Abstract
Background
Inherited dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) contributes to approximately 25% of idiopathic DCM cases, and the proportion is even higher in familial DCM patients. Most studies have focused on familial DCM, whereas the genetic profile of sporadic DCM in Chinese patients remains unknown.
Methods
Between June 2018 and September 2019, 24 patients diagnosed with idiopathic DCM without a family history were included in the present study. All patients underwent genetic screening for 80 DCM-related genes using targeted next-generation sequencing.
Results
By in silico analysis, 10 of 99 detected variants were considered pathogenic or likely-pathogenic, including seven TTN truncating variants (TTNtv), one in-frame deletion in TNNT2, one missense mutation in RBM20, and one frameshift deletion variant in FLNC. Of these variants, eight are reported for the first time.
Conclusions
Using targeted next-generation sequencing, potential genetic causes of idiopathic DCM were identified. Sarcomere mutations remained the most common genetic cause of inherited DCM in this cohort of sporadic Chinese DCM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) describes a group of myocardial disorders that lead to ventricular enlargement and compromised contraction. The reported incidence of DCM in China was 190 of every million in a stratified sampling investigation in 2002, and the 5-year mortality was ~ 50% in another report in 2014, respectively [1]. The aetiology underlying DCM is diverse and includes well-defined causes (for example, ischaemic injury) and unrecognised risk factors; hereafter, the latter condition has been referred to as idiopathic DCM. Rapid advancement in genetic technology led to the discovery of genetic mutations as direct causes of DCM 2 decades ago. Furthermore, genetic mutations were identified in 8–25% patients with idiopathic DCM [2]. Compared to sporadic cases, patients with a family history of DCM are more likely to have a genetic aetiology. Unlike the condition in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the genetic aetiology of DCM is highly heterogeneous. Thanks to high-throughput sequencing technologies, more than 50 DCM-related genes have been identified [3, 4]. The most frequent transmission mode is autosomal dominant, followed by autosomal recessive, X-linked, and mitochondrial inheritance. Most of the genes encode components of the sarcomere, cytoskeleton, or nuclear lamina. Nevertheless, few genetic variants have been proven to be disease-causing by robust experimental data [5]. Understanding the genetic background can offer new insights regarding the pathogenesis for the development of precision medicine of DCM. Most previous studies have focused on genetic screening of familial DCM. Based on these studies, familial and/or younger DCM patients are recommended for regular genetic screening at present. Otherwise, the genetic profile of sporadic DCM remains to be clarified. The current study aimed to discover the genetic background of sporadic idiopathic DCM in a group of Chinese patients.
Methods
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
This study included patients diagnosed with idiopathic DCM between June 2018 and September 2019. The diagnostic criteria for idiopathic DCM were consistent with the guidelines described by the AHA Scientific Statement and position statement of the ESC working group [3, 6].
The exclusion criteria included peripartum cardiomyopathy and secondary dilated cardiomyopathies caused by ischaemic heart diseases, hypertension, valvular diseases, endocrine disorders (such as diabetic cardiomyopathy and hyperthyroid cardiomyopathy), inflammation, toxicity, and stress. In a recently published study, Ware and his colleagues found a similar genetic profile of well-characterised DCM-causing genes between DCM and alcoholic cardiomyopathy [7]. Hence, patients who consumed excess alcohol were not excluded from the study.
Subjects and clinical evaluations
A total of 24 unrelated patients were included in the cardiology department of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital during the study period. Patients’ clinical data at the time of enrolment, including medical history, family history, physical examination, blood tests, 12-lead echocardiogram (ECG), transthoracic echocardiography, and/or cardiac magnetic resonance imaging were collected.
This study was approved by the Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital ethics committee and met the Tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. All included patients provided informed consent.
