Abstract
Background
Investigating the association between caesarean section (SC) and childhood asthma has shown contradictory results in different studies. The present study was conducted to determine the association between SC and childhood asthma.
Material and method
The present study was conducted based on the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. All the steps of the study were conducted independently by two reviewers from the inception until February 1, 2019. In case of disagreement, the third reviewer resolved it. We searched international online databases, including Scopus, Cochrane Library, PubMed/Medline, Embase, Web of Science (ISI), Science Direct, and Google scholar. The results of studies were combined using random effects model, and heterogeneity was measured through I2 index and Cochran’s Q test. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Software was used for meta-analysis. The significance level of all tests was considered to be P < 0.05.
Results
The heterogeneity rate was high (I2 = 67.31%, P < 0.001) in 37 studies. The results showed that SC increased the risk of childhood asthma (RR (relative risk) = 1.20 [95% CI 1.15–1.25, P < 0.001]). The association between emergency and elective SC and childhood asthma was significant with RR of 1.18 (95% CI 1.07–1.29, P < 0.001) in 13 studies and 1.23 (95% CI 1.20–1.26, P < 0.001) in 13 studies, respectively. The subgroup analysis for RR of childhood asthma in SC indicated that study design (P = 0.306), prospective/retrospective studies (P = 0.470), quality of studies (P = 0.514), continent (P = 0.757), age of diagnosis (P = 0.283) and year of publication (P = 0.185) were not effective in the heterogeneity of studies. Sensitivity analysis by removing one study at a time indicated that the overall estimate is robust.
Conclusion
According to the meta-analysis, SC (overall, elective, and emergency) increased the risk of childhood asthma. Therefore, it is hoped that developing clinical guidelines and implementing appropriate management plans would diminish the risk of asthma.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Asthma is one of the most common airway diseases, which involves increased response of tracheobronchial tree to various stimuli. Asthma attacks may last from a couple of minutes to a couple of hours. Continuous asthma includes successive obstructed airways, which lasts for several days or weeks [1]. The incidence of asthma is higher among people under 18 years of age and the hospitalization of children suffering from asthma is continuously rising [2]. The prevalence, incidence, mortality, and economic burden of asthma have increased since 1960, especially among children [3]. The incidence of asthma has increased in developed countries, South Africa, Eastern Europe, and Baltic countries, though this increase mainly occured in two populations (children and the elderly) [3,4,5]. The highest prevalence of asthma is in UK, New Zealand, Australia, Ireland, Canada (all above 14%), and the United States (11%); the prevalence of asthma has doubled in Western Europe over the last two decades. Asthma is the most common cause of children’s hospitalization in Europe [3]. Asthma is multifactorial, and this implies that asthma is the result of poverty and other environmental factors, smoking, air pollution, congestion, dust, house pets, psychological factors, lack of access to hygiene, genetics, history of viral infection, and low birth weight [6, 7]. Type of delivery is another contributing factor that causes allergic diseases, such as asthma. Therefore, the present study investigates the association between caesarean section (CS) and childhood asthma [7,8,9,10,11,12]. Various mechanisms have been proposed regarding the impact of delivery mode on asthma; mechanisms such as mechanical effects on lung growth, immunological mechanisms, and their impact on intestinal flora [12]. During vaginal delivery, the infant gets in touch with probiotics and the microbiome that may affect the development of atopic diseases [13]. There have been many studies all around the world on the association between CS and childhood asthma, and a meta-analysis was conducted in 2006 that reported significant association between CS and childhood asthma by analyzing 23 studies [14]. Through reviewing and synthesizing all related documents, systematic review and meta-analysis can present a more comprehensive picture of a problem in the community [15, 16]. Therefore, another study is required to represent a more panoramic image of this issue all over the world; thus, the present systematic study was conducted to investigate the association between CS and children asthma.
