Abstract
Background
Leaf Area Index (LAI) is an important parameter used in monitoring and modeling of forest ecosystems. The aim of this study was to evaluate performance of the artificial neural network (ANN) models to predict the LAI by comparing the regression analysis models as the classical method in these pure and even-aged Crimean pine forest stands.
Methods
One hundred eight temporary sample plots were collected from Crimean pine forest stands to estimate stand parameters. Each sample plot was imaged with hemispherical photographs to detect the LAI. The partial correlation analysis was used to assess the relationships between the stand LAI values and stand parameters, and the multivariate linear regression analysis was used to predict the LAI from stand parameters. Different artificial neural network models comprising different number of neuron and transfer functions were trained and used to predict the LAI of forest stands.
Results
The correlation coefficients between LAI and stand parameters (stand number of trees, basal area, the quadratic mean diameter, stand density and stand age) were significant at the level of 0.01. The stand age, number of trees, site index, and basal area were independent parameters in the most successful regression model predicted LAI values using stand parameters (R2adj. = 0.5431). As corresponding method to predict the interactions between the stand LAI values and stand parameters, the neural network architecture based on the RBF 4–19-1 with Gaussian activation function in hidden layer and the identity activation function in output layer performed better in predicting LAI (SSE (12.1040), MSE (0.1223), RMSE (0.3497), AIC (0.1040), BIC (− 77.7310) and R2 (0.6392)) compared to the other studied techniques.
Conclusion
The ANN outperformed the multivariate regression techniques in predicting LAI from stand parameters. The ANN models, developed in this study, may aid in making forest management planning in study forest stands.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Leaf Area Index (LAI) is one of the most important parameters of tree foliage, mediating many physical and biological processes in forest ecosystems (Sidabras and Augustaitis 2015). For example, processes such as evapotranspiration, transpiration, and photosynthesis are a function of LAI (Wulder et al. 1998). It is a critical parameter needed in developing environmental and ecological models such as growth and yield models, soil-water balance models, energy balance models, and climate change models (Peng et al. 2002; Wang et al. 2011; Mason et al. 2012). It is used in a large variety of studies including global change, nutrient cycling, and carbon and hydrology (Vilà et al. 2003; Liang et al. 2005; Chianucci et al. 2015).
The LAI, is a dynamic parameter, which depends on management practices, seasonality, site conditions, developmental stage, and species composition. Number of methods have been developed to determine LAI (Jonckheere et al. 2004). LAI can be predicted by direct and indirect methods (Chen et al. 1991). Direct methods are precise but tremendously hard and time-consuming and more expensive than the indirect methods; they require tree falling in some cases (Weiss et al. 2004), and they are impractical and dangerous in hardly accessed localities (Macfarlane et al. 2007). Therefore, these disadvantages of direct methods resulted in indirect measurements of LAI by ground based optical instruments to gain importance in recent decades (Chianucci et al. 2015). Indirect methods have been utilized since 1960s in forest ecology and management (Chianucci and Cutini 2012). Hemispherical photography is a valuable indirect method for estimating LAI (Jonckheere et al. 2004; Sidabras and Augustaitis 2015) beside it’s used for evaluating canopy features (Hale and Edwards 2002).
Hemispherical photographs have been widely used for determination of LAI in forest ecology and management studies (e.g. Chen et al. 1991; Walter and Torquebiau 2000; Frazer et al. 2001; Hale and Edwards 2002; Leblanc et al. 2005; Macfarlane et al. 2007; Hu and Zhu 2009; Mason et al. 2012). Many studies showed that there are significant associations between LAI and forest productivity (Vose and Allen 1988), net primary productivity (Gholz 1982), evapotranspiration (Swank et al. 1988), water balance (Grier and Running 1977), and spatiotemporal variations in forest ecosystems (Chianucci and Cutini 2012). There are also some other studies analyzing the relationships between LAI and forest stand parameters such as biomass (Nowak 1996; Madugundu et al. 2008; Jagodzinski and Kalucka 2008), density (Sidabras and Augustaitis 2015), canopy closure (Jeleska 2004), diameter at breast height (Turner et al. 2000; Arias et al. 2007; Khosravi et al. 2012; Sidabras and Augustaitis 2015), basal area (Khosravi et al. 2012), mean stand height (Khosravi et al. 2012; Sidabras and Augustaitis 2015), stand volume (Sidabras and Augustaitis 2015), and stand age (Jagodzinski and Kalucka 2008; Pokorny and Stojnic 2012).
