Abstract
Background
A previous study has shown that Japanese individuals generally exhibit behavior that suppresses the expression of positive emotions, which are strongly affected by affectivity traits. In the present study, to clarify the relationship between affectivity traits and work engagement (WE) or work-related psychosocial factors among Japanese workers, we compared it to the association between psychological distress and these same factors.
Methods
A total of 1,000 full-time Japanese regular workers responded to an online survey that measured demographic variables, negative and positive affectivity, job demands and resources, WE, and psychological distress. A hierarchical multiple regression analysis was conducted separately, which used WE and psychological distress as dependent variables.
Results
The proportion of variance explained by negative and positive affectivity was lower for WE than for psychological distress. However, the proportion of variance defined by job demands and resources was higher for WE than for psychological distress. The proportion of variance explained by all variables for negative and positive affectivity and job demands and resources, and their interactions was approximately equal for WE and psychological distress.
Conclusion
These results emphasize when researchers aim to evaluate the change of psychosocial factors in the workplace, such as improving the workplace environment among Japanese workers, it might be beneficial to measure positive indicators in addition to negative indicators. Furthermore, enriching job resources would be effective in improving WE and alleviating psychological distress.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Work engagement (WE) refers to “a positive, fulfilling, work-related state of mind characterized by vigor, dedication, and absorption” [1] and is beneficial for both individual workers and organizations. Studies have indicated that WE is associated with improved physical and mental health [2, 3]. Furthermore, WE is associated with job performance [2, 4] and business growth [5]. Therefore, several researchers have developed intervention programs and verification methods in the workplace environment to enhance WE [6, 7].
To improve the mental health of employees, industrial and organizational psychologists and practitioners who evaluate either the psychosocial environments in the workplace or the effect of workplace intervention programs ought to ensure the accurate and sensitive documentation of job stressors as well as the mind and body state of employees [8]. Furthermore, the influence of individual factors, such as sociodemographic variables and worker personalities, should be considered to a significant extent. However, it is widely known that individual characteristics are associated with stress responses [9,10,11]. For example, negative affectivity (NA) of affective dispositions [12, 13] is generally known that a personality trait strongly associated with work environment factors and stress responses [14, 15]. Therefore, statistically controlling NA had been recommended to distinctly determine the relationship between job stressors and stress responses [16, 17]. On the other hand, scholars have cautioned that statistical control removes true variance and distorts the effects of causal variables (e.g., job stressors and stress responses) and is thus undesirable [18]. Thus, the influence of a worker’s individual characteristics is exceedingly and intricately associated with workplace environmental factors or the worker’s stress response.
Similarly, this association might also be the case for the WE. The job demands-resources model includes WE as part of its motivational process [19, 20]. However, in the job demand-resource model, although individual characteristics are included in personal resources, their position remains indefinite [20]. Young et al. [21], conducting a meta-analysis of the association between personality traits and WE, demonstrated that among various personality traits, positive affectivity (PA) was most strongly associated with WE.
Watson and Tellegen [22] found that the various moods nursed by humans can be categorized into two domains, namely, negative and positive affect. Subsequently, Watson et al. [13] discovered that negative and positive affect are pertinent in both state and trait ratings and thus referred to these trait domains as NA and PA. High NA describes the ease of evoking negative emotions such as “scary” or “sluggish,” while high PA refers to the ease of evoking positive emotions such as “energetic” or “lively” [13]. This two-dimensional factor structure is common in Japan, the United States, and Europe [23], and the NA and PA roughly correspond to the dominant personality traits of neuroticism and extraversion in a five-factor model, respectively [24].
A study comparing WE measurements between Japanese and Dutch people ought to consider cultural differences when interpreting WE values as Japanese people tend to suppress positive emotions while self-enhancement for Dutch people can represent lower measurement accuracy [25]. Furthermore, studies have shown that the Japanese are more likely to suppress expressions of positive emotions in contrast to Europeans and Americans due to cultural customs [26,27,28]. Iwata et al. [29] compared the factor structure of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) between Japanese and Western individuals and found that the affectivity traits of Japanese people largely determined positive emotions. Thus, WE measurements among Japanese individuals exhibit a stronger reflection of their affectivity traits in contrast to Europeans and Americans.
