Abstract
Newly synthesized ligand 2-(2- acetamidophenyl)-2-oxo-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)acetamide and its copper(II) complex were characterized by elemental analyses, FT-IR, UV–Vis., ESR, 1H-NMR, and thermal analysis along with the theoretical quantum chemical studies. Combined experimental and theoretical DFT (density functional theory) studies showed the ligand to be a tridentate ligand with three coordinate bonds. The complex was suggested to be in a distorted octahedral structure with dx2-y2 ground state. The activation energy, ΔE*; entropy ΔS*; enthalpy ΔH* and order of reaction has been derived from differential thermogravimetric (DTA) curve, using Horowitz–Metzeger method. The nujol mull electronic spectrum of the ligand and Cu(II) complex have been recorded and the difference of the excited and ground state densities has also been theoretically calculated and plotted to investigate the movement of electrons on excitation. The Cu(II) complex was evaluated for its antibacterial activity against two bacterial species, namely Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). Antifungal screening was performed against two species (Condida albicans and Aspergillus flavus). The complex under investigation was found to possess notable biological activity. Molecular docking investigation predicted different types of non-covalent interactions of the synthesized ligand towards Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (ID: 5FXR).
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Currently, the preparation of new copper complexes and investigation of their biological activities for pharmaceutical applications is one of the most dynamic fields. Copper(II) complexes have been found to be more potent than their parent ligands in biological activity [1,2,3,4] as well as in industrial applications [5, 6]. The importance of mononuclear copper complexes also lies in the fact that these can possibly mime the active sites of metalloproteins such as the enzyme galactose oxidase [7] and nitrite reductase [8]. The structural arrangement of the complexes formed can be related to their individual molecular species and to the type and/or position of different substituents in the ligand and metal ions. A deeper understanding of the roles played by pyridine candidates in biological systems may result from the synthesis of their metal complexes. Like these ligand compounds have a wide range of medicinal applications and can coordinate with transition metal ions. Additionally, the development of new metal-based chemotherapeutic agents may be aided by these investigations.
Complexes of di- and polypyridyl ligands with transition metal ions have attracted great attention because of the coordination versatility of such ligands as well as their potential application in a number of biological, catalytic, photoactive and sensor applications [9, 10]. Picolylamine (2-Amino-methylpyridine) derivatives are known as useful chelating ligands for many metal ions. These ligands have become important for their bioinorganic and medicinal purposes [11, 12], and they may bind meridional or vicinal to a metal. Picolylamine can act as a bridging ligand as well [13] but it is known that the bridging mode of chelation of picolylamine is rare in case of copper (II) complexes [14]. The interaction of Cu(II) with various picolylamine derivatives containing substitution at the secondary nitrogen center has also been widely investigated [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25], a number of such complexes are effective reagents for the interaction and the oxidative cleavage of DNA [26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. In order to mediate the direct contact of the metal center with the substrate, the mimetic complexes’ reactivity exhibits dependency on the existence of either labile ligands or “open” coordination sites [33].
Previously, the reaction of N-acetylisatin with some alcohols, different amines and diamine, pyrrolidine and water yielded products resulting from nucleophilic attack at the C-2 carbonyl which led to the heterocyclic ring cleavage [34, 35].
The biological properties of pharmaceutical compounds are significantly influenced by the C-N bond, which is an essential and widely occurring structural motif found in thousands of natural products. In more details, cleaving activated amides selectively at the C-N bond has proven to be an effective and vital method for obtaining a variety of compounds. Recently, significant advancements were achieved and a number of methods for amide activation and C–N bond cleavage were described [36, 37] making amides interesting synthons in organic synthesis. Activated amides are novel acyl or aryl resources that are more effective than traditional acylation reagents like acid anhydride and acyl chloride.
In the present work, we report the synthesis and study of physicochemical and biological activities of of 2-(2-acetamido-phenyl)-2-oxo-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)acetamide and its copper (II) complex. The reaction of N-acetylisatin with 2-aminomethyl pyridine results in the cleavage of heterocyclic ring and lead to the production of 2-(2-acetamido-phenyl)-2-oxo-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)acetamide. Characteristic investigation was performed and computational study via DFT were applied to support the structural and electronic behavior of the synthesized complex. Antimicrobial activity of the studied compound was screened and molecular docking perturbation support the biological behavior.
Experimental
Chemicals used
All chemicals and solvents were obtained from Sigma–Aldrich Chemical Company and used as received.
Synthesis of 2-(2-acetamidophenyl)-2-oxo-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)acetamide
Conventional procedure
To the solution of N-acetylisatin (10 mmol) in acetonitrile (20 mL), pyridin-2-yl-methanamine (10 mmol) was added at room temperature. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The solvent was removed next day under vacuum and the crude product was recrystallized from dichloromethane and hexane (1:2) to obtain the pure product.
Procedure for microwave-irradiation
Employing a multimode reactor (Synthos 3000, Aton Paar GmbH, 1400W maximum magnetron); the initial step was conducted with a Teflon vessel rotor (MF 100). The vessel contained N- acetylisation mixed with pyridin-2-ylmethanamine in small amount of acetonitrile (2–5 mL). The vessel was purged with nitrogen gas for 5 min and then was placed in the corresponding rotor, fixed by screwing down the upper rotor place, and finally the rotor was closed with a protective hood. The vessel was heated for 3 min. at 80 °C and held at the same temperature for a further 2 min (~ 2 bar pressure, 200 W). Cooling was accomplished by a fan (5 min). The final product was dried, and recrystallized from dichloromethane-hexane (1:2).
The product was obtained as light beige crystals; m.p. 142–143 °C; IR peaks (cm−1): 3489 (NH + H-bonded NH), 1744 (C=O), 1697,1628 (C=O amide), 1597 (C=N py). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 2.00 (s, 3H, COCH3), 4.491, 4.503 (m, 2H, CH2), 7.215–7.793 (m, 4H, ArH), 8.502, 8.511 (m, 4H, py), 9.251, 9.263, 9.275 (m, 1H, NHCOCH3), 10.568 (s, 1H, NHCH2).