The aim of this study was to evaluate the capability of usability of the artificial neural network models for predicting the LAI by comparing the regression analysis models as the classical method in these pure and even-aged Crimean pine forest stands. The LAI was determined by operating an indirect method depend on the hemispherical photography. Forest stand parameters related to each sample plot were estimated by examining the inventory data obtained from forest inventory. The partial correlation analysis was firstly used to examine the associations between the stand LAI values and stand parameters. To model the relationships between LAI and forest stand parameters such as the number of trees of stand, stand age, site index, quadratic mean diameter, density index, stand basal area, the multivariate linear regression as the classical prediction technique and the artificial neural network models being as artificial intelligence model were used in this study.
Methods
Study site
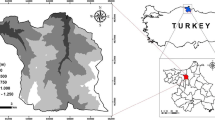
In this study, Yenice Forest Management Unit, located in the middle-north region of Turkey (Fig. 1), was selected as case study area. The study area is mostly mountainous. The climate is mainly Black Sea type. Diurnal temperature differences are high. The annual average precipitation is 474 mm. The forests in the study area are mainly coniferous, comprising approximately 1700 ha of pure even-aged Crimean pine, Pinus nigra subsp. pallasiana (Lamb.) Holmboe, forest stands.
Measurements
A total of 108 temporary sample plots were taken, considering different site classes, crown closures, and stand development stages in pure Crimean pine forest stands. Ground measurement of the sample plots was carried out in August 2014. The position of each sample plot was first determined by a hand type of a satellite-based navigation system and a global positioning system (GPS). The sizes of the sample plots were 400, 600 and 800 m2 depending on the stand crown closures. Within each sample plot, all the trees with diameters ≥8 cm were identified and measured. Tree ages in 4–5 trees near the medium diameter in each sample plots were measured by an increment borer, and the mean was calculated to determine stand age (ages). Stand age and height (in meters) were calculated from number of trees determined according to 100 trees method in hectare. Stand density, stand basal area (m2·ha− 1), stand age (yr), site index (m) and height (m), number of trees and quadratic mean diameter (cm) of each sample plots were used for determination of LAI. The summary statistics, such as the range, mean, standard deviation, variance, minimum, and maximum for the LAI and stand variables are given in Table 1.
LAI was predicted by the Hemiview system at 108 temporary sample plots of Crimean pine forest stands. Hemispherical photographs were taken by a fisheye lens mounted on a color film-mounted Cannon (EOS 50D) camera with color film. The center was set to the peak of canopy, and photographs were taken at the correct automatic pose. The camera was mounted on a tripod at 1.2–1.5 m height to avoid interference with forest soil and understory vegetation. The LAI values were quantified using the photographs, taken at the middle of each sample plot, with the Hemiview software program.
Partial correlation analysis
The partial correlation analysis (PCA) was used to evaluate the relationships between the stand LAI and stand parameters. The PCA provides the correlations between two variables by controlling other variables that have important effect on the relation among these two variables. The PCA yields the partial correlation coefficients, which depict spurious and hidden correlations, including the effects of other variables. The partial correlation coefficients were obtained using PROC CORR procedures of the SAS/ETS v9 software (SAS Institute Inc. 2012).
Multivariate linear regression
While the partial correlation analysis explains individual relationships between the LAI and some stand parameters, the multivariate linear regression predicts LAI exploiting the relationships between LAI and some stand parameters such as the stand number of trees, stand age, site index, quadratic mean diameter, density index, basal area. The Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) technique was used to obtain the parameters and other statistics of the multivariate linear regression model. The parameters were predicted using PROC REG and RSQUARE procedure, available in SAS/ETS® 9 software (SAS Institute Inc. 2012). The stepwise variable selection regression technique (SVSRT) was used to select the stand variables, which contribute LAI predictions significantly (p < 0.05). The SVSRT, a modification of the forward-selection technique, is based on the following procedure: a variable is introduced into the model and significance of its contribution in predicting the dependent variable is controlled by the partial F-test. If the variable has a significant contribution, it’s included in the model, otherwise it’s released. The SVSRT was conducted across complete fitting stages. In this study, the following linear relationship was assumed:
where LAI is the leaf area index, X1,…, Xn are parameter vectors (independent variables) corresponding to stand parameter values, β1,…, βn represent model coefficients and ε is the additive error term.
