Abstract
Background
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a considerable threat to the economics of patients, health systems, and society.
Objectives
This meta-analysis aims to quantitatively assess the global economic burden of COVID-19.
Methods
A comprehensive search was performed in the PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases to identify studies examining the economic impact of COVID-19. The selected studies were classified into two categories based on the cost-of-illness (COI) study approach: top-down and bottom-up studies. The results of top-down COI studies were presented by calculating the average costs as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) and health expenditures. Conversely, the findings of bottom-up studies were analyzed through meta-analysis using the standardized mean difference.
Results
The implemented search strategy yielded 3271 records, of which 27 studies met the inclusion criteria, consisting of 7 top-down and 20 bottom-up studies. The included studies were conducted in various countries, including the USA (5), China (5), Spain (2), Brazil (2), South Korea (2), India (2), and one study each in Italy, South Africa, the Philippines, Greece, Iran, Kenya, Nigeria, and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The results of the top-down studies indicated that indirect costs represent 10.53% of GDP, while the total estimated cost accounts for 85.91% of healthcare expenditures and 9.13% of GDP. In contrast, the bottom-up studies revealed that the average direct medical costs ranged from US $1264 to US $79,315. The meta-analysis demonstrated that the medical costs for COVID-19 patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) were approximately twice as high as those for patients in general wards, with a range from 0.05 to 3.48 times higher.
Conclusions
Our study indicates that the COVID-19 pandemic has imposed a significant economic burden worldwide, with varying degrees of impact across countries. The findings of our study, along with those of other research, underscore the vital role of economic consequences in the post-COVID-19 era for communities and families. Therefore, policymakers and health administrators should prioritize economic programs and accord them heightened attention.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory infection instigated by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2), first identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease has since proliferated globally at an alarming rate, prompting the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare a pandemic on March 11, 2020 [1]. As of February 21, 2023, the global total of confirmed COVID-19 cases stands at 757,264,511, with a death toll of 6,850,594 [2].
Patients afflicted with COVID-19 exhibit a range of symptoms, including flu-like manifestations, acute respiratory failure, thromboembolic diseases, and organ dysfunction or failure [3]. Moreover, these patients have had to adapt to significant changes in their environment, such as relocating for quarantine purposes, remote work or job loss, and air-conditioning [4, 5].
The COVID-19 pandemic has imposed substantial direct and indirect costs on patients, families, healthcare systems, and communities. These costs fluctuate significantly based on socioeconomic factors, age, disease severity, and comorbidities [6, 7]. For instance, a study conducted in the United States of America (USA) estimated the median direct medical cost of a single symptomatic COVID-19 case to be US $3045 during the infection period alone [8]. Additionally, indirect costs arising from the pandemic, such as lost productivity due to morbidity and mortality, reduced consumer spending, and supply chain disruptions, could be substantial in certain countries [9]. Studies by Maltezou et al. and Faramarzi et al. revealed that absenteeism costs accounted for a large proportion (80.4%) of total costs [10] and estimated an average cost of US $671.4 per patient [11], respectively. Furthermore, the macroeconomic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic is considerably more significant. Data from Europe indicates that the gross domestic product (GDP) fell by an average of 7.4% in 2020 [12]. Globally, the economic burden of COVID-19 was estimated to be between US $77 billion and US $2.7 trillion in 2019 [13]. Another study calculated the quarantine costs of COVID-19 to exceed 9% of the global GDP [14].
Evaluating the cost of COVID-19, encompassing both direct (medical and non-medical) and indirect costs, provides valuable insights for policymakers and healthcare managers to devise effective strategies for resource allocation and cost control, particularly in the post-COVID-19 era. Despite the abundance of literature on COVID-19, only a handful of studies have concentrated on its economic burden. Furthermore, the currency estimates provided in these articles is inconsistent. To address this gap, our study aimed to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of the global economic burden of COVID-19. The objectives of this study are twofold: firstly, to estimate the direct and indirect costs of COVID-19 as a percentage of GDP and health expenditure (HE) at the global level, and secondly, to estimate the direct medical costs based on the inpatient ward, which includes both the general ward and the intensive care unit (ICU).
