Abstract
Objectives
IL-37 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine involved in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. We aimed to investigate the association between IL-37 genetic variants, IL-37 plasma levels, and various clinical phases of gout.
Methods
The study included a control group with no history of primary hyperuricemia/gout, (n = 50), asymptomatic hyperuricemia (n = 74), intercritical gout (n = 200), acute gouty flare (n = 18), and chronic tophaceous gout (n = 30). Plasma IL-37 was analysed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. All coding regions and intron–exon boundaries of IL-37 and exons 1–5 were amplified and sequenced.
Results
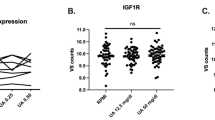
Plasma levels of IL-37 were significantly higher in asymptomatic hyperuricemic (p = 0.045), intercritical gout (p = 0.001), and chronic tophaceous gout (p = 0.021) cohorts when compared to control group. The levels of IL-37 in patients with acute gouty flare were comparable to control group (p = 0.061). We identified 15 genetic variants of IL-37: eight intron (rs2708959, rs2723170, rs2708958, rs2723169 rs2466448, rs3811045, rs3811048, rs2708944) and seven non-synonymous allelic variants (rs3811046, rs3811047, rs2708943, rs2723183, rs2723187, rs2708947, rs27231927), of which rs2708959 showed an over-presentation in gouty and acute flare cohorts (p = 0.003 and 0.033, respectively) compared to European population (minor allelic frequency MAF = 0.05) but not in control and hyperuricemic cohorts (p/MAF = 0.17/0.08 and 0.71/0.05, respectively).. On the contrary, rs3811045, rs3811046, rs3811047, and rs3811048 were underrepresented among individuals with tophaceous gout (MAF = 0.57) compared to European MAF 0.70–0.71, but not compared to the control cohort (MAF = 0.67).
Conclusions
We demonstrated the up-regulation of IL-37 levels across the clinical phases of gout: asymptomatic hyperuricemia, intercritical, and chronic tophaceous gout compared to control. Moreover, 15 genetic variants of IL-37 were identified and their associations with the clinical variants of gout were evaluated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Gout is a chronic disease with deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals, resulting from increased urate concentrations. Patients with gout experience chronic recurring attacks accompanied by a variety of symptoms including inflammation, joint, and renal damage [1]. Hyperuricemia is a risk condition that predisposes a patient to the development of gout [2]. It is characterized by elevated plasma levels of uric acid, leading to MSU crystals formation or tophi deposition, which determines the severity of the symptoms. The genetic background plays an important role in the incidence of gout [1]. Although precise mechanisms have not been explored, the imbalance of the interleukin (IL)-1 cytokine family was thought to be one of the key processes underlying the gout pathology [3].
IL-37 is a unique member of the IL-1 family that functions as a natural suppressor of inflammation [3]. IL-37 is implicated in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune rheumatic diseases [4,5,6,7]; however, only few studies have focused on IL-37 in gout arthritis so far [8]. Initially, Zeng et al. demonstrated enhanced IL-37 expression in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of patients with gout, especially in the non-acute form [9]. Others showed elevation of serum IL-37 in gout patients, particularly in the active tophaceous gout and its association with the levels of C- reactive protein (CRP) and pro-inflammatory cytokines [10]. In vitro, IL-37 suppressed the production of inflammatory cytokines in THP-1 macrophages [9]. Moreover, IL-37 inhibited the immune reaction induced by MSU crystals in human and murine gout models [11]. Additionally, four rare genetic variants of IL-37 have been identified in gout patients, indicating a possible predisposition for the development of gout [12].
It is evident that IL-37 participates in the modulation of the immune response in gout arthritis [8]; however, little is known about the role of the IL-37 gene variation in the pathogenesis of gout. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the link between plasma levels of IL-37 and genetic variants of IL-37 in relation to the development and progression of gout.
