Abstract
Background
BRCA1 mutation carriers face a high lifetime risk of developing both breast and ovarian cancer. Haploinsufficiency is thought to predispose these women to cancer by reducing the pool of available BRCA1 transcript and protein, thereby compromising BRCA1 function. Whether or not cancer-free BRCA1 mutation carriers have lower messenger (m)RNA transcript levels in peripheral blood leukocytes has not been evaluated. The primary aim of this study was to characterize an association between BRCA1 mutation status and BRCA1 mRNA leukocyte expression levels among healthy women with a BRCA1 mutation.
Method
RNA was extracted from freshly isolated peripheral blood leukocytes of 58 cancer-free, female participants (22 BRCA1 mutation carriers and 36 non-carriers). The expression levels of 236 cancer-associated genes, including BRCA1, were quantified using the Human Cancer Reference gene panel from the Nanostring Technologies nCounter Analysis System.
Results
Multivariate modeling demonstrated that carrying a BRCA1 mutation was the most significant predictor of BRCA1 mRNA levels. BRCA1 mRNA levels were significantly lower in BRCA1 mutation carriers compared to non-carriers (146.7 counts vs. 175.1 counts; P = 0.002). Samples with BRCA1 mutations within exon 11 had lower BRCA1 mRNA levels than samples with mutations within the 5′ and 3′ regions of the BRCA1 gene (122.1 counts vs. 138.9 and 168.6 counts, respectively; P = 0.003). Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of gene expression profiles from freshly isolated blood leukocytes revealed that BRCA1 mutation carriers cluster more closely with other BRCA1 mutation carriers than with BRCA1 wild-type samples. Moreover, a set of 17 genes (including BRCA1) previously shown to be involved in carcinogenesis, were differentially expressed between BRCA1 mutation carriers and non-carriers.
Conclusion
Overall, these findings support the concept of BRCA1 haploinsufficiency wherein a specific mutation results in dosage-dependent alteration of BRCA1 at the transcriptional level. This study is the first to show a decrease in BRCA1 mRNA expression in freshly isolated blood leukocytes from healthy, unaffected BRCA1 mutation carriers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Women with a mutation in the breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1) face a high lifetime risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer estimated to be as high as 80 % and 40 %, respectively [1–4]. BRCA1 regulates several key functions pertinent to cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation [5, 6]. In particular, BRCA1 helps maintain genomic stability by participating in the cellular DNA damage response through homologous recombination (HR)-mediated repair of double-stranded DNA breaks (DSBs) [7]. There is accumulating evidence that BRCA1 haploinsufficiency is a driver of tumor predisposing events in BRCA1 mutation carriers [8].
For haploinsufficiency to be an early driver of BRCA1-associated cancer development, mutation-dependent reduction in BRCA1 expression levels should be associated with a loss of function [8–10]. Most studies that have characterized phenotypic alterations suggest that BRCA1 heterozygous cells have reduced functions in DNA damage repair, hormonal regulation, cell fate changes, transcriptional regulation and autophagy [11–21]; however, little is known about whether the abrogated functions observed in BRCA1 heterozygous cells are correlated with changes in BRCA1 transcript or protein levels [19, 22–24]. This is important in light of data suggesting that the type and location of a mutation can stratify cancer risk (i.e., breast vs. ovary), and the response to treatment [25–29].
Regulation of BRCA1 gene expression is influenced by genetic and epigenetic mechanisms, and environmental factors such as genotoxic, hormonal, and metabolic stressors [30]. Understanding the contribution of the mutation status to basal expression levels of the BRCA1 gene is a crucial step to delineating BRCA1 haploinsufficiency. Previous studies using immortalized lymphoblastoid cell lines have reported differential messenger RNA (mRNA) or protein expression in BRCA1 mutation carriers compared to non-carriers, suggesting a mutation-specific dosage effect [19, 24, 31]. In contrast, Feilotter et al. [18] did not find BRCA1 to be among the set of 43 genes that can predict BRCA1 mutation status by gene expression profiling. However, differences in BRCA1 mRNA expression may have been masked by the continuous proliferative state of immortalized lymphoblastoid cell lines used in these experiments [22, 32–37]. There are no studies, to our knowledge, that have evaluated BRCA1 transcript levels in freshly isolated blood leukocytes.
Notably, reduced BRCA1 protein expression in both inherited and sporadic forms of breast and ovarian cancer has been associated with a significant reduction in the levels of BRCA1 mRNA, thereby supporting the utility of BRCA1 transcript levels as a surrogate marker of BRCA1 function [38–40]. The overall goal of the current study was to evaluate the relationship between BRCA1 mutation status (and mutation type) and mRNA expression among women with and without a BRCA1 mutation, by studying freshly isolated blood leukocytes.
