Abstract
Background
Down syndrome, typically caused by trisomy 21, may also be associated by duplications of the Down syndrome critical region (DSCR) on chromosome 21q22. However, patients with small duplications of DSCR without accompanying deletions have rarely been reported.
Case presentation
Here we report a 5½-year-old boy with clinical features of Down syndrome including distinct craniofacial dysmorphism and sandal gaps as well as developmental delay. Conventional karyotype was normal, whereas interphase FISH analysis revealed three signals for DSCR in approximately 40% of lymphocytes and 80% of buccal mucosa cells. Array-CGH analysis confirmed a 2.56 Mb duplication of chromosome 21q22.13q22.2 encompassing DYRK1A.
Conclusion
This presents one of the smallest duplications within DSCR leading to a Down syndrome phenotype. Since the dosage sensitive gene DYRK1A is the only duplicated candidate DSCR gene in our patient, this finding supports the hypothesis that DYRK1A contributes to dysmorphic and intellectual features of Down syndrome even in a mosaic state.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Down syndrome (DS), typically caused by complete trisomy 21, is associated with a wide range of clinical phenotypes including cognitive deficits, craniofacial dysmorphism, neurological, cardiovascular, immunological defects as well as ophthalmologic and hearing problems. DS is acknowledged as a gene dosage disease where overexpression of genes located on chromosome 21 distorts the balance of gene products. It has been known for decades that not the complete duplicated chromosomal region in trisomy 21 patients contributes equally to the DS phenotype. Particularly genotype-phenotype studies on partial trisomies performed by Sinet et al. [1] revealed that the genes which are essential in producing the main DS features cluster within a relatively small region in chromosomal bands 21q22.2q22.3. The minimum extent of this Down Syndrome Critical Region (DSCR), however, has been a matter of discussion. Until the year 2000, the technical options to establish a genotype-phenotype correlation were limited to targeted analyses and methods of restricted resolution, e.g. fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Today, whole-genome array technologies allow to perform high-resolution breakpoint mapping and to rule out complex imbalances. DS patients with microduplications without concomitant imbalances are extremely rare. Here, we describe a 5½-year-old boy with a 21q22.13q22.2 microduplication in a mosaic state and distinctive clinical features of DS.
Case presentation
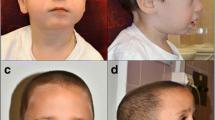
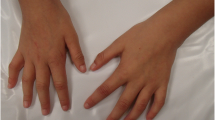
A 5½-year-old boy was referred to clinical genetic service for evaluation concerning DS. The patient is the first child of healthy non-consanguineous parents. His mother was 28 years old and his father was 31 years old when he was born. His younger sister showed no clinical abnormalities. The patient was born by vaginal delivery after a 9-week period of premature labor at 37 weeks of gestation with a birth weight of 3290 g (70th centile), length of 50 cm (50th centile) and occipitofrontal circumference of 32.5 cm (10th centile). Postnatally, the patient presented with muscular hypotonia, hyperopia and astigmatism. Throughout the first years a significant developmental delay was observed. Kiphard developmental test [2] was performed at the age of 36 months and 58 months in order to evaluate the stage of development at different levels. Optical perception was estimated as age-appropriate at both time points (39/36 and 58/58 months), whereas a delayed developmental age was observed in speech (34/36 and 45/58 months), auditory perception (35/36 and 42/58 months) and social contact (37/36 and 47/58 months). The most recent testing performed in the department of neuropediatrics at 6 years of age by Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (wppsi-III) showed a low-average overall IQ of 80. However, there were significant differences regarding specific abilities as expressive speech (VT-IQ = 88) reached just average score, whereas the ability to reason (HT-IQ = 81) and the processing speed (VG-IQ = 60) were in the low-average range. Motor development was quite normal, as he walked with support at 16 months and freely at 20 months. Echocardiography showed no abnormalities with a fractional shortening of 42%. At the age of 5½ years, his height was 113 cm (30th centile), his weight was 20.2 kg (50th centile) and his head circumference was 51 cm (25th centile). The patient presented with craniofacial dysmorphism including posterior plagiocephaly, flat face, epicanthus, upslanted palpebral fissures and anteverted nares (Fig. 1a). Furthermore he has a fused left upper lateral incisor and maxillary canine as well as sandal gaps.
