Abstract
Background
Stickler syndrome (STL) is a rare, clinically and molecularly heterogeneous connective tissue disorder. Pathogenic variants occurring in a variety of genes cause STL, mainly inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. Autosomal recessive STL is ultra-rare with only four families with biallelic COL9A3 variants reported to date.
Results
Here, we report three unrelated families clinically diagnosed with STL carrying different novel biallelic loss of function variants in COL9A3. Further, we have collected COL9A3 genotype–phenotype associations from the literature.
Conclusion
Our report substantially expands the molecular genetics and clinical basis of autosomal recessive STL and provides an overview about allelic COL9A3 disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Stickler syndrome (STL) is a rare, clinically and genetically heterogeneous connective tissue disorder divided into six clinical subtypes with overlapping features, including ocular pathologies (myopia, retinal detachment, vitreoretinal degeneration, cataract), hearing impairment (sensorineural, mixed, and/or conductive), craniofacial abnormalities (midface hypoplasia, anteverted nares, depressed nasal bridge and either Pierre Robin sequence or cleft palate and micrognathia) and joint problems (mild spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia, and precocious osteoarthritis) [1]. These features exhibit substantial variable expressivity according to clinical subtype [1]. STL is molecularly diagnosed by the presence of pathogenic variants in six collagen-type genes including COL2A1, COL11A1, COL11A2, COL9A1, COL9A2, COL9A3, and two non-collagen genes consisting of LRP2 and LOXL3 [1,2,3], following a predominantly autosomal dominant inheritance pattern.
The heteropolymer collagen XI/IX/II are critical in the extracellular matrix of joints, bones, ligaments and connective tissues throughout the body [4]. COL2A1 encodes collagen type II alpha 1 chain. Heterozygous variants that cause functional haploinsufficiency are responsible for autosomal dominant STL type I (OMIM #108300), representing the most common subtype, accounting for roughly 80–90% of STL [5, 6]. Pathogenic variants in COL11A1 cause the second most common STL subtype, type II (OMIM #604841) (10–20%). Variants in this gene likewise typically follow a dominant inheritance pattern [7], although five families have been described with STL and biallelic COL11A1 mutations [8,9,10]. COL11A2 pathogenic variants are very rare and cause autosomal dominant non-ocular Stickler syndrome (type III, OMIM#184840), also known as otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia (OSMEDA, OMIM# 120290), as well as Weissenbacher-Zweymuller syndrome (WZS) (OMIM #184840) [11]. Biallelic variants in LOXL3, a member of the lysyl oxidase family of genes, have recently been causally associated with STL in two unrelated families [2, 12]. A biallelic missense variant in LRP2 has likewise been suggested to cause STL [3].
Collagen IX proteins are encoded by COL9A1, COL9A2 and COL9A3 that together form fibril heterotrimer associated collagens and have been recently linked to autosomal recessive STL [13]. Very recently, heterozygous COL9A3 variants have been identified as causing peripheral vitreoretinal degeneration and retinal detachment [14]. COL9A1 and COL9A2 are causally associated with autosomal recessive STL type IV (OMIM #614134) and V (OMIM #61484), respectively. The main clinical characteristics of individuals affected with biallelic COL9A1 variants include moderate-to-severe sensorineural hearing loss, moderate-to-high myopia with vitreoretinopathy, and epiphyseal dysplasia, whereas COL9A2 variants are associated with high myopia, vitreoretinal degeneration, retinal detachment, hearing loss, and short stature. Only very recently, biallelic mutations in COL9A3 have been described to cause autosomal recessive STL in four unrelated families with seven patients. The main phenotypes that are common in all these patients consisted of high myopia, moderate to severe sensorineural hearing loss, and spondylo/epiphyseal dysplasia. Here, we report three additional unrelated consanguineous STL families with five affected individuals in total who each present three novel biallelic COL9A3 variants.
Results
Clinical assessments
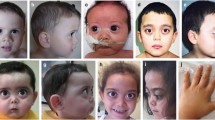
Three unrelated consanguineous families of Iranian descent were referred for genetic testing due to hearing and vision impairment (Fig. 1), as well as skeletal dysplasia that resulted in a clinical diagnosis of STL (Fig. 2).
