Abstract
Background
Aedes albopictus is an increasingly serious threat in public health due to it is vector of multiple arboviruses that cause devastating human diseases, as well as its widening distribution in recent years. Insecticide resistance is a serious problem worldwide that limits the efficacy of chemical control strategies against Ae. albopictus. Chitinase genes have been widely recognized as attractive targets for the development of effective and environmentally safe insect management measures.
Methods
Chitinase genes of Ae. albopictus were identified and characterized on the basis of bioinformatics search of the referenced genome. Gene characterizations and phylogenetic relationships of chitinase genes were investigated, and spatio-temporal expression pattern of each chitinase gene was evaluated using qRT-PCR. RNA interference (RNAi) was used to suppress the expression of AaCht10, and the roles of AaCht10 were verified based on phynotype observations, chitin content analysis and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain of epidermis and midgut.
Results
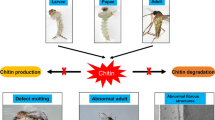
Altogether, 14 chitinase-related genes (12 chitinase genes and 2 IDGFs) encoding 17 proteins were identified. Phylogenetic analysis showed that all these AaChts were classified into seven groups, and most of them were gathered into group IX. Only AaCht5-1, AaCht10 and AaCht18 contained both catalytic and chitin-binding domains. Different AaChts displayed development- and tissue-specific expression profiling. Suppression of the expression of AaCht10 resulted in abnormal molting, increased mortality, decreased chitin content and thinning epicuticle, procuticle and midgut wall of pupa.
Conclusions
Findings of the present study will aid in determining the biological functions of AaChts and also contribute to using AaChts as potential target for mosquito management.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Arthropod-borne viruses transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes, such as dengue, yellow fever, Zika and chikungunya viruses, have been expanding their global distribution in recent years, causing significant human morbidity and mortality in affected regions [1,2,3,4]. No specific therapeutic treatment or effective vaccine is available for these arboviruses, and vector control remains the primary public health intervention to prevent and respond to epidemics [5]. As one of the major vectors of these arboviruses, Aedes albopictus, originating in Southeast Asia, has invaded more than 70 countries and regions worldwide [1]. Further global expansion is expected concerning the increases in global temperature, urbanization and travels [6, 7]. Chemical insecticide is widely used in mosquito-borne disease control and prevention [8, 9]. Besides environmental pollution and non-specific toxicity, frequent and unprecedented quantity of insecticide use exerts an exceptionally strong selective pressure for resistance. Insecticide resistance of mosquitoes to most of the WHO-approved public health insecticides has been reported worldwide [10,11,12].
Chitin is a polymer of β (1,4)-linked N-acetylglucosamine, which is the critical constituent of arthropod exoskeletons (cuticle) and the peritrophic membrane (PM) in midgut [13, 14]. The tough and durable exoskeleton provides physical support and protects insects from external damage, which also restricts the growth of insects [15]. Therefore, the old chitin degraded and new chitin is synthesized periodically to allow for molting and metamorphosis of insects [16]. As chitin is an indispensable structure for survival of insects, the balance of chitin content is crucial for individual development. Meanwhile, chitin is absent in animals and plants [17]. Hence, chitin could be used as target for mosquito control; altering the metabolism pathways to intervene formation or degradation of chitin would be helpful for exploiting novel and environmentally friendly biological control strategies.
Chitinases (Chts) are one of the largest groups of hydrolases that break down glycosidic bonds in chitin and decompose chitin into N-acetylglucosamines [18]. Several studies have been explored utilizing chitinase genes as biocontrol molecule agent to interrupt the molting process of insects, such as Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidopteran) [19], Tribolium castaneum (Coleopteran) [20], Anopheles gambiae (Dipteran) [21] and Locusta migratoria (Neopteran) [22], resulting in abnormal molting and increased mortality. Based on conserved amino acids, protein folding and conserved motifs, chitinases are classified into glycosyl hydrolase family 18 (GH18) and family 19 (GH19) [23]. These two chitinase families possess distinct sequence features and three dimensional (3D) structures; all insect chitinases belong to the GH18 [24]. Besides chitinases, some Cht-like proteins that lack chitinase activity, such as imaginal disc growth factors (IDGFs), are also included in GH18 [24]. Previous studiees have demonstrated that the number of chitinase genes varies in different species; chitinases and Cht-like proteins can be classified into different groups according to amino acid similarities and phylogenetic relationships, and functions of chitinases differ greatly among groups [15, 25]. Several chitinases were found to be essential for insect survival, molting and development [26,27,28]. Downregulating the expression level of insect chitinase genes results in severe phenotypes, including ecdysis disturbance, growth inhibition, pupation failure and death [29].
To explore members of chitinase in Ae. albopictus and the potential to use chitinases as promising targets for mosquito control, a systematic genome-wide investigation of Ae. albopictus chitinase genes was performed. The developmental- and tissue-specific expression patterns of all chitinases in Ae. albopictus (AaCht) were profiled to identify optimal candidate genes that can be used as a target to disrupt the chitin metabolism pathway. Previous work has demonstrated that Group II chitinase (ChtII, also known as chitinase 10) has multiple catalytic and chitin-binding domains, which are indispensable for insect ecdysis at all developmental stages [30]. The functions of chitinase 10 (Cht10) have been assessed by RNA interference (RNAi), and molting defects have been detected in many insect species [25, 31,32,33]. Considering the importance of Cht10 in insects, the function of AaCht10 was explored using RNAi to provide insights to design mosquito control strategy utilizing chitinase.
