Abstract
Background
Here we report a new selenium-based heterogeneous catalyst, which was prepared from the immobilization of diphenyl diselenide on amine-functionalized Santa Barbara Amorphous-15 (SBA-15). The catalyst characterization study has been confirmed by different analysis methods including Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), X-ray diffraction patterns (XRD), field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area analysis.
Results
The newly designed catalyst was successfully applied in the green dehydration reaction of oximes to corresponding nitriles in the presence of hydrogen peroxide/air.
To demonstrate the role of the catalyst in this study, the model reaction was also carried out in the absence of the catalyst and a trace yield of the relevant product was achieved.
Conclusion
In this way, a series of nitrile derivatives were obtained with 72–96% yields, also, the catalyst could be separated easily and recycled for four consecutive runs with no obvious drop in catalytic activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Organoselenium compounds have been considered a research interest because of their effective role in many organic reactions for the production of important synthons and reagents. [1,2,3,4]. Selenium is a cheap and environment-friendly element, which can be metabolized in the body, so exhibits superior activity with less harmful toxic waste in a wide range of organic transformations as the catalyst [5]. One of the serious problems in chemical reactions is the separation of catalysts from the reaction medium. For this purpose, the boost of highly efficient heterogeneous catalysts with some competencies such as facile recovery, and low catalyst leaching is prime of importance.
One of the beneficial molecular frameworks is nitrile compounds, which are used as the main part of agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and fine chemicals [6, 7]. In addition, these compounds can be rendered for the preparation of a wide range of organic materials such as heterocycles, and the compounds containing carbonyl functional groups in green reaction approaches [8, 9].
In the past decades, several protocols including transition-metal heterogeneous catalysts have been reported for the synthesis of nitrile compounds [10, 11]. However, these methods suffer from costly heterogeneous catalyst systems, metal or non-metal chemical dehydration, and producing a large number of waste products [12]. Therefore, recent protocols with subtle and inexpensive reagents with the metal-free approach under greener and milder conditions are well desired.
One of the methods for the preparation of nitriles is dehydration of oximes, which has a good atom economy. Oxime is an organic compound produced by the reaction of an aldehyde or a ketone compound, and hydroxylamine contains a polar group and can participate in several organic chemical reactions [13]. Nitriles have attracted significant attention from chemists due to their remarkable synthetic properties as important intermediates for the synthesis of carboxylic acids, esters, aldehydes, ketones, amides, and amines. Furthermore, nitriles are very useful starting materials for the production of agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and biologically active compounds such as thiazoles, tetrazoles, 2-oxazolines, oxazoles, triazoles, diarylimidazoles, and benzamidines [14,15,16,17].
However, Yu et al. reported a practical method for the synthesis of organonitrile compounds from dehydration of oximes in moderate to good yields using diaryl diselenides as the catalysts [10]. The catalyst could be reused for four to six cycles without the inevitable loss of its catalytic activity. The main drawback of this protocol was the laborious separation of the catalyst.
To overcome these disadvantages, the heterogenization of a homogeneous catalyst onto solid supports could be excitant. Recently, the development of new heterogeneous catalysts according to the concept of “Green sustainable chemistry” is highly needed. It has been estimated that almost all commercially produced chemical products utilize heterogeneous catalysts [18]. So, large attention has been devoted to the demand for material as solid support for the preparation of heterogeneous catalysts. Among them, ordered mesoporous silica materials, which are silicates obtained by hydrothermal synthesis and a liquid templating mechanism are prime of importance [19]. SBA-15 mesoporous silica is one of the popular mesoporous silicas that utilizes for the design and development of heterogeneous catalysts. It has wide applicability in the design of materials and applied catalysts due to the comparatively thicker walls resulting in higher mechanical and thermal durability [20]. Functionalization of the surface of SBA-15 with organic or inorganic functional groups [21,22,23,24] results in new chemical and physical properties [25].
Considering the aforementioned and in the continuation of our recent efforts on the design and application of organoselenium heterogeneous catalysts in organic reactions [26,27,28,29,30,31], especially our first attempt at the oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids [32], herein, we wish to report, the metal-free reaction for dehydration of oximes for producing nitrile compounds. In the present strategy, the organoselenium anchoring onto inorganic mesoporous support as a heterogeneous catalyst was employed in the presence of H2O2/air as the clean oxidant. The catalyst was easily recycled with simple filtration and reused without obvious deactivation.
