Abstract
Background
The character higher order scales (self-directedness, cooperativeness, and self-transcendence) in the temperament and character inventory are important general measures of health and well-being [Mens Sana Monograph 11:16–24 (2013)]. Recent research has found suggestive evidence of common environmental influence on the development of these character traits during adolescence. The present article expands earlier research by focusing on the internal consistency and the etiology of traits measured by the lower order sub-scales of the character traits in adolescence.
Methods
The twin modeling analysis of 423 monozygotic pairs and 408 same sex dizygotic pairs estimated additive genetics (A), common environmental (C), and non-shared environmental (E) influences on twin resemblance. All twins were part of the on-going longitudinal Child and Adolescent Twin Study in Sweden (CATSS).
Results
The twin modeling analysis suggested a common environmental contribution for two out of five self-directedness sub-scales (0.14 and 0.23), for three out of five cooperativeness sub-scales (0.07–0.17), and for all three self-transcendence sub-scales (0.10–0.12).
Conclusion
The genetic structure at the level of the character lower order sub-scales in adolescents shows that the proportion of the shared environmental component varies in the trait of self-directedness and in the trait of cooperativeness, while it is relatively stable across the components of self-transcendence. The presence of this unique shared environmental effect in adolescence has implications for understanding the relative importance of interventions and treatment strategies aimed at promoting overall maturation of character, mental health, and well-being during this period of the life span.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Cloninger’s theory of personality proposes that human beings are comprised of an integrated hierarchy of biological, psychological, and social systems that allow them to adapt more or less flexibly and maturely to changes in their external and internal milieu [1]. This model consists of a temperament domain (i.e., individual differences in behavioral learning mechanisms influencing basic emotional drives) and a character domain (i.e., self-concepts about goals and values that express what people make of themselves intentionally). For the measurement of these personality domains, Cloninger has developed the temperament and character inventory [1] composed of four dimensions of temperament (novelty seeking, harm avoidance, reward dependence, and persistence) and three dimensions of character (self-directedness, cooperativeness, and self-transcendence). These temperament and character dimensions serve as tools for disentangling personality profiles of healthy individuals, as well as of individuals with neuropsychiatric disorders [2–6]. Moreover, self-directedness, cooperativeness, and self-transcendence assessed by the Temperament and Character Inventory are important general measures of health and well-being [7–10]. Self-transcendence, however, is positively related to both positive and negative emotions during the adolescent years and during adulthood in cultures that discourage open emotional expression [4, 11].
Previous findings have shown that heritability influences on character are about the same across studies using different age groups. Nonetheless, there are some differences worth noting. For example, while the character scales do not show common environmental influences in research among older adults (e.g., [12]), a small common environmental influence for self-directedness and cooperativeness has been found among young adults (20–30 years of age; e.g., [13]). In addition, recent research using one of the largest population-based twin studies among adolescents, found suggestive evidence of common environmental influence for all of the character scales [14]. What is more, Gillespie and colleagues [12] showed in adults, and Garcia and colleagues [14] in adolescents, that the genetic structure of the temperament higher order scales shows no evidence of a shared or common environmental effect (C) across the scales. The exception being that in adolescents, in contrast to adults, there was a small shared environmental effect in the temperament dimension of reward dependence (i.e., the individuals' tendency to respond markedly to signals of social approval, social support, and sentimentality). The effect size is similar to that which is observed in adolescents’ character dimensions. Overall the effect size of additive genetics (A) to non-shared environmental effect (E) is slightly larger across the temperament dimensions in adolescents compared to adults (see Fig. 1a, b). In contrast, the genetic structure of the character scales in the adolescent sample shows a modest but noteworthy proportion of shared environmental influence that is not present in the adult sample studied by Gillespie and colleagues (Fig. 2a, b). In other words, there is greater consistency, between the adolescent and the adult sample, in the proportion of additive genetic effect to non-shared environmental effect with respect to temperament but not with respect to character. These results suggest a “shift” in the type of environmental influence (i.e., shared to non-shared) from adolescence to adulthood with regard to character. In this context, it is important to point out that interventions to enhance self-directedness and cooperativeness can alleviate dysfunction and suffering related to different psychiatric disorders [3]. Character traits improve with cognitive-behavioral treatments and baseline levels of character are strong predictors of clinical outcomes [15–18]. If the “shift” in environmental influence exists, then interventions targeting character development may be more successful if conducted during adolescence or young adulthood.
