Abstract
Background
Maladaptive remodelling mechanisms occur in patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot (rToF) resulting in a cycle of metabolic and structural changes. Biventricular shape analysis may indicate mechanisms associated with adverse events independent of pulmonary regurgitant volume index (PRVI). We aimed to determine novel remodelling patterns associated with adverse events in patients with rToF using shape and function analysis.
Methods
Biventricular shape and function were studied in 192 patients with rToF (median time from TOF repair to baseline evaluation 13.5 years). Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) and principal component analysis (PCA) were used to identify shape differences between patients with and without adverse events. Adverse events included death, arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest with median follow-up of 10 years.
Results
LDA and PCA showed that shape characteristics pertaining to adverse events included a more circular left ventricle (LV) (decreased eccentricity), dilated (increased sphericity) LV base, increased right ventricular (RV) apical sphericity, and decreased RV basal sphericity. Multivariate LDA showed that the optimal discriminative model included only RV apical ejection fraction and one PCA mode associated with a more circular and dilated LV base (AUC = 0.77). PRVI did not add value, and shape changes associated with increased PRVI were not predictive of adverse outcomes.
Conclusion
Pathological remodelling patterns in patients with rToF are significantly associated with adverse events, independent of PRVI. Mechanisms related to incident events include LV basal dilation with a reduced RV apical ejection fraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Find the latest articles, discoveries, and news in related topics.Background
Morphological descriptions of the heart have been historically imaginative. “Le Cœur en Sabot” (or the boot-shaped heart) is one such description of the appearance of the heart on a plain radiograph of patients with tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) [1]. In patients with repaired ToF (rToF), surgical relief of the right ventricular (RV) outflow tract often leads to pulmonary valve disruption, which results in chronic regurgitation, severe RV dilation, and biventricular dysfunction. For the purposes of the current study, we use the term “adaptive remodelling” to describe heart shape and size changes which help satisfy the body’s oxygen demands while maintaining pressure within the physiological range [2]. Conversely, “maladaptive remodelling” refers to shape and size changes occurring due to an adverse cycle of metabolic and structural changes resulting in heart failure. Although the hemodynamic burden from chronic RV volume load may be tolerated without symptoms during childhood, evidence suggests that the incidence of arrhythmia, heart failure, and death increases substantially in adult life [3, 4]. The identification of adaptive vs maladaptive remodelling has been difficult due to a lack of quantitative tools for shape analysis. However, new shape analysis tools enable the re-evaluation of historical morphological descriptions.
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) is considered the gold standard for assessing ventricular volumes, function, and flows in congenial heart disease [5]. Recently, biventricular atlases have enabled analysis of the RV and left ventricular (LV) shape changes simultaneously, enabling the detection of anomalous patterns of biventricular inter-relationships [6,7,8]. Although previous studies have focused on surrogate markers such as pulmonary regurgitation volume index (PRVI) to characterise adverse remodelling [8, 9], using surrogate endpoints as intermediate indicators of adverse outcomes may overlook important shape-related information associated with adverse remodelling but not captured by the surrogate marker itself. Here, we investigated relationships between shape and adverse events defined as death, life-threatening arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest in the German Competence Network for Congenital Heart Defects [10, 11].
We hypothesised that specific 3D biventricular shape features are associated with subsequent adverse events, and that these “maladaptive remodelling” scores are distinct from shape variations associated with PRVI. If so, these novel shape features may indicate specific maladaptive remodelling mechanisms leading to adverse outcomes, which can be distinguished from adaptive remodelling associated with PRVI.
Methods
Subjects
This study retrospectively re-analyzed anonymised images and associated data from a large cohort of adolescents and young adults with rToF recruited from a multicenter study of the German Competence Network for Congenital Heart Defects (study identifier: NCT00266188, title: Non-invasive Imaging and Exercise Tolerance Tests in Post-repair Tetralogy of Fallot—Intervention and Course in Patients Over 8 Years Old). Ethical approval was obtained and all participants gave informed consent. This rTOF dataset constitutes one of the most extensive compiled datasets of this pathology to date. The data was acquired at 14 different sites between 2005 and 2008 on 1.5T and 3T CMR scanners. The primary adverse outcome was defined as any cardiac arrest, ventricular tachycardia, or death until the latest outcome data collection point in 2019 with median follow-up time of ten years (Table 1). Further descriptions of clinical data can be found in [11, 12].
