Abstract
Background
Hyperoxia is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in the intensive care unit. Classical noninvasive measurements of oxygen saturation with pulse oximeters are unable to detect hyperoxia. The Oxygen Reserve Index (ORI) is a continuous noninvasive parameter provided by a multi-wave pulse oximeter that can detect hyperoxia. Primary objective was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of the ORI for detecting arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) > 100 mmHg in neurocritical care patients. Secondary objectives were to test the ability of ORI to detect PaO2 > 120 mmHg and the ability of pulse oximetry (SpO2) to detect PaO2 > 100 mmHg and PaO2 > 120 mmHg.
Methods
In this single-center study, we collected ORI and arterial blood samples every 6 h for 3 consecutive days. Diagnostic performance was estimated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC).
Results
There were 696 simultaneous measurements of ORI and PaO2 in 62 patients. Considering the repeated measurements, the correlation between ORI and PaO2 was r = 0.13. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), obtained to test the ability of ORI to detect PaO2 > 100 mmHg, was 0.567 (95% confidence interval = 0.566–0.569) with a sensitivity of 0.233 (95%CI = 0.230–0.235) and a specificity of 0.909 (95%CI = 0.907–0.910). The AUROC value obtained to test the ability of SpO2 to detect a PaO2 > 100 mmHg was 0.771 (95%CI = 0.770–0.773) with a sensitivity of 0.715 (95%CI = 0.712–0.718) and a specificity of 0.700 (95%CI = 0.697–0.703). The diagnostic performance of ORI and SpO2 for detecting PaO2 > 120 mmHg was AUROC = 0.584 (95%CI = 0.582–0.586) and 0.764 (95%CI = 0.762–0.766), respectively. The AUROC obtained for SpO2 was significantly higher than that for ORI (p < 0.01). Diagnostic performance was not affected by sedation, norepinephrine infusion, arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide, hemoglobin level and perfusion index.
Conclusion
In a specific population of brain-injured patients hospitalized in a neurointensive care unit, our results suggest that the ability of ORI to diagnose hyperoxia is relatively low and that SpO2 provides better detection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
In the late 2010s, there is growing interest in the medical literature in detecting of hyperoxia that goes undetected by the use of pulse oximeters. It has deleterious effects in numerous settings, including critical care, and has been associated with increased morbidity and mortality [1,2,3,4,5,6]. In a specific group of brain-injured patients, where oxygenation is an important goal, a study of traumatic brain injury has shown that hyperoxia increases mortality compared to normoxia, but hyperoxia was set at a very high level (PaO2 > 300 mmHg or 40 kPa) [7]. More recently, the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine has recommended that in acute brain injury with or without intracranial pressure rise, the optimal PaO2 range to meet metabolic needs is 80–120 mmHg (10–16 kPa) [8]. Thus, because of the narrow therapeutic range, monitoring hyperoxia may be important in this patient population. To date, the diagnosis of hyperoxia requires arterial blood sampling to measure partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2), which remains invasive and can lead to increased endoluminal contamination with repeated sampling. Arterial blood gas analyses are intermittent and do not allow continuous measurement of PaO2.
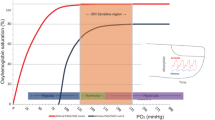
MASIMO (Irvine, USA) has developed a noninvasive, multi-wave pulse oximeter called Radical-7®. This device incorporates a conventional pulse oximeter in conjunction with two other measurements, the perfusion index (PI) and the Oxygen Reserve Index (ORI). PI is based on the ratio of pulsatile to non-pulsatile blood flow and should reflect peripheral perfusion [9]. The ORI uses the Fick equation, arterial oxygen content, and venous oxygen saturation (SvO2). Indeed, arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) increases to a maximum of 100% in hyperoxia, while SvO2 continues to increase by 80% at a PaO2 of 200 mmHg [10]. Thus, assuming that cardiac output and oxygen consumption are constant, SvO2 is directly proportional to PaO2, and ORI should detect changes in SvO2 when SaO2 reaches its maximum.