Artificial neural network modeling
The artificial neural network (ANN) technique was used to predict the stand LAI. The ANN technique includes training, verifying, and testing stages using data-subsets, which are constituted by randomly selected data values from the dataset. We partitioned total sample plots into training (75% of all data), verification (15% of all data) and testing (the remaining 10% of all data) subsets (Fausett 1994). In these network models, input variables were best predictive stand parameters, in which these independent variables were selected by the stepwise variable selection technique in regression analysis, and target variable was the stand LAI value obtained from the terrestrial measurements. Two artificial neural network model categories including the Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and the Radial Basis Function (RBF) architectures were trained by using STATISTICA® software (Statsoft Inc, 2007). A total of 800 in MLP and 50 trained networks in RBF were trained and used to obtain the LAI predictions. In ANNs training process with MLP, the number of neurons of the input layer ranged from 1 to 50 alternatives, four activation functions including the identity, logistic, tanh and exponential functions in hidden layer, correspondingly these four activation functions were used in output layer. In RBF, the number of neurons of the input layer ranged from 1 to 50 neuron alternatives and the hidden layer had always the activation function as being on isotropic Gaussian basis and identity function was used in output layer, in which the STATISTICA software does not present any activation function alternatives for RBF. Thus, the differentiation in number of training alternatives for MLP and RBF occurred for training the ANN models, because the MLP included sixteen alternatives (four activation functions in hidden layer × four activation functions in output layer) and the RBF comprised one activation function alternative (the isotropic Gaussian basis in hidden layer and the identity function in output layer). Because of the 50 neurons of the input layer for MLP and RBF, a total of 800 network alternatives in MLP (16 × 50) and a total of 50 network alternatives in RBF (50 × 1) were trained to have the predictions of the ANN models.
In MLP, feed-forward neural network architecture include input, hidden and output layers with a bias term; the training algorithm is Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno (BFGS), which is a robust training algorithm with very fast convergence with the Hessian matrix. After training these network models, five best predictive networks for MLP and RBF for the stand LAI values presented, including some evaluations of the magnitudes and distributions of models’ residual in the STATISTICA software. From these network models, six goodness-of-fit statistics, including sum of squared errors (SSE), Akaike’s information criterion (AIC), Bayesian information criterion (BIC), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Squared Error (MSE) and Adjusted Coefficient of Determination (R2adj), were calculated to evaluate and compare the performance of the predictive network models. The formulae for these statistical values are provided below (2 to 7).
where, LAIi represents the LAI values; \( \widehat{{\mathrm{LAI}}_i} \) represents the predicted stand LAI values, \( {\overline{\mathrm{LAI}}}_i \) represents average LAI value, n represents the number of data, L represents maximum value of the log likelihood function and p represents the number of parameters within the model.
The graphs including the residuals against predicted LAI values and the predicted LAI values against the observed values were presented to compare the predictions obtained by the predictive regression model, MLP model, and RBF model. Independent stand parameters, contributing the prediction of LAI significantly at the level of 0.05, were determined by SVSRT. The LAI predictions for regression model were acquired by using the best predictive regression model based on the included independent stand parameters that were selected by the stepwise variable selection regression technique in SAS software, in which are significant (p < 0.05) in predictions. The LAI predictions for ANN models based on the MLP and RBF prediction technique that included the best predictive stand parameters selected by the regression technique as input variables were achieved by using STATISTICA neural network simulation module.
Results
The correlation coefficients for the relationships between parameters of number of trees in stands, the stand density, the basal area, the stand age, and the quadratic mean diameter with the LAI values were significant at the 0.01 level (Table 2). The number of trees of stands (r = 0.564) showed the highest correlation with the LAI values. Similarly, stand density (r = 0.512) and stand basal area (r = 0.371) were positively correlated with the LAI. However, the quadratic mean diameter (r = − 0.294) and stand age (r = − 0.294) were negatively correlated with the LAI. The correlation coefficients for relationships between the quadratic mean height and site index with the LAI values were not significant at the level of 0.05. Figure 2 shows linear relationships between LAI and the stand parameters.