Materials and methods
The study cohort included a control group of 50 subjects with no history of primary hyperuricemia/gout, 74 patients with asymptomatic hyperuricemia, 200 patients with intercritical gout, 30 patients with chronic tophaceous gout, and 18 patients with acute gouty flares. Gout patients met the 1977 American Rheumatism Association preliminary classification criteria for acute arthritis of primary gout [13]. Asymptomatic hyperuricemic patients were classified as having serum uric acid (SUA) > 420 μmol/L for men and SUA > 360 μmol/L for women. Patients with secondary gout and other purine metabolic disorders associated with pathological concentrations of SUA were excluded. High-performance liquid chromatography determination of hypoxanthine and xanthine in urine was performed on an Alliance 2695 and a 2998 photodiode array detector (Waters, Milford, MA, USA) as previously described [14]. The analysed cohorts were selected based on uric acid levels from a previously reported set of 250 hyperuricemia/gout patients and 132 control subjects with no history of primary hyperuricemia, gout, or autoimmune disease [15, 16] with descending levels of serum urate. All included subjects were aged 18 years and more. Written informed consent was obtained from each subject, and all tests were performed according to standards set by the institutional ethics committee (project no. 6181/2015). All procedures were carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All demographic, biochemical, and medical treatment data are presented in Table 1.
Plasma samples were collected and stored at – 80 °C until analysis. The levels of C-reactive protein were assessed by a turbidimetric technique using an Olympus Biochemical Analyser (Olympus CO Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). IL-37 in plasma was analysed by the human enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (Adipogen Life Sciences, Liestal, Switzerland).
Genomic DNA was extracted from EDTA-treated whole blood using a Exgene™ Clinic SV (Gene All, Germany). All five protein-coding exons were amplified using PCR and purified using a PCR DNA Fragments Extraction Kit (Geneaid, New Taipei City, Taiwan). DNA sequencing was performed with a DNA sequencer (Applied Biosystems 3130 Genetic Analyzer; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Primer sequences and PCR conditions are available upon request. The reference sequence was defined as version ENST00000263326.
In the pilot analysis, 50 control subjects, 50 subjects with asymptomatic hyperuricemia, 50 patients with intercritical gout, 17 patients with acute gouty flares, and 28 patients with chronic tophaceous gout were genotyped. Variant allele frequencies in the above-mentioned groups were compared with the European MAF (EXAC database) using the binomial test. Variants with statistically significant allele frequency differences compared to the European population (p < 0.05) were genotyped in an expanded cohort of 74 hyperuricemic patients, 200 gout patients, 18 patients with gouty flares, and 30 patients with chronic tophaceous gout.
Variant allele frequencies were compared with the European MAF using the binomial test and with the control group using Fisher’s exact test. Differences in IL-37 levels between control/hyperuricemic/gout groups were compared pairwise, using the two-sample Wilcoxon test with the Benjamini–Hochberg correction for multiple testing. Spearman’s correlation was used to correlate levels of IL-37 and CRP. p values < 0.05 were considered significant. All analyses were performed using the statistical language and environment R, version 4.0.2.
Results
Plasma levels of IL-37 were significantly higher in asymptomatic hyperuricemic (p = 0.045), intercritical gout (p = 0.001), and chronic tophaceous gout (p = 0.021) cohorts when compared to control group. The levels of IL-37 in patients with acute gouty flare were not significantly different from the control group (p = 0.061) (Fig. 1), both without and with Benjamini–Hochberg correction for multiple comparisons.
Of the fifteen variants, only rs2708959 showed a significant difference in the variant allele frequency between the gout/gout flare cohorts and the European population MAF (Table 2). Compared to European MAF = 0.05, we found an allele frequency 0.085 in gout and 0.139 in the gout flare cohorts (p = 0.003 and 0.033, respectively). There was no statistically significant difference from European MAF for the control and asymptomatic hyperuricemic cohorts (p/MAF = 0.17/0.08 and 0.71/0.05, respectively). We have also found that rs3811045, rs3811046, rs3811047, and rs3811048 were underrepresented among individuals with tophaceous gout, with MAF = 0.57 for all four compared to European MAF 0.705, 0.705, 0.703, and 0.704 respectively. In no variants and no cohorts, allele frequencies varied from the frequency in the normouricemic cohort (Table 2).