Therefore, the purpose of this study was to clarify the relationship between trait affectivity and WE or work environment factors among Japanese workers. For the above reasons, the WE of Japanese workers would strongly reflect the influence of affectivity. To test this hypothesis, in addition to examining the association between WE and affectivity factors or work environment factors, this study will examine the association between psychological distress and affectivity factors or work environment factors. Previous studies show that there is no cultural difference between Japanese and Europeans or Americans in terms of stress responses comprising negative aspects such as depression and anxiety [26, 28, 30]. Thus, by comparing the results of psychological distress without cultural differences and WE with cultural differences, the extent to which affective traits influence the association between WE and work environmental factors can be clarified.
Hypothesis 1
The proportion explained by affectivity factors is higher in WE variance than in psychological distress for Japanese workers.
WE seems to be strongly influenced by work environment factors. Studies examining the relationship between workplace environmental factors and WE have been actively conducted in many countries. These studies have consistently implied that measures to enrich job resources such as job control or social support in the workplace are essential for improving WE [31, 32]. Furthermore, previous studies have shown that not only job resources but also job demands are associated with WE [33,34,35].
The job demands-resources model shows that when job resources are low, WE decreases and stress reactions increase [19, 20]. Furthermore, WE has been found to mediate the relationships between job demands and psychological distress [19, 20]. In other words, WE can be considered to influence psychological distress. Although it is widely known that psychosocial factors in the workplace are related to psychological distress [36,37,38,39], the effects of those factors would be stronger on WE than on psychological distress.
Hypothesis 2
The proportion explained by work environmental factors is higher in WE variance than in psychological distress variance.
We test the above two hypotheses. To our knowledge, no empirical study has been conducted that simultaneously measures and examines in detail the relationships between affectivity traits, work environmental factors, and WE.
Methods
Study design and data collection
A cross-sectional survey was conducted among registered marketing research monitors and an internet survey firm (Rakuten Insight, Inc). Thus, the participants provided their data using the internet. The inclusion criteria of the participants were as follows: (a) Japanese and (b) full-time employees of the organization. Self-employed, part-time, and unemployed workers were excluded from this study. The Internet survey company recruited monitor workers until the target number was reached based on the inclusion criteria. The recruited workers were able to access a self-report questionnaire of the present study.
Participants
To increase the likelihood of obtaining a representative sample of Japanese workers, the population was assigned proportions according to gender, age, and place of residence based on population estimates published by the Statistics Bureau of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications [40]. Furthermore, to minimize gender differences in the analysis, the gender proportions were set to be equal. Data were obtained from 1,000 Japanese workers (i.e., 504 men and 496 women). The mean age of the participants was 45.6 years (standard deviation, 13.0).
Measures
Affectivity traits
The negative and positive affectivity of the participants was measured using the Japanese version of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS) [41]. This version of the PANAS consists of 16 items: eight items for negative affect and eight items for positive affect. Typically, the PANAS requires respondents to rate the frequency of their feelings over four weeks on a six-point scale ranging from 1 (never) to 6 (always). However, this study focused on measuring stable traits of both negative and positive affect. Thus, the PANAS instructions were revised from “How often have you felt these moods in the past month?” to “To what extent do you usually feel these moods?” The items were scored on a six-point scale ranging from 1 (totally disagree) to 6 (totally agree).
Work-related psychosocial factors
Job demands and resources were measured using the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire (BJSQ) [42]. “Job demands” comprised three items for both the quantitative and the qualitative workload. The items were scored on a four-point scale ranging from 1 (very much) to 4 (not at all). “Job resources” consisted of nine items, namely, three for job control and six for support from supervisors and co-workers. All job resources items were scored on a four-point scale ranging from 1 (very much) to 4 (not at all). A high score for job demands indicated a high workload while a high score for job resources indicated extensive workplace resources.