DNA sample collection and targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS)
Peripheral venous blood was collected from the included patients and their relatives (if available) for genomic DNA isolation. The DNA was extracted using the Magnetic Universal Genomic DNA Kit (TIANGEN) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. To cover the coding sequence region and flanking sequences (adjacent intronic regions essential for splicing) of DCM-related genes, a customised panel of 179 genes associated with inherited heart diseases (including 80 genes related to inherited DCM, see Additional file 1) was used for the target sequence library. Genomic DNA was fragmented between 180–280 bp and 500 ng of each prepared library was recommended for hybrid capture. Amplicon libraries and hybrid capture were prepared using IDT xGen Exome Research Panel v1.0 kits, which was performed in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions (Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc. Iowa, USA). The library was quantified with a Qubit 2.0 fluorometer (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific). NGS was performed using Illumina NovaSeq 6000 System (Illumina, USA) by Novocardio Genetic Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). The sequencing data were collected and filtered for quality (see details in Additional file 2: Figure S1). The resultant data were subsequently aligned to the human reference genome assembly (Feb. 2009, GRCh37/hg19) using Burrow-Wheeler Aligner. Single nucleotide variants and insertions and deletions (indels) were detected using SAMtools [8] and an in-house filter pipeline (Additional file 2: Figure S1). At least 99% of the targeted bases were sequenced to a read depth of more than 20 times.
Variant annotation and classification
Variants were identified using the Genome Analysis Toolkit, CNVkit, and annotated with ANNOVAR (http://wannovar.wglab.org/). All variants were confirmed by traditional Sanger sequencing. Common genetic variants or single nucleotide polymorphisms [with a minor allelic frequency (MAF) ≥ 1%] were excluded by referring to genetic databases, including dbSNP database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/), 1000 Genomes Project (http://www.internationalgenome.org/categor y/dbsnp/), and Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC) database (details are provided in the Additional file 3). Variants leading to amino acid changes were predicted using the bioinformatics programmes SIFT (http://sift.jcvi.org/), Polyphen2 (http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/), and MutationTaster (http://www.mutationtaster.org/). The pathogenicity of a certain variant was defined according to the guidelines of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) and Association of Molecular Pathology (AMP) as follows: pathogenic (P), likely-pathogenic (LP), variant of uncertain significance (VUS), likely benign (LB), and benign (B) [9].
Results
Clinical characteristics
Of the 24 unrelated patients included in this study, there were 19 males and 5 females; the mean age at onset of DCM was 40 years. None of these patients had a family history of cardiomyopathy or sudden death. No extracardiac features were identified. Up to 25% of the cases had traditional cardiovascular risk factors, such as smoking and hypertension. Of these cases, 87.5% had class III or IV heart failure function. The mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) at enrolment was 27.0 ± 9.9% and mean left ventricular end diastolic dimension was 70.1 ± 7.8 mm. The median serum N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide level was 2057.5 pg/mL and it ranged from 698 to 18381 pg/mL. With regard to arrhythmias, 20% patients had either ventricular tachycardia [8%, with implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD)], atrial fibrillation (8%), or bundle branch block (4%). Most patients were treated with guideline-directed medical therapy. The patient clinical presentations are summarised in Table 1.
Genetic variants
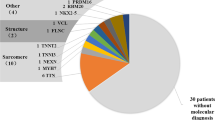
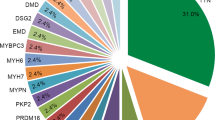
In total, 99 variants distributed across 27 DCM-related genes were identified. All variants either had an allele frequency < 1% in the 1000 genome project and ExAC projects, or could not be found in the local database. Based on in silico analysis and ACMG guidelines, 10 variants from 10 patients were considered likely-pathogenic or pathogenic. Other variants classified as VUS or benign were not included in further analysis (details are provided in the Additional file 4). The pathogenic variant was an in-frame deletion leading to an amino acid deletion in the coding sequence of TNNT2. The mutation types of other putatively likely-pathogenic variants were: three nonsense mutations and four frameshift small deletions located in TTN, one missense mutation in RBM20, and one frameshift small deletion variant in FLNC. All mutations were heterozygous. Mutations in TTN were the most common variants in this group of sporadic Chinese DCM patients. Detailed information on the putatively pathogenic/likely-pathogenic variants is summarised in Table 2.
In addition, Sanger sequencing for the detected mutations could be carried out for the relatives of three patients. For the patient with an RBM20 missense mutation, both his parents showed wild-type alleles, indicating a de novo mutation. Patient No. 15, a carrier of a heterozygous nonsense mutation in TTN, has two daughters; the older daughter showed the same mutation as the index patient, and the other was wild-type. The patient with an in-frame deletion in TNNT2 died during index hospitalisation; both his mother and uncle were heterozygous for the same TNNT2 mutation and remained healthy at the time of enrolment.
