Abstract
The acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACS) family is a subfamily of adenylate-forming enzymes, which has a close evolutionary relationship with the 4-coumarate:CoA ligase (4CL) family. In this study, two ACS genes were cloned from Populus trichocarpa and were named PtrACS1 and PtrACS2. Bioinformatics characterization of PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 showed that they contained the key ACS residues and a putative peroxisome targeting sequence 1 (PTS1) at the end of the C-terminal sequence. Real-time PCR results showed that PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 were expressed in the phloem, xylem, leaves, and roots of one-year-old P. trichocarpa, but were expressed primarily in the leaves. The ACS enzyme activity was higher in leaves than other tissues in P. trichocarpa. Two overexpressed recombinant proteins showed no catalytic activity toward the substrates of 4CL, but did have notable catalytic activity toward sodium acetate and substrates of ACS. The relative activities of PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 were 194.16 ± 11.23 and 422.25 ± 21.69 μM min−1 mg−1, respectively. The K m and V max of PtrACS1 were 0.25 mM and 698.85 μM min−1 mg−1, while those for PtrACS2 were 0.72 mM and 245.96 μM min−1 mg−1, respectively. Our results revealed that both proteins belong to the ACS family, and provide a theoretical foundation for the identification and functional analysis of members of the adenylate-forming enzyme superfamily.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
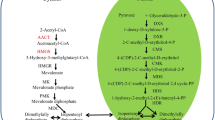
The adenylate-forming enzyme superfamily is characterized by the presence of a highly conserved putative AMP-binding domain (PROSITE PS00455) and a shared ATP-dependent, two-step reaction mechanism as follows (Schneider et al. 2005): Acid + ATP → Acyl-AMP + PPi (REACTION 1) and Acyl-AMP + CoA → acyl-CoA + AMP (REACTION 2), which contributes to the biosynthesis or degradation of diverse compounds such as fatty acids, amino acids, and a variety of secondary metabolites. In fact, diverse proteins such as fatty acyl-CoA synthetases, acetyl-CoA synthetases (ACS), 4-coumarate:CoA ligases (4CL), chlorobenzoate:CoA ligase, non-ribosomal polypeptide synthetases, and firefly luciferases are classified in one superfamily of adenylate-forming enzymes (Stuible and Kombrink 2001).
4CL is an important enzyme in lignin biosynthesis. It plays a key role in general phenylpropanoid metabolism, which is the link between lignin precursors and branched products. 4CL catalyzes the activation of various cinnamic acid derivatives (coumarate, caffeate, and ferulate) to form their corresponding CoA esters, and these activated phenolic acids serve as precursors for the biosynthesis of lignin (Stuible and Kombrink 2001; Weisshaar and Jenkins 1998). Previous studies showed that 4CL enzymes are encoded by multigene families in all vascular plants (Hamberger et al. 2007; Lindermayr et al. 2002; Kumar and Ellis 2003), and that isoenzymes of 4CL had differential enzymatic activity toward different hydroxycinnamyl substrates (Stuible and Kombrink 2001).
Sequence analysis showed that 4CL isoenzymes share structural similarities to ACS, such as a conserved substrate binding domain and Box I and II domains (Ehlting et al. 2001). However, determination of the classification of a gene family through sequence alignment analysis alone is not sufficient. In the Arabidopsis and Populus model plants, a number of genes encoding adenylate-forming enzymes are annotated as being closely related to 4CL despite having unknown specific biochemical functions. Most of these 4CL-like enzymes contain peroxisome targeting sequence 1 (PTS1) sequences in the C-terminal region, and are therefore predicted to be targeted to the peroxisome (Schneider et al. 2005; Koo et al. 2006). Some 4CL-like genes are not associated with flavonoid biosynthesis or lignification (Raes et al. 2003), and they may not have 4CL activity. In Arabidopsis, seven 4CL-like recombinant proteins (At5g63380, At4g05160, At4g19010, At3g48990, At1g20510, At1g62940, and At5g38120) had no measurable catalytic activity toward 4CL substrates, while had catalytic activity to acyl:CoA synthetases (Shockey et al. 2003). Since the Populus trichocarpa genome sequence was published, more 4CL-like genes have been found and identified, but most do not have the enzymatic activity of 4CL (Zhang et al. 2015). Which family these 4CL-like proteins belong to and what reactions they catalyze should be explored.
