Abstract
The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 (LRP4) is essential for inducing the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) formation in muscle fibers, and LRP4 plays a critical role in dendritic development and synaptogenesis in the central nervous system (CNS). As a single transmembrane protein, LRP4 contains an enormously sizeable extracellular domain (ECD), containing multiple LDLα repeats in the N-terminal of ECD. LRP4 only with extracellular domain acts as a similar mechanism of full-length LRP4 in muscles to stimulate acetylcholine receptor clustering. In this study, we elucidated that LDLα repeats of LRP4 maintained the body weight and survival rate. Dendritic branches of the pyramidal neurons in Lrp4-null mice with LRP4 LDLα repeats residue were more than in Lrp4-null mice without residual LRP4 domain. Supplement with conditioned medium from LRP4 LDLα overexpression cells, the primary culture pyramidal neurons achieved strong dendritic arborization ability. Besides, astrocytes with LRP4 LDLα repeats residue could promote pyramidal neuronal dendrite arborization in the primary co-cultured system. These observations signify that LRP4 LDLα repeats play a prominent underlying role in dendrite arborization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Synapses formed between neurons and target cells are the basis of brain function, and synaptic transmission is critical for learning, memory, and response to environmental changes. Furthermore, dysfunction of synapses involves various neuropsychiatric diseases, such as autism, schizophrenia, and epilepsy. In neuromuscular junction (NMJ) development and maintenance, LRP4 plays a vital role [1,2,3]. Lrp4 null mice die at birth because of breath deficit, and biochemical studies have confirmed that LRP4 is a crucial regulator for NMJ formation [4]. It also is the receptor of Agrin and binds explicitly to neural Agrin, which promotes NMJ development [1, 3,4,5,6]. The single transmembrane protein LRP4 contains a small intracellular domain (ICD) and an enormous extracellular domain (ECD), and LRP4 ECD has eight LDLα domains, four β-propeller domains, and a domain for O-linked oligosaccharide modification. LRP4ECD/ECD mice form partially functional NMJ, expressing only the ECD, without the transmembrane domain (TMD) and ICD [7]. The results from LRP4ECD/ECD mice suggested that the TMD and ICD are not required for NMJ formation [5, 8, 9], and the LRP4 ECD domain plays a prominent role in the NMJ formation.
Lrp4 is mainly expressed in the hippocampus, olfactory bulb, cerebellum, and neocortex, especially in the hippocampal postsynaptic membrane [10,11,12]. Early studies indicate that LRP4 is a protein present in the pyramidal neurons [12, 13]. Researchers found that LRP4 plays multiple roles in the CNS, involving hippocampal synaptic plasticity, excitatory synaptic transmission, fear regulation, and long-term enhancement [13, 14]. Furthermore, impaired synaptic plasticity and cognitive function deficits have been found in Lrp4 knockout mice [13, 15]. Recently, Astrocytic LRP4 has been shown to regulate glutamatergic synaptic transmission by regulating adenosine triphosphate (ATP) release [11]. The role of the LRP4 extracellular segment in the brain is currently unclear.
In this study, two types of muscle-rescued Lrp4-null mice were used to identify the function of LRP4 LDLα: muscle-rescued Lrp4LacZ/LacZ mice (mr-Lrp4LacZ) and muscle-rescued Lrp4mitt/mitt mice (mr-Lrp4mitt). Astonishingly, we found some intriguing differences between mr-Lrp4LacZ mice and mr-Lrp4mitt mice, which were ignored or not paid special attention in previous research. LRP4 LDLα domain affects the survival rate and bodyweight of mice. Significantly, the LRP4 LDLα domain manipulates the dendritic arborization of pyramidal neurons in vivo and in vitro. These results indicate that the LRP4 LDLα domain plays a crucial role in developing CNS during dendritic branching.
Materials and methods
Animal
Lrp4-null mice (such as Lrp4mitt/mitt and Lrp4LacZ/LacZ) died at birth because Lrp4-null mice could not move or breathe with NMJ deficits. HSA-Lrp4 transgenic mice [9] cross with Lrp4mitt/+ mice (RRID: MMRRC_048465-UCD)[4] or Lrp4LacZ/+ mice [11] to generate Lrp4-null mice with muscle-rescued Lrp4 expression (Lrp4mitt/mitt;HSA-Lrp4 Tg and Lrp4LacZ/LacZ;HSA-Lrp4 Tg, briefly as mr- Lrp4mitt and mr-Lrp4LacZ, respectively) can breathe and move freely [9, 13, 14, 16]. There is a stop code in the amino acid 377 in LRP4 in Lrp4mitt/mitt mice [4]. HSA-Lrp4 transgenic mice express exogenous wild-type Lrp4, specifically in skeletal muscle [9]. In Lrp4LacZ/+ mice, β-galactosidase protein cassette, including both stop code and a polyadenylation termination signal, was inserted into the downstream of Lrp4 promoter [11].
