Abstract
Background
Pectus excavatum is a common thoracic deformity that can be encountered during thoracoscopic esophagectomy. Here, we report two cases of esophageal cancer complicated by pectus excavatum that were treated with thoracoscopic esophagectomy with the patients in the prone position.
Case presentation
The first patient was a 64-year-old male diagnosed with esophageal cancer (cT3N0M0, Haller index 8.5) and underwent radical thoracoscopic esophagectomy in the prone position following neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The second patient was a 67-year-old male diagnosed with esophageal cancer (cT1bN0M0, Haller index 4.3), and the same procedure was performed in this patient. In cases of patients with a high Haller index, where securing the surgical field is difficult, preoperative computed tomography in the prone position can help surgeons to understand the mediastinal field of view and is safe.
Conclusions
Radical thoracoscopic esophagectomy in the prone position may be a surgical option in patients with pectus excavatum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Background
According to a nationwide survey by the Japanese association for thoracic surgery in 2017, more than 60% of esophagectomies in Japan have been performed thoracoscopically and/or laparoscopically [1]. Pectus excavatum (PE) is the most common thoracic deformity, with a prevalence of 0.1–0.2% in the general population [2]. Thus, it can be potentially encountered during esophagectomy. When we encounter such complicated case, the narrow working space and operative visual field in the mediastinum makes it difficult to perform intrathoracic surgery. There have been only a few reports on thoracoscopic esophagectomy in patients with PE, which was performed in the left lateral decubitus position [3, 4]. Herein, we report the first two cases of esophageal cancer complicated by PE that were treated with thoracoscopic esophagectomy in the prone position.
Case presentation
Patient 1
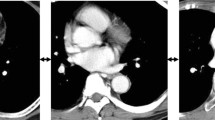
A 64-year-old Asian male was diagnosed with esophageal cancer during a routine medical checkup and was referred to our hospital for further treatment. Endoscopy revealed an elevated tumor with a flat lesion, 33–38 cm from the upper incisors (Fig. 1a, b); a biopsy revealed that it was a squamous cell carcinoma. Upon physical examination, the patient was found to have a significant PE. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) revealed a hypovascular lesion in the middle esophagus and PE (Fig. 1c). The Haller index (Fig. 1d), which is defined as the distance of the inner rib cage divided by the distance between the sternal notch and the vertebrae [5], was 8.5. The final preoperative diagnosis was a cT3N0M0 stage II squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus, according to the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) TNM classification (version 8) (used for all subsequent cancer classifications). Two courses of fluorouracil (800 mg/m2, 24 h continuous intravenous infusion on days 1–5), cisplatin (80 mg/m2, 2 h intravenous infusion on day 1), and docetaxel (30 mg/m2, 1 h intravenous infusion on days 1 and 15) were administered as neoadjuvant chemotherapy which is more intensive regimen [6, 7], instead of the Japanese standard neoadjuvant regimen (fluorouracil and cisplatin). Regarding PE treatment, the patient had no clinical symptoms, such as chest pain or dyspnea; therefore, only esophagectomy was performed after a respiratory surgeon was consulted. Radical thoracoscopic esophagectomy with three-field lymph node dissection was performed on the patient in the prone position. The patient was placed in the left semiprone position during the procedure. All procedures were performed in the prone position by rotating the surgical table. Three 12-mm ports were inserted into the fifth and seventh intercostal spaces on the posterior axillary line and the ninth intercostal space on the scapular angle line, and two 5-mm ports were inserted in the third and eighth intercostal space behind the midaxillary line. The endoscope was usually inserted through the ninth intercostal space. There were no special arrangements associated with the port settings compared to the settings during a normal esophagectomy. A 30° 10-mm videoscope was used and artificial pneumothorax using CO2 insufflation was maintained at 6 mmHg. The operative field visibility was not inferior to that of a usual esophagectomy in the upper and middle mediastinum; however, the lower mediastinum was narrow because of PE (Fig. 2a, d). The operation was difficult, especially lymph node dissection along the left pleura. An additional movie file shows this in more detail [see Additional file 1]. After esophagectomy, a gastric conduit was created laparoscopically, pulled up through the posterior mediastinal route, and the cervical esophagogastric anastomosis was then performed. The operating time was 457 min, and the estimated blood loss was 121 g. Pathological staging indicated stage IB (pT2, pN0, cM0). The postoperative course was uneventful, and the patient was discharged on postoperative day 13. The patient survived without recurrence for over 24 months postoperatively.