Work engagement
The WE among the participants was assessed using the Japanese version of the Utrecht Work Engagement Scale (UWES) [43]. The UWES consists of three subscales (i.e., vigor, dedication, and absorption); each comprise three items scored on a seven-point scale ranging from 0 (never) to 6 (always). The overall score for the UWES is the sum of the three subscales.
Psychological distress
The Kessler 6 (K6) scale [44, 45] was used to measure psychological distress. K6 requires respondents to describe how frequently they have experienced each statement during the past 30 days. The items were scored on a five-point scale ranging from 0 (none of the time) to 4 (all of the time).
Demographic variables
Several variables were analyzed in the questionnaire, namely, age, gender, educational background, marital status, number of children, occupation, duration in the current job, and night shift.
Statistical analysis
First, the correlation coefficients between each variable and Cronbach’s alpha coefficients were estimated. Thereafter, a hierarchical multiple regression analysis of WE and psychological distress was performed before entering the independent variables in Model 1 in the following order: age, gender, and career in the current job. In Model 2, job demands and resources were used as occupational factors while affective factors were used in Model 3. In Model 4, the two two-way interactions (job demands × PA or NA, and job resources × PA or NA) were inserted to analyze the interactive effects between occupational and affective factors [46]. Finally, the interactions were calculated after centering each variable using its mean to account for multicollinearity issues. The statistical analyses were performed using R, version 4.1.0.
Results
Preliminary analyses
Table 1 shows the demographic characteristics of the participants. Approximately 60% of the participants held university or graduate school degrees. Furthermore, it was estimated that 70% of the participants were non-manual workers.
Table 2 shows the correlation coefficients between the variables with Cronbach’s alpha coefficients. This study found moderate associations between age and career in terms of the current job, NA and psychological distress, PA and WE, as well as job resources and WE. Cronbach’s alpha coefficients were greater than 0.80 for all variables.
Hierarchical multiple regression analysis
Tables 3 and 4 show the hierarchical multiple regression analysis results, with WE and psychological distress as the respective dependent variables.
In Model 1, only age was positively associated with WE. Furthermore, including occupational factors in Model 2 resulted in a significant increase in the coefficient of determination (ΔR2 = 0.24). Moreover, age, job demands, and resources were all positively associated with WE. Model 3 includes affective factors and a significant increase was observed in the determination coefficient (ΔR2 = 0.17). Thus, the WE variances associated with occupational and affective factors were higher for occupation factors than for affective factors. Furthermore, age, gender, job demands, resources, and PA were positively associated while NA was negatively associated with WE. Regarding the change in the standardized regression coefficient of occupational factors in Models 2 and 3, job resources decreased (β = 0.19) despite the absence of change in job demands. In Model 4, the coefficient of determination did not increase significantly and no interactions were associated with WE.
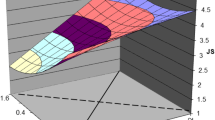
In the context of psychological distress, age was negatively associated with psychological distress in Model 1. The inclusion of occupational factors in Model 2 resulted in a significant increase in the coefficient of determination (ΔR2 = 0.16). Furthermore, job demands in Model 2 were positively associated while age or job resources were negatively associated. In Model 3, the affective factors were introduced and the coefficient of determination increased significantly (ΔR2 = 0.26). Thus, the variances in psychological distress explained by occupational and affective factors were more significant for the affective factors in contrast to the occupational factors. Moreover, age, job resources, and PA were negatively associated, while job demands and negative affectivity were positively associated. For the change in the standardized regression coefficient of occupational factors in Models 2 to 3, a decrease was found in job demands and resources (job demands: β = 0.11, resources: β = 0.21). In Model 4, the coefficient of determination increased significantly (ΔR2 = 0.01). A simple slope analysis showed that psychological distress did not change with job resources when NA was low (mean - 1 SD). However, when NA was high (mean + 1 SD), job resources significantly reduced psychological distress (see Fig. 1).