The facial appearance, FISH results and array CGH profile for the patient. a Frontal and lateral view of the patient at the age of 5½ years displays some distinctive clinical features of DS including posterior plagiocephaly, flat face, epicanthus, upslanted palpebral fissures and anteverted nares. b FISH result on metaphase spreads and interphase preparation using a probe for DSCR on chromosome 21 (orange signals) and RB-1 as a control probe on chromosome 13 (green). The fluorescence signal on one chromosome 21 is stronger as compared to the signal on the other chromosome 21 (arrows). Three orange signals for chromosome 21 are visible on interphase nuclei. c Array CGH result (Agilent, 180 K array). Zoom view of the 2.56 Mb mosaic microduplication and gene content at 21q22.13q22.2 encompassing DYRK1A (red box) as duplicated candidate DSCR gene
Methods
The karyotype of the patient was ascertained by standard cytogenetic analysis. Metaphase and interphase FISH analyses were performed using a DNA probe LSI 21 that binds to the DSCR region (21q22.13q22.2) and LSI13 RB1(13q14) as a control (Vysis, Abbott Molecular). The distribution of mosaicism was investigated on nuclei preparations from lymphocytes and non-cultured buccal cells by cohybridization of the two probes.
Genomic DNA was extracted from EDTA peripheral blood samples from the patient and his parents. The trio was investigated by microarray typing. Array comparative genomic hybridization (array-CGH) was performed on genomic DNA using the Human Genome 180 K CGH Microarray (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. The results were scanned with the SureScan Dx Microarray scanner G5761A (Agilent Technologies, USA). Image analysis was carried out using the Feature Extraction Software V10.7 (Agilent Technologies, USA) and data analysis was performed using Cytogenomics V2.9.2.4 (Agilent Technologies, USA). Interpretation was based on Human Genome Assembly 37 (GRCh37/hg19).
Results
Conventional chromosome analysis showed no numerical or structural aberration. Due to the persistent indication of DS, FISH was performed using a commercial DSCR-specific DNA probe. In approximately half of the metaphases a duplication was detected in the same cytogenetic band (karyotype: 46,XY.ish dup(21)(q22.13q22.2)(DSCR++)). Interphase FISH revealed a mosaic pattern with three signals for DSCR in approximately 40% of lymphocytes and in approximately 80% of buccal mucosa cells (Fig. 1c).
Array-CGH analysis detected a duplication at 21q22.13q22.2, spanning about 2.56 Mb (arr[GRCh37] 21q22.13q22.2(38668355_41187454)× 3 dn) (Fig. 1b), which was confirmed by qPCR. The duplication encompassed 15 OMIM genes (DYRK1A, KCNJ6, DSCR4, DSCR8, KCNJ15, ERG, LINC00114, ETS2, PSMG1, BRWD1, HMGN1, WRB, SH3BGR, B3GALT5 and IGSF5). The duplication was not found in the parents of the patient.
Discussion
In trisomy 21, not all loci are necessarily duplicated for the manifestation of DS. The concept of a DSCR on chromosome 21 is almost 30 years old [3]. Many studies were performed to define the minimum DSCR and identify those genes or contiguous genes whose overexpression provokes particular features of DS. It seems that duplications on chromosome 21 proximal from approximately 31 Mb [4] and distal from approximately 43 Mb [5] are not related to an abnormal phenotype.
Delabar et al. [6] narrowed down the critical region on chromosome 21q to a region between markers D21S17 and MX1, corresponding to approximately 35.89–41.72 Mb, whereas Lyle et al. [7] identified a minimum region of 37.94–38.64 Mb encompassing the genes KCNJ6, DSCR4 and KCNJ15 and a second one from the centromere to 26.96 Mb related to intellectual disability.