The Temperament and Character Inventory’s character scales, as well as those scales measuring temperament, are higher order scales composed of lower order sub-scales. The higher order scales have the advantage of allowing the prediction of many outcomes (e.g., personality disorders) because they represent wide-ranging descriptions of personality (see [19]). Nevertheless, one disadvantage when personality is only investigated in terms of broad scales is that the aggregation of the lower order sub-scales in one higher order scale results in a loss of information—information that might be useful for psychological description, prediction, and explanation (see [19]). The present article expands earlier research (e.g., [14]) by focusing on the etiology of the lower order sub-scales of the character dimension of personality in adolescence. Thus, it targets information that may be useful in the study of adolescents’ mental health and well-being. For a brief description of low and high scorers in each of the lower order sub-scales for the character traits of the Temperament and Character Inventory, please see the Tables 1, 2, and 3.
The present study
The present study expands earlier research by focusing on the internal consistency and the etiology of traits measured by the lower order sub-scales of the character traits in adolescence. The study was conducted using self-reported character measures from The Child and Adolescent Twin Study in Sweden (CATSS), which is an on-going large population-based longitudinal twin study targeting all twins born in Sweden since July 1, 1992. By January 2013, the CATSS comprised around 23,000 twins and it had a response rate of roughly 76 % (for a detailed description of the CATSS see [20]). We used data from a sample of 15-year-old twins (detailed in [14]) in order to capture a critical period of life where personality undergoes huge developmental processes related to adolescents’ ill- and well-being. We target the etiology of the character sub-scales to catch information that may be useful for psychological description, prediction, and explanation of mental health and well-being.
Methods
Ethical statement
The present analyses included twins who provided data at the CATSS-9/12, CATSS-15, and DOGSS studies. All data collections have separate ethical approvals from the Karolinska Institute ethical review board (DNR: 02-289, 2010/597-31/1, 2010/1356/31/1, 03-672, and 2009/739-31/5). The participants, both parent and children/adolescents are protected by informed consent process. They were informed of what is being collected and were repeatedly given the option to withdraw their consent and discontinue their participation.
Sample and procedure
In the present study we used data from the CATSS, earlier described in Garcia et al. [14], whose parents were interviewed by telephone using the Autism—Tics, ADHD ,and other Comorbidities inventory [21] when the twins were 9 or 12 years of age. At the age of 15, the twins completed a battery of questionnaires that were sent by mail (overall response rate 48 %), including the short version (125 items) of the Temperament and Character Inventory. Moreover, twins who screened positive for any neuropsychiatric disorder and controls were part of a detailed clinical interview that included the longer Temperament and Character Inventory version (238 items).Footnote 1 Previously, Garcia and colleagues [14] developed a valid and reliable item-extraction procedure to generate the short version from the larger version of temperament and character inventory. This allowed us to conduct the correlation, reliability, and the twin modeling analysis using the whole twin sample based on the short version of the Temperament and Character Inventory. Only twins who had a maximum of 5 % missed items and have answered the control questions correctly were included in the final analyses (a common procedure regarding the Temperament and Character Inventory, [22]).
For the correlation and reliability analysis, addressing the internal consistency of the lower order sub-scales (Additional file 1: Tables S1–S3), we used a total of 2714 twins (878 monozygotic, 885 same sex dizygotic, 638 different sex dizygotic, and 313 of unknown zygosity). The twin modeling analysis addressing the etiology of traits measured by the lower order sub-scales of the character traits required only twins with known zygosity. In essence the model compares traits in monozygotic twins, who are genetically identical, with traits in dizygotic twins, who on average share 50 % of their segregating alleles. The difference in genetic relatedness can then be used to disentangle the genetic and environmental contribution to a trait, in this case the lower order character traits. Hence, for this specific analysis we were only able to use 423 monozygotic pairs and 408 same sex dizygotic pairs.
Measures
Zygosity
Zygosity was determined on the basis of 48 single nucleotide polymorphisms [20]. For twins without available DNA, zygosity was determined using a validated algorithm based on five questions on twin similarity derived from 571 pairs of twins with known zygosity. Only twins with more than 95 % probability of being correctly classified, compared to DNA testing, were assigned zygosity by this method. In other words, the twins with less than 95 % probability of being correctly classified were assigned as unknown zygosity [23].
Temperament and Character Inventory
The temperament and character inventory measures the seven scales, and its sub-scales, of the psychobiological model of personality (binary answer: true = 1, false = 0). The five sub-scales of the self-directedness scales are: responsibility vs. blaming (SD1, e.g., “I often feel that I am the victim of circumstances”, reverse coded), purposefulness vs. lack of goal direction (SD2, e.g., “My behavior is strongly guided by certain goals that I have set for my life”), resourcefulness vs. inertia (SD3, e.g., “I usually look at a difficult situation as a challenge or opportunity”), self-acceptance vs. self-striving (SD4, e.g., “I often wish I was stronger than everyone else”, reverse coded), and self-actualization (former congruent second nature) vs. bad habits (SD5, e.g., “Many of my habits make it hard for me to accomplish worthwhile goals”, reverse coded).