Discussion
IL-37 is a key suppressor of innate immunity and a master regulator of inflammation at mucosal surfaces. Here, we show that IL-37 is significantly elevated in the plasma of patients with intercritical and tophaceous gout. This evidence supports the implication of IL-37 in the pathogenesis of gout. In the last decade, several research groups have focused on IL-37 and its association with gout [9,10,11]. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to demonstrate an elevation of IL-37 in the plasma of tophaceous gout Caucasian patients. Our findings are congruent with the data of Ding et al. in Chinese gout patients [10] and imply an association of IL-37 with the deposition of MSU crystals. This is further supported by the accumulation of IL-37 in the synovium surrounding the tophus [11] and by in vitro studies using MSU crystals [3, 9, 11]. In contrast to others [10], we found significant differences in the levels of IL-37 in hyperuricemic compared to control subjects. These adverse results may be caused by the fact that our cohort was about five times larger in contrast to the abovementioned study [10]. Moreover, IL-37 was not elevated in the plasma of acute gouty patients compared to controls, which is inconsistent with previous study [10]. This finding is surprising as acute gout is an inflammatory reaction to the deposition of MSU crystals. As our study involved only 20 patients with acute gouty flare, further analysis on a larger cohort is needed to confirm this result. In contrast to Ding et al. who showed an association of IL-37 with clinical inflammatory markers and cytokines in patients with gout [10], we found no correlation between IL-37 and CRP levels. It is well established that anti-rheumatic therapy can suppress inflammation and modify cytokine levels. The study by Ding et al. [10] did not include data on the therapeutic intervention, which makes the comparison with our results rather problematic. Finally, it must be noted that the data on circulating IL-37 vary across the published studies (our study included), and the levels of IL-37 also differ by an order of magnitude [9,10,11]. One reason for the high variability in circulating IL-37 levels is the use of different ELISA kits, as shown in a recently published study [17].
However, no published study has analysed IL-37 levels across the four clinical phases of gout: asymptomatic hyperuricemia, intercritical gout, gouty flares, and chronic tophaceous gout. In our study, we did not find any significant associations of common or rare IL-37 variants with the abovementioned groups; however, we demonstrated a significant underrepresentation of common variants whose functional impact on IL-37 expression or stability is currently unknown.
Clinical studies have demonstrated that IL-37 gene variant rs3811047 G > A is associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis [18] and ankylosing spondylitis [19, 20]. Notably, a recent study by Kluck et al. [12] showed a devastating impact of four rare IL-37 variants (p.A144P, p.G174Dfs*16, p.C181*, and p.N182S) on protein functions in the pathogenesis of gout. However, in our study, we have not identified any rare variants in IL-37 gene. The frequencies of minor alleles for each SNP were compared to published frequencies in dbSNP for cohorts with similar ethnic backgrounds to our subjects, i.e. majority European descent. Of the fifteen identified variants, only rs2708959 showed a significant difference in the variant allele frequency between the hyperuricemic/gout/gout flare cohorts and the European population MAF. Compared to European MAF = 0.05, we found a- significant allele frequency 0.085 in gout and 0.150 in the gout flare cohorts. However, this variant is located in upstream intronic region, and currently, there are no analyses available regarding its impact on IL-37 protein or its association with phenotype. We have also found that rs3811045, rs3811046, rs3811047, and rs3811048 were underrepresented among individuals with tophaceous gout, with MAF = 0.57 for all four compared to European MAF 0.705, 0.705, 0.703, and 0.704, respectively. Upstream intronic variants rs3811045 and rs3811046 have not been investigated in rheumatic diseases; however, a significant association of rs3811045 with an increased risk of COVID-19 [21] and an association of rs3811046 with susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis [22] were recently demonstrated.
Non-synonymous allelic variants 3811046 (p.Gly31Glu, p.Gly31Ala, and/or p.Gly31Val) and 3811047 (p.Thr42Ala, p.Thr42Ser) located in exon 2 are missense variants with reported limit observations. No associations of rs3811046 were found in rheumatoid arthritis [23], open-angle glaucoma [24], and tuberculosis [25]. However, three significant associations were reported in periodontal inflammation [26], COVID-19 [21], and as a decreased genetic risk factor in Graves’ disease [27].