In a previous study of P. trichocarpa, 18 4CL-like genes were cloned, five of which were classified into the 4CL family, while the rest were unknown (Shi et al. 2010). In this study, two different genes belonging to the 18 4CL-like genes were cloned from P. trichocarpa. Sequence and enzyme characterization analyses revealed that both belonged to the ACS family, and displayed high gene expression levels and ACS enzymatic activity in leaves.
Methods
Plant material
One-year-old P. trichocarpa samples were obtained from our experimental nursery at the Biochemical and Molecular Biology laboratory, Beijing Forestry University.
Isolation of RNA and cDNA synthesis
Total RNA was isolated from the leaf of P. trichocarpa using the TransZol UP Kit (TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and cDNA was synthesized after DNase digestion (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) with the RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions using a (dT)18 primer.
Cloning and functional analysis of P. trichocarpa ACS genes
The opening reading frames of the cDNAs encoding PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 were amplified by PCR. The primers used were as follows, for PtrACS1: 5′-GGTACCATGGAGAAATCTGGTTATGGTC-3′ and 5′- GTCGACTCATATCTTGGATTTTACTTGC-3′, and for PtrACS2: 5′- GGTACCATGGAGAAAATCTGGTTATGGCC-3′ and 5′-CTGCAGTCACATCTTGGATTTCACTTTC-3′. 3 μg RNA was used for cDNA synthesis. Then PCR was performed in a volume of 25 μL containing ~ 2 μL of the first strand cDNA, 0.75U of Taq DNA polymerase, 200 μM dNTP, 1.5 mM MgCl2 and 10 pmol of each primer. The PCR conditions were optimized and consisted of an initial denaturation of 5 min at 95 °C, followed by 30 cycles of 30 s at 94 °C, 30 s at 55 °C, and 60 s at 72 °C, with a final extension of 10 min at 72 °C. The PCR products were purified and cloned into the PMD18-T vector (Takara, Shiga, Japan), propagated in Escherichia coli (E. coli) JM109 and the inserts were confirmed by sequencing. Functional characterizations of the ACS gene sequence were obtained from the Uniprot site (http://www.expasy.org/). The primary structure was predicted using the ExPASy ProtParam server (http://expasy.org/cgi-bin/protparam). Physicochemical parameters such as molecular weight, theoretical isoelectric point, number of positively-charged (lysine, arginine, and histidine) and negatively-charged amino acids (aspartic acid and glutamic acid) were determined. Hydrophobic, hydrophilic, and aromatic amino acids were also identified. Locations of the transmembrane, intracellular, and extracellular regions were predicted using the TMHMM data bank (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/). Post-translational modifications were predicted using the Center for Biological Sequence Analysis website at http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/researchgroups/PTM.php. The 3D structures of PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 were obtained from the SWISS-MODEL website at http://swissmodel.expasy.org/interactive.
Phylogenetic tree and alignment
Sequences of the two ACS proteins and 19 protein sequences from other species were aligned with the CLUSTAL W program assembled using Mega 6.0 software (Tamura et al. 2011). A phylogenetic tree was drawn with Mega 6.0 using the neighbor-joining tree method with the p-distance substitution model, which was estimated by Mega 6.0 as the best-fit model. Reliability of the internal branches was assessed with 1000 bootstrap replicates and the values were marked above the nodes.
Heterologous expression and purification of recombinant enzymes
The plasmid vector pET30a(+) (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), digested by the KpnI and SalI restriction enzymes, was used to produce the recombinant proteins. The entire open reading frame, including the designed restriction enzyme sites, or the products obtained by digesting PMD18T-ACS1 or PMD18T-ACS2 with the respective enzymes, were inserted into pET30a(+) by ligation to form pET30a(+)-ACS1 or pET30a(+)-ACS2. These recombinant plasmids were transformed into E. coli BL21 cells and positive colonies were confirmed by sequencing. An overnight culture of E.coli BL21 transformed with recombinant plasmid was diluted 1:100 and grown in LB liquid media containing kanamycin (100 mg/L) until the absorbance at 600 nm (A600) reached 0.4–0.6. Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was added as the inducing agent at a final concentration of 0.3 mM, and incubated at 28 °C for 3 h. Cells were collected by centrifugation at 4000×g and 4 °C for 10 min and then resuspended in lysis buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl with 10 mM imidazole, pH 8.0). Cells were disrupted by sonication on ice for 150 cycles of 3-s pulses of maximal power and 7 s cooling between pulses, and the extracts were cleared by centrifugation at 12,000×g for 30 min at 4 °C. The protein was purified according to the manufacturer’s instructions for high-level expression and purification provided by QIAGEN, which was specific for the purification of 6 × His-tagged proteins from E. coli under native conditions. The purified target protein was kept at 4 °C. The sample (10 μg) and protein marker (5 μg) were loaded on a 12 % SDS-PAGE gel to verify the protein expression and purification results.
