Abstract
Background
This study aimed to assess the effects of different concentrations of silicon (Si) nutrient sources, including bulk silicon dioxide (bSiO2) and two types of silica nanoparticles, nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) at different concentrations of 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 ppm in the germination process of stevia. The priming experiment was conducted using a completely randomized design with three replicates to ensure the reliability of the results.
Results
All stevia seedlings subjected to nano-priming significantly improved the germination parameters. The germination percentage increased by 106%, reaching 68% in nano-primed seedlings. Similarly, the germination rate showed a remarkable increase of 128.12% at 7.3 day−1. Additionally, the root, shoot, and seedling dry weight increased by 283%, 168.9%, and 220% and determined 0.092, 0.078, and 0.17 g plant−1, respectively, compared to the control. Furthermore, seed priming with nSiO2 (I) at a concentration of 10 ppm resulted in an increased catalase (CAT) activity (36.15 Umg−1 protein) and peroxidase (POX) activity (approximately 0.057 U.mg−1 protein). Also, the highest sucrose amount was observed in the root (equal to 160.4 μg g−1 DW) and shoot (equal to 247 μg g−1 DW) of seedlings primed with 10 ppm of nSiO2 (I). However, it should be noted that nano-priming at the highest concentration led to oxidative damage indicated by an increase in H2O2 concentration. Conversely, bSiO2 demonstrated a lesser effect on improving germination, seedling growth, antioxidant activities, and biochemical attributes compared to nSiO2 (I), and nSiO2 (II).
Conclusions
This study established that seed priming with nSiO2 (I) at a concentration of 10 ppm was the most effective in enhancing germination percentage and rate, root/shoot/dry weight, biochemical attributes, and enzyme activities (such as α-amylase, CAT, and POX). The results suggested that seed priming with nSiO2 (I) at the optimal concentration could improve the seed germination by enhancing the antioxidant system, starch metabolism, and ultimately protecting plants from oxidative damage.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Introduction
Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni is a perennial herbaceous plant that has gained popularity in the pharmacy and food industry. Stevia leaves contain steviol glycosides (SGs), which are natural and zero-calorie sweeteners [1, 2]. These sweeteners are widely used in various food and beverage products [3]. Stevia is typically propagated through seeds [4], as it provides a cost-effective method for generating seedlings [5]. However, the poor germination rate of stevia seeds poses challenges for cultivation [4]. To address this issue, several experiments have been focused on improving stevia seeds germination [6,7,8]. In the agricultural sector, sustainability, pesticide residues, fertilizer usage, food safety, and environmental pollution are significant challenges [9].
These challenges contribute to serious problems including environmental damage, health concerns, and a lack of sustainable agriculture practices. Consequently, there is a pressing need to transition from conventional agricultural practices to sustainable agriculture [10]. Moreover, nanotechnology has emerged as a significant player in sustainable agriculture [11, 12]. It offers the potential to enhance productivity and quality in agricultural products while minimizing the reliance on agrochemicals, herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides [13]. By leveraging nanotechnology, we can address these challenges and promote a more sustainable approach to agriculture. Several research efforts have been dedicated to the development of natural, biomaterial based, and eco-friendly priming agents to ensure environmental safety [14, 15]. Among these techniques, seed priming stands out as an effective approach to enhance seed germination and positively impact on plants early growth stages [16]. This method offers benefits such as improved stress tolerance, seedling vigor, germination of weaker seeds, seed quality, and crop yields [17, 18]. Importantly, seed priming aligns with the principles of sustainable agriculture and contributes to the socio-economic well-being of farmers [19]. In support of the benefits of seed priming, experiments conducted by studies have demonstrated that nano-priming specifically enhanced the germination process in rice [20, 21]. These findings underscore the potential of nano-priming as a valuable technique to improve crop productivity. Several articles have demonstrated the positive effects of NPs on seed germination. One such example is the improvement of rice seed germination through the utilization of zero valent iron NPs (nZVI) [20]. In a separate study, the modulatory effects of selenium and zinc oxide nanoparticles (Se NPs and ZnO NPs) on the seed germination in Brassica napus were revealed [22]. These NPs exhibited a positive influence on the seed germination, specifically under salt stress conditions. The application of nano-priming treatment resulted in notable enhancements in the final germination percentage, germination rate, seed microstructure, and antioxidant enzyme activity in two different rapeseed cultivars [22].
Concerning the noteworthy physicochemical characteristics of NPs, it is logical to confer that seed nano-priming may improve the germination rate of stevia, seedling vigor, and other physiological parameters. While some experiments have explored the effect of NPs on seed germination, there has been limited research on the physiological effects and molecular mechanisms of nano-priming specifically in stevia seed germination.
Moreover, there is a lack of available reports on the impact of stevia seed priming with NPs [23,24,25], particularly with silica nanoparticles. This study aims to address this gap by investigating the potential beneficial role of different types of silica nanoparticles such as nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) in promoting seed germination in comparison with the bulk silica. The proposed mechanism includes enhancing starch-degrading enzyme activity, facilitating sucrose and starch exchange in seeds and seedlings. The goal is to identify and select the most effective nanoparticles in terms of germination parameters and physiological properties to enhance stevia seed germination. This research contributes to the development of sustainable agricultural production methods.
