Abstract
Sustainable food security is a major challenge in today’s world, particularly in developing countries. Among many factors, environmental stressors, i.e., drought, salinity and heavy metals are major impediments in achieving sustainable food security. This calls for finding environment-friendly and cheap solutions to address these stressors. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) have long been established as an environment-friendly means to enhance agricultural productivity in normal and stressed soils and are being applied at field scale. Similarly, pyrolyzing agro-wastes into biochar with the aim to amend soils is being proposed as a cheap additive for enhancement of soil quality and crop productivity. Many pot and some field-scale experiments have confirmed the potential of biochar for sustainable increase in agricultural productivity. Recently, many studies have combined the PGPR and biochar for improving soil quality and agricultural productivity, under normal and stressed conditions, with the assumption that both of these additives complement each other. Most of these studies have reported a significant increase in agricultural productivity in co-applied treatments than sole application of PGPR or biochar. This review presents synthesis of these studies in addition to providing insights into the mechanistic basis of the interaction of the PGPR and biochar. Moreover, this review highlights the future perspectives of the research in order to realize the potential of co-application of the PGPR and biochar at field scale.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Recently in agro-ecosystems, soil amendments are used to support plant growth and development, especially by adding organic and inorganic nutrients to the soil. Soil amendments are elements that are added to the soil to improve its ability to support plant life [1]. Soil amendments such as compost, animal slurry, savage sludge, green manure, farm yard manure, fly ash, biochar (BC), PGPR (plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria), etc., are the organic soil amendments have been explored as innovative strategies to increase crop productivity and soil fertility [2,3,4,5,6]. Numerous previous studies have shown that soil organic amendments can provide various benefits to soil such as improved soil texture, increased soil fertility, long-term maintenance of soil health, and in particular, crop yields [7,8,9].
However, the application of organic soil amendments to agricultural soils poses a number of threats to the agro-ecosystem and human health. Organic soil amendments often include a range of pollutants, including heavy metals, potential human pathogens, persistent organic pollutants, and emerging pollutants. From the emerging pollutants the presence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, antibiotic residues, and antibiotic-resistant genes in agricultural organic amendments is of great concern at the moment, due to the harmonious risks to human health [10]. Soil amendments should have characteristic such as environmental protection and should not have a negative impact on soil structure, soil fertility, or the ecosystem as a whole [11]. PGPR and biochar due to their different properties has attracted growing interest in the last few years to be the promising soil amendments in reducing risk associated with other soil amendments application under normal and stressed conditions [4, 12,13,14,15,16].
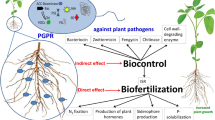
Various PGPR have been isolated and proven to alleviate various environmental stresses in plants and boost productivity. They may improve soil quality and boost plant productivity by direct and indirect mechanisms. Nitrogen fixation, phosphate and potassium solubilization, and production of growth-promoting phytohormones like indole acetic acid and siderophores are direct mechanisms through which PGPR perform these aforesaid functions; whereas, the indirect mechanisms involve production of lytic enzymes and antibiotics, lowering the soil pH, production of exopolysaccharides, etc. (Fig. 1). The effectiveness of PGPR for sustainable agro-ecosystem under normal and stress environments has been reviewed in many studies [15, 17, 18].
Biochar, a char produced by pyrolyzing organic materials particularly wastes under limited oxygen supply, has gained immense popularity for its vast range of uses like enhancing soil quality, soil carbon sequestration, adsorption and mitigation of organic and inorganic pollutants from aqueous and soil media, animal feedstock, etc. Multiple review articles and meta-analyses have summarized the positive effects of biochar on soil quality and agronomic productivity as well as the factors that contribute to the ameliorative role of biochar [19]. The biochars have also been used to alleviate various environmental stresses like salinity, drought, heavy metals, etc., from plants. This aspect has also been reviewed in multiple studies [20].
Sustainable food security is a major challenge in today’s world, more so in developing countries. The teeming millions in developing world, e.g., South Asia, South East Asia, and Africa, coupled with all around climate changes affecting agricultural operations and productivity are a major risk to sustainable food security [21]. According to Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, the COVID-19 pandemic has worsened the food security such that over 2 billion people do not have enough food to eat [22]. Food and agriculture systems have already changed considerably, but more needs to be done in this changing global environment.
Different strategies are used to improve soil quality and increase the crop yields including land reforms, better water management, stress-tolerant varieties, increasing use of fertilizers, improved seeds, use of pesticides, genetically modified crops, plant growth regulators, and soil amendments; PGPR, biochar [4, 8, 23,24,25]. Given the trade-offs between food, fuel, housing and other uses of land, the quest for long-term, sustainable, eco-friendly and cost-effective techniques and tools for boosting soil quality and agricultural productivity has never been stronger and more urgent than today.
The agricultural productivity is reduced by different abiotic stresses such as salinity, drought, and heavy metal contaminants in soils among others [26]. The world’s land affected by salinity is 1125 million hectares, which is approximately 6% of the total global area including 20% of cultivated and 33% of the irrigated land. Soil salinization reduces productivity by up to 46 million hectares per year [27]. Soil salinity accounts for 1.5 million hectares of farmland from productions annually.
Crop and livestock production are water-intensive enterprises because agriculture is the largest consumer of water globally, accounting for 70% of global water returns [28]. Agricultural drought stress is one of the major abiotic stresses that are very common in semi-arid and arid areas around the world. Moreover, climate changes are exacerbating the droughts. Global demand for water for agriculture is expected to increase by 60% by 2025 [29]. Under drought stress, crop growth and yields are generally reduced due to low amounts of nutrients, poor photosynthesis and limited water supply [30]. Furthermore, drought accelerates the biological synthesis of ethylene in plants which inhibits root length and growth [31].
Another important abiotic stress is heavy metals in soils resulting in losses of agricultural productivity. Due to various natural and human activities, significant amounts of heavy metals are regularly added to the soil worldwide [32]. More than 10 million sites of soil contamination have been reported globally, with more than 50% of sites contaminated with heavy metals [33]. These heavy metals come into the soil from expanding industries, coal burning, wastewater irrigation, petrochemical spillage, coal combustion, animal manure, and sewage sludge [34]. Recent exponential increase in production and consumption of metal based nanoparticles has been found to enhance the soil contamination with heavy metals via sewage sludge applications. Moreover, increasing use of nano-metal-based fertilizers and pesticides is an emerging source of heavy metals in soils [35].
Recently, PGPR and biochar have been co-applied in various studies in order to improve soil quality and agronomic productivity under normal and stressed conditions. The explicit or underlying assumption in these studies has been that the biochar would increase nutrient availability and provide conducive habitat for the PGPR to flourish and in response the latter would perform their designated functions (phytohormone production, nutrient solubilization, etc.) at higher rates. These studies have been performed in stress-free as well as stressed soils. However, these studies have not been comprehensively synthesized and critically reviewed. This review paper aims to fill this gap. Moreover, we also present the future directions of research in order to optimally exploit the combined potential of PGPR and biochar for sustainable agro-ecosystem.
Effect of co-application of biochar and PGPR on soil quality under normal conditions
Soil quality is a complex concept. The soils perform a variety of ecosystem services, which lead them to be defined from the point of view of those services [36]. From concurrent agricultural and environmental points of view, it is defined as the “the capacity of a soil to function within ecosystem and land-use boundaries to sustain biological productivity, maintain environmental quality, and promote plant and animal health” [37, 38]. The most commonly used chemical indicators of soil quality are soil organic matter, pH, and available macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium). Similarly, the most commonly used physical indicators include water storage, bulk density, and structural stability, whereas the biological indicators include soil respiration, microbial biomass, nitrogen mineralization, and extracellular enzymatic activities [36]. The role of co-application of biochar and PGPR in improving the soil quality would be assessed based on these indicators in this review.
Various PGPRs co-applied with biochar are proposed as a good strategy to improve soil quality [39,40,41]. The presence of biochar can increase the efficiency of PGPR, as biochar provides a substrate to PGPR due to its high surface area and enriched nutrients for their survival [42]. In the following subsections, the effect of co-application of biochar and various PGPRs on soil quality and crop productivity has been reviewed.
