Abstract
Today, there is growing interest in the potential epigenetic risk related to assisted reproductive technologies (ART). Much evidence in the literature supports the hypothesis that adverse pregnancy outcomes linked to ART are associated with abnormal trophoblastic invasion. The aim of this review is to investigate the relationship between epigenetic dysregulation caused by ART and subsequent placental response. The dialogue between the endometrium and the embryo is a crucial step to achieve successful trophoblastic invasion, thus ensuring a non-complicated pregnancy and healthy offspring. However, as described in this review, ART could impair both actors involved in this dialogue. First, ART may induce epigenetic defects in the conceptus by modifying the embryo environment. Second, as a result of hormone treatments, ART may impair endometrial receptivity. In some cases, it results in embryonic growth arrest but, when the development of the embryo continues, the placenta could bring adaptive responses throughout pregnancy. Amongst the different mechanisms, epigenetics, especially thanks to a finely tuned network of imprinted genes stimulated by foetal signals, may modify nutrient transfer, placental growth and vascularization. If these coping mechanisms are overwhelmed, improper maternal-foetal exchanges occur, potentially leading to adverse pregnancy outcomes such as abortion, preeclampsia or intra-uterine growth restriction. But in most cases, successful placental adaptation enables normal progress of the pregnancy. Nevertheless, the risks induced by these modifications during pregnancy are not fully understood. Metabolic diseases later in life could be exacerbated through the memory of epigenetic adaptation mechanisms established during pregnancy. Thus, more research is still needed to better understand abnormal interactions between the embryo and the milieu in artificial conditions. As trophectoderm cells are in direct contact with the environment, they deserve to be studied in more detail. The ultimate goal of these studies will be to render ART protocols safer. Optimization of the environment will be the key to improving the dialogue between the endometrium and embryo, so as to ensure that placentation after ART is similar to that following natural conception.
Similar content being viewed by others
Review
Introduction
Much evidence in the literature supports the hypothesis that some adverse pregnancy outcomes observed after ART originate from suboptimal placental function caused by abnormal trophoblastic invasion. Indeed in humans, after adjusting for several confounding factors, the risk of spontaneous abortion is higher in ART cohorts than in spontaneous pregnancies [1–3]. Similarly, in several animal models, more abortions are reported after IVF, culture or superovulation than with natural conception [4–6]. Then, throughout a pregnancy following ART, placental-related defects can also occur [7]. Notably, human studies found an increased risk of gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, placenta praevia and placental abruption [7]. In addition, the risks of low birth weight [8] and prematurity [9, 8] were increased after ART. In the same way, intra-uterine growth retardation (IUGR) as well as overgrowth has been described in animals following ART procedures [10, 11, 4, 12–18]. Even if co-existing maternal risk factors (such as BMI, maternal age and infertility status) may affect placental development, the artificial manipulation of gametes and/or embryos could also play a role.
The aim of this review was to investigate the phenotypic and epigenetic mechanisms by which ART could interfere with placental formation and function, resulting in placenta-related adverse pregnancy outcomes. The first paragraph will insist on the key role of epigenetics in placental function. Then, the ART-induced placental variations occurring throughout pregnancy will be reported. To finish, the potential long-term effects of these placental modifications and the future research perspectives will be addressed.
Proper epigenetic regulation is essential for a functional placenta
-
1.
Epigenetics in placental function
In mammals, the placenta is a pregnancy-specific temporary organ that creates intimate contact between mother and foetus ensuring the maintenance of gestation and foetal well-being by the exchange of gases, nutrients and waste products [19]. It originates from the peripheral multipotent cells of the blastocyst (trophectoderm). In humans, placental syncytiotrophoblasts formed by the fusion of cytotrophoblasts constitute the site of exchange between the maternal and foetal circulation. It has specific endocrine functions, such as the production of placental hormones, but it also functions as a barrier, ensuring a stable environment to a foetus deprived of efficient defence mechanisms against various stresses (oxidative, xenobiotic, chemical) [20]. A finely tuned temporal and spatial regulation of trophoblastic invasion is essential for proper future function of the placenta and foetal development [21]. This involves molecular crosstalk between the endometrium and trophoblast [21].
Notably, epigenetic regulation is a significant factor in placental development and adaptive function to environmental stress [22].
Epigenetics may be defined as a set of cell-based molecular mechanisms able to modify gene expression. These mechanisms are heritable through mitosis or even sometimes meiosis and not sustained by DNA sequence variation [23]. Epigenetic regulation controls transcription at two levels: directly on the DNA (through DNA methylation/hydroxymethylation mechanisms) and on the proteins around which the DNA is wrapped to constitute the nucleosomes (histone modifications). Epigenetic regulation also controls translation or mRNA stability by the expression of non-coding RNAs (such as microRNA, Piwi, and Miwi).
For instance, imprinted genes, which are epigenetically regulated, are abundantly expressed in foetal and placental tissues and are apparently absent in non-placental organisms [24, 25]. It is postulated that genomic imprinting coevolved with placentation or drove the evolution of the placenta [26], sometimes through modifications of retrotransposons [27]. Imprinted genes are expressed in a parent-of-origin manner thanks to epigenetic modifications silencing either the paternal or the maternal allele. These epigenetic modifications (DNA methylation being the most described) are established in a sex-specific manner during gametogenesis on regulatory sequences referred to as imprinting control regions (ICRs). After fertilization, these ICRs act in cis to achieve monoallelic expression of most imprinted genes. Up to now, approximately 150 imprinted genes have been identified in mice and humans. In mice, these are under the control of 23 identified ICRs [28–30] (http://www.geneimprint.com/site/genes-by-species). Interestingly, they are generally not imprinted in all tissues, and the imprinted pattern can be limited to a precise developmental stage. In addition, the conservation of imprinted status or even the sense of the imprinting (maternal or paternal allele expressed) may vary between mammalian species [28]. Imprinted genes, which represent a very small percentage of genes, appear to play essential roles in embryonic growth and placental development by regulating the transport capacity of the placenta thereby controlling the supply of nutrients [31, 32]. During preimplantation development, genomic imprinting is jeopardized by global DNA demethylation, and some actors such as the complex Zfp57/TRIM28/KAP1 are required to protect epigenetic imprinting marks [33]. Moreover, imprinted genes are functionally haploid by definition and thus potentially more susceptible to mutations and epimutations [34]. Their dysregulation may therefore have major consequences on the placental phenotype with long-term consequences for the developmental programming of adult health and disease [35].
-
2.
Epigenetic modifications in the placenta and adverse pregnancy outcomes
To function adequately, the developing placenta needs the proper epigenetic regulation of imprinted and non-imprinted genes. Indeed, experimental studies conducted in both humans and animals have clearly shown the importance of epigenetics in the regulation of placental development. For example, drug-induced disruption of DNA methylation was able to inhibit human trophoblastic invasion in vitro by disturbing the expression of epigenetically regulated genes such as E-cadherin [36] as well as the proliferation of trophoblast cells in rat placenta [37]. The deletion of placental-specific Igf2 in mice consistently led to reduced placental growth and subsequent foetal growth restriction [38].
In addition, numerous findings proved that disturbed placental epigenetic regulation may cause abnormal trophoblastic invasion, which may contribute to the pathophysiology of some spontaneous miscarriages, IUGR and preeclampsia.
Indeed, in humans, DNMT1 expression (DNA methyltransferase 1 involved in DNA methylation maintenance) and global DNA methylation were significantly lower in chorionic villi from early foetus losses than in those harvested following selective pregnancy termination [39].
Moreover, in humans and animals, a great number of associations have been found between IUGR and epigenetic variations of imprinted or non-imprinted genes in placentas. Notably, by analyzing more than 200 human term placentas, Banister and colleagues found that the DNA methylation pattern of 22 loci was highly predictive of IUGR [40]. In mice, induced loss of imprinting and the subsequent overexpression of the imprinted Phlda2 gene were able to trigger placental and foetal growth retardation in the offspring whereas its deletion caused overgrowth [41]. Similarly, in humans, some authors demonstrated that PHLDA2 was up-regulated in the placenta in cases of IUGR [42–44] and that its expression level correlated negatively with birth weight [45]. As it is considered a negative growth regulator, the authors suggested that this imprinted gene potentially plays a direct role in the pathophysiology of IUGR.
Other imprinted genes were also up-regulated (CDKN1C) or down-regulated (MEG3, GATM, ZAC1, GNAS, MEST, IGF2) in IUGR placentas [42, 46, 47, 44]. Some of these differential expressions were associated with decreased placental methylation, as was the case for H19/IGF2 ICR1 [48], or loss of imprinting, as was the case for ZAC1 (=PLAGL1) and H19 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) [42].
In addition, other examples of non-imprinted genes highlight the possibility that foetal growth potential could be negatively impacted by epigenetic dysregulation in the placenta. Ruebner and colleagues pointed out that expression of Syncytin-1, a protein that promotes cellular fusion in the syncytiotrophoblast, was lower in human IUGR placentas than in controls [49]. The same team recently linked decreased expression of this protein to epigenetic hypermethylation of its promoter [50].
In an induced IUGR rat model, Reamon-Buettner and colleagues reported decreased expression and aberrant DNA methylation patterns of the promoter region of the Wnt2 gene, which is known to be implicated in placental vascularization [51]. In humans, the same pattern was found with lower WNT2 expression and higher DNA methylation in growth-restricted neonates than in controls [52].