Experimental methods
Material and characterization
To investigate the impact of NPs on the stevia seed germination, a factorial experiment was conducted using completely randomized designs at the Agricultural Biotechnology Institute of Iran (ABRII) in Karaj, Iran. The seeds were subjected to surface sterilization using a 3% (w/v) sodium hypochlorite solution, followed by rinsing with distilled water. Subsequently, the seeds were pretreated with different concentrations (0, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 ppm) of nSiO2 (I), nSiO2 (II), and commercial bulk SiO2 (bSiO2). Tetraethyl orthosilicate and all chemicals for synthesis of NPs were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich.
The hydrodynamic particle size of the samples was determined using a dynamic light scattering instrument (DLS, Brookhaven, USA). Solid nanomaterials were dispersed in deionized water using an ultrasonic bath for 15 min to prepare the samples for quantification. The size and shape of the samples were characterized using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Hitachi S-4800 II, Japan) and a transmission electron microscopy (TEM, Hitachi H-7650, 80 kV, Japan). For taken TEM and SEM images, the samples were prepared by simply spreading the NPs on a grid using a suitable solvent such as ethanol. The prepared samples were dried and used for imaging. The topological features of the material were observed at room temperature using an atomic force microscope (AFM, DME-Ds95-50, Denmark). For this purpose, an ultrasonic mixture of solid nanomaterials in deionized water was distributed on the network. The necessary spectrophotometric measurements were performed using a double-beam UV–Vis spectrophotometer (UV-3100 PC, Shimadzu).
Synthesis of nanomaterials
Synthesis of silica-based nanoparticles (nSiO2)
Tetraethyl orthosilicate (2.8 mL) was added to a solution containing ammonia (2.8 mL), deionized water (dH2O, 33.75 mL), acetone (14.5 g), and cetrimonium bromide (0.64 g). The obtained mixture was allowed to stir for 24 h at 25 °C or 85 °C. Afterwards, the solid residual was separated by centrifuge (10 min at 14,000 rpm), and the separated solid was thoroughly washed with dH2O and ethanol, and dried overnight at 70 °C using a vacuum oven. The dried white powder was calcined at 540 °C for 5 h to give silica-based nanoparticles (SiO2 NPs). The synthesized NPs was named based on the reaction temperature, therefore, nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) showed the silica NPs synthesized at 85 °C and 25 °C, respectively.
Preparation and method of priming samples
The seed priming test involved the use of different concentrations of nSiO2 (I), nSiO2 (II), and bSiO2 priming solutions. Fresh solutions were prepared at six concentrations: 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 ppm. The NPs were dispersed in dH2O using an ultrasonic bath (100 w, 40 kHz) for 30 min. As a control, the hydro-priming was done using dH2O. Stevia seeds (Cultivar ‘814011) were obtained from China. Prior to germination, the seeds underwent surface sterilization with 70% ethanol followed by multiple washes with dH2O [4]. The seeds were primed for 20 h (priming time was optimized in the preliminary experiment). After the priming process, the seeds were washed with distilled water to remove the physically absorbed NPs, and then the primed seeds were dried for 24 h in the laboratory [8].
Sampling
Samples of 60 seedlings were selected randomly. The shoot (including cotyledon and stem) and roots were subsequently separated and subjected to drying in a freeze-dryer at − 60 °C for a duration of 2 days. Once dried, the samples were weighed and then finely ground using liquid nitrogen. Finally, the ground samples were stored at a temperature of − 80°C for preservation.
Germination percentage, germination rate, and seed vigor
Germination was monitored daily starting from the day of sowing, considering the radicle length surpassing 2 mm as the criterion for germination. The germination rate was determined as percentage obtained by dividing the number of germinated seeds by the total number of seeds sown. To calculate the seed vigor index, the germination index was multiplied by the shoot length.
Starch and sucrose determination
The determination of starch and sucrose was conducted by the previously reported method [26]. To separate and dry the root, shoot, and cotyledons, they were individually placed in a freeze-dryer. In 15 mL Falcon tubes, 0.1 g of each freeze-dried sample was combined with 5 mL of 70% ethanol, and the mixture was shaken for 5 min. Subsequently, the samples were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min., and the supernatant was transferred to a new 15 mL Falcon tube. This process was repeated twice. The supernatant was dried at 60 °C using a rotary vacuum concentrator (Eppendorf Concentrator plus, Germany), while the residue was used for starch measurement. To determine the total sucrose, glucose, and fructose, the samples were completely dried. The dried samples were reconstituted with 10 mL of dH2O. To the remaining residue in the tubes, 10 mL of dH2O, 0.47 mL of 0.3 M barium hydroxide, and 0.5 mL of 5% ZnSO4 were added. After centrifugation and transfer of the supernatant to a 15 mL tube, it was dried at 50 °C. Finally, the remaining residue was vigorously vortexed with 1 mL of HPLC grade water, and 20 μL was injected into the HPLC system. HPLC (KNAUER, Germany) equipped with a EURO Kat H column (10 m, 300 × 8 mm, KNAUER, Germany) was used, with the column maintained at 25 °C and an acidic mobile phase (aq. H2SO4 at pH = 2.5) flowing at a rate of 1 mL min−1. The samples were separated, and sucrose was the only component with reliable concentration results in the HPLC analysis. To determine the starch content, the dried cotyledon samples were utilized. The remaining residue in the tubes was treated with 4.5 mL of dH2O and 6 mL of 52% perchloric acid. After overnight incubation at 4 °C, the samples were centrifuged at 11,068g for 10 min. To a 0.5 mL sample of the extract, 1.25 mL of 12 M H2SO4 and 0.25 mL of 0.5% phenol were added. The absorbance of the sucrose was measured at 485 nm after 45 min.