Methods
This study was designed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [15].
Search strategy and data sources
We performed a comprehensive search in PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases to retrieve studies on the economic burden of COVID-19 disease. To this objective, we conducted a comprehensive search by combining the search terms relating to COVID-19 (coronavirus, 2019-nCoV), as a class, with the terms relating to the economic burden and terms related to it (direct cost, indirect cost, productivity cost, morbidity cost, mortality cost, cost analysis, cost of illness, economic cost, noneconomic cost, financial cost, expenditure, spending). The search was limited to English language publications and human studies that were published before September 19, 2021. The search strategy was validated by a medical information specialist. All search strategies are available in the Additional file 1.
Screening and selection
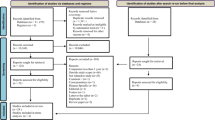
Two reviewers independently screened all distinct articles, focusing on the title and abstract and utilizing EndNote software. The reviewers were blinded to each other’s findings during the screening phase. Potential duplicates were identified and scrutinized to exclude identical entries. Any discrepancies between the reviewers were reconciled through consensus or by consulting a third reviewer. The final decision regarding inclusion was determined subsequent to a comprehensive review of the full-text article. The whole process of the study selection was outlined in a flow chart (Fig. 1).
This systematic review included all original studies that addressed the economic burden of COVID-19, provided they (1) estimated all costs associated with COVID-19, including both direct (medical and non-medical) and indirect (morbidity and mortality) costs and (2) were designed as observational studies or controlled clinical trials. Studies were excluded based on the following criteria: (1) they were review articles, commentaries, editorials, protocols, case studies, case series, animal studies, book chapters, or theses, (2) they estimated costs for a specific disease or action during the COVID-19 pandemic, and (3) they were studies assessing budget impact or economic evaluations.
Data extraction
A specific data extraction template was developed to extract relevant information from every study that satisfied our eligibility criteria. The data extracted covered the general study characteristics (authors, study publication, geographical location of data collection), cost-related information (direct medical cost, direct nonmedical cost, indirect cost, total cost, years of costing, and currency), and participants-related data (sample size and population studied for estimation).
Outcome and quality assessment
The primary outcomes were documented as the standardized mean difference (SMD) accompanied by 95% confidence intervals, representing the direct medical costs borne in general wards as compared to ICU for patients diagnosed with COVID-19. Additionally, another outcome was the estimation of these costs as a proportion of the GDP and health expenditure (HE).
A quality assessment was conducted on all the included studies, utilizing the checklist formulated by Larg and Moss [16]. This checklist comprises three domains: analytic framework, methodology and data, and analysis and reporting. The quality assessment was independently corroborated by two reviewers. In case of any discrepancies in the quality assessment, resolution was ensured through consensus or consultation with a third reviewer.
Statistical analysis
To analyze the data, we utilized the cost-of-illness (COI) study approach, which involved categorizing the studies into two groups: top-down studies and bottom-up studies. Top-down studies were defined as population-based methods that estimated costs for a specific country or group of countries, while bottom-up studies were defined as person methods that estimated costs per person [16].
In our methodological approach to the top-down studies, we initially categorized the costs into direct and indirect types. The direct costs comprised both medical and nonmedical expenses, while the indirect costs were related to potential productivity losses stemming from mortality and morbidity. Subsequently, we undertook the adjustment of all costs to the 2020 US dollar value. This was achieved based on the principle of purchasing power parity (PPP), and we utilized the currency conversion factor as recommended by the World Bank for this purpose. We employed the method proposed by Konnopka and König to present the COVID-19 cost to top-down studies. This method, which expresses the costs as a proportion of the gross domestic product (GDP) and health expenditure (HE), eliminates the need for adjustments for inflation or differences in purchasing power [17]. Moreover, we computed the costs using both an unweighted mean and a population-weighted mean.