Interestingly, epigenetic changes were also found on repeated sequences. For example, Michels and colleagues found an increased LINE-1 methylation level in placental tissues from low birth weight infants [53]. Other evidences about preeclampsia reinforce the idea that epigenetic disorders may be involved in abnormal trophoblastic invasion. Actually, mice with induced loss of expression of the imprinted Cdkn1c gene developed a preeclampsia-like syndrome, with hypertension and proteinuria [54]. Besides, widespread DNA methylation changes were found in placentas of a cohort of patients suffering from early onset preeclampsia but not in gestational age-matched controls [55]. Some of these methylation modifications correlated negatively with expressional changes, especially for genes implicated in angiogenesis (such as EPAS 1 and FLT I). Moreover, BHLHE40, a gene coding for a protein that can prevent trophoblast differentiation exhibited significantly decreased DNA methylation and increased expression in preeclampsia placentas [55]. In addition, the expression of maspin (SERPINB5), a serine protease inhibitor and an inhibitor of cell migration [56], which may modify trophoblast cell invasion in the first trimester [57], could also be modified in preeclampsia. In the same family of genes, SERPIN A3 is a specific inhibitor of elastase, which plays a crucial role during the implantation process. SERPIN A3 displayed decreased methylation and increased gene expression in placentas from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia compared with controls [58], through a complex epigenetic regulation [59]. As for IUGR, several studies highlighted the increased methylation [50] and reduced expression of syncytin-1, as well as the down-regulation of WNT2 in preeclamptic placentas. These modifications were possibly responsible for impaired placental function [60]. Interestingly, epigenetic modifications could also correlate with the severity of the disease. For instance, hypertension tended to be more severe in preeclamptic women with biallelic expression of H19, than in women with normally imprinted expression of this gene [61]. Recently, Anton and colleagues demonstrated a correlation between disease severity and alterations in DNA methylation (hypermethylation of CDH11, COL5A1, TNF, hypomethylation of NCAM1) in preeclamptic placentas [62].
In summary, there is a wealth of data highlighting the particular role of epigenetics in placental regulation and the potential link between epigenetic dysregulation and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
The notion of epigenetic risk emerged in recent decades and a recent meta-analysis confirmed the increased risk of imprinting disorders (such as Beckwith-Wiedemann and Silver-Russel syndromes) after ART [63]. This raised the issue of potential methylation defects associated with ART [64]. Most studies that have examined the methylation status of imprinting genes in foetuses or placentas in animal models or in humans have associated epigenetic anomalies with adverse effects on embryonic development [65].
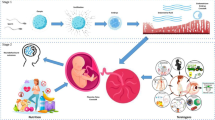
What follows aims to investigate the placental modifications induced by ART and to understand their link with adverse pregnancy outcomes. The hypothesis is that epigenetic dysregulation could constitute the logical link between environmental changes due to ART, abnormal trophoblastic invasion and subsequent adverse pregnancy outcomes. Indeed, ART, via epigenetic dysregulation, could disturb the dialogue between the embryo and endometrium and cause abnormal trophoblastic invasion, which triggers placental adaptive responses (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 ART can impair the dialogue between the endometrium and embryo and lead to suboptimal trophoblast invasion. Infertility per se could be responsible for suboptimal gametes, and several ART steps (such as superovulation and embryo culture) may also be responsible for suboptimal embryo development, both potentially leading to embryo development arrest. In addition, superovulation may impair endometrium receptivity. Later, the placentation may be suboptimal and cause miscarriage or placenta-related adverse outcomes. However, a smart dialogue between the foetus and placenta could bring adaptive responses through regulated epigenetic mechanisms leading to increased weight, cell proliferation, increased vessel density and increased transport capacity. At birth, epigenetic variations present in cord blood or placentas could either reflect persisting variations/defects or ongoing compensation at the time of birth
ART and trophoblastic invasion disturbances
-
1.
ART and the epigenetic status of the conceptus
In animal models (especially in mice), most studies have shown that ART procedures (such as superovulation and embryo culture), whether isolated or in association, could lead to blastocyst epigenetic defects in several loci (such as H19, Snrpn, Peg3, Kcnq1ot1 genes as well as repetitive sequences) [66–71].
Moreover, these epigenetic abnormalities were not restricted to the early stages. In mice, several studies reported placenta-specific imprinting defects after implantation, appearing in suboptimal culture conditions, such as in vitro culture associated with in vitro fertilization [5], embryo transfer [72], poorer media [73, 69] or increased oxygen concentration [74] (Table 1). When assessed by transcriptomics, it was clear that the modifications of placental gene expression in mice placenta at mid-gestation were very different depending on the richness of the culture milieu. They were much stronger when simple M16 culture medium was used than when the more complex G1/G2 medium was used [75]. Interestingly, amongst the modified genes, imprinted genes were overrepresented. Recently, Hossain and colleagues found that other aspects of epigenetics could be affected by in vitro manipulations by observing the down-regulation of miRNAs in bovine placentas from in vitro production (IVF and in vitro culture) compared with those from artificial insemination [76]. Even in human placentas, epigenetic modifications were observed. Indeed, ART was associated with lower DNA methylation levels and higher expression levels of SERPINF1 [77]. This protein is ubiquitously expressed and presents a potent anti-angiogenic activity [78]. Thus, its deregulation may detrimentally affect placentation and foetal development.
Table 1 Conceptuses and/or placentas in mice: resorption rate, weight, gene expression and/or DNA methylation of imprinted genes Surprisingly, placenta appears to be more susceptible to modifications in DNA methylation and/or expression of imprinted genes at mid-gestation [74, 79, 69, 72] (Table 1). Discussing this observation, Mann and colleagues proposed two scenarios to explain why the defects were apparently restricted to the trophectoderm lineage [69]. In the first hypothesis, extra-embryonic cells, in contact with the culture medium, are more severely affected by in vitro culture, which is responsible for a loss of imprinting in mid-gestation placentas. Indeed, trophectoderm (TE) cells are directly exposed to the environment. Besides, they are also the first lineage to differentiate in the embryo as trophectoderm stem cells, from which the different cell lines of the future placenta will originate [80]. Other studies are in accordance with this hypothesis. Notably, TE cells from blastocysts cultured in vitro showed strong expressional modifications with the activation of stress-related pathways and the down-regulation of genes involved in placentation [81, 82]. Specifically, Igf2 expression in TE cells was lower after IVF than in controls [81]. In the second hypothesis developed by Mann and colleagues, the embryo could be able to restore a correct imprint thanks to lineage-restricted de novo methylation occurring in inner cell mass (ICM) but not in TE cells.
A third hypothesis involves the selection of viable embryos through active selective elimination mechanisms that act to discard embryos with abnormal imprinting before mid-gestation. Indeed, the studied embryos were those that reached this developmental stage. In mice, following ART, an increased number of resorption sites was observed. This number was even higher when the embryos were fertilized and cultured in vitro than when only cultured in vitro. This could indicate that embryos with defective imprinting do not survive and that the effect is cumulative [5, 4]. Reinforcing this idea, Yin et al. showed that mice injected with an inhibitor of DNA methyltransferase 1 (Dnmt1), an enzyme responsible for methylation maintenance, had a smaller number of implanted embryos [39]. Furthermore, at mid-gestation, these embryos had a lower global DNA methylation level, which was associated with growth retardation [39]. These results strengthen earlier experimental studies in mice that highlighted the fundamental contribution of DNA methylation enzymes to embryonic development [83].
In summary, these data support the hypothesis that a suboptimal embryo environment induced by ART greatly disturbs the epigenetic status of not only the embryo (eventually causing development arrest) but also the extra-embryonic tissues.
-
2.
ART and endometrial receptivity
Apart from modifying the epigenetic status of the conceptus, another way in which ART could alter trophoblastic invasion could be its effect on the endometrium.
Much evidence has linked poor endometrium quality to abnormal early placentation. Even though some genetic causes of endometrial defects leading to recurrent miscarriages have been described [84–86], ovarian stimulation, which is required in most ART procedures, may also be responsible for poorer endometrium quality. Since the ovary and the uterus share several signalling pathways, and since hormones secreted by the ovary have a direct effect on uterus function, ovarian stimulation probably modifies the uterine environment. This is assessed by studies that demonstrated differential expression of genes in the endometrium between stimulated and natural cycles, with a dose-response effect [87, 88].
In mice, the implantation rate was lower and post-implantation foetal mortality was higher in superovulated recipients than in non-stimulated controls [89]. Similar observations were also reported in humans, with a dose-dependent effect: the risk of spontaneous abortion was significantly higher in women stimulated with high levels of hormones than in those stimulated with lower levels [3]. Besides, high serum estradiol levels at ovulation triggering after controlled ovarian stimulation are associated with placenta-related adverse pregnancy outcomes such as growth restriction or preeclampsia [90, 91].
Other evidences highlight the impact of a suboptimal endometrium induced by ovarian stimulation on placental and foetal growth. Notably, hormones are known to modify birth weight. Indeed, singletons born after IVF have on average a lower birth weight than singletons born after natural cycles with mild stimulation [92]. Moreover, an inverse correlation between birth weight and estradiol levels achieved in case of IVF [93] was found. In mice, the mean weight of foetuses was also lower in stimulated than in non-stimulated recipients [89, 94].
Surprisingly, birth weight was higher in ART-offspring after the transfer of cryopreserved/thawed embryos than with fresh embryos [95, 96]. While it could be hypothesized that this was caused by a direct effect on the embryo, differences in hormonal treatment between the two groups could have an important effect as well. In the first case (cryopreserved embryos), women are not treated with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) to induce multifollicular growth, while they are treated in the second case. In natural conception, when two children from the same mother are compared, the second one is usually heavier [97]. However, when the first is born following transfer of a frozen embryo and the second after IVF, the situation is reversed [95]. On average, birth weight following frozen embryo transfer is the same as that following natural conception [98]. The fact that frozen embryos are transferred without controlled ovarian hyperstimulation suggests that the endometrium-embryo dialogue is in this situation closer to the “natural” dialogue and enables normal placentation. It is also possible that freezing selects embryos with normal epigenetic profiles, by unknown putative mechanisms. However, recently, two different teams highlighted that the risk of large for gestational age and preeclampsia could be increased in frozen embryo cycles compared with fresh cycles or natural conception [99, 100]. Therefore, further studies are needed to determine the impact of the different protocols used in frozen embryo transfer (hormonal treatments used, duration of culture, cryoprotectants, culture media, etc.).
Other data are in keeping with the hypothesis that superovulation and hormone treatment may impair placentation. For example, a recent study examining near-term placentas in superovulated mouse recipients found altered trophoblast differentiation causing a reduced maternal-foetal exchange area [94]. Besides, in humans, pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A) levels in maternal serum were decreased in first-trimester ART pregnancies [101–105]. PAPP-A is known to play a critical role in trophoblastic invasion [106] by contributing to maternal tolerance towards the foetus [107]. Giorgetti et al. confirmed these low levels after ART and further added that maternal serum PAPP-A levels correlated strongly and inversely with estradiol levels at ovulation triggering [108]. Accordingly, PAPP-A values were lower after the transfer of fresh embryos (when ovarian stimulation was used) than after the transfer of frozen embryos or after unstimulated cycles [101, 109].