Effect on soil nutrients
A number of studies have assessed the effect of co-application of PGPR and biochar on soil quality defining physicochemical and biological properties of soils (Table 1). Co-application of biochar with PGPR has generally been found to increase the mineral nutrient content in soils when compared to sole application of either biochar or PGPR. For instance, combined use of biochar (2% w/w) and PGPR (Paenibacillus polymyxa and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens) showed 87% higher soil nitrate content than nitrogen only treatment [43]. Moreover, in the same study, soil urease activity in PGPR + biochar + nitrogen, was 34.20%, 13.51% and 44.78% higher than nitrogen only, biochar + nitrogen and PGPR + nitrogen, respectively. They found that soil NH4+-N contents in PGPR + biochar and biochar + nitrogen treatments was 136.83% and 82.07% higher than nitrogen only treatment. Jabborova et al. [44] evaluated the effect of co-inoculation of multifarious PGPRs (Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Pseudomonas putida) and different levels of maize biochar (1% and 3%) on soil nutrients. They found that co-application of the PGPR with 3% maize biochar increased available nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium by 73%, 173%, and 17%, respectively, when compared to the 3% maize biochar only treatment. Ren et al. [45] found that using Bacillus megaterium (a nitrogen-fixing bacteria) with wheat-derived biochar increased nitrate, inorganic nitrogen, and total potassium in PGPR + biochar treatment by 68%, 45%, and 21%, respectively, than PGPR only and by 22%, 16%, and 30%, respectively, than biochar only treatment. Similarly, a PGPR Bacillus megaterium, when co-applied with biochar derived from agricultural waste, was found to increase organic carbon, available phosphorus, and available nitrogen by 16%, 79%, and 15%, respectively, in comparison to the control (no PGPR and no biochar) treatment. Saxena et al. [40] found that shoot nitrogen was 1.64 mg N g−1 shoot in soil treated with PGPR (Bacillus sp.) co-inoculated with biochar, which was significantly higher than that in sole applications of Bacillus sp. (1.24 1.64 mg N g−1 shoot) or biochar (1.31 mg N g−1 shoot). Overall these studies indicate that co-application of biochar and PGPR works in synergy to raise the nutrient level higher than the individual application of any of these. Biochars are rich in macro- as well as micro-nutrients. When applied to soils, they contribute nutrients to soils as a result of dissolution and decomposition under the influence of soil conditions and microbial activity [46]. The PGPR, particularly those solubilizing the organic phosphate, apparently accelerates the accrual of available phosphorus from biochar [47]. Consequently, freeing the soil microorganisms from investing on the acquisition some nutrients, the combined application of PGPR and biochar facilitates them to invest on acquisition of other nutrients thereby leading to enhancing enzymatic activity and release of other nutrients [48].
Effect on water holding capacity of soil
The biochar has potential to improve water holding capacity of soils, particularly for coarse-textured ones, thanks to its large surface area-to-volume ratio. A number of reviews have compiled studies on this question [57, 58]. Some of the studies testing co-application of biochar and PGPR have also reported the ameliorative effect of biochar on water holding capacity. Co-application of a nitrogen-fixing PGPR, Bacillus megaterium, along with wheat-derived biochar increased soil WHC by 24% and 18% than PGPR only and biochar only treatments, respectively [45]. Although the PGPR alone has never been reported to ameliorate water holding capacity nor water content of a soil, they may enhance drought tolerance of crop plants [31]. However, it must be expected that the enhanced WHC, thanks to biochar, would synergize with PGPR given that the nutrient cycling, soil organic matter decomposition, and microbial signaling becomes better under optimum moisture conditions [59, 60]. It must be noted that this indirect benefit of co-applying biochar with PGPR has not been explored so far.
Effect on indigenous soil microbial communities
Many physicochemical properties of soil are improved by biochar, which ultimately facilitate the working of indigenous soil microbial communities. For instance, biochar may improve water holding capacity, pH (liming effect), and substrate and nutrient availability, which may lead to increase in microbial biomass, abundance and diversity [81, 82]. However, co-application of PGPR along with a biochar may also ease the nodulation process and improve symbiotic performance of a rhizobium [83]. Moreover, biochar has also been shown to improve the nodulation of the natural rhizobia with plants. This is due to the improvement in aeration by biochar that provides more air to nodule bacteria, which may survive for long on the porous surface of a biochar before ultimately colonizing a root [84, 85]. Similarly, adding biochar may further improve the mutualistic relationship of extant microbes for the benefit of plants. For instance, adding biochar and Pseudomonas sp. increased root colonization by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi when compared to sole addition of Pseudomonas sp. and/or AMF. The phosphate-solubilizing Pseudomonas sp. enhanced available phosphorus in the soil presumably by solubilizing it from the biochar thereby leading to enhanced root colonization and overall growth of the plant [39]. The combined application of biochar and PGPR may enhance the general abundance of certain microbial groups in soil, which contribute to overall improved soil quality. For example, an Alcaligenes sp. strain in interaction with a maize-stalk-derived biochar increased the population of soil bacteria by 30% when compared to sole application of Alcaligenes sp. and by 15% when compared to biochar only treatment. Similarly, inoculation by Bacillus megaterium of a eucalyptus plantation along with addition of wheat-derived biochar significantly improved the microbial community in the soil, thereby leading to improved nutrient availability. The authors attributed this increase in beneficial microbes to the enhanced soil organic matter content and its decomposition due to interactive effect of biochar and the inoculant [45].
Effect on intra- and extra-cellular enzymes
The potential beneficial effects of combined application of biochar and PGPR have also been assessed and reported by studying various intra- and extracellular enzymes. Combined application of a biochar with a nitrogen-fixing Bacillus deuterium increased soil sucrose activity to 4.8 mg.g−1 and 3.31 mg.g−1 from 2.48 mg.g−1 in PGPR only treatment [51]. Soil urease activity was 44.78%, and 13.51% higher while using Paenibacillus polymyxa and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with biochar (2% w/w) treatment than that in the sole PGPR and biochar treatments, respectively [43]. Jabborova et al. [44] found the increase in protease (twofold), alkaline (1.3 fold) and acid phosphomonoesterase (1.5-fold) using co-inoculation of PGPRs (Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Pseudomonas putida) with 3% maize biochar than PGPRs only and PGPRs with 1% maize biochar. Similarly, synergistic use of Bacillus subtilis with cotton-derived biochar was found to significantly enhance the invertase and catalase activities in soil than the biochar only treatment [86]. Co-application of B. japonicum and P. putida with the biochar (10 t ha−1) has been reported to increase the activity of different enzymes like FDA activity, alkaline phosphomonesterases and proteases in the soil than biochar only and the uninoculated control (no PGPR, no biochar) [87]. Overall PGPR in combination with biochar have found to increase soil sucrase, urease, protease, invertase, catalase, alkaline and acid phosphomonoesterase enzymatic activity. These enzymes stimulate biochemical processes in soil ecosystem and can define direction and intensity of nutrient transformation processes in soil, thus ensuring enhanced soil fertility. Enhanced activity of the enzymes in soil by PGPR and biochar has linear relationships with soil nutrients [43, 50]. It must be noted that the effect of co-application of biochar and biochar on important N-cycling enzymes, leucine aminopeptidase and N-acetyl-glucosaminidase, has not yet been explored. These enzymes catalyze complex proteinaceous materials in soil [88]. Given that the biochar are complex organic materials packing organic proteins, the activity of these enzymes in the presence of PGPR could reveal the extent of accrual of mineral nitrogen from the added biochars.