CMR imaging
CMR cine exams included multiple short-axis slices covering both RV and LV and one four chamber (4Ch) long-axis slice acquired during breath-hold. End-diastolic (ED) and end-systolic (ES) CMR images were segmented semi-automatically with a subsequent manual correction by a single reader. The LV endocardial, LV epicardial, and RV endocardial contours were defined using cvi42 software (Circle Cardiovascular Imaging, Calgary, Canada) according to the standards published by Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance [13]. Papillary muscles and trabeculae were included in the chamber volume for this analysis. Tricuspid and mitral valve hinge points and LV apex position were extracted from the 4Ch view. RV epicardial contours were not defined due to the poor reproducibility of manual delineation [14]. Pulmonary regurgitant volume was computed from phase contrast flow imaging across the main pulmonary artery, using flow measurements was performed using dedicated customized software capable of handling data of different vendors [15].
Biventricular models
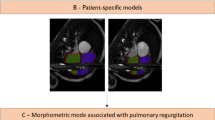
A biventricular model template was automatically customised to the extracted contours using previously validated methods [6, 7]. Briefly, short axis slice positions were first corrected for breath-hold misregistration, and the template was then rigidly aligned and fit to the contours using a diffeomorphic non-rigid registration (see Fig. 1).
Patient-specific biventricular shape modelling. Left—short axis contours, middle—long axis contours, right: biventricular shape. Contours: green—left ventricular (LV) epicardium, red—LV endocardium, yellow—right ventricle (RV) endocardium, orange—left atrium, cyan—right atrium. Surfaces: (right) green—RV, purple—LV
Volume and mass
Global functional and volumetric parameters were computed from the patient-specific shape model, including ED and ES volumes (LVEDV, RVEDV, LVESV, RVESV), stroke volumes (LV SV, RV SV), LV mass (LVM) and ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF, RVEF).
Besides global volume, regional volumes were also computed using methods similar to Bernardino et al. [16]. The total RV volume was parcellated into three different regions based on RV apex, pulmonary valve, and tricuspid valve centroids position (Fig. 2). The surface vertices were classified as inlet, outlet, and apical regions according to the closest landmark. For each region, partial volume, SV, and LVEF/RVEF were computed.
Shape modes
Patient-specific biventricular geometries were used to build a statistical cardiac atlas characterising the shape variation in patients with ToF late after repair. Details of the procedure are given in [6, 8]. Briefly, a Procrustes algorithm was used to rigidly align the ED shapes to a reference coordinate system defined by the population mean shape. The same transformation was applied to the ES shape, thereby preserving their relative position and the surface deformation from ES to ED.
Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to build a statistical shape model. Both geometry and motion were encoded by concatenation of the ED and ES shapes for each case. The statistical shape model included RV and LV endocardial and LV epicardial surfaces. However, for clarity, the figures displaying biventricular shape show the RV and LV endocardial surface only.
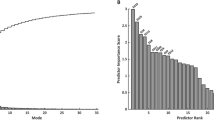
A PCA component, known as a shape mode (SM), reflects a specific shape variation pattern and encompasses attributes of size and both global and regional shapes. Any individual 3D shape can be characterised by a set of normalised scores (z-scores) specifying each SM’s contribution to the subject-specific geometry. For a robust and meaningful examination, only SMs explaining more than 1% of total variation were selected for further analysis. That resulted in 15 SMs, which in total explained 85% of the variation across the cohort.
Maladaptive remodelling
Remodelling patterns associated with adverse events were identified using linear discriminant analysis (LDA) combined with an automatic feature selection algorithm according to the area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operator characteristic, similar to the computational framework proposed by Varela et al. [17]. The shape features used in the LDA included conventional global and regional functional and volumetric measures together with the first 15 atlas-derived SMs. Prior to multivariable LDA, all clinical, demographic, or shape features were standardised and normalised. The ventricular volume and mass were indexed by body surface area (BSA) to mitigate the effects of body habitus.
Three separate preliminary LDAs were performed, each evaluated with stratified four-fold cross-validation (Additional file 1) designed to identify the shape features most associated with adverse outcomes: i) including only conventional measures (total ventricular volumes, EF, left ventricular mass (LVM) index (LVMI), QRS, and blood pressure); ii) regional functional and volumetric features derived from RV volume parcellation, and iii) including only the first 15 SMs. To avoid overfitting, the maximum number of predictors in each step was fixed to three parameters.
Finally, a composite LDA was performed by combining the predictors identified in the three preliminary analyses. The resulting LDA score was used as a new biomarker for risk quantification. The odds ratio (OR) with 95% CIs was computed to quantify the strength of the association with adverse outcomes. The cut-off value was computed by maximising the sensitivity and specificity in the ROC curves analysis.
Remodelling associated with PRVI
A surrogate multivariable LDA model was developed to explore the role that PRVI may play in the association between shape and adverse events. This model included 158 cases for which pulmonary regurgitation data were available. The correlations between critical functional and shape predictors and PRVI were studied using univariable linear regression. Then, the shape mode best explaining PRVI was computed using multivariable regression.