Enzyme assay
4CL activity was determined by spectrophotometric assay (Knobloch and Hahlbrock 1977). The standard reaction mixture contained 2 μg of purified protein, 0.33 mM coenzyme A, 5 mM ATP, 25 mM MgCl2, and 500 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.8). After incubation at room temperature for 10 min, the absorbance was monitored at wavelengths of 333, 363, and 345 nm for 4-coumaroyl-CoA, caffeoyl-CoA, and feruloyl-CoA, respectively. ACS activity was also determined by spectrophotometric assay. The reaction mixture contained 12.5 μL of 0.2 M MgCl2, 50 μL of 0.1 M ATP, 30 μL of 20 mM CoA, 30 μL of 0.2 M sodium acetate, and 50 μL of hydroxylamine solution. A volume of 450 μL of ferric-chloride reagent was adding to stop the reactions and the mixtures were kept on ice for 30 min. Next, the tubes were centrifuged for 2 min, and the red–purple color generated was measured at 540 nm with a UV-2102C spectrophotometer (Unico, Beijing, China). The extinction coefficient of acetyl hydroxamate was 0.975 mM−1 cm−1 under these conditions. Sodium acetate was used as the substrate for determining both pH and temperature optima. Phosphate buffer (10 mM) with a pH ranging from 5.0 to 9.0 was used to provide various pH conditions. The optimum pH of each ACS was fixed when analyzing the temperature profile. Enzymatic reactions were initiated by the addition of enzymes. All the mixtures were incubated for 10 min at each temperature before the reaction was initiated. The protein activity was measured by the method described earlier at temperatures of 4, 25, 30, 35, 37, 40, 50, and 55 °C, respectively. Km and Vmax values were determined by Lineweaver–Burk kinetics plotting in Excel software and using sodium acetate at concentrations ranging from 0.01 to 2 mM. The equation of K cat = V max /[E] was used to calculate turnover number (K cat ), where [E] refers to the active enzyme concentration and V max to the maximal velocity.
Quantitative real-time PCR analysis and ACS enzyme activity in P. trichocarpa
Total RNA was isolated from one-year-old P. trichocarpa, and the plant materials were divided into four parts; root, leaf, phloem, and xylem. The stem was divided into two parts using a scalpel, one part included the epidermis and phloem, (hereafter called the phloem), and the residual part of the stem we termed the xylem (Rao et al. 2015). Total RNA was isolated using the TransZol UP Kit (TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd.) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Total RNA (2 μg) was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using Superscript II Reverse Transcriptase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and oligo(dT) primers. Gene expression was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR using cDNAs equivalent to 100 ng of the total RNA. Gene-specific primers were designed for the PCR amplification (Additional file 1: Table S5). Quantitative real-time PCR assays were performed using the Mx3000P real-time PCR detection system (Stratagene, San Diego, CA, USA) and the Brilliant R SYBR Green QPCR Master Mix (Stratagene). Gene expression data were normalized using the P. trichocarpa alpha-tubulin gene (TUA1, accession number: POPTR_0002s11250.1) as a reference. Cycling parameters were as follows: 94 °C for 10 min, 30 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, and 40 cycles of 95 °C for 1 min and 60 °C for 30 s. Three plants were tested and all were analyzed separately. Error bars represent the standard error (SE) of independent triplicate assays. Data were analyzed using the iQ5 software (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA), and differences in gene expression were calculated using the 2–ΔΔC analysis method (Liu et al. 2013). Total proteins were extracted from root, leaf, phloem, and xylem using the TCA-acetone method (Saravanan and Rose, 2004). Total protein activity was determined using sodium acetate as the substrate and the same method as used for the enzyme assay.