The five sub-scales of the cooperativeness scales are: social acceptance vs. social intolerance (CO1, e.g., “I can usually accept other people as they are, even when they are very different from me”), empathy vs. social disinterest (CO2, e.g., “I often consider another person’s feelings as much as my own”), helpfulness vs. unhelpfulness (CO3, e.g., “I like to share what I have learned with other people”), compassion vs. revengefulness (CO4, e.g., “I hate to see anyone suffer”), and integrated conscience vs. self-serving advantage (CO5, e.g., “I cannot have any peace of mind if I treat other people unfairly, even if they are unfair to me”).
The three sub-scales of the self-transcendence scales are: creative self-forgetfulness vs. self-conscious experience (ST1, e.g., “I often become so fascinated with what I’m doing that I get lost in the moment—like I’m detached from time and place”), transpersonal identification vs. personal identification (ST2, e.g., “I sometimes feel so connected to nature that everything seems to be part of one living organism”), and spiritual acceptance vs. rational materialism (ST3, e.g., “I seem to have a “sixth sense” that sometimes allows me to know what is going to happen”).
Statistical treatment
All data were considered to be normally distributed after graphical exploration (histograms), thus all statistical tests were conducted using parametric methods in SPSS version 19. Cronbach ‘s alphas and Pearson’s correlations coefficients for the character lower order sub-scales are reported in Additional file 1: Table S1–S3.
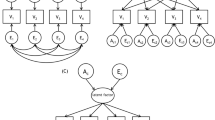
The etiology of the character lower order sub-scales was investigated using twin methodology. The genetic and environmental contributions are portioned into three variance components: additive genetic factors (A), common environmental factors that make the twins similar (C), and unique environmental factors that make the twins dissimilar (E). In the first step, intraclass correlation (ICC) coefficients, for the character sub-scales, were calculated separately for monozygotic twins and same sex dizygotic twins. As a second step, we performed univariate genetic analyses, using a model-fitting approach with structural equation-modeling techniques conducted in Mx [24].
Results
The correlation and reliability analysis addressing the internal consistency of the lower order sub-scales is presented in Additional file 1: Table S1–S3. The twin modeling analysis addressing the etiology of traits suggested a common environmental contribution for the following self-directedness sub-scales: purposefulness vs. lack of goal direction (0.14) and self-actualizing (former congruent second nature) vs. bad habits (0.23); for three of the cooperativeness sub-scales: empathy vs. social disinterest (0.10), helpfulness vs. unhelpfulness (0.07), and compassion vs. revengefulness (0.17); and for all three self-transcendence sub-scales: creative self-forgetfulness vs. self-conscious experience, transpersonal identification vs. personal identification, and spiritual acceptance vs. rational materialism (between 0.10 and .12). All sub-scales in the self-directedness scale were under a large unique environmental influence that ranged from 0.49 to 0.70 (Table 4). This pattern could be discerned in all sub-scales in the cooperativeness (Table 5) and self-transcendence (Table 6) scales as well. There was a general trend suggesting that the genetic component had a larger influence than the common environmental component, in all sub-scales of the three character dimensions. The confidence intervals were, however, overlapping in all cases.
Discussion
In the introduction section we have detailed the differences between adolescents and adults in the genetic structure of temperament and character dimensions of personality. These differences suggest a “shift” in the type of environmental influence (i.e., shared to non-shared) from adolescence to adulthood with regard to character. Our study looks in greater depth at these variations, in particular the evidence for a shared environmental effect on the lower order sub-scales of the character traits during adolescence.
In their study among older adults, Gillespie and colleagues [12] expected shared environmental effects to account for a significant proportion in character variance because character traits were earlier hypothesized by Cloninger [25] to be partly due to socio-cultural learning. Nevertheless, these researchers found that additive genetic effects alone provided the most parsimonious explanation for the source of familial aggregation in each character higher order scale. Based on their univariate analysis, genetic effects explained 27–44 % of the variance in the three character higher order scales. Despite limitations of power in their study, the rejection of an ACE model in favor of AE was consistent with other studies in adult populations [26, 27].