In the bottom-up studies, a random-effects model was employed for the meta-analysis, with the SMD serving as the measure of effect size. To mitigate the influence of heterogeneity, all costs were converted to 2020 US dollars based on PPP, utilizing the currency conversion factor suggested by the World Bank. The focus of our analysis was a comparison of the direct medical costs of patients admitted to the general ward versus those in ICU. The SMD was calculated as the measure of effect size, with the sample size acting as the weighting factor. Heterogeneity was assessed through Cochran’s Q test and the I 2 statistic. The Q-test, a classical measure with a chi-square distribution, is calculated as the weighted sum of squared differences between individual study effects and the pooled effects across studies. The I 2 statistic represents the percentage of variation across studies, with threshold values of 25%, 50%, and 75% indicating low, moderate, and high levels of heterogeneity, respectively. To assess possible publication or disclosure bias, we used funnel plots, the Begg-adjusted rank correlation test, and Egger’s test. All statistical analyses were performed using STATA version 14 (Stata Corp, College Station, TX, USA), and P-values less than 0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
Results
The study selection process is illustrated in Figure 1. The search strategy produced 3271 records (Scopus, 1450; PubMed, 1144; Web of Science, 677), from which 1358 duplicates were eliminated. Out of the remaining 1913 articles, a mere 101 satisfied the inclusion criteria and underwent a full-text review. During this full-text screening, 74 articles were excluded for various reasons, resulting in a final selection of 27 studies included in the systematic review. Among these, 20 were bottom-up studies [7, 10, 18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35], and 7 were top-down studies [36,37,38,39,40,41,42].
Characteristics of included studies
Table 1 presents the general characteristics of the included studies. Out of the 27 studies, 5 were conducted in the USA; 5 in China; 2 each in Spain, Brazil, South Korea, and India; and 1 each in Italy, South Africa, the Philippines, Greece, Iran, Kenya, Nigeria, and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Based on the methodology employed, 20 studies were categorized as bottom-up studies and seven as top-down studies.
Among the seven top-down studies, only three calculated direct medical costs [37, 38, 41], two studies examined the direct nonmedical costs [38, 41], and all but Santos et al. [37], who did not report these costs, calculated indirect costs. Of the 20 bottom-up studies, all but 1 study [31] assessed the direct medical costs. Only four studies calculated the direct nonmedical costs [10, 19, 29, 34], and seven studies reported the indirect costs [7, 10, 19, 26, 29, 31, 34].
Table 2 presents the specific characteristics of the top-down studies. These studies indicate that the direct costs of COVID-19 span from US $860 million to US $8,657 million, while indirect costs range from US $610 million to US $5,500,000 million. On average, top-down studies estimate the direct costs associated with COVID-19 to constitute 2.73% and 0.39% of healthcare expenditures, based on unweighted and weighted means, respectively. The results also reveal that, on average, indirect costs account for 10.53% of GDP, with a range of 0.02 to 30.90%. Furthermore, the total cost estimated by top-down studies comprises 85.91% of healthcare expenditure and 9.13% of GDP.
Table 3 outlines the specific characteristics of the bottom-up studies. Excluding two studies [23, 27], all reported their sample sizes, which varied from 9 to 1,470,721. The mean estimate of direct medical costs ranged from US $1264 to US $79,315. Two studies reported values for direct nonmedical costs [19, 29], with means of US $25 and US $71. The mean estimate of indirect costs ranged from US $187 to US $689,556.
Meta-analysis results
The results of the meta-analysis for the direct medical costs are shown in Figure 2. The results indicate a significant association between the mean cost of direct medical services and the inpatient ward. Specifically, the analysis yielded a standardized mean difference (SMD) of 1.62 (CI: 0.9–2.35) with a substantial degree of heterogeneity (Q = 26170, p < 0.0001; I 2 = 100%).