Assays of antioxidant enzyme activity
The supernatant determines the decrease in absorbance at 470 nm, described by Chance and Maehly in 1955 [32]. The reaction consisted of 1.99 mL of sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.0) supplemented with 0.1 μM EDTA, 10 mM guaiacol, and 15 mM H2O2, along with a 100 μL of the enzyme extract, a total volume of 2 mL.
Catalase (CAT, EC 1.11.1.6) was extracted from stevia seedlings following the method by Ramiro, et al. [27]. A 0.1 g sample of seedling was suspended in 3 mL of ice-cold HEPES buffer (25 mM, pH 7.8) containing 0.2 mM EDTA and 2% mM PVP. The resulting homogenate was then centrifuged at 12,000g for 20 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was used to determine catalase activity by measuring absorbance at 470 nm following the protocol previously described [28]. The reaction mixture contained 1.99 mL sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.0) supplemented with 0.1 μM EDTA, 10 mM guaiacol and 15 mM H2O2 and 100 μL of the enzyme extract making a total volume of 2 mL.
Statistical analysis
The data analysis was conducted using various software programs. RStudio, SPSS-24, and SAS-9.2 were utilized for data analysis. Treatment differences were assessed using LSD at a significance level of 5%. To analyze correlations between traits, the R package “corrplot” within RStudio software was employed, calculating Pearson correlation coefficient. Multiple stepwise regression analyses were performed by SPSS-24.
Results
Preparation and characterizations of NPs
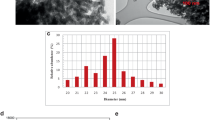
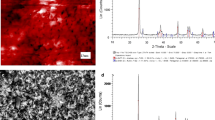
The synthesized nanoparticles were thoroughly characterized using various techniques, including XRD (X-Ray Powder Diffraction), TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy), AFM (Atomic Force Microscopy), and DLS (Dynamic Light Scattering). Size determination of nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) using TEM indicated that all nanomaterials are spherical with an average diameter of < 50 and < 100 nm, respectively (Fig. 1C and D) and it was in agreement with the AFM images (Fig. 1A and B). The results of measuring the hydrodynamic diameter of nSiO2 (I), and nSiO2 (II) using DLS, showed 128 and 248 nm, respectively.
SiO2 NPs priming
As shown in Fig. 2, the nano-priming of seeds with NPs samples including nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) at various concentrations exhibited a pronounced enhancement in the germination percentage, germination rate, and seed vigor when compared to the control and the bSiO2 priming treatments. Notably, the priming of seeds with nSiO2 (I) at 10 ppm resulted in a significant increase in seed germination percentage (68%), germination rate (7.3 day−1), and vigor index (11.6). This represented a substantial improvement of 106%, 128.12%, and 480%, respectively, compared to the control. Similarly, the priming of seeds with nSiO2 (II) at 100 ppm led to a significant enhancement in seed germination percentage (62%), germination rate (5.9 day−1) and vigor index (9.5) (p < 0.01) reflecting an increase of 87.8%, 84.3%, and 375%, respectively, compared to the control. Moreover, the germination percentage of seeds subjected to nano-priming was notably higher than that of the bSiO2 priming and control.
Impacts of different priming agents (nSiO2 (I), nSiO2 (II), and bSiO2 at concentrations of 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100) on A seed germination percentage, B germination rate, C seed vigor index D root dry weight, E shoot dry weight, and F seedling dry weight. Data are presented as means of three replicates containing 100 seeds each ± standard error of means. The color of the columns indicates the concentration based on ppm and control was water priming
Germination percentage, germination rate, and seed vigor index
We observed notable increase in the dry weight of roots, shoots and seedlings in both nano-primed and bSiO2-primed seeds. Particularly, when seeds were primed with n SiO2 (I) at 10 ppm, a significant enhancement was observed in the dry weight of roots (0.092 g plant−1), shoots (0.078 g plant−1), and seedlings (0.17 g plant−1), indicating an impressive increase of 283%, 168.9%, and 220%, respectively, compared to the control. Similarly, the application of nSiO2 (II) at 100 ppm led to a significant improvement in the average dry weight of root, shoot, and seedling measuring 0.074, 0.080, and 0.154 g plant−1, respectively (p < 0.01). Furthermore, the dry weights of roots, shoots, and seedlings in the nano-primed seeds were significantly higher than those observed in the bSiO2 primed seeds and control group. It is worth noting that bSiO2 seed priming at concentrations of 25 and 50 ppm also contributed to an increased root, shoot, and seedling dry weight when compared to the control (Fig. 2).