Materials and methods
Mosquito maintenance
Aedes albopictus samples used in this study were from a colony collected in Shandong Province (China) maintained in a laboratory and reared at 27 ± 1 °C and 65% relative humidity (RH) with a daily photoperiod of 14:10 h (L:D). Adults were maintained in a 10% sucrose solution, and the females were fed mouse blood for egg-laying. The larvae were reared on slurry that was a mixture of pork liver powder (homemade), yeast and distilled water.
Chitinase gene identification and phylogenetic analysis
Chitinase genes of Aedes aegypti (annotated based on Genome version: GCA_000004015.3) and Culex quinquefasciatus (annotated based on Genome version: GCA_015732765.1) downloaded from VectorBase database (https://www.vectorbase.org) were used as query to screen for putative chitinases and IDGFs genes in the reference genome of Ae. albopictus (Genome version: AalbF2, assembly: GCA_006496715.1, NCBI) [34]. Default parameters were used for the analyses (E-value cutoff = 1.0e− 5). Identified candidate chitinase and IDGF genes were compared with the protein database of Ae. albopictus in VectorBase using the BLASTp program [35] with the default settings.
Molecular weight, amino acid numbers and theoretical isoelectric points (pIs) of the chitinase sequences were calculated using ExPASy Proteomics Server (http://cn.expasy.org/tools/pitool.html) [36]. SMART (http://smart.emblheidelberg.de/) was used to confirm the chitin binding, catalytic and transmembrane domains. Multiple sequence alignment and identification of conserved domains were performed using MAFFT (http://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/). Then, the graphical displays of chitinase gene sequences were created using the online Gene Structure Display Server (2.071) (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/).
Altogether, 123 sequences from nine species (Ae. albopictus, Aedes aegypti, An. gambiae, Bactrocera dorsalis, Cx. quinquefasciatus, Drosophila melanogaster, Nilaparvata lugens, T. castaneum and Plutella xylostella) (Additional file 1: Table S1) were used to explore the evolutionary relationships of chitinases. The ClustalW alignment function in MEGA 7.0 [37] was used to align all chitinase sequences. An unrooted neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA 7.0 with 1000 bootstrap replicates. Chitinase and IDGF genes in this study were named as AaCht and AaIDGF; a homology sequence of each gene was represented with numbers.
Total RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis
To evaluate the expression pattern of chitinase genes, samples of different developmental stages and various tissues of pupa were prepared, respectively. Two hundred eggs were collected within 24 h after deposition by blood-fed females, and they were pooled to represent the embryonic stage. Larvae samples were divided into early (I–II instars) and late (III–IV instars) larval stage; 100 early larval and 50 late larval were collected, respectively. Fifty pupae at 12–24 h after pupate were mixed. Fifty male and fifty female adults were collected separately within 12 h after eclosion.
Pupae were first immobilized on an ice box for 6 min and then transferred to precooled PBS solution for dissection, which was performed with forceps while using a dissecting microscope. Four different tissues (cephalothorax, integument, midgut and malpighian tube) from 100 pupae were collected, respectively. All samples were flash frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately following collection and then stored at − 80 °C until RNA isolation.
Total RNA was extracted using RNA isolater total RNA extraction reagent (Vazyme, China) and treated with DNase I (Vazyme, China) to remove genomic DNA. cDNA was synthesized from 1 μl total RNA using HiScript 3 RT SuperMix for qPCR (Vazyme, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality and quantity were detected by 2% agarose gels and ScanDrop spectrophotometer (Jena, Germany).
Real-time quantitative PCR (qRT‒PCR) was carried out using ChamQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme, China) on an ABI7500 qRT-PCR platform (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). Primers used for qRT-PCR were listed in Additional file 1: Table S2. All qRT-PCRs were carried out with 20 μl reaction mixture consisting of 10 μl qPCR Master Mix, 2 μl cDNA templates and 0.4 μl each of forward and reverse primers. The processes were 95 °C for 30 s, 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s and 60 °C for 30 s. Melting curve analysis from 65 °C to 95 °C was conducted to verify a single PCR product. The expression levels of chitinase genes were normalized against β-actin. All experiments were performed in triplicate and repeated three times. The 2−ΔΔCT method was used to estimate the relative expression of chitinase gene [38]. P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Molecular cloning of AaCht10 and double-stranded RNA synthesis
The open reading frame (ORF) of AaCht10 was predicted using the ORF Finder (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html), and E-RNAi (http://www.dkfz.de/signaling/e-rnai3/idseq.php) was used to confirm target sequence of AaCht10 and enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP, used as control) (GenBank accession number: CAA58789). Then, the forward and reverse primers harboring T7 RNA polymerase promoter were designed according to the target sequence of AaCht10 and eGFP. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to amplify the target sequence of AaCht10 using 2 × Phanta Max Master Mix Kit (Vazyme, China) with specific primers (Additional file 1: Table S3). PCR reactions were set up in total volume of 50 μl, consisting of 25 μl Phanta Max Master Mix, 5 μl template DNA and 2 μl each of forward and reverse primers. PCR was performed by initially denaturing the cDNA template for 3 min at 95 °C followed by 35 cycles consisting of 15 s at 95 °C, 15 s at 60 °C, 60 s at 72 and a final extension step for 5 min at 72 °C. FastPure Gel DNA Extractin Mini Kit (Vazyme, China) was used to purify the PCR product, which was then cloned into a 5 min TM TA/Blunt-Zero Cloning Kit (Vazyme, China) for sequencing from both directions. The positive recombinant plasmid was purified using FastPure Plasmid Mini Kit (Vazyme, China). Afterwards, using the same PCR conditions as mentioned above, the plasmid DNA was amplified and used as template for synthesis of dsAaCht10 and dseGFP using T7 RNAi Transcription Kit (Vazyme, China).