Effect of co-application of biochar and PGPR on agricultural productivity under normal conditions
Sustainable agriculture requires that crops grow with a low rate of agrochemical application possessing better nutritional values and disease resistance. Widespread use of expensive agrochemicals in agriculture has led to the use of more sustainable alternatives, such as PGPR and biochar in recent decades [89, 90]. Both PGPR and biochar have been extensively documented for their positive effects on plants. But in recent years the combined use of PGPR and biochar has also proved to be more effective in plant production than using PGPR or biochar separately. Various studies have reported positive effects of combined application of PGPR and biochar [29, 70, 71, 91]. For instance, a PGPR Micrococcus yunnanensis, when co-applied with 2% biochar, increased the yield to 42.1 g pot−1 from 38.9 g pot−1 when applied alone or from 36.3 g pot−1 when biochar was applied alone [41]. Co-application of both also induced a 9% increase in 1000-kernel weight than Micrococcus yunnanensis only and 8% increase in phosphorus uptake than the 2% biochar alone treatments. Yuan et al. [43] reported an increase in tomato yield in co-applied PGPR (Paenibacillus polymyxa and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens) strains with 2% biochar derived from millet straw and nitrogen fertilizer. They recorded 32.45%, 10.44% and 45.69% higher yield in PGPR + biochar + nitrogen than nitrogen only, biochar + nitrogen and PGPR + nitrogen treatments, respectively. Jabborova et al. [44] found seed germination increased by 20%, root length by 76%, root dry weight by 56%, shoot length by 41% and shoot dry weight by 59% with co-inoculation of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Pseudomonas putida with 3% maize biochar than in 3% biochar only treatment. Similarly, combined application of Alcaligenes sp. with 0.5 t ha−1 maize biochar enhanced the shoot fresh biomass, shoot dry biomass, plant height, grain yield, and 1000-grain weight by 9, 12, 6, 14 and 5%, respectively, than PGPR alone [50]. A 3% increase in plant height, 11% in shoot weight and 61% in number of nodules of cowpea plant were found by using biofertilizer (made from consortium of Bacillus thuringiensis, Pseudomonas putida and Klebsiella variicola PGPR strains) in combination with biochar than the biofertilizer only [92]. Combination of PGPR(s) with biochar has also been tested under reduced fertilizer regime in an effort to minimize the greenhouse gas emissions associated with fabrication of ammoniac fertilizers and their volatilization. For instance, combined application of PGPRs, i.e., Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, Azospirillum, Agrobacterium and biochar raised the wheat yield to 5.04 t ha−1 than 2.56 t ha−1 PGPR only and 3.16 t ha−1 in biochar only treatments [93]. Similarly, combining Bacillus sp with biochar in French beans increased shoot biomass from 2.34 g pot−1 to 3.22 g pot−1, root length from 13.33 cm to 14.88 cm, and root biomass from 1.31 g pot−1 to 1.85 g pot−1, respectively [40]. Overall, these studies show that the combined application of PGPR and biochar can increase seed germination, plant growth such as plant height, shoot length, shoot dry weight, shoot biomass, root length, root dry weight, root biomass and plant yield than the individual application of PGPR or biochar. This combination may work in two ways. In the direct mechanism, the usual production of phytohormones by the PGPR like indole acetic acid, siderophores, etc., and increase in soil nutrients via phosphate solubilization and N2 fixation leads to higher plant growth and yield. Indirectly, the presence of biochar may facilitate the survival of the PGPR in higher numbers in addition to providing them nutrient rich substrate thereby leading enhanced performance by the PGPR ultimately resulting in higher plant production [94].
Co-application of biochar and PGPR under environmental stressors
The PGPR are known since long to help alleviate multitude of environmental stressors that hamper plant growth and development. They have been proven very effective against drought, salinity, heavy metal contamination (Fig. 2).
For instance, the potential of PGPR to secrete exopolysaccharides under dry conditions help induce drought tolerance in plants [95]. Under saline conditions, they could enhance potassium uptake at the cost of sodium thereby mitigating direct adverse effects of soil salinity, increase water uptake, reduce stomatal conductance, and antioxidant enzyme activities. All of these changes help plants to grow better under saline conditions [96]. Similarly, the PGPR have been found to immobilize and reduce uptake of heavy metals by plants in addition to improving the overall nutrient uptake thereby alleviating the heavy metal induced toxicity [97]. These findings have been reviewed in a number of papers [95, 98].
Biochar has also been shown to enhance salinity tolerance, alleviate drought stress, and mitigate the toxicity induced to plants by inorganic and organic soil pollutants. Drought stress alleviation in biochar-amended soils occurs through enhanced water holding capacity thanks to large surface area-to-volume ratio of biochar [80]. Similarly, decrease in osmotic stress thanks to improved soil water content in addition to reduced Na+ uptake due to Na+’s transient binding on sorption sites on biochar alleviate soil salinity stress for plants in biochar-amended soils [80]. Sorption is also the major mechanism through which biochar alleviates toxicity stress of organic and inorganic heavy metals. All these uses of biochar against different environmental stressors have been reviewed in multiple articles [49, 99, 100]. Recently, some studies have explored the potential of co-application of PGPR and biochar to alleviate the environmental stressors for plant growth with the assumption that both the additives would act synergistically (Table 2). Although the mechanistic synergism between the two, i.e., PGPR and biochar, has not been actively explored in these studies, synergies have indeed been found. The following sections would narrate these studies.
Effect of co-application of PGPR and biochar on soil quality under environmental stressors
The combined use of PGPR and biochar perform multiple functions in alleviation of drought stress thereby leading to improved soil quality (Table 2). Both seem to work in tandem to improve the soil functions thereby alleviating the drought stress. For instance, combined application of algal biochar (4% w/w) and a PGPR Serratia odorifera to maize, when moisture content was 50% of the field capacity, significantly improved pH by 7 and 5%, EC by 34 and 13%, nitrate by 57 and 34%, phosphorus by 54 and 49%, extractable K by 30 and 15%, and organic matter by 69 and 21% in comparison to biochar alone and PGPR alone treatments, respectively [76]. Similarly, Nafees et al. [65] co-applied Cellulomonas pakistanensis or Sphingobacterium pakistanensis with biochar to Vicia faba growing on induced drought stress. They found that the combined application increased the water-use efficiency by 43.62%. In another study, soil moisture content was significantly higher in combined application of Pseudomonas sp. and biochar derived from poplar saw dust than sole application of PGPR or biochar [79]. The emerging pattern from these studies suggest that the enhanced water holding capacity and concurrent reduction in drought stress bolsters the survival and abundance of the PGPR, which in turn, perform their functions better [76].
As far as the soil quality is concerned, salinity reduces microbial activity and biomass in addition to changing the microbial community structure in soil [101]. Moreover, in saline conditions K+ transport channels are overtaken by Na+ leading to lower and reduced plant growth [102]. However, co-application of PGPR and biochar under saline conditions has been shown to induce salt tolerance and plant growth mainly by reducing Na+ uptake and improving K+/Na+ ratio. For instance, co-application of either of the two endophytic PGPRs, Burkholderia phytofirmans or Enterobacter sp, with biochar significantly mitigated the salinity stress in maize by reducing the xylem Na + uptake [80]. Similarly, co-application of Pseudomonas koreensis and Bacillus coagulans PGPRs with biochar significantly increased the K+ and K+/Na+ ratio thereby leading to lowered salinity stress in rice plants [60]. In the same study, the sodium adsorption ratio and Na+ in soil solution were also decreased by the latter’s addition to adsorption sites and desorption of K+ by co-application of PGPRs and biochar. Another PGPR Burkholderia phytofirmans, which is capable of producing exopolysaccharides, when inoculated along with biochar significantly, decreased salinity stress for plants by lowering Na+ content in soil solution. In addition to lowering Na+ content, co-applying PGPRs with biochar enhances colonization efficiency of the former thereby leading to synergistic effects on soil quality. For instance, Akhtar et al. [80] reported an increase in colonizing efficiency of PGPRs Burkholderia phytofirmans and Enterobacter sp. strains co-applied with 5% biochar (derived from hard wood and soft wood) in a saline soil than PGPRs without biochar in soil. Enterobacter sp with 5% biochar showed high colonizing efficiency in saline soil than Burkholderia phytofirmans with and without 5% biochar. Similarly, co-application of an endophytic PGPR with biochar to Chenopodium quinoa grown in a saline soil induced an increase of ~ 150–250% in PGPR colonization in rhizosphere, root interior and shoot interior bacterial population than PGPR inoculation alone. In presence of biochar studies showed a decreased Na+/K+ ratio in soil and increased root colonizing efficiency of PGPRs hence alleviating salinity stress in soil. In soil solution, biochar and PGPRs maintain the nutrient balance by releasing mineral nutrients such K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+, thereby reducing Na+ in soil. This ultimately increased the K+/Na+ ratio in soil. Exopolysaccharide produced from PGPRs under stress binds Na+ in soil [80].