All these findings highlight a tight relationship between high hormone levels and impaired trophoblastic invasion presumably through decreased endometrium receptivity. Exposing the endometrium to high levels of estradiol and progesterone produced by multiple corpora lutea could possibly render it less efficient for embryo implantation than it is during natural cycles [110]. Thus, ART processes, and especially hormone treatments, may increase the rate of adverse pregnancy outcomes by inducing more trophoblastic invasion defects.
In addition to hormone treatments, infertility per se could involve an altered uterine environment. For example, some authors recently suggested that endometriosis may be accompanied by epigenetic modifications implicated in diminished endometrial receptivity and altered gene expression. Epigenetic modifications on the promoter of a mediator of endometrial receptivity, HOXA10, may be one of the mechanisms involved, as reported in women [111–113] and in several animal models [114, 115].
To summarize, ART, through its negative effect on the endometrium-embryo dialogue, could participate in preventing successful trophoblastic invasion. This could potentially explain the occurrence of adverse pregnancy outcomes after ART. Depending on the severity of the defects, ART could gradually lead to developmental arrest, miscarriages, preeclampsia or IUGR (Fig. 1). But in most cases, pregnancies obtained after ART are able to continue without obvious immediate adverse outcomes. This sustains the hypothesis that initial defective trophoblastic invasion could trigger placental adaptive responses during pregnancy.
ART and the possible induction of placental adaptive responses
Nuclear transplantation in animals is known to produce placental phenotypic modifications (such as placentomegaly), to modify placental metabolism and to disturb imprinted gene expression [116, 117]. Given these placental modifications after somatic cell nuclear transfer, we wondered whether ART could trigger placental responses.
-
1.
Phenotypic placental responses
In the literature, several studies in animals showed that a suboptimal placenta is created by in vitro conditions but that counterbalancing mechanisms also occurred. First, a smaller quantity of TE cells developed in mouse blastocysts from in vitro culture than in naturally conceived blastocysts [82]. At later stages (12.5 dpc), IVF embryos and placentas were smaller than those in the control group [4] (Table 1). However, the placenta was slightly larger (+9 %) at 15.5 dpc and to an even greater extent (+25 %) at 18.5 dpc, while foetus weight was 16 % lower at 15.5 dpc but only 9 % lower at 18.5 dpc in the IVF group than in controls [10] (Table 1). At this later stage, cell proliferation was greater in IVF placentas than in controls, in both the labyrinth and spongiotrophoblast layers. By birth, IVF foetuses had reached the same weight as the controls [10]. In the in vitro context, placentas were found to be lighter than control placentas at early gestation and heavier at late gestation. While a larger placenta is not necessarily synonymous of a higher efficiency in nutrient and oxygen transfer, it can in this case probably contribute to a compensatory growth of the foetus, despite initial functional limitations. Similar results were observed in the sheep model: foetuses from in vitro cultured embryos were 60 % smaller than naturally conceived foetuses at day 24 of gestation, whereas no difference was found at later stages [16].
Likewise, in humans, the enlargement of placentas has been observed in complicated pregnancies associated with low birth weight, such as pregnancies with late-onset preeclampsia, foetal death or advanced maternal age [118–120]. Interestingly, the same phenomenon was seen in singletons from ART. Placentas from ART pregnancies were overrepresented in the highest quartile of weight, and the placental weight/birth weight ratio was commonly higher, while the mean birth weight was lower, even after adjusting for potential confounding factors [121]. This increased placental weight after IVF could be the result of compensatory responses.
-
2.
Mechanisms involved in placental responses
-
Metabolic pathways
According to Coan and co-workers, the placental phenotype is responsive to nutritional conditions. When foetal nutrient availability is compromised, it adapts to maximize the nutrient transfer capacity [122]. These compensatory mechanisms may start from the blastocyst stage, within extra-embryonic lineages. Actually, using a mouse maternal protein restriction model, some authors demonstrated increased endocytosis, cell proliferation and invasiveness in the trophectoderm, which may reveal enhanced nutrient capture [123, 124]. The up-regulated expression of nutrient supply genes such as glucose and system A amino acid transporters was shown in small murine placentas during late gestation, thus reflecting a response to foetal demand signals [122]. The foetus itself plays a role in its own development and growth by sending signals to the placenta, which will respond by regulating genes involved in growth control, specific transport systems and vascularization [125].
These metabolic responses are well-illustrated in IVF studies on animal species [126, 15, 127]. Indeed, at early gestation, bovine conceptuses after IVF and culture displayed placentas with decreased blood vessel density, while at late gestation, placentas had greater blood vessel density [15, 127]. This impaired placental vasculogenesis early in gestation was also reported for sheep embryos developed in vitro [128]. This compensatory process could implicate the angiogenic pathway and particularly an angiogenic transcription factor, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARƳ) protein, which could modulate the density of maternal blood vessels throughout pregnancy [15]. In addition to the gain in vascularization, increasing cell fusion could improve foeto-maternal exchanges. Indeed, two proteins involved in membrane fusion, annexin A3 and α-SNAP, were found to be up-regulated in human term placentas obtained after ART [19].
Besides, in human placentas after ART, genome-wide mRNA expression revealed the overexpression of genes involved in metabolism, immune response, transmembrane signalling and cell cycle control [129, 130]. Similarly, transcriptomic data in mouse placental tissues show that IVF techniques trigger the induction of genes involved in cellular proliferation and cell cycle pathways [75].
In summary, the kinetics of placental and foetal growth altered by ART may be linked to modifications in various biological pathways, probably triggering the placental compensation phenomenon. While the complete picture of the systems that regulate this compensation is still blurred, epigenetic changes certainly play a part in the adaptive mechanisms.
-
Imprinted gene network
Concerning the regulation of this placental response, one interesting hypothesis is that potential primary dysfunctions of the placenta could be corrected by the imprinted gene network of placental mammals (IGN). The modulation of this network of coordinated imprinted genes (and probably non-imprinted genes), which are involved in growth control and specific placental transport systems, could contribute to the tight regulation of foetal growth during post-implantation development. This was described in mice for Igf2, Zac1 and H19 [131, 132] and recently in the human placenta for ZAC1 [133].
To support this hypothesis, in mouse placentas after ART, most genes of the IGN were up-regulated in a coordinated fashion, when compared with the control group [5]. The fact that these genes with placental reciprocal functions were up-regulated after ART despite phenotypically and morphologically normal embryos suggests that placental IGN may participate in the control of normal foetal growth in ART pregnancies. However, the methylation status of their DMRs after ART was either similar to that in controls or only slightly modified during gestation [5, 69]. In the same way, the methylation of repeated sequences (ALUYb8, α-satellites and LINE-1) were reported to be unchanged after ART [134]. Other epigenetic mechanisms, such as histone modifications, could therefore be involved. In fact, according to Lewis et al., an ancestral imprinting mechanism, restricted to the placenta, is based on histone modifications [135], which may confer the short-term and flexible response implicated in development [136–138].
Regrettably, no evidence is available in animals at birth concerning the occurrence of epigenetic modifications in the placenta. In humans, nothing is certain (Table 2). Three studies that carried out large DNA methylation analyses using arrays found conflicting data. Indeed, the first published study described quantitative differences in global DNA methylation (briefly with a higher and a lower degree of DNA methylation in post-IVF cord blood and placental samples, respectively) and for several imprinted genes [77] (Table 2). In contrast, two recent studies reported either opposite cord blood findings [139] or none variability in DNA methylation at 25 imprinted DMRs [134] (Table 2). However, the three studies are not comparable regarding the sample size (10 individuals versus 73), the mode of reproductive treatment (IVF versus unspecified ART) and the method used.
Table 2 Effects of ART on imprinted genes and retrotransposable element expression and methylation in chorionic villous samples from abortion, peripheral blood, cord blood and placenta Moreover, other studies focusing on the DNA methylation of specific imprinted genes also generated contradictory results. Indeed, although some authors reported no epigenetic changes after ART [140, 141], several authors reported variations in methylation levels in both cord blood and/or placentas for a number of imprinted genes such as MEST [142, 143], H19 [144, 142, 145], KCNQ1OT1 [146] or SNRPN [142]. However, none of them agreed on the changes in DNA methylation and these variations were mild (from 0.6 to 4.5 % differential methylation levels) (Table 2). Once again, these studies are difficult to compare given the limitations similar to those mentioned above.
However, most studies focused on normal pregnancy, thus excluding placenta-related adverse pregnancy outcomes (such as preeclampsia, hypertension, some IUGR) and therefore possibly ignoring major differences.
Concerning the expression analysis of imprinted genes, conflicting results were also reported. Dysregulation mainly took place in the placenta and only for three imprinted genes (H19, IGF2, MEST) [77, 144, 145] (Table 2).
Finally, these minimal expressional changes at term compared with more significant changes during pregnancy in animals could reflect the remains of defects that were partially compensated during prenatal life or even methylation allelic polymorphisms (placental epipolymorphism [147]).
Thus, epigenetic “defects” in animals’ placentas after in vitro manipulations are found in most studies. Most authors consider this variety of placental phenotypes triggered by ART to originate from epigenetic errors at imprinted genes [74], but should we really consider these epigenetic modifications as “errors” or should we regard them as smart adaptation mechanisms developed by the placenta? From the results above, we can postulate that these “defects” are not all harmful for the embryo and that some could be considered compensatory mechanisms. Indeed, they reflect the balance between members of the IGN in the placenta. Biallelic expression as well as the loss of imprinting of parts of the IGN in the placenta could constitute a major compensatory mechanism to allow the developing foetus to cope with a changing or adverse environment. In response to certain stress factors that modify the early environment of the embryo, the placenta could amplify these compensatory mechanisms up to a certain point. In most cases, efficient compensation ensures normal foetal growth up to term. When the compensation is unbalanced, compensation fails and pathological features such as miscarriages, low birth weight or preeclampsia could occur. However, what remains to be determined is whether this compensation step per se could be a risk factor for certain diseases later in life.