Verification of RNAi-mediated AaCht10 silencing
The concentration of purified dsRNA was measured using ScanDrop spectrophotometer (Jena, Germany). The pupae at 12 h after pupate were selected for injection. Microinjector was carried out using Nanoject III (Drummond, USA); 750 ng (0.025 μl of 0.3 μg/μl) dsAaCht10 was injected into pupa from the dorsal cuticle between the thorax and abdomen under the dissecting microscope [39]. Two control groups, i.e. dseGFP group (pupae injected with dseGFP) and control (non-injected pupae, Non-inj) were used in this study. All experiments were repeated three times.
Living pupae were collected at 12 h, 24 h and 36 h after dsRNA treatment, respectively. qRT-PCR was performed to evaluate the effects of dsAaCht10 on gene expression. The survival, malformation and eclosion rates were analyzed at 12 h, 24 h, 36 h, 48 h and 72 h after dsAaCht10 injection had been performed. Malformation phenotypes were observed under optical microscope, and the Leica Application Suite V4 program was used to take photos (Leica Microsystems, Switzerland).
Analysis of chitin content after RNAi
The method used to estimate chitin content referred to Arakane et al. (2005) [40] with some modifications. To be specific, samples at 12 h, 24 h and 36 h after treatment were collected and put into an oven (65 °C for 1 h). Then, dried samples were weighed and added to a glass grinding tube containing 1 ml sterilized ddH2O. Homogenates were transferred to new microfuge tubes (1.5 ml) and centrifuged at 5000 r/min for 15 min at room temperature, and the supernatant was discarded. The pellet was suspended in 400 μl 3% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and then heated at 100 °C for 15 min. After cooling, samples were centrifuged at 5000 r/min for 10 min, and the supernatant was discarded. The pellet was suspended in 500 μl sterilized ddH2O and then centrifuged at 5000 r/min for 10 min, and the supernatant was discarded. We added 300 μl 120% KOH to suspend the pellet and heated the samples at 130 °C for 60 min. Samples were mixed with 800 μl precooled 75% ethanol and put on ice for 15 min. After adding 30 μl 5% diatomite suspension, the samples were stirred and then centrifuged at 5000 r/min for 5 min at 4 °C, and the supernatant was discarded. The pellet was washed once using precooled 40% ethanol and then washed twice using sterilized ddH2O. Precooled sterilized ddH2O (500 μl) was used to suspend the pellet and then transfer 100 μl suspension to new microfuge tubes (1.5 ml). After mixing with 50 μl 10% NaNO2 and 50 μl 10% KHSO4, the sample was centrifuged at 5000 r/min for 15 min at 4 °C. Then, the supernatant (60 μl) was transferred to new microfuge tubes and mixed with 20 μl NH4SO3NH2. We added 20 µl freshly prepared 0.5% 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazine (MBTH) to the samples, heated them at 99 °C for 3 min and added 20 μl FeCl3 after the samples had cooled down. We transferred 100 μl of each sample to an ELISA plate, and the absorbance at 630 nm was recorded. Using acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) as template, a standard curve was drawn based on the absorbance of different concentrations (500, 400, 300, 200, 100, 80, 60, 40, 20 and 0 μg/ml).
Hematoxylin and eosin stain
To explore the effect of AaCht10 on chitin metabolism, tissue sections and hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain were performed for microscopic examination. Pupae at 36 h after injection of dsAaCht10 were chosen. Epidermis and midgut sections were obtained by transecting the middle of the third abdomen of the pupae. The dissected samples were fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde and then rinsed with running ddH2O for 20 min to remove residual paraformaldehyde. Different concentrations of ethanol were used for dehydration (75% for 3 h, 85% for 1 h, 95% for 1 h and 20 min, 100% for 20 min). Transparency was achieved by soaking samples into ethanol/xylene (1:1) mixture solution for 20 min, 100% xylene for 15 min and 100% xylene for 15 min successively. Embedding in paraffin was performed by soaking samples in melted 100% paraffin for 1 h, newly melting 100% paraffin for 2 h, newly melting 100% paraffin for 3 h and then putting samples into an embedded frame for cooling and solidification. Next, 4-μm paraffin sections were made with a RM2125 RST rotary microtome (Leica, Germany). The sections were adhered to slides, dried for 20 min and then deparaffinized using 100% xylene twice, 10 min each time. After washing using different concentrations of ethanol (100%, 95%, 85% and 75%) and ddH2O, the cleaned slide were dyed with hematine for 10 min and then washed use rinsing water for 2 min. Slides were placed in 1% hydrochloric acid (dissolved in ethanol and ddH2O) for 10 s and washed with rinsing water for 2 min. Slides were transferred to 50 °C water for 30 s and washed with rinsing water for 2 min. Counterstaining of slides was carried out with eosin for 5 min, and they were washed with rinsing water for 5 s. Finally, slides were covered and images collected using Pannoramic 250 (3DHISTECH, Hungary).