The use of PGPR in combination with biochar has also been studied in polluted soils (Table 2). On the basis of results, it emerges as a promising tool for reducing heavy metal contamination in the soil. For instance, Sabir et al. [16] found that Enterobacter sp. (PGPR) inoculums with biochar (paper and pulp derived) could be an efficient approach to accelerate remediation of soil contaminated with cadmium (Cd) (80 mg kg−1 soil). Although PGPR and biochar immobilized Cd in soil thereby mitigating its availability by 15.2% and 28.3%, respectively, their combination decreased it by 45.6%. Another PGPR, Bacillus sp. in the presence of biochar increased soil enzyme (dehydrogenase) 4.61 times high than biochar leading to increased bioremediation. This combination also decreased HOAc-extractable Cd level by 11.34% than sole applications of biochar or PGPR [70]. The application of Bacillus sp with 1% biochar significantly reduced the toxic effect of chromium and improved plant health by limiting the availability of the heavy metal [71]. Both PGPRs and biochar immobilizes metals through metal immobilizing bacteria, adsorption, co-precipitation, and complexation, thus reducing their availability in soil for uptake [103].
Effect of co-application of PGPR and biochar on agriculture productivity under different stressors
Many studies have reported the effect of combined application of PGPR and biochar on plant productivity under different environmental stressors (Table 2). They have studied and invoked various physiological attributes to explain the effect of combined application of PGPR and biochar on plant growth and productivity. For instance, one of the effects of drought stresses is increase in ethylene levels in plants. It has been shown that the drought-induced increased ethylene level in plants can be mitigated by using ACC deaminase producing PGPR in conjunction with biochar because the latter supports the survival rate of inoculants and increases colonization in the plant rhizosphere [73]. This led to increased plant yields as compared to only PGPR or biochar application. Similarly, it was found in another study that co-applying ACC deaminase producing PGPRs Achromobacter xylosoxidans, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Leclercia adecarboxylata, and Enterobacter cloacae with timber waste biochar (0.75 and 1.50% w/w) in drought conditions improved the growth of maize by inducing higher nutrients uptake and lower ethylene level than sole application of biochar or PGPR [104]. Briefly, they reported that A. xylosoxidans + 1.50% biochar showed 19 and 6% higher transpiration rate, 30 and 7% higher photosynthetic rate, and 16% and 7% higher stomatal conductance, respectively, than alone A. xylosoxidans or 1.5% biochar under severe drought. E cloacae + 1.5% biochar increased chlorophyll a by 26 and 13%, carotenoids by 28 and 4%, and total chlorophyll by 29 and 9%, respectively, than E. cloacae or 1.5% biochar, respectively. Similarly combined application of P. aeruginosa and biochar decreased electrolyte leakage by 28% and 4% than applying P. aeruginosa or biochar alone, respectively. Similarly, Nafees et al. [65] investigated combined use of Cellulomonas pakistanensis and Sphingobacterium pakistanensis PGPRs and biochar derived from wood of Morus alba (5% w/w) on Vicia faba under drought stress. They found that co-application positively ameliorated fresh and dry leaf weight by 28.57 and 10.47%, fresh and dry root weight by 36.36 and 14.28%, and fresh and dry shoot weight by 16 and 10% than sole application of biochar or PGPR, respectively. Some other ACC deaminase producing PGPRs, i.e., Agrobacterium fabrum and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens have also been found to boost wheat productivity under severe drought when used in combination with timber waste biochar [73]. B. amyloliquefaciens + biochar increased plant height by 34 and 24%, root length by 25 and 8%, and spike length by 5 and 2% than B. amyloliquefaciens or biochar alone. Similarly, A. fabrum + biochar increased 1000-grains weight by 13% when compared to sole application of A. fabrum. Ullah et al. [76] evaluated the effect of co-application of a PGPR, Serratia odorifera, and algal biochar on maize growth under drought stress. The co-application increased maize growth parameters like plant height by 38 and 16%, shoot fresh weight by 29 and 17%, shoot dry weight by 44 and 24%, root fresh weight by 60 and 27%, root dry weight by 84% and 24%, and root length by 47 and 32% than sole application of PGPR or biochar under severe drought stress, respectively. Decreased proline content due to combined application of PGPRs and biochar has also been cited as drought alleviating mechanism [60]. The PGPRs namely Pseudomonas koreensis and Bacillus coagulans, when used with biochars, on rice plant under drought conditions increased relative water content, stomatal conductance, Ca2+ and K+ content and decreased proline content in plants. Another PGPR, P. fluorescens, when applied along with biochar to cucumber under limited moisture conditions was found in much higher number than when it was applied alone [59]. Their combined application under severely limited moisture conditions improved shoot length, shoot fresh weight, root length, and root fresh weight by 10%, 10%, 29% and 16%, respectively, than the sole application of biochar. Also in PGPR + biochar treatment chlorophyll content and relative water content increased by 5% and 6% than biochar only treatment. They also found reduced electrolyte leakage which helped plants to deal with water stress conditions. Drought elevates ethylene and electrolyte leakage in plants leading to retardation of plant growth. Overall, co-application of PGPR with biochar can alleviate drought stress in plants by lowering ethylene content and electrolyte leakage in plants. PGPR with biochar found to increase to relative water content, stomatal conductance, chlorophyll, carotenoids in plants.
Soil salinity affects plant growth, development and photosynthesis. It also affects protein synthesis and lipid metabolism [105]. Plant growth under saline soils is adversely affected by osmotic effects and hormonal imbalances. It also causes malnutrition and specific ion toxicity [106]. Other reason is growth is inhibited by sodium and chloride ions as sodium ions are retained in roots and stems and in some plants only chloride ions are concentrated in the shoot which has a negative effect on plants [107, 108]. Co-application of PGPRs and biochar usually exerts synergistic effects on alleviating salinity stress and increasing plant productivity than their individual effects. For example, a siderophore-producing strain, Burkholderia phytofirmans in combination with tree-twig derived biochar improved plant height, root dry weight, shoot dry weight, grain yield, photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance of Chenopodium quinoa by 17, 26, 10, 5, 5, 16 and 12%, respectively, under saline conditions than individual PGPR application only [68]. Evidence from multi-year field studies has also confirmed the synergistic potential of combining PGPR and biochar to alleviate soil salinity stress for plants. For instance, PGPR strains Bacillus coagulans and Pseudomonas koreensis were co-applied with rice husk-derived and corn stalk-derived biochars in a rice field having electrical conductivity of 4.67 dS m−1 biochar. The co-application alleviated the negative effects of salinity by decreasing Na+ content by 15.34% and 15.73%, and proline content by 52.49% and 49.57% in first and second year of the study, respectively, in rice leaves, in comparison to the uninoculated control [60]. Similarly, Akhtar et al. [80] found 25% and 8% less Na+ uptake than biochar or PGPR sole applications, respectively, by using Enterobacter with 5% biochar and Burkholderia phytofirmans with 5% biochar derived from hard and soft wood in saline soil.
PGPR and biochar play an important role in the management of heavy metal stress in plants. They can transform, accumulate or detoxify heavy metals [109]. For instance, Zafar-ul-Hye et al. [66] found 13.5% less uptake of Pb in mint leaves after it was inoculated with ACC-deaminase producing PGPRs, Alcaligenes faecalis and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and provided with compost (mixed fruits) mixed biochar (vegetable waste). Resultantly, they found that A. faecalis strain along with compost-mixed biochar significantly improved plant chlorophyll content by 37%, root dry weight by 58%), nitrogen by 46%, phosphorus by 39%, and potassium by 63% in mint leaves than untreated control. In another study, the lead uptake in spinach decreased by 43% whereas potassium uptake increased by 10.5% over untreated control by the use of compost-mixed biochar and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain [69]. The PGPR Enterobacter sp. when co-applied along with biochar significantly enhanced growth of Brassica napus in cadmium-spiked (80 mg kg−1) soil [16]. The co-application significantly increased shoot and root length by 52.5 and 76.5%, respectively, than sole application of PGPR, by 22 and 34.8% than soil without PGPR and by 29 and 41.6% sole application of biochar under stress. PGPR + biochar treatment also decreased Cd uptake by 40.1 and 38.2% in root and shoot than PGPR (16.8 and 16.9%), and biochar (23.4 and 21.3%), respectively, as compared to control under Cd stress conditions. Ma et al. [70] found an increase in ryegrass biomass (1.96 g pot−1) than biochar only (0.42 g pot−1) and lowest Cd concentration (5.45 mg kg−1) was found in PGPR + biochar treatment as compared to biochar, PGPR and control (soil without PGPR and biochar).