Results
Molecular cloning and characterization of PtrACS1 and PtrACS2
Based on the genomic sequence of the poplar genome (http://www.jgi.doe.gov/poplar/), we cloned and characterized two complete cDNA sequences from P. trichocarpa, Ptr4CL6 (accession number: XP_006373451) and Ptr4CL8 (accession number: XP_006373451). Primary structure prediction showed that the Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8 cDNAs both contained a 1632-bp open reading frame (excluding the stop codon) and encoded peptides of 543 residues with predicted molecular masses of 59.21 and 59.43 kDa, respectively (Additional files 1: Tables S1 and S2). The isoelectric points (pI) of Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8 were 8.84 and 8.74, respectively. The TMHMM program predicts the locations of transmembrane, intracellular, and extracellular domains. As seen in Fig. 1, Ptr4CL6 was predicted to have a positive transmembrane domain from valine 234 to leucine 255, while that of Ptr4CL8 from asparagine 233 to serine 253. Ptr4CL6 was predicted to have one uncertain transmembrane domain from proline 93 to alanine 104, while that of Ptr4CL8 from phenylalanine 96 to glicine 103 (Fig. 1). Post-translational modification results revealed that Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8 were both modified post-translation. Phosphorylation, glycosylation and C-mannosylation sites were identified in both Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8. No acetylation sites were identified in either of them (Additional file 1: Table S3).
The modeling and 3D structures were predicted using the SWISS-MODEL server, and the Populus tomentosa 4CL1 was most similar to Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8, with similarities of only 42.39 and 42.86 %, respectively. Figure 2a, b shows the spatial model of P. tomentosa 4CL1, with its substrate binding sites Tyr-236, Gly-306, Gly-331, Pro-337, and Val-338 (Hu et al. 2010). Figure 2 shows the spatial model of Ptr4CL6 (Fig. 2c, d) and Ptr4CL8 (Fig. 2e, f), in which the substrate binding residues were changed on both to Phe-245, Ala-315, Gly-340, ILE-347, and Val-348. The change of the substrate binding residues may lead to Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8 having a different catalytic activity than that of P. tomentosa 4CL1.
Amino acid sequence analysis showed high similarity (92 %) between Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8. NCBI BLAST analysis showed Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8 to have 30–40 % sequence similarity to Ptr4CL. Sequence alignment revealed that the box I and box II domains (Martínez-Blanco et al. 1990) were conserved in Arabidopsis At4CL (Fig. 3), but were not conserved in Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8. In particular, the main differences were a proline change to serine or valine in box I, and the combination of cysteine–isoleucine was substituted by tryptophan–valine. Box I was relatively conserved in the adenylate-forming enzymes superfamily, while box II was only conserved in 4CL. Based on the differences in box II between 4CL and our two 4CL-like genes, we speculated that Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8 may not have the same catalytic activity as 4CL (Ehlting et al. 2005; Costa et al. 2005). However, compared with the AtACS1 protein, the conserved structure domains of motifs 1 and 2 in ACS were relatively conserved in Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8 (Costa et al. 2005), which may suggest that Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8 have ACS activity. The putative peroxisomal targeting signal type 1 (PTS1) in the C-terminal region, were the peroxisomal matrix targets sequences, displays an auxiliary targeting function (Wang et al.1999; Hayashi et al. 1997; Mullen et al. 1997; Kragler et al. 1998; Kato et al. 1998). Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8 contained PTS1, indicating that both these Ptr4CL proteins may be located in the peroxisome and be related to lipid synthesis and metabolism. Based on this possibility, the Ptr4CL6 and Ptr4CL8 genes were renamed PtrACS1 and PtrACS2, respectively.
Phylogenetic tree analysis
To investigate the evolutionary relationships of the two genes with other adenylate-forming enzymes, we performed a phylogenetic analysis using the MEGA 6.0 program. The results clearly showed that PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 had high homology (Fig. 4, Additional file 1: Table S1), and had the closest evolutionary relationships with other ACS sequences (AAB92552 Arabidopsis thaliana ACS, NP_198504 Arabidopsis thaliana ACS, AED94121 Arabidopsis thaliana ACS, EOY03030 Theobro macacao ACS isoform 1, XP_007032105 Theobro macacao ACS isoform 2, and XP_007032106 Theobro macacao ACS isoform 3).
Expression and purification of recombinant PtrACS1 and PtrACS2
The recombinant pET30a(+)/PtrACS1 and pET30a(+)/PtrACS2 vectors were transformed into the E.coli strain BL21 to obtain recombinant proteins.
After inducing with IPTG for 3 h, the target proteins encoded by the PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 genes were expressed and then purified using the Ni–NTA column method under native conditions (Fig. 5a, b).