Statistical analysis
Differences in gene expression levels were assessed using one-way analysis of variance; multiple comparisons were performed post hoc using the Tukey-Kramer honestly significant difference test with Prism 8.0 (GraphPad Software). P-value < 0.05 denoted statistical significance. The survival rate was evaluated using the log-rank test and Mantel-Cox test in Kaplan-Meier method.
Results
Identification and phylogenetic analysis of chitinase genes in Ae. albopictus
Altogether, 14 chitinase-related genes (12 chitinase genes and 2 IDGFs) encoding 17 proteins were identified from the genome sequence of Ae. albopictus (Table 1). These identified putative chitinase-like genes were assigned gene numbers according to the previously identified members of the other insect chitinase-like gene family to which they are most closely related, while genes lacking homogeny were represented by Cht-New (Table 1). The length of predicted chitinase proteins ranged from 306 amino acids (aa) (AaCht-New 2) to 2366 aa (AaCht10). The relative molecular mass ranged from 34.10 kD (AaCht-New 2) to 267.77 kD (AaCht10), and the pIs ranged from 4.18 (AaCht-New 2) to 8.28 (AaIDGF2) (Table 1).
All chitinase genes contained at least one exon, and AaCht5-1 contained 11 exons, the most of all the chitinase genes (Fig. 1A). Domain architecture analysis demonstrated that a signal peptide was found in 11 chitinase proteins. Except for AaCht-New 1 and AaCht-New 2, all other chitinase proteins contained the GH18 catalytic domain; four catalytic domains were found in AaCht5-1 and AaCht10, and two catalytic domains were found in AaCht7 and AaCht20, respectively. In addition, among all these 17 chitinase proteins, chitin binding domains were only detected in five AaChts; there were 1, 4, 1, 3 and 4 chitin binding domains in AaCht5-1, AaCht10, AaCht18, AaCht-New 1 and AaCht-New 2, respectively (Fig. 1B).
Structural features of Aedes albopictus chitinases genes. A Intron and exon structure. Yellow, coding sequence; blue, untranslated regions; black lines, intron. B Domain architectures. Green rectangle, catalytic domain; blue hexagon, chitin-binding domain; red triangle, transmembrane region; horizontal line, linker regions
The results of multiple sequence alignments suggested that 16 AaChts have four conserved motifs, KxxxxxGGW (motif I), FDGxDLDWEYP (motif II), MxYDxxG (motif III) and GxxxWxxDxDD (motif IV), whereas AaCht11 lacks motif IV (Fig. 2). The constitution of amino acid residue analysis showed that residue E in motif II was retained in AaCht2-1, AaCht2-2, AaCht5-1a, AaCht7 (a, b), AaCht10 (b, c, d) and AaCht11 (Fig. 2). Phylogenetic analysis using 123 amino acid sequences from nine insect species (Additional file 1: Table S1) demonstrated that all these chitinase proteins were clustered into nine distinct groups (I–IX). The 17 chitinase proteins of Ae. albopictus were divided into seven groups, and most of them were gathered in group IX. Both AaIDGF2 and AaIDGF4 were clustered into group V with IDGF sequences from other species, and only one AaCht was included in group II (AaCht10), III (AaCht7) and VIII (AaCht11). Furthermore, there were two AaChts in group I (AaCht5-1, AaCht5-2) and group VII (AaCht2-1, AaCht2-2), respectively (Fig. 3).
Phylogenetic relationships of chitinases from different species. Aa, Aedes albopictus; Ae, Aedes aegypti; Ag, Anopheles gambiae; Bd, Bactrocera dorsalis; Cq, Culex quinquefasciatus; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; Nl, Nilaparvata lugens; Px, Plutella xylostella; Tc, Tribolium castaneum. Numbers at branches are bootstrap support values. The red dots represent the chitinases of Ae. albopictus
Temporal-spatio expression patterns of AaChts
The expression level of all AaChts in different developmental stages were evaluated. According to the results of qRT-PCR, AaCht17 and AaIDGF2 showed high expression merely in eggs; eight AaChts (AaCht1-2, AaCht2-1, AaCht2-2, AaCht5-1, AaCht5-2, AaCht11, AaCht20 and AaCht-New 3) were highly expressed in egg, followed by pupa; AaCht10, AaCht18, AaCht-New 2, AaCht7 and AaIDGF4 had peak expression in pupa; AaCht-New 1 was expressed at a high level in late larval stages (Fig. 4).
Among four tissues of pupae, relatively high expression of AaCht2-1, AaCht2-2 and AaCht10 was found in both cephalothorax and integument; AaCht7, AaCht11, AaCht17, AaCht18 and AaCht20 were expressed at high levels in cephalothorax; the highest expression levels of AaCht5-1, AaCht5-2, AaIDGF2 and AaIDGF4 were detected in integuments; AaCht1-2, AaCht-New 1, AaCht-New 2 and AaCht-New 3 were highly expressed in the midgut, whereas all genes showed relatively low expression in malpighian tubes (Fig. 5).