Pictures of four affected individuals and standard radiographs of the spine, pelvis and limbs of two patients. A–D Pictures of two affected individuals from family 2 who both have herniated cervical discs. E, F Pictures of affected individual II1 from family 3 showing short stature, pes planus, bowed tibia, genu valga and rotated distal femura distal femur. G, H Clinical appearance of proband II1 from family 1 showing pes planus, mild midface hypoplasia, upturned nose and low set ears. I, J Hand and foot radiographs showing short metacarpalia and a broad big toe for individual II1 from family 3 at the age of 10 years. K, L Radiograph images of the right hand and wrist joint of individual II1 from family 1 at the age of 28 years, showing short metacarpalia with widened epiphyses and an irregular radius epiphysis. M, N Radiographs of the spine of II1 from family 1, showing mild platyspondyly of the thoracic spine as well as signs of ankylosing spondylitis. O Knee radiograph of proband II1 from family 3 showing genua valga and irregular femur epiphyses. P Knee radiograph of proband II1 from family 1 demonstrating genua valga and widened femur epiphyses. Q Pelvis radiograph individual II1 of from family 3 showing a flat acetabular roof with irregularities and flattened capiti femori, as well as broadened and shortened necks. R Radiograph of the pelvis of individual II1 from family 1 showing a relatively narrow intraarticular space but well developed capiti femori and no flattening of the acetabular roof
The female proband (II1) from Family 1 is the oldest and only affected individual out of three children from first cousin parents. She had a normal delivery and birth, with a birth weight of 3.2 kg (− 0.43 SD). She was 28 years old at last examination with a weight of 64 kg (+ 0.41 SD), height of 157 cm (− 0.8 SD) and occipitofrontal circumference (OFC) of 55 cm (+ 0.62 SD). She suffers from high myopia in both eyes, in addition to vitreoretinal degeneration with empty vitreous, multiple lattice degenerations and retinal pigmentary changes. There was unilateral absence of the frontal sinus in her skull X-ray. She has severe and progressive sensorineural hearing loss. X-ray and detailed examination of her joints and bones, including mobility testing and examination for signs of osteoarthritis were normal, however she complained of pain in her knee joints. Typical STL craniofacial features such as midface hypoplasia, cleft palate, micrognathia, depressed nasal bridge and anteverted nares are absent.
Family 2 presented with two affected individuals out of four children who were born from a first cousin marriage. The proband (II1) and his affected sibling (II2) both had a normal delivery around term, measurements at birth could not be obtained. Weight, height and OFC at last clinical assessment (at 65 and 57 years-old) were 68 kg (− 0.16 SD) and 66 kg (− 0.39 SD), 166 cm (− 1.4 SD) and 163 cm (− 1.8 SD), 56 cm (+ 0.62 SD) and 57 cm (+ 1.32 SD), respectively. Both had a history of multiple vitreoretinal surgeries due to recurrent rhegmatogenous retinal detachments resulting from advanced vitreoretinal degeneration. Despite vitreoretinal surgeries, the older patient is considered blind without light perception (NLP) in either eye while his sibling has counting finger vision for one eye while NLP was noted for the other eye. Both suffer from severe and progressive sensorineural hearing loss. Likewise, both show a herniated cervical disc and muscular atrophy was noted in the older sibling. No radiologic documentation was available for review.
Family 3 presented with two affected and two healthy children from first cousin parents. Both affected individuals had normal delivery with a birth weight of 3.4 kg (− 0.26 SD) and 3.75 kg (+ 0.71 SD), length of 49 cm (− 0.6 SD) and 49.5 cm (0.1 SD), and OFC of 35 cm (− 0.40 SD) and 36 cm (+ 0.62 SD). The most current weight, height and OFC measurements for the proband (II1) at age 11.8 years and his sister (II4) at age 3.1 years are 32 kg (-1.43 SD), 137 cm (0.9 SD), and 53 cm (− 0.53 SD) and 12 kg (− 0.05 SD), 84 cm (− 0.6 SD), and 48 cm (+ 0.39 SD), respectively. Both affected individuals have myopia and congenital moderate to severe progressive sensorineural hearing impairment. The affected male complains of knee joint pain, especially when he runs. X-ray and detailed examination demonstrated spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia in both children. Both individuals II1 and II4 have pes planus, depressed nasal bridge and anteverted nares, with midface hypoplasia and downslanting palpebral fissures more pronounced in II4. Detailed clinical features of all affected individuals are described in Table 1 and Additional file 1: Table S1. None of the individuals showed signs of intellectual disability.