The results of this experiment clearly demonstrate that nano-priming techniques have a significant impact on starch metabolism in stevia seedlings. Specifically, the activity of α-amylase, an enzyme involved in starch breakdown, was greatly enhanced by the application of nSiO2 (II) at 100 ppm (0.9 U g−1 FW) and nSiO2 (I) at 10 ppm (0.8 U g−1 FW). These activities were approximately 9 and 8 times higher, respectively, compared to the control. Similarly, the α-amylase activity in the seedlings subjected to bSiO2-priming at 50 ppm (0.6 U g−1 FW) was approximately 6 times higher than that of the control (Fig. 3A). Furthermore, the starch contents of seedlings were significantly reduced by nano-priming treatments using nSiO2 (II) and nSiO2 (I)) as well as bSiO2 primed seeds, in comparison to the control. Notably, the lowest starch content was observed in seeds primed with nSiO2 (I) at 10 ppm (13.7 μg g−1 DW) indicating a remarkable decrease in 83.2% compared to the control. Conversely, the control seeds exhibited the highest starch content. Additionally, seeds primed with nSiO2 (II) at the concentrations of 50 and 100 ppm displayed significantly lower (approximately 22 μg g−1 DW) represented a decrease of approximately 93% compared to the control (Fig. 3). These findings strongly suggest that nano-priming treatments have the potential to modulate starch metabolism in stevia seedlings, leading to changes in α-amylase activity and starch content.
Impacts of different priming agents (nSiO2 (I), nSiO2 (II), bSiO2, at concentrations of 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100) on A α-amylase, B cotyledon starch, C root sucrose, and D shoot sucrose content. Data are presented as means of three replicates containing 100 seeds each ± standard error of means. The color of the columns indicates the concentration based on ppm and control was water priming
Accumulation of sucrose and starch in root and shoot
The findings of the experiment revealed that the accumulation of sucrose in germinating seeds was significantly increased in both bSiO2-primed and nano-primed seeds (nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II)). In contrast, the control exhibited lower sucrose accumulation compared to the other treatment groups. Among the various treatments, the highest sucrose content in the both the root (160.4 μg g−1 DW) and shoot (247 μg g−1 DW) was observed in seeds primed with nSiO2 (II) at 100 ppm This remarkable increase represented a significant improvement of 144% and 724% compared to the control, respectively (Fig. 3). These results clearly demonstrate that the application of bSiO2 priming and nano-priming techniques, particularly nSiO2 (II) at 100 ppm, can significantly enhance the accumulation of sucrose in germinating seeds. This indicates the potential of these treatments to modulate sucrose metabolism and potentially improve the growth and development of the seedlings.
H2O2 concentration, CAT, and POX activity
Our results showed that the seed priming with bSiO2, nSiO2 (I), and nSiO2 (II) positively influenced the activities of CAT and POX enzymes in stevia seedlings. Among the treatments, the highest CAT activity (36.15 U mg−1 protein) was observed in seedlings primed with nSiO2 (II) at 10 ppm, resulting in a significant increase of 45%, compared to the control. Similarly, the highest POX activity (approximately 0.057 U mg−1 protein) was achieved in seedlings primed with nSiO2 (I) at 5, 10, and 25 ppm, as well as nSiO2 (II) at 10, 25, and 50 ppm. This represented a notable enhancement of 29% compared to the control (Table 1). Furthermore, seed priming with nSiO2 (I) up to 25 ppm and nSiO2 (II) up to 10 ppm resulted in a significant reduction in H2O2 concentration in the seedlings. However, higher concentration of nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) led to an increase in H2O2 concentration. Notably, bSiO2 priming at 100 ppm exhibited the highest H2O2 concentration (4.70 µmol g−1 FW), showing an increase of 11.37%, compared to the control. Conversely, the lowest H2O2 concentration (3.1 µmol g−1 FW) was observed in nSiO2 (I) priming at 1 ppm, representing a reduction rates of 26% compared to control (Table 1).
These findings highlight the positive impact of bSiO2 and nano-priming treatments on the activities of CAT and POX enzymes, as well as their influence on H2O2 concentration in stevia seedlings.
Correlation analysis
Analyzing the correlation coefficients between different traits in stevia seeds provides valuable insights into their relationships. The data obtained revealed significant correlations among various responses. Specifically, positive correlations were observed between seedling dry weights, seed vigor, stem dry weight, root dry weight, seed germination, germination rate, α-amylase activity, root sucrose, and stem sucrose. On the other hand, negative correlations (P = 0.01) were found between cotyledon starch and seedling dry weight, seed vigor, stem dry weight, root dry weight, seed germination, germination rate, α-amylase activity, root sucrose, and stem sucrose. The correlation coefficients for these negative correlations were − 0.66**, − 0.64**, − 0.64**, − 0.61**, − 0.61**, − 0.67**, − 0.69**, − 0.67**, − 0.64**, − 0.48, and − 0.49, respectively. Furthermore, negative correlations were observed between root starch concentration and root sucrose concentration, as well as between α-amylase activity and root starch concentration, with correlation coefficients of − 0.43** and − 0.55**, respectively (Fig. 4).