Finally, comparing the results in Tables 3 and 4, the proportion explained by affectivity factors was higher in psychological distress than in WE (WE; ΔR2 = 0.17, Psychological distress; ΔR2 = 0.26). Conversely, the proportion explained by occupational factors was higher in WE than in psychological distress (WE; ΔR2 = 0.24, Psychological distress; ΔR2 = 0.16). Excluding the association of demographic variables, the proportion explained by all variables including occupational and affectivity factors and their interactions in Models 2 to 4 nearly equal in variances of WE and psychological distress (WE; ΔR2 = 0.41 or adjusted R2 = 0.42, Psychological distress; ΔR2 = 0.43 or adjusted R2 = 0.43).
Discussion
The purpose of this study was to clarify the relationship between trait affectivity and WE or work environment factors among Japanese workers. The results indicated that the proportion of variance explained by positive and negative affectivities was lower for WE than for psychological distress, and thus hypothesis 1 was not supported. Second, the proportion of variance explained by job demands and resources was higher for WE than for psychological distress, thus supporting hypothesis 2.
In the present study, affective factors accounted for nearly 20% of the variance in the WE. Furthermore, the percentage of variances in WE associated with affective traits was approximately 30% (∆R2 = 0.324) despite changing the input order of the occupational and affective factors in Models 2 and 3. The results suggest that the influence of affective factors on WE is small when compared to the meta-analysis [21], which found that negative and positive affectivities explained nearly 40% of the variance in WE. Contrastingly, even when comparing the effects of psychological distress in the present study, the influence of affective factors on WE was small. Thus, the result differed from Iwata et al. [29]. The current results suggest that it could be more effective to focus on workplace environmental factors such as job demands or resources, rather than on individual factors such as affectivity traits for WE among Japanese workers.
High extraversion and low neuroticism tendencies are important in enhancing WE [47, 48]. Young et al. [21] found that PA accounted for 90.6% of the total proportion of both NA and PA, explaining the variance in WE (i.e., 9.4% for NA and 90.6% for PA). We entered the affective factors one by one and re-calculated the NA and PA ratio for ∆R2 in Model 3 of Table 3. The results showed that the PA and the NA were 80.8% and 19.2%, respectively. In other words, the proportion of NA was higher than the findings reported by Young et al. [21]. Several international studies comparing the five-factor model have reported high neuroticism as one of the typical personality traits among Japanese individuals [49, 50]. Particularly, Japanese people have stronger NA than individuals from other countries. Therefore, the affective factor that characterizes the high WE of Japanese workers is a high level of PA and is expressed as low NA as an essential characteristic.
Job demands and resources explained the higher percentage of the variance observed in WE as opposed to psychological distress. The change in standardized regression coefficients on job demands and resources in Model 3 (Tables 3 and 4, respectively) with affectivity factors as an input was smaller for WE than for psychological distress, and the proportion explained by affectivity traits for the variance of WE was smaller than for the variance of psychological distress. These results indicate that the association between WE and job demands or resources is less influenced by affectivity traits than the association between psychological distress and that for Japanese workers. Therefore, when researchers aim to accurately and sensitively evaluate the change of psychosocial factors in the workplace, such as improving the workplace environment among Japanese workers, it might be beneficial to measure positive indicators (e.g., WE) in addition to negative indicators (e.g., psychological stress responses). Because, positive indicators, such as WE, are less influenced by individual factors such as affective traits, and those indicators strongly reflect the influence of work environment factors.
Studies have consistently implied that measures to enrich job resources are essential for improving WE [31, 32]. Model 3 (Tables 3 and 4) shows that job resources significantly impacted all dependent variables and were more influential on WE than job demands when the demographic variables and affective factors were controlled. Similarly, job demands and resources have an equal influence on psychological distress. These findings indicate that enriching job resources can reduce psychological distress and improve WE regardless of the affective traits of the worker. Furthermore, the results of the interaction between NA and job resources on psychological distress indicate that the psychological distress of workers with higher NA is mitigated by many job resources in the workplace although they are likely to experience psychological distress [51, 52]. Therefore, enriching job resources would be effective in improving WE and alleviating psychological distress.
Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, the causal relationships between variables could not be addressed as this was a cross-sectional study. Therefore, in the future, we need to conduct a longitudinal study to verify whether the findings of this study are robustly replicated. Second, the participants in this study were all registered monitors chosen by the same internet survey company; thus, selection bias might have affected the results. Third, the variable of job demands and resources used in this study were ones included in the job demands-control-support model [53]. However, given the existence of several other variables for job demands and resources [20], it is necessary that verification be based on other variables not used in this study. Fourth, although we conducted the statistical analysis of the interaction between work environment factors and affectivity traits, we have not been able to conduct a detailed examination on why there is an interaction between negative affectivity and job resources in psychological distress and no interaction in other combinations. Finally, this survey was conducted via the Internet in November 2020, during the coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Furthermore, some of the companies where the study participants worked might have been operating remotely to prevent the spread of infection. Therefore, the changes in work patterns and daily lifestyles might have influenced the findings of this study.
Conclusion
This study indicated that for Japanese workers, the association between WE and job demands or resources was less influenced by affectivity traits than the association between psychological distress and them. Thus, these results emphasize when researchers aim to evaluate the change of psychosocial factors in the workplace, such as improving the workplace environment among Japanese workers, it might be beneficial to measure positive indicators in addition to negative indicators. Furthermore, enriching job resources would be effective in improving WE and alleviating psychological distress.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- BJSQ:
-
Brief job stress questionnaire
- COVID-19:
-
Coronavirus 2019
- K6:
-
Kessler 6
- NA:
-
Negative affectivity
- PA:
-
Positive affectivity
- PANAS:
-
Positive and negative affect schedule
- STAI:
-
State-trait anxiety inventory
- UWES:
-
Utrecht work engagement scale
- WE:
-
Work engagement
References
Schaufeli WB, Salanova M, González-Romá V, Bakker AB. The measurement of engagement and burnout: a two sample confirmatory factor analytic approach. J Happiness Stud. 2002;3(1):71–92.
Schaufeli WB, Taris TW, Bakker AB. Dr Jekyll or Mr. Hyde? On the differences between work engagement and workaholism. In: Burke RJ, editor. Research companion to working time and work addiction. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing; 2006. p. 193–217.
Schaufeli WB, Taris TW, Van Rhenen W. Workaholism, burnout, and work engagement: three of a kind or three different kinds of employee well-being? Appl Psychol. 2008;57(2):173–203.
Shimazu A, Schaufeli WB, Kubota K, Kawakami N. Do workaholism and work engagement predict employee well-being and performance in opposite directions? Ind Health. 2012;50(4):316–21.
Gorgievski MJ, Moriano JA, Bakker AB. Relating work engagement and workaholism to entrepreneurial performance. J Manag Psychol. 2014;29:106–21.
Knight C, Patterson M, Dawson J. Building work engagement: a systematic review and meta-analysis investigating the effectiveness of work engagement interventions. J Organ Behav. 2017;38:792–812.
Knight C, Patterson M, Dawson J. Work engagement interventions can be effective: a systematic review. Eur J Work Organ Psychol. 2019;28:348–72.
LaMontagne A, Keegel T. Reducing stress in the workplace: an evidence review-full report. Melbourne: Victorian Health Promotion Foundation; 2012.
Eysenck HJ. The biological basis of personality. Springfield: Thomas; 1967.
Warr P. Well-being and the workplace. Wellbeing, The foundations of hedonic psychology. New York, US: Russell Sage Foundation; 1999. p. 392–412.
Nettle D. Personality: What makes you the way you are. New York: Oxford University Press; 2007.
Clark LA, Watson D. Temperament: a new paradigm for trait psychology. In: Pervin LA, John OP, editors. Handbook of personality: Theory and research. 2nd ed. New York: Guilford Press; 1999. p. 399–423.
Watson D, Clark LA, Tellegen A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1988;54(6):1063.
Watson D, Pennebaker JW, Folger R. Beyond negative affectivity: measuring stress and satisfaction in the workplace. In: Ivancevich JM, Ganster DC, editors. Job stress: From theory to suggestion. New York: Haworth Press; 1987. p. 141–58.