Calliper measurements
Atlas SMs describe both global and regional variation of ventricular shape, but their interpretation remains a challenging task. Calliper measurements have been used to quantify RV regional remodelling response in several pathophysiological conditions in imaging studies [18] and regional shape changes are important in rTOF patients [19]. In this work, multivariable regression was used to determine relationships between SM and calliper-based measures. The resulting associations were used to interpret the effect of the SM patterns.
The calliper measurements were generalised for RV and LV chambers (see Fig. 3), as summarised in Additional file 1: Table S2. Ventricular sphericity (width divided by height) and eccentricity (anterior–posterior width divided by septal-lateral width) were computed for ED and ES using widths at 1/4 (apical), ½ (mid), and 3/4 (basal) of the ventricle height. Longitudinal shortening and apex displacement were computed for both RV and LV. Valve displacement was computed for mitral and tricuspid valves.
Definition of calliper distances. Yellow—left ventricle (LV). Blue—right ventricle (RV). HRV—the distance between tricuspid valve (TV) centroid and RV apex. HLV—the distance between the mitral valve (MV) centroid and RV apex. WRV—the distance between the RV free wall and the septum measured at mid RV height (r*HRV, r = ½) on the axis perpendicular to the septum. WLV—the distance between the LV endocardium and the septum measured at mid-LV height (r*HLV, r = ½) along the axis perpendicular to the septum. LRV—the distance between the two most distant points on the RV free wall at mid RV height (½*HLV) along the axis parallel to the septum
The multivariate regression was performed for each calliper-based measure independently using the standardised shape scores as independent variables. The magnitude of the regression coefficients defined the SM’s contribution to the calliper measurement. Finally, the shape scores were interpreted in terms of the effect on calliper distances using the respective regression coefficients to indicate the correlation strength.
Statistics
Statistical analyses were performed using Python 3.6 using the Scikit-learn package (Python Software Foundation, Wilmington, Delaware, USA). A p value of 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Subjects
Of 408 patients enrolled in the main study, 380 patients had CMR examinations, 280 of these had both long axis and short axis slices, and 192 had sufficient 3D information enabling biventricular shape analysis (a long axis view capturing mitral and tricuspid valves and the LV apex) (Additional file 1: Fig. S1). (Additional file 1: Table S1) shows that the characteristics of the 216 excluded cases had similar demographics to the 192 cases included, except for a higher number of pulmonic valve replacement (PVR) after the baseline exam and a higher number of redo surgeries prior to the CMR for the excluded group. Of the 192 patients examined, 16 subjects were identified with primary adverse outcomes (AO) and 176 with no adverse outcomes. Adverse outcomes included 4 deaths, 10 ventricular tachycardia and 2 aborted sudden cardiac death (cardiac arrest requiring defibrillation). Demographic and clinical data are summarised in Table 1. In the studied cohort, the median age at baseline evaluation was 15 years. Among the no adverse outcome group, 26 patients had a PVR in the following two years after baseline evaluation. In the adverse outcome group, one patient had PVR nine years earlier than baseline evaluation, and one patient had a PVR in the following year after baseline evaluation. Six per cent of the entire population had at least one redo surgery. The median number of redo surgical repairs in the adverse outcome group was significantly higher than in the no adverse outcome group.
Functional and volumetric variables are summarised in Table 2. RVEF and LVM was significantly reduced in the adverse outcome group. Partial volume and regional EF for the RV is shown in Table 3. Regional RVEF was significantly reduced in the apical and inlet regions. The total RV volumes were similar between groups; however, the adverse outcome group showed an increased ES inflow and apical regional volume.
Maladaptive remodelling
In the first LDA model comparing conventional predictors (volumes and EF), the RVEF had the best ability to discriminate the patients with adverse outcomes (AUC = 0.72). The cross-validation feature selection algorithm could not find any combination of additional features improving the model predictive power without the risk of overfitting.
The second LDA model (using predictors derived from RV volume parcellation only) resulted in an equivalent discriminative power (AUC = 0.73) when using apical ejection fraction (RV APEF) as the unique predictor. Both models resulted in a negative correlation between the RVEF and the probability of having an adverse outcome (RVEF coeff = − 0.55, RV APEF coeff = − 0.69).
The third LDA model, which included only PCA SMs, the best discriminative power was obtained (AUC = 0.66) with a linear combination of 2 components: SM6 and SM8. Small but significant correlations were found between SM6 and RVEF and RV APEF (R2 = 0.097, p < 0.001 for RVEF and R2 = 0.179, p < 0.001 for RV APEF. However no significant correlation was found between SM8 and RV APEF or RVEF ( SM8: R2 = 0.004, p = 0.624 and R2 = 0.003 p = 0.582 respectively). Additional figures supporting these results are provided in Additional file 1: Fig. S2–S5.