Variant rs3811047 has been associated with susceptibility to or protection against several infectious, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases as ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, auto-immune thyroid disease, Behcet’s disease, and Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease [28]. The current study showed that TG genotype of rs3811046 may increase the risk of developing COVID-19 [21].
This finding may be influenced by study limitations—first, although our sample size of 372 hyperuricemia/gout subjects is large for studies involving deep physiological phenotyping of hyperuricemia/gout, it is quite small for genetic studies, which often include hundreds to thousands of subjects—some functional variants may have gone undetected. Second, we studied genetic variants in transcribed regions and exon–intron boundaries only, and therefore, genetic variants outside these regions would have gone undetected.
The “Common Disease, Multiple Common and Rare Variant” model argues that genetic susceptibility to common diseases such as gout does not reside only in common genetic variants but rather in a multiplicity of individually rare variants with high penetrance. This theory has been fully confirmed by the relationship between hyperuricemia, gout, and functional variants in the major uric acid transporter ABCG (ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member) [15]. Our results suggest that not only rare variants but also reduced presentation of common variants in the IL-37 gene may influence disease progression. Therefore, haplotype analysis is a useful approach to understanding the genetic association between IL37 gene SNPs and diseases, but due to the limited data available, further studies and experimental verifications are necessary.
Conclusion
Taken all together, we showed an elevation of serum IL-37 across the clinical phases of gout compared to controls. Furthermore, the detection of 15 genetic variants of IL-37 and their association with the clinical phases of gout indicates that underrepresentation of common variants in the IL-37 gene may potentially influence progression of gout.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Dalbeth N, Choi HK, Joosten LAB, Khanna PP, Matsuo H, Perez-Ruiz F, et al. Gout Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:69.
Dalbeth N, Phipps-Green A, Frampton C, Neogi T, Taylor WJ, Merriman TR. Relationship between serum urate concentration and clinically evident incident gout: an individual participant data analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:1048–52.
Klück V, Liu R, Joosten LAB. The role of interleukin-1 family members in hyperuricemia and gout. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88: 105092.
Cavalli G, Dinarello CA. Suppression of inflammation and acquired immunity by IL-37. Immunol Rev. 2018;281:179–90.
Chen B, Huang K, Ye L, Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang J, et al. Interleukin-37 is increased in ankylosing spondylitis patients and associated with disease activity. J Transl Med. 2015;13:36.
Ye L, Ji L, Wen Z, Zhou Y, Hu D, Li Y, et al. IL-37 inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: its correlation with disease activity. J Transl Med. 2014;12:69.
Yuan ZC, Wang JM, Huang AF, Su LC, Li SJ, Xu WD. Elevated expression of interleukin-37 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019;22:1123–9.
Nold MF, Nold-Petry CA, Zepp JA, Palmer BE, Bufler P, Dinarello CA. IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:1014–22.
Zeng M, Dang W, Chen B, Qing Y, Xie W, Zhao M, et al. IL-37 inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in MSU crystal-induced inflammatory response. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35:2251–8.
Ding L, Li H, Sun B, Wang T, Meng S, Huang Q, et al. Elevated interleukin-37 associated with tophus and pro-inflammatory mediators in Chinese gout patients. Cytokine. 2021;141: 155468.
Liu L, Xue Y, Zhu Y, Xuan D, Yang X, Liang M, et al. Interleukin 37 limits monosodium urate crystal-induced innate immune responses in human and murine models of gout. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:268.
Klück V, van Deuren RC, Cavalli G, Shaukat A, Arts P, Cleophas MC, et al. Rare genetic variants in interleukin-37 link this anti-inflammatory cytokine to the pathogenesis and treatment of gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:536–44.
Wallace SL, Robinson H, Masi AT, Decker JL, McCarty DJ, Yü TF. Preliminary criteria for the classification of the acute arthritis of primary gout. Arthritis Rheum. 1977;20:895–900.
Stiburkova B, Krijt J, Vyletal P, Bartl J, Gerhatova E, Korinek M, et al. Novel mutations in xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase cause severe hypouricemia: biochemical and molecular genetic analysis in two Czech families with xanthinuria type I. Clin Chim Acta. 2012;413:93–9.