Mice were housed in ventilated cages. Five or fewer adult mice were feed in each cage. Sufficient water and food were free intakes to mice, with a 12-h light/dark cycle, room temperature at 22 to 25 °C, and humidity is 50–60%. All experiments involving animals were conducted according to the “guidelines for the care and use of experimental animals” issued by Nanchang University. The Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of the University of Nanchang approved the protocol (Permit Number: 2016–0002). For in vivo experiment, surgery was performed under sodium pentobarbital anesthesia (50 mg/kg, ip. injection), and all efforts were made to minimize suffering. After terminal experiments, mice were euthanized by carbon dioxide inhalation.
Nissl’s staining
Brain slides were cut in 40 μm, washing with distilled water for 3 min. Dyeing in the staining buffer (0.2% Cresyl Violet solution) for 5 min at 60 °C. Then dehydrating slides with 50%, 75%, 90% ethanol (Cat.# A500737, Sangon Biotech) for 20 s. Putting the slides into 100% ethyl alcohol 3 times, each time for 20 s, transferring slides into xylene (Cat.# A530011, Sangon Biotech) 3 times, each time for 10 min. Samples were mounted in Hydromount (National Diagnostics, USA, HD-106).
Golgi staining
Golgi staining was performed using the FD Rapid Golgi Stain™ Kit (FD NeuroTechnologies, USA, PK-401). Staining solution D, solution E, and ultra-pure water were mixed in a ratio of 1:1:2. Slides were incubated with staining solution at room temperature for 10 min and washed twice with ultra-pure water each time for 4 min. Transferring brain slides to the plate hole containing 50%, 75%, and 90% ethanol for 4 min each time, the brain slides were put into the holes containing 10 ml 90% ethanol or 100% ethanol for 3 times, 4 min for each time. Followed the samples were put into the xylene for 1 h. Images were randomly taken. Pyramidal neurons with clear dendritic branches were subjected to Sholl analysis by using ImageJ. The investigator who performed the analysis was blinded to genotypes.
Cell culture and plasmid transfection
HEK293T (RRID: CVCL_0063) cells were cultured with media (DMEM + 10% Fetal bovine serum + 1% Pens/Strep) in a cell culture incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2 and changed the medium once every 3 days. After the cell density reached about 60%, added the plasmids (pFLAG-CMV1 vector, pFLAG-CMV1-Lrp4-LDLα, or pFLAG-CMV1-Reelin) and polyethyleneimine (Cat.# 24314, Ploysciences) to 50 μl of serum-free DMEM culture medium according to the ratio of 3 μg of the plasmid to 15 μl of PEI, then mixed at room temperature. 20 min later, the mixture was added to HEK293T cells. After cultured in an incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 4–8 h, the culture medium was replaced with a new HEK293T culture medium. After 24 h, the conditioned medium collected from the supernatant was added into the primary neurons from the hippocampi of wild-type mice (DIV4). Primary neurons were changed half-medium every other day, and after 6 days (DIV10), the neurons were preformed to immunofluorescent staining.
Immunoprecipitation (IP) and Western blotting
Anti-Flag beads (Cat. # M8823, Sigma Aldrich) were used to immunoprecipitate target protein from the cell culture medium. Western blotting was performed as described previously [17]. In brief, total proteins were extracted by RIPA. After SDS-PAGE, samples were transferred to the PVDF membrane (Millipore, USA) with transfer membrane apparatus (BIO-RAD, USA). The membrane was blocked by 5% milk in blocking buffer for 2 h. Wash the membrane with a washing buffer 3 times. Anti-Flag (Cat.# F1804, Sigma Aldrich) and anti-β-Actin (Cat.# ab8227, Abcam) primary antibody was added and incubated at 4 °C overnight. The HRP-labeled secondary antibody was added (1:2000, Abcam) to incubate at room temperature for 2 h and then washed 3 times. Luminata TM Crescendo Western HRP Substrate was added. Immunoreacted bands were captured by an enhanced chemiluminescence system (BIO-RAD, USA).
Astrocyte and neuron co-culture
Primary cell separation and co-culture were performed as described previously [11] with minor modifications. The isolated hippocampi or the cerebral cortexes of E18 mice were cut into small pieces and digested in 0.25% trypsin at 37 °C for 10–15 min. For primary neuron culture, dissociated cells were resuspended in primary culture medium (Neurobasal + 1% GlutaMax™ + 5% FBS + 1% Pens/Strep) and plated onto poly-L-lysine–coated coverslips in 12 well-plates for 4 h. And then replacing medium with serum-free medium (Neurobasal + 1% GlutaMAX™ + 2% B27 + 1% Pens/Strep) and cytosine arabinoside (Cat.# HY-13605, Med ChemExpress) (10 μM) to inhibit glial proliferation. Half of the medium was changed every other day. For astrocyte culture, dissociated cells from the cerebral cortexes were resuspended in the plating medium (DMEM + 10% Fetal bovine serum + 1% GlutaMAX™ + 1% Pens/Strep) and plated into culture flasks for 3 d. The flasks were shaken at 250 rpm for 24 h to remove microglia and oligodendrocytes. Astrocytes were passaged every 3 d at a ratio of 1:3 and seeded onto coverslips before co-culture. After neurons were cultured 8 d (DIV8), three coverslips seeded astrocytes were placed with one neuron coverslip in one 35-mm dish containing serum-free medium for incubating 7 d (DIV15) until immunofluorescent staining. Co-culture primary neurons were also isolated from the cerebral cortexes, the same brain part as the astrocytes.