Verification of effective of RNAi
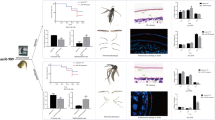
After injection of dsRNA, qRT-PCR was performed to evaluate gene expression levels at 12 h, 24 h and 36 h, respectively. Results showed that the expression levels of AaCht10 were significantly downregulated by 84.9% (P < 0.0001), 93.8% (P < 0.0001) and 74.7% (P < 0.0001) compared with the Non-inj group and suppressed by 82.1% (P < 0.0001), 92.0% (P < 0.0001) and 69.0% (P = 0.0003) compared with the dseGFP group (Fig. 6A).
Effects of deficiency of AaCht10 on pupae
One hundred sixty pupae in each group were used to evaluate the survival rate, and results suggested that, compared with the Non-inj group, the mortality of pupae was significantly increased at 48 h, 60 h and 72 h after injection of dsAaCht10. At 72 h, the survival rate of the treated group was reduced to 34.4%, which was significantly decreased by 61.3% (P < 0.05) and 43.9% (P < 0.05) compared to the Non-inj group and dseGFP group, respectively (Fig. 6B; Table 2). Correspondingly, a significant difference in eclosion rate was detected at 60 h and 72 h. Only 55 pupae in the dsAaCht10-treated group were in eclosion, while 98 and 142 pupae were successfully in eclosion in the dseGFP group and Non-inj group (Fig. 6C; Table 3). Two kinds of malformations were detected in adult mosquitoes in the dsAaCht10-treated group. The first was splitting of the pupal cuticle, where adult mosquitoes failed to detach from the pupal shell completely; in the second, newly emerged adult mosquitoes could not fly because of deformed wings (Fig. 6D). The malformation rate in the dsAaCht10-treated group was up to 15%.
The chitin content assay indicated that there was no significant difference in the chitin content among groups at 12 h and 24 h after silencing of AaCht10. However, the average chitin content of pupae in the dsAaCht10-treated group was 5.0 mg/g at 36 h, much lower than that of dseGFP (9.2 mg/g) (P < 0.0001) and Non-inj groups (8.8 mg/g) (P < 0.0001) (Fig. 6E). The result of H&E staining suggested that the average thickness of the epicuticle in the dsAaCht10-treated group was 1.49 ± 0.1 µm, which was obviously thinner than in the dseGFP (2.42 ± 0.14 µm) and Non-inj groups (2.56 ± 0.06 µm); the thickness of the procuticle (1.05 ± 0.03 µm) in the treated group showed no significant difference compared with the dseGFP group (1.35 ± 0.15 µm), but it was much thinner than in the control group (2.23 ± 0.24 µm) (Fig. 7A). A similar result was also detected in the midgut; the midgut wall in the treated group (12.17 ± 0.21 µm) was significantly thinner than in the dseGFP (18.89 ± 0.35 µm) and Non-inj (16.14 ± 0.19 µm) groups (Fig. 7B).
Discussion
Chitin represents up to 60% of dry weight in some insect species, which illustrates the importance of this component for insect survival [41]. As one of the structural components essential for insect growth and development, many studies have attempted to disrupt the regulatory pathways of chitin biosynthesis and degradation to control pests [42,43,44,45].
Chitinases are a large family of enzymes that degrade chitin by hydrolysis [46]; they differ substantially in their enzymatic properties, stage- and tissue-specific expression, domain organization and size [30, 31, 47]. A total of 17 Cht-related proteins were identified based on a genome-wide screen of the Ae. albopictus genome in this study. Previous research demonstrated that insect chitinases clustered into eight groups based on phylogenetic analysis of their catalytic domains [48], while AaChts were clustered into seven groups. Except for several members that were in accordance with the previous model of evolution of the chitinase family GH18 [25, 48], most of the AaChts were gathered with chitinases of Ae. aegypti and Cx. quinquefasciatus in group IX (Fig. 3). Cht1 and Cht3 in D. melanogaster were designated as portions of DmCht10 [15], whereas Cht1 of Ae. albopictus, Ae. aegypti and Cx. quinquefasciatus was identified and included in group IX (Fig. 3). This differential in composition of chitinase members among species may be driven by functional differentiation with the evolution of chitinase gene families. Consistent with the previous studies that showed only one member in group I in all insects with the exception of An. gambiae and Ae. aegypti [48], phylogenetic analysis showed that two chitinase members (AaCht5-1, AaCht5-2) were clustered into group I in Ae. albopictus (Fig. 3). Similarly, there were two members in AaCht1 (AaCht1-1, AaCht1-2) and AaCht2 (AaCht2-1, AaCht2-2), which were classified into group VII and IX, respectively. These results were caused by gene duplications resulting in two or more additional members [48, 49]. Duplicated genes may gain new structures and functions over the process of biological evolution, resulting in chitinases with different numbers among species, diverse functions and expression patterns [50, 51]. Notably, the numbers in the nomenclature of chitinases were assigned based on their sequence similarities to the correspondingly numbered Chts from other insect species. However, no orthologous genes were currently found for chitinase genes of AaCht-New 1, AaCht-New 2 and AaCht-New 3. Further investigations are needed to rename these chitinases and exploit their properties and physiological functions.