In a population of healthy volunteers and patients under general anesthesia in the operating room, ORI seems to be related to PaO2 and could also predict desaturation before pulse oximetry (SpO2) [11,12,13]. In ICU patients, the results are still unclear because several factors (vasomotor tone, use of vasopressor, degree of sedation) may alter the plethysmographic signal. Although ORI cannot replace arterial blood gas analysis, it could avoid hyperoxia thanks to its continuous monitoring and a specific protocol to lower the percentage of inspired oxygen. In the context of our study evaluating ORI in patients with acute brain injury, two thresholds for hyperoxia can be discussed: 100 mmHg as proposed by Massimo for ORI and 120 mmHg according to the recommendations of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine in brain-injured patients.
The primary objective of the study was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of ORI for detecting PaO2 > 100 mmHg. Secondary objectives were to evaluate the ability of ORI to detect PaO2 > 120 mmHg, the ability of SpO2 to detect PaO2 > 100 mmHg and PaO2 > 120 mmHg and to evaluate the relationship between ORI and PaO2 in the ICU.
Materials and methods
Study
We performed this observational, single-center study in the neurological ICU of the Bordeaux University Hospital. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (CERAR IRB 00010254-2018-119). According to French law, written consent was not required, and patients and/or their next of kin were informed that their anonymized data would be included in the database. No one refused to participate.
Patients
The inclusion criteria were patients aged 18 years or older, admitted to the medical-surgical neurological ICU, who had arterial access and a pulse oximetry sensor on the patient middle or index finger (RD Rainbow Lite SET™, Masimo, Irvine, CA), connected to a Radical-7 pulse oximeter (Masimo, Irvine, CA), and who had a blood gas measurement every 6 h according to the local protocol (GEM® Premier™ 5000, Instrumentation Laboratory, Bedford, MA, United States). There were no restrictions on ventilation mode or drug infusion.
Data were collected every 6 h for 3 consecutive days. We collected measurements of Radical-7®: SpO2, ORI (after visual inspection of the quality and stability of the signal) and PI at the time of blood gas sampling, as well as an arterial blood gas sample.
We also collected: demographic data, reason for ICU admission, Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II); ventilatory settings (in patients with a simple nasal cannula, FiO2 was estimated as follows: oxygen flow (l/min) × 3 + 21) [15]; neurological status data: Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale (RASS) if subjects were sedated or Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) if not, and hemodynamic data. Finally, we collected information on the use of commonly used drugs that might affect vasomotion (remifentanil, sufentanil, propofol, midazolam, norepinephrine, milrinone, urapidil and nicardipine).
Statistical analysis
Because of insufficient data on ORI, no sample size calculation was performed. We chose to include every patient who met the inclusion criteria for one year. Based on usual recruitment we assumed that we would include more than 50 patients. Continuous data were reported as mean (standard deviation) or median [interquartile range] depending on the distribution of the data. Qualitative data were expressed as number (percentage). The correlation between PaO2 and ORI was crudely estimated first and considering repeated measurements second [16]. Diagnostic performance included the ability of the ORI to detect a PaO2 greater than 100 mmHg and greater than 120 mmHg. We also evaluated the ability of SpO2 to detect a PaO2 greater than 100 mmHg and greater than 120 mmHg. Diagnostic performance was estimated by the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV). Because of repeated measurements, 95% confidence intervals (CI) around the parameters were estimated using a 1000 individual bootstrap. The influence of different factors such as PaCO2, hemoglobin, perfusion index, or norepinephrine dose on the diagnostic performance of ORI was estimated by using the semiparametric approach proposed by Farragi et al. [17]. The data analysis and the statistical plan were written and submitted to the Institutional Review Board (CERAR IRB 00010254-2018-119) before accessing the data. All analyses were performed using R version 4.0.3 (Vienne, Austria).