Immunofluorescent staining
The coverslips of cultured neurons were fixed at room temperature for 20 min in 4% paraformaldehyde. After rinsing 10 min with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (0.01 M, pH 7.4) at room temperature, the coverslips were immersed in antibody blocking solution (10% donkey serum, 1% calf serum albumin, 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS) at room temperature for 2 h. After this, the coverslips were rinsed with 0.01 M PBS at room temperature 3 times. The primary antibody (anti-β3-Tubulin antibody, Cat.# PA5-95875, Thermo Fisher Scientific) was diluted 1:1000 with an antibody blocking solution and was added into the coverslips for 4 °C overnight. The coverslips were washed with 0.01 M PBS at room temperature 3 times, each time for 10 min. The secondary antibody (anti-IgG, Cat.# 1832035, Invitrogen) was diluted 1:1000 with an antibody blocking solution, and then the coverslips were incubated at room temperature for 2 h in the dark. After washing 3 times for 10 min with PBST, samples were mounted in Hydromount (National Diagnostics). Images were collected with an Olympus fluorescence microscope (FSX100) and collapsed into a single image. Same areas as the Nissl staining, the brain slice was also used for anti-NeuN (Cat.# MAB377, Merck Millipore) staining, a similar procedure to the above.
Experimental design and statistical analysis
The study was not pre-registered. For the assignment of experimental groups, no unique randomization methods were employed. Sample sizes and the number of cells were determined by experience and not by a statistical sample size calculation. The experiments reported in this work did not require institutional approval. Exclusion criteria were not pre-determined in this study. Data were statistically analyzed using GraphPad Prism 5.0 (RRID: SCR_002798, GraphPad Software, CA, USA), and the results were expressed as mean ± standard error (Mean ± SEM). A different person performed the analysis and experimental group assignments than the experimenter. Two-way ANOVA analyzed the measurement data; an independent sample T-test analyzed the comparison between groups. The mice numbers of independent experiments were noted in the figure legend. The difference was considered statistically significant, and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant, P > 0.05 was considered no significant.
Results
LRP4 LDLα domain was necessary to keep body weight and survival rate
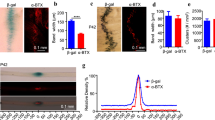
Bodyweight and survival rate of mr-Lrp4LacZ mice, mr-Lrp4mitt mice, and the control mice were monitored for more than 60 d. Compared with the control mice, the survival rate was significantly lower in the mr-Lrp4LacZ group (Fig. 1b). The mr-Lrp4LacZ mice gained significantly less body weight and brain weight (Fig. 1c-e). However, mr-Lrp4mitt mice appeared healthy and were indistinguishable from the control mice. There was no significant difference between mr-Lrp4mitt mice and the control mice in body weight, survival rate, and brain weight (Fig. 1b–e ). mr-Lrp4mitt mice and mr-Lrp4LacZ mice were all Lrp4-null mice, but there were significant differences in phenotype between mr-Lrp4LacZ and mr-Lrp4mitt mice. The mr-Lrp4mitt mice remained the LDLα domain of LRP4 theoretically, as shown in Fig. 1a. Therefore, we speculate whether the LDLα domain played a particular function to keep mice alive and body weight, which leads to phenotypic differences between the two types of mice.
LRP4 LDLα domain is necessary to keep body weight and survival rate. a Schematic diagram of Lrp4-LacZ and Lrp4-mitt; b Comparing with mr-Lrp4mitt and the control mice, the survival rate of mr-Lrp4LacZ mice reduced. Control mice, n = 51; mr-Lrp4mitt mice, n = 53; mr-Lrp4LacZ mice, n = 39; c Compared with the other two types of mice, the bodyweight of mr-Lrp4LacZ mice reduced. Multiple comparisons were made between the control and mr-Lrp4LacZ mice (Above the curves) or between mr-Lrp4mitt and mr-Lrp4LacZ mice (Between the curves). All mice were male. Control mice, n = 21; mr-Lrp4LacZ mice, n = 18; mr-Lrp4mitt mice, n = 22; d Representative brain of the control, mr-Lrp4LacZ and mr-Lrp4mitt mice; e Brain weights of the three types of mice; Mice per type, n = 3. (Values are means ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA and t-test were used for analysis. n.s., not significant, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001)
The thickness of the cerebral cortex reduced in mr-Lrp4 LacZ mice
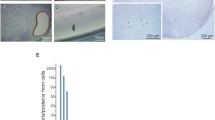
Nissl’s staining was carried out to observe the somatosensory cortex region (Fig. 2a) of the mice. The somatosensory cortex of mr-Lrp4LacZ mice was markedly thinner in layer I, II/III, V, and VI than those of the control group, except layer IV increased. However, mr-Lrp4mitt mice showed no difference from those of the control mice (Fig. 2b, d). The somatosensory cortical neuron density was similar in the three types of mice (Fig. 2c, e). In light of the remarkable difference in the thickness of mr-Lrp4LacZ mice compared with mr-Lrp4mitt or the control mice, we speculated that the LDLα domain of LRP4 maintained the typical structure of the cerebral cortex.