For ease of interpretation, the SMs most associated with adverse events were correlated with calliper measures (Fig. 4). Univariate analysis revealed no significant differences between adverse outcome and no adverse outcome groups. However, SM6 was found to be mostly correlated with LV ES shape and RV ED shape (Fig. 5). A negative SM6 (associated with higher risk of adverse outcomes) resulted in a more elliptical LV ES (decreased eccentricity) and a more annular RV base at ED (decreased mid and basal eccentricity—short axis). SM6 also significantly affected the mitral valve and LV apex position at the ES phase, resulting in a more annular LV at ES (increased sphericity) (Fig. 6). On the other hand, SM8 was mostly correlated with the biventricular mid and basal shape. In the adverse outcome group, the LV sphericity and RV eccentricity increased when compared to the no adverse outcome cohort. Additional material to visualize shape differences between the reference population and patients with adverse events can be found in Additional file 1.
TOP: Association between geometrical features and the shape modes (SM): a SM6, b SM8. BOTTOM: Box-plots—score distribution of SM6 (a), SM8 (b) across the studied population for adverse outcomes (AO) and no adverse outcomes (NAO). The box denotes Q1 and Q3, whiskers Q1-1.5*IQR and Q3 + 1.5*IQR and diamonds are outliers. ED end-diastole, ES end-systole, LV left ventricle, RV right ventricle
Shape pattern associated with adverse events a and pulmonary regurgitation (b). Low risk: shape associated with no adverse outcomes. High risk: shape associated with adverse outcomes. Low pulmonary regurgitation: shape associated with reduced pulmonary regurgitation. High P: shape associated with high pulmonary regurgitation. Green and blue surfaces show LV and RV (respectively) at ES. Wireframe: LV and RV at ED. Red arrow: RV basal remodelling; purple—LV basal remodelling; orange—RV apical remodelling and LV apical displacement; blue—RV apical dilatation. Yellow circles illustrate the contrast between circular shape versus elliptical shape. Box plots: a Distribution of the risk score for adverse outcomes and no adverse outcomes, b) distribution of PR score for adverse outcomes and no adverse outcomes. The box denotes Q1 and Q3, whiskers Q1-1.5*IQR and Q3 + 1.5*IQR and diamonds are outliers. Red lines: + 2std and −2std representing the score of the plotted shapes
The final multivariable LDA was built using the previously identified predictors: RVEF, RV APEF, and the two shape modes (SM6 and SM8). The optimal model included only RV APEF and SM6 and improved the discriminative performance from AUC = 0.73 to AUC = 0.77. A high LDA score was significantly associated with an increased odds ratio (OR = 2.06; 95% CI = 1.08 to 3.93). The cut-off value maximising sensitivity and specificity was equal to -0.18.
Pulmonic regurgitation remodelling
A surrogate model using data from 158 subjects with available pulmonic regurgitation data were computed to investigate the impact on the model discriminative power (Additional file 1: Fig. S6). The LDA analysis showed that the PRVI had lower discriminative power than RV APEF (AUC = 0.60 versus AUC = 0.71) and had no added value when used as a predictor along with RV APEF and SM6 (AUC = 0.73 versus AUC = 0.72).
Further analysis was performed to investigate the PRVI’s relationship with the predictors of adverse events using linear regression (Fig. 6). There was a weak correlation (R2 = 0.14, p = 0.000) with the risk score, and no relation was found with either apical or total RVEF.
The shape pattern associated with PRVI was computed using LDA, and it resulted in a linear combination of 3 shape modes: SM7, SM2 and SM4 (R2 = 0.50) (Additional file 1: Fig. S7). The biventricular SMs associated with increased PRVI was compared to those identified with AO (Fig. 5). RV dilation was observed in both groups yet with different dilatation patterns. In patients with high PRVI, the RV dilatation was consistent over the RV volume (blue arrows). On the other hand, in the adverse outcome group, the RV dilatation was more prominent in the apical region, with RV basal constriction (red arrows). The combination of LV basal dilatation and RV base constriction led to an elliptical shape of the heart base in patients with adverse outcomes (yellow circle, view 3). Additional files 2 and 3: Videos S1 and S2 show a continuous animation of this remodelling.
Discussion
This preliminary study investigated the relationships between adverse events and complex multi-dimensional biventricular shape features in rToF patients. Specific shape changes were found to be significantly associated with a subsequent composite endpoint of death, arrhythmia, or cardiac arrest. In particular, RV apical sphericity and RVEF were indicative of higher risk. We also identified “maladaptive remodelling” features using atlas-based shape scores associated with future adverse events. Furthermore, this study highlights new insights into the relationship between PRVI and adverse events. Our results suggest that remodelling associated with increased PRVI may not be in itself maladaptive. Differences were found in remodelling patterns between hearts ultimately associated with adverse events and hearts with increased PRVI. The old descriptor “Le Cœur en Sabot'', although originally used to describe a combination of adaptive and maladaptive remodelling, can also be used to describe the high-risk shape in rTOF. Here, shape changes show a more prominent toe of the boot corresponding to the dilated LV, revealed more in the anterior view in the high risk shape (Additional file 1).
