Dear Editor,
I have read with interest the published article entitled “Mortality rate of acute kidney injury in SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis” by Chen et al. [1]. The article is well written, and I have three concerns as explained below.
Firstly, the mortality rate for COVID-19 patients with AKI is different in the text (i.e., 76.5%; 95% CI 61.0–89.0) from one reported in the authors’ Figure 1 (i.e., 78.0%; 95% CI 63.0–90.0). The authors might need to clarify this discrepancy.
Secondly, the authors mistakenly made a duplicate entry of the study by Chen et al. (2020) in the COVID-19 forest plot. This mistake resulted in a pooled AKI mortality rate of 78.0% (CI 63.0–90.0), I2 = 97.1%, P < 0.0001, instead of 53.99% (CI 52.34–55.65), I2 = 98.4%, P < 0.0001, had the authors sorted the duplicate-entry problem.
Thirdly, the authors concluded the mortality rate for COVID-19 patients with AKI from an otherwise a high heterogeneity of I2 = 97.1%, P < 0.0001. This strongly impacts the reliability of the conclusion drawn [2].
I, on the other hand, reanalyzed authors’ data and performed sensitivity analysis according to the Cochrane Library recommendation [3]. I excluded six peculiar studies from the analysis. Alberici et al. and Banerjee et al. involved kidney transplant patients, unlike the rest of the studies. Wang et al. utilized intensive care unit patients, unlike other studies. Moreover, Alberici et al., Banerjee et al., Hirsch et al., Suwanwongse et al., and Richardson et al. included racially diverse participants. Different races have different COVID-19 mortalities [4, 5]. The nine remaining studies represented all-Asian Chinese hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and AKI. The newly obtained mortality rate for COVID-19 patients with AKI was 94.90% (CI 91.47–98.34), with non-statistically significant heterogeneity, I2 = 7.4%, P < 0.375, see Fig. 1. Sensitivity analysis could not be conducted in MERS and SARS outcomes because of an insufficient number of studies.
Authors’ response to “Joel Swai. Letter to the editor—Mortality rate of acute kidney injury in SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis”
We thank Dr. Joel Swai for the interest in our research letter. As the author pointed out, the reported results of mortality rate for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) is different from the text and Figure 1c in the original publication of our article [1]. The problem is that we mistakenly made a duplicate entry of the Chen et al. (2020) study while performing the COVID-19 forest plot. We have noticed this critical issue and sent the correct proof before the article publication; unfortunately, this mistake had not been accurately revised by the production team. We sincerely regret the inaccuracy may cause any inconvenience to the readers. However, there are no changes to the interpretation of the results, conclusions, and applications of our article. In details:
-
1.
There was no evidence of statistical heterogeneity among studies reporting AKI mortality in SARS (I2 = 0.0%, P = 0.589) and MERS (I2 = 0.0%, P = 0.758), but there was for COVID-19 infection (I2 = 97.0%, P < 0.0001).
-
2.
Figure 1c:
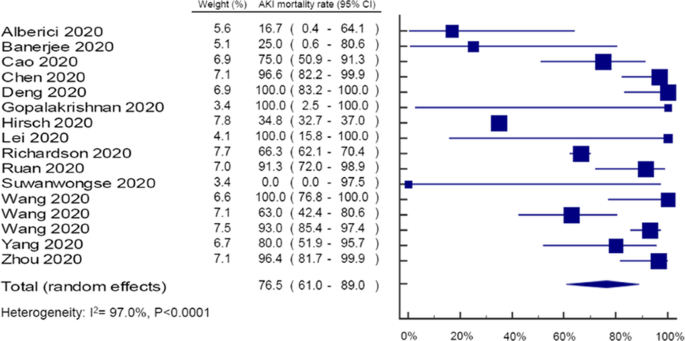
In addition, our research letter aimed to overview the AKI mortality in patients with different coronaviruses, but the clinical heterogeneity between studies should be also noted. One of the important factors may be the racial difference between studies as Dr. Joel Swai noted. Even if the recent study from Fisher et al. indicated the races are not associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients developing AKI [6], future large meta-analyses may be suggested to explore the clinical impacts from different races in AKI mortality in COVID-19 patients.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Chen YT, Shao SC, Lai EC, Hung MJ, Chen YC. Mortality rate of acute kidney injury in SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2020;24(1):439.
Imrey PB. Limitations of meta-analyses of studies with high heterogeneity. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(1):e1919325.
Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JP, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;10:Ed000142.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 in Racial and Ethnic Minority Groups, Inc.; c2020 [Updated 2020 Jun 25; cited 2020 Jul 22]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/racial-ethnic-minorities.html.
Golestaneh L, Neugarten J, Fisher M, Billett HH, Gil MR, Johns T, et al. The association of race and COVID-19 mortality. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;8(1):38.
Fisher M, Neugarten J, Bellin E, et al. AKI in hospitalized patients with and without COVID-19: a comparison study [published online ahead of print, 2020 Jul 15]. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020:ASN.2020040509. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2020040509.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
There was no external funding regarding the letter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JS drafted the manuscript. JS revised the manuscript critically for valuable intellectual content. JS approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author has no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Swai, J. Letter to the editor—Mortality rate of acute kidney injury in SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care 24, 555 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-020-03239-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-020-03239-0