Spector PE, O’Connell BJ. The contribution of personality traits, negative affectivity, locus of control and Type A to the subsequent reports of job stressors and job strains. J Occup Organ Psychol. 1994;67(1):1–2.
Brief AP, Burke MJ, George JM, Robinson BS, Webster J. Should negative affectivity remain an unmeasured variable in the study of job stress? J Appl Psychol. 1988;73:193–8.
Payne R. A longitudinal study of the psychological well-being of unemployed men and the mediating effect of neuroticism. Hum Relat. 1988;41:119–38.
Spector PE, Zapf D, Chen PY, Frese M. Why negative affectivity should not be controlled in job stress research: don’t throw out the baby with the bath water. J Organ Behav. 2000;21:79–95.
Bakker AB, Demerouti E. The job demands–resources model: state of the art. J Manag Psychol. 2007;22:309–28.
Schaufeli WB. Applying the job demands-resources model. Organ Dyn. 2017;46:120–32.
Young HR, Glerum DR, Wang W, Joseph DL. Who are the most engaged at work? A meta-analysis of personality and employee engagement. J Organ Behav. 2018;39:1330–46.
Watson D, Tellegen A. Toward a consensual structure of mood. Psychol Bull. 1985;98(2):219.
Arimitsu A, et al. Individual difference of affect/emotion. In: Ninomiya K, Ukiya S, Horike K, Ando J, Fujita S, Oshio A, et al., editors. Handbook of personality. Tokyo: Fukumura Shuppan, Inc.; 2013. p. 159–65. In Japanese.
Costa P, McCrae R. Neo PI-R professional manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources; 1992.
Shimazu A, Schaufeli WB, Miyanaka D, Iwata N. Why Japanese workers show low work engagement: an item response theory analysis of the Utrecht Work Engagement scale. Biopsychosoc Med. 2010;4(1):1–6.
Iwata N, Higuchi HR. Responses of Japanese and American university students to the STAI items that assess the presence or absence of anxiety. J Pers Assess. 2000;74:48–62.
Iwata N, Mishima N, Shimizu T, Mizoue T, Fukuhara M, Hidano T. The Japanese adaptation of the STAI form Y in Japanese working adults. The presence or absence of anxiety. Ind Health. 1998;36:8–13.
Iwata N, Roberts CR, Kawakami N. Japan-U.S. comparison of responses to depression scale items among adult workers. Psychiatry Res. 1995;58:237–45.
Iwata N, Mishima N, Okabe K, Kobayashi N, Hashiguchi E, Egashira K. Psychometric properties of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory among Japanese clinical outpatients. J Clin Psychol. 2000;56:793–806.
Iwata N, Buka S. Race/ethnicity and depressive symptoms: a cross-cultural/ethnic comparison among university students in East Asia, North and South America. Soc Sci Med. 2002;55:2243–52.
Leiter MP, Bakker AB. Work engagement: A handbook of essential theory and research. New York: Psychology Press; 2010.
Lesener T, Guys B, Wolter C. The job demands-resources model: a meta-analytic review of longitudinal studies. Work Stress. 2019;33:76–103.
Inoue A, Kawakami N, Tsutsumi A, Shimazu A, Miyaki K, Takahashi M, et al. Association of job demands with work engagement of Japanese employees: comparison of challenges with hindrances (J-HOPE). PLoS One. 2014;9:e91583.
Van den Broeck A, De Cuyper N, De Witte H, Vansteenkiste M. Not all job demands are equal: differentiating job hindrances and job challenges in the Job Demands-Resources model. Eur J Work Organ Psychol. 2010;19:735–59.
Oshio T, Inoue A, Tsutsumi A. Associations among job demands and resources, work engagement, and psychological distress: fixed-effects model analysis in Japan. J Occup Health. 2018;60:254–62.
Kawakami N, Araki S, Kawashima M. Effects of job stress on occurrence of major depression in Japanese industry: a case-control study nested in a cohort study. J Occup Med. 1990;32:722–5.