Although identification of adaptive vs maladaptive remodelling is hampered by many factors, including tissue structure and mechanical factors, outcome-related shape change provides a new method for studying the mechanisms behind the development of heart failure. In particular, this study supports previous findings that traditional indices, such as ejection fraction (EF), mass, or blood-pool volume, do not fully utilise the rich information provided by the CMR data and may not be sufficient to allow early identification of patients at high risk [20]. Previous studies have also shown that ventricular shape features extracted from CMR images can provide additional information to quantify the unique, abnormal remodelling patterns occurring in adults with rToF [19, 21]. Initially, these studies relied on 2D regional shape indices extracted from CMR images. However, 2D measurements cannot capture the complex ventricular geometry, hence the more recent use of 3D models and atlas-based shape scores [6, 9, 22, 23]. Only a few studies have included the full 3D biventricular geometry [6,7,8], the main focus remaining on the RV or LV ventricular shape independently [16, 17, 19, 21]. A strong correlation between RV and LV dysfunction was found in patients with rToF [24], and LV systolic function was already associated with ventricular tachycardia and death in this population [25]. Recently, right atrial area and RV longitudinal strain were significantly associated with adverse events [11].
The shape features derived in this study can be automatically computed, using machine learning image analysis combined with an automated modelling pipeline, as demonstrated recently for the LV [26, 27]. Routine computation of shape scores will add to the spectrum of imaging biomarkers, including tissue characterization, fluid dynamics, and stress imaging in order to improve patient characterization and risk prediction. The advantage of shape features is that they can be interpreted in terms of mechanical remodelling mechanisms, particularly regarding interactions between the two ventricles. In conjunction with longitudinal imaging, changes in shape scores could indicate deterioration, or conversely the benefit of a particular treatment.
Regarding the LV shape, the remodelling pattern that predicted adverse events displayed basal dilation and a decreased eccentricity index (Fig. 4), consistent with previous studies [9]. Additionally, the maladaptive SM6 also captured a difference in LV apical displacement from ED to ES phase: in patients with adverse events, the LV apex moves further toward the RV (paradoxical septal motion). By moving toward the RV, the ventricular septum contributes to the RV SV to the detriment of LV SV, therefore changing the RV pumping physiology [28]. This specific behaviour was supported by a reduced RV APEF and may be a sign of failure or apical contractile function impairment. These results are consistent with a previous analysis of 2D function in the same cohort, in which right atrial area and RV longitudinal strain were found to be most predictive of adverse events [11]. RV and LV volumes obtained from the 3D model were different from those obtained directly from the contours [11] due to differences in the methodology of volume calculation, although trends were similar.
Visual inspection of the 3D remodelling patterns further highlights that the RV maladaptive remodelling consisted of an RV apical dilatation in the diaphragm direction, while the outflow and basal regions were more constricted. In the study by Bodhey et al. [29], the authors analysed three RV compartments’ functional characteristics (apex, inflow, outflow) between patients with rToF and healthy subjects. The results showed that the inlet and outlet volumes (unlike apical volume) were not substantially affected by the conditions and extent of RV loading. Our data suggest that the inflow and outflow regions tend to dilate in patients with rToF with increased PRVI creating a basal bulge that is therefore considered adaptive. Nevertheless, the basal bulge is less evident in patients with adverse events suggesting that adaptive remodelling is suppressed (Fig. 5).
It should be noted that, in patients with adverse outcomes, the heart base (RV and LV as a complex) remodels towards an elliptical display in contrast to the no adverse outcome group where the base is maintaining a more circular display (see Fig. 5, view 3). These observations may be a combined consequence of changes in external loads imposed by surrounding anatomical structures (e.g., a more relaxed or elastic diaphragm or a larger atrium taking over space in the pericardial sac) and in ventricle properties (relatively softer material properties in RV apical region or LV basal region). However, it remains uncertain which events are the cause and which ones are the effect in this specific global remodelling process.
Our study agrees with previous studies which did not find independent associations between pulmonary regurgitation and adverse outcomes. Although initial studies have shown an association between pulmonary regurgitation and the occurrence of adverse events [3, 30], later studies with more detailed analysis have identified a multitude of other risk factors not directly related to pulmonary regurgitation [31]. Several studies have suggested that an increased pulmonary regurgitation is associated with RV dilation and outlet bulging [21, 23]. Consequently, similar shape patterns were intuitively associated with adverse outcomes. In the INDICATOR study [4], which followed 873 rToF patients over ~ 2 years, RV hypertrophy, LV and RVEF, and atrial tachyarrhythmias were predictive of outcomes (death and ventricular tachycardia), but not pulmonary regurgitation fraction. In our study, PRVI did not add value to the RV APEF + SM6 risk score, and a weak correlation was found with pulmonary regurgitation and RV apical dysfunction. Furthermore, evidence of different remodelling patterns was found between adverse outcomes and PRVI. In patients with increased PRVI, RV volume dilated almost uniformly, taking over the major part of the pericardial sac. Consequently, the LV size and sphericity were reduced. On the contrary, in patients at risk of adverse events, the remodelling process resulted in a specific apicobasal volumetric redistribution (Fig. 5).