Methods
Study protocol
The present study was conducted based on the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) [17]. All steps of the study were conducted independently by two researchers (M.A and Sh.R). In case of disagreement, the third researcher resolved it.
Search strategy
We searched international online databases, including Scopus, Cochrane Library, PubMed/Medline, Embase, Web of Science (ISI), Science Direct, and Google scholar from the inception until February 1, 2019. Search was preformed based on the following keywords: “Cesarean Section”[MeSH], “Asthma”[MeSH], “Child”[MeSH], and “Mode of Delivery” [Text word]. References of the searched articles were reviewed to ensure literature saturation on the topic.
Definitions
The definition of asthma was based on physician’s diagnosis, hospitalization for asthma, medication use for asthma, asthma reported by the child/patient, his or her parents, or both, and the history of asthma. Elective CS is a planned CS designed for pregnant women for any maternal or embryonic indications before the onset of labor. The emergency CS in the women’s emergency care department is generally defined after the onset of labor.
Qualitative assessment
The modified Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for non-randomized studies was used to conduct qualitative assessment [18]. This checklist covered 4 criteria, which includes 8 sections. Finally, the two researchers compared the points given to each article. The minimum acceptable score was considered 5. The total score of NOS was 10 and the qualified articles were divided into three groups of low quality (0 to 4), medium quality (5 to 7), and high quality (8 to 10).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria [19] were determined with respect to prospective and retrospective studies that assessed SC and childhood asthma.
Exclusion criteria of the present meta-analysis were: (1) studies that did not focus on the SC as the exposure and childhood asthma as outcome; (2) duplicated studies; (3) non-English full text; (4) non-accessible full text [i.e. articles that were not available through my Institution]; (5) review articles, case reports, letters to the editor, comments, or conference papers; and (6) low quality studies according to NOS checklist.
Selection of studies
At the end of the search, the articles were entered into the EndNote software, and after the “Find References Updates”, duplicate studies were omitted. After blinding the studies (hiding the name of the authors, the name of the journal and the year of publication), each study was evaluated independently by two authors at the screening stage (by reading titles and abstracts), through scanning the titles of studies and evaluating the inclusion and exclusion criteria (the eligibility stage). In case of disagreement between the two researchers, the expert researcher made the final decision.
Data extraction
First, a checklist was designed according to the objectives of the study. The designed checklist included the following: the name of the author(s), the year of publication, the location of the study, the sample size, the duration of the follow-up, relative risk (RR), odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI), age category, and the number of events in both groups (case and control), which was extracted by two independent researchers, while the name of the author, the institute and the journal was blinded. If necessary, further details and the raw data were requested by contacting the author (the first author, the corresponding author or the group of authors).
Statistical analysis
Cochran’s Q test and I2 index were used to evaluate the heterogeneity of the studies. There are four categories for I2 index: I2 index below 25% is low heterogeneity, 25–50% is moderate heterogeneity, 51–75% is substantial heterogeneity and above 75% is considerable heterogeneity. The random effects model was used to generate the pooled RR or OR and 95% CI in case of significant heterogeneity, otherwise, a fixed-effects model was used [20]. Subgroup analysis was used to find the cause of heterogeneity between the studies. Sensitivity analysis was used to measure the predictive power by excluding one study. Finally, the publication bias was investigated using funnel plot and Egger and Begg’s tests. Statistical analysis was performed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Software version 2. The significance level of the tests was considered to be P < 0.05.
Results
Search results
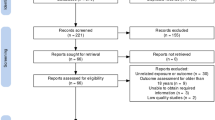
A total of 1909 studies were identified by two researchers by searching the databases and manual search identified eleven more studies, and 960 studies were excluded due to duplication. After screening the titles and abstracts, 886 studies were excluded due to irrelevancy and after assessing the full text, 35 studies were excluded due to lack of focus on the association between SC and childhood asthma (n = 19), non-English or non-accessible full text (n = 6), letters to the editor without original data, review article and case report (n = 10), and low quality (n = 0). Finally, 39 studies (37, 13, and 13 studies for overall SC, emergency and elective SC) with appropriate quality entered the meta-analysis (Fig. 1 and Table 1).
