Abstract
Motivated by the needs of the high-voltage power transmission industry, we use data from the high-latitude IMAGE magnetometer array to study characteristics of extreme geoelectric fields at regional scales. We use 10-s resolution data for years 1993–2013, and the fields are characterized using average horizontal geoelectric field amplitudes taken over station groups that span about 500-km distance. We show that geoelectric field structures associated with localized extremes at single stations can be greatly different from structures associated with regionally uniform geoelectric fields, which are well represented by spatial averages over single stations. Visual extrapolation and rigorous extreme value analysis of spatially averaged fields indicate that the expected range for 1-in-100-year extreme events are 3–8 V/km and 3.4–7.1 V/km, respectively. The Quebec reference ground model is used in the calculations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Findings
Introduction
Extreme space weather events have recently received increased federal regulatory, science, industry, and public interest. Much of the attention is motivated by the ongoing solar maximum and by the increasing vulnerability of the modern society to major solar events (e.g., National Research Council 2008). While we have not experienced any extreme geomagnetic storms during the current solar cycle, major non-Earth-directed coronal mass ejections (CMEs) have been observed and analyzed in the extreme event context (e.g., Baker et al. 2013; Ngwira et al. 2013). These analyses remind us of the important fact that extreme events do take place also during lower activity solar cycles such as the ongoing cycle number 24.
The awareness about the hazards related to geomagnetic disturbances (GMD) has generated a well-defined practical need for quantification of extreme space weather impact on high-voltage power transmission systems. To address this need, the scientific community needs to specify the geoelectric field conditions that can generate extreme geomagnetically induced currents (GIC). In this paper, we aim to provide information applicable to engineering hazards analyses and correspondingly to provide information that can assist the work on the GMD standards development.
One of the key requirements for the engineering GIC hazard analyses is to specify the geoelectric field at the area of the power transmission system being considered. Specifying the geoelectric field at one single point such as at individual magnetometer stations used for the geoelectric field modeling is generally not directly applicable unless a spatially uniform field can be assumed. To move beyond single point analyses, we advocate the notion of relevant spatial scales for the analyzed and applied geoelectric fields. Since in GIC computation geoelectric fields are applied across hundreds of kilometers, the estimation of extreme geoelectric fields should reflect the field magnitude across the same spatial scales.
The typical distance between high-voltage power transmission system nodes is about 100 km. As GIC is basically proportional to the spatial integral of the geoelectric field along the transmission lines, one usually does not need to consider smaller than about 100-km-scale features. On the other hand, for a system-wide impact, the enhanced geoelectric field needs to be determined over the entire system. We argue that the selection of an area of 500 km, albeit subjective, provides an adequate scale for its intended application in power systems, and by the patterns exhibited by the ground magnetic field measurements as will be seen below. If substantial geoelectric fields occur at about 500-km scales, the possible effects are not anymore localized and the power transmission system as a whole needs to be considered.
A body of work can be found on magnetometer station-specific statistics (e.g., Boteler 2001; Langlois et al. 1996; Pulkkinen et al. 2008; Thomson et al. 2011). Also, actual geoelectric field distributions have been used to compute GICs and the corresponding statistics (e.g., Myllys et al. 2014; Viljanen et al. 2013). However, to our knowledge, regional-scale geoelectric fields have not been considered earlier from the statistical and extreme analyses standpoint. Based on the considerations above, we define regional here as distances of the order of 500 km and set out to characterize geoelectric fields, especially in extreme situations, at those scales.
Data and analysis
Geomagnetic field recordings with 10-s temporal resolution from 23 high-latitude IMAGE magnetometer array sites for the period January 1993–December 2013 are used. Data used in the study have only a small amount of gaps in coverage, and the array is spatially fairly dense with station spacing of the order 100 km in the central and northern parts of the array. We note that the usage of 10-s data is important for capturing the fastest fluctuations associated with the extreme GIC events (Pulkkinen et al. 2006). The 10-s IMAGE data covers almost two solar cycles, which will make the extrapolation of the statistics to 100-year amplitudes possible. The IMAGE stations are located in Northern Europe and cover approximately from 55 ° to 75 ° of geomagnetic latitude. The array experiences magnetic field fluctuations mostly due to high-latitude ionospheric currents.