Limitations
Our study has several limitations. Heart failure was not included as an endpoint, since it was not an endpoint in the main study. Although surrogate measures can be difficult to define, future studies should evaluate symptomatic outcomes. This relatively young cohort may have different characteristics to older cohorts with a greater proportion of transannular patch repairs. A limited number of patients may impact the classification models’ statistical significance. Only 16 subjects with sufficient imaging data for 3D modelling had adverse events; thus, factors such as the effect of PVR could not be analysed. We did not remove cases with subsequent valve replacement (26 no adverse outcomes, 1 adverse outcome) or the case with PVR prior to baseline evaluation (1 adverse outcome), to avoid selection bias. Future work should include the analysis of a larger population to confirm our findings and control for heterogeneous factors. A larger dataset would also include other variables in the model without predisposing to type 1 errors. Future large studies incorporating temporal analyses through machine learning [11] will be able to examine the relationships between shape features and other indices such as dyssynchrony, strain, and atrial morphometry.
Over half the full cohort did not have adequate 3D slices to enable construction of a shape model (Additional file 1: Fig. S1). Additional file 1: Table S1 shows excluded patients had similar demographics but a higher number of PVR’s after the baseline exam and a higher number of redo surgeries prior to the CMR. The main reason for missing or inadequate long axis slices was variation in CMR protocol with many studies not capturing a true 4Ch view. Cases were not rejected due to scan quality or patient status, but further study is needed to determine the relationships between PVR, shape changes and outcomes. Furthermore, the dataset included only one long axis view (4Ch), resulting in relatively sparse contours in the RV outflow tract region. In patients with rToF, dilatation may occur around the pulmonary valve position as a result of RV remodelling. If not captured by short axis contours, such geometrical patterns were partially unseen by the statistical atlas. Finally, RV epicardial contours were not defined in this study due to poor reproducibility [14], although RV hypertrophy was found to be a predictor of adverse outcome in INDICATOR [4]. New machine learning methods [11] may enable a more reproducible delineation of the RV epicardium.
Conclusion
Adverse events in ToF are associated with changes in biventricular geometry, with increased LV basal sphericity in combination with increased RV apical sphericity. Maladaptive cardiac remodelling corresponds to specific changes in shape, rather than size, suggesting different disease mechanisms leading to adverse events from adaptive shape changes related to RV volume overload. A further assessment of shape and regional functional features in a larger cohort is needed to determine whether these measures independently predict adverse outcomes in patients with rToF.
Availability of data and materials
Data are available on request from the authors and GCN.
Abbreviations
- 4Ch:
-
Four chamber
- APEF:
-
Apical ejection fraction
- BSA:
-
Body surface area
- CMR:
-
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- ED:
-
End-diastolic
- EF:
-
Ejection fraction
- ES:
-
End-systolic
- LDA:
-
Linear discriminant analysis
- LV:
-
Left ventricle/left ventricular
- LVEDV:
-
Left ventricular end-diastolic volume
- LVEF:
-
Left ventricular ejection fraction
- LVESV:
-
Left ventricular end-systolic volume
- LVM:
-
Left ventricular mass
- LVMI:
-
Left ventricular mass index
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- PRVI:
-
Pulmonary regurgitant volume index
- PVR:
-
Pulmonic valve replacement
- rTOF:
-
Repaired tetralogy of Fallot
- RV:
-
Right ventricle/right ventricular
- RVEDV:
-
Right ventricular end-diastolic volume
- RVEF:
-
Right ventricular ejection fraction
- RVESV:
-
Right ventricular end-systolic volume
- SM:
-
Shape mode
- SV:
-
Stroke volume
- TOF:
-
Tetralogy of Fallot
References
Ferguson EC, Krishnamurthy R, Oldham SA. Classic imaging signs of congenital cardiovascular abnormalities. Radiographics. 2007;27(5):1323–34.
Cohn JN, Ferrari R, Sharpe N. Cardiac remodeling–concepts and clinical implications: a consensus paper from an international forum on cardiac remodeling. Behalf of an International Forum on Cardiac Remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35(3):569–82.
Geva T, Sandweiss BM, Gauvreau K, Lock JE, Powell AJ. Factors associated with impaired clinical status in long-term survivors of tetralogy of Fallot repair evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(6):1068–74.