Preparation of the Cu(II) complex
The Cu(II) complex was prepared by adding a solution of CuCl2·2H2O (0.8524 g, 5 mmol, in 25 mL methanol) to a hot 50 mL methanol solution of the organic ligand, (5 mmol). This solution was refluxed for 3 h. After that, the resulting solution was allowed to evaporate at room temperature to give the turquoise blue Cu(II) complex, which was collected and washed with cold methanol. The product was dried over anhydrous calcium chloride in a desiccator (~ 70% yield). However, our attempts to isolate single crystals suitable for X-ray crystal structure determination were not successful. Thus, theoretical DFT studies were done in order to elucidate the structure of the ligand and complex under study. Scheme 1 displays the synthetic pathway of the studied Cu(II) complex.
The analytical data showed that the turquoise blue complex is mononuclear with a 1:1 (M:L) mole ratio. Molecular formula C16 H21 O6 N3 Cl2 Cu, formula weight (485.805); %C: 39.558 (found: 39.627%), %H: 4.359 (found: 4.122%); %N: 8.649 (found: 8.876%), %O: 19.759 (found: 20.011%), %Cu: 13.079 (found: 13.326). m.p. ˃ 300 °C; IR (cm−1): 3489 (NH + H-bonded NH), 1744 (C=O), 1697,1628 (C=O amide), 1597 (C=N py). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 1.880 (s, 3H, COCH3), 4.581 (m, 2H, CH2), 7.051–7.912 (t, 4H, ArH), 8.077, 8.928 (m, 4H, py), 9.323, 9.709 (m, 1H, NHCOCH3), 10.480, 10.599 (s, 1H, NHCH2).
Physicochemical studies
The elemental analyzer of type 240 Perkin Elmer, was used to perform (C, H and N) elemental analyses. Additionally, content of metal ion was measured using the computer controlled atomic absorption spectrophotometer of type 850-Fisher Jarrell-Ash [1]. IR spectra of the studied ligand and its Cu complex were recorded with a Perkin-Elmer FT-IR of type 1650 spectrophotometer in region of wavenumber 4000–400 cm-1. 1H-NMR spectra were studied using the solvent DMSO-d6 (Merck). The thermal analyses curves were performed using thermal analyzer in platinum crucibles. UV–Vis spectra were studied in range 200-1000 nm. Magnetic properties, involving molar magnetic susceptibility, was measured at 298 K. ESR spectra were studied at room temperature (298 K). All experimental measurements were determined using fresh prepared solutions.
Biological activity
Antimicrobial activity of the Cu(II) complex was conducted using a modeled Kirby–Bauer disc method of diffusion [38]. Practically, growing a certain volume of tested bacteria or fungi (100 µL) fresh media (10 ml) was initiated to reach about 108 cells / mL bacterial growth or 105 cells / mL fungi growth [39]. A definite volume of microbial suspension (100 µL) was used for spreading into plates of agar. The Plates were prepared with filamentous fungi such A. flavus at room temperature(25 °C) for 48 h; Staphylococcus aureus (Gram +) bacteria, Escherichia coli (Gram −) bacteria at 35 to 37 °C for 24 to 48 h, and C. Albicans, as yeast, incubated at 30 °C from 24 to 48 h. The inhibition zone diameters were measured in millimeters [38].
Computational methodology
Density functional theory [40] with hybrid Becke’s three parameters and the Lee–Yang–Parr functional (B3LYP) [41,42,43] using LANL2DZ basis set for the Cu metal centers and 6-31G (d) basis set for the H, C, N and O atoms in the gas phase has been employed in the present investigation [44,45,46]. Full geometry optimizations and vibrational analyses have been performed using the Gaussian 09 software [47]. DFT methods are recurrently used in modelling metal complexes and have good experimental consonance with the infrared frequencies. Gauss-view 5 molecular visualization software with the VEDA 4 software [48] have been used for the vibrational assignments of the normal modes. Theoretical investigation of the electronic structure of the ligand and its metal complex have also been carried out and the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) have been plotted at the same level of theory.
Molecular docking performance
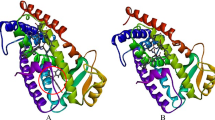
The potent docking pose was predicted for the studied ligand using autodock 4.2. software [49] for conformational calculations and studio discovery (http://www.accelrys.com) program for docking visualization. The protein target was selected for Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (ID: 5FXR). The receptors were prepared by removing any ions, water molecules, small ligands and the addition of polar hydrogens [50]. The crystal structures of the bacterial proteins were obtained from the protein data bank (http://www.rcsb.org./pdb). Initial preparation steps were considered before the docking process started, such as water and hetatoms removal from protein crystallographic structure. additionally, charge adjustment and polar hydrogen inclusion for getting the protein and ligands ready in the right format. The expected active spots were identified and the grid box dimensions were created. The grid box size was approximated with dimensions of 64 × 72 × 60 (Å3), 0.375 Å spacing, and grid centers x, y, and z of 18.822, 2.975 and 49.895, respectively. Genetic Algorithm (LGA) was thought to be the binding affinity mechanism [51, 52].
Results and discussion
The structures of the newly prepared 2-(2-acetamidophenyl)-2-oxo-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-acetamide ligand (L) and its [Cu.L.Cl2.H2O].2H2O complex were studied experimentally using elemental analyses, IR, 1H-NMR, UV–Vis. spectra, thermal analysis, magnetic moment for the copper (II) complex and theoretically using the density functional theory. In the absence of the X-ray crystal structure data of the ligand and its complex, quantum chemical calculations were employed to obtain the ground state optimized structure of the ligand (L) and its complex ([Cu.L.Cl2.H2O].2H2O) (Fig. 1).
Geometry
The structure of the ligand as well as its Cu(II) complex were fully optimized using density functional theory. The stability of both the structures was verified by all positive wave-numbers from the output of frequency calculation. The ground state energies for ligand and the complex have been calculated to be − 1008.69854 a.u. and − 2201.48603 a.u., respectively. The optimized parameters of ligand and the complex are collected in Table 1. The [Cu.L.Cl2.H2O].2H2O complex was formed by the binding of the Cu metal ion to the N atom of the pyridine ring and the N atom of the CH2NHC=O group forming a five membered ring. Another five membered ring is formed by the binding of Cu ion to O22 and N23. The dihedral C11-C20-N23-C24 at − 152.9° in the ligand is changed to − 161.4° in [Cu.L.Cl2.H2O].2H2O. The dihedral C20-N23-C24-C26 which determines the orientation of pyridine ring with the amide (C20=O21-N23-H36) group in the metal complex is calculated at 67.0°, whereas the pyridine ring is almost planar in the ligand. The bond length of three C20=O21, C11=O22 and C12=O18 bonds in the ligand/Complex are calculated at 1.240/1.235, 1.227/1.236, 1.224/1.222 Å.