Geomagnetic data from each IMAGE station are used to compute the local horizontal geoelectric field E. The field is calculated by applying the plane wave method, which has been shown in numerous studies to be a good approximation for GIC purposes (e.g., Ngwira et al. 2008; Trichtchenko and Boteler 2004; Viljanen et al. 2006a; Wik et al. 2008). Reader is encouraged to consult Appendix A in Pulkkinen et al. (2012) for practical instructions on application of the plane wave method. The plane wave method is applied here using the Canadian Quebec Province ground model (Boteler et al. 1998). Since the Quebec model is known to represent the resistive end of typical ground structures, it is used here to gauge the possible upper bounds for the geoelectric field magnitudes.
It is important to note that we are not specifying the geoelectric fields pertaining to local geological conditions at the area of the IMAGE array. As is commonly done in space physics research analyses, we use the IMAGE array observations to specify the external near-space electric current conditions. The external conditions are then applied to geological conditions of interest using the 1D ground model and the plane wave method. The decoupled external source versus ground response approach is valid because, excluding regions close to strong conductivity anomalies, to a good approximation, the same magnetospheric-ionospheric source current will produce similar horizontal magnetic field variations at regions with different ground conductivity structures. See Pulkkinen et al. (2008) for a more detailed discussion on this.
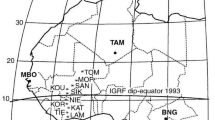
For visual inspection of field structures at storm times, Fig. 1 shows the computed geoelectric field distribution on November 24, 2001 at 07:32 UT, which is the time instant that had the second largest spatially averaged field of the entire data set. The largest mean geoelectric field magnitudes were observed in the local morning.
Computed geoelectric field distribution on November 24, 2001 at 07:32 UT. The colored circles show the three station groups used in spatial averaging: blue, green, and red groups. The green group generates the largest average geoelectric field magnitude of 2.8 V/km. Note that the maximum geoelectric field amplitude indicated in the top of the figure refers to a single station maximum, not to group average. Corrected geomagnetic coordinates and Oblique Mercator map projection are used
Figure 2 shows the geoelectric field on October 30, 2003 at 20:08 UT, when the largest spatially averaged field of the entire data set occurred. The largest mean magnitudes were observed in this case close to the local midnight.
Same as Fig. 1 but for October 30, 2003 at 20:08 UT. The red group generates the largest average geoelectric field magnitude of 4.0 V/km
To show the contrast between the spatially averaged extreme geoelectric fields and single station extreme fields, Fig. 3 shows an example of single station extreme geoelectric field. The extreme field took place October 30, 2003 at 16:49 UT. The peak geoelectric field was very localized around one station in the blue group and was observed in the local late afternoon. Figure 4 shows the magnetic field and the computed geoelectric field at the blue group stations on October 30, 2003 around the time of the localized peak at 16:49 UT. As is seen, the localized peak geoelectric field is associated with rapid enhancement of the field at one of the stations. The entire sequence takes place over a period of couple minutes, and thus, the geoelectric field peak is both spatially and temporally localized.
Same as Fig. 1 but for October 30, 2003 at 16:49 UT. A station in the blue group experiences the largest single station geoelectric field magnitude of 5.7 V/km. The spatially averaged field magnitudes for blue, green, and red groups are 1.5, 0.6, and 0.1 V/km, respectively
Times series of the geomagnetic north-south component of the magnetic field (B x ) observed by the blue station group (see Fig. 3) on October 30, 2003 (top panel). The computed geoelectric field magnitude at the blue group stations on October 30, 2003 (bottom panel)
To carry out initial characterization of the geoelectric field at 500-km spatial scales, we compute the average magnitudes E=|E| over three different subsets of IMAGE stations. More specifically, the geoelectric field was computed first individually for each station, and the corresponding time series of station-specific magnitudes E were calculated. The station-specific geoelectric field magnitudes were then used to compute average over groups of stations for each time step of the data. For brevity, refer to http://space.fmi.fi/image for details on individual stations. The blue, green, and red groups span distances of approximately 550, 430, and 510 km (see Fig. 1), respectively, so the average over the sites in each group provides a measure of the geoelectric fields with a spatial scale of the order of 500 km. These are referred to as spatially averaged geoelectric fields. It is noted that the five stations in the green group in Fig. 1 are a subset of all available stations in the corresponding latitude band. The subset was selected visually to provide approximately uniform station distribution and about 500-km span.