Experimental
Materials
Aryloximes were prepared according to the reported method in the literature [33]. Arylaldehdyes, hydroxylamine hydrochloride, sodium borohydride, p-aminobenzoic acid, N–N’-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC), (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane (APTES), selenium element, and common reagents were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich company and used as received. All the solvents were obtained from Amertatco and used without further purification.
The procedure for steps of the synthesis of catalyst SBA-15-Se)2.
SBA-15-NH2 synthesis
The inorganic mesoporous silica (SBA-15) was synthesized according to the reported procedure [34], and then modified using (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane (APTES) as follows: In a 100 mL flask, 3 g of mesoporous SBA-15 silica was refluxed with 3 mL of 3-(3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (12.8 mmol) in the 10 mL of toluene for 18 h. After that, the resulting solid product is filtered and dried in an oven at 90 °C during the night [35].
4,4′-diselanediyldibenzoic acid synthesis
The 4,4′-diselanediyldibenzoic acid was synthesized according to our previous report [32].
Immobilization of organic selenium ligand on SBA-15; Synthesis of SBA-15-Se)2
0.15 g of 4,4′-diselanediyldibenzoic acid, 0.1 g of N, N-dicyclohexyl carbamide (DCC), and 0.1 mL of triethylamine were added to approximately 10–15 mL of degassed CH2Cl2 and was stirred at 0 °C under nitrogen atmosphere for 30 min. Thereupon, a suspension of 0.1 g of mesoporous silica in 10 mL of dichloromethane was added to that mixture and magnetically stirred for an additional 1 h. It was then stirred at room temperature for 16 h. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was stirred at 40 °C for another 3 h, the solid was filtered and washed with dichloromethane, and dried at 60 °C.
General procedure for preparation of arylnitriles
Oxime (1 mmol), acetonitrile (2 mL), hydrogen peroxide 0.025 mL, and SBA-15-Se)2 (0.02 g) as catalyst were mixed thoroughly. The reaction mixture was stirred under airflow at 65 °C and the progress of the reaction was followed by thin-layer chromatography (TLC). After completion of the reaction, the mixture was cooled to room temperature. Hot ethanol was added to the reaction mixture, and the catalyst was separated from the reaction mixture by centrifugation. After the separation of the catalyst, the goal products were purified by recrystallization from hot ethanol or by plate chromatography using n-hexane/ethyl acetate (9/1 ratio) as the mobile phase and silica gel 60 HF254 as the stationary phase. All the products were known and identified by the appearance of the absorption spectral band related to the cyanide (CN) functional group in FTIR spectra and comparison of melting points with those reported in the literature or handbooks.
Results and discussion
Fabrication and characterization of SBA-15-Se)2
4,4′-diselanediyldibenzoic acid (II) was obtained from the azotization reaction of para-aminobenzoic acid in the presence of Na2Se2. The obtained product was treated with aminopropyl modified SBA-15 in appropriate conditions to afford the organoselenium grafted onto inorganic mesoporous support as depicted in Fig. 1 in two steps.
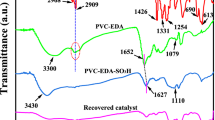
Figure 2 contains three FT-IR spectra that represent SBA-15, SBA-15-NH2, and SBA-15-Se)2. The absorption bands at 1080, 796, and 462 cm−1, which were clearly observed can be attributed to’ Si–O-Si, Si–O, and Si–O-Si vibrations in SBA-15, respectively. The vibrations of Si–OH groups appeared at 950 and 3380 cm−1 [35]. The presence of a weak peak at 2890 cm−1 is supposed to be C-H stretching vibration, and it suggests that almost all surfactant was ousted (Fig. 2a). After modification of SBA-15 with APTES, the vibration peaks of -CH2 and -CH groups were detected at 2890 cm−1. Meanwhile, two distinct absorption bands of NH2 were observed at 1591 and 1531 cm−1, which approved the successful grafting of amine groups to the surface of inorganic mesoporous support (Fig. 2b) [36]. The spectrum of SBA-15-Se)2 (Fig. 2c) displayed weak absorption bands due to the placement of functional groups in the holes of SBA-15. Therefore, the results above proved that the organoselenium segment was successfully functionalized.