Methods
Study design and population
There were 58 women enrolled in the current study: 22 BRCA1 mutation carriers and 36 non-carriers. All women were 18 years of age or older, none had a personal history of cancer, and none were pregnant or breastfeeding. The first group included women with a BRCA1 mutation, identified from an existing database at the Familial Breast Cancer Research Unit, Women’s College Research Institute (WCRI, Toronto, Canada) who were contacted by letter. The second group included women from the general population who were recruited using various methods such as posters, newsletters or social media. A 30-minute study appointment was then scheduled at the WCRI for all the eligible participants. This research received approval from the Research Ethics Board at the Women’s College Hospital (number 2012-0055-B). All women provided informed consent to participate in the study by signing the provided consent form.
Data and biological sample collection
Study participants completed a questionnaire, which collected information on various exposures, including reproductive and lifestyle factors, medical history, and family history of cancer. Standardized procedures were used to collect measurements of weight (kg) and height (m) to calculate body mass index (BMI; kg/m2). A phlebotomist drew blood into two labeled EDTA-containing tubes (approximately 8 mL) by venipuncture. The samples were placed on ice and delivered immediately to the Women’s College Hospital research laboratory for RNA extraction.
RNA isolation and quantification
RNA was isolated from one of the two EDTA tubes using the LeukoLOCK Total RNA Isolation System (Ambion, USA). This system is optimized for use with human blood and offers the isolation of total RNA from the leukocyte population [41]. In order to maximize RNA isolation yield, all samples were stabilized with RNALater® within 35 minutes of the blood draw. The nucleic acid content was quantified using the Nanodrop spectrophotometer (ThermoScientific). Total RNA quality and quantity was then determined using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (The Centre for Applied Genomics, Toronto, Canada). The resulting extracted RNA was stored at -80 °C until required for further analysis.
nCounter NanoString gene expression profiling
The nCounter Analysis System (NanoString Technologies) was used to measure mRNA gene expression (expressed as counts) at the University Health Network (Toronto, Canada) [42] using the Human Cancer Reference Kit consisting of 236 cancer-related genes. Briefly, the nCounter Analysis System probe library contains two sequence-specific probes, the capture probe and the reporter probe, for each gene of interest. Probe pairs are mixed with total RNA in one hybridization reaction, and then the structures are imaged with the use of fluorescent microscopy. Expression is measured by counting the number of unique color tags within the gene-probe tripartite structures and is reported as counts, a direct measure of the number of RNA transcripts of each gene of interest.
Data acquisition and normalization was carried out using the nSolver Analysis software version 2.0 (NanoString Technologies). Positive and negative controls were used to check for background expression. Reference housekeeping gene normalization was then performed to adjust counts relative to probes that are not expected to vary between samples or replicates, allowing meaningful comparisons between samples. We chose the set of housekeeping genes recommended by Nanostring, which comprised the following genes: CLTC (clathrin, heavy chain), GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase), GUSB (glucuronidase, beta), HPRT1 (hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1), TUBB (tubulin, beta class 1), and PGK1 (phosphoglycerate kinase 1).
Statistical analysis
Student’s t test was used to compare continuous variables in mutation carriers and non-carriers and the chi-square test was used to test for differences in categorical variables. The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to verify the normality of BRCA1 mRNA expression. As expression of BRCA1 was normally distributed (P = 0.26), the Pearson correlation coefficient (ρ) was used to evaluate the correlation between BRCA1 mRNA expression, BRCA1 mutation status and various reproductive and lifestyle factors. Linear regression was used to evaluate the relationship between BRCA1 mutation status and mRNA expression, adjusting for significant predictors of BRCA1 mRNA levels including parity (parous/nulliparous), breastfeeding (ever/never), and menopausal status (premenopausal/postmenopausal). A significance level of P <0.05 was used as the criterion for including variables in the multivariate model.
We assigned the BRCA1 mutations into one of three mutation clusters reported to be differentially associated with the risk of breast vs. ovarian cancer: group 1 contained mutations in exons 1–10; group 2 contained mutations in exon 11; and group 3 contained mutations in exons 12–22 [28]. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare mean BRCA1 expression levels between the three mutation clusters.
Unsupervised hierarchical clustering was performed using Pearson-centered correlation metric with centroid linkage to categorize samples into homogenous groups based on similar levels of gene expression. Heat maps were generated using Java Treeview [43]. Student’s t test was used to identify genes expressed differentially between BRCA1 mutation carriers and non-carriers by testing for differences in mean gene expression levels with a Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate of P < 0.05. The PathDIP database (http://ophid.utoronto.ca/pathDIP) was used to identify over-represented signaling pathways using data from significantly upregulated and downregulated genes through functional enrichment analysis. Statistical significance was defined at the level of P < 0.05 and all analyses were carried out using SPSS, IBM® SPSS® Statistics, version 23, 2015.
Results
Characteristics of study participants
Characteristics of the study subjects are provided in Table 1. Women with a BRCA1 mutation were significantly older than women without a BRCA1 mutation (43.6 vs. 34.4 years; P = 0.007), more likely to be of Ashkenazi Jewish descent (32 % vs. 8 %; P = 0.04), to be parous (77.3 % vs. 33.3 %; P = 0.003), and to have had a prophylactic mastectomy (41 % vs. 0 %; P <0.001). BRCA1 mutation carriers were also more likely than non-carriers to have undergone a prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy (59 % vs. 3 %; P < 0.001), and consequently, a greater proportion were postmenopausal (59 % vs. 11 %; P < 0.001) and had used hormone replacement therapy (HRT) (32 % vs. 8 %; P = 0.03). The two groups were similar in terms of breastfeeding, age at menarche, oral contraceptive (OC) use, smoking status, alcohol consumption, and BMI (P ≥ 0.20).
