Abstract
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is a minimally invasive treatment proposed as an alternative to open repair in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms. EVAR consists in a stent-graft placement within the aorta in order to exclude the aneurysm from arterial circulation and reduce the risk of rupture. Knowledge of the various types of devices is mandatory because some stents/grafts are more frequently associated with complications. CT angiography is the gold standard diagnostic technique for preprocedural planning and postprocedural surveillance. EVAR needs long-term follow-up due to the high rate of complications. Complications can be divided in endograft device-related and systemic complications. The purpose of this article is to review the CT imaging findings of EVAR complications and the key features for the diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Key points
-
The rate of complications after endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is 16–30%.
-
CT angiography is the reference standard for postprocedural surveillance of EVAR.
-
Knowledge of implanted device allows adequate interpretation of post-EVAR CT angiography.
-
Complications after EVAR can be divided in endograft device-related and systemic.
-
The most common endograft device-related complications are endoleak and device migration.
Introduction
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is a minimally invasive procedure introduced as an alternative to open repair (OR) in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) [1]. EVAR consists of placing a stent-graft within the aorta to exclude the aneurysm from arterial circulation and reduce the risk of rupture [2]. Compared to OR, EVAR has a lower operative mortality and a shorter hospital stay [1]. Conversely, OR is known to be more durable and the repair is likely to last for the rest of the patient’s lifetime [1]. Since EVAR has an early survival benefit but an inferior prolonged survival benefit compared to OR, it needs long-term post-repair surveillance and possible reintervention to correct graft-related complications [1]. CT angiography (CTA) plays a crucial role for both preprocedural planning and postprocedural surveillance [2, 3]. The rate of complication after EVAR is high, ranging between 16 and 30% [4]. Complications can be divided in endograft device-related and systemic complications [3], as summarized in Table 1. Concerning the degree of severity, a non-standardized classification of complication in “minor,” “moderate” and “severe” one, can be replaced by a standardized and reproducible CIRSE (Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe) complication classification system [5, 6].
The purpose of this article is to review the CT imaging findings of EVAR complications and the key features for the diagnosis. We firstly describe EVAR eligibility, CT angiography technique and the different types of devices used for EVAR and then discuss the various types of endograft device-related and systemic complications.
Evar eligibility
The indication for AAA treatment (surgical or EVAR) includes aneurysm diameter > 5.0–5.5 cm or symptomatic, and an increase in aneurysm size > 5 mm in a 6-month interval and > 10 mm per year [3, 7].
The choice of EVAR instead of OR depends on both patient’s contraindication to surgery and aneurysm characteristics [8].
Patients ≥ 80 years old, obese, diabetic, with cardiac, pulmonary or renal disfunction, and American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) III/IV are considered at high risk for surgery and may be eligible for EVAR [8, 9].
Preprocedural CT angiography allows to define aneurysm morphology and preprocedural planning.
The aneurysm anatomical characteristics suitable for EVAR include aneurysm sac diameter < 7 cm, iliac artery angulation > 90° (< 90° without diffuse calcification) and external iliac artery diameter > 7 mm and < 14 mm [9]. To emphasize the importance of proximal neck evaluation, an “aortic neck scoring system” was introduced in order to stratify the risk of graft failure [10].
This score considers proximal neck length, diameter, angulation and the amount of calcification and thrombus, which must be, in an ideal situation, ≥ 15 mm of lenght, < 30 mm in diameter, > 120° of angulation, and with wall calcification extending to less than half of its circumference without significant thrombus apposition, respectively [9, 10].
EVAR contraindications include, in addition to the lack of the above-mentioned criteria, aneurysm involving both iliac arteries, or a hypogastric artery in the case of contralateral occlusion, Marfan syndrome or acute inflammatory AAA [9].
CT angiography technique
CTA is considered the reference standard for both preprocedural planning and postprocedural surveillance [2, 3]. Preprocedural CTA imaging allows to define aneurysm size and morphology, proximal and distal landing zones and access vessel assessment [7]. Postprocedural surveillance allows confident assessment of endograft device-related and systemic complications both early and late ones [7].
A triphasic CTA study is typically performed before and after the intravenous injection of a 90–130 ml bolus of iodinated high-concentration contrast medium through an automated injector (flow rate of 3–5 ml/s, and, sometimes, even higher) in an antecubital vein [11].
The CTA protocol includes a non-contrast acquisition to differentiate calcifications from contrast leakage, an early arterial phase (12 s after the bolus-tracking threshold) to detect most of endoleaks, and a delayed phase (120–300 s) to detect low-flow endoleaks (usually type II endoleaks) [3, 12, 13].
CTA allows postprocessing reconstructions such as maximum intensity projection (MIP), curvilinear reformation (CVR) and volume rendering (VR), that facilitate the detection of complications [11].
Considering the requirement of a lifelong surveillance, patients treated with EVAR may absorb a substantial cumulative radiation dose [14]. Current guidelines recommend as time interval of follow-up, CTA at 1 month, 6 months, and 12 months or whenever complications are suspected [3, 15, 16]. Therefore, for radioprotection purposes, the acquisition of non-enhanced CT scan (NECT) is generally avoided after the first CT follow-up. New generation dual-energy CT (DECT) scanners can obtain unenhanced images by subtracting iodine density from contrast-enhanced acquisitions without the need of a separate NECT scan [5, 17].