Genetic analysis
The DNA of probands from the three unrelated families (family 1 Proband II1, family 2 proband II1, family 3 proband II1) was subjected to Exome Sequencing (ES), revealing three different novel, homozygous loss of function (LOF) variants in COL9A3, NM_001853.3. The proband in Family 1 was found to have a COL9A3 deletion (c.107_116del, p.(Pro36Argfs*49), rs1470627424), causing a frameshift in exon 2. The allele frequency in gnomAD is 0.00001390 with two carriers, while other public genomic databases such as Iranome and GME, and 1000 genomes have not reported this variant. The proband in family 2 disclosed a COL9A3 nonsense variant (c.1204C > T, p.(Arg402*), rs989413835) in exon 23, while the proband in Family 3 showed a one base pair deletion in COL9A3 [c.355delC, p.(Leu119Serfs*9)] in exon 7. Both variants have not been reported in public databases.
Discussion
Here, we report three families with five affected individuals clinically diagnosed with autosomal recessive STL due to biallelic LOF variants in COL9A3. Our report re-affirms previous studies that have described four families with biallelic LOF causing autosomal recessive STL, increasing the total number of families reported to date to seven [13, 15, 16]. These COL9A3 variants as well a other disease causing COL9A3 variants submitted to HGMD are visualized in Fig. 3 for localization on cDNA as well as on protein level.
Overview of known and novel variants in COL9A3 at the cDNA and protein levels. All variants have been reported by HGMD Professional 2020.1.and classified as pathogenic in ClinVar or are reported but have not yet been classified in ClinVar. The black words indicate heterozygous variants, the blue words show homozygous variants and the green words show the heterozygous compound variants. A Variants on cDNA level; B variants on protein level
COL9A3, along with two other heterodimers (COL9A1 and COL9A2), belongs to the collagen IX complex, forming a fibril-associated collagen with interrupted triple (FACIT) helices and connecting with collagen II and XI fibrils. A Col9a1 knockout mouse study previously demonstrated that absence of this protein in mice results in the loss of the entire collagen IX heterotrimer complex [17]. Recent reports on the clinical phenotype of STL and MED syndromes that are caused by variants affecting different members of collagen IX have supported the hypothesis that each of the three proteins is essential for collagen IX function [13, 18].
While a variety of disorders have been described to result from heterozygous pathogenic variants in COL9A3, only four unrelated STL families and one family with nonsyndromic hearing loss have been reported to date carrying biallelic variants (Table 2). Allelic disorders resulting from COL9A3 variants include nonsyndromic hearing loss, MED, pseudoachondroplasia, cerebral palsy, and lumbar disc disease and severe peripheral vitreoretinal degeneration and retinal detachment (Table 2).
Consistent clinical features among STL patients with biallelic COL9A3 LOF alleles comprise moderate-to-profound progressive sensorineural hearing loss and moderate high myopia with vitreoretinal degeneration. Retinal detachment and cataract occur occasionally. In contrast, skeletal involvement seems to be more variable. For instance, Nixon et al. [13] reported a family with two affected siblings where the oldest affected sibling had severe arthropathy in the shoulders and hip, requiring a wheelchair. The X-ray of this patient showed spinal scoliosis and narrowing of the articular space in both knees, while the younger affected sibling did not show any of these signs. In line with this report, we also observed that the affected individuals in family 2, at the ages of 65 and 57 years-old, suffer only from myopia, hearing loss and each have a herniated cervical disc while the two much younger affected individuals in family 3, at ages 3 and 11 years-old, have more prominent skeletal findings that include radiological signs of spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia as well as craniofacial abnormalities including depressed nasal bridge and anteverted nares (Table 1). Moreover, Nixon et al. [13] observed that carrier parents can manifest mild STL phenotypes, while our report and others [15, 16, 19] have not observed mild phenotypes in heterozygous individuals. Besides Nixon’s report, Markova et al. [19] introduced a more severe case with compound heterozygous variants with vitreoretinal degeneration, early onset osteoarthritis, midface hypoplasia, hip dysplasia, speech developmental delay, spina bifida, kyphosis, and eye pigment rearrangement.
Conclusion
In summary, our report consolidates that homozygous loss of function variants in COL9A3 cause STL (type VI). We find high myopia and moderate-severe hearing loss to be consistent features amongst all cases while skeletal findings seem more variable.
Material and methods
Subjects
Three unrelated Iranian families with syndromic phenotypes including hearing loss, vision impairment and skeletal dysplasia were referred for clinical genetic diagnostics. Blood samples were collected after obtaining informed consent from patients or their parents. Molecular genetic diagnostic testing was performed in Nijmegen via the Radboud innovative diagnostics programme and at the University of Tuebingen (197/2019BO01). Informed consent from the parents or legal guardians of the patients/participants was obtained for the publication of their data.