BRCA1 mutation status significantly contributes to lower overall BRCA1 expression levels
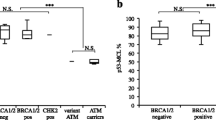
The nCounter Analysis System allows the direct measurement of the number of RNA transcripts of the BRCA1 gene, herein, expressed as counts. In the univariate analysis, BRCA1 mutation carriers had significantly lower mean BRCA1 mRNA expression compared to non-carriers (146.7 counts vs. 175.1 counts; P = 0.002) (Fig. 1, Table 1 and Additional file 1: Table S1). As BRCA1 mRNA expression levels had a normal distribution as determined by the Shapiro-Wilk test of normality, we employed linear regression modeling to investigate factors associated with BRCA1 expression (Tables 2 and 3 and Additional file 2: Table S2). We found that mutation status, parity, breastfeeding, menopause, and oophorectomy were each significantly correlated with lower BRCA1 mRNA levels (P ≤ 0.02) (Table 3). Although not significant, age, age at menarche, current OC use and smoking status were negatively associated with BRCA1 mRNA counts while current alcohol consumption and HRT use were positively associated with BRCA1 mRNA counts.
BRCA1 mRNA expression levels are mutation specific. a Box plot analysis of mean BRCA1 mRNA expression counts in 22 BRCA1 mutation carriers compared to 36 non-carriers, (146.7 vs. 175.1, P = 0.002, respectively). b Distribution of BRCA1 mRNA expression across BRCA1 mutation carriers compared to non-carriers (i.e., control). Control denotes the mean BRCA1 mRNA expression levels across 36 participants with wild-type BRCA1 gene status. Error bars represent the standard deviation of mean BRCA1 mRNA expression counts. UI mutation is unidentified
As BRCA1 mutation status was the most significant contributor to reduced BRCA1 mRNA expression counts in the univariate analysis, we also evaluated this relationship after adjusting for parity, breastfeeding, menopause, and oophorectomy. Covariates were selected based on the univariate analysis showing statistically significant correlations with BRCA1 mRNA counts (Table 2 and Additional file 2: Table S2). For the final regression model, parity, breastfeeding, menopause and mutation status were included in the analysis. As oophorectomy results in menopause, it was excluded from the analysis to prevent over-adjustment. Multivariate modeling demonstrated that carrying a BRCA1 mutation remained the most significant predictor of BRCA1 mRNA levels (Table 3). After adjusting for other important covariates, women with a BRCA1 mutation had 22.5 lower counts of BRCA1 mRNA levels compared to non-carriers (P = 0.04). These data suggest that BRCA1 mutation status alone predicts BRCA1 mRNA expression levels.
BRCA1 mRNA expression levels are mutation specific
Next we characterized BRCA1 mRNA expression by mutation position and type (Table 4 and Fig. 1). Germline mutations in BRCA1 may be located within any of the 22 exons of the gene, with the majority of known pathogenic mutations generating premature termination codons (PTCs). mRNA transcripts with PTCs are typically degraded by a mechanism called nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) in order to prevent the synthesis of potentially harmful truncated protein products [44]. The decay of mutant BRCA1 mRNA has been shown to result in a 1.5 to 5-fold decrease in mRNA abundance; however, PTCs located very close to the translation initiation codon in exon 2 (185delAG) or in the last exon (i.e., 5382insC) may escape NMD [44, 45]. Table 4 outlines the mutation type and location within the gene and whether the mutation type results in NMD [28, 44, 46]. There were seven distinct BRCA1 mutations among the 22 study participants with a known BRCA1 mutation. The mutation type for two of the 22 mutation carriers was unknown. Fourteen of the 22 mutation carriers shared one of two specific mutations: (1) 185delAG or (2) 5382insC, both of which are likely to escape nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Three distinct mutations, including, 2190delA, 1293del40, and 3748G > T, were suggested to undergo NMD and had lower BRCA1 mRNA expression counts compared to mutations that escape NMD, though not statistically significant (mean counts of 130.5 vs. 153 counts, respectively, P = 0.15). Large rearrangement mutations, including deletion exons 1–2 and deletion exons 4–6, had different expression levels at 95.56 counts and 157.12 counts, respectively. Interestingly, participants with mutations that do not undergo NMD had variable expression levels, suggesting that additional factors might regulate BRCA1 mRNA levels (Fig. 1b). For example, 185delAG BRCA1 mutation carriers had expression levels ranging between 109.9 and 153.3 counts. Similarly, 5382insC BRCA1 mutation carriers had expression levels ranging between 118.4 and 195.9 counts. Overall, the data suggest BRCA1 basal mRNA expression levels may be mutation specific.