Figure 5 shows the ten largest spatially averaged geoelectric field magnitudes per year, and Fig. 6 shows the occurrence distributions of the spatially averaged electric fields as the number of occurrences per 100 years. Since only time instants that had data for all stations that are part of the group were used for the statistics, the data points in Fig. 6 cannot fully cover the entire 1993–2013 period. The gray lines in Fig. 6 indicate rough visual extrapolation of the statistics to the occurrence of one 10-s value per 100 years. The gray lines bound 1-in-100-year spatially averaged geoelectric field magnitudes of 3–8 V/km.
The statistical occurrence of spatially averaged geoelectric field magnitudes. The averaging was carried out over the station groups shown in Fig. 1. The colors of the curves correspond to color coding of the groups in Fig. 1. Gray lines show the 3 and 8 V/km bounds for visually extrapolated statistics. The inset shows the return periods obtained from peaks over threshold analyses. The circle in the inset shows the largest spatially averaged magnitude in the data set. The box in the top right corner indicates the amount of data that were available for computing the statistics for each group
We note that there is a deviation of the tail of the red station group distribution in Fig. 6 from the general downward slope. The deviation is associated with the data from the October 29–31, 2003 geomagnetic storm. We attribute the feature to finite-size effects of the statistics and to the fact that the October 29–31, 2003 geomagnetic storm is possibly less frequent than a 20-year event. We show in the next section that based on the extreme value analysis, 4.0 V/km average fields can be expected to occur about 1-in-50 years.
Extreme value statistics
We carried out extreme value analysis to provide robust extrapolation of the statistics in Fig. 6 to the expected range of 100-year field magnitudes (for more details on extreme values analysis, see Coles (2001)). In particular, we are concerned with estimating the 95 % confidence interval for the 100-year return period.
From the daily maxima for spatially averaged fields of the three station groups discussed in the “Data and analysis” section, the allover maximum values for all three groups have been selected to create a single time series for the entire domain. As can be seen from Fig. 5, both the amplitude and standard deviation of extreme geoelectric fields depend on the solar cycle. The data clearly exhibits heteroskedasticity and an 11-year seasonality in the mean. Heteroskedasticity is the statistical behavior of a process to produce different variances at different times (i.e., the variance is not constant over time).
The peaks over threshold (POT) extreme value method was then applied to the data (Coles 2001). This method is adept at exploiting all the available extreme observations, improving the efficiency of the estimation. The POT is estimated using normalized excesses over a threshold; the selection of the threshold is a compromise between bias and uncertainty. The asymptotic basis of the model relies on a high threshold; a threshold that is too low will likely lead to bias. On the other hand, a threshold that is too high will reduce the sample size and result in high variance.
The data were declustered, and a threshold of 1 V/km was selected for the analysis. The parameters were estimated using the maximum likelihood estimator (MLE). The traditional POT method relies on independent and identically distributed (iid) data. As illustrated by the scatter plot in Fig. 5, the iid statistical assumption is not warranted by the data. To address this, we carried out a re-parametrization of POT by calculating a 11-year seasonality of the standard deviation σ of the time series, defined as
where α 0 represents the offset in the standard deviation, α 1 describes the 11-year seasonality, T is the period (365.25 × 11), and ϕ is a constant phase shift. The parameter α 1 is statistically significant; the null hypothesis is rejected with a p value of 0.001. The fitted values for α 0 and α 1 are 0.3 (0.03) and 0.2 (0.04), respectively. The σ was used to rescale the 11-year heteroskedasticity at each time step to achieve a closer-to-iid data for improved POT result.
The 95 % confidence interval of the 100-year return level was calculated using the delta method and the profile likelihood. The inset in Fig. 6 shows the derived return period. The mean expected amplitude of the geolectric field for a 100-year return level is 4.3 V/km. The confidence interval, calculated at solar maximum, is [3.4, 7.1] V/km. Note that the confidence interval in Fig. 6 is highly asymmetric with a positive skew. The largest observation of 4.0 V/km is also shown in Fig. 6; it lies above the expected mean return level and is expected to occur about 1-in-50 years.