Meanwhile, to further verify the element composition of the final catalyst, energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy was performed. Figure 3 depicts the results of the EDX spectrum obtained from sample of SBA-15-Se)2. The EDX spectrum of SBA-15-Se)2 shows the presence of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, silicon, and selenium atoms, thus confirming the successful functionalization of SBA-15 using organoselenium compounds. 6.36 wt% selenium was extended in the SBA-15-Se)2 as displayed in the Fig. 3b. Furthermore, the selected area was subjected to elemental mapping patterns, which shows the homogeneous dispersal of all the component elements in the SBA-15-Se)2 (Fig. 4).
The low-angle XRD pattern of SBA-15-Se)2 in the range of 0.4–12° was represented in Fig. 5. The hexagonal symmetry of three-dimensional inorganic mesoporous support (SBA-15) was confirmed with three typical diffraction peaks of (1 0 0), (1 1 0), and (2 0 0), which indicates the hexagonal structure of SBA-15 was maintained after functionalized with organoselenium moiety [37]. Only a certain decrease in the intensity of peaks (in comparison with literature) mentions that the mesoporous ordering reduced when it was treated with organic groups. However, the indicating peak pattern demonstrates that the inside of the mesoporous channels was grafted mainly with selenium organic functions [36]. In addition, the broad band between 2θ = 20–30° illustrates the amorphous nature of the organic matter, which was encapsulated in the channel of SBA-15 (inset of Fig. 5).
As shown in the FE-SEM images of the SBA-15-Se)2 sample, the presence of good-ordered particles that array regularity was seen. The particles are ranging from 900 to 1300 nm with uniform distribution. In addition, the ordered mesoporous structure of SBA-15 support was similar to that of reported ones, and remained unchanged after the grafting of the organoselenium part present in both the surface and channels of SBA-15 as depicted in Fig. 6 [38]. The bright spots are selenium, which appears bright in an SEM image compared to lighter elements, such as silicon because more backscattered electrons are emitted from the sample surface [39].
Figure 7 shows the thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) curve of SBA-15-Se)2, which shows weight loss due to decomposition on heating. The first minor amount of mass loss (about 5–6%) below 200 °C is related to the departure of physicosorbed solvent molecules [27]. The second breakdown in the range of 200–550 °C (nearly 33%) corresponds to the decomposition of organoselenium functional groups [32]. In continue, a tangible increase in weight is.
observed at 600–800 °C, which may be due to the re-adsorption of the combusted materials [40]. The estimated amount of grafted organoselenium compounds, which can be obtained by the residue of SBA-15 in the sample, is 1.23 mmol g−1 of inorganic mesoporous support. Therefore, the thermogravimetric analysis supported that adequate organoselenium functional groups have been chemically linked on the SBA-15 surface.
The isotherm of the SBA-15-Se)2 could be categorized as a type of IV with an H1 hysteresis loop, by mesoporous materials [41] (Fig. 8). The as-prepared catalyst exhibited a lower Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area (SBET, 212.06 m2/g) in comparison with unmodified SBA-15 (Table 1). The decrease in SBET can be attributed to the incorporation of at least part of the organoselenium groups inside the mesoporous. Evidently, the rapid N2 adsorption–desorption rate in P/P0 between 0.68 and 0.8 demonstrated a typical capillary adsorption phenomenon with uniform pore distribution. Apparently, with increasing the P/P0 to 0.8–1.00, N2 adsorption rarely changed, which suggested the adsorption had reached saturation [35].
Investigation of the catalytic activity of SBA-15-Se)2 in the synthesis of nitriles
Optimization of reaction conditions
To optimize the conditions, the conversion of 4-chlorobenzaldehyde oxime to 4-chlorobenzonitrile was initially chosen as the pattern transformation. So, on heating in 1 mL water at 65 °C, 1 mmol oxime with 0.25 mL H2O2 (2.45 mmol) in the presence of 0.02 g SBA-15-Se)2 as the catalyst was mixed under airflow. The corresponding nitrile product was generated in trace yield (Table 2, entry 6). The reaction was performed in other protic solvents such as MeOH and EtOH but led to low yield as well (Table 2 entries 7 and 8). Using acetonitrile as a solvent gave higher yields to 95% and it was the best solvent choice. The non-polar solvents were also tested, but they were unfavorable for this reaction (Table 2, entries 9 and 10).
To attain more transformation of the starting material, the temperature of the reaction was raised from 65 °C to 75 °C, but it was found that 65 °C was the superior temperature, which gives the product of the model reaction in 95% yield (Table 2, entry13). After determining the best solvent and setting the reaction temperature, the amount of H2O2 was also optimized. This revealed that the reduction of H2O2 dosage dejected the yield of the reaction (Table 2, entry 11) but using more than H2O2 did not prosper the product yield as anticipated (Table 2, entry 12). When no catalyst was added, the reaction gave a poor yield of the product (Table 2, entry 1).