Association between caesarean section and childhood asthma
Heterogeneity rate was high (I2 = 67.31%, P < 0.001) in 37 studies. The association between SC and childhood asthma was significant (RR = 1.20 [95% CI 1.15–1.25, P < 0.001]) (Fig. 2). Sensitivity analysis by removing one study at a time indicated that the overall estimate is robust (Fig. 3).
The subgroup analysis for caesarean section and childhood asthma
The subgroup analysis for RR of childhood asthma in SC indicated that study design (P = 0.306), prospective/retrospective studies (P = 0.470), quality of studies (P = 0.514), continent (P = 0.757), age of diagnosis (P = 0.283) and year of publication (P = 0.185) were not effective in the heterogeneity of studies (Table 2).
Relative risks of childhood asthma in emergency and elective cesarean section
The association between emergency and elective SC and childhood asthma was significant with RR of 1.18 (95% CI 1.07–1.29, P < 0.001) in 13 studies and 1.23 (95% CI 1.20–1.26, P < 0.001) in 13 studies, respectively (Fig. 4a, b). Sensitivity analysis by removing one study at a time indicated that the overall estimate is robust (Fig. 5a, b).
Publication bias
The statistical tests of publication bias were not significant for the RR of childhood asthma in the overall SC (Begg’s = 0.187, Egger = 0.569), emergency CS (Begg’s = 0.999, Egger = 0.291) and elective CS (Begg’s = 0.474, Egger = 0.607) (Fig. 6).
Discussion
The present study is a systematic review and meta-analysis regarding CS and childhood asthma. In the final analysis of 37 studies, the relationship between CS and childhood asthma was statistically significant compared to vaginal delivery with a RR of 1.20 (95% CI 1.15–1.25). The results of different studies are reported to be contradictory; this relationship was significant in some studies [8,9,10,11, 21, 23, 24, 27, 28, 30, 32, 33, 35, 38, 40, 42,43,44,45,46] and it was not significant in others [12, 22, 25, 26, 29, 31, 34, 36, 37, 39, 41]. In a meta-analysis carried out in 2008, combination of 13 studies showed that cesarean delivery increases the risk of asthma [48]. According to the hygiene hypothesis, there are two possible causes: 1. Lack of contact of infants with mother’s bacteria during labor in CS, while these bacteria are necessary for the growth and development of the immune system. 2. Since infants are less in contact with stress hormone and chest pressure in CS, they suffer from more respiratory problems after birth. That’s because these mechanisms are associated with the emptying of the lungs from the amniotic fluid. This may have a negative effect on lung function in the long run [12, 13].
According to a study by Ghaffari et al. children with asthma have experienced shorter breastfeeding period, especially in the first 6 months of their lives, and this may be a potential mechanism to justify the role of delivery mode and breastfeeding duration on asthma incidence [49].
The present study also showed that there is a significant relationship between emergency and elective CS and childhood asthma, which is consistent with the studies of Tollånes et al. and Metsälä et al. [32, 33]. Some evidence suggest that perinatal metabolic changes may affect children’s immune system and increase the sensitivity of allergic diseases [50].
According to the findings of the present study, the association between CS and childhood asthma in developed countries is significant, which is consistent with the results of Thavagnanam’s meta-analysis [14].
Publication bias for studies on the relationship between CS and childhood asthma was evaluated according to Begg and Egger’s tests. The results showed that publication bias in the present study was not significant. It is assumed that the observed differences are due to different sampling and differences in the measured parameters in different societies.
Weaknesses of the present study
(1) The omission of some studies, such as medical thesis and low-sample-size studies, due to their low quality; (2) the omission of several studies due to inharmonious reports and biased publications; (3) Europe was the context of most of the studies; (4) individual patients might have been included multiple times.