After verifying linear relationships between LAI and stand parameters by linear correlation and regression techniques, the multivariate linear regression models were developed to predict the LAI as a function of the selected stand parameters (stand basal area, site index, number of trees and stand age), which are significant at the 0.05 level (Table 3). In this regression model for LAI values, the F statistics and its coefficients were significant at a probability level of 95% (p < 0.05). In Table 3, the standardized coefficients for independent variables were presented to display the contribution of stand parameters to the explained variance by the regression model. The number of trees has the highest contribution values (42.09%) of stand parameters to the explained variance, and other stand parameters such as site index (23.01%), age (19.39%) and basal area (15.51%) were ranked by the contribution values for the prediction of the LAI values.
Values of goodness-of-fit statistics of SSE, AIC, BIC, RMSE, MSE and \( {R}_{\mathrm{adj}}^2 \) for the regression equation and five best predictive networks of MLP and RBF are presented in Table 4. SSE was between 12.1040 and 15.3269, MSE between 0.1223 and 0.1548, RMSE was between 0.3497 and 0.3935, AIC was between 10.44 and 0.2690, and BIC was between 77.7310 and 64.5107, and Radj2 between 0.4864 and 0.6392 in all fitting techniques. These goodness-of-fit statistics show that the neural network architecture based on the RBF 4–19-1 with Gaussian activation function in hidden layer and the identity activation function in output layer showed better fitting ability with SSE (12.1040), MSE (0.1223), RMSE (0.3497), AIC (0.1040), BIC (− 77.7310) and R2 (0.6392) than the other studied ANN prediction techniques. Also, this best predictive artificial neural network models provided better results based on the SSE, AIC, BIC, RMSE, MSE and \( {R}_{\mathrm{adj}}^2 \) than multivariate linear regression model.
Figures 3, 4, and 5 show the residuals for predicted LAI-values (a) and the predicted and observed LAI-values (b). The LAI predictions were obtained from three prediction methods: (1) the multivariate regression analysis (Fig. 3), (2) the ANN technique based on the MLP 4–13-1 (Fig. 4), and (3) the ANN technique based on the RBF 4–19-1 (Fig. 5). These LAI prediction techniques presented casual trend of residual around zero and no important relations, suggesting that there is no serious failure of homoscedasticity, violations of the assumption of constant variance, in the LAI prediction of ANN models based on the RBF and MLP and the best predictive regression model.
Discussion
We studied the performance of the artificial neural network (ANN) models and compared them with classical regression models to predict leaf area index (LAI) in pure-even aged Crimean pine stands. The results showed that the ANN models outperformed the classical regression models in predicting LAI, which may be attributed to ability of the ANN models to describe complex and nonlinear relationships between various variables. The ANN models have been successfully used to predict several stand attributes, for example, Hasenauer et al. (2001); Diamantopoulou (2005); Özçelik et al. (2008); Diamantopolou and Milios (2010); Özçelik et al. (2010); Leite et al. (2011); Diamantopolou and Özçelik (2012); Özçelik et al. (2013); Ashraf et al. (2013) and Özçelik et al. (2017). This study presents better predictive leaf area index results with the ANN models than the ones with the regression models. This finding may be explained by the ability of the ANN model for predicting complex and nonlinear relationships between various variables, which it is provided that this capability of the ANN in many studies. This ability of the ANN models depends on modeling such complexity and nonlinearity that overlooked by the traditional statistical regression models by the architecture of an ANN by allowing highly correlated inputs to be used to enhance its modelling capability. Thus, ANN models are becoming a widespread prediction method, because of the unnecessary of some statistical assumptions that are important for accurately predicting regression models that may fit the observed data in nowadays.