Exome and Sanger sequencing
After extraction of DNAs from whole blood by standard protocol, proband DNA samples were subjected to exome capture using the Agilent SureSelect Human All Exon V6 Kit and exome sequencing (ES) was performed on an Illumina HiSeq 2500 sequencer for an average 50 × sequencing depth, resulting in sequences of greater than 100 bases from each end of the fragments [Cambridge (Novogene UK)]. Exome data were processed for analysis using a GATK-based pipeline [20] that uses Burrows-Wheeler alignment [21] to the GRCh37/UCSC hg19 (Families 1 and 2) and GRCh38/UCSC hg38 (Family 3). VarScan version 2.2.5, MuTec and GATK Somatic Indel Detector were used to detect SNV and InDels, respectively. The protocol to interpret potential pathogenic variants was previously described [22]. For population-specific filtering, gnomAD [23], Iranome [24] and Greater Middle East (GME) Variome Project [25] databases were used.
Segregation analysis using Sanger sequencing was performed in available family members to confirm variant segregation after PCR amplification. Primers are available upon request.
Web resources
ClinVar, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/.
Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC), http://exac.broadinstitute.org.
Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD), http://gnomad.broadinstitute.org/.
Availability of data and materials
Data can be made available on personal request. Variants reported in this study have been deposited in the Leiden Open Variation Database (LOVD) and are available through the following variant accession numbers: 0000364418, 0000364419 and 0000364420.
Abbreviations
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- ES:
-
Exome sequencing
- FACIT:
-
Fibril-associated collagen with interrupted triple helicies
- GATK:
-
Genome Analysis Toolkit
- GME:
-
Greater Middle East
- LOF:
-
Loss of function
- MED:
-
Multiple Epiphyseal Dysplasia
- OFC:
-
Occipitofrontal circumference
- PCR:
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SNV:
-
Single Nucleotide Variant
- STL:
-
Stickler syndrome
References
Robin NH, Moran RT, Ala-Kokko L. Stickler syndrome. GeneReviews®[Internet]: University of Washington, Seattle; 2021.
Alzahrani F, Al Hazzaa SA, Tayeb H, Alkuraya FS. LOXL3, encoding lysyl oxidase-like 3, is mutated in a family with autosomal recessive Stickler syndrome. Hum Genet. 2015;134(4):451–3.
Schrauwen I, Sommen M, Claes C, Pinner J, Flaherty M, Collins F, et al. Broadening the phenotype of LRP2 mutations: a new mutation in LRP2 causes a predominantly ocular phenotype suggestive of Stickler syndrome. Clin Genet. 2014;86(3):282–6.
Kadler KE, Hill A, Canty-Laird EG. Collagen fibrillogenesis: fibronectin, integrins, and minor collagens as organizers and nucleators. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20(5):495–501.
Liberfarb RM, Levy HP, Rose PS, Wilkin DJ, Davis J, Balog JZ, et al. The Stickler syndrome: genotype/phenotype correlation in 10 families with Stickler syndrome resulting from seven mutations in the type II collagen gene locus COL2A1. Genet Med. 2003;5(1):21–7.
Hoornaert KP, Vereecke I, Dewinter C, Rosenberg T, Beemer FA, Leroy JG, et al. Stickler syndrome caused by COL2A1 mutations: genotype–phenotype correlation in a series of 100 patients. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010;18(8):872–80.
Majava M, Hoornaert KP, Bartholdi D, Bouma MC, Bouman K, Carrera M, et al. A report on 10 new patients with heterozygous mutations in the COL11A1 gene and a review of genotype–phenotype correlations in type XI collagenopathies. Am J Med Genet A. 2007;143(3):258–64.
Alzahrani F, Alshammari MJ, Alkuraya FS. Molecular pathogenesis of fibrochondrogenesis: is it really simple COL11A1 deficiency? Gene. 2012;511(2):480.
Richards AJ, Fincham GS, McNinch A, Hill D, Poulson AV, Castle B, et al. Alternative splicing modifies the effect of mutations in COL11A1 and results in recessive type 2 Stickler syndrome with profound hearing loss. J Med Genet. 2013;50(11):765–71.
Nixon T, Richards AJ, Lomas A, Abbs S, Vasudevan P, McNinch A, et al. Inherited and de novo biallelic pathogenic variants in COL11A1 result in type 2 Stickler syndrome with severe hearing loss. Mol Genet Genom Med. 2020;8:e1354.