DECT angiography could be used as a single-phase examination with lower radiation exposure to the patient compared to the standard triple-phase CTA [17]. Although DECT has the advantage of a higher contrast-to-noise ratio of iodine in the blood which improves the detection of endoleaks, virtual non-contrast images may reduce the perceived visibility of calcifications [5, 17, 18].
Other diagnostic techniques include digital subtraction angiography (DSA), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) [19]. DSA is an invasive procedure currently reserved for preprocedural planning or intraprocedural guidance [3]. Contrast-enhanced-MRA with gadolinium may be useful in patients with contraindications to iodinated contrast administration (i.e., iodine allergy) [3]. MRA has the advantage of the possibility to avoid the use of contrast medium, with techniques such as time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF-MRA) [3, 19].
CEUS is a minimally invasive modality in detection of complications, cost-effective, with lack of ionizing radiation use, but difficult to reproduce [19].
Type of device
Figure 1 depicts the various types of metal ring and stent-grafts used for EVAR. In regard of the material, the device is formed by a metal-structure (i.e., stainless steel nitinol or cobalt-chromium alloys), while the graft is composed of polyester or polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) fabric [20, 21]. Based on the anatomical structure, stent-grafts can be divided in bifurcated (aorto-bi-iliac) or aorto-uni-iliac [20]. Stent-grafts usually adopt a modular design with at least two component grafts: in detail two (bimodular) or three (trimodular) separate components, including an aortic bifurcated main body and one or two iliac limbs [20, 22]. More rarely, some stent-graft can be unibody (e.g., Powerlink) [20]. Depending on the level of fixation relative to the renal arteries, they are also subdivided into suprarenal (proximal to renal arteries, e.g., Zenith low profile, Endurant II, Aorfix) or infrarenal (distal to renal arteries, e.g., Excluder) [20, 21].
The most common and old type is the AneuRx (Medtronic, Santa Rosa, Calif) formed by nitinol stent rings and woven polyester graft material; each stent ring is a series of diamond-shaped segments connected side to side [23]. The C3 Excluder (W. L. Gore & Associates, Flagstaff, Ariz) is a modular bifurcated system composed of PTFE approved for infrarenal necks measuring ≥ 15 mm in length and ≤ 60 degrees angulation [24]. The Endurant II (Medtronic, Santa Rosa, CA) is a modular bifurcated stent-graft composed of M-shaped nitinol stents and polyester graft. It is approved for infrarenal necks of ≥ 10 mm length with angulation ≤ 60 degrees or of 15 mm and ≤ 75 degrees [25]. The Zenith low profile (Cook Medical, Bloomington, USA) is a modular bifurcated system consisting of a nitinol Z-stents sutured to a woven polyester graft material. The proximal stent contains barbs for suprarenal fixation. It is approved for a minimum 15 mm infrarenal neck and an infrarenal angulation of ≤ 60 degrees [21].
The AFX stent-graft, as well as its predecessor Powerlink (Endologix, Inc. Irvine, Calif), is a unibody stent-graft consisting of an inner endoskeleton with multiple metallic struts of cobalt–chromium alloy covered by a thin-walled ePTFE-graft fabric outer cover; these two stent-graft layers are sutured only at the proximal and distal ends [26, 27]. The Aorfix stent-graft (Lombard Medical Technologies, Oxfordshire, UK) is composed of saddle or fish mouth-shaped nitinol rings on a polyester fabric. This shape allows the rings to be placed trans-renally with the fish mouth trough aligned with the renal arteries juxta-renally and the fish mouth peak extending suprarenally. It is approved for a neck length of ≥ 20 mm, and it is the only available endograft that can be used in infrarenal angulation up to 90° [25].
Although EVAR was initially limited to aneurysms with a neck long enough to accommodate the stent-graft, for AAAs with a short or absent neck involving visceral arteries (superior mesenteric artery, right renal artery or left renal artery), a fenestrated and branched stent-grafts (f/b EVAR) are proposed [28].
Evar complication classification
EVAR complications can be classified by time of onset, cause and severity.
Based on the time of appearance, they can be divided into immediate (days 0–1), early (days 2–30) and late complications (days 31 +) [29].
Regarding the cause, complications can be divided in endograft device-related and systemic complications [3], as summarized in Table 1.
Concerning the degree of severity, a non-standardized classification divides complications in “minor,” “moderate” and “severe” ones [5]. In 2017, CIRSE Standards of Practice committee introduced a standardized and reproducible system for the classification of complications consisting in a grading scale from one to six where grade “one” is assigned to a complication that may be solved within the procedure operative session without additional therapy, sequelae or deviation from the normal post-therapeutic course, and “six” is assigned in case of death [6].
Endograft device-related complications
Endograft device-related complications occur in 16–30% of patients after EVAR; the most common types include endoleak (occurring in 15–30%) followed by device migration (1–10%), graft limb thrombosis (0.5–11%), and structural endograft failure (5.5%) [3, 4, 30, 31].
Endoleak
Endoleak (EL) is considered the most frequent complication after EVAR, occurring in 15–30% of patients within the first 30 postoperative days [3]. EL is defined as the persistent perigraft blood flow within the aneurysm sac with contrast opacification changing in degree and shape between the arterial and delayed phases [32, 33]. ELs are classified in five types (Table 1) according to the origin of the blood flow [34].