LRP4 LDLα domain affects the thickness of mouse cerebral cortex. a Schematic diagram of somatosensory cortex area selected in Nissl staining and neuron staining. b Representative images of Nissl’s staining of the control, mr-Lrp4LacZ, and mr-Lrp4mitt mice brain; c Representative images of neuron staining (anti-NeuN) of the three types of mice brain; d The thickness of the somatosensory cortex in most layers (I, II/III, V and VI) decreased in mr-Lrp4LacZ mice, except layer IV increased. Mice per group, n = 3; e The neuron density was not different in the somatosensory cortical indicated layers in the three types of mice. Mice per type, n = 3. (Scale bar = 50 μm; Values are means ± SEM. t-test was used for analysis. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01)
The dendritic branches of pyramidal neurons increased in mr-Lrp4 mitt mice
Golgi staining was performed to identify the morphological structure of cerebral cortex pyramidal neurons in mr-Lrp4LacZ, mr-Lrp4mitt mice, and the control mice. The complexity of pyramidal neurons in layer 4–5 of the somatosensory cortex was analyzed by Sholl analysis. Sholl analysis centered on the pyramidal neuronal cell body, a series of concentric circles were drawn and obtained the number of intersections of pyramidal neuronal processes varying with the cell body’s distance. Compared with the control mice, there was no difference in total dendrites length presented in mr-Lrp4LacZ mice, but the total dendrite length in mr-Lrp4mitt mice was longer (Fig. 3b). In mr-Lrp4LacZ mice, we observed no significant difference in the somatosensory cortex pyramidal neurons’ total dendrites branches than the control group (Fig. 3c, d). More dendrite branches were showed in mr-Lrp4mitt mice than the control mice (Fig. 3c, d). These indicated that the LRP4 LDLα domain might play a prominent role in promoting dendritic arborization.
LRP4 LDLα domain enhances the dendrite arborization of neurons in mr-Lrp4mitt mice. a Representative images of Golgi staining the neurons in the cerebral cortex of the control, mr-Lrp4LacZ, and mr-Lrp4mitt mice; using the ImageJ plugin for Sholl analysis; b The total dendrite length of neurons in mr-Lrp4mitt mice increased; c The total dendrite branch number of neurons in mr-Lrp4mitt mice increased. d Sholl analysis of dendrite branch number of the three types of mice. Multiple comparisons were made between mr-Lrp4mitt and the control mice (Above the curves) or between mr-Lrp4mitt and mr-Lrp4LacZ mice (Below the curves). Control mice, n = 6; mr-Lrp4LacZ mice, n = 3; mr-Lrp4mitt mice, n = 3; Neuron per group, n = 34. (Scale bar = 30 μm; Values are means ± SEM. t-test and two-way ANOVA were used for analysis. n.s., not significant, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001)
LRP4 LDLα domain increased dendrite arborization in vitro
To assess whether the LRP4 LDLα domain played a role in the pyramidal neuronal dendritic arborization, we transfected pFLAG-CMV1-Lrp4 LDLα into HEK293T cells, pFLAG-CMV1-vector as the negative control, and pFLAG-CMV1-Reelin plasmid was a positive control. REELIN and LRP4 LDLα secreted into the cell culture medium were confirmed by immunoprecipitation (IP) assay (Fig. 4c). The conditioned medium collected from HEK293T cell culture was added to the primary cultured neurons isolated from wild-type mice’s hippocampi. The number of dendrites branches increased when the conditioned medium containing LRP4 LDLα, compared with the negative control (Fig. 4b, d). In mr-Lrp4mitt mice, the LDLα domain was secreted because of LRP4 lack of transmembrane domain, similar to the plasmid expression in HEK293T cells.