Expression and purification of recombinant PtrACS1 and PtrACS2. a Marker: Shanghai biochemical low molecular weight protein MARKER standard; lanes 1 and 2: total protein from BL21 (DE3) cells harboring pET-30a(+)-ACS1 not induced by IPTG; lane 3: total protein from BL21 (DE3) cells harboring pET-30a(+)-ACS1 induced by IPTG for 3 h; lane 4: 250 mM imidazole-eluted sample. b Marker: Shanghai biochemical low molecular weight protein MARKER standard; lane 1: total protein from BL21 (DE3) cells harboring pET-30a(+)-ACS2 not induced by IPTG; lane 2: total protein from BL21 (DE3) cells harboring pET-30a(+)-ACS2 induced by IPTG for 3 h; lane 3: the flow-through sample; lane 4: 250 mM imidazole-eluted sample
Enzyme activity and kinetic analysis of recombinant PtrACS1 and PtrACS2
To further clarify the enzymatic characteristics of the recombinant PtrACS1 and PtrACS2, we examined their substrate specificities. In plants, 4CLs usually display high activity toward 4-coumarate, ferulate, and caffeate, while ACSs usually display high activity toward sodium acetate (Lindermayr et al. 2002; Hu et al. 1998; Ehlting et al. 1999; Hamberger and Hahlbrock 2004). We used various substrates (sodium acetate, coumarate, caffeate, and ferulate) to detect the activities of the recombinant PtrACS1 and PtrACS2. PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 showed high activity toward sodium acetate but little or no activity toward various cinnamic acid derivatives (coumarate, caffeate, and ferulate), with relative activities of PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 of 194.16 ± 11.23 and 422.25 ± 21.69 μM min−1 mg−1, respectively. This result provided additional proof that PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 belonged to the ACS protein family, and not to the 4CL protein family.
The steady state kinetics of both PtrACS enzymes were investigated in assays using 0.01, 0.02, 0.1, 0.2, 1.0, and 2.0 M sodium acetate. The kinetic parameters of the recombinant PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 were analyzed using a Lineweaver–Burk plot. The K m and V max for PtrACS1 were 0.25 mM and 698.85 μM min−1 mg−1, respectively, while for PtrACS2 they were 0.72 mM and 245.96 μM min−1 mg−1, respectively (Table 1, Additional file 2: Table S6a; Additional file 3: Table S6b).
Effects of pH and temperature on enzyme activity and stability of recombinant PtrACS1 and PtrACS2
We evaluated the effects of pH on enzyme activity. The results showed that the activities of the recombinant PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 were pH-dependent. Recombinant PtrACS1 showed high levels of activity in a pH range of 7.0–8.0, with a pH optimum of 7.5. PtrACS2 functioned at a pH optimum of 8.0, and showed high levels of activity in a pH range of 7.5–8.5. Little activity was detected for either PtrACS1 or PtrACS2 at pH levels below 5.0 or above 9.0 (Fig. 6a).
Temperature profile analysis of the recombinant PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 indicated a temperature optimum for enzymatic activity of 35 °C. The enzymatic activities were >90 % of maximum over a broad temperature range between 25 and 40 °C, and both recombinant proteins retained >60 % of their maximum enzymatic activity at temperatures between 15 and 45 °C. PtrACS1 enzyme activity decreased to 12 % of its maximum at 55 °C (Fig. 6b). The enzyme activity trend at different temperatures was similar to that of the ACS isoenzyme from spinach leaves (Zeiher and Randall 1991).
Gene expression patterns in P. trichocarpa
To investigate the gene expression profile in various tissues, we measured PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 transcript levels quantitatively by quantitative real-time PCR in the xylem, phloem, leaf, and root of one-year-old P. trichocarpa using gene-specific primers. PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 were expressed in all of these tissues, indicating that their expression was widely distributed in the plant. However, PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 were expressed mainly in the leaves, while their expression levels exhibited no significant differences in the phloem, xylem, or root (Fig. 7a).
We detected ACS enzyme activity in various tissues of P. trichocarpa with all of the tissues tested showing activity toward the sodium acetate substrate. The highest activity was detected in the leaf, and lower activity was present in the root, phloem, and xylem; however, there were no significant differences between the phloem and xylem (Fig. 7b).
Discussion
The adenylate-forming superfamily enzymes play a key role in lignin and flavonoid biosynthesis and, therefore, exploration of their biochemical characteristics has been a hot topic in plant metabolism research. However, the high level of structural similarities in the amino acids has made it difficult to identify single members, including ACS or the 4-coumarate:CoA ligases. 4CL activates 4-coumaric, caffeic, and ferulic acids to the corresponding CoA esters. These activated cinnamic acid derivatives serve as precursors for the biosynthesis of numerous plant secondary compounds, such as flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, lignin, suberin, anthocyanins, and wall-bound phenolics, which have essential functions in plant development and environmental interactions (Weisshaar and Jenkins 1998).