In contrast to this evidence from adults, we provide evidence to support the role of shared environmental effects (C) on character variability in adolescence. Our findings support an ACE model and are therefore more consistent with earlier theoretical expectations [25] and recent empirical findings about the important influence of parental rearing and cultural norms on character development [28, 29]. The importance of both the underlying biological and social determinants during this critical phase of personality development are therefore likely to be critical in character maturation. It may be that this common environmental effect supported by our study in adolescents operates primarily in early development or that the methodology is concealing the effect in adults.
The genetic structure at the level of the character lower order sub-scales in adolescents shows that the proportion of the shared environmental component varies among sub-scales of self-directedness and cooperativeness, while it is relatively stable across the trait of self-transcendence (see Figs. 3a, b, 4). We also note that SD4 (self-acceptance vs. self-striving), CO1 (social acceptance vs. social intolerance), and CO5 (integrated conscience vs. self-serving advantage) have no evidence of shared environmental effects. This is also what is observed among adult populations. On the other hand, in adolescents a shared environmental effect is clearly present in all of the lower order sub-scales of self-transcendence and some of the other lower order sub-scales of cooperativeness and self-directedness (see Fig. 5). In particular the common environment influence is substantial for adolescents to develop purposefulness (i.e., SD2), self-actualization (i.e., SD5), and compassion (i.e., CO4). Therefore, it is important to consider how these traits might be related to the processes of socio-cultural learning. We know that character develops in directions that correspond to socially sanctioned norms [28, 29], but we know little about the details of the psychobiological mechanisms by which such socio-cultural learning occurs. However, we also know that individual differences in character traits, measured by the temperament and character inventory, are correlated with variability in the structure and function of particular networks in the human cerebral cortex [30–32]. The processes of purposefulness and self-actualization requires regulating and cultivating particular lifestyle habits consistent with personally chosen goals and values, which requires personal discipline but also may be strongly reinforced or extinguished by cultural effects. Similarly, the development of compassion, forgiving others and not holding grudges, and the development of a purpose have strong cultural connections [33, 34].
A smaller effect size for common environmental influence and social learning is also seen in the sub-scales of self-transcendence (ST1–ST3). This might at first glance seem paradoxical since self-transcendence is often associated with the religious cultural environment [1]. However, while there is clearly an overlap with religious experience and religiosity, self-transcendence is measuring a phenomenon quite distinct from notions of religion, an observation supported by the neurophysiological data [35]. That being said, Magen’s [36] research suggests that adolescents address simple forms of self-transcendence—usually not referring to a macrocosmic unity. Perhaps because adolescents' pursuit of positive emotions tend to be egocentric and directed by their own desires, which in turn is contradictory to the willingness to become dedicated to the well-being of others or pro-social causes that transcend the self [37]. Nonetheless, Magen [36] points out that some adolescents can express transcendent feelings (e.g., mystical identification with a crowd on a strike in the streets) and that even adolescents’ homelier joys uncover “those universals that lead from and go beyond personal experience” (pp. 167). Finally, a slightly smaller size effect size is seen in CO2 (empathy vs. social disinterest), SD3 (resourcefulness vs. inertia), and CO3 (helpfulness vs. unhelpfulness), while SD1 (responsibility vs. blaming) has a very small effect size.
The presence of a shared environmental effect in all character traits in this adolescent sample is suggestive of the greater significance of socio-cultural learning at this critical developmental stage in the human life cycle. Something unique may be taking place not just biologically and psychologically, but also at a socio-cultural level during this phase. The power of cultural reinforcement and the impact of shared narratives may be at its greatest during the adolescent phase of development, compared to adults [38–41]. It may be that in children there is a greater shared environmental effect that is tailing off in adolescence or that the peak period of a shared environmental effect is occurring in adolescence and that the effect sizes might therefore vary for each lower order sub-scale. For instance, Erikson’s stage of identity vs. role confusion [42], which occurs during adolescence, underscores the interaction between the internal drives of identity and socio-cultural awareness of place and identity in the community or environment. To some extent every adolescent must reconcile the identity which she ascertains from the family culture and wider social culture that she happens to be born into with her identity; which is a result from her growing awareness of her individual differences, whether they be relatively common (e.g., being sporty, being tall, being intellectual) or more profound (e.g., being physically different, sexual orientation or, indeed, being a twin).
We are, indeed, beginning to understand how the current models of genetic effects and genetic architecture might be inadequate because they have neglected the cultural inheritance [43, 44] and the complex adaptive processes that are crucial in personality development (e.g., [45]). Personality maturity is itself a complex dynamic system [3, 46]. It is therefore likely that the power of the shared environmental effects across the lifespan is underestimated when complex dynamical patterns of development are neglected.