Most of the phenotype-genotype data for partial trisomy 21 were collected at pre-array days when additional imbalances due to unbalanced reciprocal translocations could not be ruled out [7, 8]. In this discussion, we focus on patients with pure microduplication of less than 5 Mb in size, which were investigated by array-CGH. All chromosomal coordinates were transformed to GRCh37(hg19). Microduplications with their respective sizes are summarized in Table 1. In addition to our patient, two other corresponding microduplications of chromosome 21q with a DS phenotype could be found in the literature [9, 10]. Furthermore, two microduplications of chromosome 21q without a DS phenotype have also been reported [11, 12]. Within the range of microduplication in 21q22 the physical size of the duplicated region itself does not seem to play a major role. While mother and daughter reported by Ronan et al. [9] show DS appearance and learning disabilities, mother and daughter reported by Su et al. [12] do not show this disease phenotype. Both families present with a 4.4 to 4.5 Mb duplication. Instead, the implementation of specific genes in the duplicated region is relevant for the phenotype.
Candidate genes for the key clinical features of DS (classical DSCR) are APP, DSCR1 (RCAN1), DYRK1A and DSCAM [1, 6]. Our patient presented with a 2.56 Mb microduplication in the 21q22.13q22.2 region in a mosaic state which overlaps in part with the distal region of the 4.3 Mb microduplication in the three members of a family described by Ronan et al. [9]. Both microduplications encompass DYRK1A but none of the other classical DSCR genes (Fig. 1b and Table 1). The four patients share similar DS dysmorphic features and mild intellectual disability but no cardiac or other malformations.
DYRK1A (Dual Specificity Tyrosine Phosphorylation Regulated Kinase 1A) is a highly conserved proline-directed protein kinase with multiple domains, a high substrate diversity and known to be involved in neuronal processes [13, 14]. From mice data it was proposed that DYRK1A contributes together with DSCR1 to the typical DS phenotype only in a synergistic way [15]. In both, the family studied by Ronan et al. [9] and our patient with DS phenotype, only DYRK1A is duplicated, but not DSCR1. Thus, the duplication of DYRK1A alone seems to be sufficient to impair normal intellectual development in those two families. DYRK1A belongs to the haploinsufficient genes on chromosome 21, meaning that loss-of-function mutations in DYRK1A can lead to a dominant form of intellectual disability [16]. On the assumption that haploinsufficient genes are sensitive to overexpression in partial trisomy, DYRK1A is a candidate gene for the intellectual phenotype in DS [17]. Overexpression of DYRK1A in transgenic mice induces dramatic deficits of serotonin levels in the brain [18] and has been shown to contribute to DS craniofacial dysmorphology [19].
All these findings on DYRK1A suggest that certain kinase inhibitors, such as polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate, feature potential pharmacotherapy for cognitive impairment in DS. There are already therapeutic attempts and even clinical trials for the evaluation of DYRK1A kinase inhibitors [19,20,21]. Children with a microduplication involving DYRK1A such as described in our patient and the patients reported by Ronan et al. [9] could benefit from the development of new therapeutic options.
However, the pathogenesis of DS cannot be simply reduced to DYRK1A. Weisfeld-Adams et al. [10] reported a child with intellectual disability and distinct dysmorphic features of DS without heart defect. Array-CGH revealed a de novo 2.78 Mb microduplication on chromosome 21q22.11 involving none of the DSCR candidate genes. This duplication does not overlap with the duplicated region in our patient. This supports the hypothesis that more than the duplication of a single gene is causative for the DS phenotype. It seems that also other genes or other mechanisms contribute to the pathogenesis of DS. As further candidate genes, Weisfeld-Adams et al. [10] suggested SOD1, SYNJ1 and/or ITSN1, which were included in the duplicated region in their patient.