Patient 1. a Endoscopic findings. An elevated tumor with flat mucosal erosion was detected 33–38 cm from the upper incisors and suspected muscle invasion. b Narrow band imaging. c Contrast-enhanced CT reveals a hypovascular mass lesion in the middle esophagus and pectus excavatum. The Haller index score was 8.5. d Schema of the Haller index
Thoracoscopic intraoperative findings of Patient 1. a Top-down visual field at the start of surgery. b Bottom-up visual field and the posterior mediastinum was found to be narrow because of pectus excavatum. V Vertebra, PL pulmonary ligament, RIPV right inferior pulmonary vein, E esophagus, Ao aorta
Patient 2
A 67-year-old Asian man was diagnosed with esophageal cancer during an annual routine medical checkup. His medical history included anti-phospholipid antibody syndrome with regular use of 2.5 mg of warfarin. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy showed a widespread flat lesion in the middle esophagus, 35–40 cm from the upper incisors (Fig. 3a, b), and biopsy indicated moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Contrast-enhanced CT could not detect the main tumor, but revealed PE with a Haller index of 4.3 (Fig. 4a–d). A CT scan in the prone position was also performed (Fig. 4e–h). However, the patient had no clinical symptoms associated with PE. The preoperative diagnosis was stage I squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus (cT1b, cN0, cM0). Using Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine (DICOM) data in the spine position, three-dimensional (3D) images were created using volume analysis software, SYNAPSE VINCENT™ (Fujifilm Medical, Tokyo, Japan) for preoperative simulation (Fig. 5a, b). Using these, we assessed that the mediastinum of this patient was relatively wider than that of patient 1; therefore, only esophagectomy was performed. Radical thoracoscopic esophagectomy, with two-field lymph node dissection, was performed with the patient in the prone position. The operative field visibility was better than that obtained in patient 1 (Fig. 6a, b). The operating time was 413 min, and the estimated blood loss was 34 g. The pathological staging indicated stage IB (pT1b, pN0, cM0). The postoperative course was uneventful, and the patient was discharged on postoperative day 17. The patient was in good condition at the 18-month follow-up visit.
Discussion and conclusion
In radical esophagectomy, especially in minimally invasive esophagectomy (MIE), the narrow mediastinum, a typical feature of PE, can increase the difficulty of surgery [8]. The Haller index score is widely used to evaluate the severity of PE; the normal range is from 2.5 to 2.7, whereas a value of 3.25 or higher is indicative of a need for surgery. The Nuss procedure [9], a treatment method for PE in which a metal intrathoracic bar is placed behind the sternum under a thoracoscope, is currently widely used in adults and has low complication rates and short hospital stays. However, a surgery is required to remove the metal bar 2–3 years later.
To the best of our knowledge, there are only two previous reports of patients with PE who have undergone thoracoscopic esophagectomy (Table 1). However, both cases were performed with the patients in the left lateral decubitus position. While Sato et al. reported the usefulness of video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery in a case of a patient with Haller index of 4.83 [3], Hatoyama et al. reported a case of a patient with a severely narrow mediastinum (Haller index, 9.9) and recommended a simultaneous PE repair by Nuss procedure [4].
MIE in the prone position is generally considered to provide a better surgical view of the mid-lower mediastinum than that in the left lateral position. In our study, the patients had no clinical symptoms associated with PE; therefore, we decided not to perform PE repair simultaneously. The most important factor that contributed to the difficulty of the surgery, especially in Case 1, was the relatively high Haller index score, because it was difficult to maintain a good surgical view. Furthermore, patients with bulky tumors or apparent metastatic lymph nodes with a narrow mediastinum are more difficult to operate and may require simultaneous PE repair. 3D-CT evaluation and a CT in the prone position before surgery, as used in Case 2, can help predict if the mediastinal field of view could be secured; the surgery can then be performed with relative ease.
During perioperative management, MIE in the prone position is associated with some disadvantages during emergent thoracotomy. If an accident such as uncontrollable intraoperative bleeding occurs, the left lateral decubitus and prone hybrid position enables us to immediately convert from thoracoscopic to open surgery [10]. Regarding reconstruction, it is necessary to use a narrowed (3–3.5 cm) gastric conduit and to raise it slightly to the right of the midline in order to avoid cardiopulmonary compression during posterior mediastinal route reconstruction. In cases of simultaneous PE repair, pain control is important as a postoperative management that should be noted. In addition, infectious complications after the Nuss procedure are potentially devastating [11]. From our experience, patients who are asymptomatic preoperatively do not have many problems after surgery. However, the posterior mediastinal route reconstruction may cause tachyarrhythmia due to retraction of the left atrium by the reconstructed organ.
In previous large-scale reports of cases treated with the Nuss procedure, the mean Haller index was 5.15 ± 2.32 (mean ± SD) [9]. Therefore, based on previous case reports [3, 4] and our experience, in cases with a Haller index is 5 or higher, simultaneous PE repair may be indicated. However, performing MIE in the prone position cannot be recommended after PE repair because of sternal instability. In advanced cases of PE, as reported by Hatoyama et al., left lateral decubitus esophagectomy, which allows simultaneous PE repair, may be preferred [4]. However, in cases with a relatively low Haller index score (< 5), specifically in cases with large mediastinal space as confirmed by preoperative CT in the prone position (as in Case 2), a good surgical view can be secured in the prone position without simultaneous PE repair.