The evidence we provide for the presence of this unique shared environmental effect in adolescence implies that socio-cultural effects may have implications for understanding the relative importance of interventions and treatment strategies aimed at promoting overall maturation of character. The development of a mature character has been found to correlate with health, happiness, and well-being in the adult human. (e.g., [25]). One of the ways this maturity influences well-being is by the increased ability to temper the emotions. The adolescent is exercising her character’s influence over her temperament in new and important ways, developing her relationship with herself, her fellow humans, and the complex and awe-inspiring universe in which she finds herself. In addition to her self-narrative, the narratives that she is exposed to through the cultural milieu in which she moves will significantly influence this maturation [36, 37, 39–41, 47].
Narratives of unity and connectedness foster the sense of her place in the universe [7]. A culture that fosters tolerance, empathy, and compassion fosters love and cooperativeness. Narratives of responsibility and purpose in life might strengthen her self-exploration in hope and increase her self-directedness. We might consider that in the development of brain connectedness and personality structure, we know the infant draws greatly on the material plasticity of her brain; the adolescent draws in addition the flexibility of her response to and learning from the socio-cultural environment. In later life, as adults mature in character, they may become more self-aware thus increasing the importance of their individual experiences and their expressions of individual virtue in action [3].
Limitations
It is possible that our findings regarding the genetic structure of Cloninger’s model of personality differ from those of earlier research because of differences in measurement. Most research has been done using the longer version of the Temperament and Character Inventory, but similar results to those obtained with the long version have been found using shorter versions (e.g., Gillespie and colleagues used a 35-item version for measuring the character dimensions). Nonetheless, the short version character scores that were extracted from the clinical sample are highly correlated to their respective long version character scores (see [14]), thus, suggesting that it will produce comparable results when the genetic structure of the model is investigated. In addition, of the 13 character sub-scales only one (SD5) has a 95 % CI for common environmental effects (C) that does not include zero. The estimates of common environmental effects (C) are quite small: 3 are zero, 5 more are .10 or less, and 3 of the remaining 5 are under .15. Such a relatively small shared environmental contributions would seem to provide very little guidance for intervention, except, perhaps, to suggest that the environmental variables currently differing among families in Sweden don’t have much effect on the character traits measured by the sub-scales, so something quite different should be tried if one aspires to change them much. Indeed, well-being interventions recently developed (e.g., well-being coaching; http://www.anthropedia.org/learn-more/) require the development of self-awareness and personality of the whole human being (i.e., body, mind, and psyche or soulFootnote 2).
Conclusion and final remarks
In thinking about the influence of socio-cultural learning we must consider character development at the lower order sub-scale level: each of the lower sub-scales demonstrates the possibility for an outlook of unity [e.g., being able to show integrity (SD5), to be forgiving (CO4), and creative (ST3)] and an outlook of separation (e.g., undisciplined, revengeful, and judgmental) [52]. The cultural learning environment of the adolescent can support this process of discriminating the two. In the development of self-actualization (SD5) and compassion (CO3) for example, we can see that an outlook of unity might be reinforced by socio-cultural learning experiences. An outlook of unity reinforces the awareness of how our actions have consequences not only for ourself, but also for others and the universe as a whole. With such insight, people become motivated to exercise discipline in changing their daily habits in order to live in accord with their most deeply held values and understanding of their place in the world [3, 7].
On the other hand a narrative of separation will reinforce the almost magical notion that we exist in separation to any consequences, or that consequences themselves do not exist. The balance between our outlooks of separation and unity, therefore, has important and far-reaching implications for happiness, well-being, and mental health. Self-defeating behaviors, often witnessed in adolescence, might continue into adulthood despite evidence of the negative consequences, because the connectedness is not directly understood. New approaches to counteract bullying in schools implicitly acknowledge the importance of this learning. In an outlook of separation, the consequences of the behaviors are rarely appreciated and hardly seem relevant. Approaches based on restorative justice [47], for instance, aim to create a socio-cultural experience for the adolescent allowing them to connect consequences and people affected by her behaviors, thus providing opportunities of learning that integrate values with behavior (see [53]).
“Harry, I owe you an explanation,ʹ said Dumbledore. `An explanation of an old manʹs mistakes. For I see now that what I have done, and not done, with regard to you, bears all the hallmarks of the failings of age. Youth cannot know how age thinks and feels. But old men are guilty if they forget what it was to be young … and I seem to have forgotten, lately …ʹ”
Harry Potter and the Order of the Phoenix by J. K. Rowling.