-
Potential long-term effects of ART-related compensation during pregnancy
These modified maternal-foetal interactions, here after ART, might have consequences for outcomes in infancy and even in adulthood, especially by inducing metabolic and cardiovascular conditions [148–152]. For instance, in humans, new-borns that are either too small or too big may be vulnerable to heart disease, hypertension, type II diabetes and obesity [153–155]. In addition, the size and shape of the placenta have been related to life expectancy in men [156] and their risk for coronary heart disease [157]. Similarly, a high placenta/foetus weight ratio, considered a marker of intra-uterine stress, has been associated with hypertension later in life [158].
As mentioned above, these phenotype modifications of the foetus and placenta are found in ART pregnancies. Thus, the modified intra-uterine environment after ART may be one cause of late-onset diseases [159]. Indeed, although the majority of ART children are healthy, the available data about long-term follow-up of ART children revealed cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors [159]. Notably, children born after ART may exhibit increases in peripheral adipose tissue mass, in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, in fasting glucose levels and IGF-I and IGF-II levels as well as changes in the lipid profile [160–164]. In addition, transcriptomic data at birth revealed activation of metabolic pathways implicated in chronic disorders such as obesity and type II diabetes [77]. However, further large longitudinal studies are needed to confirm these poor outcomes.
Portha and colleagues proposed that the link between the prenatal environment and adverse long-term effects could be written through epigenetic modifications of the conceptus. These plastic responses to the early environment could be kept in memory throughout life, due to epigenetic changes such as DNA methylation and histone modifications [165]. We can postulate that ART could trigger similar processes.
Nevertheless, in humans, there is no evidence of epigenetic changes persisting into childhood. Indeed, in children conceived after IVF, reassuring data have been reported for DNA methylation for four imprinted genes and even on a global scale [166, 167]. Only one recent study observed that some epigenetic errors can still be observed during childhood, though this concerned only the imprinted gene SNRPN [168] whose DNA methylation levels were not found to be modified at birth after ART in either cord blood or in the placenta. However, the heterogeneity of biological samples (blood or buccal cells), age range, type of reproductive technique and the analysis of methylation could hide potential underlying differences.
Another hypothesis might reside in tissue-specific epigenetic modifications. This could explain the absence of DNA methylation variations in blood and buccal cells. Therefore, studying other tissues may reveal defects linked to specific metabolic conditions. Notably, Scherrer’s team found increased DNA methylation on the promoter of the gene encoding eNOS (NO synthase) in vascular tissues in mice obtained after ART. This resulted in reduced plasma NO concentrations, increased blood pressure and a shorter lifespan [169].
It is also interesting to consider that tissue-specific epimutations for H19, Snrpn and Peg3 genes were described in individual mice generated by ART (ICSI or superovulation) [170].
Ways for medical improvement and future research
Ways to improve actual ART protocols
Finally, as placental defects seem to originate from an altered endometrium-embryo dialogue, optimization of the environment during ART is a cornerstone and may improve early placentation. Hence, several simple and practical improvements can be proposed. First, it is possible to optimize the quality of oocytes and the endometrial milieu by using lower doses of hormones. Second, the culture media must be optimized to limit trophectoderm cell stress. Even though the parameters of this optimization are far from being mastered, it has been clearly shown that specific culture media generate a lower degree of stress for the embryo [5, 70]. Third, the embryo and endometrium should be better synchronized either by transferring blastocyst-stage embryos (even if extended embryo culture may have per se an impact the epigenetic regulation) and/or by developing molecular diagnostic tests (for example transcriptomic, lipidomic and proteomic profiles) to assess the quality of the endometrium in order to target the best timing of endometrial receptivity [171]. Fourth, another practice recently developed by some teams, could be to freeze all embryos and transfer them during subsequent cycles with an optimally prepared endometrium [172]. However, the endometrial tests and the fourth solution need to add an embryo cryopreservation step. Recent data reported poorer obstetrical outcomes after frozen embryo cycles (reported above) and a potential negative impact of the cryopreservation itself on the regulation of DNA methyltransferases in preimplantation frozen/thawed embryos [173]. Thus, further studies are required before these strategies can be applied safely.
Another way to improve the chances of success could be post-natal correction. Since imprinted genes in the placenta appear to be major operators in regulating foetal growth, further research is needed to better understand the link they may have with future disease. All in all, imprinted genes could eventually be used as sensors to predict and better prevent diseases later in life. Interestingly, some studies suggest that customized interventions might be implemented to correct effects on phenotypic changes [153]. One example is the post-natal administration of leptin in rats, which was able to reverse the adverse effects of mother-undernutrition: the offspring phenotype as well as the expression and methylation of several hepatic genes were corrected [174]. One other example is the post-natal administration of butyrate (histone deacetylase inhibitor) in the mouse model, which normalized both DNA methylation of the promoter of the eNOS gene and vascular function [169]. Further studies in animals are needed to better understand tissue-specific epigenetic regulation in ART. Thus, screening for epigenetic markers during early life could be used to identify more vulnerable patients and to define an appropriate treatment to potentially correct various epigenetic defects.
Future research to assess the impact of ART on health
More research is needed to better understand the disturbed interactions between the embryo and the milieu, especially in artificial conditions. New insights about the regulation of actors involved in the protection/maintenance of DNA methylation at imprinted genes in a context of ART are now necessary [33]. Moreover, to our knowledge, epigenetic defects have not been studied separately in TE and ICM cells so far. Nonetheless, knowing whether epigenetic dysregulation occurs in all blastocyst cells or only in TE cells could lead to better understanding of the mechanisms implicated in placental defects caused by ART. Knowledge of such mechanisms would be important to evaluate possible consequences for the developing individual soon after birth or even later in life.
Furthermore, although placental compensation enables mice to reach a normal birth weight [10], evidence in humans shows that ART pregnancies still carry a higher risk of placenta-related adverse pregnancy outcomes [7]. These differences may stem from overwhelmed compensation mechanisms, which, in certain cases, are not fully successful. Several potential reasons may explain this limited correction in humans as compared with mice. First, although placentation is haemochorial in both humans and mice [175, 176], their placentas are not organized in the same way (labyrinth and spongiotrophoblast in mice versus villous trophoblast in humans) and differ in their morphogenesis and exchange functions [175, 177]. Second, in human ART, the cumulative effects are possibly at their utmost point because the standard method is to transfer fresh embryos from a superovulated cycle, which is not performed in mice because pseudopregnant females are used. The effects observed in animal models are therefore possibly exacerbated in humans. Third, contrary to animal models, parental infertility is the major reason why ART is used in humans, and this infertility may be partly responsible for the epigenetic disorders and abnormal placentation leading to maternal pathologies, such as abruptio placentae and preeclampsia [178–180]. Therefore, any extrapolation of animal studies to humans should be done with caution.
Moreover, concerning the methodology, most epigenetic studies have addressed the effects of ART stressors on DNA methylation at the individual gene level and often analyze one or few CpG. Thus, genome-wide as well as gene-specific approaches that can target regulatory regions (promoters, enhancers, gene body, or elsewhere) and assess functional significance is now needed. High-throughput tools, which are becoming available, may be applied more widely to study the epigenomic changes associated with ART. Otherwise, in most studies, only overall expression and methylation levels are examined (Tables 1 and 2). Although it could be valuable, monoallelic expression of imprinted genes is hard to perform, given the need for informative SNPs in parents to perform this analysis.
From a global DNA methylation point of view, placenta tissue has been shown to display a very low DNA methylation profile compared with other somatic tissues [181]. More recently, human studies on placenta samples using high-throughput tools (methylome) revealed that placenta presents large partially methylated domains (PMD) which are stable during pregnancy [182]. This unique property of the placenta might contribute to the regulation of the expression of key genes important for foetal development. Besides, in placenta samples, the genes enriched in the highly methylated regions (HMD) are involved in defence responses. The review that we present here focuses on imprinted genes, but research aiming to delineate the variations that exist at such loci, between placenta from ART and spontaneous pregnancies, would help us to understand how this alternative epigenetic mechanism may contribute to placental remodelling and pregnancy outcomes.
In addition, to date, no study has focused on histone modifications in ART placentas, although higher concentrations of H3K4 trimethylation have been found in mouse blastocysts cultured in vivo than in vitro [183]. Recently, Court and colleagues suggested that placental-specific imprinted loci could be imprinted by an epigenetic mechanism, such as histone modification, independent of germline methylation [30]. Furthermore, other interesting data about miRNAs indicate that they also deserve to be studied in more detail [76, 184]. Studies on combinations of epigenetic factors would also bring additional knowledge about the respective roles of the different epigenetic alterations after ART.
Besides, since gene expression and DNA methylation are sexually dimorphic in male and female placentas it is also important for future epigenetic placental studies to take into account the sex of the foetuses [185]. For example, a study that investigated the epigenetic variations of ZAC1 in cases of IUGR revealed down-regulated expression in placentas from girls but not boys [133].
Moreover, the link between placental growth and epigenetics was not investigated. It would be interesting to carry out studies comparing placental development during the early steps of foetal life with placental epigenetic results at birth to unravel the sequence of epigenetic events and distinguish between causal changes and the resulting epigenetic landscape.
Conclusions
Much evidences support the hypothesis that suboptimal trophoblastic invasion due to a disturbed dialogue during the early phases of placentation could potentially explain the higher frequency of adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as miscarriages or preeclampsia, associated with ART. The dialogue between the endometrium and embryo is a crucial step to achieve successful trophoblastic invasion, ensuring a non-complicated pregnancy and the development of healthy offspring. This dialogue seems to be disturbed by ART, either by impairing endometrial receptivity or by modifying the early steps in the epigenetic development of the embryo. But this initially disturbed placentation also gives rise to a smart dialogue between the foetus and placenta, which may bring adaptive responses, notably through epigenetic mechanisms. Indeed, a coordinated group of genes called the imprinted gene network, stimulated by foetal signals, may modify nutrient transfer as well as placental growth and vascularization.