Mechanistic understanding of interaction of PGPR and biochar
The synthesis of literature so far in this paper has amply highlighted that the biochar and PGPRs work synergistically in improving the soil quality and agriculture productivity. When biochar is applied with PGPR inoculants, it provides habitat for PGPR (i.e., colonization, reproduction and growth) due to its porous structure and high surface area and also the ability to adsorb microorganisms and organic compounds [110]. Some studies cited in the previous sections have suggested this by showing higher growth and abundance of PGPR inoculants when biochar is also applied to soils. Biochar also protects them from other harmful pathogens [111]. Owing to richness in carbon, i.e., substrate, and essential nutrients, it provides both energy and the required nutritive building blocks for inoculants’ survival and growth [112]. In addition, biochar modifies physicochemical properties of soils that may lead to increase in soil microbial biomass and enzymatic activity [29, 98]. Biochar is rich in a range of mineral nutrients including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, etc., depending upon the feedstock type and pyrolysis temperature [113]. Upon addition to soil, it is decomposed gradually to release these nutrients in the soil solution [114,115,116].
PGPRs are involved in plant growth promotion under normal and stressed conditions through their direct and indirect mechanisms. Similar to biochar, the PGPR may either bring in a nutrient from outside through their direct mechanism such as nitrogen fixation (by nitrogen-fixing bacteria) or solubilize the immobilized nutrients (by phosphate-solubilizing bacteria) thereby contributing to plant nutrition. For instance, nitrogen-fixing PGPRs such as Paenibacillus polymyxa, Rahnella sp., Serratia sp. have the ability to enhance the mineral nitrogen content in soil solution through their nitrogen-fixing traits and prevents its leaching in soil [56, 117]. A large number of phosphate-solubilizing PGPRs, e.g., Bacillus sp., Bacillus lentus, B. subtilis, Bacillus megaterium, Burkholderia sp., Glomus etunicatum, G. mosseae, Pseudomonas species, Pseudomonas fluorescencs Penicillium strains, Lysinibacillus fusiformis, Azotobacter chroococcum, Azospirillum brasilense, Arthrobacter, Streptomyces, have been shown to solubilize and provide phosphate in soil for plant uptake [40, 49, 51, 53, 56, 77, 91, 112, 117, 118]. While the direct accrual of phosphorus from biochar by co-applied PGPR has not been demonstrated in any study, it can be safely speculated that such a mechanism exists. A similar mechanism of enhanced availability of potassium can be assumed because PGPR are known for lowering the soil pH and making the soil potassium available to plants and biochar are known to be rich in potassium [28, 96]. Another direct mechanism is production of ACC deaminase which lowers the production of ethylene elevated level produced under stress conditions through its breakdown into ammonia and alpha ketobutyrate [119]. PGPRs such as Enterobacter sp., Alcaligenes sp., Pseudomonas fluorescens, Serratia odorifera. Leclercia adecarboxylata, Agrobacterium fabrum, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc., have the ability to produce ACC deaminase. These strains show synergistic effects with biochar in abiotic stress alleviation [59, 72, 73, 80, 104]. PGPRs through their indirect mechanisms such as pH regulations, production of exopolysaccharides, protection against plant diseases are also involved in plant growth promotions [120].
Conclusions and perspective
Under different environmental stresses, low crop growth and crop failure is the norm across many important food and cash crops. Co-application of PGPR and biochar offers a sustainable, cost-effective, and environment-friendly technique for increasing crop productivity and improving soil quality. Even under normal conditions, this combination may act synergistically to improve crop productivity as well as soil quality in addition to lowering the need for chemical fertilizers. However, as is highlighted by this review, there are not many field experiments that have been conducted to explore the potential of combined application of the PGPR and biochar for sustainable food production. Given the state-of-the-art of the subject, we have following recommendations for future studies:
-
Mechanistic understanding of the interaction between PGPR and biochar needs further exploration. For instance, currently we don’t know exactly if the synergistic effect of the two is because of the conducive habitat afforded to the PGPR by biochar or it is due to the enhanced availability of substrate and nutrients due to biochar that sustains and promotes the PGPR. It can be done by using isotopically labeled biochar (i.e., 13C, 15 N, 33P) in order to trace the carbon and nutrients accrued into microbial biomass. Concurrently, the colonization efficiency of the PGPR should also been estimated.
-
Long-term field experiments could be a highly effective way of evaluating the combined effect of the PGPR and biochar. Individually, the PGPR and biochar have been assessed in reasonably long-term experiments for their potential for sustainable food production [12,13,14, 121]. However, they should now be assessed together in multi-year field experiments under the assumption that the biochar keeps influencing soil properties with aging, whereas the PGPR might persist longer in biochar-amended soils.
-
The PGPR technology is not very successful in degraded soils situated in semi-arid and arid areas, especially which are poor in soil organic matter, because the PGPR have not good reserves of substrate and nutrient-source for their growth and function. Combined application of the PGPR and biochar in these soils could be a very good strategy and needs to be assessed. The biochar may provide the PGPR the habitat to survive and flourish as well as the necessary substrates, which are lacking in such soils, and is the key reason of failure of PGPR technology there.
-
Meta-analyses of the studies on biochar vis-à-vis agricultural productivity have revealed that the major mechanism by which they improve productivity is the liming effect [19, 82]. Such biochars, when combined with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria that prefer acidic or near-neutral pH will not give good results. Therefore, the studies should combine the biochar and PGPR after keeping into account such complementarities.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- PGPR:
-
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria
- BC:
-
Biochar
- NUE:
-
Nitrogen use efficiency
- SOC:
-
Soil organic carbon
- IAA:
-
Indole acetic acid
- NaCl:
-
Sodium chloride
- FC:
-
Field capacity
- N:
-
Nitrogen
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- K:
-
Potassium
- Pb:
-
Lead
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
References
Abdul Halim NSA, Abdullah R, Karsani SA, Osman N, Panhwar QA, Ishak CF. Influence of soil amendments on the growth and yield of rice in acidic soil. Agronomy. 2018;8(9):1–11.
Villa YB, Khalsa SDS, Ryals R, Duncan RA, Brown PH, Hart SC. Organic matter amendments improve soil fertility in almond orchards of contrasting soil texture. Nutr Cycl Agroecosystems. 2021;120(3):343–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-021-10154-5.
Siedt M, Schäffer A, Smith KEC, Nabel M, Roß-Nickoll M, van Dongen JT. Comparing straw, compost, and biochar regarding their suitability as agricultural soil amendments to affect soil structure, nutrient leaching, microbial communities, and the fate of pesticides. Sci Total Environ. 2021;751:141607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141607.
Singh G, Mavi MS, Choudhary OP, Gupta N, Singh Y. Rice straw biochar application to soil irrigated with saline water in a cotton-wheat system improves crop performance and soil functionality in north-west India. J Environ Manag. 2021;295:113277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113277.
Ahmad S, Ghaffar A, Rahman MHU, Hussain I, Iqbal R, Haider G, et al. Effect of application of biochar, poultry and farmyard manures in combination with synthetic fertilizers on soil fertility and cotton productivity under arid environment. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal. 2021;52(17):2018–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2021.1908324.
Kishor P, Ghosh AK, Kumar D. Use of fly ash in agriculture: a way to improve soil fertility and its productivity. Asian J Agric Res. 2010;4(1):1–14.
Liang X, Chen Q, Rana MS, Dong Z, Liu XD, Hu C, et al. Effects of soil amendments on soil fertility and fruit yield through alterations in soil carbon fractions. J Soils Sediments. 2021;21(7):2628–38.
Khatoon Z, Huang S, Rafique M, Fakhar A, Kamran MA, Santoyo G. Unlocking the potential of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on soil health and the sustainability of agricultural systems. J Environ Manag. 2020;273:111118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111118.
Goswami L, Nath A, Sutradhar S, Bhattacharya SS, Kalamdhad A, Vellingiri K, et al. Application of drum compost and vermicompost to improve soil health, growth, and yield parameters for tomato and cabbage plants. J Environ Manag. 2017;200:243–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.073.