Type I EL is considered a leakage from the attachment sites of the stent-graft and native artery [33]. Type I EL (Fig. 2) can be divided into type Ia (involving the proximal attachment site, Fig. 3), Ib (involving the distal attachment site) and Ic (involving the iliac occluder) [32]. Type Ic EL refers to the failure of occlusion of the contralateral common iliac artery in patients with aorto-uniliac endograft placed in conjunction with a femoral-femoral bypass. Type I EL is more frequent in patients with complex arterial anatomy: short, angulated, or tapered proximal necks leading to an imperfect seal between the stent-graft and the aortic walls, resulting in type Ia EL [32]. In the same way, dilated, irregular and tortuous iliac arteries increase the risk of type Ib EL [27, 35]. CT scan may show the presence of contrast agent extravasation more pronounced in the central part of the aneurysm sac, close to an attachment site of the endograft. Due to the direct communication with the aortic blood flow, Type I ELs tend to evolve and usually need to be treated [32]. Endovascular repair for Type I EL is successful in acute and asymptomatic presentation, but surgical conversion must always be considered if endovascular approach is unsuccessful [36].
Drawings illustrating the physiopathology of type I endoleak. a A typical EVAR device consisting of a main body for the aorta and one “limb” for each common iliac artery; b type Ia endoleak; c type Ib endoleak; d EVAR with an aorto-uniliac device, a femoral-femoral bypass and an iliac occluder; e type Ic endoleak with failure of the iliac occluder, resulting in retrograde blood flow through the common iliac artery and the aneurysm sac
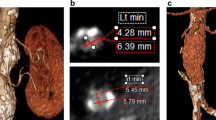
a Sagittal maximum intensity projection and (b, c) axial CT angiography images at different levels show type Ia endoleak in a 67-year-old man detected as contrast agent extravasation outside stent-graft within aneurysm sac (arrows), close to the proximal attachment site of the endograft; d intraoperative aortography performed by the pigtail catheter with tip positioned above the proximal endograft fixation shows a type Ia endoleak (arrowhead) in a 82-year-old man; e the same angiographic image shows a type Ia endoleak profile remarked with a black line
Type II EL is the most common type of endoleak with a reported prevalence between 8 and 44% [36]. In type II EL, the persistent perfusion of the aneurysm sac is caused by retrograde blood flow via collateral vessels (most commonly the inferior mesenteric artery and lumbar arteries) [38]. Based on the number of patent branches involved, type II EL (Fig. 4) can be classified into type IIa (only one collateral artery, Fig. 5) and type IIb (two or more arteries) [31]. Up to 40% of type II EL spontaneously resolve with collateral thrombosis [30]. Therefore, the “wait and see” approach is accepted for stable aneurysms at follow-up [32, 38]. Type II EL treatment is advisable for cases persistent over 6 months and with more than 5 mm of sac expansion compared to preprocedural CT measurements [39]. CT scan shows the presence of contrast agent in the peripheral part of the aneurysm sac, close to the origin of the involved vessels (anterior wall of the sac for inferior mesenteric artery, posterior wall of the sac for lumbar arteries). Minimally invasive treatment includes embolization through transarterial, transcaval, translumbar and transabdominal approaches. The translumbar embolization is a safe and effective treatment for type II EL, with low complication and reintervention rate [38].
Drawing illustrating the physiopathology of type II endoleak. a Schematic representation of an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) with a normal bowel circulation, supplied by superior mesenteric artery (SMA) and inferior mesenteric artery (IMA); b blood circulation after a typical EVAR: normal flow in the SMA, that provides blood to the major part of the bowel through collateral circles shared with the territories irrigated by the IMA; no flow in the IMA, that originates from the excluded aneurysm sac; c type II endoleak: collateral vessels provide retrograde blood flow to the IMA, bringing blood inside the aneurysm sac
Type III EL is a rare complication (incidence of 4% beyond 1 year) attributed to structural stent-graft failure or disconnection between modular components (Fig. 6) [32]. Type III EL can be divided into IIIa (junctional separation of modular components of the device) (Fig. 7) and IIIb (stent-graft fabric disruption, Fig. 8) [32, 40]. CT scan shows the presence of contrast extravasation at the central of the aneurysm sac, adjacent to the endograft but not immediately close to its attachment sites (may be close to the junction of modular components in case of type IIIa endoleak). As type I EL, type III ELs are considered high-pressure, high-risk leaks and always warrant urgent management [32]. Treatment of type III EL includes endovascular approach with placement of a covered stent across the gap between the original stent-graft components or across the fabric disruption [40].
67-year-old woman with type IIIb endoleak: Axial CT images on (a) pre-contrast, (b) arterial and (c) delayed phases and (d) coronal arterial phase show a type IIIb endoleak (arrows); intraoperative aortography in (e) anteroposterior and (f) caudo-cranial projections performed in the same patient confirmed endoleak (arrowheads) with profile remarked through a black line
Type IV EL is a complication caused by porosity of the endograft fabric, which can be angiographically seen during the placement of the device or immediately after (Fig. 9) [34]. Type IV EL is related to the anticoagulant treatment of the patient and it spontaneously resolves within 30 days [32]. It is uncommon with new generation devices. Angiographic study shows hazy opacification around the stent-graft, without detectable sources of EL.