If these mechanisms are overwhelmed, improper maternal-foetal exchanges could occur, potentially leading to abortion or adverse pregnancy outcomes. Fortunately, in most cases, successful adaptation enables normal progress of the pregnancy and healthy offspring. However, these adaptation mechanisms per se could have adverse effects later in life. More research is thus needed to assess the real impact of ART on future health. The better understanding of the placental mechanisms triggered by ART will aim in fine to render the ART protocols safer.
References
Brandes M, Verzijden JC, Hamilton CJ, de Weys NP, de Bruin JP, Bots RS, et al. Is the fertility treatment itself a risk factor for early pregnancy loss? Reprod Biomed Online. 2011;22:192–9.
Chaveeva P, Carbone IF, Syngelaki A, Akolekar R, Nicolaides KH. Contribution of method of conception on pregnancy outcome after the 11–13 weeks scan. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2011;30:9–22.
Wang JX, Norman RJ, Wilcox AJ. Incidence of spontaneous abortion among pregnancies produced by assisted reproductive technology. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:272–7.
Delle Piane L, Lin W, Liu X, Donjacour A, Minasi P, Revelli A, et al. Effect of the method of conception and embryo transfer procedure on mid-gestation placenta and fetal development in an Ivf mouse model. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:2039–46.
Fauque P, Ripoche MA, Tost J, Journot L, Gabory A, Busato F, et al. Modulation of imprinted gene network in placenta results in normal development of in vitro manipulated mouse embryos. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19:1779–90.
Van der Auwera I, D'Hooghe T. Superovulation of female mice delays embryonic and fetal development. Hum Reprod. 2001;16:1237–43.
Thomopoulos C, Tsioufis C, Michalopoulou H, Makris T, Papademetriou V, Stefanadis C. Assisted reproductive technology and pregnancy-related hypertensive complications: a systematic review. J Hum Hypertens. 2013;27:148–57.
Jackson RA, Gibson KA, Wu YW, Croughan MS. Perinatal outcomes in singletons following in vitro fertilization: a meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;103:551–63.
Pinborg A, Wennerholm UB, Romundstad LB, Loft A, Aittomaki K, Soderstrom-Anttila V, et al. Why do singletons conceived after assisted reproduction technology have adverse perinatal outcome? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2013;19:87–104.
Bloise E, Lin W, Liu X, Simbulan R, Kolahi KS, Petraglia F, et al. Impaired placental nutrient transport in mice generated by in vitro fertilization. Endocrinology. 2012;153:3457–67.
Chen Z, Robbins KM, Wells KD, Rivera RM. Large offspring syndrome: a bovine model for the human loss-of-imprinting overgrowth syndrome Beckwith-Wiedemann. Epigenetics. 2013;8:591–601.
Grazul-Bilska AT, Johnson ML, Borowicz PP, Baranko L, Redmer DA, Reynolds LP. Placental development during early pregnancy in sheep: effects of embryo origin on fetal and placental growth and global methylation. Theriogenology. 2013;79:94–102.
Hiendleder S, Mund C, Reichenbach HD, Wenigerkind H, Brem G, Zakhartchenko V, et al. Tissue-specific elevated genomic cytosine methylation levels are associated with an overgrowth phenotype of bovine fetuses derived by in vitro techniques. Biol Reprod. 2004;71:217–23.
Hori N, Nagai M, Hirayama M, Hirai T, Matsuda K, Hayashi M, et al. Aberrant Cpg methylation of the imprinting control region Kvdmr1 detected in assisted reproductive technology-produced calves and pathogenesis of large offspring syndrome. Anim Reprod Sci. 2010;122:303–12.
Miles JR, Farin CE, Rodriguez KF, Alexander JE, Farin PW. Angiogenesis and morphometry of bovine placentas in late gestation from embryos produced in vivo or in vitro. Biol Reprod. 2004;71:1919–26.
Ptak GE, D'Agostino A, Toschi P, Fidanza A, Zacchini F, Czernik M, et al. Post-implantation mortality of in vitro produced embryos is associated with DNA methyltransferase 1 dysfunction in sheep placenta. Hum Reprod. 2013;28:298–305.
Sinclair KD, Young LE, Wilmut I, McEvoy TG. In-utero overgrowth in ruminants following embryo culture: lessons from mice and a warning to men. Hum Reprod. 2000;15 Suppl 5:68–86.
Young LE, Sinclair KD, Wilmut I. Large offspring syndrome in cattle and sheep. Rev Reprod. 1998;3:155–63.
Zhang Y, Zhang YL, Feng C, Wu YT, Liu AX, Sheng JZ, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of human placenta derived from assisted reproductive technology. Proteomics. 2008;8:4344–56.
Huang Q, Li J, Wang F, Oliver MT, Tipton T, Gao Y, et al. Syncytin-1 modulates placental trophoblast cell proliferation by promoting G1/S transition. Cell Signal. 2013;25:1027–35.
Chelbi ST, Vaiman D. Genetic and epigenetic factors contribute to the onset of preeclampsia. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008;282:120–9.
Novakovic B, Saffery R. The ever growing complexity of placental epigenetics—role in adverse pregnancy outcomes and fetal programming. Placenta. 2012;33:959–70.
Nelissen EC, van Montfoort AP, Dumoulin JC, Evers JL. Epigenetics and the placenta. Hum Reprod Update. 2011;17:397–417.
Reik W, Walter J. Genomic imprinting: parental influence on the genome. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:21–32.
Wilkins JF, Haig D. What good is genomic imprinting: the function of parent-specific gene expression. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4:359–68.
Renfree MB, Hore TA, Shaw G, Graves JA, Pask AJ. Evolution of genomic imprinting: insights from marsupials and monotremes. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2009;10:241–62.
Suzuki S, Ono R, Narita T, Pask AJ, Shaw G, Wang C, et al. Retrotransposon silencing by DNA methylation can drive mammalian genomic imprinting. PLoS Genet. 2007;3:e55.
Barbaux S, Gascoin-Lachambre G, Buffat C, Monnier P, Mondon F, Tonanny MB, et al. A genome-wide approach reveals novel imprinted genes expressed in the human placenta. Epigenetics. 2012;7:1079–90.
Proudhon C, Duffie R, Ajjan S, Cowley M, Iranzo J, Carbajosa G, et al. Protection against de novo methylation is instrumental in maintaining parent-of-origin methylation inherited from the gametes. Mol Cell. 2012;47:909–20.
Court F, Tayama C, Romanelli V, Martin-Trujillo A, Iglesias-Platas I, Okamura K, et al. Genome-wide parent-of-origin DNA methylation analysis reveals the intricacies of human imprinting and suggests a germline methylation-independent mechanism of establishment. Genome Res. 2014;24:554–69.
Angiolini E, Fowden A, Coan P, Sandovici I, Smith P, Dean W, et al. Regulation of placental efficiency for nutrient transport by imprinted genes. Placenta. 2006;27(Suppl A):S98–102.
Ferguson-Smith AC, Moore T, Detmar J, Lewis A, Hemberger M, Jammes H, et al. Epigenetics and imprinting of the trophoblast—a workshop report. Placenta. 2006;27(Suppl A):S122–6.
Messerschmidt DM. Should I, stay or should I go: protection and maintenance of DNA methylation at imprinted genes. Epigenetics. 2012;7:969–75.
Fowden AL, Coan PM, Angiolini E, Burton GJ, Constancia M. Imprinted genes and the epigenetic regulation of placental phenotype. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011;106:281–8.
Varmuza S, Miri K. What does genetics tell us about imprinting and the placenta connection? Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72:51–72.
Rahnama F, Shafiei F, Gluckman PD, Mitchell MD, Lobie PE. Epigenetic regulation of human trophoblastic cell migration and invasion. Endocrinology. 2006;147:5275–83.
Serman L, Vlahovic M, Sijan M, Bulic-Jakus F, Serman A, Sincic N, et al. The impact of 5-azacytidine on placental weight, glycoprotein pattern and proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in rat placenta. Placenta. 2007;28:803–11.
Constancia M, Hemberger M, Hughes J, Dean W, Ferguson-Smith A, Fundele R, et al. Placental-specific Igf-Ii Is a major modulator of placental and fetal growth. Nature. 2002;417:945–8.
Yin LJ, Zhang Y, Lv PP, He WH, Wu YT, Liu AX, et al. Insufficient maintenance DNA methylation is associated with abnormal embryonic development. BMC Med. 2012;10:26.
Banister CE, Koestler DC, Maccani MA, Padbury JF, Houseman EA, Marsit CJ. Infant growth restriction is associated with distinct patterns of DNA methylation in human placentas. Epigenetics. 2011;6:920–7.
Salas M, John R, Saxena A, Barton S, Frank D, Fitzpatrick G, et al. Placental growth retardation due to loss of imprinting of Phlda2. Mech Dev. 2004;121:1199–210.
Diplas AI, Lambertini L, Lee MJ, Sperling R, Lee YL, Wetmur J, et al. Differential expression of imprinted genes in normal and Iugr human placentas. Epigenetics. 2009;4:235–40.
Kumar N, Leverence J, Bick D, Sampath V. Ontogeny of growth-regulating genes in the placenta. Placenta. 2012;33:94–9.
McMinn J, Wei M, Schupf N, Cusmai J, Johnson EB, Smith AC, et al. Unbalanced placental expression of imprinted genes in human intrauterine growth restriction. Placenta. 2006;27:540–9.
Apostolidou S, Abu-Amero S, O'Donoghue K, Frost J, Olafsdottir O, Chavele KM, et al. Elevated placental expression of the imprinted Phlda2 gene is associated with low birth weight. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007;85:379–87.
Guo L, Choufani S, Ferreira J, Smith A, Chitayat D, Shuman C, et al. Altered gene expression and methylation of the human chromosome 11 imprinted region in small for gestational age (Sga) placentae. Dev Biol. 2008;320:79–91.
Koukoura O, Sifakis S, Soufla G, Zaravinos A, Apostolidou S, Jones A, et al. Loss of imprinting and aberrant methylation of Igf2 in placentas from pregnancies complicated with fetal growth restriction. Int J Mol Med. 2011;28:481–7.