Discussion
Seed germination parameters
Long-term exposure of soil to fertilizers can lead to various detrimental effects such as fertilizers leaching, deterioration of the micro-ecological environment in the rhizosphere, nutritional imbalances, soil acidification caused by an increase in hydrogen cations, and significant enhancement of heavy metal ion activity in the soil [29]. Seed priming is known to improve seed germination, thereby potentially increasing plant growth and yield. However, there is a need to optimize and test low-cost, environmentally friendly seed treatment methods for high-value specialty crops [19].
This research aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of seed priming using silicon dioxide nanoparticles (including nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) with different average sizes) in stevia rebaudiana, an important medical and industrial plant. The obtained results have demonstrated that the nano-primed seeds showed improved seed germination compared to the bSiO2 NPs. Also, the findings suggested that seed nano-priming with suitable concentrations of nSiO2 (I), and nSiO2 (II) not only accelerated the germination rate, but also significantly enhanced seed vigor, as indicated by increased weight of the root, shoot, and seedling compared to the control. It should be noted that the nanoparticles’ type, concentration, and application method play crucial roles in plant behavior and reactivity [30].
Furthermore, our results indicated that priming with nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) improved different germination parameters. Similar findings were reported by Behboudi et al. [30] who observed increased germination index in barley with nano-priming using 30 and 60 SiO2 NPs. However, higher concentrations of SiO2 NPs showed more pronounced toxic effects on seedling length, shoot length and root length [30]. In our study, the highest concentration of nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) reduced the germination parameters. This suggests that priming with an appropriate concentration of NPs plays a critical role in germination parameters particularly seedling growth. Although there are limited studies on nano-priming with nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) specifically in stevia seeds. Some of studies suggested that the application of SiO2 NPs improved germination parameters in Agropyron elongatum [31]. Seed priming with SiO2 NPs may stimulate pre-germination metabolic events such as increased water imbibition, cell elongation, and division, repair of damaged of nucleic acids, activation of reserve mobilizing enzymes, enhancement of antioxidant enzyme activities, and improvement of seedling emergence parameters [32].
In the present study, nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) demonstrated great potential for agricultural applications as they enhanced the germination rate and physiological processes when compared to the control. However, the mechanism underlying nano-priming with nSiO2 (I), and nSiO2 (II) in inducing seed germination has not yet been reported in the literature.
α-Amylase activity and starch concentration
Priming is a controlled method of hydrating seeds that triggers pre-germination metabolic processes, including enhanced water absorption and the activation of reserve enzymes such as amylase, cellulase, and xylanase without initiating actual germination [32]. Nano-priming at a suitable concentration can stimulate seed germination of seeds by increasing α-amylase activity and starch metabolism [21]. In the present investigation, the seedlings primed with bSiO2 at 50 ppm showed higher α-amylase activity compared to the control. However, priming with nSiO2 (I) at 10 ppm, and nSiO2 (II) at 100 ppm induced the highest α-amylase activity. Additionally, the results showed a negative and significant relationship between starch and α-amylase activity. This correlation aligns with the observed starch decomposition and higher germination percentage in nano-primed seeds compared to the other priming treatments and control.
Enhanced germination and establishment of seedlings can be attributed to efficient starch metabolism, whereas reduced activities of α-amylase and dehydrogenase, along with a lower accumulation of soluble sugars, contribute to inadequate stand establishment characteristics [33]. Furthermore, it can be proposed an additional hypothesis suggesting that the penetration of nSiO2 (I), and nSiO2 (II) into seeds may play a crucial role as nano-catalyst in the hydrolysis of starch catalyzed by α-amylase, thereby increasing the rate of reaction. The utilization of micronutrient encapsulating biopolymer-based nano-system has been recommended as a smart priming agent for several applications ensuring soil fertility and environmental safety are not compromised [15]. Increasing α-amylase activity in primed seeds can enhance seedling vigor and embryo development [34]. This increased α-amylase activity promotes the breakdown of starch and subsequent increase in sucrose levels in the roots and shoot of stevia seedlings.
In a prior study discovered that the priming of stevia seeds using hydro-priming with dH2O, ascorbic acid, potassium chloride, and benzylamine purine resulted in a significant increase in α-amylase enzyme activity [33]. The researchers proposed that the observed enhancement in α-amylase and dehydrogenase activities likely contributed to improvements in germination percentage and rate [33]. Seed priming with all concentrations of nSiO2 (I) and nSiO2 (II) significantly enhanced α-amylase activity compared to bSiO2 and the control. These findings are consistent with other research conducted on wheat, which has also shown that Zn-CNPs priming leads to an increase in α-amylase activity [35]. Consequently, nano-primed seeds exhibited increased hydrolysis of starch and the subsequent release of soluble sugars [30]. Although starch is vital of energy storage polysaccharides are involved in seedling growth [36]. Our results revealed a reduction in starch content in nano-primed seeds. Similarly, seed priming with nSiO2 (I), and nSiO2 (II) led to a decreased starch concentration in stevia seedlings. The reduction of starch during seed germination is critical as dry seeds require the mobilization the storage compounds within the starchy endosperm to initiate cellular metabolism and growth [37]. The elevated activity of α-amylase, a crucial enzyme in starch degradation, observed in the cotyledons of nano-priming treatments can be attributed to the increased concentration of sucrose resulting from its utilization as an energy source by the seeds. The relationship between α-amylase activity and the conversion of starch to sucrose contributes to improved seed germination and seedling growth. Results of some studies also indicated a positive correlation between sucrose levels and the germination percentage of Medica gotruncatula seeds [38]. Notably, the highest concentration of sucrose in the root and shoot tissues of seedlings was observed in the seeds primed with nSiO2 (II) at concentrations of 100 ppm.