Discussion
Mutations in TTN were the most common variants in the current group of sporadic Chinese DCM patients. Together with an identified TNNT2 variant, sarcomere mutations seemed to contribute most to the genetic cause of this idiopathic DCM cohort, which is consistent with previous reports [4, 10, 11]. However, mutations in MYBPC3 and other sarcomere genes were not detected in this cohort.
Variants in TTN
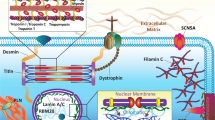
The TTN gene encodes the sarcomere protein titin, the third most abundant striated-muscle protein after myosin and actin. Two titin molecules with opposite polarity span each sarcomere, the contractile unit in the myocardium. Thereafter, normal expression of TTN is essential for sarcomere assembly and function as a contractile unit. Titin is a large human protein, composed of approximately 34,000 amino acids at full length. There are different isoforms of titin depending on alternative splicing, of which, N2BA and N2B isoforms are dominantly expressed in the adult myocardium. The N2BA isoform, which is longer and more compliant than N2B, is abundant in foetal and neonatal heart. During development, a smaller and stiffer N2B isoform is predominantly expressed. Hence, the ratio of titin isoforms plays a key role in regulating cardiac diastolic function [12].
TTN heterozygous mutations are reported to be major genetic causes of DCM [13, 14]. Herman and his team revealed that TTN truncating variants (TTNtv) are a common cause of DCM, with a reported incidence rate of approximately 25% and 18% in familial idiopathic DCM and sporadic cases, respectively [10]. Nevertheless, not all TTNtv genes are pathogenic. It has been reported that TTNtv occurs in ~ 2% of the general population [15]. DCM-associated mutations are usually enriched in the titin A-band, which is close to the carboxy-terminus of the protein and highly conserved across most isoforms (Additional file 5: Figure S3). In other words, the clinical significance of TTNtv is mainly predicted by exon usage and variant location. In addition, in vitro analysis demonstrated that the mutant truncated titin protein in iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes resulted in sarcomere insufficiency and impaired cell signalling activation, which might be the underlying mechanism of DCM-associated TTNtv [16]. However, the exact mechanisms by which TTNtv leads to DCM remain unknown.
In our study, TTN truncating variants were detected in 7 of the 24 tested patients; these included four frameshift deletions and three nonsense mutations. Except for Arg26949* (rs748689777), six variants are reported for the first time. The Arg26949* variant has been reported previously in both DCM and peripartum cardiomyopathy [10, 17]. It’s located in the A-band region of titin, where most DCM-related TTN truncating mutations are clustered. Among the six novel mutations, four clustered in the A-band, and the other two variants were located in exon 195 of the I-band region. Except for in silico functional prediction, no functional analysis of these variants was available. According to the pathogenicity prediction model by Roberts et al. TTNtv affecting highly-expressed exons have a predicted 93% probability of pathogenicity in DCM patients [15]. Another study of several large DCM cohorts confirmed this prediction model for the pathogenicity of TTNtv in DCM patients [18]. Exon 195 was highly expressed in the I-band. Therefore, together with the in silico analysis, we assumed that all seven TTNtv genes were likely pathogenic.
It is noteworthy that there is an observed association between TTNtv location and patient phenotype in a small cohort. Patients with a carboxy-terminal TTNtv, which truncates principal isoforms, are likely to present with severely impaired left ventricular function and life-threatening ventricular arrythmias [15, 19]. However, in a larger prospective study that included 83 DCM patients carrying TTNtv [20], no significant relationship between TTNtv location and severity of the phenotype was observed. Furthermore, except for an earlier onset age, a higher proportion of positive family DCM history, a higher occurrence of ventricular tachycardia, and fewer conduction diseases for patients with TTNtv, significant differences were not observed in clinical features or the medium-term cardiac outcome including cardiovascular death, arrhythmic events, and heart failure between patients with and without TTNtv.
