Abstract
Background
Prone positioning (PP) is a low-cost method with minimal risk to the patient that improves the oxygenation of patients with acute hypoxic respiratory failure (AHRF) due to COVID-19 pneumonia, thereby reducing their need for tracheal intubation (TI) and transferring to the intensive care unit (ICU). We aimed to overview the results of all previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses to examine the net effect of PP on oxygenation, the rate of TI and mortality in COVID-19 patients.
Methods
We searched PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library databases from December 2019 through 2022 without publication language restriction for systematic reviews and meta-analysis studies on PP vs. supine position (SP) in conscious patients with hypoxic respiratory failure COVID-19. After study selection, data were extracted from published meta-analyses and pooled by comprehensive meta-analysis (CMA) software version 2.2.064 to achieve effect sizes. They were analyzed for TI and mortality rates dichotomous variables, and the results were shown as pooled odds ratios (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). Continuous variables such as oxygenation indices (PaO2/FiO2 and SpO2) were also analyzed, and the data were shown as mean differences (MD) with lower and upper CI. The level of statistical significance was set at p ≤ 0.05.
Results
Twelve systematic reviews and meta-analyses with 19,651 patients and six systematic reviews with 2,911 patients were included in this Review of Reviews (total: 22,562). PP treatment significantly reduced the rate of TI (OR = 0.639, %95 CI (0.492, 0.829); P-value = 0.001) and decreased mortality (OR = 0.363, %95 CI (0.240, 0.549), P-value < 0.001). There was no difference in PaO2/FiO2 (MD = 3.591[− 40.881, 48.062]; P-value = 0.874) and SpO2 percent (MD = 1.641[− 4.441, 7.723]; P-value = 0.597).
Conclusion
Prone positioning can be recommended in conscious ICU patients with COVID-19 pneumonia to reduce mortality and intubation.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO registration number: CRD42022326951. Registered 25 April 2022.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Due to the rapid spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in the severe COVID-19 pneumonia during the pandemic, significant alveolar involvement progresses to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) [1, 2]. With the subsequent reduction in lung capacity and the development of severe ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch, the induced lung injury leads to severe shunting and oxygen desaturation [3]. Prone positioning (PP) is among the physical methods which have effectively improved pulmonary ventilation and the oxygenation profile [4,5,6]. The prone position is a low-cost, low-risk method for reducing the need for tracheal intubation and transfer to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) in awake non-intubated patients with severe hypoxic COVID-19 [7,8,9,10,11].
An increase in lung volumes occurs due to PP, especially in the lower lobes [12, 13]. Several observational studies have been published about the positive effects of PP in conscious non-intubated patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia and oxygen-resistant hypoxemia [14,15,16]. Several clinical trials have confirmed that PP improves oxygenation and reduces the respiratory rate (RR) in awake patients [7, 11]. In patients with ARDS due to severe COVID-19 infection with the involvement of the lungs, one way to control the extent of pulmonary shunting and correct the resulting V/Q mismatch is to use PP by placing them in a face-down position on their abdomen. There is evidence that the interstitial fluid congestion caused by the accumulation of perialveolar fluid and pulmonary airway pressures are reduced in PP, thereby improving oxygenation and decreasing the need for tracheal intubation (TI) and mechanical ventilation in awake patients [17].
The range for the duration of PP varies from 30 min to 2 h in each position [18]. Prasad et al. have recommended periods as long as 2–3 h up to 4–5 h per day [19]. Following the application of PP, the clinical condition of the patients recovers rapidly as the basilary atelectasis ceases to progress in the lungs [20]. In a case–control study of 600 conscious, non-intubated COVID-19 patients hospitalized in three principal urban hospitals, there was no increase in the rate of TI with mechanical ventilation and mortality in those treated with PP [21].
This Review of Reviews aims to combine the existing meta-analyses and systematic reviews and examines the effect of PP on the rates of TI and mortality along with the oxygenation profile in a large number of awake Covid-19 patients with increased statistical power. Several meta-analyses have systematically reviewed PP in awake patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure caused by moderate to severe COVID-19 against the traditional supine position (SP) with varying degrees of head elevation.
Methods
Our Review of Reviews were performed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) checklist. The protocol was prospectively registered at PROSPERO, the International Prospective Registry of Systematic Reviews (ID: CRD42022326951).