Recently, Rebbeck et al. [28] reported that mutations in the 5′ and 3′ regions of BRCA1 were associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, while mutations in exon 11 were associated with an increased risk of ovarian vs. breast cancer. To determine if these specific mutation clusters were associated with differential BRCA1 mRNA expression in our cohort, mutations were pooled into three groups: group 1 containing mutations in exons 1–10; group 2 containing mutations in exon 11; and group 3 containing mutations in exons 12–22 (Fig. 2a, b) [28]. Mutations within exon 11 had lower mRNA expression levels (122.1 counts) compared to mutations within the 5′ (138.9 counts) and 3′ (168.6 counts) regions of the BRCA1 gene (P = 0.003) (Fig. 2a, b).
Stratification of mean BRCA1 mRNA expression counts by BRCA1 mutation clusters associated with differential risk for breast and/or ovarian cancers. a Box plot distribution of mean BRCA1 mRNA counts by location of mutation compared to non-carriers. ANOVA analysis of variance. b 1Mutations were sub-classified into three clusters: mutations in the 5′ terminal (Exons 1-10) and 3′ terminal (Exons 12-22) of exon 11 include three previously identified breast cancer cluster regions (BCCRs) proposed to have increased risk for breast vs. ovarian cancer. Mutations within exon 11 were shown to have increased risk for ovarian vs. breast cancer [28]
BRCA1 mutation carriers have similar gene expression profiles
To further characterize the gene expression profiles of freshly isolated blood leukocytes from women with and without a BRCA1 mutation, unsupervised clustering, using a Pearson-centered correlation metric with centroid linkage rules of the normalized genes, was performed across all the samples. Interestingly, the samples tended to cluster based on BRCA1 mutation status (Fig. 3). Out of 236 genes included in the nCounter® GX Human Cancer Reference Kit, we identified eight genes to be significantly downregulated in carriers (Table 5), including BRCA1, CSK, NRAS, PCTK1, TGFBR2, TNFSF10, TOP1, and XPC. Nine genes were significantly upregulated in carriers, including BCR, CLTC, FLT3, IL8, LMO2, PTPN11, REL, TGFB1 and TNFRSF10B at a Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate <0.05 using the t test (Table 6). PathDIP (http://ophid.utoronto.ca/pathDIP) was used for pathway enrichment analysis and identified pathway associations for 94 % of genes. PathDIP analysis showed significant enrichment for cancer pathways (especially colorectal and pancreatic cancers), Toll-like receptor signaling, RAS signaling, and numerous other pathways (Additional file 3: Table S3) (P < 0.0000001). Upregulated genes were most enriched for integrins in angiogenesis, advanced glycation end products and receptor AGE-RAGE in inflammation, and apoptosis pathways (P < 0.0000001). Downregulated genes were most enriched for EGF, RAS, and DNA repair pathways, and for hearing and vision proteins (P < 0.0001).
Comparison of gene expression profiles of BRCA1 mutation carriers (n = 22) and non-carriers (n = 36). a Heat map showing unsupervised hierarchical clustering of 236 genes from the Nanostring Cancer Reference gene panel across BRCA1 mutation carriers and non-carriers. BRCA1 Mut: BRCA1 mutation carrier status and type; BRCA1 WT: BRCA1 wild-type gene status. b Unsupervised hierarchal clustering of gene expression profiles of freshly isolated blood leukocytes from BRCA1 mutation carriers and non-carriers, showing samples cluster by BRCA1 mutation status: 9/22 BRCA1 mutation carriers share similar gene expression profiles and cluster more closely together. Heat map shows the top differentially expressed genes and corresponding gene pathway enrichment analysis; green shows relatively under expressed genes and pathways, respectively; red shows relatively over-expressed genes and pathways, respectively
Discussion
The goal of the current study was to evaluate whether BRCA1 mRNA expression levels are reduced in the leukocytes of women with a BRCA1 mutation. We found that carrying a BRCA1 mutation was the most significant predictor of BRCA1 mRNA levels. BRCA1 mRNA levels were significantly lower in mutation carriers compared to non-carriers (146.7 counts vs. 175.1 counts; P = 0.002). Furthermore, mutations within exon 11 were associated with lower mRNA expression levels compared to mutations within the 5′ and 3′ regions of the BRCA1 gene (122 counts vs. 138 and 167 counts, respectively; P = 0.003). In addition, 17 other genes in a panel of 236 genes, some of which have been previously shown to be involved in breast and ovarian carcinogenesis, were also differentially expressed between the two groups of women. Overall, these findings support the concept of BRCA1 haploinsufficiency, whereby a dosage-dependent effect of the BRCA1 gene is associated with molecular alterations at the transcriptional level. Reduced BRCA1 mRNA expression levels were previously reported in BRCA1-associated cancer [38]. To our knowledge, this is the first study to identify lower BRCA1 expression in leukocytes from healthy, unaffected BRCA1 mutation carriers. Whether lower BRCA1 transcript levels translate to changes in protein levels or to carcinogenesis remains to be determined.