In this study, all seven TTNtv carriers presented with clinical symptoms of heart failure after 30 years of age, with mean onset age of 42 years around. The mean LVEF was 26.6 ± 6.8% and the mean LVEDD was 68.4 ± 2.7 mm. Out of seven TTNtv carriers, six had class III or IV heart failure function. No extracardiac features or ventricular arrhythmias were detected. With regard to arrhythmias, one patient had atrial fibrillation and another had complete right bundle branch block at enrolment. As the most frequent variants detected in this small cohort, there were no significant differences between TTNtv carriers and those without TTNtv regarding onset age, LVEF and LVEDD (see Additional file 6: Table S3). However, all TTNtv carriers were males and none of them had ventricular tachycardia with or without ICD implanted, which were inconsistent with previous reports [10, 20]. As a small cohort, the association between genetic variants and clinical features should not be overinterpreted. The patient with the Gln16316* mutation had two daughters; the older daughter carrying the same TTNtv mutation was 8 years old and no cardiac abnormality was detected. Hence, the penetrance of all detected TTNtv was 87.5%, which was lower than the 95% penetrance reported in previous reports [10, 15]. This might be due to a younger age at genetic screening in this study, four of whom completed the genetic test before the age of 40.
TNNT2 mutation
Since the first DCM pedigree with TNNT2 mutation reported in 2000, the role of troponin complex mutations in the pathogenesis of inherited DCM has been extensively explored. The overall frequency of troponin complex mutations in familial DCM was reported to be 6% in one large genetic study of idiopathic DCM [21]. TNNT2 encodes troponin T, a subunit of the troponin complex, which plays an important role in generating cardiac contractility. The pathogenic mutation K217del (also known as p.K210del) in this study resulted in deletion of one lysine in the troponin T protein, leading to significant protein function abnormality. It has previously been reported in different familial DCM pedigrees [21,22,23,24]. The mutation results in a lysine deletion localised in exon 13, a conserved and functionally important domain involved in interaction with other troponin subunits or tropomyosin [21]. Functional analysis has demonstrated that the mutant proteins reduce the Ca2+ sensitivity of cardiac muscle contraction, resulting in force generation deficiency by sarcomere [25]. Furthermore, introduction of the TNNT2 K217del mutation in mouse led to induction of a DCM phenotype with reduced survival [26].
In most pedigrees, the mutant allele co-segregated well with the DCM phenotype and was believed to be a recurrent mutation observed in DCM patients across different races [21, 22, 27]. Although most K217del carriers presented with early onset (usually before age 30) and aggressive DCM or even a sudden death, a milder presentation occurred in a few patients who stayed alive until their 60 s and 70 s [22, 23]. In our study, the patient who had the K217 deletion in TNNT2 presented with acute heart failure at 14 years of age, and it deteriorated rapidly after onset of cardiac shock. Over a month of advanced medical support including IABP and ventilation, he did not survive in the end. We collected his parents’ and uncle’s blood sample for genetic testing, which revealed that both the mother and uncle were carriers for the same mutation as in the proband. Further clinical evaluation was performed for both mutation carriers, but no cardiac abnormalities were detected. Hence, the genotype–phenotype relationship in inherited DCM is complicated, even in troponin T cardiomyopathy, which is usually expressed as an aggressive and early onset disease, accompanied by considerable mortality.
RBM20 variant
RBM20 encodes an RNA binding motif protein 20, a member of the SR protein family (serine/arginine-rich protein), which is highly expressed in the heart and regulates alternative RNA splicing by processing pre-messenger RNA (Additional file 7: Figure S4). In fact, RBM20 regulates splicing of a set of genes, including TTN, and these target proteins are necessary for normal cardiac structure and signal transduction [12]. According to published large cohort studies, RBM20 mutations account for approximately 3% of all DCM cases [28, 29].
Brauch et al. first reported five unique RBM20 mutations co-segregating with DCM across eight pedigrees. They found all five mutations clustered within exon 9, encoding an RS-rich domain (a major domain of RS protein, rich in arginine–serine repeats). The altered amino acid residues (residues 634, 636, 637, and 638) were highly conserved across different species and were demonstrated to be a mutation hotspot [28]. In addition, Filippello and his colleagues revealed that the amino acids 491–658 contributed to RBM20 nuclear localisation and normal function of alternative splicing [30]. An in vivo functional analysis with a missense mutation S635A in RBM20 revealed that the mutant RBM20 changed the titin isoform expression, leading to the production of an abnormal higher-molecular-weight titin isoform, thereby promoting cardiac diastolic function and fibrosis [31]. In our study, the P638S mutation was identified in one patient who presented with heart failure at the age of 17 years. Both parents were screened negative for this variant, indicating a de novo mutation. The altered residue occurred in the mutation hotspot for RBM20. Although this amino acid change is first reported herein, missense mutations at the same residue, such as P638L, has been reported previously [28]. As functional analysis has demonstrated the loss of function of mutant P638L [31], combined with ACMG criteria, P638S is assumed to be likely-pathogenic.