Valente AM, Gauvreau K, Assenza GE, Babu-Narayan SV, Schreier J, Gatzoulis MA, Groenink M, Inuzuka R, Kilner PJ, Koyak Z, et al. Contemporary predictors of death and sustained ventricular tachycardia in patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot enrolled in the INDICATOR cohort. Heart. 2014;100(3):247–53.
Pushparajah K, Duong P, Mathur S, Babu-Narayan S. Educational series in congenital heart disease: cardiovascular MRI and CT in congenital heart disease. Echo Res Pract. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERP-19-0048.
Mauger C, Gilbert K, Lee AM, Sanghvi MM, Aung N, Fung K, Carapella V, Piechnik SK, Neubauer S, Petersen SE, et al. Right ventricular shape and function: cardiovascular magnetic resonance reference morphology and biventricular risk factor morphometrics in UK Biobank. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2019;21(1):41.
Gilbert K, Mauger C, Young AA, Suinesiaputra A. Artificial intelligence in cardiac imaging with statistical atlases of cardiac anatomy. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020;7:102.
Mauger CA, Govil S, Chabiniok R, Gilbert K, Hegde S, Hussain T, McCulloch AD, Occleshaw CJ, Omens J, Perry JC, et al. Right-left ventricular shape variations in tetralogy of Fallot: associations with pulmonary regurgitation. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021;23:105.
Mansi T, Voigt I, Leonardi B, Pennec X, Durrleman S, Sermesant M, Delingette H, Taylor AM, Boudjemline Y, Pongiglione G, et al. A statistical model for quantification and prediction of cardiac remodelling: application to tetralogy of Fallot. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2011;30(9):1605–16.
Sarikouch S, Koerperich H, Dubowy KO, Boethig D, Boettler P, Mir TS, Peters B, Kuehne T, Beerbaum P. German competence network for congenital heart defects I: impact of gender and age on cardiovascular function late after repair of tetralogy of Fallot: percentiles based on cardiac magnetic resonance. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011;4(6):703–11.
Diller GP, Orwat S, Vahle J, Bauer UMM, Urban A, Sarikouch S, Berger F, Beerbaum P, Baumgartner H. German competence network for congenital heart defects I: prediction of prognosis in patients with tetralogy of fallot based on deep learning imaging analysis. Heart. 2020;106(13):1007–14.
Koehler S, Hussain T, Blair Z, Huffaker T, Ritzmann F, Tandon A, Pickardt T, Sarikouch S, Sarikouch S, Latus H, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation from axial to short-axis multi-slice cardiac mr images by incorporating pretrained task networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2021;40:2939–53.
Schulz-Menger J, Bluemke DA, Bremerich J, Flamm SD, Fogel MA, Friedrich MG, Kim RJ, von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff F, Kramer CM, Pennell DJ, et al. Standardized image interpretation and post processing in cardiovascular magnetic resonance: Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) board of trustees task force on standardized post processing. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2013;15:35.
Blalock SE, Banka P, Geva T, Powell AJ, Zhou J, Prakash A. Interstudy variability in cardiac magnetic resonance imaging measurements of ventricular volume, mass, and ejection fraction in repaired tetralogy of Fallot: a prospective observational study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;38(4):829–35.
Beerbaum P, Korperich H, Barth P, Esdorn H, Gieseke J, Meyer H. Noninvasive quantification of left-to-right shunt in pediatric patients: phase-contrast cine magnetic resonance imaging compared with invasive oximetry. Circulation. 2001;103(20):2476–82.
Bernardino G, Hodzic A, Langet H, Legallois D, De Craene M, Gonzalez Ballester MA, Saloux E, Bijnens B. Volumetric parcellation of the cardiac right ventricle for regional geometric and functional assessment. Med Image Anal. 2021;71: 102044.
Varela M, Bisbal F, Zacur E, Berruezo A, Aslanidi OV, Mont L, Lamata P. Novel computational analysis of left atrial anatomy improves prediction of atrial fibrillation recurrence after ablation. Front Physiol. 2017;8:68.
Howard LS, Grapsa J, Dawson D, Bellamy M, Chambers JB, Masani ND, Nihoyannopoulos P, Simon RGJ. Echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary hypertension: standard operating procedure. Eur Respir Rev. 2012;21(125):239–48.
Sheehan FH, Ge S, Vick GW 3rd, Urnes K, Kerwin WS, Bolson EL, Chung T, Kovalchin JP, Sahn DJ, Jerosch-Herold M, et al. Three-dimensional shape analysis of right ventricular remodeling in repaired tetralogy of Fallot. Am J Cardiol. 2008;101(1):107–13.
Therrien J, Siu SC, McLaughlin PR, Liu PP, Williams WG, Webb GD. Pulmonary valve replacement in adults late after repair of tetralogy of fallot: are we operating too late? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36(5):1670–5.