FTIR spectral analysis
The infrared spectra (FTIR) of the organic ligand and [Cu.L.Cl2.H2O].2H2O complex were analyzed and the proposed assignments of the bands are shown in Table 2. Experimental and simulated spectra for the ligand and the complex are given in Figs. 2 and 3 respectively. The N–H band of amines and amides absorb in the same region as O–H bond, but due to the greater electronegativity of oxygen than nitrogen, the O–H stretching band is much stronger than the N–H stretching band. N–H peaks usually are sharper, but weaker peaks than O–H bands [53]. The wavenumbers corresponding to three C=O bonds [54] in the ligand are calculated at 1735, 1687 and 1602 cm−1 with experimental values at 1744, 1697 and 1597 cm−1. The infrared spectral bands due to –NH groups in Cu complex, are shifted to lower frequencies at 3240 and 3179 cm−1 as compared to the NH bands of ligand (3480 and 3240 cm−1) either due to the participation in complex formation or involvement in H-bonding with a C=O group. One C=O band out of three bands in the ligand, disappeared completely in the Cu(II) complex indicating its participation in complex formation. The bands at 1697 and 1597 attributed to C=O amide I and II were blue shifted (1673 and 1585 cm−1) as a result of complex formation and H-bonding with -NH group. A new band appeared at 3672 cm−1 as a result of the presence of a coordinated water molecule [54] and / or H-bonded –NH group [55]. The characteristic pyridine stretching mode having contribution from C=C as well as C=N stretch at 1628 cm−1 shifted to 1606 cm−1 due to its contribution in complex formation. This is corroborated by the increase in C26-N32 and C25-N32 bond lengths on complexation. The CH2 scissoring calculated at 1470 cm−1 (L) is in good agreement with peak at 1476 cm−1 in IR spectrum. C12-N17 stretching observed and calculated at 1310 and 1301 cm−1 respectively is a mixed mode with contribution from C–C stretch and C–C–C bending of phenyl ring. Methylene C24H2 stretching being a part of five membered ring in the metal complex shows strong IR peaks on complexation at 2987 and 2972 cm−1 in comparison to the weak CH2 stretching vibration in the ligand at slightly lower wavenumbers. New bands at 656 and 677 cm−1 were observed corresponding to the stretching vibration of M–O and M–N, respectively [56].
1H-NMR spectral analysis
On the other hand, the 1H-NMR spectra of the ligand gave six peaks at δ = 2.00, 4.50, (7.215–7.794, 8.511), (9.251–9.275) and 10.568 ppm assigned to CH3, CH2 groups, hydrogens of benzene and pyridine rings, –NH of [(CO)NHCH2] and -NH of [Ph.NH.(CO)CH3] groups respectively [57, 58], (Table 3, Fig. 4). All these peaks were shifted as a result of complex formation (Table 3, Fig. 5). The persistence of the hydrogens of the two -NH groups suggested that one –NH group acted as a neutral rather than an acidic group in complex formation, the other contributed in a H-bond. The band at δ = 4.581 ppm in the complex is attributed to the –OH groups of H2O molecule coordinated to Cu(II) [59] and assigned to hydrogen bonded OH groups of acidic character [60]. New peaks at δ = 10.9976, 11.1810, 11.5051 and 12.1042 ppm were observed as a result of H-bonding between –NH group and –C=O group and also between –NH group and the DMSO solvent used [61]. The band at 12.00 ppm can be attributed to the OH proton, indicating coordination of H2O molecule to the metal ion [62]. The optimized structures of the ligand and its metal complex were used to simulate their 1H NMR spectrum at DFT-B3LYP/6-31G(d, p) level using the Gauge-Including Atomic Orbital (GIAO) method [63]. The calculated 1H chemical shifts in DMSO, with Tetramethylsilane (TMS) as internal standard are given in Table 3 along with the experimental shifts. A good coherence between the theoretical and experimental chemical shifts for both ligand and its complex has been achieved.
Thermal analyses
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of the Cu(II) complex was performed to get information about the thermal stability of the complex and to gauge whether the water molecules are in the ionic or the coordination sphere of the central metal ion. Heating rates were at 10 °C min−1 under nitrogen atmosphere with flow rate of 20 mL min−1 and weight losses were measured from ambient temperature up to 800 °C. Thermogravimetric analysis results agreed with the proposed structure.
The TGA of the [Cu.L.Cl2.H2O].2H2O complex (Fig. 6), showed the decomposition of the complex to occur in a three-step mechanism. It was mostly reported that the detached or non-coordinate water can be assigned in the TGA-temperature range from 30 °C to − 100 °C, while the coordinated water is mostly losing in between 100 °C and 150 °C [64,65,66,67]. It was observed that the first step between 40 and 252 °C is due to the decomposition of 3H2O (non-coordinated and coordinated) + NHCOCH3 moiety, (found: 23.455%; calculated: 23.067%). DTGA analysis described presence of the bands at (55.20, 95.00,130, 209 °C), in which water molecules were decayed and referred within these bands (55.20, 95.00 and 130 °C). The second step between 252 and 403 °C was attributed to the decomposition of Cl atom, (found: 7.643%; calculated: 7.312%) and the third step at the temperature range 403–659 °C assigned to the decomposition of Cl + (py-CH2NHCO.CO) + 4C atoms, (found: 50.314; calculated: 50.770%), with DTGA at 569°C, respectively and left with a residue of Cu + 2C atoms, (found: 18.328%; calculated: 18.031%).
On the other hand, the DTA curve of the complex (Fig. 7), showed multiple exothermic peaks at 72.12 °C, 220.31 °C and 551.53 °C. Calculations were performed for the well resolved peaks only (the first and third). The thermodynamic parameters of decomposition processes of the complex, namely, activation energy (ΔEa*), enthalpy change (ΔH*) and entropy (ΔS*) were calculated by employing the Horowitz–Metzger equation [68] and are collected in Table 4. The order of chemical reactions (n) was calculated via the peak symmetry method by Kissinger [69] and the asymmetry of the peak, S, was calculated as follows:
The value of the decomposed substance fraction, \({\alpha }_{m}\), at the moment of maximum development of the reaction (with \(T= {T}_{m}\)) was determined from the relation [70]
The values of collision factor, Z, can be obtained by making the use of the relation:
where \(R\) = the molar gas constant, \(\beta \) is the heating rate (Ks−1), \({T}_{m}\) is the peak temperature.