Discussion
By comparing Figs. 1, 2, and 3, it is immediately clear that the station-specific and spatially averaged extreme geoelectric fields can have very different spatial structures. While spatial correlations are clearly present in the form of alignment of the computed field vectors in Fig. 3, the magnitude in one of the locations is about five times larger than at the nearby sites at about 240- and 280-km distance. While this specific example is quite extreme in terms of local field enhancement, it does illustrate that localized features are observed during extreme storm conditions. In contrast, when spatial average is used to identify the maximum geoelectric field, as in Figs. 1 and 2, the geoelectric field structure is much more coherent over regional scales. We note that using spatial average as a metric does not imply coherence or uniformity of the field. However, as can be seen from Figs. 1 and 2, in these two cases that are the most extreme in the utilized data set, extreme spatial averages are associated with fairly uniform fields over regional scales. This indicates that spatial average is capable of capturing regional-scale geoelectric field features and is thus applicable measure for characterizing spatially uniform or coherent fields.
As is seen from Fig. 6, the spatially averaged distributions do not decrease monotonously as a function of magnitude and thus the most likely magnitude is non-zero. This illustrates the fact that the high-latitude geomagnetic field is constantly varying and the rate of change of the field rarely vanishes. Correspondingly, there is a non-zero geoelectric field at high-latitude locations most of the time. We also observe a systematic shift of the most likely geoelectric field magnitudes to lower values in Fig. 6 at more southern station groups. This shift indicates that on average, the geoelectric field has larger magnitudes at higher latitudes. However, the tails of the distributions in Fig. 6 converge, which is most likely caused by the fact that during major storms, auroral oval “sweeps” across the IMAGE array, thus exposing all stations to similar geomagnetic and geoelectric field conditions.
Visual extrapolation and rigorous extreme value analysis of spatially averaged high-latitude geoelectric fields indicated that the expected range for 1-in-100-year extreme events for the Quebec reference ground model, in a sense of single 10-s value, is 3–8 V/km and 3.4–7.1 V/km, respectively. We thus conclude that the two extrapolations are in good agreement and provide reasonable expected range for spatially averaged field magnitudes of a 100-year event.
Many different solar wind-magnetosphere-ionosphere processes can drive large geoelectric field and GIC events. The examples in Figs. 1, 2, and 3 correspond to a wide range of local times that reflect a variety of different magnetosphere-ionosphere current systems that drive geomagnetic induction process. While, for example, substorms and geomagnetic pulsations have shown to be responsible for some of the largest GIC at high latitudes (e.g., Pulkkinen et al. 2003; Pulkkinen and Kataoka 2006; Viljanen et al. 2006b), the challenge is to explore and understand what are the physical processes responsible for both regional-scale and localized geoelectric field enhancements illustrated in this paper. We also note that while we believe the features presented in this paper reflect mostly the spatial structure of the external source, also localization of the fields enhancements due to the lateral inhomogeneities in the ground conductivity structures, such as at coastal areas, need improved quantification for GIC purposes (e.g., Pirjola 2013; Thomson et al. 2005). New understanding about appropriate spatial scales of geospace and geomagnetic induction processes responsible for extreme geoelectric fields and GIC is needed to better address the high-voltage bulk-power system-related societal need.
Finally, we emphasize that the work described in this paper is only the beginning in our exploration of spatial geoelectric field structures pertaining to extreme GIC. We will carry out detailed investigations of physical processes responsible for different field structures and expand the statistical analyses to include characterization of multiple different spatial scales. We are also in the process of conducting analyses to quantify the spatial localization of the most extreme geoelectric fields and to study the power engineering implications of extreme fields at different spatial scales. These follow-up works will be published elsewhere in the near future.
References
Baker, D, Li X, Pulkkinen A, Ngwira C, Mays M, Galvin A, Simunac K (2013) A major solar eruptive event in July 2012 defining extreme space weather scenarios. Space Weather 11(Issue 10): 585–591.
Boteler, DH, Pirjola RJ (1998) The complex-image method for calculating the magnetic and electric fields produced at the surface of the Earth by the auroral electrojet. Geophys J Int 132(1): 31–40.
Boteler, DH (2001) Assessment of geomagnetic hazard to power systems in Canada. Nat Hazards 23: 101–120.
Coles, S (2001) An introduction to statistical modelling of extreme values. Springer-Verlag, London.
Langlois, P, Bolduc L, Chouteau MC (1996) Probability of occurrence of geomagnetic storms based on a study of the distribution of the electric field amplitudes measured in Abitibi, Québec, in 1993-94. J Geomagn Geoelectr 48: 1033–1041.
Myllys, M, Viljanen A, Rui ØA, Ohnstad TM (2014) Geomagnetically induced currents in Norway: the northernmost high-voltage power grid in the world. J Space Weather Space Clim 4: A10. doi:10.1051/swsc/2014007.