Free carbohydrate (sucrose)
Sugar metabolism plays a key role in determining seedling vigor during germination and early seedling development. Carbohydrates, which serve as crucial carbon sources for living cells, are utilized in various biosynthetic processes. During seed germination, a complex physiological process, storage materials are broken down, leading to the production of small molecules such as sucrose and glucose. These molecules play essential roles in sustaining the growth and development of emerging seedling [39]. Sucrose is the primary form of free carbohydrate in seedlings. Although fructose and glucose were not detected in the HPLC analysis, this could be attributed to their rapid conversion into energy or utilization in other germination mechanisms.
Our findings align with previous studies that have shown the stimulatory effect of exogenous applications of SiO2 on carbohydrate accumulation. For instance, Simlat et al. [16] demonstrated that low doses of SiO2 (5 and 20 µM) significantly improved seed germination and plantlet properties in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni, while higher doses had an inhibitory effect. Soluble sugars, including sucrose, undergo dynamic changes during seed germination and early seedling growth, and they serve as reliable indicators of seedling emergence and growth [19].
Our result indicated that nano-priming with nSiO2 (II) at concentrations up to 100 ppm increased the level of sucrose compared to the control (Fig. 3). Despite the reduction in starch concentration during the seed germination, there was an increase in sucrose concentration suggesting a significant mobilization of reserves for seedling growth.
H2O2 concentration, CAT and POX activity
If nano-priming leads to toxicity the germination and seedling growth, we would expect to observe an increase in oxidative damage and a decrease in antioxidant enzyme activity. Conversely, if nano-priming improves seedling parameters, we would anticipate an increase in antioxidant enzymes activity compared with control. In our experiment, we evaluated the effects of seed priming with bSiO2, nSiO2 (I), and nSiO2 (II) on seedling H2O2 concentration, CAT, and POX activity (Table 1).
Based on recent concepts in plant seed physiology, it has been established that seed germination is completed when the reactive oxygen species (ROS) signaling occurs within an oxidative window [21]. Therefore, the presence of ROS as a signal is necessary for the initiation of germination. However, excessive ROS concentration can cause oxidative damage and hinder germination. In our results, germination parameters decreased at higher concentrations of NPs-priming agents. We quantified the H2O2 concentration in the seedlings. H2O2 concentration, as an important ROS species, is associated with the weakening of the endosperm cap and an increase in embryo elongation during seed germination [39]. A significant increase in H2O2 concentration was observed in the primed seeds with high concentrations of nano-priming agents.
Additionally, it was found that primed seeds with 1 ppm nSiO2 (I) were more effective than none-primed seeds in reducing the accumulation of H2O2. However, nSiO2 (I) up to 25 ppm and nSiO2 (II) up to 10 ppm increased the H2O2 concentration compared to the control. In our experiment, to some extent, the reduction in H2O2 level might be attributed to the repair of the seed and organelle membranes after priming. Therefore, the nano-priming technique could act as a highly effective factor in protecting plant cells from oxidative degradation by decreasing H2O2 concentration (Table 1).
Enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants play a crucial role in seed germination. These antioxidant systems effectively control ROS accumulation and regulate germination processes [40]. Our results indicate that nano-priming increased CAT and POX activity. CAT and POX activity showed a positive correlation with germination parameters, particularly seed vigor. It appears that the enhanced antioxidant properties in nano-primed seeds may have a positive effect on seed vigor [41]. The high levels of CAT and POX activity observed in nano-priming may be attributed to the induction of H2O2 by high concentrations of nSiO2 (I), and nSiO2 (II) given the correlation between antioxidant enzymes and H2O2. In addition to germination, nutritional quality is of great importance. Interestingly, pretreatment that modifies seed metabolism not only improves germination but also has a positive impact on productivity [42]. For instance, a previous study [19] demonstrated that nano-priming increased the growth and yield of watermelons while maintaining nutritional quality. As part of our ongoing research, we are investigating the effects of nano-priming on stevia plant growth, yield, steviol glycosides, and plant safety.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the seed priming technique using nSiO2 (I) at 10 ppm demonstrated significant positive effects on seed germination and subsequent seedling growth. This was achieved through the enhancement of various physio-biochemical processes, such as the activation of amylase, degradation of cotyledon starch, increase in sucrose concentration in seedlings, and augmentation of antioxidant enzyme activity in stevia seedlings. These improvements directly contributed to improved germination rates and the development of stronger seedlings. Moreover, the utilization of nano-priming with n SiO2 (I) at 10 ppm resulted in superior outcomes compared to higher doses of nanoparticles, making it a more efficient and cost-effective approach. The affordability of the materials used in this method further supports its feasibility for commercial implementation.