Search strategy
A database search by medical subject heading (MESH) terms and keywords used for each database according to Additional file 1: Table S1 was done comprehensively from December 1st, 2019, to July 1st, 2022, in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, the Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar, and some references cited in relevant meta-analysis studies selected manually. After deleting the duplicate articles, the titles and abstracts of the articles were reviewed for APP in hypoxic COVID-19 patients without any language restrictions and type of published articles. These steps were performed by two authors, S.T. and H.S. In the inclusion or exclusion of articles, if the problems did not solve by discussion, to disagreement management, the third author, M.G should have interfered and solved. Finally, eighteen studies were selected, including twelve systematic reviews and meta-analyses and six systematic reviews.
Inclusion criteria
Systematic review studies or systematic review and meta-analysis studies meeting the following criteria were included in this overview and meta-analysis study:
-
a.
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses in which patients over 18 years of age, no gender restriction, and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure because of severe COVID-19 pneumonia were compared for the effect of PP vs. SP on TI rates, mortality, and oxygenation improvement parameters.
-
b.
The data have been meta-analyzed.
-
c.
There should be no language restrictions on the selection of articles.
Participant Intervention-Comparison-Outcome (PICO) in this study is defined as follows:
Participants (P): awake adult severe COVID-19 patients with acute hypoxic respiratory failure;
Interventions (I): PP; Comparison group(C): SP or standard of care (SOC); Outcome measures (O): TI rate (dichotomous), the mortality rate (dichotomous) and oxygenation parameters such as the ratio of arterial partial pressure of oxygen and fraction inspiratory oxygen (PaO2/FiO2) and pulse-oximetric saturation of oxygen (SpO2) as continuous outcome variables.
To make sure we haven't lost any data, the data related to the effects of PP in non-intubated conscious patients were also extracted from the studies that evaluated the impact of PP vs. SP in non-intubated and intubated patients. Studies that examined PP compared to SP in intubated and unconscious patients or children under 18 years of age were excluded.
Data extraction
The following items were extracted from systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Types and number of observational or clinical trial studies each included systematic reviews and meta-analysis studies, number of patients in each study, variables and outcomes, methodology, confidence interval (CI), mean difference (MD), and odds ratio (OR), heterogeneity of each study in terms of I-squared index (I2) and P-values, assess the quality of studies and the risk of bias (ROB). Two authors performed data extraction individually; if necessary, the third author was consulted. Data were then finalized and with the agreement of all authors.
Statistical analysis
The relative risk values for tracheal intubation and mortality variables and the mean difference values before and after the intervention (prone positioning) for PaO2/FiO2 and SpO2 variables were selected as effect indicators.
The I2 was used to determine the heterogeneity among the studies. I2 values greater than 0.50 were considered heterogeneous. By computing the I2 for heterogeneity, when there was no statistically significant difference in heterogeneity, a fixed effect model was utilized to analyze the data. In the absence of this, a random effect model was used. A funnel diagram and Begg’s test were utilized to examine diffusion bias. A probability value of less than 0.05 was considered a significant level. All data analyses were conducted with CMA software version 2.2.064 (Biostat Inc., Englewood, NJ, USA).
Results
Search results
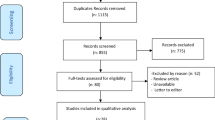
In the initial search we found 903 articles. After careful stepwise review according to the PRISMA flow diagram, eighteen systematic reviews were included, including twelve meta-analyses and six systematic narrative reviews. Meta-analyses in which PP was examined on intubated patients and under mechanical ventilation were excluded.
How selection of articles and the initial search in the form of a PRISMA chart is shown in Fig. 1.
Characteristics of included meta-analyses
Table 1 shows the essential characteristics of each included study, including country of origin, database search, type and number of studies entered in each meta-analysis, including clinical trial or observational studies, case reports or case series. The number of patients has been shown in each of the studies (a total of 22,562 patients in twenty included studies, separately 19,651 and 2911 patients in meta-analyses (twelve studies) and systematic reviews (six studies), respectively) [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39].
A summary of included study methods covering inclusion and exclusion criteria, characteristics of patients, mean age, and intervention or control categories is fully shown in Table 2.
The investigated variables, software used for statistical analysis, primary and secondary outcomes, risk of bias assessment, publication bias, and quality of all included studies are shown in detail in Table 3.