Notes
“The exact algorithm to select candidates for the questionnaire study was a DSM A-TAC score for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder ≥8, autism spectrum disorders ≥4.5, conduct ≥1, opposition ≥2, compulsions ≥1, Tics ≥1, eating problems ≥1 and an endorsement of dysfunction and/or suffering related to the symptoms (a problem score of ≥1), or had a parentally reported clinical diagnosis of one or more of these conditions, in total corresponding to 7 % of the children in 13 % of the twin pairs, and a random sample of control twin pairs (1 in 20 interviews). Since November 2008, with access to new validation information, the questionnaires have also been sent to pairs in which one or both twins scored ≥8 in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder, ≥4.5 in autism spectrum disorders, ≥1.5 in eating problems, ≥3 in oppositional/conduct ≥2 in Tics, ≥1 in compulsions, ≥1 in motor control, or ≥3 in Learning using the DSM score regardless of whether they indicated dysfunction or suffering related to the problems or characteristics” [20].
Abbreviations
- A:
-
additive genetics factors
- C:
-
common environmental factors
- E:
-
non-shared environmental factors
- CATSS:
-
The Child and Adolescent Twin Study in Sweden
- MZ:
-
monozygotic
- DZ:
-
dizygotic
- ICC:
-
intraclass correlation
- SD1:
-
responsibility vs. blaming
- SD2:
-
purposefulness vs. lack of goal direction
- SD3:
-
resourcefulness vs. inertia
- SD4:
-
self-acceptance vs. self-striving
- SD5:
-
self-actualizing vs. bad habits
- CO1:
-
social acceptance vs. social intolerance
- CO2:
-
empathy vs. social disinterest
- CO3:
-
helpfulness vs. unhelpfulness
- CO4:
-
compassion vs. revengefulness
- CO5:
-
integrated conscience vs. self-serving advantage
- ST1:
-
creative self-forgetfulness vs. self-conscious experience
- ST2:
-
transpersonal identification vs. personal identification
- ST3:
-
spiritual acceptance vs. rational materialism
References
Cloninger CR, Svrakic DM, Przybeck TR. A Psychobiological model of temperament and character. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993;50:975–89.
Anckarsäter H, Ståhlberg O, Larson T, Håkansson C, Jutblad SB, Niklasson L, Råstam M. The impact of ADHD and autism spectrum disorders on temperament, character, and personality development. [Comparative Study Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:1239–44. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.163.7.1239.
Cloninger CR. Feeling good: The science of well-being. New York: Oxford University Press; 2004.
Schütz E, Archer T, Garcia D. Character profiles and adolescents’ self-reported happiness. Personality Individ Differ. 2013;54:841–4. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2012.12.020.
Svrakic DM, Whitehead C, Przybeck T, Cloninger R. Differential diagnosis of personality disorders by the seven-factor model of temperament and character. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993;50:991–9.
Söderström H, Råstam M, Gillberg C. Temperament and character in adults with Asperger syndrome. Autism. 2002;6:287–97.
Cloninger CR. What makes people healthy, happy, and fulfilled in the face of current world challenges? Mens Sana Monograph. 2013;11:16–24.
Cloninger CR, Zohar AH. Personality and the perception of health and happiness. J Affect Disord. 2011;128:24–32.
Garcia D, Kerekes N, Andersson-Arntén A-C, Archer T. Temperament, character, and adolescents’ depressive symptoms: focusing on affect. Depression Res Treat. 2012;. doi:10.1155/2012/925372.
Moreira PAS, Cloninger CR, Dinis L, Sá L, Oliveira JT, Dias A, Oliveira J. Personality and well-being in adolescents. Front Psychol. 2015;e5:1494. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01494.
Josefsson K, Cloninger CR, Hintsanen M, Jokela M, Pulkki-Råback L, Keltikangas-Järvinen L. Associations of personality profiles with various aspects of well-being: a population-based study. J Affect Disord. 2011;133:265–73.
Gillespie NA, Cloninger CR, Heath AC, Martin NG. The genetic and environmental relationship between Cloninger’s dimensions of temperament and character. Personality Individ Differ. 2003;35:1931–46.
Ando J, Suzuki A, Yamagata S, Kijima N, Maekawa H, Ono Y, Jang KL. Genetic and environmental structure of Cloninger’s temperament and character dimensions. J Pers Disord. 2004;18:379–93. doi:10.1521/pedi.18.4.379.40345.
Garcia D, Lundström S, Brändström S, Råstam M, Cloninger CR, Kerekes N, Nilsson T, Anckarsäter H. Temperament and character in the child and adolescent twin study in sweden (catss): comparison to the general population, and genetic structure analysis. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(8):e70475. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070475.
Anderson CB, Joyce PR, et al. The effect of cognitive-behavioral therapy for bulimia nervosa on temperament and character as measured by the temperament and character inventory. Compr Psychiatry. 2002;43:182–8.