Type V EL, also named “endotension,” is referred to the expansion of the aneurysm sac without signs of other types of EL (Fig. 10) [3]. Type V EL is a diagnosis of exclusion, thus an occult endoleak has to be investigated using other techniques (MRA, CEUS). Other causes of endotension include ultrafiltration of blood through the stent-graft fabric, transmission of the blood pressure to the aortic wall through the thrombus around the device, infection and seroma. No specific treatment is recommended for type IV and type V ELs [3].
The presence of EL (expecially type I) exposes to the risk of aneurysm sac rupture (Fig. 11) [41].
In clinical practice, differential diagnosis can be difficult to establish in case of Endologix AFX/Powerlink stent-graft placement, due to the presence of “billowing phenomenon,” which may mimic an EL [28]. On CT scan, the billowing phenomenon appears as a slightly hyperdense rim of density beyond the endoskeleton within the outer fabric material, with typical cauliflower-like shape [42]. On CT angiography, contrary to endoleak, in Endologix stent-graft, the intravenous contrast agent stays confined inside the curvilinear thin hyperdense line of the graft cover, without any connection to the excluded aneurysm sacs, and maintains the same curvilinear configuration as before the contrast [43]. Although billowing was firstly considered a benign condition, the progression of this phenomenon may cause a continued pressurization of the AAA sac with risk of rupture [42].
Suture breaks and metal-ring fractures
The structure of AneuRx stent-graft predisposes the device to two kinds of mechanical damage: metal-ring fracture and suture break [24]. At CT scan, metal-ring fracture appears as a discontinuity of a metallic frame [24]. Suture break is defined as breakage of the polyester sutures that connect adjacent rings leading to their separation and discontinuity of consecutive suture points [24]. Based on the proportion of the circumference of two adjacent metallic ring of stent involved, suture breaks can be classified as minor (< 180° of the circumference) or major (> 180° of the circumference) [24]. Particularly, major suture breaks and metallic stent-ring fractures demonstrated at CT scan are associated with delayed type I and III endoleaks and with stent-graft migration after EVAR [24].
Both suture breaks and metal-frame fractures can involve one of the seven segments of the endograft: (a) the main body, (b) the junction between the main body and the limbs of the bifurcated graft, (c) the long limb of the bifurcated graft, (d) the extender cuff attached to the long limb, (e) the short limb of the bifurcated graft, (f) secondary limb attached to the short limb in the aorta (excluding overlap with short limb), and (g) the extender cuff attached to the secondary limb [24].
In other stent-graft without any suture point, e.g., the Excluder type (W. L Gore and Associates, Flagstaff, Ariz), a rupture of PTFE graft material as a fabric disruption could be detected and be the underlying cause of IIIa endoleaks [44] (Fig. 12).
85-year-old man with a probable rupture of PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) graft material and type IIIa endoleak. a Coronal, (b) sagittal, and (c) axial maximum intensity projection CT angiography images show contrast agent outside stent-graft (arrows) consisting in type III endoleak caused by probable PTFE fabric erosion (arrowheads)
Device migration
Device migration is defined as device movement of more than 10 mm on the centerline or movement of more than 15 mm on either the anterior or posterior aortic margin [3, 24]. Some authors considered device migration as a change of > 10 mm in the distance between the reference vessel (celiac axis or superior mesenteric artery) and the first visible portion of the stent-graft on a sagittal multiplanar CT reconstruction [45].
Device migration can affect both the proximal and distal fixation of stent-graft [46]. Changes of width and length of the aneurysm sac, hemodynamic forces and inadequate overlap between the device and the aneurysm neck can lead to device migration [47]. Stent-graft migration can be the underlying cause of type I EL (since the attachment sites of the endograft can be moved to a section of the vessel that do not correspond to the size and the shape of the device), type III EL (because of rupture of the device or disjunction of modular components) and device kinking [46,47,48]. Migration of the iliac limb can lead to type Ib EL and type III EL [46]. The risk factors potentially influencing limb migration include a large aneurysm (> 6 cm), dilated or aneurysmal common iliac artery (> 18 mm), short length of fixation (< 70%), and lower degree of iliac limb oversizing (< 10–20%) [46].
In case of f/b EVAR with placement of visceral arteries stents (superior mesenteric artery, right renal artery or left renal artery), these latter could migrate (Fig. 13).
78-year-old man with stents migration. a Volume rendering reconstruction and b sagittal oblique CT images show a thoracoabdominal aneurysm treated with a f/b EVAR and three stent-grafts placement in aortic branches: celiac artery (CA), superior mesenteric artery (SMA) and right renal artery (RRA); the last one appears occluded. c Volume rendering and (d) sagittal oblique CT images after 3 years show distal migration of all three stent-grafts. In both examinations, there is contrast agent inside the aneurismal sac (*), likely a type IIIb endoleak due to imperfect junction of the branches with the main device body
Device kinking
Device kinking may occur in 2–4% of patients, due to size reduction in the residual aneurysm sac over time, severe proximal aortic neck angulation and a narrow diameter of the distal aortic neck [3, 49, 50]. Device kinking (Fig. 14) can be localized at stent-graft limb and is defined as a sharp localized angulation > 90° on radiological examination [50, 51]. Kinking can lead to device migration, type I and type III EL, endograft thrombosis and occlusion [49]. Limb kinking treatments include percutaneous angioplasty with or without placement of reinforcing stents or additional endograft limbs within the original graft [49].