Zhang H, Wahle A, Johnson RK, Scholz TD, Sonka M. 4-D cardiac MR image analysis: left and right ventricular morphology and function. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010;29(2):350–64.
Leonardi B, Taylor AM, Mansi T, Voigt I, Sermesant M, Pennec X, Ayache N, Boudjemline Y, Pongiglione G. Computational modelling of the right ventricle in repaired tetralogy of Fallot: can it provide insight into patient treatment? Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;14(4):381–6.
Lamata P, Sinclair M, Kerfoot E, Lee A, Crozier A, Blazevic B, Land S, Lewandowski AJ, Barber D, Niederer S, et al. An automatic service for the personalization of ventricular cardiac meshes. J R Soc Interface. 2014;11(91):20131023.
Davlouros PA, Kilner PJ, Hornung TS, Li W, Francis JM, Moon JC, Smith GC, Tat T, Pennell DJ, Gatzoulis MA. Right ventricular function in adults with repaired tetralogy of Fallot assessed with cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging: detrimental role of right ventricular outflow aneurysms or akinesia and adverse right-to-left ventricular interaction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40(11):2044–52.
Knauth AL, Gauvreau K, Powell AJ, Landzberg MJ, Walsh EP, Lock JE, del Nido PJ, Geva T. Ventricular size and function assessed by cardiac MRI predict major adverse clinical outcomes late after tetralogy of Fallot repair. Heart. 2008;94(2):211–6.
Suinesiaputra A, Mauger CA, Ambale-Venkatesh B, Bluemke DA, Dam Gade J, Gilbert K, Janse MHA, Hald LS, Werkhoven C, Wu CO, et al. Deep learning analysis of cardiac MRI in legacy datasets: multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8: 807728.
Corral Acero J, Schuster A, Zacur E, Lange T, Stiermaier T, Backhaus SJ, Thiele H, Bueno-Orovio A, Lamata P, Eitel I, et al. Understanding and improving risk assessment after myocardial infarction using automated left ventricular shape analysis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2021.11.027.
Stephensen S, Steding-Ehrenborg K, Munkhammar P, Heiberg E, Arheden H, Carlsson M. The relationship between longitudinal, lateral, and septal contribution to stroke volume in patients with pulmonary regurgitation and healthy volunteers. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014;306:H895-903.
Bodhey NK, Beerbaum P, Sarikouch S, Kropf S, Lange P, Berger F, Anderson RH, Kuehne T. Functional analysis of the components of the right ventricle in the setting of tetralogy of Fallot. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2008;1(2):141–7.
Senthilnathan S, Dragulescu A, Mertens L. Pulmonary regurgitation after tetralogy of fallot repair: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Cardiovasc Echogr. 2013;23(1):1–9.
Wald RM, Valente AM, Gauvreau K, Babu-Narayan SV, Assenza GE, Schreier J, Gatzoulis MA, Kilner PJ, Koyak Z, Mulder B, et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance markers of progressive RV dilation and dysfunction after tetralogy of Fallot repair. Heart. 2015;101(21):1724–30.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding was provided by the National Institutes of Health (USA) R01HL121754. This work was supported in part by the Competence Network for Congenital Heart Defects, which has received funding from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, grant number 01GI0601 (until 2014), and the DZHK (German Centre for Cardiovascular Research; as of 2015); by the W. B. & Ellen Gordon Stuart Trust, The Communities Foundation of Texas and by the Pogue Family Distinguished Chair (award to Dr F. Gerald Greil in February 2015). PL holds a Wellcome Trust Senior Research Fellowship (209450/Z/17/Z). SE is supported in part by Informatics for Life funded by the Klaus Tschira Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AM performed the analyses. All authors participated in concept development and research design, and revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was obtained and all participants gave informed consent.
Consent for publication
No identifiable individual information was included in this study.
Competing interests
A.D.M. and J.H.O. are co-founders of and have an equity interest in Insilicomed, and A.D.M. has an equity interest in Vektor Medical. A.D.M. and J.H.O. serve on the scientific advisory board of Insilicomed, and A.D.M. as scientific advisor to both companies. Some of their research grants have been identified for conflict of interest management based on the overall scope of the project and its potential benefit to these companies. The authors are required to disclose this relationship in publications acknowledging the grant support; however, the research subject and findings reported in this study did not involve the companies in any way and have no specific relationship with the business activities or scientific interests of either company. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of California San Diego in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
Additional data.
Additional file 2: Video S1.
Animations of shape variations associated with adverse outcomes.
Additional file 3: Video S2.
Animations of shape variations associated with pulmonary regurgitation.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Mîra, A., Lamata, P., Pushparajah, K. et al. Le Cœur en Sabot: shape associations with adverse events in repaired tetralogy of Fallot. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 24, 46 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-022-00877-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-022-00877-x