LRP4 LDLα domain increases the dendrites arborization in primary culture neurons. a Schematic diagram of time course dealing with the primary culture neurons. pFLAG-CMV1-Lrp4-LDLα, pFLAG-CMV1-Reelin, and pFLAG-CMV1 vector plasmids were transfected into HEK293T cells, and then the conditioned medium was collected to add into primary cultured wild-type mice neurons, respectively. In panel B-D, pFLAG-CMV1 vector group, pFLAG-CMV1-Lrp4-LDLα group, and pFLAG-CMV1-Reelin group were abbreviated as control, LRP4 LDLα and REELIN, respectively; b Representative images of neurons staining in primary culture; Using the ImageJ plugin tracing the neurite branches; c Western blotting check the expression of the plasmids after transfected into HEK293T cells. Anti-Flag for LRP4 and REELIN immunoprecipitation from the cell culture medium. The input was from the cell lysis; d LRP4 LDLα domain improved the number of dendritic branches in primary neurons. The ImageJ plugin was used for Sholl analysis. Multiple comparisons with two-way ANOVA analyses were made between the LRP4 LDLα group and the control (between the curves). (Scale bar = 30 μm; Wild-type mice, n = 8; Neuron number, control n = 11, LRP4 LDLα n = 10 and REELIN n = 13. Values are means ± SEM. * P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, *** P < 0.001)
Studies showed that Lrp4 was expressed in neurons and astrocytes, and Lrp4 knockout in astrocytes suppressed glutamatergic release by increasing ATP release [11]. To explore whether the LRP4 LDLα promoting dendritic arborization were from neuron or astrocyte, we co-cultured the astrocytes with the neurons from wild type mice or mr-Lrp4mitt mice. Pyramidal neurons of wild type mice showed more branches being co-cultured with astrocytes from mr-Lrp4mitt mice than astrocytes from wild type mice (Fig. 5b, c). Without controversy, the mr-Lrp4mitt mice pyramidal neurons boosted more dendritic arborization co-cultured with astrocytes from mr-Lrp4mitt mice than astrocytes from wild type mice (Fig. 5b, d). The data further confirmed that free LRP4 LDLα promoted dendrite arborization of pyramidal neurons.
LRP4 LDLα domain in astrocytes promotes dendrite arborization in primary co-cultured neurons. a Schematic diagram of time course dealing with co-culture neurons with astrocytes. b Representative images of neurons staining in co-culture. Primary neurons of mr-Lrp4mitt mice or wild-type mice were co-cultured with astrocytes from mr-Lrp4mitt mice or wild-type mice; Using the ImageJ plugin tracing the neurite branches; c Co-cultured with astrocytes from mr-Lrp4mitt mice, neuronal dendrite branch number of wild-type mice was more than co-cultured with astrocytes from wild-type mice. A similar difference is present in the co-cultured neurons of mr-Lrp4mitt mice with astrocytes from mr-Lrp4mitt mice or wild-type mice. Using the ImageJ plugin for Sholl analysis. (Scale bar = 30 μm; Wild-type mice, n = 7; mr-Lrp4mitt mice, n = 8; Neuron per group, n = 52. Values are means ± SEM. Multiple comparisons with two-way ANOVA analyses were also made between the groups. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001)
Discussion
Here we demonstrated that the survival rate and bodyweight of mr-Lrp4LacZ mice were lower than mr-Lrp4mitt mice and the control mice. The brain tissue also was smaller. Second, the somatosensory cortex was thinner in layer I, II/III, V and VI of mr-Lrp4LacZ mice than those of the control group, except layer IV increased. In mr-Lrp4mitt mice, LRP4 has the LDLα domain, but this domain was missing in mr-Lrp4LacZ mice. We speculated that these changes might be related to the function of the LDLα domain. Therefore, to clarify the LRP4 LDLα domain’s role, we performed Golgi staining to observe pyramidal neuronal dendritic branches. The results showed more dendritic branches in the pyramidal neurons of mr-Lrp4mitt mice than in the control group. On the contrary, there was no difference between mr-Lrp4LacZ mice and the control group.
Third, neuronal cells supplementary with the conditioned medium collected from HEK293T cells, which were transfected with LRP4 LDLα plasmids, had more dendritic branches than the control group. When neurons were co-cultured with astrocytes of mr-Lrp4mitt mice, the number of dendritic branches increased. These results indicated that the LDLα domain of LRP4 promoted more dendritic arborization in pyramidal neurons.
N-terminal region of LRP4 is an enormous ECD, which has eight LDLα domains (class A repeats), four β-propeller domains (class B repeats). LRP4 has a fundamental role during the formation, maintenance, and regeneration of the NMJ [18]. LRP4 β1 domain binds with Agrin to form the Agrin-LRP4 binary complex to activate acetylcholine receptor (AChR) clustering in NMJ [5, 6]. Study results showed that treatment ecto-LRP4 (Lrp4 ECD only) into myotubes, ecto-LRP4 increases the number of Agrin-induced AChR clusters. It indicates that soluble ecto-LRP4 is sufficient to serve as a receptor for Agrin to initiate AChR clustering pathways. Ecto-LRP4 acts via a similar mechanism of full-length LRP4 in muscles to stimulate AChR clustering [1]. In this experiment, the release of LDLα domain in mr-Lrp4mitt mice may promote the increase of pyramidal neuronal branches.