In studies about modeling LAI from stand parameters, Kashian et al. (2005) reported a significant but weak relationship between LAI or BAI and stand density (r2 < 0.20) at stand ages characterized by canopy closure. DeRose et al. (2010) developed some nonlinear regression equations, which indicated that LAI was significantly related to relative density, site quality, and stand top height, and concluded that LAI increased nonlinearly with increasing relative density holding stand top height constant. Sidabras and Augustaitis (2015) found indirect relationships between LAI and stand mean diameter and height in a multi-aged mixture of coniferous forest, while they found no significant relationships between LAI and stand sum square basal area. In the same study, the authors found a significant relationship between LAI and stand density and volume of the pure pine forest stands. Dantec et al. (2000) found that there were significant relationships between LAI and stand basal area and number of trees of stands. Özbayram et al. (2015) reported positive correlations between LAI and stand age, mean diameter, top height, green tree height, basal area, and litter in Turkish red pine stands, but negative correlation between LAI and stand age and mean diameter in black pine stands. The ANN models have been used for predicting LAI from remotely sensed data, for example, Bacour et al. (2006), Shoemaker and Cropper (2008), Verger et al. (2008), Omer et al. (2016), and Wang et al. (2017). Beyond these studies about the LAI predictions from the remote sensing data by the ANN models, the present study has underlined that the ANN models may be used alternatively to traditional regression techniques for predicting LAI predictions from terrestrial measurements such as some stand parameters.
The mechanisms underlying the relationships between LAI and the included stand parameters depend on the positive or negative effect of these stand parameters on the LAI. Particularly, the stand basal area, site index, and stand number of trees have positive effect, while the stand age has negative effect on the LAI. This positive effect of the stand basal area and number of trees on the LAI can be explained by the increase or crowding of trees in any forest stands, because increasing basal area and number of trees result in further trees in a forest stand and so increasing tree crown cover with further LAI values in these stands. In addition to stand parameters including the stand basal area and number of trees, the site index has a significantly positive effect on the LAI, since forest areas of high site quality with higher site index values are more favorable areas for growth of forest species, especially tree crown growth, and thus more LAI in these stands. However, the stand age showed a negative relationship with the LAI, since the number of trees decreases with increasing age due to age-related tree mortality and thus these decreases of stand number of tress result in less LAI values in forest stands. Khosravi et al. (2012) tried to determine the relations between LAI values and some stand parameters and found that there were moderate relationships (R2 = 0.36 for stand mean diameter, R2 = 0.36 for stand basal area, R2 = 0.45 for stand mean height) when the results obtained were evaluated. Some studies showed that LAI values decreased as the stand age increased (Sonohat et al. 2004; Homolova et al. 2007; Pokorny and Stojnic 2012). Bequet et al. (2012) also showed that the stand age was an important parameter in estimating stand LAI.
Among different ANN structures, the neural network architecture, based on the Radial Basis Function (RBF) architectures, showed greater performance in predicting LAI from stand parameters. These results may depend on the tree crown characteristics of a species growing in different regional and local forest conditions. Certain ANN models with different modeling architectures will provide better information for calibration response than other alternatives at various forest sites and for various tree species. Our results revealed that the use of hemispheric photography for LAI estimation in pure pine forest stands is rather appropriate. Because of time-consuming and labor-intensive nature of direct LAI determination methods, analysis of hemispherical photographs, which are fast, cheap and accurate can be successfully used to characterize forest canopy structure and to find relationships between LAI and forest stand parameters.
Conclusion
We evaluated the performance of ANN models for predicting LAI from stand parameters in pure-even-aged Crimean pine forests in Turkey. The ANN modeling proved useful in predicting LAI in study forests, suggesting that the ANN may be used in lieu of classical regression equations in cases the regression equations fails to perform adequately. However, weights of ANN models are specific to the study species and site conditions. Further studies should be conducted with different plant and site conditions to generalize the results across forest ecosystems. Especially, the ANN model provided better information for decision-making in management of forest resources, likely fulfilling the needs of field foresters to assess LAI as a measure of site potential when suitable site trees are not available in forest areas. The LAI predictions are reliable and accurate within the ecological ranges of the original data. However; these results may not be extrapolated outside the study area, as the relationships found in this study between LAI and stand parameters and these weights of ANN model are specific for this species and this study area.