Corchs F, Corregiari F, et al. Personality traits and treatment outcome in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria. 2008;30:246–50.
Mortberg E, Andersson G. Predictors of response to individual and group cognitive behaviour therapy of social phobia. Psychol Psychother. 2013;87:32–43.
Rowe S, Jordan J, et al. Dimensional measures of personality as a predictor of outcome at 5-year follow-up in women with bulimia nervosa. Psychiatry Res. 2010;185:414–20.
Soto CJ, John OP. Ten facet scales for the big five inventory: convergence with NEO PI-R facets, self-peer agreement, and discriminant validity. J Res Pers. 2009;43:84–90.
Anckarsäter H, Lundström S, Kollberg L, Kerekes N, Palm C, Carlström E, Långström N, Magnusson PKE, Bölte S, Gillberg C, Gumpert C, Råstam M, Lichtenstein P. The Child and Adolescent Twin Study in Sweden (CATSS). Twin Res Hum Genet. 2011;14:495–508. doi:10.1375/twin.14.6.495.
Hansson SL, Svanström-Röjvall A, Råstam M, Gillberg C, Gillberg C, Anckarsater H. Psychiatric telephone interview with parents for screening of childhood autism-tics, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and other comorbidities (A-TAC) 1. Preliminary reliability and validity. Br J Psychiatry. 2005;187:262–7.
Brändström S, Schlette P, Przybeck TR, Lundberg M, Forsgren T, Sigvardsson S, et al. Swedish normative data on personality using the temperament and character inventory. Compr Psychiatry. 1998;39:122–8.
Hannelius U, Gherman L, Mäkelä V, Lindstedt A, Zucchelli M, Lagerberg C, Tybring G, Lindgren CM. Large-scale zygosity testing using single nucleotide polymorphisms. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2007;10:604–25.
Neale MC. Mx: Statistical Modeling. Box 710 MCV, Richmond, VA 23298: Department of Psychiatry. 2nd ed. 1994.
Cloninger CR, Przybeck TR, Svrakic DM, Wetzel RD. The temperament and character inventory (Temperament and character inventory): A guide to its development and use. St. Louis: Washington University Center for Psychobiology of Personality; 1994.
Heath AC, Madden PA, Cloninger CR, Martin NG. Genetic and environmental structure of per- sonality. In: Cloninger CR, editor. Personality and psychopathology. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Press; 1994.
Stallings MC, Hewitt JK, Cloninger CR, Heath AC, Eaves LJ. Genetic and environmental structure of the tridimensional personality questionnaire: three or four temperament dimensions? J Personal Soc Psychol. 1996;70:127–40.
Josefsson K, Jokela M, Cloninger CR, Hintsanen M, Salo J, Hintsa T, Pilkki-Råback L, Keltikangas-Järvinen L. Maturity and change in personality: developmental trends of temperament and character in adulthood. Dev Psychopathol. 2013;25:713–27.
Josefsson K, Jokela M, Hintsanen M, Cloninger CR, Pilkki-Råback L, Merjonen P, Hutri-Kähönen N, Keltikangas-Järvinen L. Parental care-giving and home envinronment predicting offspring’s temperament and character traits after 18 years. Psychiatry Res. 2013;209:643–51.
Gardini S, Cloninger CR, et al. Individual differences in personality traits reflect structural variance in specific brain regions. Brain Res Bull. 2009;79:265–70.
Kaasinen V, Maguire RP, et al. Mapping brain structure and personality in late adulthood. Neuroimage. 2005;24:315–22.
Van Schuerbeek P, Baeken C, et al. Individual differences in local gray and white matter volumes reflect differences in temperament and character: a voxel-based morphometry study in healthy young females. Brain Res. 2011;1371:32–42.
Eisenberg N, Eggum ND. Empathy-related and prosocial responding. Conceptions and correlates during development. In: Sullivan BA, Snyder M, Sullivan JL (eds.), Cooperation. The political psychology of effective human interaction. Singapore: Blackwell Publishing; 2008. p. 53–74.
Sussman RW, Cloninger CR. Origins of altruism and cooperation. New York: Springer; 2011.
d’Aquili ED, Newberg A. The Neuropsychological Basis of Religions, or Why God Won’t Go Away. Zygon. 1998;33:187–201.
Magen Z. Exploring adolescent happiness. Commitment, purpose and fulfillment. London: Sage Publications, Inc. 1998.
Magen Z. Commitment beyond self and adolescence: the issue of happiness. Soc Indic Res. 1996;37:235–67.