Assessment of publication bias
Figure 3 presents the information related to publication bias. The funnel plot, constructed from the studies included, does not suggest the presence of potential publication bias. Moreover, the application of Begg’s and Egger’s tests in the statistical analysis resulted in P-values of 0.788 and 0.789, respectively, indicating an absence of significant bias.
Discussion
This investigation represents the initial systematic review and meta-analysis conducted on the topic of the global economic impact of COVID-19. Furthermore, it is the first study to evaluate economic burden research related to COVID-19 using both top-down and bottom-up approaches, and it has conducted a meta-analysis of medical direct expenses based on hospitalization wards. In general, studies examining the economic impact of COVID-19 are scarce, with a greater proportion of studies employing a bottom-up approach. More than 30% of these studies were conducted in the USA and China. Patients admitted to the ICU ward exhibited higher costs than those admitted to the general ward.
Admission to the ICU significantly escalated the medical expenditure associated with COVID-19 treatment. This study discovered that the medical costs for COVID-19 patients in the ICU were approximately twice as high as those for patients in general wards, with a range from 0.05 to 3.48 times higher. This finding aligns with existing literature, which suggests that ICU patients with COVID-19 are more likely to require expensive treatments such as mechanical ventilation and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, compared to those in general wards [44, 45]. Consistent with this, other studies have reported an increase in medical expenditures with the hospitalization of COVID-19 patients in the ICU. For instance, a study conducted in the USA found a fivefold increase in costs for patients in the ICU who required invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), compared to those not in the ICU or without IMV [22]. Similarly, a study in China reported a 2.5-fold increase in costs for severe COVID-19 patients compared to mild cases [30]. Given the elevated medical costs associated with treating COVID-19 patients in the ICU or those with severe symptoms, health policymakers must concentrate on implementing programs that promote early diagnosis. Consequently, healthcare providers could initiate treatment at an earlier stage, potentially reducing the severity of the disease and associated costs.
Our research indicates that significant variations in estimated costs would be observed if these costs were reported in PPP, particularly in relation to direct medical expenses. The lowest value was calculated in India, amounting to US $1264, while the highest value was observed in the USA, reaching US $54,165. Furthermore, the calculated medical costs varied across countries. For example, in the USA, direct medical expenditures ranged from US $1701 to US $54,156 [21, 35]. In contrast, in China, the reported costs fluctuated between US $5264 and US $79,315 [7, 25]. Several factors contribute to this variation in the estimation of direct medical costs. Primarily, direct medical costs cover a spectrum of services, including diagnosis, medication, consumables, inpatient care, and consultation services. Consequently, each study may have estimated the direct medical costs for a subset or the entirety of these services, leading to differences in the estimated costs. For instance, Nguyen et al. demonstrated a nearly threefold increase in direct costs for COVID-19 patients managed with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) compared to patients not receiving ECMO [35]. This highlights the impact of specific treatments on the overall cost. Secondly, the sample size may vary between studies, resulting in different cost estimates. Larger sample sizes typically provide more accurate and reliable estimates, but they also require more resources to collect and analyze. Lastly, the studies may have estimated costs for patients with varying conditions, such as those in acute status, patients hospitalized in general wards, or those admitted to ICU wards.
In addition to direct medical expenditures, the indirect costs arising from productivity losses due to COVID-19 have substantial societal implications. This study discovered that direct medical expenses attributable to COVID-19 varied from US $860 million (representing 0.11% of China’s healthcare expenditure) as reported by Zhao et al. [38] in China to US $8657 million (equivalent to 7.4% of Spanish healthcare expenditure) as reported by Gonzalez Lopez et al. [41] in Spain. On a global scale, direct medical costs due to COVID-19 constituted 2.73% of healthcare expenditure and 0.25% of GDP. The results also unveiled that the indirect costs of the COVID-19 pandemic impacted different countries to varying extents. The minimum value of indirect costs was estimated in Italy [40] and India [39] at US $610 million and US $658 million, respectively. Interestingly, when reported as a percentage of GDP, India had a lower cost (0.02% of GDP) compared to China (0.03% of GDP). The maximum value of indirect costs was calculated in the USA at US $5,500,000 million, which accounted for approximately 26.32% of the USA’s GDP [36]. Despite the numerical value of indirect costs being lower in Spain than in the USA and China, it represented a higher percentage of GDP (30.90%). The resulting pooled estimate indicated that the indirect costs due to COVID-19 were responsible for 10.53% of global GDP. The review underscores the significant economic repercussions of COVID-19. The total costs in the USA accounted for about 157% of healthcare expenditure and 26% of GDP, in China for 80% of healthcare expenditure and 4.28% of GDP, and in Spain for approximately 345% of healthcare expenditure and 32% of GDP. Globally, the total costs of COVID-19 accounted for about 86% of healthcare expenditure and 9.13% of GDP. This highlights the profound economic impact of the pandemic on both healthcare systems and economies worldwide.