LRP4 plays a crucial role in CNS, including maintaining synapses, especially in synaptic transmission [19, 20]. Studies demonstrated that in the brain, glutamate release is reduced in lacking Lrp4 mice. Lrp4 knockout astrocytes suppress presynaptic glutamatergic release by increasing ATP release. ATP released from astrocytes is converted to adenosine that activates adenosine A1 receptors in glutamatergic pre-synapses. Herein, synaptic plasticity is affected [11].
Besides, LRP4 plays a role in dendritic development and synaptogenesis in the CNS. Lrp4 knockdown or deficiency in embryonic cortical and hippocampal neurons causes a reduction in density of primary dendrites [20, 21], and Agrin induces an LRP4-independent increase in dendritic branch complexity [21, 22]. Lrp4 knockdown by in utero electroporation of Lrp4 miRNA also results in neurons with fewer primary dendrites in the developing cortex and hippocampus in vivo [20]. Furthermore, overexpression of Lrp4 in these cultured neurons has the opposite effect inducing more but shorter primary dendrites [20]. Karakatsani et al. study [20] showed that the dendritic branching of the primary culture neurons significantly reduces upon Lrp4 knockdown (DIV3 to DIV12), and the differences disappear during the maturation period (DIV12 to DIV21). In this study, mr-Lrp4LacZ mice did not exhibit a difference in dendritic arborization than the control mice. There may be a mechanism to compensate for Lrp4 knockdown or deletion in vitro and in vivo.
Lacking LRP4 ICD in mr-Lrp4mitt mice is indeed the difference between mr-Lrp4mitt and the control mice. This result suggests two main possible mechanisms. The LRP4 ICD may inhibit dendritic arborization, or LRP4 LDLα may promote the dendrite arborization. LRP4 LDLα in mr-Lrp4mitt mice is the big difference between mr-Lrp4mitt and mr-Lrp4LacZ mice. Therefore, we consider that soluble LDLα promotes the dendrite arborization in mr-Lrp4mitt mice. Pohlkamp et al. [14] indicated that the soluble LRP4 extracellular segment may negatively impact the other receptors in Lrp4ECD/ECD mice. However, Lrp4ΔICD/ΔICD mice that maintain the transmembrane have no such effect. The possibility of LRP4 LDLα secreted by cells was verified by IP assay from the cell culture medium (Fig. 4c).
Pyramidal neuronal LRP4 LDLα domain may be functional via a cell-autonomous manner in mr-Lrp4mitt mice. Lrp4 is mainly expressed in astrocytes [11], and recent research found that Lrp4 also is expressed in neuron stem/progenitor cells [23] and neurons at a low level [20]. It is hard to distinguish the distinct effects of pyramidal neuronal LDLα domain and astrocyte-derived LDLα domain on pyramidal neuronal dendrite arborization in this study. It is an enhancement of astrocytic LRP4 LDLα on pyramidal neuronal dendritic arborization. If Lrp4flox/flox mice build up Lrp4 knockout in specific cells, primary culture neurons from astrocyte knockout Lrp4 mice may eliminate astrocytic effect Lrp4 in co-culture assay.
Overall, our data point to functional links between the LRP4 LDLα domain in modulating dendritic branching in developing CNS neurons. LRP4 LDLα domain promoted more dendritic branch formation. LRP4 LDLα domain binds with DKK1, Sclerostin, ApoE, Gremlin1, Wise. DKK1, Sclerostin, and Wise are factors that inhibit Wnt signaling by binding LRP5/6 [24,25,26]. DKK1 mutation causes the phenotypes of a double ridge and polysyndactyly [27]. Mutation of Sclerostin results in sclerosteosis [28]. Moreover, LRP4 ECD enhances sclerostin-mediated inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling [29]. Lrp4 mutation increases serum sclerostin levels in osteocytes [16]. However, the LRP4 interaction’s significance with the Wnt signaling pathway in the brain remains unclear [30]. LRP4 and Wise interaction is revealed to regulate the patterning and formation of gland development [31]. ApoE can bind with LRP4 [8, 23, 32, 33]. Moreover, ApoE, as one of the LRP4 ligands, is essential for developing the nervous system, regulating synaptic plasticity, neuroprotection, and the innervation of the muscle [8]. LRP4 interaction with ApoE promotes Aβ uptake [34]. ApoE also interacts with Reelin [8] and inhibits Reelin boost dendritic arborization [35,36,37,38]. Therefore, we speculated that free LRP4 LDLα in mr-Lrp4mitt mice might promote dendritic arborization by relieving the inhibition of ApoE on the Reelin.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AChR:
-
Acetylcholine receptor
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DIV:
-
Days in vitro
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium
- ECD:
-
Extracellular domain
- ICD:
-
Intracellular domain
- IP:
-
Immunoprecipitation
- LRP4:
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4
- NMJ:
-
Neuromuscular junction
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- TMD:
-
Transmembrane domain
References
Wu H, Lu Y, Shen C, Patel N, Gan L, Xiong WC, Mei L. Distinct roles of muscle and motoneuron LRP4 in neuromuscular junction formation. Neuron. 2012;75(1):94–107.