Garcia D, Anckarsäter H, Kjell ONE, Archer T, Rosenberg P, Cloninger CR, Sikström S. Agentic, communal, and spiritual traits are related to the semantic representation of written narratives of positive and negative life events. Psychol Well-Being: Theory, Res Pract. 2015;5:1–20. doi:10.1186/s13612-015-0035-x.
McAdams DP. The psychology of life stories. Rev Gen Psychol. 2001;5:100–22.
McLean KC, Pasupathi M, Pals JL. Selves creating stories creating selves: a process model of narrative self development in adolescence and adulthood. Personal Soc Psychol Rev. 2007;11:262–78.
Weeks TL, Pasupathi M. Autonomy, identity, and narrative construction with parents and friends. In: McLean KC, Pasupathi M (eds.), Narrative development in adolescence, advancing responsible adolescent development. New York: Springer; 2010. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-89825-4_4.
Erikson EH. Identity: youth and crisis. New York: Norton; 1968.
Cloninger CR, Rice J, et al. Multifactorial inheritance with cultural transmission and assortative mating. II. a general model of combined polygenic and cultural inheritance. Am J Hum Genet. 1979;31:176–98.
Cloninger CR, Rice J, et al. Multifactorial inheritance with cultural transmission and assortative mating. III. Family structure and the analysis of separation experiments. Am J Hum Genet. 1979;31:366–88.
Arnedo J, Svrakic DM, del Val C, Romero-Zaliz R, Hernandez-Cuervo H, Fanous AH, Pato MT, Pato CN, de Erausquin GA, Cloninger CR, Zwir I. Uncovering the hidden risk architecture of the schizophrenias: confirmation in three independent genome-wide association studies. Am J Psychiatry. 2014;172:139–53.
Pettersson E, Turkheimer E. Self-reported personality pathology has complex structure and imposing simple structure degrades test information. Multivar Behav Res. 2014;49:372–89. doi:10.1080/00273171.2014.911073.
Marty P. Personalizing crime. Dispute Resolut Mag. 2000;7:8–11.
Cloninger CR, Cloninger KM. Person-centered Therapeutics. Int J Pers Centered Med. 2011;1(1):43–52.
Cloninger CR, Cloninger KM. Development of instruments and evaluative procedures on contributors to illness and health. Int J Pers Centered Med. 2011;1(3):446–55.
Cloninger CR, Salloum IM, Mezzich JE. The dynamic origins of positive health and wellbeing. Int J Pers Centered Med. 2012;2(2):179–87.
Falhgren E, Nima AA, Archer T, Garcia D. Person-centered osteopathic practice: patients’ personality (body, mind, and soul) and health (ill-being and well-being). PeerJ. 2015;3:e1349. doi:10.7717/peerj.1349.
Cloninger CR, Svrakic NM, Svrakic DM. Role of personality self-organization in development of mental order and disorder. Dev Psychopathol. 1997;9:881–906.
Hopkins B. Restorative justice in schools. Support Learn. 2002;17:144–9.
Authors’ contributions
NL and DG wrote the paper, prepared figures and/or tables, reviewed drafts of the paper. SL SB and DG analyzed the data, prepared figures and/or tables, reviewed drafts of the paper. CRC, TN, NK, and HA reviewed drafts of the paper. DG and HA conceived and designed the experiments, performed the experiments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The CATSS is supported by the Swedish Council for Working Life and Social Research, the Swedish Research Council, Systembolaget, the National Board of Forensic Medicine, Swedish prison and Probation Services, and Bank of Sweden Tercentenary Foundation. The development of this article was supported by AFA Insurance (Dnr. 130345), Stiftelsen Kempe-Carlgrenska Fonden, and the Swedish Research Council (Dnr. 2015-01229). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Danilo Garcia is the director of the Blekinge Center of Competence, which is the research and development unit of the Blekinge County Council and the municipalities in Blekinge, Sweden. Researchers, experts, and practitioners work at the Blekinge Center of Competence for higher quality of life among the habitants of Blekinge by innovating health care through person-centered methods.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
12991_2016_94_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Additional file 1: Table S1. Correlations between the five lower order sub-scales that compose the self-directedness (SD) scale of the temperament and character inventory (N = 2714). Table S2. Correlations between the five lower order sub-scales that compose the Cooperativeness (CO) scale of the temperament and character inventory (N = 2714). Table S3. Correlations between the three lower order sub-scales that compose the self-transcendence (ST) scale of the temperament and character inventory (N = 2714).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Lester, N., Garcia, D., Lundström, S. et al. The genetic and environmental structure of the character sub-scales of the temperament and character inventory in adolescence. Ann Gen Psychiatry 15, 10 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12991-016-0094-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12991-016-0094-2