The entropies of activation,\(\Delta {S}^{*}\), are calculated from the equation [71]:
where \(k\) is Boltzmann constant and \(h\) is Planck’s constant.
The change in enthalpy \(\Delta {H}^{*}\), taking place at any peak temperature, \({T}_{m}\), can be given by the following equation:
Based on least square calculations, the ln Δt versus 1000/T plot for the complex, for each peak (Fig. 8), gave straight lines from which the activation energies were calculated according to the method of Piloyan et al. [72]. The slope is of Arrhenius type and equals − Ea* / R.
According to the data obtained from the DTA curve, some conclusions can be achieved as follows: (i) the appearance of fractional orders (n) suggested that the reaction proceeds via complicated mechanisms but approaching first order. (ii) The change of entropy values, ΔS*, for the complex, (Table 4), are nearly of the same magnitude (− 0.234 and − 0.242) kJ K−1 mol−1 indicating that the transition states are more ordered, thus in a less random molecular configuration than the reactants [73] (iii) The values of ∆E* were 127.204 and 144.879 kJ/mol, and ∆H* values were − 82.00 and − 209.02 kJ/mol for the first and third peaks, respectively.
The negative values of ∆H* indicated the exothermic nature of the metal–ligand interaction. Negative values of ∆G* showed spontaneous formation of the complexes [74]. The entropy change (∆S*), which is a measure of disorder or randomness in the system, are negative, indicating that complex formation is favorable [5]. The enthalpy change is large and is enough to overcome the entropy change which favors the spontaneous formation of the complex [75, 76].
Experimental UV–vis and ESR spectra
Experimental electronic absorption and ESR spectra of the Cu(II) complex were recorded in order to understand the spatial arrangement of the metal ion around the ligand. Intense electronic spectral bands for the ligand were observed between 243 and 371 nm assigned to π→π* transition originating in the phenyl ring and C=O groups [77], the bands at 440 and 475 nm are attributed to n→π* transitions originating in the –NH-CO chromophores. In the spectrum of the Cu(II) complex, these bands were shifted to lower energies as a result of complex formation.
The nujol mull electronic spectrum of the copper(II) complex showed a broad d-d band in the 540 nm region (18,518 cm−1) which can be assigned to 2T2g → 2Eg transition of an octahedral geometry [33]. Though under the influence of the tetragonal distortion, the 2Eg and 2T2g states of the octahedral Cu(II) ion (d9) split, and three transitions 2B1g→2Eg, 2B1g →2B2g, and 2B1g → 2A1g are expected [78,79,80], but their very close energies makes them appear in the form of one broad band. However, in ethanol solvent, these bands were detected at 540 nm (18,518 cm−1), 656nm (15,244 cm−1) and 715 nm (13,986 cm−1), which are in good agreement with those reported for a distorted octahedral geometry around Cu(II) ion [76]. The magnetic moment value of 1.92 BM together with the electronic data suggested the existence of the Cu(II) complex in a monomeric form with a distorted octahedral environment with dx2-y2 ground state [81].
The X-band ESR spectrum of the copper(II) complex in the polycrystalline state was recorded at 298 K and studied in the 2300–4000 G region (Fig. 9), to elucidate the geometry and degree of covalency of the metal–ligand bond or environment around the metal ion. The g-factors were measured using DPPH as standard. The spectrum exhibited an axial behavior with g// (2.107) and g┴ (2.022) values. The geometric parameter “G” which is a measure of the exchange interaction between the copper(II) centers in the polycrystalline compound was calculated using the equation: G = (g// − 2.0023) / (g┴ − 2.0023) [81]. It was found that g// > g┴ > 2.0023 and G = 4.707. According to Hathaway [82], if G > 4.0, the local tetragonal axes are aligned parallel or only slightly misaligned. If G < 4.0, significant exchange coupling is present and the misalignment is appreciable. The g- and G-values were consistent with a dx2-y2 ground state in a monomeric distorted octahedral structure [83].
Electronic absorption spectra (TD-DFT)
The highest occupied molecular orbital, HOMO (electron donor orbital) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) (electron acceptor orbital) are well known quantum chemical descriptors. The energy gap between HOMO and LUMO is used as an indicator for chemical reactivity and kinetic stability of a molecule. A molecule is said to be soft with a high chemical reactivity, if it has a small HOMO–LUMO gap [84, 85]. In order to have a better insight and further understanding of the structures of ligand (L) and its metal complex, their electronic structures have been probed theoretically. The energy of the HOMO and LUMO orbitals and their orbital energy gap are calculated using the TD-DFT method, and the pictorial illustrations of these frontier orbitals for both the ligand and its Cu(II) complex are shown in Fig. 10. Theoretical vertical excitation energies (E), oscillator strengths (f) and the corresponding absorption wavelengths (λ) are collected in Table 5.
In the ligand the calculations predict one intense electronic transition at 295.38 nm with an oscillator strength 0.0499, in agreement with the experimental value shown in Fig. 11. This electronic absorption mainly corresponds to the transition from the molecular orbital HOMO(H)-4 to LUMO(L). The other two peaks at 279.10 and 403.31 nm in the calculated UV spectrum in gas phase arises mainly due to the electronic transition given by H → L + 1 and H → L respectively. In the metal complex [Cu.L.Cl2.H2O].2H2O the highest peak with oscillator strength 0.0121 appears at 509.95 nm in line with the experimental peak at 540 nm. As the spin of the complex is 1/2, this corresponds to transition between beta orbitals H-1 → L. The HOMO–LUMO energy gap (∆E) for the ligand and complex are calculated to be 3.68660 and 3.72378 eV respectively. To analyze the charge transfer characteristics of the electronic excitation, the net electron density difference between ground and excited states have been plotted for ligand as well as complex (Fig. 12). In Fig. 12, the pink color represents where the electrons are coming from, and the light blue color represents where the electrons are going. The electron density difference plot of the ligand indicates the large pink lobes around the oxygen atoms and blue antibonding orbitals around phenyl ring thus the transition at λ = 403.31 nm to be n → π* type. The transition at λ = 279.10 nm shows the transfer of electron charge density from pyridin-2-ylmethyl)acetamide moiety to acetamidophenyl moiety and to be of π → π* type. In Cu (II) complex the major charge density is transferred around metal binding site for λ = 540 nm.