ACS (AMP forming; EC 6.2.1.1.) is an enzyme that first converts acetate and ATP into an acetyl-adenylate intermediate and then transfers the activated acetyl moiety to CoA, forming acetyl-CoA (Costa et al. 2005; Shockey et al. 2003; Reumann et al. 2004). Due to the high similarity in the protein structures of ACS and 4CL, it is difficult to determine the relationship between these two groups.
However, in vivo and in vitro enzyme activity analysis is a useful method to classify ACS and 4CL proteins into their respective groups. In this study, phylogenetic tree analysis revealed that some key residues, which were conserved among 4CL proteins, were changed in the PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 amino acid sequences, but PTS1 sequences, which represent a conserved domain of the ACS family, were found in the C-terminal regions of both PtrACS proteins. Although these two proteins displayed high similarity and identity to P. tomentosa 4CL1 based on 3D structural prediction, their similarity was quite low, and their substrate binding residues were different, which may result in different catalytic activity compared to 4CL. Taken together, this suggests that some key residues and targeting sequences, together with structural prediction should be helpful to distinguish the different classes of members in one family.
The recombinant PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 proteins did not react with the substrates of 4CL, but were able to react with the substrate sodium acetate, indicating that they belong to the ACS family. Compared to phylogenetic tree analysis and structure prediction, enzyme analysis could represent a better method to characterize these proteins.
PTS1 sequence has been founded at the end of the C-terminal of PtrACS1 and PtrACS2, suggests that they are targeted to peroxisome. The PTS1 sequence also reported in a group of acyl-CoA synthetase proteins from Arabidopsis, poplar and rice. Among of them, it was confirmed that PoptrACS5 subcellular localized in the peroxisome of mesophyll cell and epidermal cells using GFP fusion as a reporter (Souza Cde et al. 2008). In photosynthetic tissue ACS catalyzes the conversion of acetate to acetyl-CoA, which provides a key source for fatty acid, isoprenoid, and branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis (Kuhn et al. 1981; Zeiher and Randall 1991). This explains, to a certain extent, the higher gene expression levels of PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 in the leaves than in other tissues (Fig. 7a). The ACS enzyme activity results agreed with the gene expression profiles.
For many years, ACS was considered to be the primary source of acetyl-CoA for fatty acid biosynthesis, but metabolic and genetic studies have shown that this is not the case (Bao et al. 1998; Ke et al. 2000; Behal et al. 2002; Lin et al. 2003; Schwender et al. 2006). In research using Arabidopsis ACS mutants, ACS1 was shown to detoxify the products of aerobic fermentation (Lin and Oliver, 2008). Therefore, further studies are needed to understand how PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 regulate metabolism during P. trichocarpa growth, which metabolic process these ACS genes participate in, and the functional similarities and differences between them and other adenylate-forming enzymes.
Conclusions
In this paper, we provided evidence from sequence analysis, and substrate specificity- and enzyme-activity assays to show that two 4CL-like genes, PtrACS1 and PtrACS2, cloned from P. trichocarpa could be classified into the ACS family. Their high gene expression and ACS enzyme activity in leaves may suggest that they play a role in photosynthetic tissues.