The extracted data related to selected parameters, including TI rate, mortality, and measures of PaO2/FiO2 and SpO2 for all included studies, are displayed in Table 4.
A summary of the results and conclusions of all included studies are displayed in Table 2 (Additional file 2: Table S2).
Tracheal intubation rates
Eleven studies were included in this study. The heterogeneity between the studies was significant (Q = 119.4, P < 0.001, I2 = 91.6%). To estimate the pooled relative risk between the two groups, the OR values for each included study were entered into the data analysis. Figure 2(A1) illustrates the forest plot for the pooled effect size of the selected studies. Based on the random effect model, the pooled relative risk to assess the effect of the awake prone position in non-intubated patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure caused by severe COVID-19 on tracheal intubation rate was equal to 0.639 units, which was statistically significant (Pooled R.R = 0.639, %95 CI = (0.492, 0.829), P-value = 0.001). The publication bias was not significant as tested by Begg’s test (P-value = 0.350) (Fig. 2A2).
A1 The forest plot shows the Odds ratios of the individual effect of APP versus SP on the tracheal intubation of awake non-intubated patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. A2 Funnel plot standard error by log risk ratio to assess diffusion bias related to the effect of PP versus SP on the tracheal intubation of awake non-intubated patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. B1 The forest plot shows the Odds ratios of the individual effect of APP versus SP on the mortality of awake non-intubated patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. B2 Funnel plot standard error by log risk ratio to assess diffusion bias related to the effect of PP versus SP on the mortality rate of awake non-intubated patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. C1 The forest plot shows differences in means of the effect of the PaO2/FiO2 of the awake non-intubated patients with COVID-19 pneumonia before and after PP. C2 Funnel plot diagram to assess diffusion bias related to PaO2/FiO2 of the awake non-intubated patients with COVID-19 pneumonia before and after PP. D1 The forest plot shows differences in the means of the effect of the SpO2 (%) of the awake non-intubated patients with COVID-19 pneumonia before and after PP. D2 Funnel plot diagram to assess diffusion bias related to the SpO2 (%) of the awake non-intubated patients with COVID-19 pneumonia before and after PP
Mortality rate
Twelve studies were included in this study. The heterogeneity between the studies was significant (Q = 147.3, P < 0.001, I2 = 92.5%). To estimate the pooled relative risk between the two groups, the relative risk associated with the study's purpose for each included study was entered into the data analysis. Figure 2B1 illustrates the forest plot for the pooled effect size of the selected studies. Based on the random effect model, the pooled relative risk to assess the effect of the awake prone position in non-intubated patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure caused by severe COVID-19 on mortality rate was equal to 0.363 units, which was statistically significant (pooled relative risk = 0.363 [0.240, 0.549], P-value < 0.001). There was no perceived publication bias despite an asymmetric funnel plot (P-value = 0.115) (Fig. 2B2).
PaO2/FiO2
Four studies that reported on this outcome variable were included in this analysis. The heterogeneity between the studies was significant (Q = 48.1, P < 0.001, I2 = 93.8%). To estimate the pooled mean differences, the MD values from the individual meta-analyses before and after the application of PP in awake patients were entered for a pooled analysis. Figure 2C1 illustrates the forest plot for the pooled effect size of the selected studies. Based on the random effect model, the pooled mean differences to assess the effect of the awake prone position in non-intubated patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure caused by severe COVID-19 on the PaO2/FiO2 ratio was equal to 3.59 units [− 40.881, 48.062], P-value = 0.874, which wasn’t statistically significant. The funnel plot and Begg’s test were used to evaluate publication bias, and the results indicated that publication bias with a P-value = 0.734 was not significant (Fig. 2C2).
Oxygen saturation
Three studies were included in this study. The heterogeneity between the studies was significant (Q = 24.5, P < 0.001, I2 = 91.8%). To estimate the pooled mean differences, the MD values before and after the PP in awake COVID-19 patients for the included studies were entered into the analysis. Figure 2D1 illustrates the forest plot for the pooled effect size of the selected studies. Based on the random effect model, the pooled mean difference to assess the effect of the PP in awake non-intubated patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure caused by severe COVID-19 on SpO2 (%) was equal to 1.64 units [− 4.441, 7.723]; with a non-significant P-value of 0.597. Additionally, there was no evidence of publication bias (P = 0.999) (Fig. 2D2).