Urra J, Alkorta I, Garbisu C. Potential benefits and risks for soil health derived from the use of organic amendments in agriculture. Agronomy. 2019;9(9):1–23.
Paz-Ferreiro J, Lu H, Fu S, Méndez A, Gascó G. Use of phytoremediation and biochar to remediate heavy metal polluted soils: a review. Solid Earth. 2014;5(1):65–75.
Khan Z, Rahman MHU, Haider G, Amir R, Ikram RM, Ahmad S, et al. Chemical and biological enhancement effects of biochar on wheat growth and yield under arid field conditions. Sustainability. 2021;13(11):1–18.
Sciences L, Jayanti K, Autonomous C, Narayanapura K, Po K, et al. Rhizosphere competent Pseudomonas indoloxydans (F3–47) as a plant growth promoter and enhancer of Zea mays L. under greenhouse and field trials. Curr Trends Biotechnol Pharm. 2021;15:411.
Gholami A, Biyari A, Gholipoor M, Asadi RH. Growth promotion of maize (Zea mays L.) by plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria under field conditions. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal. 2012;43(9):1263–72.
Singh I. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) and their various mechanisms for plant growth enhancement in stressful conditions: a review. Eur J Biol Res. 2018;8(4):191–213.
Sabir A, Naveed M, Bashir MA, Hussain A, Mustafa A, Zahir ZA, et al. Cadmium mediated phytotoxic impacts in Brassica napus: managing growth, physiological and oxidative disturbances through combined use of biochar and Enterobacter sp. MN17. J Environ Manag. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110522.
Goswami D, Thakker JN, Dhandhukia PC. Portraying mechanics of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR ): a review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016;19(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311932.2015.1127500.
Review SAA, Kenneth C. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): a bioprotectant bioinoculant for sustainable agrobiology. A review. Int J Adv Res Biol Sci. 2017. https://doi.org/10.22192/ijarbs.2017.04.05.014.
Biederman LA, Stanley HW. Biochar and its effects on plant productivity and nutrient cycling: a meta-analysis. GCB Bioenergy. 2013;5(2):202–14.
Abbas T, Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Mahmood A, Zia-ur-Rehman M, et al. Biochar application increased the growth and yield and reduced cadmium in drought stressed wheat grown in an aged contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018;148:825–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.063.
Maja MM, Ayano SF. The impact of population growth on natural resources and farmers’ capacity to adapt to climate change in low-income countries. Earth Syst Environ. 2021;5(2):271–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-021-00209-6.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The state of food security and nutrition in the world. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization; 2020.
Ayranci R. Utilization of stress tolerant local genotypes in wheat breeding program in context to global climate change. Ekin J Crop Breed Genet. 2020;6(1):11–26.
Sikka AK, Islam A, Rao KV. Climate-smart land and water management for sustainable agriculture. Irrig Drain. 2018;67(1):72–81.
Egamberdieva D, Li L, Ma H, Wirth S, Bellingrath-Kimura SD. Soil amendment with different maize biochars improves chickpea growth under different moisture levels by improving symbiotic performance with Mesorhizobium ciceri and soil biochemical properties to varying degrees. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:1–14.
Yadav S, Modi P, Dave A, Vijapura A, Patel D, Patel M. Effect of abiotic stress on crops. Sustain Crop Prod. 2020. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.88434.
Sanower Hossain M, Sultan Ahmad Shah J. Present scenario of global salt affected soils, its management and importance of salinity research. Int Res J Biol Sci Perspect. 2019;1:2663–5976.
Islam M, Halder M, Siddique MAB, Razir SAA, Sikder S, Joardar JC. Banana peel biochar as alternative source of potassium for plant productivity and sustainable agriculture. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric. 2019;8(s1):407–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40093-019-00313-8.
Boretti A, Rosa L. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. Npj Clean Water. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-019-0039-9.
Fang Z, Wang X, Zhang X, Zhao D, Tao J. Effects of fulvic acid on the photosynthetic and physiological characteristics of Paeonia ostii under drought stress. Plant Signal Behav. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2020.1774714.
Zhang M, Yang L, Hao R, Bai X, Wang Y, Yu X. Drought-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria isolated from jujube (Ziziphus jujuba) and their potential to enhance drought tolerance. Plant Soil. 2020;452(1–2):423–40.
Saif S, Zaidi A, Khan MS. Understanding the role of microbes and plants in the management of heavy metal stress: a current perspective. Microbes signal biomol against plant stress. Singapore: Springer; 2021. p. 239–67.
He Z, Shentu J, Yang X, Baligar VC, Zhang T, Stoffella PJ. Heavy metal contamination of soils: sources, indicators, and assessment. J Environ Indic. 2015;9:17–8.
Manzoor MM, Goyal P, Gupta AP, Gupta S. Heavy metal soil contamination and bioremediation. Bioremediation Biotechnol. 2020;2:221.
Gruère G, Narrod C, Abbott L. Agricultural, food, and water nanotechnologies for the poor opportunities, constraints, and role of the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research. Communications. Washington: International Food Policy Research Institute; 2011.
Bünemann EK, Bongiorno G, Bai Z, Creamer RE, De Deyn G, de Goede R, et al. Soil quality—a critical review. Soil Biol Biochem. 2018;120:105–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.01.030.
Doran JW, Parkin TB. Defining and assessing soil quality. Defin soil Qual Sustain Environ. 1994;35:1–21.
Doran JW, Parkin TB. Quantitative indicators of soil quality: a minimum data set. Methods Assess soil Qual. 1997;49:25–37.
Ning Y, Xiao Z, Weinmann M, Li Z. Phosphate uptake is correlated with the root length of celery plants following the association between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, Pseudomonas sp. and biochar with different phosphate fertilization levels. Agronomy. 2019;9(12):1–12.
Saxena J, Rana G, Pandey M. Impact of addition of biochar along with bacillus sp. on growth and yield of French beans. Sci Hortic. 2013;162:351–6.
Hosseini E, Zarei M, Sepehri M, Safarzadeh S. Do bagasse biochar and microbial inoculants positively affect barley grain yield and nutrients, and microbial activity? J Plant Nutr. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2021.1952229.
Lehmann J, Rillig MC, Thies J, Masiello CA, Hockaday WC, Crowley D. Biochar effects on soil biota—a review. Soil Biol Biochem. 2011;43(9):1812–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.04.022.
Wang Y, Li W, Du B, Li H. Effect of biochar applied with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on soil microbial community composition and nitrogen utilization in tomato. Pedosphere. 2021;31(6):872–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(21)60030-9.
Jabborova D, Wirth S, Kannepalli A, Narimanov A, Desouky S, Davranov K, et al. Co-inoculation of rhizobacteria and biochar application improves growth and nutrients in soybean and enriches soil nutrients and enzymes. Agronomy. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10081142.
Ren H, Huang B, Fernández-García V, Miesel J, Yan L, Lv C. Biochar and rhizobacteria amendments improve several soil properties and bacterial diversity. Microorganisms. 2020;8(4):1–17.
El-Naggar A, Lee SS, Awad YM, Yang X, Ryu C, Rizwan M, et al. Influence of soil properties and feedstocks on biochar potential for carbon mineralization and improvement of infertile soils. Geoderma. 2018;332:100–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.06.017.
Yazdani M, Bahmanyar MA, Pirdashti H, Esmaili MA. Effect of phosphate solubilization microorganisms (PSM) and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on yield and yield components of corn (Zea mays L.). World Acad Sci Eng Technol. 2009;37:90–2.
Zheng H, Vesterdal L, Schmidt IK, Rousk J. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry can reflect microbial resource limitation, substrate quality, or both in forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem. 2022;167:108613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2022.108613.
Heidari E, Mohammadi K, Pasari B, Rokhzadi A, Sohrabi Y. Combining the phosphate solubilizing microorganisms with biochar types in order to improve safflower yield and soil enzyme activity. Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2020;66(2):255–67.
Hussain A, Ahmad M, Zahid Mumtaz M, Nazli F, Aslam Farooqi M, Khalid I, et al. Impact of integrated use of enriched compost, biochar, humic acid and Alcaligenes sp. AZ9 on maize productivity and soil biological attributes in natural field conditions. Ital J Agron. 2019;14(2):101–7.