Emerging evidence from epidemiologic studies, from human tissue culture model systems and from murine studies supports a continuum of tumor suppression where BRCA1 expression levels might be tightly correlated with function [9]. Recently, Pathania et al. reported that human breast epithelial and skin fibroblast cells from BRCA1 mutation carriers had lower BRCA1 protein levels that were associated with haploinsufficiency for stalled replication fork repair/replication stress and conditional haploinsufficiency for HR-DSB [22]. Under concurrent forms of stress, such as UV and IR that require BRCA1 mediated HR-DSB, the pool of available BRCA1 is not sufficient to repair all the damage, thereby leading to the accumulation of small genomic aberrations. When these aberrations reach a threshold above which the damage is irreparable, genomic instability ensues and drives malignant transformation [8]. Consequently, identifying BRCA1 mutations that result in low basal expression levels might help stratify cancer risk. More recently, Sedic et al. showed that BRCA1 mutation carriers exhibit cell-type-specific haploinsufficiency for genomic instability, whereby human mammary epithelial cells from BRCA1 mutation carriers had shorter telomeres that contributed to premature senescence compared to non-carriers [23]. If these in vitro findings translate to mammary epithelial cells having a reduced life span in vivo, then additional genomic alterations are required to bypass premature senescence. Whether BRCA1 expression levels can predict cells that are at increased risk of escaping senescence remains to be determined.
A number of epidemiologic reports suggest tumor type predisposition differs according to the position of the BRCA1 mutation [27–29]. In an analysis of 60 families with a history of breast or ovarian cancer, Gayther et al. showed that BRCA1 mutations mapping up to and including exon 12 were linked to a higher ratio of ovarian to breast cancers compared to mutations mapping to the C-terminal portion of the BRCA1 gene [29]. Moreover, using genotype-phenotype correlations in 356 families with pathogenic BRCA1 mutations, Thompson et al. showed that the ovarian to breast cancer ratio was higher with mutations in the central region of the BRCA1 gene (nucleotides 2401-4190; predominantly within exon 11) [27]. In a systemic analysis of 19,581 carriers of BRCA1 mutations, Rebbeck et al. identified that mutation clusters mapped to the 5′ (BCCR1, c.179 to c.505) and 3′ (BCCR2, c.4328 to c.4945 and BCCR2′, c.5261 to c.5563) regions of BRCA1 were associated with increased breast cancer risk, while mutations mapped to exon 11 were associated with increased ovarian cancer risk [28].
In the current study, we showed that mutations within exon 11 had the lowest mRNA expression levels compared to mutations within the 5′ and 3′ regions of the BRCA1 gene, with nonsense-mediated decay being the most likely mechanism mediating mutation-dependent reduced transcript level readout. It remains to be determined how mutation-dependent modulation of BRCA1 expression levels affects the different functions of BRCA1, i.e., which mutations confer a dominant negative role compared to mutations that retain partial wild-type BRCA1 function, whether functions involving domains within exon 11 are more relevant to ovarian epithelium function and whether those within domains of the 3′ and 5′ regions more relevant to breast epithelium functioning [29].
Conditional Brca1 mouse models have also provided insight into functional correlates of different BRCA1 mutations. Mouse strains carrying loss of Brca1 and heterozygous p53 mutations are conditionally targeted to mammary epithelial cells using Cre-lox system. Shakya et al. showed that introduction of a brca1 mutation I26A, which impairs E3 ubiquitin ligase activity but maintains the interaction with Bard1, does not lead to tumor formation; whereas mutation of the BRCT domain (S1598F) that disrupts phosphoprotein binding resulted in a high rate of tumor formation [26]. Drost et al. demonstrated that the Brca1 (C61G) missense mutation, which impairs BRCA1/BARD1 heterodimerization and ubiquitin ligase activity, resulted in mammary tumors that were resistant to cisplatin and PARP inhibitors compared to Brca1 null mice [25]. Overall, these studies suggest that all BRCA1 mutations are not equivalent in their tumorigenic potential, and consequently, cancer risk assessment might be mutation specific.
The present study also highlights BRCA1 mutation status as a significant classifier based on global gene expression profiling. Pathway enrichment analysis revealed gene expression alterations that are tissue specific, including genes that mediate acute/chronic leukemia. Interestingly, enrichment of genes involved in Toll-like receptor signaling and IL-2-mediated signaling in BRCA1 mutation carriers, suggests that changes in the immune microenvironment might occur early on in heterozygous cells and may be useful for targeted prevention strategies. Furthermore, downregulated genes were enriched in DNA damage response pathways, thereby supporting the growing evidence for BRCA1 haploinsufficiency in DNA damage repair as a potential early tumor predisposing event.