Scope of reaction
Under the optimized case, means 0.02 g SBA-15-Se)2 (equals to 1.6 mol% Se) as heterogeneous organocatalyst, 2.45 mmol H2O2, 3 mL acetonitrile as a solvent, and airflow, the series of aryloximes was engaged to the synthesize of the corresponding arylnitriles. A series of aldoximes including electron-enriched or electron-donation substrates gave desired products in moderate to high yields (Table 3, entries 1, 2, 8, and 9). The substrates with electron-deficient groups were obviously preferred better and arylnitriles produced in high yields (Table 3, entries 3–7). Therewith, this protocol could be applied to the bulky and heterocycle-containing substrate, and desired product occurred an acceptable yield (Table 3, entries 10 and 11).
Plausible reaction mechanism
A proposed mechanism for the aldoxime dehydration reaction is displayed in Fig. 9 based on the previous literature [3, 10, 42]. Initially, selenenic acid (1) is generated through diselenide oxidation using hydrogen peroxide, which is then converted into the relevant selenenic anhydride (2). In the next step, condensation of aldoxime (3) with selenenic anhydride (2) gives intermediate (4). The rearrangement of (4) lids to the intramolecular hydrogen bond-stabilized intermediate (5), which decomposes to product nitrile (6) and regenerated the catalytic species (1) using a selenoxide syn-elimination process.
Reusability of SBA-15-Se)2
Eventually, to validate the durability and industrial applicability of SBA-15-Se)2, recycling tests were carried out under optimized conditions. After completion of the reaction, the catalyst was recollected using a centrifuge, washed thoroughly with acetone and ethanol, and then dried at 60 °C for other cycles. Figure 10 displays that the SBA-15-Se)2 can be reutilized for at least four consecutive runs with no considerable decrease in catalytic activity.
Conclusion
In summary, we have demonstrated a facilitated strategy to prepare a heterogeneous selenium-based catalyst via immobilization of organic selenium on SBA-15 modified with APTES. The as-synthesized catalyst was used as an efficient catalyst for the conversion of aldoximes to arylnitriles using hydrogen peroxide and air. Various characterization techniques such as FTIR, XRD, FESEM, EDX-Mapping and BET were performed to confirm the formation of as-obtained catalyst. Based on its catalytic performance, this heterogeneous selenium-based catalyst with high recycling efficiency has huge potential to be explored in environmental remediation. The excellent recyclability, mild reaction condition, using green oxidant, metal free catalyst, and durability of the catalyst are highlights of this transformation. No reference standards or controls are indicated for comparison in regards to the performance of the new-catalyst. This study endeavors to add to the existing library of catalysts that can potentially be exploited in the future for industrial conversions of oximes to nitrile products in perhaps more efficient ways.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- SBA-15:
-
Santa barbara amorphous-15
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- TGA:
-
Thermogravimetric analysis
- EDX:
-
Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- FE-SEM:
-
Field emission scanning electron microscopy
- BET:
-
Brunauer emmett-teller
- DCC:
-
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
- APTES:
-
(3-Aminopropyl) triethoxysilane
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- TLC:
-
Thin-layer chromatography
- CH2Cl2 :
-
Dichloromethane
- EtOH:
-
Ethanol
- MeOH:
-
Methanol
- CHCl3 :
-
Chloroform
References
Pop A, Silvestru C, Silvestru A. Organoselenium and organotellurium compounds containing chalcogen-oxygen bonds in organic synthesis or related processes. Sci Rev Phys. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1515/psr-2018-0061.
Xiao X, Shao Z, Yu L. A perspective of the engineering applications of carbon-based selenium-containing materials. Chin Chem Lett. 2021;32:2933.
Xiao X, Guan C, Xu J, Fu W, Yu L. Selenium-catalyzed selective reactions of carbonyl derivatives: state-of-the-art and future challenges. Green Chem. 2021;23:4647.
Chen X, Mao J, Liu C, Chen C, Cao H, Yu L. An unexpected generation of magnetically separable Se/Fe3O4 for catalytic degradation of polyene contaminants with molecular oxygen. Chin Chem Lett. 2020;31:3205.
Rathore V, Jose C, Kumar S. Organoselenium small molecules as catalysts for the oxidative functionalization of organic molecules. New J Chem. 2019;43:8852.