Conclusion
This meta-analysis showed that CS (overall, elective, and emergency) increased the risk of childhood asthma.
This may reflect the hygiene hypothesis, according to which these children are likely to be less exposed to environmental microbes in early life. Future studies are needed to identify the effective factors in reducing this risk (especially in cases where elective or elective CS is not available) that can have important clinical and public health implications.
Availability of data and materials
Because the present article is a meta-analysis, the data extracted from the relevant articles from all over the world is available.
Abbreviations
- CS:
-
caesarean section
- UK:
-
United Kingdom
- SE:
-
standard error
- RR:
-
relative risk
- CI:
-
confidence interval
References
Longo DL. Harrisons principles of internal medicine. 18th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2012.
Moussa MA, Skaik MB, Yaghy OY, Salwanes SB, Bin Othman SA. Factors associated with asthma in school children. Eur J Epidemiol. 1996;12(6):583–8.
Masoli M, Fabiann D, Holt S, Beasley R. The global burden of asthma: executive summery of the gina dissemination committee report. Allergy. 2004;59(5):469–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2004.00526.x.
Brama SS. Asthma in the elderly. Exp lung res. 2005;31(suppl 1):6–7.
Braman SS. Asthma in the elderly. Clingerriatr Med. 2003;19(1):57–75.
Subbarao P, Mandhane PJ, Sears MR. Asthma: epidemiology, etiology and risk factors. CMAJ. 2009;181(9):E181–90. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.080612 (Epub 2009 Sep 14).
Barnes KC. Genetic studies of the etiology of asthma. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2011;8(2):143–8. https://doi.org/10.1513/pats.201103-030ms.
Kero J, Gissler M, Grnlund MM, Kero P, Koskinen P, Hemminki E, et al. Mode of delivery and asthma is there a connection? Pediatr Res. 2002;52(1):6–11. https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200207000-00004.
Bager P, Melbye M, Rostgaard K, Benn CS, Westergaard T. Mode of delivery and risk of allergic rhinitis and asthma. J Allergy ClinImmunol. 2003;111(1):51–6. https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2003.34.
Hakansson S, Kallen K. Caesarean section increases the risk of hospital care in childhood for asthma and gastroenteritis. ClinExp Allergy. 2003;33(6):757–64. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2222.2003.01667.x.
McKeever TM, Lewis SA, Smith C, Hubbard R. Mode of delivery and risk of developing allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109(5):800–2. https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2002.124046.
Maitra A, Sherriff A, Strachan D, Henderson J. Mode of delivery is not associated with asthma or atopy in childhood. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004;34(9):1349–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.02048.x.
Vejdani R, Zali MR. Probiotics and their mechanism of action in the prevention and treatment of human disease. J Shaheed Beheshti Univ Med Sci. 2003;27(4):319–30.
Thavagnanam S, Fleming J, Bromley A, et al. A meta-analysis of the association between caesarean section and childhood asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008;38:629–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.2007.02780.x.
Mansouri A, Norouzi S, Sharifi A, Yektakooshali MH, Azami M. The relationship of maternal subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy and preterm birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. IJOGI. 2017;19(40):69–78.
Sayehmiri K, Azami M, Nikpey S, Borji M, Sayehmiri F. Hepatitis B vaccination coverage in health personnel of Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis study. irje. 2015;11(3):1–10.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336–41.
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle–Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603–5.
Santos CMC, Pimenta CAM, Nobre MRC. The PICO strategy for the research question construction and evidence search. Revista latino-americana de enfermagem. 2007;15(3):508–11.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2.
Xu B, Pekkanen J, Jarvelin MR. Obstetric complications and asthma in childhood. J Asthma. 2000;37:589–94.
Nafstad P, Magnus P, Jaakkola JK. Risk of childhood asthma and allergic rhinitis in relation to pregnancy complications. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;106:867–73. https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2000.110558.