Abbreviations
- AIC:
-
Akaike’s information criterion
- BA:
-
The basal area (m2·ha− 1)
- BFGS:
-
Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno
- BIC:
-
Bayesian information criterion
- Dq:
-
The quadradic mean diameter (cm)
- Hq:
-
The quadratic mean height (m)
- LAI:
-
Leaf Area Index
- MLP:
-
Multilayer Perceptron
- MSE:
-
Mean Squared Error
- N:
-
The number of trees of stands
- OLS:
-
Ordinary Least Squares
- R 2 adj :
-
Adjusted Coefficient of Determination
- RBF:
-
Radial Basis Function
- RMSE:
-
Root Mean Square Error
- SI100:
-
The site index calculated at base age of 100
- SSE:
-
Sum of squared errors
References
Arias D, Calvo-Alvarado J, Dohrenbusch A (2007) Calibration of LAI-2000 to estimate leaf area index (LAI) and assessment of its relationship with stand productivity in six native and introduced tree species in Costa Rica. Forest Ecol Manage 247:185–193
Ashraf MI, Zhao Z, Bourque A, MacLean DA, Meng F (2013) Integrating biophysical controls in forest growth and yield predictions generated with artificial intelligence technology. Can J For Res 43:1162–1171
Bacour C, Baret F, Béal D, Weiss M, Pavageau K (2006) Neural network estimation of LAI, fAPAR, fCover and LAI×cab, from top of canopy MERIS reflectance data: principles and validation. Remote Sens Environment 105:313–325
Bequet R, Kint V, Campioli M, Vansteenkiste D, Muys B, Ceulemans R (2012) Influence of stand, site and meteorological variables on the maximum leaf area index of beech, oak and scots pine. Eur J Forest Res 131(2):283–295
Chen JM, Black TA, Adams RS (1991) Evaluation of hemispherical photography for determining plant area index and geometry of a forest stand. Agric For Meteorol 56:129–143
Chianucci F, Cutini A (2012) Digital hemispherical photography for estimating forest canopy properties: current controversies and opportunities. iForest 5:290–295
Chianucci F, Macfarlane C, Pisek J, Cutini A, Casa R (2015) Estimation of foliage clumping from the LAI-2000 plant canopy analyzer: effect of view caps. Trees 29:355–366
Dantec VL, Dufrene E, Saugier B (2000) Interannual and spatial variation in maximum leaf area index of temperate deciduous stands. For Ecol Manag 134:71–81
DeRose RJ, Seymour RS (2010) Patterns of leaf area index during stand development in even-aged balsam fir - red spruce stands. Can J For Res 40(4):629–637
Diamantopoulou MJ (2005) Predicting fir trees stem diameters using artificial neural network models, southern forests. J South Afr Forest Assoc 205:39–44
Diamantopoulou MJ, Milios E (2010) Modelling total volume of dominant pine trees in reforestations via multivariate analysis and artificial neural network models. Biosyst Eng 105:306–315
Diamantopoulou MJ, Özçelik R (2012) Evaluation of different modeling approaches for total tree-height estimation in Mediterranean region of Turkey. Forest Syst 21(3):383–397
Fausett L (1994) Fundamentals of neural network architectures: algorithms and application. Prentice Hall, USA
Frazer GW, Fournier RA, Trofymow JA, Hall JR (2001) A comparison of digital and film fisheye photography for analysis of forest canopy structure and gap light transmission. Agric For Meteorol 109:249–263
Gholz HL (1982) Environmental limits on above ground net primary production, leaf area and biomass in vegetation zones of the Pacific northwest. Ecology 53:469–481
Grier CC, Running SW (1977) Leaf area of mature northwestern coniferous forests: relation to water balance. Ecology 58:893–899
Hale SE, Edwards C (2002) Comparison of film and digital hemispherical photography across a wide range of canopy densities. Agric For Meteorol 112:51–56
Hasenauer H, Merkl D, Weingartner M (2001) Estimating tree mortality of Norway spruce stands with neural networks. Adv Environ Res 5(4):405–414
Homolova L, Malenovsk YZ, Hanus J, Tomask OI, Dvorakova M, Pokorny R (2007) Comparison of different ground techniques to map leaf area index of Norway spruce forest canopy. In: Schaepm ME, Liang S, Groot NE, Kneubuhler M (eds) 10th international symposium on physical measurements and spectral signatures in remote sensing. Davos, Switzerland, pp 499–504