Strengths of the current study include the use of RNA from blood leukocytes that was stabilized within 30 minutes of collection, resulting in high quality RNA (mean RNA integrity number, RIN = 8.7), and the use of the NanoString nCounter Analysis System to quantify mRNA expression, which helps to achieve high validity, reproducibility, and sensitivity [42]. The primary limitation of our study is that the BRCA1 expression analysis was not allele-specific, i.e., the lower mRNA counts in leukocytes of BRCA1 mutation carriers extend beyond nonsense-mediated decay of the mutant allele to include mechanisms, such as microRNA-mediated regulation of expression levels of wild-type or mutant-type alleles, and altered expression levels of regulators of BRCA1 mRNA levels in BRCA1 mutation carriers vs. non-carriers. Future studies using RNA sequencing, which can discriminate between levels of the wild-type and mutant allele are warranted. Other limitations include the relatively small sample size that allowed for the evaluation of a narrow spectrum of BRCA1 mutations and their effects on BRCA1 gene expression levels.
Collectively, these data support the concept of BRCA1 haploinsufficiency, whereby BRCA1 heterozygous cells have lower BRCA1 mRNA expression levels. Since the evaluation of BRCA1 protein levels as a surrogate marker of BRCA1 haploinsufficiency posits a challenge, especially in freshly isolated leukocytes, our study highlights the role of using BRCA1 mRNA levels as an indicator of prospective BRCA1 functional levels. Factors that increase BRCA1 levels to a normal level might restore BRCA1 function. We recently demonstrated that daily oral supplementation with 3,3′-diindolylmethane (i.e., DIM) for 4–6 weeks resulted in a significant 34 % increase in BRCA1 mRNA expression in leukocytes from women with a BRCA1 mutation [47]. Elsewhere, sedentary behavior was associated with significantly lower BRCA1 mRNA levels in women with and without a mutation [48]. These studies provide important mechanistic insight into how a lifestyle factor may mediate cancer risk in this high-risk population.
Conclusions
In summary, our findings suggest that BRCA1 mutation status is a significant predictor of lower BRCA1 mRNA levels in peripheral blood leukocytes. In turn, this may provide a feasible tool whereby modulation of BRCA1 levels through different interventions can be monitored in the clinical setting or can stratify risk. The possibility of mitigating the effect of an inherited deleterious BRCA1 mutation by increasing the physiologic expression of the gene and normalizing protein levels represents a clinically important paradigm shift in the prevention strategies available to these high-risk women.
Abbreviations
AGE-RAGE, advanced glycation end products-receptor for advanced glycation end products; ANOVA, analysis of variance; BCCR, breast cancer cluster region; BRCA1, Breast cancer 1, early onset; DSB, double strand break; HR, homologous recombination; HR-DSB, homologous recombination mediated repair of double-stranded DNA breaks; HRT, hormone replacement therapy; mRNA, messenger RNA; NMD, nonsense mediated decay; PTC, premature termination codon; WCRI, Women’s College Research Institute
References
Antoniou A, Pharoah PD, Narod S, Risch HA, Eyfjord JE, Hopper JL, Loman N, Olsson H, Johannsson O, Borg A, et al. Average risks of breast and ovarian cancer associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations detected in case series unselected for family history: a combined analysis of 22 studies. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;72(5):1117–30.
Thompson D, Easton DF, Consortium BCL. Cancer Incidence in BRCA1 mutation carriers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94(18):1358–65.
Chen S, Parmigiani G. Meta-analysis of BRCA1 and BRCA2 penetrance. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(11):1329–33.
Ford D, Easton DF, Bishop DT, Narod SA, Goldgar DE. Risks of cancer in BRCA1-mutation carriers. Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Lancet. 1994;343(8899):692–5.
Foulkes WD. BRCA1 functions as a breast stem cell regulator. J Med Genet. 2004;41(1):1–5.
Narod SA, Foulkes WD. BRCA1 and BRCA2: 1994 and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(9):665–76.
Gudmundsdottir K, Ashworth A. The roles of BRCA1 and BRCA2 and associated proteins in the maintenance of genomic stability. Oncogene. 2006;25(43):5864–74.
Bartek J, Lukas J, Bartkova J. DNA damage response as an anti-cancer barrier: damage threshold and the concept of ‘conditional haploinsufficiency’. Cell Cycle. 2007;6(19):2344–7.
Berger AH, Knudson AG, Pandolfi PP. A continuum model for tumour suppression. Nature. 2011;476(7359):163–9.
Berger AH, Pandolfi PP. Haplo-insufficiency: a driving force in cancer. J Pathol. 2011;223(2):137–46.
Savage KI, Matchett KB, Barros EM, Cooper KM, Irwin GW, Gorski JJ, Orr KS, Vohhodina J, Kavanagh JN, Madden AF, et al. BRCA1 deficiency exacerbates estrogen-induced DNA damage and genomic instability. Cancer Res. 2014;74(10):2773–84.
Salmena L, Narod S. BRCA1 haploinsufficiency: consequences for breast cancer. Womens Health (Lond Engl). 2012;8(2):127–9.
Rennstam K, Ringberg A, Cunliffe HE, Olsson H, Landberg G, Hedenfalk I. Genomic alterations in histopathologically normal breast tissue from BRCA1 mutation carriers may be caused by BRCA1 haploinsufficiency. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2010;49(1):78–90.