Domain architecture analysis demonstrated that the number of catalytic and chitin-binding domains was different among different chitinases; only AaCht5-1, AaCht10 and AaCht18 possess both of these two important domains (Fig. 1B). Chitin-binding domain is supposed to anchor the enzyme tightly onto the large insoluble polymeric substrate, facilitating the hydrolytic process catalyzed by catalytic domain [52, 53]. The degradative process of chitin is a dynamic process that requires coordinated action of both domains [52]. Therefore, AaCht5-1, AaCht10 and AaCht18 would be priority selections as a target used for Ae. albopictus control. According to previous studies, the glutamate residue (E) in motif II is the most critical residue, which is likely to be the proton donor required for cleavage of the glycosidic bond. Replacement of this residue with others resulted in total loss of activity [54]. Except for AaCht2-1, AaCht2-2, AaCht5-1a, AaCht7 (a, b), AaCht10 (b, c, d) and AaCht11, residue E in the amino acid sequence of all other chitinases has been replaced by other residues (Fig. 2), indicating that catalytic ability of these chitinases might be inactive. In addition, the developmental and tissue expression patterns suggested that chitinase genes are stage- and tissue-specific (Figs. 4, 5), which further support that these genes may have distinct functions involved in the specific stage transition and turnover of chitin in specific tissue. Results of these analyses will give clues toward choosing a suitable chitinase as a candidate target for mosquito control.
Although this is the first experimental evidence for the potential function of chitinase in Ae. albopictus to our knowledge, several studies have demonstrated that chitinases (e.g. Cht10) are essential for insect survival, molting and development [19,20,21,22, 29, 33, 49, 55, 56]. Based on the results of this study, AaCht10 contains both catalytic and chitin-binding domains, retains residue E in motif II and is expressed in multiple stages and tissues. The function of AaCht10 was verified using RNAi, and results suggested that injection of dsAaCht10 caused high mortality (about 65.6% in the injected group) (Fig. 6B; Table 2) and significantly reduced the eclosion rate of pupae (Fig. 6C; Table 3). Furthermore, several adult survivors after dysfunction of AaCht10 displayed defective morphology (e.g. failed to shed the old cuticle, wrinkled wings) (Fig. 6D). Similar results were also reported in P. xylostella and Sogatella furcifera; silencing of PxCht10 and SfCht10 caused high mortalities and lethal phenotypes [57, 58]. The high levels of mortality and developmental arrest after silencing AaCht10 demonstrated that AaCht10 is crucial for shedding of the old cuticular shell and eclosion of pupae, which can be used as a promising target to disrupt the pupa-adult transition and develop an efficient pesticide for the control of Ae. albopictus.
In addition, the suppression of AaCht10 had a negative impact on chitin content of Ae. albopictus (Fig. 6E), and this result was corroborated by the microstructure shown by H&E stain, which showed that RNAi of AaCht10 resulted in a thinner epicuticle, procuticle and midgut wall (Fig. 7). However, the previous research on D. melanogaster suggested that chitin content was significantly increased in wings of Cht10 knockdown flies [33]. Given that enzymatic properties and tissue-specific expression of chitinases vary with species [30, 31, 47], the inconformity results after dysfunction of Cht10 may be caused by the different tissues used to observe microstructure and quantify chitin content. The significantly reduced thickness of epicuticle, procuticle and midgut wall (Fig. 7) may be caused by reduction of chitin synthesis after dysfunction of AaCht10. Nonetheless, the mechanisms by which AaCht10 influences cuticle metabolism need to be explore in future studies.
Conclusion
In summary, we performed a systematic genome-wide analysis of chitinase genes in Ae. albopictus. Structural features and expression patterns of 17 candidate chitinases were generated, which provide the first comprehensive information for chitinase genes of Ae. albopictus to our knowledge. Differences in their biochemical properties reinforce the notion of distinctive biological functions for specific AaCht. The high efficiency of AaCht10 in disrupted pupa-adult transition presents an opportunity to make use of AaChts as efficient targets in mosquito control.
Availability of data and materials
The authors declare that all the data related to this study are cited in the text, and data are also available in additional files.
References
Benelli G, Wilke A, Beier JC. Aedes albopictus (Asian Tiger Mosquito). Trends Parasitol. 2020;36:942–3.
Salles TS, da Encarnação S-G, de Alvarenga ESL, Guimarães-Ribeiro V, de Meneses MDF, de Castro-Salles PF, et al. History, epidemiology and diagnostics of dengue in the American and Brazilian contexts: a review. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11:264.
Brady OJ, Hay SI. The global expansion of dengue: how Aedes aegypti mosquitoes enabled the first pandemic arbovirus. Annu Rev Entomol. 2020;65:191–208.
Patterson J, Sammon M, Garg M. Dengue, Zika and chikungunya: emerging arboviruses in the new world. West J Emerg Med. 2016;17:671–9.
Robert MA, Stewart-Ibarra AM, Estallo EL. Climate change and viral emergence: evidence from Aedes-borne arboviruses. Curr Opin Virol. 2020;40:41–7.
Bhatt S, Gething PW, Brady OJ, Messina JP, Farlow AW, Moyes CL, et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature. 2013;496:504–7.
Kraemer MUG, Reiner RC Jr, Brady OJ, Messina JP, Gilbert M, Pigott DM, et al. Past and future spread of the arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Nat Microbiol. 2019;4:854–63.
Li Y, Zhou G, Zhong D, Wang X, Hemming-Schroeder E, David RE, et al. Widespread multiple insecticide resistance in the major dengue vector Aedes albopictus in Hainan Province. China Pest Manag Sci. 2021;77:1945–53.