National Research Council (2008) Severe space weather events–understanding societal and economic impacts: a workshop report. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC.
Ngwira, CM, Pulkkinen A, McKinnell L-A, Cilliers PJ (2008) Improved modeling of geomagnetically induced currents in the South African power network. Space Weather 6: S11004. doi:10.1029/2008SW000408.
Ngwira, CM, Pulkkinen A, Mays L, Kuznetsova M, Galvin AB, Simunac K, Baker D, Li X, Zheng Y, Glocer A (2013) Simulation of the 23 July 2012 extreme space weather event: what if the extremely rare CME was Earth-directed?Space Weather 11(12): 671–679.
Pirjola, R (2013) Practical model applicable to investigating the coast effect on the geoelectric field in connection with studies of geomagnetically induced currents. Adv Appl Phys 1(1): 9–28.
Pulkkinen, A, Thomson A, Clarke E, McKay A (2003) April 2000 geomagnetic storm: ionospheric drivers of large geomagnetically induced currents. Ann Geophys 21: 709–717.
Pulkkinen, A, Viljanen A, Pirjola R (2006) Estimation of geomagnetically induced current levels from different input data. Space Weather 4: S08005. doi:10.1029/2006SW000229.
Pulkkinen, A, Kataoka R (2006) S-transform view of geomagnetically induced currents during geomagnetic superstorms. Geophys Res Lett 33: L12108. doi:10.1029/2006GL025822.
Pulkkinen, A, Pirjola R, Viljanen A (2008) Statistics of extreme geomagnetically induced current events. Space Weather 6: S07001. doi:10.1029/2008SW000388.
Pulkkinen, A, Bernabeu E, Eichner J, Beggan C, Thomson A (2012) Generation of 100-year geomagnetically induced current scenarios. Space Weather 10: S04003. doi:10.1029/2011SW000750.
Thomson, AWP, McKay AJ, Clarke E, Reay SJ (2005) Surface electric fields and geomagnetically induced currents in the Scottish power grid during the 30 October 2003 geomagnetic storm. Space Weather 3: S11002. doi:10.1029/2005SW000156.
Thomson, A, Reay S, Dawson E (2011) Quantifying extreme behaviour in geomagnetic activity. Space Weather 9(10): S10001. doi:10.1029/2011SW000696.
Trichtchenko, L, Boteler D (2004) Modeling geomagnetically induced currents using geomagnetic indices and data. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 32(4): 1459–1467.
Viljanen, A, Pulkkinen A, Pirjola R, Pajunpää K, Posio P, Koistinen A (2006a) Recordings of geomagnetically induced currents and a nowcasting service of the Finnish natural gas pipeline system. Space Weather 4: S10004. doi:10.1029/2006SW000234.
Viljanen, A, Tanskanen EI, Pulkkinen A (2006b) Relation between substorm characteristics and rapid temporal variations of the ground magnetic field. Ann Geophys 24: 725–733.
Viljanen, A, Pirjola R, Pracser E, Ahmadzai S, Singh V (2013) Geomagnetically induced currents in Europe: characteristics based on a local power grid model. Space Weather 11: 575–584. doi:10.1002/swe.20098.
Wik, M, Viljanen A, Pirjola R, Pulkkinen A, Wintoft P, Lundstedt H (2008) Calculation of geomagnetically induced currents in the 400 kV power grid in southern Sweden. Space Weather 6: S07005. doi:10.1029/2007SW000343.
Acknowledgements
We thank the institutes who maintain the IMAGE magnetometer array. The IMAGE array data used in this paper are publicly available at http://space.fmi.fi/image. We acknowledge discussions with Drs L. Marti (Hydro One), R. Horton (Southern Company), as well as with Mr. F. Koza (PJM) and Mr M. Olson (NERC). The work of A.V. was partially supported from the EU’s 7th Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement no. 260330 (EURISGIC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
AP led the group work on the topic and carried out the geomagnetic field processing and geoelectric field modeling. EB carried out the extreme value analysis. JE assisted with the extreme value analysis. AV and CN assisted with the geomagnetic field and geoelectric field analyses and provided expert views on the geophysical interpretation of the results. All authors read, commented, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Pulkkinen, A., Bernabeu, E., Eichner, J. et al. Regional-scale high-latitude extreme geoelectric fields pertaining to geomagnetically induced currents. Earth Planet Sp 67, 93 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-015-0255-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-015-0255-6