Graft thrombosis and occlusion
Graft thrombosis is reported in 4% of patients and often related to device kinking, migration and dislocation [2, 7, 40]. Excessive oversizing can also result in folding of the graft material, with twisting of the limbs and subsequent endograft limb thrombosis [2, 40]. CT angiography scan shows a non-enhancing concentric or eccentric tissue along the internal wall of the endograft (Fig. 15). Treatment options include thrombectomy and stent placement of the thrombosed limb [2]. Sometimes, a surgical femoral-to-femoral artery bypass may be required [2].
Infection
Endograft infection is an uncommon complication (< 1%) with a high mortality rate [3, 7]. It is usually caused by procedural contamination or eventually by device colonization from remote sites of infection [52]. Patients with endograft infection typically show fever, leucocytosis, and back pain [3, 53]. CT scan can demonstrate periaortic fat stranding adjacent to the stent-graft, perigraft fluid collections, abnormal enhancement, air bubbles, and erosion into adjacent structures [52]. Cases of aorto-enteric fistulas (Fig. 16) have been described in the literature with significant poor prognosis [52, 54].
Endograft infections may be managed conservatively with antibiotics and possible percutaneous drainage; severe cases could require endograft removal [52, 53, 55, 56].
Access site complications
The EVAR percutaneous procedure begins with the puncture of the femoral artery as access site which can be associated with several local complications reported in 3–5% of patients [7]. These latter can be related to patients’ predisposition (i.e., obesity or severe femoral artery calcification) or access technique (i.e., lack of operator experience, repeated groin access, large sheath size) [57, 58]. Access site complications include arterial thrombosis, pseudoaneurysm, dissection and other local wound complications (i.e., groin hematoma, lymphocele and infection) [2, 58]. In order to avoid these complications, some authors suggest preprocedural CT scans for common femoral artery calcium arcs and meticulous ultrasound-guided arterial puncture [58, 59].
CT scan can show pseudoaneurysm, thrombosis, dissection and other local wound complications, i.e., hematoma, infection and lymphocele. On CT scan, pseudoaneurysm appears as a tear of the arterial wall with a hematic collection, contained by the adventitia or by the surrounding perivascular soft tissues (Fig. 17).
75-year-old man who underwent EVAR with right superficial femoral artery access. a Axial, (b) sagittal, and (c, d) volume rendering reconstruction CT angiography images show an access site complication: a pseudoaneurysm (*) of the right superficial femoral artery (arrows). It is also possible to see a contrast jet originating from the artery (arrowheads)
Systemic complication
Ischemia
Ischemic complications are reported in approximately 9% of patients causing by arterial thrombosis, embolism, dissection, or obstruction occurring as a result of endograft malposition [3]. It can involve the lower extremities and also the kidneys, bowel and pelvic organs.
Lower Limb ischemia is the most common type of ischemia after EVAR, and it may be the result of endograft limb occlusion [59]. Patients may complain with pain, paresthesia, intermittent claudication and decreased femoral pulse [59]. CT angiography scan is helpful to underlain the cause of the ischemia such as endograft thrombosis, occlusion (Fig. 18), and kinking.
Renal ischemia could be secondary to arterial thrombosis embolus, dissection, and inadvertent coverage of the origin of the renal arteries in patients with multiple accessory arteries by the endograft or endograft migration (Fig. 19) [3, 60]. The inadvertent coverage of the renal arteries by the endograft may be more frequent in case of a short aortic neck [3]. In addition to ischemia, kidney may be exposed to contrast nephropathy [61].
68-year-old man with segmental renal ischemia. a Sagittal CT angiography image shows left kidney normally perfused by the main left renal artery (not showed) and by an accessory renal artery (arrowheads); b sagittal CT image obtained from the same patient after EVAR shows occlusion of the accessory renal artery and lack of enhancement in the lower renal pole (*), which appears reduced in volume, due to chronic ischemia
Bowel ischemia after EVAR most commonly involves the left colon. It results from embolus or endograft coverage of the inferior mesenteric artery origin. Albeit this latter occurs in all cases of EVAR, it becomes clinically relevant in case of insufficient mesenteric collateral circulation [62]. Small bowel or right colonic ischemia is less common [3].
Pelvic ischemia after EVAR is more frequent in case of intentional embolization of the internal iliac arteries as in the case of internal iliac artery aneurysms exclusion. Clinical signs may include buttock claudication, rectal ischemia, erectile dysfunction and possible skin necrosis [3].
Spinal cord ischemia, although rare, is reported in the literature as EVAR-related complication [59, 63, 64]. It typically develops within 12 h following EVAR and may cause paraplegia [3, 64]. The underlying causes include intraoperative hypotension, embolism and interruption of the collateral circulation from the iliolumbar and internal iliac arteries [64].
Conclusion
EVAR complications are common and can be life-threatening if not early identified by the radiologist on CTA and promptly treated. They can usually be eligible for an endovascular treatment. EVAR complications can be classified by time of onset, cause and severity. Careful detection and precise description of image findings are essential prerequisites for treatment success. CTA is currently the gold standard diagnostic technique used for the assessment of EVAR. In future perspectives, further possible new technologies (post-elaboration techniques with DECT acquisition, DSA, MRI and CEUS) can help where critical issues still arise.