Results
Patients
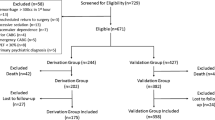
We included 62 patients between August 2018 and August 2019. The main characteristics are listed in Table 1. Patients had a high SAPS 2 score (mean: 43), were frequently hospitalized after subarachnoid hemorrhage (66%), and were intubated in 53% of cases. Subjects were included in the early days of hospitalization in ICU (median: 3rd). Measurements were mostly performed without sedation. Of the 744 measurements, 714 PaO2 (242 of which > 100 mmHg and 82 of which > 120 mmHg) and 698 ORI values (98 of which > 0.0) were recorded with a total of 696 simultaneous measurements (Fig. 1). All ORI values were included, regardless of the PI value. Missing data were not considered in the statistical analysis.
Correlation between ORI and PaO2
Blood gas analysis and ORI data are shown in Table 2. The conditions during the measurements are listed in Table 3. For all measurements, crude correlation between ORI and PaO2 was r = 0.16; p < 0.001 (Fig. 2); when repeated measurements were taken into account correlation was r = 0.13; p < 0.001 (Additional file 1: Fig. S1).
The ability of ORI and SpO2 to predict hyperoxia
The ability of ORI to predict PaO2 > 100 mmHg was low; AUROC = 0.567 [95% CI = 0.566–0.569] (Fig. 3). The abilities of ORI to predict PaO2 > 120 mmHg and the ability of SpO2 to predict hyperoxia, defined by PaO2 > 100 mmHg and > 120 mmHg are shown in Table 4. AUROC, which was generated for SpO2, was significantly different from AUROC generated for ORI in order to detect hyperoxia (Fig. 3). An SpO2 value less than or equal to 94% allows a PaO2 > 100 mmHg to be excluded with a sensitivity of 100%. An SpO2 value less than or equal to 95% allows to exclude with a sensitivity of 100% a PaO2 > 120 mmHg. Diagnostic performance did not appear to be affected by sedation, norepinephrine infusion, PaCO2 value, hemoglobin value and perfusion index (Additional file 2: Fig. S2, Additional file 3: Fig. S3).
Discussion
Our results, based on a large number of simultaneous measurements of PaO2 and ORI performed in a neuro-ICU population, show that: (i) the ability of ORI to detect hyperoxia (defined by PaO2 > 100 mmHg or PaO2 > 120 mmHg) was low; (ii) the diagnostic performance of SpO2 to detect hyperoxia was better than that of ORI, and that (iii) ORI and PaO2 were poorly correlated. Diagnostic performance did not appear to be affected by patient conditions such as perfusion index, use of vasoactive drugs such as norepinephrine, or metabolic parameters (PCO2 and hemoglobin). We chose to investigate two PaO2 thresholds. The definition of hyperoxia is not uniform and it seemed interesting to us to study the threshold proposed by Masimo for the capacities of the ORI (100 mmHg) and the threshold used in our population of brain-injured patients (120 mmHg).
Several studies suggest that hyperoxia may increase both morbidity and mortality. In a large multicenter cohort study of patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest, excessive oxygen tension was associated with an increased risk of in-hospital death [18]. A meta-analysis that included 25 randomized control trials involving more than 16,000 patients with sepsis, critical illness, stroke, trauma, myocardial infarction, or cardiac arrest, as well as patients undergoing emergency surgery, showed that liberal oxygen therapy increased mortality without improving other outcomes important to the patient [19]. Other work has found that short-term hyperoxia after intubation in the emergency department was associated with increased mortality in the intensive care unit [20]. Randomized controlled trials have shown that lower oxygenation targets (PaO2 < 100 mmHg (< 13 kPa) and SpO2 < 97%) are associated with higher survival rates and shorter duration of mechanical ventilation in ICU patients [21, 22]. However, the data are not entirely conclusive, as some studies have reached different conclusions. Two recent randomized control trials failed to find a benefit of normoxia compared with moderate hyperoxia [23, 24].