Smith G, Wood A, White I, Pell J, Cameron A, Dobbie R. Neonatal respiratory morbidity at term and the risk of childhood asthma. Arch Dis Child. 2004;89(10):956–60.
Renz-Polster H, David MR, Buist AS, et al. Caesarean sectiondelivery and the risk of allergic disorders in childhood. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005;35:1466–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.02356.x.
Bernsen RM, Jongste JC, Koes BW, Aardoom HA, Van deWouden JC. Perinatal characteristic and obstetric complications as risk factors for asthma, allergy & eczema at the age of 6 years. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005;35:1135–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.2155.x.
Juhn YJ, Weaver A, Katusic S, Yunginger J. Mode of delivery at birth and development of asthma: a population-based cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;116(3):510–6.
Debley JS, Smith JM, Redding GJ, Critchlow CW. Childhood asthma hospitalization risk after cesarean delivery in former term and premature infants. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005;94(2):228–33.
Salam MT, Margolis HG, McConnell R, McGregor JA, Avol EL, Gilliland FD. Mode of delivery is associated with asthma and allergy occurrences in children. Ann Epidemiol. 2006;16(5):341–6.
Werner A, Ramlau-Hansen CH, Jeppesen SK, Thulstrup AM. Caesarean delivery and risk of developing asthma in the offspring. Acta Paediatric. 2007;96(4):595. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2006.00150.x.
Roduit C, Scholtens S, Jongste JC, Wijga AH, Gerritsen J, Postma DS, et al. Asthma at 8 years of age in children born by caesarean section. Thorax. 2009;64:107–13.
Pistiner M, Gold DR, Abdulkerim H, Hoffman E, Celedón JC. Birth by cesarean section, allergic rhinitis, and allergic sensitization among children with a parental history of atopy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122(2):274–9.
Tollånes MC, Moster D, Daltveit AK, Irgens LM. Cesarean section and risk of severe childhood asthma: a population-based cohort study. J Pediatrics. 2008;153(1):112–6.
Metsälä J, Kilkkinen A, Kaila M, Tapanainen H, Klaukka T, Gissler M, et al. Perinatal factors and the risk of asthma in childhood—a population-based register study in Finland. Am J Epidemiol. 2008;168(2):170–8.
Mohammadzadeh F, Babazadeh E, AlizadehNavaei R. Association between Asthma in Children and Mode of Delivery. Babol University of Medical Sciences J. 2009;11(2):38–41.
Davidson R, Roberts SE, Wotton CJ, Goldacre MJ. Influence of maternal and perinatal factors on subsequent hospitalisation for asthma in children: evidence from the Oxford record linkage study. BMC Pulmonary Med. 2010;10(1):14.
Park YH, Kim KW, Choi BS, Jee HM, Sohn MH, Kim K-E. Relationship between mode of delivery in childbirth and prevalence of allergic diseases in Korean children. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010;2(1):28–33.
van Nimwegen FA, Penders J, Stobberingh EE, Postma DS, Koppelman GH, Kerkhof M, et al. Mode and place of delivery, gastrointestinal microbiota, and their influence on asthma and atopy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128(5):948–55.
Magnus MC, Håberg SE, Stigum H, Nafstad P, London SJ, Vangen S, et al. Delivery by Cesarean section and early childhood respiratory symptoms and disorders: the Norwegian mother and child cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 2011;174(11):1275–85.
Nathan AM, de Bruyne J, Khalid F, Arumugam K. Caesarean section and asthma in Malaysian children: a case–control study. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2012;30(3):204–8.
Almqvist C, Cnattingius S, Lichtenstein P, Lundholm C. The impact of birth mode of delivery on childhood asthma and allergic diseases—a sibling study. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012;42(9):1369–76.
Hancox R, Landhuis C, Sears M. Forceps birth delivery, allergic sensitisation and asthma: a population-based cohort study. Clin Exp Allergy. 2013;43(3):332–6.