Wu H, Xiong WC, Mei L. To build a synapse: signaling pathways in neuromuscular junction assembly. Development. 2010;137(7):1017–33.
Yumoto N, Kim N, Burden SJ. Lrp4 is a retrograde signal for presynaptic differentiation at neuromuscular synapses. Nature. 2012;489(7416):438–42.
Weatherbee SD, Anderson KV, Niswander LA. LDL-receptor-related protein 4 is crucial for formation of the neuromuscular junction. Development. 2006;133(24):4993–5000.
Kim N, Stiegler AL, Cameron TO, Hallock PT, Gomez AM, Huang JH, Hubbard SR, Dustin ML, Burden SJ. Lrp4 is a receptor for Agrin and forms a complex with MuSK. Cell. 2008;135(2):334–42.
Zhang B, Luo S, Wang Q, Suzuki T, Xiong WC, Mei L. LRP4 serves as a coreceptor of Agrin. Neuron. 2008;60(2):285–97.
Johnson EB, Hammer RE, Herz J. Abnormal development of the apical ectodermal ridge and polysyndactyly in Megf7-deficient mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14(22):3523–38.
Choi HY, Liu Y, Tennert C, Sugiura Y, Karakatsani A, Kroger S, Johnson EB, Hammer RE, Lin W, Herz J. APP interacts with LRP4 and Agrin to coordinate the development of the neuromuscular junction in mice. Elife. 2013;2:e00220.
Gomez AM, Burden SJ. The extracellular region of Lrp4 is sufficient to mediate neuromuscular synapse formation. Dev Dyn. 2011;240(12):2626–33.
Lein ES, Hawrylycz MJ, Ao N, Ayres M, Bensinger A, Bernard A, Boe AF, Boguski MS, Brockway KS, Byrnes EJ, et al. Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature. 2007;445(7124):168–76.
Sun XD, Li L, Liu F, Huang ZH, Bean JC, Jiao HF, Barik A, Kim SM, Wu H, Shen C, et al. Lrp4 in astrocytes modulates glutamatergic transmission. Nat Neurosci. 2016;19(8):1010–8.
Tian QB, Suzuki T, Yamauchi T, Sakagami H, Yoshimura Y, Miyazawa S, Nakayama K, Saitoh F, Zhang JP, Lu Y, et al. Interaction of LDL receptor-related protein 4 (LRP4) with postsynaptic scaffold proteins via its C-terminal PDZ domain-binding motif, and its regulation by Ca/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;23(11):2864–76.
Gomez AM, Froemke RC, Burden SJ. Synaptic plasticity and cognitive function are disrupted in the absence of Lrp4. Elife. 2014;3:e04287.
Pohlkamp T, Durakoglugil M, Lane-Donovan C, Xian X, Johnson EB, Hammer RE, Herz J. Lrp4 domains differentially regulate limb/brain development and synaptic plasticity. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(2):e0116701.
Kucukdereli H, Allen NJ, Lee AT, Feng A, Ozlu MI, Conatser LM, Chakraborty C, Workman G, Weaver M, Sage EH, et al. Control of excitatory CNS synaptogenesis by astrocyte-secreted proteins Hevin and SPARC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(32):E440-449.
Xiong L, Jung JU, Wu H, Xia WF, Pan JX, Shen C, Mei L, Xiong WC. Lrp4 in osteoblasts suppresses bone formation and promotes osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(11):3487–92.
Yu Z, Lin D, Zhong Y, Luo B, Liu S, Fei E, Lai X, Zou S, Wang S. Transmembrane protein 108 involves in adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Cell Biosci. 2019;9:9.
Tintignac LA, Brenner HR, Ruegg MA. Mechanisms Regulating Neuromuscular Junction Development and Function and Causes of Muscle Wasting. Physiol Rev. 2015;95(3):809–52.
Mosca TJ, Luginbuhl DJ, Wang IE, Luo L: Presynaptic LRP4 promotes synapse number and function of excitatory CNS neurons. Elife 2017, 6.
Karakatsani A, Marichal N, Urban S, Kalamakis G, Ghanem A, Schick A, Zhang Y, Conzelmann KK, Ruegg MA, Berninger B, et al. Neuronal LRP4 regulates synapse formation in the developing CNS. Development. 2017;144(24):4604–15.
Handara G, Hetsch FJA, Juttner R, Schick A, Haupt C, Rathjen FG, Kroger S. The role of Agrin, Lrp4 and MuSK during dendritic arborization and synaptogenesis in cultured embryonic CNS neurons. Dev Biol. 2019;445(1):54–67.
Handara G, Kroger S. Alternative splicing and the intracellular domain mediate TM-agrin’s ability to differentially regulate the density of excitatory and inhibitory synapse-like specializations in developing CNS Neurons. Neuroscience. 2019;419:60–71.