Ren H, Lv C, Fernández-García V, Huang B, Yao J, Ding W. Biochar and PGPR amendments influence soil enzyme activities and nutrient concentrations in a eucalyptus seedling plantation. Biomass Convers Biorefinery. 2021;11(5):1865–74.
Tripti, Kumar A, Usmani Z, Kumar V, Anshumali. Biochar and flyash inoculated with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria act as potential biofertilizer for luxuriant growth and yield of tomato plant. J Environ Manag. 2017;190:20–7.
Rafique M, Sultan T, Ortas I, Chaudhary HJ. Enhancement of maize plant growth with inoculation of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and biochar amendment in soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2017;63(5):460–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2017.1373599.
Kareem Abdulrahman D, Binti Othman R, Mohd Saud H, Binti Abu Bakr R. Effect of biochar on soil and growth of sweet corn effects of biochar and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (SB16) on soil properties and growth of sweet corn. J Agric Res. 2017;55(3):485–99.
Awtar S, Singh AP, Singh SK, Singh CM. Effect of biochar along with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on growth and total dry matter yield of rice. J Pure Appl Microbiol. 2015;9(2):1627–32.
Shanta N, Schwinghamer T, Backer R, Allaire SE, Teshler I, Vanasse A, et al. Biochar and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria effects on switchgrass (Panicum virgatum cv. Cave-in-Rock) for biomass production in southern Québec depend on soil type and location. Biomass Bioenergy. 2016;95:167–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2016.10.005.
Lone AH, Najar GR, Ganie MA, Sofi JA, Ali T. Biochar for sustainable soil health: a review of prospects and concerns. Pedosphere. 2015;25(5):639–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(15)30045-X.
Ding Y, Liu Y, Liu S, Li Z, Tan X, Huang X, et al. Biochar to improve soil fertility. A review. Agron Sustain Dev. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-016-0372-z.
Nadeem SM, Imran M, Naveed M, Khan MY, Ahmad M, Zahir ZA, et al. Synergistic use of biochar, compost and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for enhancing cucumber growth under water deficit conditions. J Sci Food Agric. 2017;97(15):5139–45.
Hafez EM, Alsohim AS, Farig M, Omara AED, Rashwan E, Kamara MM. Synergistic effect of biochar and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on alleviation of water deficit in rice plants under salt-affected soil. Agronomy. 2019;9(12):1–24.
Waqar A, Bano A, Ajmal M. Effects of PGPR bioinoculants, hydrogel and biochar on growth and physiology of soybean under drought stress. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal. 2022;53(7):826–47. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2022.2028818.
Lalay G, Ullah S, Ahmed I. Physiological and biochemical responses of Brassica napus L. to drought-induced stress by the application of biochar and Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria. Microsc Res Tech. 2022;85(4):1267–81.
Nafees M, Ullah S, Ahmed I. Modulation of drought adversities in Vicia faba by the application of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and biochar. Microsc Res Tech. 2022;85(5):1856–69.
Rhizobacteria PG, Maize E, Nehela Y, Mazrou YSA, Alshaal T, Rady AMS, et al. (Zea mays L.) resilience to water salinity. Plants. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091960.
Nafees M, Ullah S, Ahmed I. Morphological and elemental evaluation of biochar through analytical techniques and its combined effect along with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on Vicia faba L. under induced drought stress. Microsc Res Tech. 2021;84(12):2947–59.
Zafar-ul-Hye M, Tahzeeb-ul-Hassan M, Wahid A, Danish S, Khan MJ, Fahad S, et al. Compost mixed fruits and vegetable waste biochar with ACC deaminase rhizobacteria can minimize lead stress in mint plants. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86082-9.
Danish S, Zafar-Ul-Hye M, Hussain S, Riaz M, Qayyum MF. Mitigation of drought stress in maize through inoculation with drought tolerant ACC deaminase containing PGPR under axenic conditions. Pak J Bot. 2020;52(1):49–60.
Naveed M, Ramzan N, Mustafa A, Samad A, Niamat B, Yaseen M, et al. Alleviation of salinity induced oxidative stress in chenopodium quinoa by Fe biofortification and biochar-endophyte interaction. Agronomy. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10020168.
Zafar-ul-Hye M, Tahzeeb-ul-Hassan M, Abid M, Fahad S, Brtnicky M, Dokulilova T, et al. Potential role of compost mixed biochar with rhizobacteria in mitigating lead toxicity in spinach. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-69183-9.
Ma H, Wei M, Wang Z, Hou S, Li X, Xu H. Bioremediation of cadmium polluted soil using a novel cadmium immobilizing plant growth promotion strain Bacillus sp. TZ5 loaded on biochar. J Hazard Mater. 2020;388:1–9.
Mazhar R, Ilyas N, Arshad M, Khalid A, Hussain M. Isolation of heavy metal-tolerant PGPR strains and amelioration of chromium effect in wheat in combination with biochar. Iran J Sci Technol Trans A Sci. 2020;44(1):1–12.
Zafar-Ul-Hye M, Danish S, Abbas M, Ahmad M, Munir TM. ACC deaminase producing PGPR Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and agrobacterium fabrum along with biochar improve wheat productivity under drought stress. Agron. 2019;9(7):1–16.
Danish S, Zafar-ul-Hye M. Co-application of ACC-deaminase producing PGPR and timber-waste biochar improves pigments formation, growth and yield of wheat under drought stress. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1–13.
Chuaphasuk C, Prapagdee B. Effects of biochar-immobilized bacteria on phytoremediation of cadmium-polluted soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2019;26(23):23679–88.
Sadegh Kasmaei L, Yasrebi J, Zarei M, Ronaghi A, Ghasemi R, Saharkhiz MJ, et al. Influence of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria, compost, and biochar of azolla on rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) growth and some soil quality indicators in a calcareous soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal. 2019;50(2):119–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2018.1554669.
Ullah N, Ditta A, Khalid A, Mehmood S, Rizwan MS, Ashraf M, et al. Integrated effect of algal biochar and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on physiology and growth of maize under deficit irrigations. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2020;20(2):346–56.
Rékási M, Szili-Kovács T, Takács T, Bernhardt B, Puspán I, Kovács R, et al. Improving the fertility of sandy soils in the temperate region by combined biochar and microbial inoculant treatments. Arch Agron Soil Sci. 2019;65(1):44–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2018.1482536.
Seneviratne M, Weerasundara L, Ok YS, Rinklebe J, Vithanage M. Phytotoxicity attenuation in Vigna radiata under heavy metal stress at the presence of biochar and N fixing bacteria. J Environ Manage. 2017;186:293–300.
Fazal A, Bano A. Role of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR), biochar, and chemical fertilizer under salinity stress. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal. 2016;47(17):1985–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2016.1216562.
Akhtar SS, Andersen MN, Naveed M, Zahir ZA, Liu F. Interactive effect of biochar and plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes on ameliorating salinity stress in maize. Funct Plant Biol. 2015;42(8):770–81.
Kolton M, Graber ER, Tsehansky L, Elad Y, Cytryn E. Biochar-stimulated plant performance is strongly linked to microbial diversity and metabolic potential in the rhizosphere. New Phytol. 2017;213(3):1393–404.
Jeffery S, Verheijen FGA, van der Velde M, Bastos AC. A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agric Ecosyst Environ. 2011;144(1):175–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.08.015.
Egamberdieva D, Wirth S, Behrendt U, Abd-Allah EF, Berg G. Biochar treatment resulted in a combined effect on soybean growth promotion and a shift in plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:1–11.
Iijima M, Yamane K, Izumi Y, Daimon H, Motonaga T. Continuous application of biochar inoculated with root nodule bacteria to subsoil enhances yield of soybean by the nodulation control using crack fertilization technique. Plant Prod Sci. 2015;18(2):197–208.
Vanek SJ, Thies J. Pore-size and water activity effects on survival of Rhizobium tropici in biochar inoculant carriers. J Microb Biochem Technol. 2016. https://doi.org/10.4172/1948-5948.1000300.
Tao S, Wu Z, Wei M, Liu X, He Y, Ye BC. Bacillus subtilis SL-13 biochar formulation promotes pepper plant growth and soil improvement. Can J Microbiol. 2019;65(5):333–42.