DCM patients carrying pathogenic RBM20 mutations were reported to have an early onset of disease compared to those without a definite genetic cause [28]. In addition, male carriers tended to have an aggressive disease progression, and one-third of the affected cases died suddenly or experienced episodes of ventricular tachycardia [32]. However, over 30% of mutation carriers were asymptomatic upon genetic screening, and most of them were younger than their affected probands, suggesting an age-dependent penetrance of RBM20 mutations. In this study, the patient with the P638S mutant presented with heart failure at his teenage years, which was consistent with previous reports [28, 32]. During the index hospitalisation, no ventricular arrhythmia was observed.
FLNC mutation
FLNC encodes protein filamin C, which cross-links actin filaments and constitutes a widespread network in both cardiac and skeletal muscle cells (Additional file 8: Figure S5). In cardiac myocytes, filamin C protein is highly expressed and participates in mechanical and signal transduction between sarcomeres and plasmatic membranes [33]. FLNC mutations were first recognised as genetic defects causing skeletal myofibrillar myopathy. As ~ 30% of affected myofibrillar myopathy patients carrying FLNC mutations presented with both skeletal myopathies and unspecified forms of cardiomyopathy [34], screening for FLNC mutations has been included in the genetic diagnosis of inherited cardiomyopathies since 2012. Ortiz-Genga et al. screened 2877 patients diagnosed with different inherited cardiovascular diseases for FLNC mutations and identified 23 truncating mutations in 28 probands [35]. Of these, 20 cases were diagnosed with DCM, and seven were arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathies. The prevalence of FLNC mutations in DCM patients was 3.9%. None of these patients expressed skeletal myopathies. However, a specific phenotype of a combination of significant left ventricle systolic dysfunction, myocardial fibrosis predominantly affecting the left wall, and a high burden of ventricular arrhythmias (approximately 82%) was observed in most affected patients carrying FLNC truncating mutations. Such clinical features observed in FLNC truncating mutations were confirmed in another genetic study of 319 DCM families, which identified 13 FLNC truncation carriers, with 85% having either ventricular arrhythmias or sudden cardiac death [36]. In addition, a histological study detected cardiac interstitial fibrosis in the right ventricle and fibrofatty infiltration in the left ventricle, which mimicked arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy to some extent. Except for DCM, some FLNC mutations were also related to hypertrophic and restrictive cardiomyopathies [37, 38]. However, consistent with the case of myofibrillar myopathy, variants leading to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) or restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) were mostly missense mutations. Immunohistochemical staining of myocardial tissue from patients carrying FLNC truncations revealed no abnormal cytoplasmic filamin C aggregates, which was previously described in myofibrillar myopathy as well as in HCM and RCM patients, but showed decreased levels of normal filamin C [35,36,37,38,39]. Hence, a haploinsufficiency hypothesis for the underlying mechanism of FLNC truncating mutations was proposed.
The FLNC mutation detected in this study was a novel truncating variant. The patient who carried this K895Rfs mutation was a female, presenting with ventricular tachycardia and aborted ventricular fibrillation at the age of 26 years. An ICD was implanted for secondary prevention during index hospitalisation. No skeletal myopathy was detected, which was consistent with other previously reported FLNC truncating mutation carriers.