Hu L, Zhu J (2009) Determination of the tridimensional shape of canopy gaps using two hemispherical photographs. Agric For Meteorol 149:862–872
Jagodziński AM, Kalucka IL (2008) Age-related changes in leaf area index of young scots pine stands. Dendrobiology 59:57–65
Jeleska SD (2004) Analysis of canopy closure in the dinaric silver fir-beech forests in Crotia using hemispherical photography. Hacquetia 3(2):43–49
Jonckheere I, Fleck S, Nackaerts K, Muys B, Coppin P, Weiss M, Baret F (2004) Review of methods for in situ leaf area index determination part I. Theories, sensors and hemispherical photography. Agric For Meteorol 121:19–35
Kashian DM, Turner MG, Romme WH (2005) Variability in leaf area and stemwood increment along a 300-year lodgepole pine chronosequence. Ecosystems 8:48–61
Khosravi S, Namiranian M, Ghazanfari H, Shirvani A (2012) Estimation of leaf area index and assessment of its allometric equations in oak forests: northern Zagros, Iran. J Forest Sci 58(3):116–122
Leblanc SG, Chen JM, Fernandes R, Deering DW, Conley A (2005) Methodology comparison for canopy structure parameters extraction from digital hemispherical photography in boreal forests. Agric For Meteorol 129:187–207
Leite HG, Marques da Silva ML, Binoti DHB, Fardin L, Takizawa FH (2011) Estimation of inside-bark diameter and heartwood diameter for Tectona grandis Linn. Trees using artificial neural networks. Eur J Forest Res 130:263–269
Liang J, Buongiorno J, Monserud RA (2005) Growth and yield of all-aged Douglas-fir western hemlock forest stands: a matrix model with stand diversity effects. Can J For Res 35(10):2368–2381
Macfarlane C, Grigg A, Evangelista C (2007) Estimating forest leaf area using cover and fullframe fisheye photography: thinking inside the circle. Agric For Meteorol 146:1–12
Madugundu R, Nizalapur V, Jha CS (2008) Estimation of LAI and above ground biomass in decisious forests: western Ghats of Karnataka, India. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geoinform 10:211–219
Mason EG, Diepstraten M, Pinjuv GL, Lasserre JP (2012) Comparison of direct and indirect leaf area index measurements of Pinus radiate D. Don Agr Forest Meteorol:166–167
Nowak DJ (1996) Estimating leaf area and leaf biomass of open-grown deciduous urban trees. For Sci 42(4):504–507
Omer G, Mutanga O, Abdel-Rahman EM, Adam E (2016) Empirical prediction of leaf area index (LAI) of endangered tree species in intact and fragmented indigenous forests ecosystems using worldview-2 data and two robust machine learning algorithms. Remote Sens 8:324–350
Özbayram AK, Çiçek E, Yılmaz F (2015) Relationships between leaf area index (lai) and some stand properties in Turkish red pine and black pine stands. Kastamonu Univ J Forest Faculty 15(1):78–85
Özçelik R, Diamantopoulou MJ, Crecente-Campo F, Eler Ü (2013) Estimating Crimean juniper tree height using nonlinear regression and artificial neural network models. For Ecol Manag 306:52–60
Özçelik R, Diamantopoulou MJ, Eker M, Gürlevik N (2017) Artificial neural network models: an alternative approach for reliable above-ground pine-tree biomass prediction. For Sci 63(3):291–302
Özçelik R, Diamantopoulou MJ, Wiant HV, Brooks JR (2008) Comparative study of standard and modern methods for estimating tree bole volume of three species in Turkey. Forest Prod J 58:73–81
Özçelik R, Diamantopoulou MJ, Wiant HV, Brooks JR (2010) Estimating tree bole volume using artificial neural network models for four species in Turkey. J Environ Manag 91(3):742–753
Peng C, Liu J, Dang Q, Apps MJ, Jiang H (2002) TRIPLEX: a generic hybrid model for predicting forest growth and carbon and nitrogen dynamics. Ecol Model 153:109–130
Pokorný R, Stojnič S (2012) Leaf area index of Norway spruce stands in relation to age and defoliation. Beskydy 5(2):173–180
SAS Institute Inc (2012) SAS/ETS® 9.1 User’s Guide. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc
Shoemaker DA, Cropper WP (2008) Prediction of leaf area index for southern pine plantations from satellite imagery using regression and artificial neural networks. Proceedings of the 6th southern forestry and natural resources GIS conference. Warnell School of Forestry and Natural Resources, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia, USA
Sidabras N, Augustaitis A (2015) Application perspectives of the leaf area index (LAI) estimated by the Hemiview system in forestry. Proceedings of the Latvia University of Agriculture, p 26
Sonohat G, Balandier P, Ruch AF (2004) Predicting solar radiation transmittance in the understory of even-aged coniferous stands in temperate forests. Ann Forest Sci 61:629–641
Statsoft Inc (2007) Statistica: Data analysis software system, version 7
Swank WT, Swift LT, Douglas JE (1988) Streamflow changes associated with forest cutting, species conversions, and national disturbances. Forest hydrology and ecology at Coweeta, pp 297–312
Turner DP, Acker SA, Means JE, Garman SL (2000) Assessing alternative allometric algorithms for estimating leaf area of Douglas-fir trees and stands. For Ecol Manag 126:61–76
Verger A, Baret F, Weiss M (2008) Performances of neural networks for deriving LAI estimates from existing CYCLOPES and MODIS products. Remote Sens Environ 112:2789–2803
Vilà M, Vayreda J, Gracia C, Ibáñez JJ (2003) Does tree diversity increase wood production in pine forests? Oecologia 135:299–303
Vose JM, Allen HL (1988) Leaf area, stemwood growth and nutrient relationships in loblolly pine. Forest Science 34:547–563.
Walter JMN, Torquebiau EF (2000) The computation of forest leaf area index on slope using fish-eye sensors. Life Sci 323:801–813
Wang T, Zhiqiang XZ, Liu Z (2017) Performance evaluation of machine learning methods for leaf area index retrieval from time-series MODIS reflectance data. Sensors 17:81–96
Wang W, Lei X, Ma Z, Kneeshaw DD, Peng C (2011) Positive relationship between aboveground carbon stocks and structural diversity in spruce dominated forest stands in New Brunswick. For Sci 57:506–515
Weiss M, Baret F, Smith GJ, Jonckheere I, Coppin P (2004) Review of methods for in situ leaf area index (LAI) determination part II. Estimation of LAI, errors and sampling. Agric For Meteorol 121:37–53
Wulder MA, LeDrew EF, Franklin SE, Lavigne MB (1998) Aerial image texture information in the estimation of northern deciduous and mixed wood forest leaf area index (LAI). Remote Sens Environ 64:64–76
Funding
Funding from The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (Project No: 213O026) is gratefully acknowledged.
Availability of data and materials
Available on request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IE contributed the manuscript as supervising the work, conception, administrative, design, material support, critical revision and statistical analysis. AG donated the manuscript as material support, design, analysis and critical revision. MŞ provided the manuscript as material support, analysis and critical revision. SK aided the manuscript as design, analysis and critical revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Authors’ information
İlker ERCANLI is an associated professor at Çankırı Karatekin University, Forest faculty, Department of Forest Yield Studies. He is a forest biometrician, focused on forest growth modeling. Alkan GÜNLÜ is an associated professor at Çankırı Karatekin Univeristy, Forest faculty, Department of Forest Management. He is studying forest remote sensing. Muammer ŞENTYURT is an assistant professor at Çankırı Karatekin Univeristy, Forest faculty, Department of Forest Yield Studies. He is a forest biometrician, focused on forest growth modeling. Sedat Keleş is Professor at Çankırı Karatekin Univeristy, Forest faculty, Department of Forest Managemnt. He is studying forest management and Planning.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Ercanlı, İ., Günlü, A., Şenyurt, M. et al. Artificial neural network models predicting the leaf area index: a case study in pure even-aged Crimean pine forests from Turkey. For. Ecosyst. 5, 29 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40663-018-0149-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40663-018-0149-8