Furthermore, employing these novel technological systems for seed treatment holds great potential for achieving higher agricultural yields. Importantly, the treatment exclusively targeted the seeds, ensuring that these formulations did not come into direct contact with the environment. This safeguarded against any potential risk of nanoparticle contamination in water bodies or the soil, emphasizing the sustainability and food safety aspects of this approach. By utilizing this seed priming technique, farmers can enhance crop productivity while minimizing environmental concerns.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- AFM:
-
Atomic force microscopy
- bSiO2 :
-
Bulk silicon dioxide
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- DLS:
-
Dynamic light scattering
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- NPs:
-
Nanoparticles
- nSiO2 :
-
Silica nanoparticles
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- POX:
-
Peroxidase
References
Tavakoli H, Tavakoli N, Moradi F. The effect of the elicitors on the steviol glycosides biosynthesis pathway in Stevia rebaudiana. Funct Plant Biol. 2019;46:787–95.
Tavakoli H, EbadiKhazineh Ghadim A, Moradi F, Jahanbakhsh Ghodehkahriz S, Gholipouri A. The Effects of NH4+ and NO3− and plant growth regulators on the accumulation of nutrients, carbohydrates and secondary metabolites of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Sugar Tech. 2021;23:65–76.
Prakash I, Sai V, Chaturvedula P. Steviol glycosides:natural non-caloric sweeteners. Cham: Springer; 2016.
Simlat M, Skrzypek E, Warcho M, Maciaszek I, Ptak A. Evaluation on Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni seed germination and seedling development under phytohormones treatment. Sci Hortic. 2019;257: 108717.
Angelini LG, Martini A, Passera B, Tavarina S. Cultivation of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni and Associated Challenges. Sweeteners. Springer: Cham; 2018.
Liopa-Tsakalidi A, Kaspiris G, Salahas G, Barouchas P. Effect of salicylic acid (SA) and gibberellic acid (GA3) pre-soaking on seed germination of stevia (Stevia rebaudiana) under salt stress. J Med Plants Res. 2012;6:416–23.
Uçar E, Özyiğit Y, Turgut K. The Effects of Light and Temperature on Germination of Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana BERT) Seeds. Türkiye Tarımsal Araştırmalar Derg. 2016;3:37–40.
Aghighi Shahverdi M, Omidi H, Tabatabaei SJ. Determination of optimum duration and concentration of Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bert.) seed priming with boric acid (H3BO3). Türkiye Tarımsal Araştırmalar Derg. 2017;4:24–24.
Norton LR. Is it time for a socio-ecological revolution in agriculture? Agric Ecosyst Environ. 2016;235:13–6.
Mishra S, Keswani C, Abhilash PC, Fraceto LF, Singh HB. Integrated approach of agri-nanotechnology: challenges and future trends. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1–12.
Raiesi-Ardali T, Maˈmani L, Chorom M, Moezzi A. Improved iron use efficiency in tomato using organically coated iron oxide nanoparticles as efficient bioavailable Fe sources. Chem Biol Technol Agric. 2022;9:1–16.
Nami B, Tofighi M, Molaveisi M, Mahmoodan A, Dehnad D. Gelatin-maltodextrin microcapsules as carriers of vitamin D3 improve textural properties of synbiotic yogurt and extend its probiotics survival. Food Biosci. 2023;53:102524.
Iavicoli I, Leso V, Beezhold D, Shvedova AA. Nanotechnology in agriculture: opportunities, toxicological implications, and occupational risks. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017;329:96–111.
Katiyar D, Hemantaranjan A, Singh B. Chitosan as a promising natural compound to enhance potential physiological responses in plant: a review. Indian J Plant Physiol. 2015;20(1):1–9.
Hameed A, Khalid A, Ahmed T, Farooq T. Nano-priming with Zn-chitosan nanoparticles regulates biochemical attributes and boost antioxidant defence in wheat seeds. Agrochimica. 2020.
Ibrahim EA. Seed priming to alleviate salinity stress in germinating seeds. J Plant Physiol. 2015;192:38–46.
Chen K, Arora R. Priming memory invokes seed stress-tolerance. Environ Exp Bot. 2013;94:33–45.
Dragicevic V, Spasic M, Simic M, Dumanovic Z, Nikolic B. Stimulative influence of germination and growth of maize seedlings originating from aged seeds by 2,4-D potencies. Homeopathy Elsevier Ltd. 2013;102:179–86.
Acharya P, Jayaprakasha GK, Crosby KM, Jifon JL, Patil BS. nanoparticle-mediated seed priming improves germination, growth, yield, and quality of watermelons (Citrullus lanatus) at multi-locations in Texas. Sci Rep. 2020;10:1–16.
Guha T, Ravikumar KVG, Mukherjee A, Mukherjee A, Kundu R. Nanopriming with zero valent iron (nZVI) enhances germination and growth in aromatic rice cultivar (Oryza sativa cv. Gobindabhog L.). Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018;127:403–13.
Mahakham W, Sarmah AK, Maensiri S, Theerakulpisut P. Nanopriming technology for enhancing germination and starch metabolism of aged rice seeds using phytosynthesized silver nanoparticles. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):8263.
El-Badri AM, Batool M, Wang C, Hashem AM, Tabl KM, Nishawy E, et al. Selenium and zinc oxide nanoparticles modulate the molecular and morpho-physiological processes during seed germination of Brassica napus under salt stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;225:112695.