Availability of data and materials
All data are included in this manuscript.
Abbreviations
- AAAs:
-
Abdominal aortic aneurysms
- CA:
-
Celiac artery
- CEUS:
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound
- CT:
-
Computer tomography
- CTA:
-
Computer tomography angiography
- CVR:
-
Curvilinear reformation
- DECT:
-
Dual-energy computer tomography
- DSA:
-
Digital subtraction angiography
- EL:
-
Endoleak
- ePTFE:
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene
- EVAR:
-
Endovascular aneurysm repair
- f/b EVAR:
-
Fenestrated and branched endovascular aneurysm repair
- MIP:
-
Maximum intensity projection
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- NECT:
-
Non-enhanced computer tomography
- OR:
-
Open repair
- RRA:
-
Right renal artery
- SMA:
-
Superior mesenteric artery
- TOF-MRA:
-
Time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography
- VR:
-
Volume rendering
References
Patel R, Powell JT, Sweeting MJ et al (2018) The UK EndoVascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) randomised controlled trials: long-term follow-up and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess 22(5):1–132. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta22050
Picel CA, Kansal N (2014) Essentials of endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair imaging: postprocedure surveillance and complications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 203(4):W358–W372. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.13.11736
Daye D, Walker TG (2018) Complications of endovascular aneurysm repair of the thoracic and abdominal aorta: evaluation and management. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther 8(Suppl 1):S138–S156. https://doi.org/10.21037/cdt.2017.09.17
d’Audiffret A, Desgranges P, Kobeiter DH, Becquemin JP (2001) Follow-up evaluation of endoluminally treated abdominal aortic aneurysms with duplex ultrasonography: validation with computed tomography. J Vasc Surg 33:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1067/mva.2001.112215
Clavien PA, Barkun J, de Oliveira ML et al (2009) The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: five-year experience. Ann Surg 250(2):187–196. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b13ca2
Castiglione D, Easwaran A, Prashar A et al (2021) Assessment of EVAR complications using CIRSE complication classification system in the UK tertiary referral centre: a ∼6-year retrospective analysis (2014–2019). Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 44(8):1174–1183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-021-02847-9
Hallett RL, Ullery BW, Fleischmann D (2018) Abdominal aortic aneurysms: pre- and post-procedural imaging. Abdom Radiol (NY) 43(5):1044–1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-018-1520-5
Walker TG, Kalva SP, Yeddula K et al (2010) Society of Interventional Radiology Standards of Practice Committee; Interventional Radiological Society of Europe; Canadian Interventional Radiology Association. Clinical practice guidelines for endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: written by the Standards of Practice Committee for the Society of Interventional Radiology and endorsed by the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe and the Canadian Interventional Radiology Association. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21(11):1632–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2010.07.008.
Cotroneo AR, Iezzi R, Giancristofaro D et al (2006) Endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: how many patients are eligible for endovascular repair? Radiol Med 111(4):597–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-006-0054-z
Chaikof EL, Fillinger MF, Matsumura JS et al (2002) Identifying and grading factors that modify the outcome of endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 35(5):1061–1066. https://doi.org/10.1067/mva.2002.123991
Iezzi R, Santoro M, Dattesi R et al (2012) Multi-detector CT angiographic imaging in the follow-up of patients after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR). Insights Imaging 3(4):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-012-0173-0
Caruana G, Vernuccio F, Giambelluca D et al (2017) Evaluation of EVAR complications: a practical radiological approach. ECR. https://doi.org/10.1594/ecr2017/C-2227
Lehmkuhl L, Andres C, Lücke C et al (2013) Dynamic CT angiography after abdominal aortic endovascular aneurysm repair: influence of enhancement patterns and optimal bolus timing on endoleak detection. Radiology 268(3):890–899. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13120197
Di Leo G, Spadavecchia C, Zanardo M et al (2017) Should the automatic exposure control system of CT be disabled when scanning patients with endoaortic stents or mechanical heart valves? A phantom study. Eur Radiol 27(7):2989–2994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4676-9
Tillich M, Hausegger KA, Tiesenhausen K et al (1999) Helical CT angiography of stent-grafts in abdominal aortic aneurysms: morphologic changes and complications. Radiographics 19(6):1573–1583. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiographics.19.6.g99no091573
Hiratzka LF, Bakris GL, Beckman JA et al (2010) American College of Cardiology Foundation; American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines; American Association for Thoracic Surgery; American College of Radiology; American Stroke Association; Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions; Society of Interventional Radiology; Society of Thoracic Surgeons; Society for Vascular Medicine. 2010 ACCF/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with thoracic aortic disease: executive summary. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American College of Radiology, American Stroke Association, Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and Society for Vascular Medicine. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 76(2):E43–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccd.22537
Ascenti G, Mazziotti S, Lamberto S et al (2011) Dual-energy CT for detection of endoleaks after endovascular abdominal aneurysm repair: usefulness of colored iodine overlay. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196(6):1408–1414. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.10.4505