The overall prevalence of putatively pathogenic/likely-pathogenic mutations in this sporadic DCM cohort was 10 out of 24, indicating a higher proportion of genetic causes in idiopathic DCM even without a definite family history. Of course, this prevalence is overestimated due to lack of robust evidence to confirm the causative relationship between detected variants and DCM phenotype. Accidently, three relatives of the index patients were mutation carriers, as detected by genetic screening, suggesting that periodic cardiac evaluation ahead of any incidence of cardiac dysfunction might be useful. To our knowledge, the correlation between conduction or ventricular arrhythmia and LMNA mutations is the only confirmed genotype/phenotype relationship for genetic DCM based on meta-analysis of multiple DCM genetic studies [11]. The heterogeneous clinical presentations in genetic DCM with the same mutant gene might be a result of modifying factors, such as modifier genes and epigenetic factors. Therefore, the effect of genetic testing on clinical feature prediction and therapeutic guidance is limited. In specific genotypes, such as FLNC mutations, an ICD for primary prevention should be considered earlier.
This study has several limitations. First, it is based on a small cohort; hence, the result should not be over-interpreted. In addition, data are limited for analysis of genotype–phenotype correlation or clinical features for a specific genotype. Second, except for in silico analysis, our study does not yet provide robust evidence to confirm the causation between genetic variants and DCM phenotypes. Furthermore, we have not performed variants detection in healthy Chinese individuals as control. Hence, for previously reported variants we listed the allele frequency by referring to the public online database, such as the ExAC and the dbSNP database (see details in Table 2) and used the information as control. However, in order to save the cost of the study, the newly identified variants have no such background population variation for control.
Conclusions
In conclusion, in a small Chinese cohort of sporadic idiopathic DCM, we identified a high proportion of inherited DCM, with frequently detected sarcomere mutations, especially mutations in the titin gene. Therefore, given patients’ willingness, genetic screening should be considered in young patients with idiopathic DCM, even without a positive family history.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its Additional files.
Abbreviations
- ACMG:
-
American college of medical genetics and genomics
- AHA:
-
American Heart Association
- DCM:
-
Dilated cardiomyopathy
- ESC:
-
The European Society of Cardiology
- ExAC:
-
Exome aggregation consortium database
- HCM:
-
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- ICD:
-
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
- LP:
-
Likely pathogenic
- MAF:
-
Minor allele frequency
- NGS:
-
Next generation sequencing
- P:
-
Pathogenic
- RCM:
-
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
- TTNtv:
-
TTN Truncating variants
- VUS:
-
Uncertain significance variants
References
Cardiology, CSo, Group CMaCC. Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy. J Clin Cardiol. 2018, 034:421–434.
van Spaendonck-Zwarts KY, van Rijsingen IA, van den Berg MP, Lekanne Deprez RH, Post JG, van Mil AM, Asselbergs FW, Christiaans I, van Langen IM, Wilde AA, et al. Genetic analysis in 418 index patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy: overview of 10 years’ experience. Eur J Heart Fail. 2013;15:628–36.
Pinto YM, Elliott PM, Arbustini E, Adler Y, Anastasakis A, Bohm M, Duboc D, Gimeno J, de Groote P, Imazio M, et al. Proposal for a revised definition of dilated cardiomyopathy, hypokinetic non-dilated cardiomyopathy, and its implications for clinical practice: a position statement of the ESC working group on myocardial and pericardial diseases. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:1850–8.
McNally EM, Golbus JR, Puckelwartz MJ. Genetic mutations and mechanisms in dilated cardiomyopathy. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:19–26.
Horvat C, Johnson R, Lam L, Munro J, Mazzarotto F, Roberts AM, Herman DS, Parfenov M, Haghighi A, McDonough B, et al. A gene-centric strategy for identifying disease-causing rare variants in dilated cardiomyopathy. Genet Med. 2019;21:133–43.
Bozkurt B, Colvin M, Cook J, Cooper LT, Deswal A, Fonarow GC, Francis GS, Lenihan D, Lewis EF, McNamara DM, et al. Current diagnostic and treatment strategies for specific dilated cardiomyopathies: a scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation. 2016;134:e579–646.
Ware JS, Amor-Salamanca A, Tayal U, Govind R, Serrano I, Salazar-Mendiguchia J, Garcia-Pinilla JM, Pascual-Figal DA, Nunez J, Guzzo-Merello G, et al. Genetic etiology for alcohol-induced cardiac toxicity. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:2293–302.
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R. Genome project data processing S: the sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:2078–9.
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405–24.
Herman DS, Lam L, Taylor MR, Wang L, Teekakirikul P, Christodoulou D, Conner L, DePalma SR, McDonough B, Sparks E, et al. Truncations of titin causing dilated cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:619–28.