Toyoda Y, Mančíková A, Krylov V, Morimoto K, Pavelcová K, Bohatá J, et al. Functional characterization of clinically-relevant rare variants in ABCG2 identified in a gout and hyperuricemia cohort. Cells. 2019;8:363.
Pavelcova K, Bohata J, Pavlikova M, Bubenikova E, Pavelka K, Stiburkova B. Evaluation of the influence of genetic variants of SLC2A9 (GLUT9) and SLC22A12 (URAT1) on the development of hyperuricemia and gout. J Clin Med. 2020;9:2510.
Santarelli DM, Vincent FB, Rudloff I, Nold-Petry CA, Nold MF, Russo MA. Circulating interleukin-37 levels in healthy adult humans - establishing a reference range. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 708425.
Pei B, Xu S, Liu T, Pan F, Xu J, Ding C. Associations of the IL-1F7 gene polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese Han population. Int J Immunogenet. 2013;40:199–203.
Pan F, Liao F, Xia G, Ge R, Mei Y, Tang X, et al. Association of IL-1F7 gene with susceptibility to human leukocyte antigen-B27 positive ankylosing spondylitis in Han Chinese population. Clin Chim Acta. 2010;411:124–6.
Ge R, Pan F, Liao F, Xia G, Mei Y, Shen B, et al. Analysis on the interaction between IL-1F7 gene and environmental factors on patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a case-only study. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38:2281–4.
Ahmed AA, Ad’hiah AH. Interleukin-37 gene polymorphism and susceptibility to coronavirus disease 19 among Iraqi patients. Meta Gene. 2022;31:100989.
Ali ZA, Mankhi AA, Ad’hiah AH. Interleukin-37 gene polymorphism and susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis among Iraqi patients. Indian J Tuberc. 2022;69:191–200.
Zhang XY, Zuo Y, Li C, Tu X, Xu HJ, Guo JP, et al. IL1F7 gene polymorphism is not associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in the Northern Chinese Han population: a case-control study. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131:171–9.
Mookherjee S, Banerjee D, Chakraborty S, Mukhopadhyay I, Sen A, Ray K. Evaluation of the IL1 gene cluster single nucleotide polymorphisms in primary open-angle glaucoma pathogenesis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2016;20:633–6.
Allam G, Gaber AM, Othman SI, Abdel-Moneim A. The potential role of interleukin-37 in infectious diseases. Int Rev Immunol. 2020;39:3–10.
Cirelli T, Nepomuceno R, Orrico SRP, Rossa C Jr, Cirelli JA, North KE, et al. Validation in a Brazilian population of gene markers of periodontitis previously investigated by GWAS and bioinformatic studies. J Periodontol. 2021;92:689–703.
Yan N, Meng S, Song RH, Qin Q, Wang X, Yao Q, et al. Polymorphism of IL37 gene as a protective factor for autoimmune thyroid disease. J Mol Endocrinol. 2015;55:209–18.
Lin XY, Guo XJ, He YZ, Hou SF, Zhu HB, Cheng Y, et al. Association between interleukin 37 (rs3811047) polymorphism and multiple autoimmune diseases in a Chinese population: a PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97: e0386.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Eliška Tůma Streitová and Veronika Voclonová for sequencing analysis and Xiao Švec for proofreading our manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the grant from the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic NU22-01–00465, RVO 00023728 (Institute of Rheumatology), RVO VFN64165, and BBMRI-CZ LM2018125.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design: BS; acquisition of data: AN, HH, LAC; recruitment of patients and clinical data collection: JZ, KP; analysis and interpretation of data: BS, AN, LAC, MP. LS; writing a manuscript: BS, LAC. All authors were involved in drafting the manuscript or revising it critically for content. All the authors approved the final version for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from each subject, and all tests were performed according to standards set by the local Ethics Committee of the Institute of Rheumatology in Prague, Czech Republic (project no. 6181/2015).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Andres Cerezo, L., Navrátilová, A., Hulejová, H. et al. Interleukin-37: associations of plasma levels and genetic variants in gout. Arthritis Res Ther 25, 203 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-023-03188-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-023-03188-3