Fleming FF, Yao L, Ravikumar P, Funk L, Shook BC. Nitrile-containing pharmaceuticals: efficacious roles of the nitrile pharmacophore. J Med Chem. 2010;53:7902.
Murphy ST, Case HL, Ellsworth E, Hagen S, Huband M, JoannidesT LC, Marotti KR, Ottolini AM, Rauckhorst BM. The synthesis and biological evaluation of novel series of nitrile-containing fluoroquinolones as antibacterial agents. Bioorganic Med Chem Lett. 2007;17:2150.
Rai A, Yadav LDS. Cyclopropenone-catalyzed direct conversion of aldoximes and primary amides into nitriles. Eur J Org Chem. 2013;2013:1889.
Yadav LDS, Srivastava VP, Patel R. Bromodimethylsulfonium bromide a useful reagent for conversion of aldoxim es and primary amides to nitriles. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009;50:5532.
Yu L, Li H, Zhang X, Ye J, Liu J, Xu Q, Lautens M. Organoselenium-catalyzed mild dehydration of aldoximes: An unexpected practical method for organonitrile synthesis. Org Lett. 2014;16:1346.
de DomínguezMaría P. Nitrile synthesis with aldoxime dehydratases: a biocatalytic platform with applications in asymmetric synthesis, bulk chemicals, and biorefineries. Molecules. 2021;26:4466.
Jing X, Wang T, Ding Y, Yu L. A scalable production of anisonitrile through organoselenium-catalyzed dehydration of anisaldoxime under solventless conditions. Appl Catal A Gen. 2017;541:107.
Chen K, Wang Z, Ding K, Chen Y, Asano Y. Recent progress on discovery and research of aldoxime dehydratases. Green Synth. 2021;2(2):179.
Niknam K, Karami B, Kiasat AR. Basic Al2O3/PCl5 as an efficient reagent for the direct synthesis of nitriles from aldehydes under solvent-free conditions. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 2005;26:975.
Chill ST, Mebane RC. A facile one-pot conversion of aldehydes into nitriles. Synth Commun. 2009;39:3601.
Khalafi-Nezhad A, Mohammadi S. Chitosan supported ionic liquid: a recyclable wet and dry catalyst for the direct conversion of aldehydes into nitriles and amides under mild conditions. RSC Adv. 2014;4:13782.
Narsaiah AV, Nagaiah K. An efficient and improved method for the preparation of nitriles from primary amides and aldoximes. Adv Synth Catal. 2004;346:1271.
Rangraz Y, Heravi MM. Recent advances in metal-free heteroatom-doped carbon heterogonous catalysts. RSC Adv. 2021;11:23725.
AL Othman ZA. A review: fundamental aspects of silicate mesoporous materials. Materials. 2012;5:2874.
Verma P, Kuwahara Y, Mori K, Raja R, Yamashita H. Functionalized mesoporous SBA-15 silica recent trends and catalytic applications. Nanoscale. 2020;12:11333.
Hachemaoui M, Boukoussa B, Ismail I, Mokhtar A, Taha I, Iqbal J, Hacini S, Bengueddach A, Hamacha R. CuNPs-loaded amines-functionalized-SBA-15 as effective catalysts for catalytic reduction of cationic and anionic dyes colloids surf. A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2021;623: 126729.
Li H, She T, Chen G, Sun M, Niu L, Bai G. Pd nanoparticles supported on amine-functionalized SBA-15 for the selective hydrogenation of phenol. Mol Catal. 2021;504: 111493.
Ziarani GM, Roshankar S, Mohajer F, Badiei A. The synthesis and application of functionalized mesoporous silica SBA-15 as heterogeneous catalyst in organic synthesis. Curr Org Chem. 2021;25:361.
Long G, Su K, Dong H, Zhao T, Yang C, Liu F, Hu X. Straightforward construction of amino via mechanochemical grafting for one-pot synthesis of cyclic carbonates from aromatic olefins and Co2. J Co2 Util. 2022;59:101962.
Lashgari N, Badiei A, Mohammadi ZG. Modification of mesoporous silica SBA-15 with different organic molecules to gain chemical sensors: a review. Nanochem Res. 2016;1:127.
Rangraz Y, Nemati F, Elhampour A. Magnetic chitosan composite as a green support for anchoring diphenyl diselenide as a biocatalyst for the oxidation of sulfides. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;117:820.