Antimicrobial and antifungal activities
The fate of novel bioactive substances in terms of therapy is heavily influenced by chelation and were reported as a significant antimicrobial agent [86]. The antibacterial and antifungal activities of the synthesized Cu(II) complex were screened against a Gram-negative (E. coli) and a Gram-positive (S. aureus) bacteria in addition to A. flavus, and C. albicans fungi. The Cu(II) complex was found to have considerable effect on both gram positive and gram negative bacteria as well as on Aspergillus flavus and Candida albicans fungus as given in Table 6.
Molecular docking simulation with insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R)
Data processing and prediction
Molecular docking was processed using Autodock accurate settings involving 50 conformational structures to be analyzed according to binding energy (B.E), intermolecular energy (InterM.E) and internal energy (I.E) with inhibition constant evaluating values [87]. 5FXR protein target was prepared and become ready as a receptor input for the synthesized ligand. the conformational structures are present in Table 7 investigating the most important analyzable energies that mainly help in the ligand-target stability. Figure 13 shows a correlation between the different types of energies come from docking analysis of 50 conformational ligand structures.
Conformational docking analysis
As shown from Fig. 13, the preferable energetic pose is located in conformational structure 5 and 41 (B.E = − 6.40 kcal/mol and − 6.35 kcal/mol) (Table 7). The types of non-covalent interactions mainly identify the stability of each conformational structure. Figure 14 represents the types of complex-ligand interactions for the poses of 5 and 41. In Fig. 14a, amino acids of HIS 1133.A, ARG 1134.A are interacted with the ligand by conventional H-bonding. Additionally, GLY 1155.A is interacted by carbon-H bond. These types of H-bonds mainly affect on the inhibitory ability of the ligand towards the target. Also, the π-electrons help in bio-complex stability and then inhibition efficiency. There are a number of π-interactions such π-anion, π-sigma, π–π stacked and amide- π stacked, that participate in selection of pose stabilization, also van der Waals interaction is present profusely around the conformational complexed structure. Furthermore, the complexed pose of 41 (Fig. 14b) shows similar interaction types mainly present in HIS1133.A and ARG 1134.A showing conventional H-bonding and ARG 1134.A showing carbon-H bonding. Other non-covalent interactions are prevalent around the bio-complex and slightly differ from pose 5 in presence of π-alkyl instead of π-sigma and presence additional π-π T-shaped interaction. Figure 15 correlates the binding energy with the inhibition constant values.
Conclusions
The Cu(II) complex, synthesized using the ligand 2-(2- acetamidophenyl)-2-oxo-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)acetamide, was investigated using elemental, spectral, magnetic measurement, molar conductivity, and thermal analysis. The magnetic moment value together with the electronic spectrum suggested the existence of the Cu(II) complex in a monomeric form with a distorted octahedral environment with dx2-y2 ground state. Computational studies revealed that the HOMO positions of the complexes are localized mostly around the acetamidophenyl group of the ligand while the LUMO is distributed around the metal centre. The plots of total electron density difference between ground and excited states in ligand clearly illustrates the transition corresponding to λ = 403.31 nm and λ = 279.10 nm to be respectively of n → π* and π → π* type. The synthesized complex was screened for its antibacterial activity against S. aureus and E. coli and for antifungal activity against A. flavus and C. albicans and found to have considerable activity against these. Conformational analysis illustrated presence of most stable conformational structure of the synthesized ligand around Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (ID: 5FXR).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Soayed AA, Refaat HM, Noor El-Din DA. Metal complexes of moxifloxacin-imidazole mixed ligands: characterization and biological studies. Inorganica Chim Acta. 2013;406:230–40.
Soayed AA, Refaat HM, Sinha L. Syntheses, structural elucidation, thermal properties, theoretical quantum chemical studies (DFT) and biological studies of barbituric hydrazine complexes. J Saudi Chem Soc. 2015;19(2):217–26.
Soayed AA, Refaat HM, Noor El-Din DA. Characterization and biological activity of Pefloxacin–imidazole mixed ligands complexes. Inorganica Chim Acta. 2014;421:59–66.
Pahontu E, Julea F, Rosu T, Purcarea V, Chumakov Y, Petrenco P, Gulea A. Antibacterial, antifungal and in vitro antileukaemia activity of metal complexes with thiosemicarbazones. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(4):865–78.
Que L Jr, Tolman WB. Biokatalytisch relevante rautenförmige Bis(μ-oxo)dimetall-Kerne in Kupfer- und Eisenkomplexen. Angew Chem. 2002;114:1160–85.
Dede B, Ozmen I, Karipcin F. Synthesis, characterization, catalase functions and DNA cleavage studies of new homo and heteronuclear Schiff base copper(II) complexes. Polyhedron. 2009;28:3967–74.
Whittaker MM, Duncan WR, Whittaker JM. Synthesis, structure, and properties of a model for galactose oxidase. Inorg Chem. 1996;35:382–6.
Ruggiero CE, Carrier SM, Antholine WE, Whittaker JW, Cramer CJ, Tolman WB. Synthesis and structural spectroscopic characterization of mononuclear copper nitrosyl complexes: models for nitric oxide adducts of copper proteins and copper exchange zeolites. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115:11285–98.
Constable EC. 2,2’:6’,2’’-terpyridines: from chemical obscurity to common supramolecular motifs. Chem Soc Rev. 2007;36:246–53.
Glasson CRK, Lindoy LF, Meehan GV. Recent developments in the d-block metallo-supramolecular chemistry of polypyridyls. Coord Chem Rev. 2008;252:940–63.
Moro AJ, Cywinski PJ, Korsten S, Mohr GJ. An ATP fluorescent chemosensor based on a Zn(II)-complexed dipicolylamine receptor coupled with a naphthalimide chromophore. Chem Commun. 2010;46:1085–7.
Zhang SH, Wang J, Han LA, Li CG, Wang W, Yuan Z. Colorimetric detection of bis-phosphorylated peptides using zinc(ii) dipicolylamine-appended gold nanoparticles. Sens Actuator B Chem. 2010;147:687–90.