Discussion
The use of non-drug approaches, such as changing the patient's position to prone, can significantly help to improve oxygenation parameters in patients with ARDS. In hypoxemic COVID-19 patients, the APP method is used to avoid tracheal intubation, but its effectiveness is unclear. The early and timely use of the PP method in awake, non-intubated patients is one of the strategies to reduce ICU transfer and endotracheal intubation during the COVID-19 pandemic, following health system control and optimal ventilator use and reducing the economic burden. In this field, twelve systematic review and meta-analysis studies and six systematic review studies have been conducted [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. This Review of Reviews will discuss a comprehensive review of the studies above.
In a case–control study of 29 patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia, PP was started within the first 12 h of hospitalization, 18 patients tolerated it for at least 10 h per day, and 11 patients had no issues with it. According to the findings of this study, oxygenation improves in COVID-19-induced ARDS with early PP for 10 h per day [40]. The PaO2/FiO2 ratio in non-invasively ventilated patients such as the prone position is much higher than other methods of ventilatory support [41]. Burton-Papp et al. discovered a significant role for the combination of NIV and PP in improving oxygenation in a study of 20 conscious patients with COVID-19 pneumonia by measuring the PaO2/FiO2 ratio [42]. The standard treatment method was compared to the PP method in 60 non-intubated awake patients in a multicenter RCT in patients with acute respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 infection. The results showed that awake PP was functional and valuable in improving the oxygenation [43]. In a cohort study of 25 patients with severe respiratory failure due to COVID-19 (12 intubated patients and 13 conscious patients), patients with SaO2 > 95% improved their oxygenation parameters. They were less likely to require intubation after one hour of PP [44].
The effects of improving oxygenation were permanent even after repositioning in the prospective cohort study by Coppo et al. on the physiological impact of PP in 56 patients with COVID-19 with severe respiratory failure [45]. According to previous studies, the rate of intubation did not decrease in a randomized multicenter clinical trial in patients with moderate to severe respiratory failure due to COVID-19 treated with high flow nasal oxygen or NIV and a PaO2/FiO2 ratio ≤ 200 by randomly dividing them into two groups of 16 h of PP per day or standard treatment [46].
In a retrospective cohort study of 97 hospitalized patients with COVID-19, it was discovered that measuring the respiratory oxygenation (ROX) index and the PaO2/FiO2 (partial pressure of oxygen/fraction of inspired oxygen) ratio in awake patients on PP can predict the time required for intubation [47]. Evidence suggests that the benefits of PP decline after significant disease progression and the onset of pulmonary fibrosis, emphasizing the significance of early PP initiation [48]. One study found that the prophylactic beginning of PP in COVID-19 patients significantly increased oxygenation [5]. The positive effects of PP outweighed its negative impact in a scoping review of its effects in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia [49]. The advantage of using this method in non-intubated, conscious patients who are not intubated is that complications like endotracheal tube displacement and dislocation in PP are not present in these patients [50]. The improvement in SpO2/FiO2 in the study of the effect of serial APP on oxygenation of non-intubated patients admitted to the ICU is usually temporary and often occurs in the first episode of this procedure, which may be the reason for not reporting the effect of APP on mortality in recent studies [51, 52]. In a narrative review, the APP method is recommended in critically ill patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure due to moderate to severe COVID-19, as long as there is no delay in mechanical ventilation [53].
The limitation of the study was the identification of systematic review studies conducted prone position on intubated patients from conscious patients. Especially, in some studies, PP was performed on both conscious and intubated patients, which made it difficult to extract the results related to conscious patients.
Each of the 18 review studies recommended using APP in COVID-19 pneumonia. To reach a more definitive conclusion about the effect of APP on COVID-19 pneumonia, the results of this Review of Reviews, which is a comprehensive study of all previous reviews and meta-analyses, show that APP has a significant effect on reducing tracheal intubation and mortality, but not on PaO2/FiO2 and SpO2 (%). According to the results of 18 systematic reviews on 22,562 patients, the results of this Review of Reviews can be generalized, and APP can be recommended with certainty in the treatment of conscious and non-intubated patients with COVID-19 pneumonia to reduce mortality and tracheal intubation.
Conclusion
With more confidence, the results of this Review of Reviews showed the influential role of APP in reducing mortality and intubation, which can be recommended in the treatment period of conscious patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. It is advisable to consider the use of prone positioning in conscious patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU as a means to decrease mortality rates and the need for intubation.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its additional information files).