Lopes RP, Lima JBP, Martins AJ. Insecticide resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus say, 1823 in Brazil: a review. Parasit Vectors. 2019;12:591.
Moyes CL, Vontas J, Martins AJ, Ng LC, Koou SY, Dusfour I, et al. Contemporary status of insecticide resistance in the major Aedes vectors of arboviruses infecting humans. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11:e0005625.
Auteri M, La Russa F, Blanda V, Torina A. Insecticide resistance associated with kdr mutations in Aedes albopictus: an update on worldwide evidences. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:3098575.
Ranson H, N’guessan R, Lines J, Moiroux N, Nkuni Z, Corbel V. Pyrethroid resistance in African anopheline mosquitoes: what are the implications for malaria control? Trends Parasitol. 2011;27:91–8.
Hogenkamp DG, Arakane Y, Zimoch L, Merzendorfer H, Kramer KJ, Beeman RW, et al. Chitin synthase genes in Manduca sexta: characterization of a gut-specific transcript and differential tissue expression of alternately spliced mRNAs during development. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2005;35:529–40.
Doucet D, Retnakaran A. Insect chitin: metabolism, genomics and pest management. Adv Insect Phys. 2012;43:437–511.
Zhu Q, Arakane Y, Banerjee D, Beeman RW, Kramer KJ, Muthukrishnan S. Domain organization and phylogenetic analysis of the chitinase-like family of proteins in three species of insects. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;38:452–66.
Liu SH, Li HF, Yang Y, Yang RL, Yang WJ, Jiang HB. Genome-wide identification of chitinase and chitin deacetylase gene families in the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2018;27:13–22.
Saito S, Odagiri M, Furuya S, Suzuki S, Takayanagi T. Inhibitory effect of chitinases isolated from Semillon grapes (Vitis vinifera) on growth of grapevine pathogens. J Plant Biochem Biot. 2011;20:47–54.
Zhu KY, Merzendorfer H, Zhang W, Zhang J, Muthukrishnan S. Biosynthesis, turnover, and functions of chitin in insects. Annu Rev Entomol. 2016;61:177–96.
Khajuria C, Buschman LL, Chen M-S, Muthukrishnan S, Zhu KY. A gut-specific chitinase gene essential for regulation of chitin content of peritrophic matrix and growth of Ostrinia nubilalis larvae. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2010;40:621–9.
Arakane Y, Specht CA, Kramer KJ, Muthukrishnan S, Beeman RW. Chitin synthases are required for survival, fecundity and egg hatch in the red flour beetle. Tribolium castaneum Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;38:959–62.
Zhang X, Zhang J, Zhu K. Chitosan/double-stranded RNA nanoparticlemediated RNA interference to silence chitin synthase genes through larval feeding in the African malaria mosquito (Anopheles gambiae). Insect Mol Biol. 2010;19:683–93.
Zhang J, Liu X, Zhang J, Li D, Sun Y, Guo Y. Silencing of two alternative splicing-derived mRNA variants of chitin synthase 1 gene by RNAi is lethal to the oriental migratory locust, Locusta migratoria manilensis (Meyen). Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2010;40:824–33.
Henrissat B. Classification of chitinases modules. EXS. 1999;87:137–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-8757-1_10.
Funkhouser JD, Aronson NN Jr. Chitinase family GH18: evolutionary insights from the genomic history of a diverse protein family. BMC Evol Biol. 2007;7:96.
Tetreau G, Cao X, Chen YR, Muthukrishnan S, Jiang H, Blissard GW, et al. Overview of chitin metabolism enzymes in Manduca sexta: identification, domain organization, phylogenetic analysis and gene expression. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2015;62:114–26.
Tachu B, Pillai S, Lucius R, Pogonka T. Essential role of chitinase in the development of the filarial nematode Acanthocheilonema viteae. Infect Immun. 2008;76:221–8.
Ganbaatar O, Cao B, Zhang Y, Bao D, Bao W, Wuriyanghan H. Knockdown of Mythimna separata chitinase genes via bacterial expression and oral delivery of RNAi effectors. BMC Biotechnol. 2017;17:9.
Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhang S, Kong X, Liu F, Zhang Z. RNAi-mediated silencing of the chitinase 5 gene for fall webworm (Hyphantria cunea) can inhibit larval molting depending on the timing of dsRNA injection. Insects. 2021;12:406.
Muthukrishnan S, Merzendorfer H, Arakane Y, Yang Q. Chitin organizing and modifying enzymes and proteins involved in remodeling of the insect cuticle. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1142:83–114.
Merzendorfer H, Zimoch L. Chitin metabolism in insects: structure, function and regulation of chitin synthases and chitinases. J Exp Biol. 2003;206:4393–412.
Zhu Q, Arakane Y, Beeman RW, Kramer KJ, Muthukrishnan S. Functional specialization among insect chitinase family genes revealed by RNA interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:6650–5.
Su C, Tu G, Huang S, Yang Q, Shahzad MF, Li F. Genome-wide analysis of chitinase genes and their varied functions in larval moult, pupation and eclosion in the rice striped stem borer. Chilo suppressalis Insect Mol Biol. 2016;25:401–12.
Dong W, Gao YH, Zhang XB, Moussian B, Zhang JZ. Chitinase 10 controls chitin amounts and organization in the wing cuticle of Drosophila. Insect Sci. 2020;27:1198–207.