Shukla M, Srivastava N, Saha S, Rao TR, Sunkari S. Synthesis, structure, UV–Vis–IR spectra, magnetism and theoretical studies on CuII[(2-aminomethyl)pyridine](thiocyanate)2and comparisons with an analogous CuII complex. Polyhedron. 2011;30:754–63.
Zabierowski P, Matoga D, Nitek W. Cobalt(II) and copper(II) supramolecular networks with a 1-iminoisoindoline asymmetric pincer. RSC Adv. 2015;33:25911–8.
Kim M, Mora C, Lee YH, Clegg JK, Lindoy LF, Min KS, Thuéry P, Kim Y. Interaction of copper(II) with N-substituted bis(2-pyridylmethyl)amine derivatives New discrete and 1-D polymeric complex systems—the latter displaying ferromagnetic behavior. Inorg Chem Commun. 2010;13:1148–51.
Kunishita A, Scanion JD, Ishimaru H, Honda K, Ogura T, Suzuki M, Cramer CJ, Itoh S. Reactions of copper(II)-H2O2 adducts supported by tridentate bis(2-pyridylmethyl)amine ligands: sensitivity to solvent and variations in ligand substitution. Inorg Chem. 2008;47:8222–32.
Turba S, Walter O, Schindler S, Nielsen LP, Hazell A, McKenzieF CJ, Lloret J, Cano MJ. Syntheses, structures, and properties of copper(II) complexes of Bis(2-pyridylmethyl) derivatives of o-, m-, and p-phenylenediamine and aniline. Inorg Chem. 2008;47:9612–23.
Belousoff MJ, Tjioe L, Graham B, Spiccia L. Synthesis, X-ray crystal structures, and phosphate ester cleavage properties of bis (2-pyridylmethyl) amine copper (II) complexes with guanidinium pendant groups. Inorg Chem. 2008;47:8641–51.
Sugai Y, Fujii S, Fujimoto T, Yano S, Mikata Y. Asymmetric sulfur atom coordination in a copper(II) dipicolylamine (DPA) complex with a thioglycoside ligand. Dalton Trans. 2007;33:3705–9.
Nielsen A, Veltzé S, Bond AD, McKenzie CJ. Isomerism in copper(II) chloride complexes of bis(2pyridylmethyl)amine and N-substituted derivatives: synthesis and X-ray structural Characterization. Polyhedron. 2007;26:1649–57.
Yano M, Fujita M, Miyake M, Tatsumi M, Yajima T, Yamauchi O, Oyana M, Sato K, Takuui T. Synthesis and properties of a redox active ligand with bispicoryalmino groups and its dinuclear complex. Polyhedron. 2007;26:2174–8.
Kova IA, Akhideno H, Tanase S, Belle C, Duboc C, Saint-Aman ET, Duncan PM, Spek AL, Pierre JL, Reedijk J. Changes in magnetic properties from solid state to solution in a trinuclear linear copper(II) complex. New J Chem. 2007;31:512–8.
Choi K-Y. Synthesis, properties, and X-ray crystal structure of copper(II) complex with Bis[(2-pyridyl)methyl]-2-(2-pyridyl)ethylamine. J Korean Chem Soc. 2007;51:31–5.
Mikata Y, Fujimoto T, Sugai Y, Yano S. Control of intramolecular oxygen coordination in the crystal structure of the copper(II) complexes with dipicolylamine (DPA)-derived ligands. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2007; 1143–1149.
Foxon S, Xu JY, Turba S, Leibold M, Hampel F, Heinemann FW, Walter O, Würtele C, Holthausen M, Schindler S. Syntheses, characterization and reactivity of iron(II), Nickel(II), Copper(II) and Zinc(II) complexes of the ligand N,N,N′,N′-Tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)benzene-1,3-diamine (1,3-tpbd) and its phenol derivative 2,6-Bis[bis(2-pyridylmethyl)amino]-p-cresol (2,6-tpcd). Eur J Inorg Chem. 2007(3): 429–443.
Yusuf TL, Oladipo SD, Zamisa S, Kumalo HM, Lawal IA, Lawal MM, Mabuba N. Design of new schiff-base copper(II) complexes: synthesis, crystal structures, DFT study, and binding potency toward cytochrome P450 3A4. ACS Omega. 2021;21:13704–18. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00906.
Zhao Y, Zhu J, He W, Yang Z, Zhu Y, Li Y, Zhang J, Guo Z. Oxidative DNA cleavage promoted by multinuclear copper complexes: activity dependence on the complex structure. Chem Eur J. 2006;12:6621–9.
Kirin SI, Duebon P, Weyhermueller T, Bill E, Metzler-Nolte N. Amino acid and peptide bioconjugates of copper(II) and Zinc(II) complexes with a modified N, N-Bis(2-picolyl)amine ligand. Inorg Chem. 2005;44:5405–15.
Niklas N, Heinemann FW, Hampel F, Clark T, Alsfasser R. The activation of tertiary carboxamides in metal complexes: an experimental and theoretical study on the methanolysis of acylated bispicolylamine copper(II) complexes. Inorg Chem. 2004;43:4663–73.
Lucchese B, Humphreys KJ, Lee D-H, Incarvito CD, Sommer RD, Rheingold AL, Karlin KD. Mono-, Bi-, and Trinuclear CuII-Cl containing products based on the tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine chelate derived from copper(I) complex dechlorination reactions of chloroform. Inorg Chem. 2004;43:5987–98.
He Z, Craig DC, Colbran SB. Structures and properties of 6-aryl substituted tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine transition metal complexes. J Chem Soc Dalton Trans. 2002; 4224–4235.
Antonioli B, Büchner B, Clegg JK, Gloe K, Gloe K, Götzke L, Heine A, Jäger A, Jolliffe KA, Kataeva O, Kataev V, Klingeler R, Krause T, Lindoy LF, Popa A, Seichter W, Wenzel M. Interaction of an extended series of N-substituted di(2-picolyl)amine derivatives with copper(II). Synthetic, structural, magnetic and solution studies. Dalton Trans. 2009;24:4795–805.
Fernandes C, Neves A, Bortoluzzi AJ, Mangrich AS, Rentschler E, Szpoganicz B, Schwingel E. A new dinuclear unsymmetric copper(II) complex as model for the active site of catechol oxidase. Inorg Chim Acta. 2001;320(1–2):12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1693(01)00470-4.