In our patient the microduplication on chromosome 21q was present in a mosaic state. Mosaicism for trisomy 21 has been known since decades [22]. It has been even proposed that a low-grade mosaicism of trisomy 21 is present in the general population without any phenotypical resemblance of DS. Furthermore, the incidence of both, trisomy and microdeletions/−duplications in different tissues are underestimated and may contribute to different medical problems [23]. To our knowledge a mosaic microduplication with a DS phenotype has not been reported to date. The mosaic pattern of trisomic cells in our patient had a ratio of approximately 40% in lymphocytes and approximately 80% in buccal mucosa cells. A phenotype-genotype study showed that the trisomy level in mucosa cells is strongly correlated with phenotypic findings of ectodermal origin, whereas the trisomy level in lymphocytes is associated with heart malformations [24]. This might explain the intellectual impairment without heart phenotype in our patient.
Conclusion
In summary, to the best of our knowledge this is the first report on a patient with a DS phenotype resulting from mosaicism for a microduplication of chromosome 21q. Since DYRK1A is the only duplicated candidate DSCR gene in our patient, this result reinforces the hypothesis that DYRK1A duplication contributes essentially to the intellectual phenotype even in a mosaic state. Current progress in the development of drugs such as DYRK1A kinase inhibitors may provide promising therapeutic options for such patients.
Abbreviations
- CGH:
-
Comparative genome hybridization
- DS:
-
Down syndrome
- DSCR:
-
Down syndrome critical region
- DYRK1A:
-
Dual Specificity Tyrosine Phosphorylation Regulated Kinase 1A
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
References
Sinet PM, Théophile D, Rahmani Z, Chettouh Z, Blouin JL, Prieur M, et al. Mapping of the Down syndrome phenotype on chromosome 21 at the molecular level. Biomed Pharmacother. 1994;48(5–6):247–52.
Kiphard EJ. Wie weit ist ein Kind entwickelt. 12th ed. Verlag modernes lernen: Dortmund; 2006.
Rahmani Z, Blouin JL, Créau-Goldberg N, Watkins PC, Mattei JF, Poissonnier M, et al. Down syndrome critical region around D21S55 on proximal 21q22.3. Am J Med Gen. 1990;7:98–103.
Capkova P, Misovicova N, Vrbicka D. Partial trisomy and tetrasomy of chromosome 21 without Down syndrome phenotype and short overview of genotype-phenotype correlation. A case report. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2014;158(2):321–5.
Gijsbers ACJ, van Haeringen A, Bosch CAJ, Hansson K, Verschuren M, Bakker E, et al. A subtle familial translocation t(3;21)(p26.3;q22.3): an apparently healthy boy with a 3p deletion and 21q duplication. Cytogenetic Genome Res. 2010;128(4):245–9.
Delabar JM, Theophile D, Rahmani Z, Chettouh Z, Blouin JL, Prieur M, et al. Molecular mapping of twenty-four features of Down syndrome on chromosome 21. Eur J Hum Gen. 1993;1(2):114–24.
Lyle R, Béna F, Gagos S, Gehrig C, Lopez G, Schinzel A, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations in Down syndrome identified by array CGH in 30 cases of partial trisomy and partial monosomy chromosome 21. Eur J Hum Gen. 2009;17(4):454–66.
Pelleri MC, Cicchini E, Locatelli C, Vitale L, Caracausi M, Piovesan A, et al. Systematic reanalysis of partial trisomy 21 cases with or without Down syndrome suggests a small region on 21q22.13 as critical to the phenotype. Hum Mol Genet. 2016;25(12):2525–38.
Ronan A, Fagan K, Christie L, Conroy J, Nowak NJ, Turner G. Familial 4.3 Mb duplication of 21q22 sheds new light on the Down syndrome critical region. J Med Genet. 2007;44(7):448–51.
Weisfeld-Adams JD, Edelmann L, Gadi IK, Mehta L. Phenotypic heterogeneity in a family with a small atypical microduplication of chromosome 22q11.2 involving TBX1. Eur J Hum Gen. 2012;55(12):732–6.