Strengths and limitation
Our study possesses several significant strengths. It is the inaugural meta-analysis of the worldwide costs associated with COVID-19, supplementing a systematic review conducted by Richards et al. on the economic burden studies of COVID-19 [12]. A considerable number of studies was conducted in the USA and China, but our analysis also incorporated studies from other high- and low-income countries, potentially enhancing the generalizability of our findings. Recognizing that economic burden studies often display significant heterogeneity, we endeavored to minimize this by distinguishing between bottom-up and top-down studies and standardizing currencies to US dollars in terms of PPP.
However, our study is not without limitations. As is typical with all meta-analyses of economic burden studies, the most substantial limitation is heterogeneity. This heterogeneity can originate from various factors, including differences in study design, the range of services included in individual studies, the year of estimation, the currencies used for estimation, the study population, among other factors. Our systematic review only incorporated studies that estimated costs for an actual population, thereby excluding a wide array of studies on the economic burden of COVID-19 that employed modeling techniques. Future research could potentially conduct systematic reviews and meta-analyses on cost estimation modeling studies for COVID-19. Lastly, while no publication bias was detected through statistical analysis, our study was limited to papers written in English. As a result, numerous papers published in other languages were inevitably excluded.
Conclusion
Our research indicates that the COVID-19 pandemic has imposed a substantial economic strain worldwide, with the degree of impact varying across nations. The quantity of studies examining the economic repercussions of COVID-19 is limited, with a majority employing a bottom-up methodology. The indirect costs ascribed to COVID-19 constituted 10.53% of the global GDP. In total, the costs linked to COVID-19 represented 9.13% of GDP and 86% of healthcare spending. Moreover, our meta-analysis disclosed that the direct medical expenses for COVID-19 patients in the ICU were almost twice those of patients in general wards. The results of our research, along with those of others, underscore the pivotal role of economic outcomes in the post-COVID-19 era for societies and families. Consequently, it is imperative for policymakers and health administrators to prioritize and pay greater attention to economic programs.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable as no new data were generated during the study. The data analysis file during this study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Lu H, Stratton CW, Tang YW. Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: the mystery and the miracle. J Med Virol. 2020;92(4):401–2.
Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
Gautier JF, Ravussin Y. A new symptom of COVID-19: loss of taste and smell. Obesity. 2020;28(5):848.
Delikhoon M, Guzman MI, Nabizadeh R, Norouzian BA. Modes of transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and factors influencing on the airborne transmission: a review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(2):395.
Alimohammadi M, Abolli S, Ghordouei ME. Perceiving effect of environmental factors on prevalence of SARS-Cov-2 virus and using health strategies: a review. J Adv Environ Health Res. 2022;10(3):187–96.
Li XZ, Jin F, Zhang JG, Deng YF, Shu W, Qin JM, et al. Treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 in Shandong, China: a cost and affordability analysis. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020;9(1):78.
Jin H, Wang H, Li X, Zheng W, Ye S, Zhang S, et al. Economic burden of COVID-19, China, January–March, 2020: a cost-of-illness study. Bull World Health Organ. 2021;99(2):112.