References
Shahsavarinia K, Ghojazadeh M, Ghabousian A, Hatefnia F, Soleimanpour M, Soleimanpour H. An umbrella review of clinical efficacy and adverse cardiac events associated with hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine with or without azithromycin in patients with COVID-19. Anesth Pain Med. 2021;11(4): e115827.
Shadvar K, Tagizadiyeh A, Gamari AA, Soleimanpour H, Mahmoodpoor A. Hemoperfusion as a potential treatment for critically ill COVID-19 patients with cytokine storm. Blood Purif. 2021;50(3):405–7.
Shahsavarinia K, Ghojazadeh M, Sanaie S, Vahedi L, Ahmadpour M, Mahmoodpoor A, et al. Clinical efficacy of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine in patients with COVID-19: an umbrella review. Pharm Sci. 2021;27(4):481–8.
Bagi HM, Soleimanpour M, Abdollahi F, Soleimanpour H. Evaluation of clinical outcomes of patients with mild symptoms of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) discharged from the emergency department. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(10): e0258697.
Mahmoodpoor A, Shadvar K, Ghamari AA, Mohammadzadeh Lameh M, Asghari Ardebili R, Hamidi M, et al. Management of critically ill patients with COVID-19: what we learned and what we do. Anesth Pain Med. 2020;10(3): e104900.
Tekantapeh ST, Mikaeili H, Suleimanpour H. The role of respiratory system surface area and ventilation volume in severity and mortality of COVID-19 infection. Front Emerg Med. 2021;5(3): e27.
Bhurayanontachai R. Mechanical ventilator support and prone positioning in COVID-19 related pneumonia: mechanical ventilator support in COVID-19. Clin Crit Care. 2021;2021(29): e0004.
Ng Z, Tay WC, Ho CHB. Awake prone positioning for non-intubated oxygen dependent COVID-19 pneumonia patients. Eur Respir J. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01198-2020.
Seckel MA. Awake self-prone positioning and the evidence. Crit Care Nurse. 2021;41(4):76–9.
Sodhi K, Chanchalani G. Awake proning: current evidence and practical considerations. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2020;24(12):1236–41.
Touchon F, Trigui Y, Prud’homme E, Lefebvre L, Giraud A, Dols AM, et al. Awake prone positioning for hypoxaemic respiratory failure: past, COVID-19 and perspectives. Eur Respir Rev. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.0022-2021.
Taboada M, Bermudez A, Perez M, Campana O. Supine versus prone positioning in COVID-19 Pneumonia: comment. Anesthesiology. 2020;133(5):1155–7.
Tahsini Tekantapeh S, Ghojazadeh M, Ghamari AA, Mohammadi A, Soleimanpour H. Therapeutic and anti-inflammatory effects of baricitinib on mortality, ICU transfer, clinical improvement, and CRS-related laboratory parameters of hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1080/17476348.2022.2114899.
Hasan N. Awake prone positioning in Sars-CoV-2 (COVID-19) non-intubated patients with acute respiratory failure in adult population: a literature review. Med Sci Discov. 2021;8(9):505–8.
Koeckerling D, Barker J, Mudalige NL, Oyefeso O, Pan D, Pareek M, et al. Awake prone positioning in COVID-19. Thorax. 2020;75(10):833–4.
Stilma W, Akerman E, Artigas A, Bentley A, Bos LD, Bosman TJC, et al. Awake proning as an adjunctive therapy for refractory hypoxemia in non-intubated patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory failure: guidance from an international group of healthcare workers. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2021;104(5):1676–86.
Khan S, Choudry E, Mahmood SU, Mulla AY, Mehwish S. Awake proning: a necessary evil during the COVID-19 pandemic. Cureus. 2020;12(7): e8989.
Bentley SK, Iavicoli L, Cherkas D, Lane R, Wang E, Atienza M, et al. Guidance and patient instructions for proning and repositioning of awake, nonintubated COVID-19 patients. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(8):787–91.
Prasad M, Visrodia K. Should I prone non-ventilated awake patients with COVID-19? Cleve Clin J Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc050.
Fiorentino G, Esquinas AM, Piervincenzi E. Insights about prone and lateral positioning in spontaneously breathing patients with COVID-19 pneumonia undergoing noninvasive helmet CPAP treatment. Chest. 2021;159(6):2506–7.