Nisman B, Kadouri L, Allweis T, Maly B, Hamburger T, Gronowitz S, Peretz T. Increased proliferative background in healthy women with BRCA1/2 haploinsufficiency is associated with high risk for breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2013;22(11):2110–5.
Konishi H, Mohseni M, Tamaki A, Garay JP, Croessmann S, Karnan S, Ota A, Wong HY, Konishi Y, Karakas B, et al. Mutation of a single allele of the cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 leads to genomic instability in human breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(43):17773–8.
Lim E, Vaillant F, Wu D, Forrest NC, Pal B, Hart AH, Asselin-Labat ML, Gyorki DE, Ward T, Partanen A, et al. Aberrant luminal progenitors as the candidate target population for basal tumor development in BRCA1 mutation carriers. Nat Med. 2009;15(8):907–13.
Proia TA, Keller PJ, Gupta PB, Klebba I, Jones AD, Sedic M, Gilmore H, Tung N, Naber SP, Schnitt S, et al. Genetic predisposition directs breast cancer phenotype by dictating progenitor cell fate. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8(2):149–63.
Feilotter HE, Michel C, Uy P, Bathurst L, Davey S. BRCA1 haploinsufficiency leads to altered expression of genes involved in cellular proliferation and development. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100068.
Vaclová T, Gómez-López G, Setién F, Bueno JM, Macías JA, Barroso A, Urioste M, Esteller M, Benítez J, Osorio A. DNA repair capacity is impaired in healthy BRCA1 heterozygous mutation carriers. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015;152:271–82.
George SH, Greenaway J, Milea A, Clary V, Shaw S, Sharma M, Virtanen C, Shaw PA. Identification of abrogated pathways in fallopian tube epithelium from BRCA1 mutation carriers. J Pathol. 2011;225(1):106–17.
Tang MK, Kwong A, Tam KF, Cheung AN, Ngan HY, Xia W, Wong AS. BRCA1 deficiency induces protective autophagy to mitigate stress and provides a mechanism for BRCA1 haploinsufficiency in tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2014;346(1):139–47.
Pathania S, Bade S, Le Guillou M, Burke K, Reed R, Bowman-Colin C, Su Y, Ting DT, Polyak K, Richardson AL, et al. BRCA1 haploinsufficiency for replication stress suppression in primary cells. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5496.
Sedic M, Skibinski A, Brown N, Gallardo M, Mulligan P, Martinez P, Keller PJ, Glover E, Richardson AL, Cowan J, et al. Haploinsufficiency for BRCA1 leads to cell-type-specific genomic instability and premature senescence. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7505.
Baldeyron C, Jacquemin E, Smith J, Jacquemont C, De Oliveira I, Gad S, Feunteun J, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Papadopoulo D. A single mutated BRCA1 allele leads to impaired fidelity of double strand break end-joining. Oncogene. 2002;21(9):1401–10.
Drost R, Bouwman P, Rottenberg S, Boon U, Schut E, Klarenbeek S, Klijn C, van der Heijden I, van der Gulden H, Wientjens E, et al. BRCA1 RING function is essential for tumor suppression but dispensable for therapy resistance. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(6):797–809.
Shakya R, Reid LJ, Reczek CR, Cole F, Egli D, Lin CS, deRooij DG, Hirsch S, Ravi K, Hicks JB, et al. BRCA1 tumor suppression depends on BRCT phosphoprotein binding, but not its E3 ligase activity. Science. 2011;334(6055):525–8.
Thompson D, Easton D, Consortium BCL. Variation in BRCA1 cancer risks by mutation position. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2002;11(4):329–36.
Rebbeck TR, Mitra N, Wan F, Sinilnikova OM, Healey S, McGuffog L, Mazoyer S, Chenevix-Trench G, Easton DF, Antoniou AC, et al. Association of type and location of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations with risk of breast and ovarian cancer. JAMA. 2015;313(13):1347–61.
Gayther SA, Warren W, Mazoyer S, Russell PA, Harrington PA, Chiano M, Seal S, Hamoudi R, van Rensburg EJ, Dunning AM, et al. Germline mutations of the BRCA1 gene in breast and ovarian cancer families provide evidence for a genotype-phenotype correlation. Nat Genet. 1995;11(4):428–33.
Xu CF, Chambers JA, Solomon E. Complex regulation of the BRCA1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(34):20994–7.
Ribieras S, Magdinier F, Leclerc D, Lenoir G, Frappart L, Dante R. Abundance of BRCA1 transcripts in human cancer and lymphoblastoid cell lines carrying BRCA1 germ-line alterations. Int J Cancer. 1997;73(5):715–8.
Somasundaram K, Zhang H, Zeng YX, Houvras Y, Peng Y, Wu GS, Licht JD, Weber BL, El-Deiry WS. Arrest of the cell cycle by the tumour-suppressor BRCA1 requires the CDK-inhibitor p21WAF1/CiP1. Nature. 1997;389(6647):187–90.
Larson JS, Tonkinson JL, Lai MT. A BRCA1 mutant alters G2-M cell cycle control in human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1997;57(16):3351–5.