Meyer M, Nelson RC, Vernuccio F et al (2019) Virtual unenhanced images at dual-energy CT: influence on renal lesion characterization. Radiology 291(2):381–390. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2019181100
Salehi Ravesh M, Langguth P, Pfarr JA et al (2019) Non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for visualization and quantification of endovascular aortic prosthesis, their endoleaks and aneurysm sacs at 15 T. Magn Reson Imaging 60:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2019.05.012
Droc I, Raithel D, Calinescu B (2012) Abdominal aortic aneurysms - actual therapeutic strategies. Aneurysm. https://doi.org/10.5772/48596
Eckroth-Bernard K, Garvin R, Ryer E (2013) Current status of endovascular devices to treat abdominal aortic aneurysms. Biomed Eng Comput Biol 5:25–32. https://doi.org/10.4137/BECB.S10970
Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I et al (2019) Editor’s Choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Abdominal Aorto-iliac Artery Aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 57(1):8–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.09.020(Erratum.In:EurJVascEndovascSurg.2020;59(3):494)
Ueda T, Takaoka H, Petrovitch I, Rubin GD (2014) Detection of broken sutures and metal-ring fractures in AneuRx stent-grafts by using three-dimensional CT angiography after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: association with late endoleak development and device migration. Radiology 272(1):275–283. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14130920
Verhoeven EL, Katsargyris A, Bachoo P et al (2014) Real-world performance of the new C3 Gore excluder stent-graft: 1-year results from the European C3 module of the Global Registry for Endovascular Aortic Treatment (GREAT). Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 48(2):131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2014.04.009
Georgakarakos E, Schoretsanitis N (2018) The various types of endovascular stent grafts for EVAR. In: New approaches to aortic diseases from valve to abdominal bifurcation, pp 415–421
Wang GJ, Carpenter JP (2008) The powerlink system for endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: six-year results. J Vasc Surg 48(3):535-545.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2008.04.031
Wu A, Karuppasamy K, Wang W (2016) Billowing of endologix powerlink stent mimicking endoleaks. Res Cardiovasc Med 5(2):e32448. https://doi.org/10.5812/cardiovascmed.32448
Michel M, Becquemin JP, Marzelle J, Quelen C, Durand-Zaleski I (2018) WINDOW trial participants. Editor’s Choice—a study of the cost-effectiveness of fenestrated/branched EVAR compared with open surgery for patients with complex aortic aneurysms at 2 years. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 56(1):15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2017.12.008
Kieffer WK, Sonnenberg S, Windhaber RA, Pal N, Pemberton RM (2012) Complications and reintervention following elective open abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a 10-year retrospective analysis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 94(3):177–180. https://doi.org/10.1308/003588412X13171221501465
Liaw JVP, Clark M, Gibbs R, Jenkins M, Cheshire N, Hamady M (2009) Update: complications and management of infrarenal EVAR. Eur J Radiol 71(3):541–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.05.015
Walker TG, Kalva SP, Yeddula K et al (2010) Clinical practice guidelines for endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: written by the Standards of Practice Committee for the Society of Interventional Radiology and endorsed by the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe and the Canadian Interventional Radiology Association. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:1632–1655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2010.07.008
Rand T, Uberoi R, Cil B, Munneke G, Tsetis D (2013) Quality improvement guidelines for imaging detection and treatment of endoleaks following endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR). Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 36:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-012-0439-4
Helo N, Chang AC, Hyun C et al (2017) Retrospective review of billowing phenomenon–a mimic of endoleak following placement of endologix covered stent for the treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Ann Vasc Surg 45:239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2017.06.127
Bryce Y, Rogoff P, Romanelli D, Reichle R (2015) Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms: vascular anatomy, device selection, procedure, and procedure-specific complications. Radiographics 35(2):593–615. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.352140045
Gray D, Shahverdyan R, Reifferscheid V, Gawenda M, Brunkwall JS (2017) EVAR with flared iliac limbs has a high risk of late type 1b Endoleak. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 54(2):170–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2017.05.008
Naughton PA, Garcia-Toca M, Rodriguez HE et al (2011) Endovascular treatment of delayed type 1 and 3 endoleaks. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34(2):440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-010-0020-y
Loy LM, Chua JME, Chong TT et al (2020) Type 2 Endoleaks: common and hard to eradicate yet benign? Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-020-02497-3
Thomas WR, Karkhanis S, Hopkins J, Duddy M (2020) Translumbar embolization of type II endoleaks: 12 years of experience at a regional vascular centre. Vasc Endovascular Surg 54(5):389–394. https://doi.org/10.1177/1538574420918972
Patatas K, Ling L, Dunning J, Shrivastava V (2012) Static sac size with a type II endoleak post-endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: surveillance or embolization? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 15(3):462–466. https://doi.org/10.1093/icvts/ivs201
Maleux G, Koolen M, Heye S (2009) Complications after endovascular aneurysm repair. In: Seminars in interventional radiology. © Thieme Medical Publishers, pp 003–009. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1208377.