Nauka PC, Chekuri S, Aboodi M, Hope AA, Gong MN, Chen JT. A case-control study of prone positioning in awake and nonintubated hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 patients. Crit Care Explor. 2021;3(2): e0348.
Chua EX, Zahir S, Ng KT, Teoh WY, Hasan MS, Ruslan SRB, et al. Effect of prone versus supine position in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Anesth. 2021;74: 110406.
Fazzini B, Page A, Pearse R, Puthucheary Z. Prone positioning for non-intubated spontaneously breathing patients with acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2022;128(2):352–62.
Ponnapa Reddy M, Subramaniam A, Afroz A, Billah B, Lim ZJ, Zubarev A, et al. Prone positioning of nonintubated patients with coronavirus disease 2019—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2021;49(10):e1001–14.
Schmid B, Griesel M, Fischer AL, Romero CS, Metzendorf MI, Weibel S, et al. Awake prone positioning, high-flow nasal oxygen and non-invasive ventilation as non-invasive respiratory strategies in COVID-19 acute respiratory failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11020391.
Pavlov I, He H, McNicholas B, Perez Y, Tavernier E, Trump MW, et al. Awake prone positioning in non-intubated patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure due to COVID-19. Respir Care. 2021.
Pb S, Mittal S, Madan K, Mohan A, Tiwari P, Hadda V, et al. Awake prone positioning in non-intubated patients for the management of hypoxemia in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2021. https://doi.org/10.4081/monaldi.2021.1623.
Ni Z, Wang K, Wang T, Ni Y, Huang W, Zhu P, et al. Efficacy of early prone or lateral positioning in patients with severe COVID-19: a single-center prospective cohort. Precis Clin Med. 2020;3(4):260–71.
Beran A, Mhanna M, Srour O, Ayesh H, Sajdeya O, Ghazaleh S, et al. Effect of prone positioning on clinical outcomes of non-intubated subjects with COVID-19. Respir Care. 2022;67(4):471–9.
Cardona S, Downing J, Alfalasi R, Bzhilyanskaya V, Milzman D, Rehan M, et al. Intubation rate of patients with hypoxia due to COVID-19 treated with awake proning: a meta-analysis. Am J Emerg Med. 2021;43:88–96.
Li J, Luo J, Pavlov I, Perez Y, Tan W, Roca O, et al. Awake prone positioning for non-intubated patients with COVID-19-related acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Respir Med. 2022;10(6):573–83.
Santa Cruz R, Irrazabal C, Gonzalez L, Geloso A, Nunez C, Cornejo R. Analytic review and meta-analysis of awake prone positioning in patients with COVID-19. Med Intensiva. 2022;46(10):580–2.
Tan W, Xu DY, Xu MJ, Wang ZF, Dai B, Li LL, et al. The efficacy and tolerance of prone positioning in non-intubation patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and ARDS: a meta-analysis. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021;15:17534666211009408.
Alhazzani W, Evans L, Alshamsi F, Moller MH, Ostermann M, Prescott HC, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign guidelines on the management of adults with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the ICU: first update. Crit Care Med. 2021;49(3):e219–34.
Anand S, Baishya M, Singh A, Khanna P. Effect of awake prone positioning in COVID-19 patients—a systematic review. Trends Anaesth Crit Care. 2021;36:17–22.
Chilkoti GT, Mohta M, Saxena AK, Ahmad Z, Sharma CS. Awake prone positioning in the management of COVID-19 pneumonia: a systematic review. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2021;25(8):896–905.
Ko HK, Yu WK, Pan SW, Chen WC, Yang KY, Lin YT, et al. Consensus statement and recommendations on the treatment of COVID-19: 2021 update. J Chin Med Assoc. 2022;85(1):5–17.
Parashar S, Karthik AR, Gupta R, Malviya D. Awake proning for nonintubated adult hypoxic patients with COVID-19: a systematic review of the published evidence. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2021;25(8):906–16.
Senderovich H, Vinoraj D, Stever M, Waicus S. Efficacy of COVID-19 treatments among geriatric patients: a systematic review. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2022;9:20499361221095664.
Simioli F, Annunziata A, Langella G, Martino M, Musella S, Fiorentino G. Early prone positioning and non-invasive ventilation in a critical COVID-19 subset. A single centre experience in southern Italy. Turk Thorac J. 2021;22(1):57–61.