Bourque DK, Avila L, Penaherrera M, von Dadelszen P, Robinson WP. Decreased placental methylation at the H19/Igf2 imprinting control region is associated with normotensive intrauterine growth restriction but not preeclampsia. Placenta. 2010;31:197–202.
Ruebner M, Strissel PL, Langbein M, Fahlbusch F, Wachter DL, Faschingbauer F, et al. Impaired cell fusion and differentiation in placentae from patients with intrauterine growth restriction correlate with reduced levels of herv envelope genes. J Mol Med (Berl). 2010;88:1143–56.
Ruebner M, Strissel PL, Ekici AB, Stiegler E, Dammer U, Goecke TW, et al. Reduced syncytin-1 expression levels in placental syndromes correlates with epigenetic hypermethylation of the Ervw-1 promoter region. PLoS One. 2013;8:e56145.
Reamon-Buettner SM, Buschmann J, Lewin G. Identifying placental epigenetic alterations in an intrauterine growth restriction (Iugr) rat model induced by gestational protein deficiency. Reprod Toxicol. 2014;45:117–24.
Ferreira JC, Choufani S, Grafodatskaya D, Butcher DT, Zhao C, Chitayat D, et al. Wnt2 promoter methylation in human placenta is associated with low birthweight percentile in the neonate. Epigenetics. 2011;6:440–9.
Michels KB, Harris HR, Barault L. Birthweight, maternal weight trajectories and global DNA methylation of line-1 repetitive elements. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25254.
Kanayama N, Takahashi K, Matsuura T, Sugimura M, Kobayashi T, Moniwa N, et al. Deficiency in P57kip2 expression induces preeclampsia-like symptoms in mice. Mol Hum Reprod. 2002;8:1129–35.
Blair JD, Yuen RK, Lim BK, McFadden DE, von Dadelszen P, Robinson WP. Widespread DNA hypomethylation at gene enhancer regions in placentas associated with early-onset pre-eclampsia. Mol Hum Reprod. 2013;19:697–708.
Khalkhali-Ellis Z. Maspin: the new frontier. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:7279–83.
Dokras A, Gardner LM, Kirschmann DA, Seftor EA, Hendrix MJ. The tumour suppressor gene maspin is differentially regulated in cytotrophoblasts during human placental development. Placenta. 2002;23:274–80.
Chelbi ST, Mondon F, Jammes H, Buffat C, Mignot TM, Tost J, et al. Expressional and epigenetic alterations of placental serine protease inhibitors: serpina3 is a potential marker of preeclampsia. Hypertension. 2007;49:76–83.
Chelbi ST, Wilson ML, Veillard AC, Ingles SA, Zhang J, Mondon F, et al. Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms collaborate to control serpina3 expression and its association with placental diseases. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:1968–78.
Huang Q, Chen H, Li J, Oliver M, Ma X, Byck D, et al. Epigenetic and non-epigenetic regulation of syncytin-1 expression in human placenta and cancer tissues. Cell Signal. 2014;26:648–56.
Yu L, Chen M, Zhao D, Yi P, Lu L, Han J, et al. The H19 gene imprinting in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Placenta. 2009;30:443–7.
Anton L, Brown AG, Bartolomei MS, Elovitz MA. Differential methylation of genes associated with cell adhesion in preeclamptic placentas. PLoS One. 2014;9:e100148.
Lazaraviciute G, Kauser M, Bhattacharya S, Haggarty P. A systematic review and meta-analysis of dna methylation levels and imprinting disorders in children conceived by Ivf/Icsi compared with children conceived spontaneously. Hum Reprod Update. 2014;20(6):840–52.
Vermeiden JP, Bernardus RE. Are imprinting disorders more prevalent after human in vitro fertilization or intracytoplasmic sperm injection? Fertil Steril. 2013;99:642–51.
van Montfoort AP, Hanssen LL, de Sutter P, Viville S, Geraedts JP, de Boer P. Assisted reproduction treatment and epigenetic inheritance. Hum Reprod Update. 2012;18:171–97.
Doherty AS, Mann MR, Tremblay KD, Bartolomei MS, Schultz RM. Differential effects of culture on imprinted H19 expression in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Biol Reprod. 2000;62:1526–35.
Fauque P, Jouannet P, Lesaffre C, Ripoche MA, Dandolo L, Vaiman D, et al. Assisted reproductive technology affects developmental kinetics, H19 imprinting control region methylation and H19 gene expression in individual mouse embryos. BMC Dev Biol. 2007;7:116.
Liang XW, Cui XS, Sun SC, Jin YX, Heo YT, Namgoong S, et al. Superovulation induces defective methylation in line-1 retrotransposon elements in blastocyst. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2013;11:69.
Mann MR, Lee SS, Doherty AS, Verona RI, Nolen LD, Schultz RM, et al. Selective loss of imprinting in the placenta following preimplantation development in culture. Development. 2004;131:3727–35.
Market-Velker BA, Fernandes AD, Mann MR. Side-by-side comparison of five commercial media systems in a mouse model: suboptimal in vitro culture interferes with imprint maintenance. Biol Reprod. 2010;83:938–50.
Market-Velker BA, Zhang L, Magri LS, Bonvissuto AC, Mann MR. Dual effects of superovulation: loss of maternal and paternal imprinted methylation in a dose-dependent manner. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19:36–51.
Rivera RM, Stein P, Weaver JR, Mager J, Schultz RM, Bartolomei MS. Manipulations of mouse embryos prior to implantation result in aberrant expression of imprinted genes on day 9.5 of development. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:1–14.
Khosla S, Dean W, Brown D, Reik W, Feil R. Culture of preimplantation mouse embryos affects fetal development and the expression of imprinted genes. Biol Reprod. 2001;64:918–26.
de Waal E, Mak W, Calhoun S, Stein P, Ord T, Krapp C, et al. In vitro culture increases the frequency of stochastic epigenetic errors at imprinted genes in placental tissues from mouse concepti produced through assisted reproductive technologies. Biol Reprod. 2014;90:22.
Fauque P, Mondon F, Letourneur F, Ripoche MA, Journot L, Barbaux S, et al. In vitro fertilization and embryo culture strongly impact the placental transcriptome in the mouse model. PLoS One. 2010;5:e9218.
Hossain MM, Tesfaye D, Salilew-Wondim D, Held E, Proll MJ, Rings F, et al. Massive deregulation of Mirnas from nuclear reprogramming errors during trophoblast differentiation for placentogenesis in cloned pregnancy. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:43.
Katari S, Turan N, Bibikova M, Erinle O, Chalian R, Foster M, et al. DNA methylation and gene expression differences in children conceived in vitro or in vivo. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18:3769–78.
Yamagishi S, Matsui T, Nakamura K, Yoshida T, Shimizu K, Takegami Y, et al. Pigment-epithelium-derived factor (Pedf) inhibits angiotensin-ii-induced vascular endothelial growth factor (Vegf) expression in molt-3 T cells through anti-oxidative properties. Microvasc Res. 2006;71:222–6.
Fortier AL, Lopes FL, Darricarrere N, Martel J, Trasler JM. Superovulation alters the expression of imprinted genes in the midgestation mouse placenta. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:1653–65.
Niwa H, Toyooka Y, Shimosato D, Strumpf D, Takahashi K, Yagi R, et al. Interaction between Oct3/4 and Cdx2 determines trophectoderm differentiation. Cell. 2005;123:917–29.
Giritharan G, Delle Piane L, Donjacour A, Esteban FJ, Horcajadas JA, Maltepe E, et al. In vitro culture of mouse embryos reduces differential gene expression between inner cell mass and trophectoderm. Reprod Sci. 2012;19:243–52.
Giritharan G, Talbi S, Donjacour A, Di Sebastiano F, Dobson AT, Rinaudo PF. Effect of in vitro fertilization on gene expression and development of mouse preimplantation embryos. Reproduction. 2007;134:63–72.
Bourc'his D, Xu GL, Lin CS, Bollman B, Bestor TH. Dnmt3l and the establishment of maternal genomic imprints. Science. 2001;294:2536–9.
Mercier E, Lissalde-Lavigne G, Gris JC. Jak2 V617f mutation in unexplained loss of first pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1984–5.
Vatin M, Bouvier S, Bellazi L, Montagutelli X, Laissue P, Ziyyat A, et al. Polymorphisms of human placental alkaline phosphatase are associated with in vitro fertilization success and recurrent pregnancy loss. Am J Pathol. 2014;184:362–8.
Pereza N, Ostojic S, Volk M, Kapovic M, Peterlin B. Matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2, 3 and 9 functional single-nucleotide polymorphisms in idiopathic recurrent spontaneous abortion. Reprod Biomed Online. 2012;24:567–75.
Haouzi D, Assou S, Dechanet C, Anahory T, Dechaud H, De Vos J, et al. Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation for in vitro fertilization alters endometrial receptivity in humans: protocol effects. Biol Reprod. 2010;82:679–86.
Horcajadas JA, Riesewijk A, Polman J, van Os R, Pellicer A, Mosselman S, et al. Effect of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation in Ivf on endometrial gene expression profiles. Mol Hum Reprod. 2005;11:195–205.
Ertzeid G, Storeng R. The impact of ovarian stimulation on implantation and fetal development in mice. Hum Reprod. 2001;16:221–5.
Farhi J, Ben-Haroush A, Andrawus N, Pinkas H, Sapir O, Fisch B, et al. High serum oestradiol concentrations in Ivf cycles increase the risk of pregnancy complications related to abnormal placentation. Reprod Biomed Online. 2010;21:331–7.
Imudia AN, Awonuga AO, Doyle JO, Kaimal AJ, Wright DL, Toth TL, et al. Peak serum estradiol level during controlled ovarian hyperstimulation is associated with increased risk of small for gestational age and preeclampsia in singleton pregnancies after in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2012;97:1374–9.
Pelinck MJ, Keizer MH, Hoek A, Simons AH, Schelling K, Middelburg K, et al. Perinatal outcome in singletons after modified natural cycle Ivf and standard Ivf with ovarian stimulation. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2010;148:56–61.
Hu XL, Feng C, Lin XH, Zhong ZX, Zhu YM, Lv PP, et al. High maternal serum estradiol environment in the first trimester is associated with the increased risk of small-for-gestational-age birth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:2217–24.