Under study conditions, we found no association between ORI and PaO2 levels. Although we acknowledge that the ORI is not marketed as a noninvasive PaO2 monitor, our results are not consistent with previous studies. This may be explained by several factors. Several positive studies have focused on the ability of the ORI to predict desaturations in the operating room, in pediatrics, in emergencies, in obese patients, or in thoracic surgery [14, 25,26,27,28,29]. These results are very interesting, but address a completely different question than ours (desaturation versus prediction of hyperoxia). Other works found a good correlation between ORI and PaO2. These studies included healthy volunteers or surgical patients under general anesthesia [10,11,12,13]. In a study of 20 healthy volunteers, Vos et al. found a strong and positive correlation between ORI and PaO2 (R = 0.8) [13]. In studies conducted in the operating room, a correlation between ORI and PaO2 was found, ranging from r2 = 0.54 to r2 = 0.71 (12,13). In another study, ORI was found to be able to detect PaO2 > 100 mmHg (threshold = 0.24) [12]. Compared to patients under general anesthesia in the operating room, patients in the ICU differ in many ways. General inflammation can cause peripheral edema, which can alter the plethysmographic signal. ICU patients are more likely to receive vasoactive medications that may alter vasomotor tone, but they do not appear to alter the diagnostic performance of ORI in our study. Anesthesia patients are also all perfectly quiet, which is not the case in the ICU; this element could also explain a signal alteration in the ICU. All these elements could partially explain our results.
ORI has been much less studied in the ICU. To our knowledge, the only study that investigated ORI in the ICU found a significant reduction in hyperoxia when using an ORI-based protocol [30]. In this monocentric study, patients with ORI monitoring were more likely to be ventilated with a FiO2 of 0.21, which probably secured the main outcome. The results of our study suggest that ORI does not seem to be suitable for detecting hyperoxia situations in the ICU. Moreover, there seem to be very large individual variations (Fig. 2).
Our study has several limitations. First, we measured a PaO2 greater than 100 mmHg in 34% of cases, which is less than in other studies [4, 20, 31]. However, the sensitivity and specificity of a test are not affected by the prevalence of the disease. We may already have restrictive oxygen targets in our ICU because nurses are allowed to lower the inspiratory O2 fraction when SpO2 is higher than physician orders, and repeated arterial blood gas measurements have been used to lower FiO2, which is done routinely. However, lowering FiO2 based on ORI was not allowed. In particular, we found a single PaO2 measurement higher than 200 mmHg, which precluded analysis of ORI in the presence of high hyperoxia (PaO2 > 200 mmHg). Considering the medical literature, it seems unethical to voluntarily increase PaO2 in ICU patients to study the correlation. Second, all ORI values were considered, regardless of the PI value. This can be considered a limitation since a minimum PI is required to obtain adequate ORi measurements. Third, we have 46 missing data, which is low given the number of measurements we performed, but they may have been emergencies in unstable patients in whom our team could have increased FiO2. Finally, our results focused on a very specific population of brain-injured patients, mostly after subarachnoid hemorrhage, for whom PaO2 values are challenging in both respects. The results remain to be confirmed in other populations.
Conclusion
Under the conditions of the study, our results suggest that ORI is unable to detect hyperoxia and that ORI and PaO2 are poorly correlated in neurocritical care patients.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AUROC:
-
Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- FiO2 :
-
Fraction of inspired oxygen
- ICU:
-
Intensive Care Unit
- kPa:
-
Kilopascals
- mmHg:
-
Millimeters of mercury
- NPV:
-
Negative predictive value
- ORI:
-
Oxygen Reserve Index
- PaCO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide arterial partial pressure
- PaO2 :
-
Arterial oxygen tension
- PI:
-
Perfusion index
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- SaO2 :
-
Arterial oxygen saturation
- SAPS II:
-
Simplified Acute Physiology Score
- SpO2 :
-
Pulse oximetry
- SvO2 :
-
Venous oxygen saturation
References
Helmerhorst HJF, Arts DL, Schultz MJ, van der Voort PHJ, Abu-Hanna A, de Jonge E, et al. Metrics of arterial hyperoxia and associated outcomes in critical care. Crit Care Med. 2017;45:187–95.