Zhang H, Sathyamurthy A, Liu F, Li L, Zhang L, Dong Z, Cui W, Sun X, Zhao K, Wang H et al: Agrin-Lrp4-Ror2 signaling regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Elife 2019, 8.
Bafico A, Liu G, Yaniv A, Gazit A, Aaronson SA. Novel mechanism of Wnt signalling inhibition mediated by Dickkopf-1 interaction with LRP6/Arrow. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3(7):683–6.
Balemans W, Devogelaer JP, Cleiren E, Piters E, Caussin E, Van Hul W. Novel LRP5 missense mutation in a patient with a high bone mass phenotype results in decreased DKK1-mediated inhibition of Wnt signaling. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(5):708–16.
Semenov MV, Tamai K, Brott BK, Kuhl M, Sokol S, He X. Head inducer Dickkopf-1 is a ligand for Wnt coreceptor LRP6. Curr Biol. 2001;11(12):951–61.
Adamska M, MacDonald BT, Meisler MH. Doubleridge, a mouse mutant with defective compaction of the apical ectodermal ridge and normal dorsal-ventral patterning of the limb. Dev Biol. 2003;255(2):350–62.
Brunkow ME, Gardner JC, Van Ness J, Paeper BW, Kovacevich BR, Proll S, Skonier JE, Zhao L, Sabo PJ, Fu Y, et al. Bone dysplasia sclerosteosis results from loss of the SOST gene product, a novel cystine knot-containing protein. Am J Hum Genet. 2001;68(3):577–89.
Leupin O, Piters E, Halleux C, Hu S, Kramer I, Morvan F, Bouwmeester T, Schirle M, Bueno-Lozano M, Fuentes FJ, et al. Bone overgrowth-associated mutations in the LRP4 gene impair sclerostin facilitator function. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(22):19489–500.
Chang MK, Kramer I, Huber T, Kinzel B, Guth-Gundel S, Leupin O, Kneissel M. Disruption of Lrp4 function by genetic deletion or pharmacological blockade increases bone mass and serum sclerostin levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(48):E5187-5195.
Ahn Y, Sims C, Logue JM, Weatherbee SD, Krumlauf R. Lrp4 and Wise interplay controls the formation and patterning of mammary and other skin appendage placodes by modulating Wnt signaling. Development. 2013;140(3):583–93.
Lu Y, Tian QB, Endo S, Suzuki T. A role for LRP4 in neuronal cell viability is related to apoE-binding. Brain Res. 2007;1177:19–28.
Trommsdorff M, Borg JP, Margolis B, Herz J. Interaction of cytosolic adaptor proteins with neuronal apolipoprotein E receptors and the amyloid precursor protein. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(50):33556–60.
Zhang H, Chen W, Tan Z, Zhang L, Dong Z, Cui W, Zhao K, Wang H, Jing H, Cao R, et al. A role of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 (LRP4) in Astrocytic Abeta Clearance. J Neurosci. 2020;40(28):5347–61.
Chai X, Fan L, Shao H, Lu X, Zhang W, Li J, Wang J, Chen S, Frotscher M, Zhao S. Reelin induces branching of neurons and radial glial cells during corticogenesis. Cereb Cortex. 2015;25(10):3640–53.
Jossin Y, Goffinet AM. Reelin signals through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt to control cortical development and through mTor to regulate dendritic growth. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27(20):7113–24.
Durakoglugil MS, Chen Y, White CL, Kavalali ET, Herz J. Reelin signaling antagonizes beta-amyloid at the synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(37):15938–43.
Kim J, Park TJ, Kwon N, Lee D, Kim S, Kohmura Y, Ishikawa T, Kim KT, Curran T, Je JH. Dendritic planarity of Purkinje cells is independent of Reelin signaling. Brain Struct Funct. 2015;220(4):2263–73.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Baoming Li (Hangzhou Normal University), Dr. Bingxing Pan (Nanchang University), and Dr. Shangdong Liang (School of Basic Medical Sciences at Nanchang University) for their assistance in this project. Thanks to Dr. Shiwen Luo for providing the HEK293T cells line. Thanks to Dr. Haitao Wu for providing the Lrp4 plasmids.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81860242, 31460260, 31400936), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20171BAB205036, 160102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YM and WSQ initiated and designed the study. GAM and CP performed the Nissl’s staining and Golgi staining. YM and JHY performed Cell culture and plasmid transfection. RDY, ZYZ, WYQ, FEK, ZSQ, and LXS analyzed data. YM and WSQ wrote the manuscript with input from all coauthors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments involving animals were conducted according to the “guidelines for the care and use of experimental animals” issued by Nanchang University. The Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of the University of Nanchang approved the protocol.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, M., Guo, A., Chen, P. et al. LRP4 LDLα repeats of astrocyte enhance dendrite arborization of the neuron. Mol Brain 13, 166 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-020-00708-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-020-00708-z