Ramírez-Mosqueda MA, Sánchez-Segura L, Hernández-Valladolid SL, Bello-Bello E, Bello-Bello JJ. Influence of silver nanoparticles on a common contaminant isolated during the establishment of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni culture. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2020;143:609–18.
Javed R, Usman M, Yücesan B, Zia M, Gürel E. Effect of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles on physiology and steviol glycosides production in micropropagated shoots of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2017;110:94–9.
Singh D, Patel RM. Phytotoxicity of zinc-nanoparticles and its influence on stevioside production in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Appl Biol Res. 2015;17(1):1–7.
Walker D, Romero P, de Hoyos A, Correal E. Seasonal changes in cold tolerance, water relations and accumulation of cations and compatible solutes in Atriplex halimus L. Environ Exp Bot. 2008;64:217–24.
Ramiro D, Guerreiro-Filho O, Mazzafera P. Phenol Contents, oxidase activities, and the resistance of coffee to the leaf miner Leucoptera coffeella. J Chem Ecol. 2006;32:1977–88.
Chance B, Maehly A. Assay of catalase and peroxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1955;2:764–817.
Lin W, Lin M, Zhou H, Wu H, Li Z, Lin W. The effects of chemical and organic fertilizer usage on rhizosphere soil in tea orchards. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:1–16.
Behboudi F, Tahmasebi Sarvestani Z, Kassaee MZ, Modares Sanavi SAM, Sorooshzadeh A. Phytotoxicity of chitosan and SiO2 nanoparticles to seed germination of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Plants. Not Sci Biol. 2017;9:242–9.
Azimi R, Borzelabad MJ, Feizi H, Azimi A. Interaction of SiO2 nanoparticles with seed prechilling on germination and early seedling growth of tall wheatgrass (Agropyron Elongatum L.). Polish J Chem Technol. 2014;16:25–9.
Ali LG, Nulit R, Ibrahim MH, Yien CYS. Efficacy of KNO3, SiO2 and SA priming for improving emergence, seedling growth and antioxidant enzymes of rice (Oryza sativa), under drought. Sci Rep Nature Publish Group UK. 2021;11:1–11.
Haider I, Ur Rehman H. The impact of different seed priming agents and priming durations on stand establishment and biochemical attributes of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022;29:2210–8.
Mahakham W, Theerakulpisut P, Maensiri S, Phumying S, Sarmah AK. Science of the Total Environment Environmentally benign synthesis of phytochemicals-capped gold nanoparticles as nanopriming agent for promoting maize seed germination. Sci Total Environ. 2016;573:1089–102.
Tymoszuk A, Wojnarowicz J. Zinc oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles impact on in vitro germination and seedling growth in Allium cepa L. Materials. 2020;13:1–16.
Li Y, Liang L, Li W, Ashraf U, Ma L, Tang X, et al. ZnO nanoparticle-based seed priming modulates early growth and enhances physio-biochemical and metabolic profiles of fragrant rice against cadmium toxicity. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19:1–19.
Wolny E, Betekhtin A, Rojek M, Braszewska-Zalewska A, Lusinska J, Hasterok R. Germination and the early stages of seedling development in brachypodium distachyon. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):2916.
Li J, Baroja-Fernández E, Bahaji A, Muñoz FJ, Ovecka M, Montero M, et al. Enhancing sucrose synthase activity results in increased levels of starch and adp-glucose in maize (Zea mays L.) seed endosperms. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013;54:282–94.
Cao Q, Li G, Cui Z, Yang F, Jiang X, Diallo L, et al. Seed priming with melatonin improves the seed germination of waxy maize under chilling stress via promoting the antioxidant system and starch metabolism. Sci Rep. 2019;9:1–12.
Soil LS, Alhammad BA, Ahmad A, Seleiman MF. Seed priming with nanoparticles and 24-epibrassinolide improved seed germination and enzymatic performance of Zea mays L. Salt-Stressed Soil. Plants. 2023;12(4):690.
Pereira ADES, Oliveira HC, Fraceto LF, Santaella C. Nanotechnology potential in seed priming for sustainable agriculture. Nanomaterials. 2021;11:1–29.
do Pereira AES, Oliveira HC, Fraceto LF. Polymeric nanoparticles as an alternative for application of gibberellic acid in sustainable agriculture: a field study. Sci Rep. 2019;9:1–10.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial and scientific support of the Agricultural Biotechnology Research Institute of Iran.
Funding
This work was supported by the Agricultural Biotechnology Research Institute of Iran (ABRII) (Grant No. 12-05-05-027-95027-950753).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was a collaborative effort involving several authors. MM prepared the nanomaterials, while NT, HT, and VM conducted the in vitro experiments. NT and HT were responsible for writing the paper and performing the editing. LM supervised and contributed to the conception and design of the study, as well as providing assistance with the writing and editing of the paper. FM and YD provided valuable improvement during the process. All authors have carefully reviewed and approved the final manuscript. Correspondence regarding the study can be directed to LM as the corresponding author.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Hasanaklou, N.T., Mohagheghi, V., Hasanaklou, H.T. et al. Seed nano-priming using silica nanoparticles: effects in seed germination and physiological properties of Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 10, 96 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-023-00445-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-023-00445-0