Eggermann T, Schönherr N, Spengler S, Jäger S, Denecke B, Binder G, et al. Identification of a 21q22 duplication in a silver-Russell syndrome patient further narrows Down the Down syndrome critical region. Am J Med Gen A. 2010;152A(2):356–9.
Su M-T, Kuan L-C, Chou Y-Y, Tan S-Y, Kuo T-C, Kuo P-L. Partial trisomy of chromosome 21 without the Down syndrome phenotype. Prenat Diagn. 2016;36(5):492–5.
Dowjat WK, Adayev T, Kuchna I, Nowicki K, Palminiello S, Hwang YW, Wegiel J. Trisomy-driven overexpression of DYRK1A kinase in the brain of subjects with Down syndrome. Neurosci Lett. 2007;413(1):77–81.
Park J, Song W-J, Chung KC. Function and regulation of Dyrk1A: towards understanding Down syndrome. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66(20):3235–40.
Arron JR, Winslow MM, Polleri A, Chang CP, Wu H, Gao X, et al. NFAT dysregulation by increased dosage of DSCR1 and DYRK1A on chromosome 21. Nature. 2006;441(7093):595–600.
Ji J, Lee H, Argiropoulos B, Dorrani N, Mann J, Martinez-Agosto JA, et al. DYRK1A haploinsufficiency causes a new recognizable syndrome with microcephaly, intellectual disability, speech impairment, and distinct facies. Eur J Hum Gen. 2015;23(11):1473–81.
Antonarakis SE. Down syndrome and the complexity of genome dosage imbalance. Nat Rev Genet. 2017;18(3):147–63.
London J, Rouch C, Bui LC, Assayag E, Souchet B, Daubigney F, et al. Overexpression of the DYRK1A gene (dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A) induces alterations of the serotoninergic and dopaminergic processing in murine brain tissues. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(5):3822–31.
McElyea SD, Starbuck JM, Tumbleson-Brink DM, Harrington E, Blazek JD, Ghoneima A, et al. Influence of prenatal EGCG treatment and Dyrk1a dosage reduction on craniofacial features associated with Down syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2016;25(22):4856–69.
de la Torre R, de Sola S, Hernandez G, Farré M, Pujol J, Rodriguez J, et al. Safety and efficacy of cognitive training plus epigallocatechin-3-gallate in young adults with Down’s syndrome (TESDAD): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(8):801–10.
Stringer M, Goodlett CR, Roper RJ. Targeting trisomic treatments: optimizing Dyrk1a inhibition to improve Down syndrome deficits. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2017;5(5):451–65.
Clarke CM, Edwards JH, Smallpeice V. 21-trisomy/normal mosaicism in an intelligent child with some mongoloid characters. Lancet. 1961;1(7185):1028–30.
Hulten MA, Jonasson J, Iwarsson E, Uppal P, Vorsanova SG, Yurov YB, et al. Trisomy 21 mosaicism: we may all have a touch of Down syndrome. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2013;139:189–92.
Papavassiliou P, York TP, Gursoy N, Hill G, Nicely LV, Sundaram U, et al. The phenotype of persons having mosaicism for trisomy 21/Down syndrome reflects the percentage of trisomic cells present in different tissues. Am J Med Gen A. 2009;149A(4):573–83.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patient and his family for their interest and support.
Funding
We acknowledge support by the German Research Foundation and the Open Access Publication Funds of the Goettingen University. No further funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
Please contact author for data requests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RF and FS contributed to clinical evaluation. MS, FS and SP counselled the parents. IB, BP and MS performed genetic testing and interpretation. FS, MS and IB structured and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from both parents of the patient for all genetic tests. These were a part of routine clinical genetic evaluation.
Consent for publication
The parents gave written informed consent for publication for images and other clinical information relating to this case to be reported for academic purpose.
A copy of the written consent is available for review by the editor of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Schnabel, F., Smogavec, M., Funke, R. et al. Down syndrome phenotype in a boy with a mosaic microduplication of chromosome 21q22. Mol Cytogenet 11, 62 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-018-0410-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-018-0410-4