Kayvanpour E, Sedaghat-Hamedani F, Amr A, Lai A, Haas J, Holzer DB, Frese KS, Keller A, Jensen K, Katus HA, Meder B. Genotype-phenotype associations in dilated cardiomyopathy: meta-analysis on more than 8000 individuals. Clin Res Cardiol. 2017;106:127–39.
Ma J, Lu L, Guo W, Ren J, Yang J. Emerging role for RBM20 and its splicing substrates in cardiac function and heart failure. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22:4744–51.
Gerull B, Gramlich M, Atherton J, McNabb M, Trombitas K, Sasse-Klaassen S, Seidman JG, Seidman C, Granzier H, Labeit S, et al. Mutations of TTN, encoding the giant muscle filament titin, cause familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Nat Genet. 2002;30:201–4.
Lu C, Wu W, Liu F, Yang K, Li J, Liu Y, Wang R, Si N, Gao P, Liu Y, et al. Molecular analysis of inherited cardiomyopathy using next generation semiconductor sequencing technologies. J Transl Med. 2018;16:241.
Roberts AM, Ware JS, Herman DS, Schafer S, Baksi J, Bick AG, Buchan RJ, Walsh R, John S, Wilkinson S, et al. Integrated allelic, transcriptional, and phenomic dissection of the cardiac effects of titin truncations in health and disease. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7:270ra276.
Hinson JT, Chopra A, Nafissi N, Polacheck WJ, Benson CC, Swist S, Gorham J, Yang L, Schafer S, Sheng CC, et al. Heart disease. Titin mutations in iPS cells define sarcomere insufficiency as a cause of dilated cardiomyopathy. Science. 2015;349:982–6.
Ware JS, Li J, Mazaika E, Yasso CM, DeSouza T, Cappola TP, Tsai EJ, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Kamiya CA, Mazzarotto F, et al. Shared genetic predisposition in peripartum and dilated cardiomyopathies. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:233–41.
Mazzarotto F, Tayal U, Buchan RJ, Midwinter W, Wilk A, Whiffin N, Govind R, Mazaika E, de Marvao A, Dawes TJW, et al. Reevaluating the genetic contribution of monogenic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 2020;141:387–98.
Tharp CA, Haywood ME, Sbaizero O, Taylor MRG, Mestroni L. The giant protein titin’s role in cardiomyopathy: genetic, transcriptional, and post-translational modifications of TTN and their contribution to cardiac disease. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1436.
Tayal U, Newsome S, Buchan R, Whiffin N, Halliday B, Lota A, Roberts A, Baksi AJ, Voges I, Midwinter W, et al. Phenotype and clinical outcomes of titin cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:2264–74.
Mogensen J, Murphy RT, Shaw T, Bahl A, Redwood C, Watkins H, Burke M, Elliott PM, McKenna WJ. Severe disease expression of cardiac troponin C and T mutations in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:2033–40.
Hanson EL, Jakobs PM, Keegan H, Coates K, Bousman S, Dienel NH, Litt M, Hershberger RE. Cardiac troponin T lysine 210 deletion in a family with dilated cardiomyopathy. J Card Fail. 2002;8:28–32.
Hershberger RE, Pinto JR, Parks SB, Kushner JD, Li D, Ludwigsen S, Cowan J, Morales A, Parvatiyar MS, Potter JD. Clinical and functional characterization of TNNT2 mutations identified in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2009;2:306–13.
Kamisago M, Sharma SD, DePalma SR, Solomon S, Sharma P, McDonough B, Smoot L, Mullen MP, Woolf PK, Wigle ED, et al. Mutations in sarcomere protein genes as a cause of dilated cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1688–96.
Morimoto S, Lu QW, Harada K, Takahashi-Yanaga F, Minakami R, Ohta M, Sasaguri T, Ohtsuki I. Ca(2+)-desensitizing effect of a deletion mutation Delta K210 in cardiac troponin T that causes familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:913–8.
Du CK, Morimoto S, Nishii K, Minakami R, Ohta M, Tadano N, Lu QW, Wang YY, Zhan DY, Mochizuki M, et al. Knock-in mouse model of dilated cardiomyopathy caused by troponin mutation. Circ Res. 2007;101:185–94.