Palatini U, Masri RA, Cosme LV, Koren S, Thibaud-Nissen F, Biedler JK, et al. Improved reference genome of the arboviral vector Aedes albopictus. Genome Biol. 2020;21:215.
Altschul SF, Lipman DJ. Protein database searches for multiple alignments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87:5509–13.
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud S, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, et al. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In: Walker JM, editor., et al., The proteomics protocols handbook. Totowa: Humana Press; 2005. p. 571–607.
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K. MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform. 2008;9:299–306.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Regna K, Harrison RM, Heyse SA, Chiles TC, Michel K, Muskavitch MA. RNAi trigger delivery into Anopheles gambiae pupae. J Vis Exp. 2016;109:53738.
Arakane Y, Muthukrishnan S, Kramer KJ, Specht CA, Tomoyasu Y, Lorenzen MD, et al. The Tribolium chitin synthase genes TcCHS1 and TcCHS2 are specialized for synthesis of epidermal cuticle and midgut peritrophic matrix. Insect Mol Biol. 2005;14:453–63.
Doucet D, Retnakaran A. Insect chitin: metabolism, genomics and pest management. Adv Insect Physiol. 2012;43:437–511.
Yang X, Yin Q, Xu Y, Li X, Sun Y, Ma L, et al. Molecular and physiological characterization of the chitin synthase B gene isolated from Culex pipiens pallens (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasit Vectors. 2019;12:614.
Zhang C, Hu W, Yu Z, Liu X, Wang J, Xin T, et al. Characterization of chitin synthase A cDNA from Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae) and its response to diflubenzuron. Insects. 2022;13:728.
Chen L, Liu T, Zhou Y, Chen Q, Shen X, Yang Q. Structural characteristics of an insect group I chitinase, an enzyme indispensable to moulting. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014;70:932–42.
Anwar W, Javed MA, Shahid AA, Nawaz K, Akhter A, Ur Rehman MZ, et al. Chitinase genes from Metarhizium anisopliae for the control of whitefly in cotton. R Soc Open Sci. 2019;6:190412.
Kramer KJ, Muthukrishnan S. Insect chitinases: molecular biology and potential use as biopesticides. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1997;27:887–900.
Arakane Y, Dixit R, Begum K, Park Y, Specht CA, Merzendorfer H, et al. Analysis of functions of the chitin deacetylase gene family in Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;39:355–65.
Arakane Y, Muthukrishnan S. Insect chitinase and chitinase-like proteins. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010;67:201–16.
Zhang J, Zhang X, Arakane Y, Muthukrishnan S, Kramer KJ, Ma E, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel chitinase-like gene cluster (AgCht5) possibly derived from tandem duplications in the African malaria mosquito. Anopheles gambiae Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2011;41:521–8.
Zhang J. Evolution by gene duplication: an update. Trends Ecol Evol. 2003;18:292–8.
Ganko EW, Meyers BC, Vision TJ. Divergence in expression between duplicated genes in Arabidopsis. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:2298–309.
Arakane Y, Zhu Q, Matsumiya M, Muthukrishnan S, Kramer KJ. Properties of catalytic, linker and chitin-binding domains of insect chitinase. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;33:631–48.
Boot RG, Blommaart EF, Swart E, Ghauharali-van der Vlugt K, Bijl N, Moe C, et al. Identification of a novel acidic mammalian chitinase distinct from chitotriosidase. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:6770–8.
Lu Y, Zen KC, Muthukrishnan S, Kramer KJ. Site-directed mutagenesis and functional analysis of active site acidic amino acid residues D142, D144 and E146 in Manduca sexta (tobacco hornworm) chitinase. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;32:1369–82.
Xia WK, Shen XM, Ding TB, Niu JZ, Zhong R, Liao CY, et al. Functional analysis of a chitinase gene during the larval-nymph transition in Panonychus citri by RNA interference. Exp Appl Acarol. 2016;70:1–15.
Qu MB, Sun SP, Liu YS, Deng XR, Yang J, Yang Q. Insect group II chitinase OfChtII promotes chitin degradation during larva-pupa molting. Insect Sci. 2021;28:692–704.
Yang X, Zhou C, Long G, Yang H, Chen C, Jin D. Characterization and functional analysis of chitinase family genes involved in nymph-adult transition of Sogatella furcifera. Insect Sci. 2021;28:901–16.
Zhu B, Shan J, Li R, Liang P, Gao X. Identification and RNAi-based function analysis of chitinase family genes in diamondback moth. Plutella xylostella Pest Manag Sci. 2019;75:1951–61.
Funding
The funding was provided from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (no. 81871686).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SA and RZ conceived and designed the experiments; SA, WL and JF performed the experiments and analyzed the data. SA and WL wrote the manuscript. ZZ and RZ edited and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Information on insect protein sequences used for phylogenetic analysis. The protein symbols of Aedes albopictus and Ae. aegypti are temporary names used in this study. Table S2. Primers used for qRT-PCR. Table S3. Primers of dsAaCht10 and dseGFP.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
An, S., Liu, W., Fu, J. et al. Molecular identification of the chitinase genes in Aedes albopictus and essential roles of AaCht10 in pupal-adult transition. Parasites Vectors 16, 120 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-023-05733-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-023-05733-0