reduce the Incidence of ACL Injury in Male Soccer Players? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(10):2447–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-017-5342-5.
Sugimoto D, Myer GD, Micheli LJ, Hewett TE. ABCs of evidence-based anterior cruciate ligament injury prevention strategies in female athletes. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. 2015;3(1):43–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40141-014-0076-8.
Finch C. A new framework for research leading to sports injury prevention. J Sci Med Sport. 2006;9(1-2):3–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2006.02.009.
Steffen K, Emery CA, Romiti M, Kang J, Bizzini M, Dvorak J, Finch CF, Meeuwisse WH. High adherence to a neuromuscular injury prevention programme (FIFA 11+) improves functional balance and reduces injury risk in Canadian youth female football players: A cluster randomised trial. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(12):794–802. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2012-091886.
Barengo NC, Meneses-Echávez JF, Ramírez-Vélez R, Cohen DD, Tovar G, Enrique Correa Bautista J. The impact of the fifa 11+ training program on injury prevention in football players: A systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;11(11):11986–2000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph111111986.
Leddy JJ, Haider MN, Hinds AL, Darling S, Willer BS. A preliminary study of the effect of early aerobic exercise treatment for sport-related concussion in males. Clin J Sport Med. 2019;29(5):353–60. https://doi.org/10.1097/JSM.0000000000000663.
Langevin P, FrÉMont P, Fait P, DubÉ M-O, Bertrand-Charette M, Roy J-S. Aerobic exercise for sport-related concussion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020;52(12):2491–9. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000002402.
Arksey H, O'Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O'Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5(1):69. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-5-69.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O'Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, Moher D, Peters MDJ, Horsley T, Weeks L, Hempel S, Akl EA, Chang C, McGowan J, Stewart L, Hartling L, Aldcroft A, Wilson MG, Garritty C, Lewin S, Godfrey CM, Macdonald MT, Langlois EV, Soares-Weiser K, Moriarty J, Clifford T, Tunçalp Ö, Straus SE. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73. https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850.
Attwood MJ, Roberts SP, Trewartha G, England ME, Stokes KA. Efficacy of a movement control injury prevention programme in adult men's community rugby union: a cluster randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(6):368–74. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2017-098005.
Becker S, Berger J, Backfisch M, Ludwig O, Kelm J, Fröhlich M. Effects of a 6-week strength training of the neck flexors and extensors on the head acceleration during headers in soccer. J Sports Sci Med. 2019;18(4):729–37.
Caccese JB, Buckley TA, Tierney RT, Arbogast KB, Rose WC, Glutting JJ, Kaminski TW. Head and neck size and neck strength predict linear and rotational acceleration during purposeful soccer heading. Sports Biomech. 2018;17(4):462–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/14763141.2017.1360385.
Eckersley CP, Nightingale RW, Luck JF, Bass CR. The role of cervical muscles in mitigating concussion. J Sci Med Sport. 2019;22(6):667–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2019.01.009.
Eckner JT, Oh YK, Joshi MS, Richardson JK, Ashton-Miller JA. Effect of neck muscle strength and anticipatory cervical muscle activation on the kinematic response of the head to impulsive loads. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(3):566–76.
Hislop M, Stokes K, Williams S, Mckay CD, England M, Kemp S, et al. Reducing musculoskeletal injury and concussion risk in schoolboy rugby players with a pre-activity movement control exercise programme: A cluster randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(15):1140–6. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2016-097434.
Lisman P, Sigorile J, Del Rossi G, Asfour S, Eltoukhy M, Stambolian D, et al. Investigation of the Effects of Cervical Strength Training on Neck Strength, EMG, and Head Kinematics during a Football Tackle. Int J Sports Sci Eng. 2012;6(3):131–40.
Mansell J, Tierney RT, Sitler M, Swanik K, Stearne D. Resistance training and head-neck segment dynamic stabilization in male and female collegiate soccer players. J Athl Train. 2005;40(4):310–9.
Hislop M, Stokes K, Williams S, Mckay CD, England M, Kemp S, et al. The efficacy of a movement control exercise programme to reduce injuries in youth rugby: a cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2016;2(1):e000043. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjsem-2015-000043.
Sandmo SB, Andersen TE, Koerte IK, Bahr R. Head impact exposure in youth football-Are current interventions hitting the target? Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020;30(1):193–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13562.
White AJ, Batten J, Kirkwood G, Anderson E, Pollock AM. ‘Pre-activity movement control exercise programme to prevent injuries in youth rugby’: some concerns. Br J Sports Med. 2018; bjsports-2018-099051:525–6.
Harries SK, Lubans DR, Callister R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of linear and undulating periodized resistance training programs on muscular strength. J Strength Conditioning Res. 2015;29(4):1113–25. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000000712.
Dempsey AR, Fairchild TJ, Appleby BB. The relationship between neck strength and head accelerations in a rugby tackle. Poitiers: 33rd International Conference on Biomechanics in Sports; 2015.
Bartolomei S, Hoffman JR, Merni F, Stout JR. A comparison of traditional and block periodized strength training programs in trained athletes. J Strength Conditioning Res. 2014;28(4):990–7. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000000366.
Myers T. Fascial fitness: Training in the neuromyofascial web. IDEA Fitness J. 2011;8(4):36–43.
Adstrum S, Hedley G, Schleip R, Stecco C, Yucesoy CA. Defining the fascial system. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2017;21(1):173–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbmt.2016.11.003.
Levin S, de Solorzano SL, Scarr G. The significance of closed kinematic chains to biological movement and dynamic stability. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2017;21(3):664–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbmt.2017.03.012.
Geary K, Green BS, Delahunt E. Effects of neck strength training on isometric neck strength in rugby union players. Clin J Sport Med. 2014;24(6):502–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/JSM.0000000000000071.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JP study design; interpretation of data; preparation of manuscript. SC study design; interpretation of data; preparation of manuscript. DG study design; data acquisition; interpretation of data; preparation of manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The author, Jon Patricios, is a board member of the Concussion in Sport group (CISG) and sports concussion advisor to the South African Rugby Union; both positions are unpaid.
The authors, Daniel Garnett and Saul Cobbing, declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
Appendix A.
Additional file 2.
Appendix B.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Garnett, D., Patricios, J. & Cobbing, S. Physical Conditioning Strategies for the Prevention of Concussion in Sport: a Scoping Review. Sports Med - Open 7, 31 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40798-021-00312-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40798-021-00312-y