Mainigi MA, Olalere D, Burd I, Sapienza C, Bartolomei M, Coutifaris C. Peri-implantation hormonal milieu: elucidating mechanisms of abnormal placentation and fetal growth. Biol Reprod. 2014;90:26.
Henningsen AK, Pinborg A, Lidegaard O, Vestergaard C, Forman JL, Andersen AN. Perinatal outcome of singleton siblings born after assisted reproductive technology and spontaneous conception: Danish national sibling-cohort study. Fertil Steril. 2011;95:959–63.
Pelkonen S, Koivunen R, Gissler M, Nuojua-Huttunen S, Suikkari AM, Hyden-Granskog C, et al. Perinatal outcome of children born after frozen and fresh embryo transfer: the finnish cohort study 1995-2006. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:914–23.
Romundstad LB, Romundstad PR, Sunde A, von During V, Skjaerven R, Gunnell D, et al. Effects of technology or maternal factors on perinatal outcome after assisted fertilisation: a population-based cohort study. Lancet. 2008;372:737–43.
Pinborg A, Loft A, Aaris Henningsen AK, Rasmussen S, Andersen AN. Infant outcome of 957 singletons born after frozen embryo replacement: the Danish National Cohort Study 1995-2006. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1320–7.
Pinborg A, Henningsen AA, Loft A, Malchau SS, Forman J, Andersen AN. Large baby syndrome in singletons born after frozen embryo transfer (Fet): is it due to maternal factors or the cryotechnique? Hum Reprod. 2014;29:618–27.
Sazonova A, Kallen K, Thurin-Kjellberg A, Wennerholm UB, Bergh C. Obstetric outcome in singletons after in vitro fertilization with cryopreserved/thawed embryos. Hum Reprod. 2012;27:1343–50.
Amor DJ, Xu JX, Halliday JL, Francis I, Healy DL, Breheny S, et al. Pregnancies conceived using assisted reproductive technologies (Art) have low levels of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-a (Papp-a) leading to a high rate of false-positive results in first trimester screening for Down syndrome. Hum Reprod. 2009;24:1330–8.
Bellver J, Casanova C, Garrido N, Lara C, Remohi J, Pellicer A, et al. Additive Effect of factors related to assisted conception on the reduction of maternal serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein a concentrations and the increased false-positive rates in first-trimester Down syndrome screening. Fertil Steril. 2013;100:1314–20.
Engels MA, Kooij M, Schats R, Twisk JW, Blankenstein MA, van Vugt JM. First-trimester serum marker distribution in singleton pregnancies conceived with assisted reproduction. Prenat Diagn. 2010;30:372–7.
Geipel A, Gembruch U, Berg C. Are first-trimester screening markers altered in assisted reproductive technologies pregnancies? Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2011;23:183–9.
Tul N, Novak-Antolic Z. Serum Papp-a levels at 10-14 weeks of gestation are altered in women after assisted conception. Prenat Diagn. 2006;26:1206–11.
Fournier T, Handschuh K, Tsatsaris V, Guibourdenche J, Evain-Brion D. Role of nuclear receptors and their ligands in human trophoblast invasion. J Reprod Immunol. 2008;77:161–70.
Zhabin SG, Gorin VS, Judin NS. Review: immunomodulatory activity of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A. J Clin Lab Immunol. 2003;52:41–50.
Giorgetti C, Vanden Meerschaut F, De Roo C, Saunier O, Quarello E, Hairion D, et al. Multivariate analysis identifies the estradiol level at ovulation triggering as an independent predictor of the first trimester pregnancy-associated plasma protein-a level in Ivf/Icsi pregnancies. Hum Reprod. 2013;28:2636–42.
Gjerris AC, Loft A, Pinborg A, Christiansen M, Tabor A. First-trimester screening markers are altered in pregnancies conceived after Ivf/Icsi. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2009;33:8–17.
Bourgain C, Devroey P. The endometrium in stimulated cycles for Ivf. Hum Reprod Update. 2003;9:515–22.
Borghese B, Mondon F, Noel JC, Fayt I, Mignot TM, Vaiman D, et al. Gene expression profile for ectopic versus eutopic endometrium provides new insights into endometriosis oncogenic potential. Mol Endocrinol. 2008;22:2557–62.
Szczepanska M, Wirstlein P, Luczak M, Jagodzinski PP, Skrzypczak J. Reduced expression of Hoxa10 in the midluteal endometrium from infertile women with minimal endometriosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2010;64:697–705.
Wu Y, Halverson G, Basir Z, Strawn E, Yan P, Guo SW. Aberrant methylation at Hoxa10 may be responsible for its aberrant expression in the endometrium of patients with endometriosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;193:371–80.
Kim JJ, Taylor HS, Lu Z, Ladhani O, Hastings JM, Jackson KS, et al. Altered expression of Hoxa10 in endometriosis: potential role in decidualization. Mol Hum Reprod. 2007;13:323–32.
Lee B, Du H, Taylor HS. Experimental murine endometriosis induces DNA methylation and altered gene expression in eutopic endometrium. Biol Reprod. 2009;80:79–85.
Chavatte-Palmer P, Camous S, Jammes H, Le Cleac'h N, Guillomot M, Lee RS. Review: placental perturbations induce the developmental abnormalities often observed in bovine somatic cell nuclear transfer. Placenta. 2012;33(Suppl):S99–S104.
Suemizu H, Aiba K, Yoshikawa T, Sharov AA, Shimozawa N, Tamaoki N, et al. Expression profiling of placentomegaly associated with nuclear transplantation of mouse Es cells. Dev Biol. 2003;253:36–53.
Eskild A, Romundstad PR, Vatten LJ. Placental weight and birthweight: does the association differ between pregnancies with and without preeclampsia? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201:595. e1-5.
Haavaldsen C, Samuelsen SO, Eskild A. The association of maternal age with placental weight: a population-based study of 536,954 pregnancies. BJOG. 2011;118:1470–6.
Nelson DB, Ziadie MS, McIntire DD, Rogers BB, Leveno KJ. Placental pathology suggesting that preeclampsia is more than one disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;210:66. e1-7.
Haavaldsen C, Tanbo T, Eskild A. Placental weight in singleton pregnancies with and without assisted reproductive technology: a population study of 536,567 pregnancies. Hum Reprod. 2012;27:576–82.
Coan PM, Vaughan OR, Sekita Y, Finn SL, Burton GJ, Constancia M, et al. Adaptations in placental phenotype support fetal growth during undernutrition of pregnant mice. J Physiol. 2010;588:527–38.
Eckert JJ, Porter R, Watkins AJ, Burt E, Brooks S, Leese HJ, et al. Metabolic induction and early responses of mouse blastocyst developmental programming following maternal low protein diet affecting life-long health. PLoS One. 2012;7:e52791.
Sun C, Velazquez MA, Marfy-Smith S, Sheth B, Cox A, Johnston DA, et al. Mouse early extra-embryonic lineages activate compensatory endocytosis in response to poor maternal nutrition. Development. 2014;141:1140–50.
Constancia M, Kelsey G, Reik W. Resourceful imprinting. Nature. 2004;432:53–7.
Grazul-Bilska AT, Johnson ML, Borowicz PP, Bilski JJ, Cymbaluk T, Norberg SS, et al. Placental development during early pregnancy in sheep: effects of embryo origin on vascularization. Reproduction. 2014;147(5):639–48.
Miles JR, Farin CE, Rodriguez KF, Alexander JE, Farin PW. Effects of embryo culture on angiogenesis and morphometry of bovine placentas during early gestation. Biol Reprod. 2005;73:663–71.
Fidanza A, Toschi P, Zacchini F, Czernik M, Palmieri C, Scapolo P, et al. Impaired placental vasculogenesis compromises the growth of sheep embryos developed in vitro. Biol Reprod. 2014;91:21.
Nelissen EC, Dumoulin JC, Busato F, Ponger L, Eijssen LM, Evers JL, et al. Altered gene expression in human placentas after Ivf/Icsi. Hum Reprod. 2014;29(12):2821–31.
Zhang Y, Cui Y, Zhou Z, Sha J, Li Y, Liu J. Altered global gene expressions of human placentae subjected to assisted reproductive technology treatments. Placenta. 2010;31:251–8.
Varrault A, Gueydan C, Delalbre A, Bellmann A, Houssami S, Aknin C, et al. Zac1 regulates an imprinted gene network critically involved in the control of embryonic growth. Dev Cell. 2006;11:711–22.
Al Adhami H, Evano B, Le Digarcher A, Gueydan C, Dubois E, Parrinello H, et al. A systems-level approach to parental genomic imprinting: the imprinted gene network includes extracellular matrix genes and regulates cell cycle exit and differentiation. Genome Res. 2015;25:353–67.
Iglesias-Platas I, Martin-Trujillo A, Petazzi P, Guillaumet-Adkins A, Esteller M, Monk D. Altered expression of the imprinted transcription factor Plagl1 deregulates a network of genes in the human Iugr placenta. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(23):6275–85.
Camprubi C, Iglesias-Platas I, Martin-Trujillo A, Salvador-Alarcon C, Rodriguez MA, Barredo DR, et al. Stability of genomic imprinting and gestational-age dynamic methylation in complicated pregnancies conceived following assisted reproductive technologies. Biol Reprod. 2013;89:50.
Lewis A, Mitsuya K, Umlauf D, Smith P, Dean W, Walter J, et al. Imprinting on distal chromosome 7 in the placenta involves repressive histone methylation independent of DNA methylation. Nat Genet. 2004;36:1291–5.
Boyer LA, Plath K, Zeitlinger J, Brambrink T, Medeiros LA, Lee TI, et al. Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2006;441:349–53.
Lee TI, Jenner RG, Boyer LA, Guenther MG, Levine SS, Kumar RM, et al. Control of developmental regulators by polycomb in human embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:301–13.
Reik W. Stability and flexibility of epigenetic gene regulation in mammalian development. Nature. 2007;447:425–32.
Melamed N, Choufani S, Wilkins-Haug LE, Koren G, Weksberg R. Comparison of genome-wide and gene-specific DNA methylation between art and naturally conceived pregnancies. Epigenetics. 2015;10(6):474–83.