Karkos CD, Mitka M, Pliatsios I et al (2018) Rupture after previous endovascular aneurysm repair due to type IA endoleak: complete endograft preservation is feasible with proximal suturing, aortic neck banding, and sac plication. Ann Vasc Surg 49:317.e5-317.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2018.01.078
Armerding MD, Rubin GD, Beaulieu CF et al (2000) Aortic aneurysmal disease: assessment of stentgraft treatment-CT versus conventional angiography. Radiology 215(1):138–146. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.215.1.r00ap28138
Chang H, Hadro NC, Norris MA, Rhee SW, Morris ME (2019) The progression of billowing of endologix AFX2® abdominal aortic aneurysm device as a precursor for the rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Ann Vasc Surg 54:335.e11-335.e14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2018.06.019
Dayama A, Tsilimparis N, Kasirajan K, Reeves JG (2013) Late Gore Excluder endoprosthesis fabric tear leading to abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture 5 years after initial implant. J Vasc Surg 57(1):221–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2012.06.102
England A, Butterfield JS, Jones N et al (2004) Device migration after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: experience with a talent stent-graft. J Vasc Interv Radiol 15(12):1399–1405. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.rvi.0000142601.10673.00
Wang Y, Li C, Xin H, Li J, Wang H (2019) Predisposing factors for migration of the iliac limb and reintervention after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Ann Vasc Surg 59:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2019.01.007
Stavropoulos SW, Charagundla SR (2007) Imaging techniques for detection and management of endoleaks after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair 1. Radiology 243(3):641–655. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2433051649
Sampaio SM, Panneton JM, Mozes G et al (2005) AneuRx device migration: incidence, risk factors, and consequences. Ann Vasc Surg 19(2):178–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10016-004-0166-7
Fransen GA, Desgranges P, Laheij RJ, Harris PL, Becquemin JP (2003) EUROSTAR Collaborators. Frequency, predictive factors, and consequences of stent-graft kink following endovascular AAA repair. J Endovasc Ther 10(5):913–918. https://doi.org/10.1177/152660280301000511
Oh PC, Kim M, Shin EK, Kang WC (2018) Prevention of kinked stent graft limb due to severe angulated proximal neck during endovascular repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 24(2):106–109. https://doi.org/10.5761/atcs.cr.17-00072
Cochennec F, Becquemin JP, Desgranges P, Allaire E, Kobeiter H, Roudot-Thoraval F (2007) Limb graft occlusion following EVAR: clinical pattern, outcomes and predictive factors of occurrence. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 34(1):59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2007.01.009
Murphy EH, Szeto WY, Herdrich BJ et al (2013) The management of endograft infections following endovascular thoracic and abdominal aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 58(5):1179–1185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2013.04.040
Smeds MR, Duncan AA, Harlander-Locke MP et al (2016) Treatment and outcomes of aortic endograft infection. J Vasc Surg 63(2):332–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2015.08.113
Arima D, Suematsu Y, Kurahashi K, Shimizu T, Nishi S, Yoshimoto A (2020) Recurrence of aortoenteric fistula after endovascular aortic repair. Ann Vasc Dis 13(1):90–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvssr.2018.05.004
Zhu F, Ge X, Ci H, Guan S (2020) Antibiotics and percutaneous drainage for treating stent-graft infection after EVAR. Ann Vasc Surg 65:289.e1-289.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2019.12.009
Fernandez Prendes C, Riedemann Wistuba M, Zanabili Al-Sibbai AA, Del Castro Madrazo JA, Santervas LAC, Perez MA (2019) Infrarenal aortic endograft infection: a single-center experience. Vasc Endovascular Surg 53(2):132–138. https://doi.org/10.1177/1538574418813606
Bensley RP, Hurks R, Huang Z et al (2012) Ultrasound- guided percutaneous endovascular aneurysm repair success is predicted by access vessel diameter. J Vasc Surg 55:1554–1561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2011.12.042
Mousa AY, Campbell JE, Broce M et al (2013) Predictors of percutaneous access failure requiring open femoral surgical conversion during endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 58:1213–1219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2013.04.065
Maldonado TS, Rockman CB, Riles E et al (2004) Ischemic complications after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 40(4):703–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2004.07.032
Brown LC, Brown EA, Greenhalgh RM, Powell JT, Thompson SG (2010) UK EVAR Trial Participants. Renal function and abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA): the impact of different management strategies on long-term renal function in the UK EndoVascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) Trials. Ann Surg 251(5):966–975. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181d9767c
Walsh SR, Tang TY, Boyle JR (2008) Renal consequences of endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther 15(1):73–82. https://doi.org/10.1583/07-2299.1
Becquemin JP, Majewski M, Fermani N et al (2008) Colon ischemia following abdominal aortic aneurysm repair in the era of endovascular abdominal aortic repair. J Vasc Surg 47(2):258–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2007.10.001
Freyrie A, Testi G, Gargiulo M, Faggioli G, Mauro R, Stella A (2011) Spinal cord ischemia after endovascular treatment of infrarenal aortic aneurysm. Case report and literature review. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 52(5):731–734
Morisaki K, Matsumoto T, Matsubara Y et al (2016) A rare complication of spinal cord ischemia following endovascular aneurysm repair of an infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm with arteriosclerosis obliterans: report of a case. Ann Vasc Dis 9(3):255–257. https://doi.org/10.3400/avd.cr.16-00063
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CG and GC contributed to collecting data, manuscript preparation/editing, literature research; CG, GC, RC, AF, DG and ED contributed to study concept and design; RC and FV contributed to data analysis and interpretation, and for manuscript editing; AB and MM contributed to study design/planning and final approval. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All the authors have nothing to disclose for this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Gozzo, C., Caruana, G., Cannella, R. et al. CT angiography for the assessment of EVAR complications: a pictorial review. Insights Imaging 13, 5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13244-021-01112-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13244-021-01112-4