Bartsch SM, Ferguson MC, McKinnell JA, O'Shea KJ, Wedlock PT, Siegmund SS, et al. The potential health care costs and resource use associated with COVID-19 in the United States. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(6):927–35.
Juranek S, Paetzold J, Winner H, Zoutman F. Labor market effects of COVID-19 in Sweden and its neighbors: evidence from novel administrative data. NHH Dept of Business and Management Science Discussion Paper. (2020/8); 2020.
Maltezou H, Giannouchos T, Pavli A, Tsonou P, Dedoukou X, Tseroni M, et al. Costs associated with COVID-19 in healthcare personnel in Greece: a cost-of-illness analysis. J Hosp Infect. 2021;114:126–33.
Faramarzi A, Javan-Noughabi J, Tabatabaee SS, Najafpoor AA, Rezapour A. The lost productivity cost of absenteeism due to COVID-19 in health care workers in Iran: a case study in the hospitals of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):1169.
Richards F, Kodjamanova P, Chen X, Li N, Atanasov P, Bennetts L, et al. Economic burden of COVID-19: a systematic review. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2022;14:293–307.
Forsythe S, Cohen J, Neumann P, Bertozzi SM, Kinghorn A. The economic and public health imperatives around making potential coronavirus disease–2019 treatments available and affordable. Value Health. 2020;23(11):1427–31.
Rodela TT, Tasnim S, Mazumder H, Faizah F, Sultana A, Hossain MM. Economic impacts of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in developing countries; 2020.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group* t. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–9.
Larg A, Moss JR. Cost-of-illness studies: a guide to critical evaluation. Pharmacoeconomics. 2011;29:653–71.
Konnopka A, König H. Economic burden of anxiety disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2020;38:25–37.
Jeck J, Jakobs F, Kron A, Franz J, Cornely OA, Kron F. A cost of illness study of COVID-19 patients and retrospective modelling of potential cost savings when administering remdesivir during the pandemic “first wave” in a German tertiary care hospital. Infection. 2022;50(1):191–201.
Kotwani P, Patwardhan V, Pandya A, Saha S, Patel GM, Jaiswal S, et al. Valuing out-of-pocket expenditure and health related quality of life of COVID-19 patients from Gujarat, India. J Commun Dis (E-ISSN: 2581-351X & P-ISSN: 0019-5138). 2021;53(1):104–9.
Tsai Y, Vogt TM, Zhou F. Patient characteristics and costs associated with COVID-19–related medical care among Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(8):1101–9.
Weiner JP, Bandeian S, Hatef E, Lans D, Liu A, Lemke KW. In-person and telehealth ambulatory contacts and costs in a large US insured cohort before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(3):e212618-e.
Di Fusco M, Shea KM, Lin J, Nguyen JL, Angulo FJ, Benigno M, et al. Health outcomes and economic burden of hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the United States. J Med Econ. 2021;24(1):308–17.
Edoka I, Fraser H, Jamieson L, Meyer-Rath G, Mdewa W. Inpatient care costs of COVID-19 in South Africa’s public healthcare system. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2022;11(8):1354.
Tabuñar SM, Dominado TM. Hospitalization expenditure of COVID-19 patients at the university of the Philippines-Philippine general hospital (UP-PGH) with PhilHealth coverage. Acta Med Philipp. 2021;55(2)
Zhao J, Yao Y, Lai S, Zhou X. Clinical immunity and medical cost of COVID-19 patients under grey relational mathematical model. Results Phys. 2021;22:103829.
Ghaffari Darab M, Keshavarz K, Sadeghi E, Shahmohamadi J, Kavosi Z. The economic burden of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): evidence from Iran. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):1–7.
Barasa E, Kairu A, Maritim M, Were V, Akech S, Mwangangi M. Examining unit costs for COVID-19 case management in Kenya. BMJ Glob Health. 2021;6(4):e004159.
Seon J-Y, Jeon W-H, Bae S-C, Eun B-L, Choung J-T, Oh I-H. Characteristics in pediatric patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(20):e148.