Shi X, Ni Y, Zheng H, Chen S, Zhong M, Wu F, et al. Abnormal methylation patterns at the Igf2/H19 imprinting control region in phenotypically normal babies conceived by assisted reproductive technologies. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2011;158:52–5.
Wong EC, Hatakeyama C, Robinson WP, Ma S. DNA methylation at H19/Igf2 Icr1 in the placenta of pregnancies conceived by in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil Steril. 2011;95:2524–6. e1-3.
Rancourt RC, Harris HR, Michels KB. Methylation levels at imprinting control regions are not altered with ovulation induction or in vitro fertilization in a birth cohort. Hum Reprod. 2012;27:2208–16.
Tierling S, Souren NY, Gries J, Loporto C, Groth M, Lutsik P, et al. Assisted reproductive technologies do not enhance the variability of DNA methylation imprints in human. J Med Genet. 2010;47:371–6.
Nelissen EC, Dumoulin JC, Daunay A, Evers JL, Tost J, van Montfoort AP. Placentas from pregnancies conceived by Ivf/Icsi have a reduced dna methylation level at the H19 and mest differentially methylated regions. Hum Reprod. 2013;28:1117–26.
Turan N, Katari S, Gerson LF, Chalian R, Foster MW, Gaughan JP, et al. Inter- and intra-individual variation in allele-specific DNA methylation and gene expression in children conceived using assisted reproductive technology. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1001033.
Zechner U, Pliushch G, Schneider E, El Hajj N, Tresch A, Shufaro Y, et al. Quantitative methylation analysis of developmentally important genes in human pregnancy losses after art and spontaneous conception. Mol Hum Reprod. 2010;16:704–13.
Yuen RK, Avila L, Penaherrera MS, von Dadelszen P, Lefebvre L, Kobor MS, et al. Human placental-specific epipolymorphism and its association with adverse pregnancy outcomes. PLoS One. 2009;4:e7389.
Barker DJ. The origins of the developmental origins theory. J Intern Med. 2007;261:412–7.
Isles AR, Holland AJ. Imprinted genes and mother-offspring Interactions. Early Hum Dev. 2005;81:73–7.
Nathanielsz PW. Animal models that elucidate basic principles of the developmental origins of adult diseases. ILAR J. 2006;47:73–82.
Reynolds LP, Caton JS. Role of the pre- and post-natal environment in developmental programming of health and productivity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;354:54–9.
Gillman MW. Developmental origins of health and disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1848–50.
Gluckman PD, Hanson MA, Cooper C, Thornburg KL. Effect of in utero and early-life conditions on adult health and disease. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:61–73.
Simmons RA, Templeton LJ, Gertz SJ. Intrauterine growth retardation leads to the development of type 2 diabetes in the rat. Diabetes. 2001;50:2279–86.
Simmons RA. Developmental origins of adult disease. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2009;56:449–66. Table of Contents.
Barker DJ, Osmond C, Thornburg KL, Kajantie E, Eriksson JG. The lifespan of men and the shape of their placental surface at birth. Placenta. 2011;32:783–7.
Eriksson JG, Kajantie E, Thornburg KL, Osmond C, Barker DJ. Mother's body size and placental size predict coronary heart disease in men. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:2297–303.
Barker DJ, Bull AR, Osmond C, Simmonds SJ. Fetal and placental size and risk of hypertension in adult life. BMJ. 1990;301:259–62.
Hart R, Norman RJ. The longer-term health outcomes for children born as a result of Ivf treatment: part I—general health outcomes. Hum Reprod Update. 2013;19:232–43.
Ceelen M, van Weissenbruch MM, Prein J, Smit JJ, Vermeiden JP, Spreeuwenberg M, et al. Growth during infancy and early childhood in relation to blood pressure and body fat measures at age 8-18 years of Ivf children and spontaneously conceived controls born to subfertile parents. Hum Reprod. 2009;24:2788–95.
Ceelen M, van Weissenbruch MM, Roos JC, Vermeiden JP, van Leeuwen FE. Delemarre-van de Waal HA. Body composition in children and adolescents born after in vitro fertilization or spontaneous conception. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:3417–23.
Ceelen M, van Weissenbruch MM, Vermeiden JP, van Leeuwen FE. Delemarre-van de Waal HA. Growth and development of children born after in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2008;90:1662–73.
Miles HL, Hofman PL, Peek J, Harris M, Wilson D, Robinson EM, et al. In vitro fertilization improves childhood growth and metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:3441–5.
Sakka SD, Loutradis D, Kanaka-Gantenbein C, Margeli A, Papastamataki M, Papassotiriou I, et al. Absence of insulin resistance and low-grade inflammation despite early metabolic syndrome manifestations in children born after in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1693–9.
Portha B, Fournier A, Kioon MD, Mezger V, Movassat J. Early environmental factors, alteration of epigenetic marks and metabolic disease susceptibility. Biochimie. 2014;97:1–15.
Oliver VF, Miles HL, Cutfield WS, Hofman PL, Ludgate JL, Morison IM. Defects in imprinting and genome-wide DNA methylation are not common in the in vitro fertilization population. Fertil Steril. 2012;97:147–53. e7.
Puumala SE, Nelson HH, Ross JA, Nguyen RH, Damario MA, Spector LG. Similar DNA methylation levels in specific imprinting control regions in children conceived with and without assisted reproductive technology: a cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2012;12:33.
Whitelaw N, Bhattacharya S, Hoad G, Horgan GW, Hamilton M, Haggarty P. Epigenetic status in the offspring of spontaneous and assisted conception. Hum Reprod. 2014;29:1452–8.
Rexhaj E, Paoloni-Giacobino A, Rimoldi SF, Fuster DG, Anderegg M, Somm E, et al. Mice generated by in vitro fertilization exhibit vascular dysfunction and shortened life span. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:5052–60.
de Waal E, Yamazaki Y, Ingale P, Bartolomei M, Yanagimachi R, McCarrey JR. Primary epimutations introduced during intracytoplasmic sperm injection (Icsi) are corrected by germline-specific epigenetic reprogramming. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:4163–8.
Ruiz-Alonso M, Blesa D, Diaz-Gimeno P, Gomez E, Fernandez-Sanchez M, Carranza F, et al. The endometrial receptivity array for diagnosis and personalized embryo transfer as a treatment for patients with repeated implantation failure. Fertil steril. 2013;100:818–24.
Maheshwari A, Bhattacharya S. Elective frozen replacement cycles for all: ready for prime time? Hum Reprod. 2013;28:6–9.
Petrussa L, Van de Velde H, De Rycke M. Dynamic regulation of DNA methyltransferases in human oocytes and preimplantation embryos after assisted reproductive technologies. Mol Hum Reprod. 2014;20:861–74.
Gluckman PD, Lillycrop KA, Vickers MH, Pleasants AB, Phillips ES, Beedle AS, et al. Metabolic plasticity during mammalian development is directionally dependent on early nutritional status. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:12796–800.
Malassine A, Frendo JL, Evain-Brion D. A comparison of placental development and endocrine functions between the human and mouse model. Hum Reprod Update. 2003;9:531–9.
Wang H, Dey SK. Roadmap to embryo implantation: clues from mouse models. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:185–99.
Rossant J, Cross JC. Placental development: lessons from mouse mutants. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:538–48.
Basso O, Weinberg CR, Baird DD, Wilcox AJ, Olsen J. Subfecundity as a correlate of preeclampsia: a study within the Danish National Birth Cohort. Am J Epidemiol. 2003;157:195–202.
Pandian Z, Bhattacharya S, Templeton A. Review of unexplained infertility and obstetric outcome: a 10 year review. Hum Reprod. 2001;16:2593–7.
Horsthemke B, Ludwig M. Assisted reproduction: the epigenetic perspective. Hum Reprod Update. 2005;11:473–82.
Christensen BC, Houseman EA, Marsit CJ, Zheng S, Wrensch MR, Wiemels JL, et al. Aging and environmental exposures alter tissue-specific DNA methylation dependent upon Cpg island context. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000602.
Schroeder DI, Blair JD, Lott P, Yu HO, Hong D, Crary F, et al. The human placenta methylome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:6037–42.
Wu FR, Liu Y, Shang MB, Yang XX, Ding B, Gao JG, et al. Differences in H3k4 trimethylation in in vivo and in vitro fertilization mouse preimplantation embryos. Genet Mol Res. 2012;11:1099–108.
Rosenbluth EM, Shelton DN, Sparks AE, Devor E, Christenson L, Van Voorhis BJ. Microrna expression in the human blastocyst. Fertil Steril. 2013;99:855–61. e3.
Clifton VL. Review: sex and the human placenta: mediating differential strategies of fetal growth and survival. Placenta. 2010;31(Suppl):S33–9.
Feil D, Lane M, Roberts CT, Kelley RL, Edwards LJ, Thompson JG, et al. Effect of culturing mouse embryos under different oxygen concentrations on subsequent fetal and placental development. J Physiol. 2006;572:87–96.
Wang Z, Xu L, He F. Embryo vitrification affects the methylation of the H19/Igf2 differentially methylated domain and the expression of H19 and Igf2. Fertil Steril. 2010;93:2729–33.
Gomes MV, Huber J, Ferriani RA, Amaral Neto AM, Ramos ES. Abnormal methylation at the Kvdmr1 imprinting control region in clinically normal children conceived by assisted reproductive technologies. Mol Hum Reprod. 2009;15:471–7.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Charlotte, 12WG. The authors also thank Philip Bastable for the improvement of the English language and Hélène Jammes for comments on the manuscript.
Funding
The research fellowships of Cécile Choux and Virginie Carmignac were supported by the Burgundy University of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
CC and PF played a role in the conception of the review. CC, VC and PF took part in the collection and assembly of data. CC, VC and PF carried out data analysis and interpreted the findings. CC, VC, CB, DV, PS and PF drafted the manuscript. CC, DV and PF wrote the critical discussion. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Choux, C., Carmignac, V., Bruno, C. et al. The placenta: phenotypic and epigenetic modifications induced by Assisted Reproductive Technologies throughout pregnancy. Clin Epigenet 7, 87 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-015-0120-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-015-0120-2