Barbateskovic M, Schjørring OL, Russo Krauss S, Jakobsen JC, Meyhoff CS, Dahl RM, et al. Higher versus lower fraction of inspired oxygen or targets of arterial oxygenation for adults admitted to the intensive care unit. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD012631.pub2.
Rincon F, Kang J, Maltenfort M, Vibbert M, Urtecho J, Athar MK, et al. Association between hyperoxia and mortality after stroke: a multicenter cohort study. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:387–96.
de Jonge E, Peelen L, Keijzers PJ, Joore H, de Lange D, van der Voort PHJ, et al. Association between administered oxygen, arterial partial oxygen pressure and mortality in mechanically ventilated intensive care unit patients. Crit Care. 2008;12:R156.
Bellomo R, Bailey M, Eastwood GM, Nichol A, Pilcher D, Hart GK, et al. Arterial hyperoxia and in-hospital mortality after resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Crit Care. 2011;15:R90.
Ni Y-N, Wang Y-M, Liang B-M, Liang Z-A. The effect of hyperoxia on mortality in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta analysis. BMC Pulm Med. 2019;19:53.
Rincon F, Kang J, Vibbert M, Urtecho J, Athar MK, Jallo J. Significance of arterial hyperoxia and relationship with case fatality in traumatic brain injury: a multicentre cohort study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014;85:799–805.
Robba C, Poole D, McNett M, Asehnoune K, Bösel J, Bruder N, et al. Mechanical ventilation in patients with acute brain injury: recommendations of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine consensus. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46:2397–410.
Gayat E, Aulagnier J, Matthieu E, Boisson M, Fischler M. Non-invasive measurement of hemoglobin: assessment of two different point-of-care technologies. PLoS ONE. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030065.
Scheeren TWL, Belda FJ, Perel A. The oxygen reserve index (ORI): a new tool to monitor oxygen therapy. J Clin Monit Comput. 2018;32:379–89.
Yoshida K, Isosu T, Noji Y, Ebana H, Honda J, Sanbe N, et al. Adjustment of oxygen reserve index (ORiTM) to avoid excessive hyperoxia during general anesthesia. J Clin Monit Comput. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-019-00341-9.
Applegate RL, Dorotta IL, Wells B, Juma D, Applegate PM. The relationship between oxygen reserve index and arterial partial pressure of oxygen during surgery. Anesth Analg. 2016;123:626–33.
Vos JJ, Willems CH, van Amsterdam K, van den Berg JP, Spanjersberg R, Struys MMRF, et al. Oxygen reserve index: validation of a new variable. Anesth Analg. 2019;129:409–15.
Alday E, Nieves JM, Planas A. Oxygen reserve index predicts hypoxemia during one-lung ventilation: an observational diagnostic study. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020;34:417–22.
Nugent AO, Kelly PT, Stanton J, Swanney MP, Graham B, Beckert L. Measurement of oxygen concentration delivered via nasal cannulae by tracheal sampling. Respirology. 2014;19:538–43.
Bakdash JZ, Marusich LR. Repeated measures correlation. Front Psychol. 2017;8:456.
Faraggi D. Adjusting receiver operating characteristic curves and related indices for covariates. J R Stat Soc Ser Stat. 2003;52:179–92.
Kilgannon JH, Jones AE, Parrillo JE, Dellinger RP, Milcarek B, Hunter K, et al. Relationship between supranormal oxygen tension and outcome after resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Circulation. 2011;123:2717–22.
Chu DK, Kim LH-Y, Young PJ, Zamiri N, Almenawer SA, Jaeschke R, et al. Mortality and morbidity in acutely ill adults treated with liberal versus conservative oxygen therapy (IOTA): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2018;391:1693–705.
Page D, Ablordeppey E, Wessman BT, Mohr NM, Trzeciak S, Kollef MH, et al. Emergency department hyperoxia is associated with increased mortality in mechanically ventilated patients: a cohort study. Crit Care. 2018;22:9.
Girardis M, Busani S, Damiani E, Donati A, Rinaldi L, Marudi A, et al. Effect of conservative vs conventional oxygen therapy on mortality among patients in an intensive care unit: the oxygen-ICU randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;316:1583–9.