Capsoni N, Privitera D, Airoldi C, Gheda S, Mazzone A, Terranova G, Galbiati F, Bellone A. Evaluation of PaCO 2 trend in COVID-19 patients undergoing helmet CPAP in the emergency department. Emerg Care J. 2023. https://doi.org/10.4081/ecj.2023.11274.
Burton-Papp HC, Jackson AIR, Beecham R, Ferrari M, Nasim-Mohi M, Grocott MPW, et al. Conscious prone positioning during non-invasive ventilation in COVID-19 patients: experience from a single centre. F1000Res. 2020;9:859.
Jayakumar D, Ramachandran Dnb P, Rabindrarajan Dnb E, Vijayaraghavan Md BKT, Ramakrishnan Ab N, Venkataraman AR. Standard care versus awake prone position in adult nonintubated patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 infection—a multicenter feasibility randomized controlled trial. J Intensive Care Med. 2021;36(8):918–24.
Thompson AE, Ranard BL, Wei Y, Jelic S. Prone positioning in awake, nonintubated patients with COVID-19 hypoxemic respiratory failure. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(11):1537–9.
Coppo A, Bellani G, Winterton D, Di Pierro M, Soria A, Faverio P, et al. Feasibility and physiological effects of prone positioning in non-intubated patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19 (PRON-COVID): a prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(8):765–74.
Rosen J, von Oelreich E, Fors D, Jonsson Fagerlund M, Taxbro K, Skorup P, et al. Awake prone positioning in patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure due to COVID-19: the PROFLO multicenter randomized clinical trial. Crit Care. 2021;25(1):209.
Downing J, Cardona S, Alfalasi R, Shadman S, Dhahri A, Paudel R, et al. Predictors of intubation in COVID-19 patients undergoing awake proning in the emergency department. Am J Emerg Med. 2021;49:276–86.
Adeola JO, Patel S, Goné EN, Tewfik G. A quick review on the multisystem effects of prone position in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) including COVID-19. Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med. 2021;15:11795484211028526.
Araújo MS, Santos M, Silva CJA, Menezes RMP, Feijão AR, Medeiros SM. Prone positioning as an emerging tool in the care provided to patients infected with COVID-19: a scoping review. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2021;29: e3397.
Venus K, Munshi L, Fralick M. Prone positioning for patients with hypoxic respiratory failure related to COVID-19. CMAJ. 2020;192(47):E1532–7.
Barker J, Pan D, Koeckerling D, Baldwin AJ, West R. Effect of serial awake prone positioning on oxygenation in patients admitted to intensive care with COVID-19. Postgrad Med J. 2022;98(1159):360–4.
Ehrmann S, Li J, Ibarra-Estrada M, Perez Y, Pavlov I, McNicholas B, Roca O, Mirza S, Vines D, Garcia-Salcido R, Aguirre-Avalos G. Awake prone positioning for COVID-19 acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure: a randomised, controlled, multinational, open-label meta-trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9(12):1387–95.
Qadri SK, Ng P, Toh TSW, Loh SW, Tan HL, Lin CB, et al. Critically ill patients with COVID-19: a narrative review on prone position. Pulm Ther. 2020;6(2):233–46.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the cooperation of the Clinical Research Development Unit, Imam Reza General Hospital, Tabriz, Iran, for conducting this research.
Funding
None was requested.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HS and STT designed this review, developed the inclusion criteria, screened titles and abstracts, appraised the quality of included papers, and drafted the manuscript. HS, STT, and MG reviewed the study protocol and inclusion criteria and provided substantial input to the manuscript. HS, STT, MG and FF reviewed the study protocol. STT, MG read and screened articles for inclusion. All authors critically reviewed drafts and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was not required in this Review of Reviews. The code of ethics is IR.TBZMED.REC.1401.379.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Search Strategy Using database-appropriate syntax with parentheses, Boolean operators, and field codes.
Additional file 2: Table S2.
Results and conclusions of the included systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Tekantapeh, S.T., Nader, N.D., Ghojazadeh, M. et al. Prone positioning effect on tracheal intubation rate, mortality and oxygenation parameters in awake non-intubated severe COVID-19-induced respiratory failure: a review of reviews. Eur J Med Res 29, 63 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-024-01661-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-024-01661-6