Kolokotroni O, Middleton N, Gavatha M, Lamnisos D, Priftis N, Yiallouros P. Asthma and atopy in children born by caesarean section: effect modification by family history of allergies—a population based cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatrics. 2012;12:179–89. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2431-12-179.
Bråbäck L, Ekéus C, Lowe AJ, Hjern A. Confounding with familial determinants affects the association between mode of delivery and childhood asthma medication—a national cohort study. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2013;9(1):14.
Guibas GV, Moschonis G, Xepapadaki P, Roumpedaki E, Androutsos O, Manios Y, et al. Conception via in vitro fertilization and delivery by Caesarean section are associated with paediatric asthma incidence. Clin Exp Allergy. 2013;43(9):1058–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.12152.
Black M, Bhattacharya S, Philip S, Norman JE, McLernon DJ. Planned repeat cesarean section at term and adverse childhood health outcomes: a record-linkage study. PLoS Med. 2016;13(3):e1001973. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001973.
Lavin T, Franklin P, Preen DB. Association between caesarean delivery and childhood asthma in India and Vietnam. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2017;31(1):47–54.
Brix N, Stokholm L, Jonsdottir F, Kristensen K, Secher NJ. Comparable risk of childhood asthma after vaginal delivery and emergency caesarean section. Danish medical journal. 2017;64(1):1–4.
Bager P, Wohlfahrt J, Westergaard T. Caesarean delivery and risk of atopy and allergic disesase: meta-analyses. J Clin Exp Allergy. 2008;38:634–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.02939.x.
Ghaffari J, Nazari Z, Qrgzlv M. Investigate the association between pre-term, type of delivery and duration of breastfeeding with asthma. Mazandaran J. 2008;18(65):87–90.
Kauppila A, Koivisto M, Pukka M, Tuimala R. Umbilical cord and neonatal cortisol levels. Effect of gestational and neonatal factors. Obstet Gynecol. 1978;52:666–72.
van Berkel AC, den Dekker HT, Jaddoe VW, Reiss IK, Gaillard R, Hofman A, et al. Mode of delivery and childhood fractional exhaled nitric oxide, interrupter resistance and asthma: the generation R study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2015;26(4):330–6.
Kristensen K, Henriksen L. Cesarean section and disease associated with immune function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137(2):587–90.
Sevelsted A, Stokholm J, Bisgaard H. Risk of asthma from cesarean delivery depends on membrane rupture. J Pediatrics. 2016;171(38–42):e4.
Chu S, Chen Q, Chen Y, Bao Y, Wu M, Zhang J. Cesarean section without medical indication and risk of childhood asthma, and attenuation by breastfeeding. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(9):e0184920.
Rusconi F, Zugna D, Annesi-Maesano I, Baïz N, Barros H, Correia S, et al. Mode of delivery and asthma at school age in 9 European birth cohorts. Am J Epidemiol. 2017;185(6):465–73.
Acknowledgements
Hereby, we would like to thank the deputy of research and technology of Behbahan Faculty of Medical Sciences and the professors who helped us with their guidance and all individuals who cooperated in the implementation of the project.
Funding
Behbahan Faculty of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed to the conducting of this study. BD participated in the study design, data extraction and search for article, and interpretation of data, read and approved the final manuscript. SHR participated in the study design, data extraction and search for article, and interpretation of data and assisted in drafting the manuscript. GHB participated in the study design, editing the article and drafting the manuscript. MH participated in the study design and editing the language and text content. MA participated in the study design, data analysis, data extraction and search for article, analysis, and interpretation of data and assisted in drafting the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval is obtained from Behbahan Faculty of Medical Sciences.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Darabi, B., Rahmati, S., HafeziAhmadi, M.R. et al. The association between caesarean section and childhood asthma: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 15, 62 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-019-0367-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-019-0367-9