Ylipaavalniemi J, Kivimäki M, Elovainio M, Virtanen M, Keltikangas-Järvinen L, Vahtera J. Psychosocial work characteristics and incidence of newly diagnosed depression: a prospective cohort study of three different models. Soc Sci Med. 2005;61:111–22.
Inoue A, Kawakami N, Haratani T, Kobayashi F, Ishizaki M, Hayashi T, et al. Job stressors and long-term sick leave due to depressive disorders among Japanese male employees: findings from the Japan Work Stress and Health Cohort study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2010;64:229–35.
Shields M. Stress and depression in the employed population. Health Rep. 2006;17:11–29.
Statistics Bureau of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. Population Estimates. 2019. http://www.stat.go.jp/data/jinsui/2019np/index.html#a05k01-b. Accessed 21 June 2020.
Sato A, Yasuda A. Development of the Japanese version of Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS) scales. Pasonariti Kenkyu. 2001;9:138–9. In Japanese.
Shimomitsu T, Haratani T, Nakamura K, Kawakami N, Hayashi T, Hiro H, et al. Final development of the brief job stress questionnaire mainly used for assessment of the individuals. In: Kato M, editor., et al., The Ministry of Labor sponsored grant for the prevention of work-related illness. Tokyo: Tokyo Medical University; 2000. p. 126–64. In Japanese.
Shimazu A, Schaufeli WB, Kosugi S, Suzuki A, Nashiwa H, Kato A, et al. Work engagement in Japan: validation of the Japanese version of the Utrecht Work Engagement Scale. Appl Psychol. 2008;57(3):510–23.
Kessler RC, Barker PR, Colpe LJ, Epstein JF, Gfroerer JC, Hiripi E. Screening for serious mental illness in the general population. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60:184–9.
Furukawa TA, Kawakami N, Saitoh M, Ono Y, Nakane Y, Nakamura Y, et al. The performance of the Japanese version of the K6 and K10 in the World Mental Health Survey Japan. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2008;17:152–8.
Cohen J, Cohen P, West SG, Aiken LS. Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. 3rd ed. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers; 2003.
Langelaan S, Bakker AB, Van Doornen LJP, Schaufeli WB. Burnout and work engagement: do individual differences make a difference? Pers Individ Differ. 2006;40:521–32.
Fukuzaki T, Iwata N. Association between the five-factor model of personality and work engagement: a meta-analysis. Ind Health. 2022;60:154–63.
McCrae RR, Terracciano A. Personality profiles of cultures: aggregate personality traits. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2005;89:407–25.
Schmitt DP, Allik J, McCrae RR, Benet-Martínez V. The geographic distribution of Big Five personality traits: patterns and profiles of human self-description across 56 nations. J Cross-Cult Psychol. 2007;38(2):173–212.
Bolger N, Schilling EA. Personality and the problems of everyday life: the role of neuroticism in exposure and reactivity to daily stressors. J Pers. 1991;59:355–86.
Hills H, Norvell N. An examination of hardiness and neuroticism as potential moderators of stress outcomes. Behav Med. 1991;17:31–8.
Johnson JV, Hall EM. Job strain, workplace social support, and cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional study of a random sample of the Swedish working population. Am J Public Health. 1988;78:1336–42.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all individuals who participated in this study.
Funding
This study was supported by a 2019 Productivity Research Grant, administered by the Japan Productivity Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This work was carried out in collaboration with all authors. Author TF designed the study, managed the analyses of the study, and prepared the draft of the manuscript. Author NI participated in the statistical analysis and assisted in the draft of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, Tottori University, Japan (no. 20A100). All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments. Informed consent was obtained from all participants using a web-based form before the research commenced. The instructions guaranteed: (a) the protection of personal information, (b) the removal of personally identifiable information from the data, and (c) that there would be no disadvantage to individuals who did not participate in the survey.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Appendix 1.
The factor structure of PANAS in Japanese workers (N = 1000).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuzaki, T., Iwata, N. The impact of negative and positive affectivity on the relationship between work-related psychological factors and work engagement in Japanese workers: a comparison of psychological distress. BMC Psychol 11, 219 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01250-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01250-y