References
Bao X, Pollard M, Ohlrogge J (1998) The biosynthesis of erucic acid in developing embryos of Brassica rapa. Plant Physiol 118:183–190
Behal RH, Lin M, Back S, Oliver DJ (2002) Role of acetyl-CoA synthetase in the leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana. Arch Biochem Biophys 402:259–267
Costa MA, Bedgar DL, Moinuddin SG, Kim KW, Cardenas CL, Cochrane FC, Shockey JM, Helms GL, Amakura Y, Takahashi H, Milhollan JK, Davin LB, Browse J, Lewis NG (2005) Characterization in vitro and in vivo of the putative multigene 4-coumarate:CoA ligase network in Arabidopsis: syringyl lignin and sinapate/sinapyl alcohol derivative formation. Phytochemistry 66:2072–2091
Ehlting J, Büttner D, Wang Q, Douglas CJ, Somssich IE, Kombrink E (1999) Three 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligases in Arabidopsis thaliana represent two evolutionarily divergent classes in angiosperms. Plant J. 19:9–20
Ehlting J, Shin JJ, Douglas CJ (2001) Identification of 4-coumarate: coenzyme A ligase (4CL) substrate recognition domains. Plant J 27:455–465
Ehlting J, Mattheus N, Aeschliman DS, Li E, Hamberger B, Cullis IF, Zhuang J, Kaneda M, Mansfield SD, Samuels L, Ritland K, Ellis BE, Bohlmann J, Douglas CJ (2005) Global transcript profiling of primary stems from Arabidopsis thaliana identifies candidate genes for missing links in lignin biosynthesis and transcriptional regulators of fiber differentiation. Plant J. 42:618–640
Hamberger B, Hahlbrock K (2004) The 4-coumarate:CoA ligase gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana comprises one rare, sinapate-activating and three commonly occurring isoenzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2209–2214
Hamberger B, Ellis M, Friedmann M, de Azevedo Souza C, Barbazuk B, Douglas C (2007) Genome-wide analyses of phenylpropanoid-related genes in Populus trichocarpa, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Oryza sativa: the Populus lignin toolbox and conservation and diversification of angiosperm gene families. Can J Botany 85:1182–1201
Hayashi M, Aoki M, Kato A, Nishimura M (1997) Changes in targeting efficiencies of proteins to plant microbodies caused by amino acid substitutions in the carboxyl-terminal tripeptide. Plant Cell Physiol 38:759–768
Hu WJ, Kawaoka A, Tsai CJ, Lung J, Osakabe K, Ebinuma H, Chiang VL (1998) Compartmentalized expression of two structurally and functionally distinct 4-coumarate:CoA ligase genes in aspen (Populus tremuloides). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5407–5412
Hu YL, Gai Y, Yin L, Wang XX, Feng CY, Feng L, Li DF, Jiang XN, Wang DC (2010) Crystal structures of a Populus tomentosa 4-Coumarate:CoA ligase shed light on its enzymatic mechanisms. Plant Cell 22:3093–3104
Kato A, Takeda-Yoshikawa Y, Hayashi M, Kondo M, Hara-Nishimura I, Nishimura M (1998) Glyoxysomal malate dehydrogenase in pumpkin: cloning of a cDNA and functional analysis of its presequence. Plant Cell Physiol 39:186–195
Ke J, Behal RH, Yunker S, Nikolau BJ, Wurtele ES, Oliver DJ (2000) The role of pyruvate dehydrogenase and acetyl-CoA synthetase in fatty acid synthesis in developing Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Physiol 123:497–508
Knobloch KH, Hahlbrock K (1977) 4-Coumarate:CoA ligase from cell suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense Hoffm. Partial purification, substrate specificity, and further properties. Arch Biochem Biophys 184:237–248
Koo AJ, Chung HS, Kobayashi Y, Howe GA (2006) Identification of a peroxisomal acyl-activating enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of jasmonic acid in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 281:33511–33520
Kragler F, Lametschwandtner G, Christmann J, Hartig A, Harada JJ (1998) Identification and analysis of the plant peroxisomal targeting signal 1 receptor NtPEX5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13336–13341
Kuhn DN, Knauf M, Stumpf PK (1981) Subcellular localization of acetyl-CoA synthetase in leaf protoplasts of Spinacia oleracea. Arch Biochem Biophys 209:441–450
Kumar A, Ellis BE (2003) 4-coumarate:CoA ligase gene family in Rubus idaeus: cDNA structures, evolution, and expression. Plant Mol Biol 51:327–340
Lin M, Oliver DJ (2008) The role of acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 147:1822–1829
Lin M, Behal RH, Oliver DJ (2003) Disruption of plE2, the gene for the E2 subunit of the plastid pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, in Arabidopsis causes an early embryo lethal phenotype. Plant Mol Biol 52:865–872
Lindermayr C, Mollers B, Fliegmann J, Uhlmann A, Lottspeich F, Meimberg H, Ebel J (2002) Divergent members of a soybean (Glycine max L.) 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase gene family. Eur J Biochem 269:1304–1315