Banke-Thomas A, Makwe CC, Balogun M, Afolabi BB, Alex-Nwangwu TA, Ameh CA. Utilization cost of maternity services for childbirth among pregnant women with coronavirus disease 2019 in Nigeria’s epicenter. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2021;152(2):242–8.
Li X-Z, Jin F, Zhang J-G, Deng Y-F, Shu W, Qin J-M, et al. Treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 in Shandong, China: a cost and affordability analysis. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020;9(03):31–8.
Kirigia JM, Muthuri RNDK. The fiscal value of human lives lost from coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in China. BMC Res Notes. 2020;13:1–5.
Lee JK, Kwak BO, Choi JH, Choi EH, Kim J-H, Kim DH. Financial burden of hospitalization of children with coronavirus disease 2019 under the national health insurance service in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(24):e224.
Khan AA, AlRuthia Y, Balkhi B, Alghadeer SM, Temsah M-H, Althunayyan SM, et al. Survival and estimation of direct medical costs of hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(20):7458.
Mas Romero M, Avendaño Céspedes A, Tabernero Sahuquillo MT, Cortés Zamora EB, Gómez Ballesteros C, Sánchez-Flor Alfaro V, et al. COVID-19 outbreak in long-term care facilities from Spain. Many lessons to learn. PLoS One. 2020;15(10):e0241030.
Nguyen NT, Sullivan B, Sagebin F, Hohmann SF, Amin A, Nahmias J. Analysis of COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome managed with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation at US academic centers. Ann Surg. 2021;274(1):40.
Viscusi WK. Economic lessons for COVID-19 pandemic policies. South Econ J. 2021;87(4):1064–89.
Santos HLPC, Maciel FBM, Santos Junior GM, Martins PC, Prado NMBL. Public expenditure on hospitalizations for COVID-19 treatment in 2020, in Brazil. Rev Saude Publica. 2021;55:52.
Zhao J, Jin H, Li X, Jia J, Zhang C, Zhao H, et al. Disease burden attributable to the first wave of COVID-19 in China and the effect of timing on the cost-effectiveness of movement restriction policies. Value Health. 2021;24(5):615–24.
John D, Narassima M, Menon J, Rajesh JG, Banerjee A. Estimation of the economic burden of COVID-19 using disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) and productivity losses in Kerala, India: a model-based analysis. BMJ Open. 2021;11(8):e049619.
Nurchis MC, Pascucci D, Sapienza M, Villani L, D’Ambrosio F, Castrini F, et al. Impact of the burden of COVID-19 in Italy: results of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) and productivity loss. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(12):4233.
González López-Valcárcel B, Vallejo-Torres L. The costs of COVID-19 and the cost-effectiveness of testing. Appl Econ Anal. 2021;29(85):77–89.
Debone D, Da Costa MV, Miraglia SG. 90 days of COVID-19 social distancing and its impacts on air quality and health in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Sustainability. 2020;12(18):7440.
Ghaffari Darab M, Keshavarz K, Sadeghi E, Shahmohamadi J, Kavosi Z. The economic burden of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): evidence from Iran. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):132.
Oliveira TF, Rocha CAO, Santos AGG, Silva Junior LCF, Aquino SHS, Cunha EJO, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in COVID-19 treatment: a systematic literature review. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;36:388–96.
Petrilli CM, Jones SA, Yang J, Rajagopalan H, O’Donnell L, Chernyak Y, et al. Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1966.
Funding
There was no funding utilized in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AF was principal investigators of designing the study, conducted analysis, and was major contributor in writing the manuscript. SN, HD, and SA conducted the literature search, conducted the screening and data extraction. HY and JJ contributed in designing the study and writing the manuscript. All authors contributed, reviewed, and approved this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Urmia University of Medical Sciences (IR.UMSU.REC.1400.121).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1.
Search strategies
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Faramarzi, A., Norouzi, S., Dehdarirad, H. et al. The global economic burden of COVID-19 disease: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev 13, 68 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02476-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02476-6