Sarfraz R, Hussain A, Sabir A, Ben Fekih I, Ditta A, Xing S. Role of biochar and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria to enhance soil carbon sequestration—a review. Environ Monit Assess. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7400-9.
Arnosti C, Bell C, Moorhead DL, Sinsabaugh RL, Steen AD, Stromberger M, et al. Extracellular enzymes in terrestrial, freshwater, and marine environments: perspectives on system variability and common research needs. Biogeochemistry. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-013-9906-5.
Semida WM, Beheiry HR, Sétamou M, Simpson CR, Abd El-Mageed TA, Rady MM, et al. Biochar implications for sustainable agriculture and environment: a review. S Afr J Bot. 2019;127:333–47.
Vejan P, Abdullah R, Khadiran T, Ismail S, Nasrulhaq BA. Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in agricultural sustainability—a review. Molecules. 2016;21(5):1–17.
Kumar A, Singh VK, Tripathi V, Singh PP, Singh AK. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): perspective in agriculture under biotic and abiotic stress. In: New and future developments in microbial biotechnology and bioengineering: crop improvement through microbial biotechnology. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2018. p. 333–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63987-5.00016-5.
Taiwo LB, Adesokun KT, Olatoberu FT, Oyedele AO, Ojo AO, Olayinka AA. Effect of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) and biochar on soil properties and performance of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp). Ife J Agric. 2018;30(3):56–71.
Ijaz M, Sher A, Sattar A, Naeem WHM. Cumulative effect of biochar, microbes and herbicide on the growth and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Pak J Life Soc Sci. 2015;13(2):73–8.
Hussain A, Ahmad M, Mumtaz MZ, Ali S, Sarfraz R, Naveed M, et al. Integrated application of organic amendments with Alcaligenes sp. AZ9 improves nutrient uptake and yield of maize (Zea mays). J Plant Growth Regul. 2020;39(3):1277–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10067-7.
Vurukonda SSKP, Vardharajula S, Shrivastava M, SkZ A. Enhancement of drought stress tolerance in crops by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Microbiol Res. 2016;184:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.12.003.
Gupta R, Anshu, Noureldeen A, Darwish H. Rhizosphere mediated growth enhancement using phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria and their tri-calcium phosphate solubilization activity under pot culture assays in Rice (Oryza sativa). Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021;28(7):3692–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.05.052.
Hansda A, Kumar V, Usmani Z. Phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soil using plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): a current perspective. Recent Res Sci Technol. 2014;6(1):131–4.
Rashid MI, Mujawar LH, Shahzad T, Almeelbi T, Ismail IMI, Oves M. Bacteria and fungi can contribute to nutrients bioavailability and aggregate formation in degraded soils. Microbiol Res. 2016;183:26–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.11.007.
Ali MA, Ajaz MM, Rizwan M, Qayyum MF, Arshad M, Hussain S, et al. Effect of biochar and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on growth and phosphorus uptake by maize in an Aridisol. Arab J Geosci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05326-6.
Zaheer MS, Ali HH, Soufan W, Iqbal R, Habib-ur-Rahman M, Iqbal J, et al. Potential effects of biochar application for improving wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) growth and soil biochemical properties under drought stress conditions. Land. 2021;10(11):1125.
Yan N, Marschner P, Cao W, Zuo C, Qin W. Influence of salinity and water content on soil microorganisms. Int Soil Water Conserv Res. 2015;3(4):316–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2015.11.003.
Cheng D, Wu G, Zheng Y. Positive correlation between potassium uptake and salt tolerance in wheat. Photosynthetica. 2015;53(3):447–54.
Cheng C, Luo W, Wang Q, He L, Sheng X. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety Combined biochar and metal-immobilizing bacteria reduces edible tissue metal uptake in vegetables by increasing amorphous Fe oxides and abundance of Fe- and Mn-oxidising Leptothrix species. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020;206:111189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111189.
Danish S, Zafar-Ul-Hye M, Mohsin F, Hussain M. ACC-deaminase producing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and biochar mitigate adverse effects of drought stress on maize growth. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(4):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230615.
Parida AK, Das AB. Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2005;60(3):324–49.
Panuccio MR, Jacobsen SE, Akhtar SS, Muscolo A. Effect of saline water on seed germination and early seedling growth of the halophyte quinoa. AoB Plants. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plu047.
Tester M, Davenport R. Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot. 2014;91(5):503–27.
Mäser P, Gierth M, Schroeder JI. Molecular mechanisms of potassium and sodium uptake in plants. Prog Plant Nutr Plenary Lect XIV Int Plant Nutr Colloq. 2002. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00281.
Mishra J, Singh R, Arora NK. Alleviation of heavy metal stress in plants and remediation of soil by rhizosphere microorganisms. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:1–7.
Palansooriya KN, Wong JTF, Hashimoto Y, Huang L, Rinklebe J, Chang SX, et al. Response of microbial communities to biochar-amended soils: a critical review. Biochar. 2019;1(1):3–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-019-00009-2.
Ajeng AA, Abdullah R, Ling TC, Ismail S, Lau BF, Ong HC, et al. Bioformulation of biochar as a potential inoculant carrier for sustainable agriculture. Environ Technol Innov. 2020;20:101168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101168.
Singh RP, Jha PN. The multifarious PGPR Serratia marcescens CDP-13 augments induced systemic resistance and enhanced salinity tolerance of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). PLoS ONE. 2016;11(6):1–24.
Tomczyk A, Sokołowska Z, Boguta P. Biochar physicochemical properties: pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2020;19(1):191–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09523-3.
Riaz M, Roohi M, Arif MS, Hussain Q, Yasmeen T, Shahzad T, et al. Corncob-derived biochar decelerates mineralization of native and added organic matter (AOM) in organic matter depleted alkaline soil. Geoderma. 2017;294:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.02.002.
Shemawar, Mahmood A, Hussain S, Mahmood F, Iqbal M, Shahid M, et al. Toxicity of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles to soil organic matter cycling and their interaction with rice-straw derived biochar. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88016-x.
El-Naggar A, Shaheen SM, Ok YS, Rinklebe J. Biochar affects the dissolved and colloidal concentrations of Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn and their phytoavailability and potential mobility in a mining soil under dynamic redox-conditions. Sci Total Environ. 2018;624:1059–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.190.
Prasad R, Kumar M, Varma A. Role of PGPR in soil fertility and plant health. Cham: Springer; 2015. p. 247–60.
Efthymiou A, Grønlund M, Müller-Stöver DS, Jakobsen I. Augmentation of the phosphorus fertilizer value of biochar by inoculation of wheat with selected Penicillium strains. Soil Biol Biochem. 2018;116:139–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.10.006.
Gupta S, Pandey S. ACC deaminase producing bacteria with multifarious plant growth promoting traits alleviates salinity stress in French Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) plants. Front Microbiol. 2019;10(JULY):1–17.
Riddech N, Phibunwatthanawong T, Sarin P. Suitable formulation of microbial inoculants as a bio-fertilizer for promoting growth of hairy-leafed apitong (Dipterocarpus alatus). Waste Biomass Valorization. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01526-7.
Krey T, Vassilev N, Baum C, Eichler-Löbermann B. Effects of long-term phosphorus application and plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria on maize phosphorus nutrition under field conditions. Eur J Soil Biol. 2013;55:124–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2012.12.007.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the funding provided to them by Higher Education Commission of Pakistan and Government College University Faisalabad, Pakistan.
Funding
LM is a PhD student funded by Higher Education Commission through “‘Indigenous PhD Fellowship Program For 5000 Scholars, HEC (Phase-II, Batch-V, 2018)” and this work is a part of her PhD dissertation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, TS, and LM; literature search, LM, MS, and FM; data duration, SH, MHS, and FA; writing—original draft preparation, LM, and TS; writing—review and editing, MS, FM, MHS, SH, FA: supervision, TS; funding acquisition, TS. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors gave their consent for publication of this article.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no competing interest among the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Malik, L., Sanaullah, M., Mahmood, F. et al. Unlocking the potential of co-applied biochar and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) for sustainable agriculture under stress conditions. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 9, 58 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-022-00327-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-022-00327-x