El-Faham A, Khattab SN, Ghabbour HA, Fun H-K, Siddiqui MRH. Microwave irradiation: synthesis and characterization of α-ketoamide and bis (α-ketoamide) derivatives via the ring opening of N-acetylisatin. Chem Central J. 2014;8(1):27.
da Silva JFM, Garden SJ, Pinto AC. The chemistry of isatins: a review from 1975 to 1999. J Braz Chem Soc. 2001;12(3):273–324.
Xiong Li, Deng R, Liu T, Luo Z, Wang Z, Zhu X-F, Wang H, Zeng Z. Selective C−N bond cleavage of N-acylisatins: towards high performance acylation/arylation/transamination reagents. Appl Organomet Chem. 2019;361(23):5383–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201900819.
Baker EL, Yamano MM, Zhou Y, Anthony SM. A two-step approach to achieve secondary amide transamidation enabled by nickel catalysis. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11554. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11554.
Bauer AW, Kirby MDK, Sherris JC, Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by standard single disc diffusion method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966;45:493–6.
Pfaller MA, Burmeister L, Bartlett MA, Rinaldi MG. Multicenter evaluation of four methods of yeast inoculum preparation. J Clin Microbiol. 1988;26:1437–41.
Kohn W, Sham LJ. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys Rev. 1965;140:A1133–8.
Becke AD. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J Chem Phys. 1993;98:5648–52.
Lee C, Yang W, Parr RG. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys Rev B. 1998;37:785–9.
Abdelrehim EM, El-Sayed DS. Synthesis, screening as potential antitumor of new poly heterocyclic compounds based on pyrimidine-2-thiones. BMC Chem. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-022-00810-4.
Elbadawy HA, Ali AE, Elkashef AA, Foro S, El-Sayed DS. Zinc(II)-facilitated nucleophilic addition on N-(4-chlorophenyl) carbon hydrazonoyl dicyanide and hybrid complex formation: X-ray, spectral characteristics, DFT, molecular docking, and biological studies. Appl Org Chem. 2022;36(9):6793.
El-Sayed DS, Tawfik EM, Elhusseiny AF, et al. A perception into binary and ternary copper (II) complexes: synthesis, characterization, DFT modeling, antimicrobial activity, protein binding screen, and amino acid interaction. BMC Chem. 2023;17:55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-023-00962-x.
El Sayed DS, Abdelrehim M. Computational details of molecular structure, spectroscopic properties, topological studies and SARS-Cov-2 enzyme molecular docking simulation of substituted triazolo pyrimidine thione heterocycles. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120006.
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Caricato M, Li X, Hratchian HP, Izmaylov AF, Bloino J, Zheng G, Sonnenberg JL, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Vreven T, Montgomery JA Jr., Peralta JE, Ogliaro F, Bearpark M, Heyd JJ, Brothers E, Kudin KN, Staroverov VN, Kobayashi R, Normand J, Raghavachari K, Rendell A, Burant JC, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Cossi M, Rega N, Millam JM, Klene M, Knox JE, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Martin RL, Morokuma K, Zakrzewski VG, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Farkas O, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cioslowski J, Fox DJ. Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT, 2009.
Jamroz MH. Vibrational energy distribution analysis, VEDA4 Computer Program, Poland, 2004.
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ. Autodock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexiblity. J Comput Chem. 2009;16:2785–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21256.
Elhusseiny AF, El-Dissouky A, Mautner F, Tawfk EM, El-Sayed DS. An insight into non-covalent interactions in binary, ternary and quaternary copper (II) complexes: synthesis, X-ray structure, DFT calculations, antimicrobial activity and molecular docking studies. Inorg Chim Acta. 2022;532: 120748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2021.120748.
Noreen S, Sumrra SH. Correlating the charge transfer efficiency of metallic sulfa-isatins to design efficient NLO materials with better drug designs. Biometals. 2022;35:519–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00385-6.
Nkungli NK, Fouegue ADT, Tasheh SN, et al. In silico investigation of falcipain-2 inhibition by hybrid benzimidazole-thiosemicarbazone antiplasmodial agents: a molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation, and kinetics study. Mol Divers. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-022-10594-3.
Sharma BK. Spectroscopy. GOEL Publishing House, Twentieth Edition. 2007.
Serna C, VanScoyoc GE, Ahlrichs JL. Hydroxyl groups and water in palygorskite. Am Mineral. 1977;62:784–92.
Ben Hadda T, Stoeckli-Evans H, Kerbal A, El Fatmi A, Filali Baba M, Ben Larbi N, Daoudi M, Patel RN. Cobalt(II) and copper(II) in selective coordination of armed ligands: {[(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methyl]amino}acetic acid and {[bis-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methyl]amino}acetic acid. Arkivoc xv. 2007; 215–224.
Visser H, Dubé CE, Armstrong WH, Sauer K, Yachandra VK. FTIR spectra and normal-mode analysis of a tetranuclear manganese adamantane-like complex in two electrochemically prepared oxidation states: relevance to the oxygen-evolving complex of photosystem II. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124(37):11008–17.
Chun-Hua G, Xiang-Dong Z, Wei G, Fang G, Qi-Tao L. Roles of anions in pyridinecarboxamide-copper(II) supramolecular networks. Chin J Chem. 2005;23(8):1001–6.
Idemudia OG, Sadimenko AP, Hosten EC. Metal complexes of new bioactive pyrazolone phenylhydrazones; crystal structure of 4-acetyl-3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazoline-5-one phenylhydrazone Ampp-Ph. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(5):687.
Schwanninger M, Rodrigues JC, Pereira H, Hinterstoisser B, Schwanninger M, Rodriguez JC, Pereira H, Hinterstoisser B. Effects of short-time vibratory ball milling on the shape of FT-IR spectra of wood and cellulose. Vib Spectrosc. 2004;36(1):23–40.
Chizallet C, Costentin G, Lauron-Pernot H, Maquet J, Che M. 1H MAS NMR study of the coordination of hydroxyl groups generated upon adsorption of H2O and CD3OH on clean MgO surfaces. Appl Catal A. 2006;307:239–44.
Gunther H, Spectroscopy NMR. Basic principles, concepts and applications in chemistry. 2nd ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons; 1995.
Tella AC, Obaleye JA. Divalent metal complexes of 4-amino-n-pyrimidin-2-ylbenzene sulphonamide and their antimalarial activities against plasmodium berghei. Bull Chem Soc Ethiop. 2011;25(3):371–80.