Sutton ADJ, Bailey M, Bellomo R, Eastwood GM, Pilcher DV. The association between early arterial oxygenation in the ICU and mortality following cardiac surgery. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2014;42:730–5.
ICU-ROX Investigators and the Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society Clinical Trials Group, Mackle D, Bellomo R, Bailey M, Beasley R, Deane A, et al. Conservative oxygen therapy during mechanical ventilation in the ICU. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:989–98.
Schjørring OL, Klitgaard TL, Perner A, Wetterslev J, Lange T, Siegemund M, et al. Lower or higher oxygenation targets for acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1301–11.
Koishi W, Kumagai M, Ogawa S, Hongo S, Suzuki K. Monitoring the Oxygen Reserve Index can contribute to the early detection of deterioration in blood oxygenation during one-lung ventilation. Minerva Anestesiol. 2018;84:1063–9.
Fleming NW, Singh A, Lee L, Applegate RL. Oxygen Reserve Index: utility as an early warning for desaturation in high-risk surgical patients. Anesth Analg. 2021;132:770–6.
Szmuk P, Steiner JW, Olomu PN, Ploski RP, Sessler DI, Ezri T. Oxygen Reserve Index: a novel noninvasive measure of oxygen reserve—a pilot study. Anesthesiology. 2016;124:779–84.
Tsymbal E, Ayala S, Singh A, Applegate RL, Fleming NW. Study of early warning for desaturation provided by Oxygen Reserve Index in obese patients. J Clin Monit Comput. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-020-00531-w.
Yoshida K, Isosu T, Noji Y, Hasegawa M, Iseki Y, Oishi R, et al. Usefulness of oxygen reserve index (ORiTM), a new parameter of oxygenation reserve potential, for rapid sequence induction of general anesthesia. J Clin Monit Comput. 2018;32:687–91.
Lasocki S, Brochant A, Leger M, Gaillard T, Lemarié P, Gergaud S, et al. ORI monitoring allows a reduction of time with hyperoxia in critically ill patients: the randomized control ORI2 study. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45:1661–2.
Egi M, Kataoka J, Ito T, Nishida O, Yasuda H, Okamaoto H, et al. Oxygen management in mechanically ventilated patients: a multicenter prospective observational study. J Crit Care. 2018;46:1–5.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Catherine Bigotto and Laure Estève for technical support.
Funding
This work was supported by institutional funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HdC: study design and data analysis, patient recruitment, writing paper; JTL: patient recruitment and data analysis, writing paper; DG: patient recruitment and data analysis, writing paper; PB: patient recruitment, revision of the manuscript; EV: patient recruitment; revision of the manuscript; MB: study design and data analysis, patient recruitment, writing paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study received approval from the Institutional Review Board (CERAR IRB 00010254-2018-119). According to French law, written consent was unnecessary, and the patients and/or next of kin were informed about the inclusion of their anonymized data in the database.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Pr. Biais received honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, California, and Pulsion Medical System, Munich, Germany, for lectures. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Fig. S1.
Repeated-measurements correlation between oxygen partial pressure (PaO2) and Oxygen Reserve Index.
Additional file 2: Fig. S2.
Area Under the Receiving operating characteristics (AUROC) curves according to norepinephrine dosage and dioxide carbon arterial partial pressure (PaCO2) value. Hyperoxemia defined by a PaO2 > 100 mmHg. Hyperoxemia defined by a PaO2 > 120 mmHg
Additional file 3: Fig. S3.
Area Under the Receiving operating characteristics (AUROC) curves according to hemoglobin et perfusion index. A Hyperoxemia defined by a PaO2 > 100 mmHg; B Hyperoxemia defined by a PaO2 > 120 mmHg.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visithttp://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
de Courson, H., Julien-Laferrière, T., Georges, D. et al. The ability of Oxygen Reserve Index® to detect hyperoxia in critically ill patients. Ann. Intensive Care 12, 40 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-022-01012-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-022-01012-w