Vuoristo MM, Pappas JG, Jansen V, Ala-Kokko L. A stop codon mutation in COL11A2 induces exon skipping and leads to non-ocular Stickler syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2004;130(2):160–4.
Chan TK, Alkaabi MK, ElBarky AM, El-Hattab AW. LOXL3 novel mutation causing a rare form of autosomal recessive Stickler syndrome. Clin Genet. 2019;95(2):325–8.
Nixon TR, Alexander P, Richards A, McNinch A, Bearcroft PW, Cobben J, et al. Homozygous Type IX collagen variants (COL9A1, COL9A2, and COL9A3) causing recessive Stickler syndrome—expanding the phenotype. Am J Med Genet A. 2019;179(8):1498–506.
Nash BM, Watson CJG, Hughes E, Hou AL, Loi TH, Bennetts B, et al. Heterozygous COL9A3 variants cause severe peripheral vitreoretinal degeneration and retinal detachment. Eur J Hum Genet. 2021;29(5):881–6.
Faletra F, D’Adamo AP, Bruno I, Athanasakis E, Biskup S, Esposito L, et al. Autosomal recessive Stickler syndrome due to a loss of function mutation in the COL9A3 gene. Am J Med Genet A. 2014;164(1):42–7.
Hanson-Kahn A, Li B, Cohn DH, Nickerson DA, Bamshad MJ, Genomics UoWCfM, et al. Autosomal recessive Stickler syndrome resulting from a COL9A3 mutation. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2018;176(12):2887–91.
Hagg R, Hedbom E, Möllers U, Aszódi A, Fässler R, Bruckner P. Absence of the α1 (IX) chain leads to a functional knock-out of the entire collagen IX protein in mice. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(33):20650–4.
Jackson GC, Marcus-Soekarman D, Stolte-Dijkstra I, Verrips A, Taylor JA, Briggs MD. Type IX collagen gene mutations can result in multiple epiphyseal dysplasia that is associated with osteochondritis dissecans and a mild myopathy. Am J Med Genet A. 2010;152(4):863–9.
Markova T, Sparber P, Borovikov A, Nagornova T, Dadali E. Clinical and genetic characterization of autosomal recessive stickler syndrome caused by novel compound heterozygous mutations in the COL9A3 gene. Mol Genet Genom Med. 2021;9:e1620.
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, et al. The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010;20(9):1297–303.
Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(5):589–95.
Rad A, Altunoglu U, Miller R, Maroofian R, James KN, Çağlayan AO, et al. MAB21L1 loss of function causes a syndromic neurodevelopmental disorder with distinctive cerebellar, ocular, craniofacial and genital features (COFG syndrome). J Med Genet. 2019;56(5):332–9.
Karczewski KJ, Francioli LC, Tiao G, Cummings BB, Alföldi J, Wang Q, et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature. 2020;581(7809):434–43.
Fattahi Z, Beheshtian M, Mohseni M, Poustchi H, Sellars E, Nezhadi SH, et al. Iranome: a catalog of genomic variations in the Iranian population. Hum Mutat. 2019;40(11):1968–84.
Scott EM, Halees A, Itan Y, Spencer EG, He Y, Azab MA, et al. Characterization of Greater Middle Eastern genetic variation for enhanced disease gene discovery. Nat Genet. 2016;48(9):1071–6.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the families for their participation in this study.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. This research was supported by Intramural Funding (fortüne) at the University of Tübingen (2545-1-0 to B.V.) and the Ministry of Science, Research and Art Baden-Württemberg (to B.V.). MS acknowledges funding form the European Research Council (ERC): ERC starting grant TREATCilia (Grant Agreement No. 716344) and funding from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation)—Project-ID 431984000—SFB 1453 (CRC Nephgen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FS, RM, EGK, ND, MD, AM, HA, HS, MR and NH recruited the probands and/or were involved in their clinical care. AR, MN, SL and DM conducted genetic data analysis. AR, MN, BV and MS conceived the study. AR, MN, BV and MS drafted the manuscript. BV and MS supervised the study. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Molecular genetic diagnostic testing was performed in Nijmegen via the Radboud innovative diagnostics programme and at the University of Tuebingen (197/2019BO01).
Consent for publication
Informed consent from the parents or legal guardians of the patients/participants was obtained for the publication of their data.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1
. Table S1: Clinical features of probands affected by COL9A3 variants.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Rad, A., Najafi, M., Suri, F. et al. Identification of three novel homozygous variants in COL9A3 causing autosomal recessive Stickler syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis 17, 97 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-022-02244-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-022-02244-6