Liu Z, Zhang D, Liu D, Li F, Lu H (2013) Exon skipping of AGAMOUS homolog PrseAG in developing double flowers of Prunus lannesiana (Rosaceae). Plant Cell Rep 32:227–237
Martínez-Blanco H, Reglero A, Rodriguez-Aparicio LB, Luengo JM (1990) Purification and biochemical characterization of phenylacetyl-CoA ligase from Pseudomonas putida. A specific enzyme for the catabolism of phenylacetic acid. J Biol Chem 265:7084–7090
Mullen RT, Lee MS, Flynn CR, Trelease RN (1997) Diverse amino acid residues function within the type 1 peroxisomal targeting signal.Implications for the role of accessory residues upstream of the type 1 peroxisomal targeting signal. Plant Physiol 115:881–889
Raes J, Rohde A, Christensen JH, van de Peer Y, Boerjan W (2003) Genome-wide characterization of the lignification toolbox in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 133:1051–1071
Rao G, Pan X, Xu F, Zhang Y, Cao S, Jiang X, Lu H (2015) Divergent and overlapping function of five 4-coumarate/coenzyme A ligases from Populus tomentosa. Plant Mol Biol Rep 33:841–854
Reumann S, Ma C, Lemke S, Babujee L (2004) AraPerox. A database of putative Arabidopsis proteins from plant peroxisomes. Plant Physiol 136:2587–2608
Saravanan R, Rose J (2004) A critical evaluation of sample extraction techniques for enhanced proteomic analysis of recalcitrant plant tissues. Proteomics 4:2522–2532
Schneider K, Kienow L, Schmelzer E, Colby T, Bartsch M, Miersch O, Wasternack C, Kombrink E, Stuible HP (2005) A new type of peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A synthetase from Arabidopsis thaliana has the catalytic capacity to activate biosynthetic precursors of jasmonic acid. J Biol Chem 280:13962–13972
Schwender J, Shachar-Hills Y, Ohlrogge JB (2006) Mitochondrial metabolism in developing embryos of Brassica napus. J Biol Chem 281:34040–34047
Shi R, Sun YH, Li Q, Heber S, Sederoff R, Chiang VL (2010) Towards a systems approach for lignin biosynthesis in Populus trichocarpa: transcript abundance and specificity of the monolignol biosynthetic genes. Plant Cell Physiol 51:144–163
Shockey JM, Fulda MS, Browse J (2003) Arabidopsis contains a large superfamily of acyl-activating enzymes. Phylogenetic and biochemical analysis reveals a new class of acyl-coenzyme a synthetases. Plant Physiol 132:1065–1076
Souza Cde A, Barbazuk B, Ralph SG, Bohlmann J, Hamberger B, Douglas CJ (2008) Genome-wide analysis of a land plant-specific acyl:coenzymeA synthetase (ACS) gene family in Arabidopsis, poplar, rice and Physcomitrella. New Phytol 179:987–1003
Stuible HP, Kombrink E (2001) Identification of the substrate specificity-conferring amino acid residues of 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase allows the rational design of mutant enzymes with new catalytic properties. J Biol Chem 276:26893–26897
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Wang S, Nakashima S, Numata O, Fujiu K, Nozawa Y (1999) Molecular cloning and cell-cycle-dependent expression of the acetyl-CoA synthetase gene in Tetrahymena cells. Biochem J 343:479–485
Weisshaar B, Jenkins GI (1998) Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis and its regulation. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:251–257
Zeiher CA, Randall DD (1991) Subcellular localization of acetyl-CoA synthetase in leaf protoplasts of Spinacia oleracea. Plant Physiol 96:382–389
Zhang CH, Ma T, Luo WC, Xu JM, Liu JQ, Wan DS (2015) Identification of 4CL genes in desert poplars and their changes in expression in response to salt stress. Genes. 6:901–917
Authors’ contributions
DL and HL designed the experiments. SC, HL, X-Y Y, L-H L, L-Y J, Q Z and J-X Z performed the experiments and statistical analysis. SC and HL wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (TD2012-02, JC2015-01), the 111 Project (Project No. B13007) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570582).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Shan Cao, Hui Li, Xiaoyun Yao and Lihong Li contributed equally to this work
Additional files
40064_2016_2532_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Additional file 1. Table S1. Physicochemical properties of PtrACS1. Table S2. Physicochemical properties of PtrACS2. Table S3. Predicted post-translational modification of PtrACS1 and PtrACS2. Table S4. The similarity between PtrACS1 and PtrACS2 as other Ptr4CLs. Table S5. Gene-specific primers used in real-time PCR analysis.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, S., Li, H., Yao, X. et al. Enzymatic characterization of two acetyl-CoA synthetase genes from Populus trichocarpa . SpringerPlus 5, 818 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2532-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2532-7