Rangraz Y, Nemati F, Elhampour A. Organoselenium-palladium(II) complex immobilized on functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as a promising retrievable nanocatalyst for the “phosphine-free” Heck-Mizoroki coupling reaction. New J Chem. 2018;42:15361.
Rangraz Y, Nemati F, Elhampour A. Design, synthesis, and characterization of a novel magnetically recoverable copper nanocatalyst containing organoselenium ligand and its application in the A3 coupling reaction. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2019;58:17308.
Rangraz Y, Nemati F, Elhampour A. A novel magnetically recoverable palladium nanocatalyst containing organoselenium ligand for the synthesis of biaryls via Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. J Phys Chem Solids. 2020;138: 109251.
Rangraz Y, Nemati F, Elhampour A. Selenium-doped graphitic carbon nitride decorated with Ag NPs as a practical and recyclable nanocatalyst for the hydrogenation of nitro compounds in aqueous media. Appl Surf Sci. 2020;507: 145164.
Yourdkhani M, Nemati F, Rangraz Y, Elhampour A. Magnetic selenium-doped graphitic carbon nitride nanocomposite as an effective catalyst support for stabilization of Cu NPs. Diam Relat Mater. 2020;110: 108136.
Rangraz Y, Nemati F, Elhampour A. Diphenyl diselenide immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles: a novel and retrievable heterogeneous catalyst in the oxidation of aldehydes under mild and green conditions. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;509:485.
Vilela GD, da Rosa RR, Schneider PH, Bechtold IH, Eccher J, Merlo AA. Expeditious preparation of isoxazoles from Δ2-isoxazolines as advanced intermediates for functional materials. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011;52:6569.
Jahanshahi R, Akhlaghinia B. Cu (ii)-grafted SBA-15 functionalized S-methylisothiourea aminated epibromohydrin (SBA-15/E-SMTU-Cu II): a novel and efficient heterogeneous mesoporous catalyst. New J Chem. 2017;41:7203.
Xue G, Yurun F, Li M, Dezhi G, Jie J, Jincheng Y, Haibin S, Hongyu G, Yujun Z. Phosphoryl functionalized mesoporous silica for uranium adsorption. Appl Surf Sci. 2017;402:53.
Chen F, Jiang X, Kuang T, Chang L, Fu D, Yang J, Fan P. Zhong M Polyelectrolyte/mesoporous silica hybrid materials for the high performance multiple-detection of pH value and temperature. Polym Chem. 2015;6:3529.
Su HL, Xu L, Hu XJ, Chen FF, Li G, Yang ZK, Wang LP, Li HL. Polymer grafted mesoporous SBA-15 material synthesized via metal-free ATRP as pH-sensitive drug carrier for quercetin. Eur Polym J. 2021;148: 110354.
Ghorbani-Choghamarani A, Mohammadi M, Tamoradi T, Ghadermazi M. Covalent immobilization of co complex on the surface of SBA-15: Green, novel and efficient catalyst for the oxidation of sulfides and synthesis of polyhydroquinoline derivatives in green condition. Polyhedron. 2019;158:25.
Kowoll T, Müller E, Fritsch-Decker S, Hettler S, Störmer H, Weiss C, Gerthsen D. Contrast of backscattered electron SEM images of nanoparticles on substrates with complex structure. Scanning. 2017;5:1–12
Taheri-Ledari R, Qazi FS, Saeidirad M, Maleki A. A diselenobis-functionalized magnetic catalyst based on iron oxide/silica nanoparticles suggested for amidation reactions. Sci Rep. 2022;12:1.
ALOthman Z A. A review fundamental aspects of silicate mesoporous materials. Materials. 2012;5:2874.
Zhang X, Sun J, Ding Y, Yu L. Dehydration of aldoximes using PhSe(O)OH as the pre-catalyst in air. Org Lett. 2015;17:23.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful from Semnan University Research Council for its financial support.
Funding
The research leading to these results received funding from Semnan University under Grant Agreement No 140007251157.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MB: did the experimental work and methodology FN: Supervision, financial support, writing the manuscript, and is the primary corresponding author of the manuscript YR: Advisor, reviewing and editing the manuscript and is the secondary corresponding author of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Bigdelo, M., Nemati, F. & Rangraz, Y. Organoselenium functionalized SBA-15 as a new catalyst for the cyanide-free conversion of oximes to nitriles. BMC Chemistry 16, 99 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-022-00899-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-022-00899-7