Aprelikova ON, Fang BS, Meissner EG, Cotter S, Campbell M, Kuthiala A, Bessho M, Jensen RA, Liu ET. BRCA1-associated growth arrest is RB-dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(21):11866–71.
Somasundaram K. Breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1): role in cell cycle regulation and DNA repair–perhaps through transcription. J Cell Biochem. 2003;88(6):1084–91.
Gudas JM, Li T, Nguyen H, Jensen D, Rauscher FJ, Cowan KH. Cell cycle regulation of BRCA1 messenger RNA in human breast epithelial cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1996;7(6):717–23.
Sourvinos G, Spandidos DA. Decreased BRCA1 expression levels may arrest the cell cycle through activation of p53 checkpoint in human sporadic breast tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;245(1):75–80.
Kainu T, Kononen J, Johansson O, Olsson H, Borg A, Isola J. Detection of germline BRCA1 mutations in breast cancer patients by quantitative messenger RNA in situ hybridization. Cancer Res. 1996;56(13):2912–5.
An J, Wei Q, Liu Z, Lu KH, Cheng X, Mills GB, Wang LE. Messenger RNA expression and methylation of candidate tumor-suppressor genes and risk of ovarian cancer - a case-control analysis. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet. 2010;1(1):1–10.
Miyamoto K, Fukutomi T, Asada K, Wakazono K, Tsuda H, Asahara T, Sugimura T, Ushijima T. Promoter hypermethylation and post-transcriptional mechanisms for reduced BRCA1 immunoreactivity in sporadic human breast cancers. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2002;32(3):79–84.
Bayatti N, Cooper-Knock J, Bury JJ, Wyles M, Heath PR, Kirby J, Shaw PJ. Comparison of blood RNA extraction methods used for gene expression profiling in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e87508.
Geiss GK, Bumgarner RE, Birditt B, Dahl T, Dowidar N, Dunaway DL, Fell HP, Ferree S, George RD, Grogan T, et al. Direct multiplexed measurement of gene expression with color-coded probe pairs. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(3):317–25.
Saldanha AJ. Java Treeview–extensible visualization of microarray data. Bioinformatics. 2004;20(17):3246–8.
Perrin-Vidoz L, Sinilnikova OM, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Lenoir GM, Mazoyer S. The nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway triggers degradation of most BRCA1 mRNAs bearing premature termination codons. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11(23):2805–14.
Buisson M, Anczuków O, Zetoune AB, Ware MD, Mazoyer S. The 185delAG mutation (c.68_69delAG) in the BRCA1 gene triggers translation reinitiation at a downstream AUG codon. Hum Mutat. 2006;27(10):1024–9.
Liu HX, Cartegni L, Zhang MQ, Krainer AR. A mechanism for exon skipping caused by nonsense or missense mutations in BRCA1 and other genes. Nat Genet. 2001;27(1):55–8.
Kotsopoulos J, Lubinski J, Moller P, Lynch HT, Singer CF, Eng C, Neuhausen SL, Karlan B, Kim-Sing C, Huzarski T, et al. Timing of oral contraceptive use and the risk of breast cancer in BRCA1 mutation carriers. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;143(3):579–86.
Pettapiece-Phillips R, Kotlyar M, Chehade R, Salmena L, Narod SA, Akbari MR, Jurisica I, Kotsopoulos J. Uninterrupted sedentary behavior downregulates BRCA1 gene expression. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2015;9(1):83–8.
Acknowledgements
JK is the recipient of a Cancer Care Ontario Research Chair in Population Studies. JK and MA are recipients of a Canadian Cancer Society Career Development Award in Prevention. SAN and IJ are recipients of a Tier I Canada Research Chair. LS is the recipient of a Tier II Canada Research Chair. This study was supported by a Cancer Care Ontario Population Studies Research Network Pilot Study grant. The authors would like to thank Jennifer Cruickshank for her valuable comments on this manuscript.
Authors’ contributions
JK, SAN, MA, RC, and LS conceived and designed the study. JK was involved in the management and funding of the study. RC and RP enrolled the study participants, collected data and biological specimens and performed the processing of the specimens as well as RNA extraction. RC, MK, and IJ performed the statistical analyses. RC and JK drafted the manuscript and were both involved in data analysis and interpretation of the results. All authors contributed to the critical revision and editing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional files
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Distribution of mean BRCA1 mRNA expression counts in BRCA1 mutation carriers and non-carriers. (DOC 31 kb)
Additional file 2: Table S2.
BRCA1 mutation status is a predictor of BRCA1 mRNA expression. (DOC 32 kb)
Additional file 3: Table S3.
Pathway enrichment analysis of genes differentially expressed between BRCA1 mutation carriers and non-carriers. (XLS 205 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Chehade, R., Pettapiece-Phillips, R., Salmena, L. et al. Reduced BRCA1 transcript levels in freshly isolated blood leukocytes from BRCA1 mutation carriers is mutation specific. Breast Cancer Res 18, 87 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-016-0739-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-016-0739-8