Wolinski K, Haacke R, Hinton JF, Pulay P. Methods for parallel computation of SCF NMR chemical shifts by GIAO method: efficient integral calculation, multi-Fock algorithm, and pseudodiagonalization. J Comp Chem. 1997;18(6):816–25.
Özkınalı S, Yavuz S, Tosun T, Köse DA, Gür M, Kocaokutgen H. Synthesis, spectroscopic and thermal analysis and investigation of dyeing properties of o-hydroxy Schiff bases and their metal complexes. Chemistry. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202002470.
DagLi Z, Kose DA, Sahin O, Sahin ZS. The synthesis and structural characterization of transition metal coordination complexes of coumarilic acid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;128:1373–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-6053-y.
Herena Z, Pasaoglub H, Kastasb G, Vurucua L, Buyukgungor O. Synthesis, spectral and thermal properties, and crystal structure of Bis(ethylenediamine)(aqua)copper(II) (Bis)syringate ethylenediamine dihydrate [Cu(en)2(H2O)](sy)2(en)(H2O)2. Z Naturforsch. 2006;61(3):287–91. https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-2006-0308.
Fouad R, Shaaban IA, Ali TE, Assirib MA, Shenouda SS. Co(ii), Ni(ii), Cu(ii) and Cd(ii)-thiocarbonohydrazone complexes: spectroscopic, DFT, thermal, and electrical conductivity studies. RSC Adv. 2021;11:37726–43. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA06902K.
Horowitz HH, Metzger G. A new analysis of thermogravimetric traces. Anal Chem. 1963;35(10):1464–8.
Kissinger HE. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1957;29(11):1702–6.
Oswald HR, Dubler E. Thermal analysis: inorganic chemistry, vol. II. Base: Birkhauser; 1972.
Dhar ML, Singh O. Kinetics and thermal decomposition of Fe(III) and UO2(II) complexes with embelin (2,5-dihydroxy-3-undecyl-P-benzoquinone). J Therm Anal. 1991;37(2):259–65.
Piloyan GO, Ryabchikov ID, Novikova OS. Determination of activation energies of thermal analysis chemical reactions by differential thermal analysis. Nature (London). 1996;212:1229–1229.
Mallikarjun KG, Naidu RS. Thermal decomposition kinetics of Cu (II) chelates of substituted chalcones. Thermochim Acta. 1992;206:273–8.
Chang R. Physical chemistry for the biosciences. Sansalito: University Sciences; 2005.
Atkins P, de Paula J. Physical chemistry for the life sciences. New York: W. H. Freeman and Company; 2006.
Stryer L. Biochemistry (Third Edition). New York: W.H. Freeman and Company; 1988.
Jaber Al-Jeboori M, Al-Dujaili AH, Al-Janabi AE. Coordination of carbonyl oxygen in the complexes of polymeric N-crotonyl-2-hydroxyphenylazomethine. Transit Metal Chem. 2009;34(1):109–13.
Lever APB. Inorganic electronic spectroscopy. 2nd ed. New York: Elsevier Science; 1984.
Pahonțu E, Ilieș DC, Shova S, Paraschivescu C, Badea M, Gulea A, Roșu T. Synthesis, characterization, crystal structure and antimicrobial activity of copper(II) complexes with the schiff base derived from 2-hydroxy-4- methoxybenzaldehyde. Molecules. 2015;20:5771–92.
Sathyanarayana DN. Electronic Absorption spectroscopy and related techniques. Universities Press (India) Ltd; 2001.
Seena EB, Sithambaresan M, Vasudevan S, et al. Structural and spectral characterization of Cu(II) complexes of N(4)-substituted thiosemicarbazones derived from 2-hydroxyacetophenone: crystal structure of a dinuclear Cu(II) complex. J Chem Sci. 2020;132:149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-020-01845-7.
Hathaway BJ, Tomlinson AAG. Copper(II) ammonia complexes. Coord Chem Rev. 1970;5(1):1–43.
Bew MJ, Hathaway BJ, Faraday RR. Electronic properties and stereochemistry of the copper(II) ion. Part VII. Mono(diethylenetriamine)copper(II) complexes. J Chem Soc Dalton Trans. 1972;12:1229–37.
Miar M, Shiroudi A, Pourshamsian K, Oliaey AR, Hatamjafari F. Theoretical investigations on the HOMO–LUMO gap and global reactivity descriptor studies, natural bond orbital, and nucleus-independent chemical shifts analyses of 3-phenylbenzo[d]thiazole-2(3H)-imine and its para-substituted derivatives: solvent and substituent effects. J Chem Res. 2021;45(1–2):147–58. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747519820932091.
El Sayed DS, Abdelrehim EM. Spectroscopic details on the molecular structure of pyrimidine-2-thiones heterocyclic compounds: computational and antiviral activity against the main protease enzyme of SARS-CoV-2. BMC Chem. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-022-00881-3.
Hassan AU, Sumrra SH, Zafar MN, et al. New organosulfur metallic compounds as potent drugs: synthesis, molecular modeling, spectral, antimicrobial, drug likeness and DFT analysis. Mol Divers. 2022;26:51–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-020-10157-4.
El-Sayed DS, El Badawy HA, Khalil TE. Rational modulation of N and O binding in Fe(III) complex formation derived from hydroxychloroquine: synthesis, Spectroscopic, Computational, and Docking Simulation with Human Thrombin Plasma. J Mol Struct. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.132268.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the financial support from smart critical infrastructure research center Alexandria University– High performance computing Lab.
Funding
Open access funding provided by The Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) in cooperation with The Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB). This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Doaa S. El-Sayed: Investigation, Software, Methodology, Validation, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing –original draft, Writing – review & editing. Leena Sinha: Software, Formal analysis, Resources, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Data curation, Writing –original draft, Writing – review & editing. Amina A. Soayed: Conceptualization, Supervision, Software, Formal analysis, Resources, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Data curation, Writing –original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
El-Sayed, D.S., Sinha, L. & Soayed, A.A. Experimental and theoretical quantum chemical studies of 2-(2-acetamidophenyl)-2-oxo-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)acetamide and its copper(II) complex: molecular docking simulation of the designed coordinated ligand with insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R). BMC Chemistry 18, 112 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-024-01217-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-024-01217-z