A trans-mediastinal or trans-hiatal approach [12] can be considered in similar cases. However, regarding reconstruction, when using any kind of approach to esophagectomies, surgeons should note that the anterior thoracic and posterior sternal routes are considered unfavorable with PE repair because of technical difficulty. To avoid injuring the gastric conduit, a posterior mediastinal route must be selected. The posterior sternal route may also be an option for patients with relatively mild (the Haller index < 5) and asymptomatic PE who do not need a simultaneous repair.
In conclusion, radical thoracoscopic esophagectomy in the prone position can be explored as a surgical option if PE repair is not required. The indications for simultaneous PE repair are still controversial. Further case accumulations are required. Furthermore, preoperative imaging in the prone position was found to be a help while determining the appropriate surgical procedure.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article, since datasets were neither generated nor analyzed for the case report.
Abbreviations
- PE:
-
Pectus excavatum
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- UICC:
-
Union for International Cancer Control
- DICOM:
-
Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine
- MIE:
-
Minimally invasive esophagectomy
References
Committee for Scientific Affairs, The Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery, Shimizu H, Okada M, Tangoku A, Doki Y, et al. Thoracic and cardiovascular surgeries in Japan during 2017: annual report by the Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020;68:414–49.
Shamberger RC. Congenital chest wall deformities. Curr Probl Surg. 1996;33:469–542.
Sato S, Nagai E, Hazama H, Taki Y, Takahashi M, Kyoden Y, et al. Video-assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy in the left lateral decubitus position in an esophageal cancer patient with pectus excavatum. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2015;8:333–6.
Hatoyama K, Taniyama Y, Sakurai T, Sato C, Okamoto H, Onodera Y, et al. Esophageal cancer with severe funnel chest treated by simultaneous funnel chest surgery and thoracoscopic esophagectomy: a case report. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:1212.
Haller JA Jr, Kramer SS, Lietman SA. Use of CT scans in selection of patients for pectus excavatum surgery: a preliminary report. J Pediatr Surg. 1987;22:904–6.
Hironaka S, Tsubosa Y, Mizusawa J, Kii T, Kato K, Tsushima T, et al. Phase I/II trial of 2-weekly docetaxel combined with cisplatin plus fluorouracil in metastatic esophageal cancer (JCOG0807). Cancer Sci. 2014;105:1189–95.
Kataoka K, Tsushima T, Mizusawa J, Hironaka S, Tsubosa Y, Kii T, Japan Esophageal Oncology Group/Japan Clinical Oncology. A randomized controlled Phase III trial comparing 2-weekly docetaxel combined with cisplatin plus fluorouracil (2-weekly DCF) with cisplatin plus fluorouracil (CF) in patients with metastatic or recurrent esophageal cancer: rationale, design and methods of Japan Clinical Oncology Group study JCOG1314 (MIRACLE study). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2015;45:494–8.
Okamura A, Watanabe M, Mine S, Nishida K, Imamura Y, Kurogochi T, et al. Factors influencing difficulty of the thoracic procedure in minimally invasive esophagectomy. Surg Endosc. 2016;30:4279–85.
Kelly RE, Goretsky MJ, Obermeyer R, Kuhn MA, Redlinger R, Haney TS, et al. Twenty-one years of experience with minimally invasive repair of pectus excavatum by the Nuss procedure in 1215 patients. Ann Surg. 2010;252:1072–81.
Kawakubo H, Takeuchi H, Kitagawa Y. Current status and future perspectives on minimally invasive esophagectomy. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013;46:241–8.
Calkins CM, Shew SB, Sharp RJ, Ostlie DJ, Yoder SM, Gittes GK, et al. Management of postoperative infections after the minimally invasive pectus excavatum repair. J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40:1004–8.
Fujiwara H, Shiozaki A, Konishi H, Kosuga T, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Okamoto K, et al. Single-port mediastinoscopic lymphadenectomy along the left recurrent laryngeal nerve. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;100:1115–7.
Acknowledgments
We thank Wiley Editing Services (https://wileyeditingservices.com/en/) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TT drafted the manuscript, and MK supervised the writing of the manuscript. TT performed the operations. TT, YK, and YS performed perioperative management of the patients. The manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and there are no other persons who have satisfied the criteria for authorship, but are not listed. We further confirm that the order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written consents were obtained from the patients for publication of this case report and the accompanying images.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Summary video of the surgery in Patient 1. Thoracoscopic video of mid-lower mediastinal area in the prone position.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsukada, T., Kitano, Y., Sugimoto, Y. et al. Thoracoscopic esophagectomy in the prone position for esophageal cancer patients with pectus excavatum: a report of two cases. surg case rep 7, 113 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-021-01193-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-021-01193-9