Otten E, Deprez LDRH, Weiss MM, van Slegtenhorst M, Joosten M, van der Smagt JJ, de Jonge N, Kerstjens-Frederikse WS, Roofthooft MT, Balk AH, et al. Recurrent and founder mutations in the Netherlands: mutation p.K217del in troponin T2, causing dilated cardiomyopathy. Neth Heart J. 2010;18:478–85.
Brauch KM, Karst ML, Herron KJ, de Andrade M, Pellikka PA, Rodeheffer RJ, Michels VV, Olson TM. Mutations in ribonucleic acid binding protein gene cause familial dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:930–41.
Refaat MM, Lubitz SA, Makino S, Islam Z, Frangiskakis JM, Mehdi H, Gutmann R, Zhang ML, Bloom HL, MacRae CA, et al. Genetic variation in the alternative splicing regulator RBM20 is associated with dilated cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm. 2012;9:390–6.
Filippello A, Lorenzi P, Bergamo E, Romanelli MG. Identification of nuclear retention domains in the RBM20 protein. FEBS Lett. 2013;587:2989–95.
Guo W, Schafer S, Greaser ML, Radke MH, Liss M, Govindarajan T, Maatz H, Schulz H, Li S, Parrish AM, et al. RBM20, a gene for hereditary cardiomyopathy, regulates titin splicing. Nat Med. 2012;18:766–73.
Hey TM, Rasmussen TB, Madsen T, Aagaard MM, Harbo M, Molgaard H, Moller JE, Eiskjaer H, Mogensen J. Pathogenic RBM20-variants are associated with a severe disease expression in male patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Heart Fail. 2019;12:e005700.
Stossel TP, Condeelis J, Cooley L, Hartwig JH, Noegel A, Schleicher M, Shapiro SS. Filamins as integrators of cell mechanics and signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:138–45.
Kley RA, Hellenbroich Y, van der Ven PF, Furst DO, Huebner A, Bruchertseifer V, Peters SA, Heyer CM, Kirschner J, Schroder R, et al. Clinical and morphological phenotype of the filamin myopathy: a study of 31 German patients. Brain. 2007;130:3250–64.
Ortiz-Genga MF, Cuenca S, Dal Ferro M, Zorio E, Salgado-Aranda R, Climent V, Padron-Barthe L, Duro-Aguado I, Jimenez-Jaimez J, Hidalgo-Olivares VM, et al. Truncating FLNC mutations are associated with high-risk dilated and arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:2440–51.
Begay RL, Graw SL, Sinagra G, Asimaki A, Rowland TJ, Slavov DB, Gowan K, Jones KL, Brun F, Merlo M, et al. Filamin C truncation mutations are associated with arrhythmogenic dilated cardiomyopathy and changes in the cell-cell adhesion structures. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2018;4:504–14.
Valdes-Mas R, Gutierrez-Fernandez A, Gomez J, Coto E, Astudillo A, Puente DA, Reguero JR, Alvarez V, Moris C, Leon D, et al. Mutations in filamin C cause a new form of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5326.
Brodehl A, Ferrier RA, Hamilton SJ, Greenway SC, Brundler MA, Yu W, Gibson WT, McKinnon ML, McGillivray B, Alvarez N, et al. Mutations in FLNC are associated with familial restrictive cardiomyopathy. Hum Mutat. 2016;37:269–79.
Janin A, N’Guyen K, Habib G, Dauphin C, Chanavat V, Bouvagnet P, Eschalier R, Streichenberger N, Chevalier P, Millat G. Truncating mutations on myofibrillar myopathies causing genes as prevalent molecular explanations on patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Clin Genet. 2017;92:616–23.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the patients and their families for their cooperation.
Funding
Funding was provided by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (No. 2017A030313476); Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital Clinical Research Fund (No. Y012018085); Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Coronary Artery Disease Prevention Fund (No. Z02207016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XH and LL conceived and designed the study. ML, LX, SX, JY and ZW carried out the study. ML, SX and LX interpreted the NGS data and drafted this manuscript. XH and HT revised this manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital ethics committee and met the Tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. All included patients provided informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
List of DCM related genes sequenced in this study.
Additional file 2: Figure S1.
Variants filtration pipeline
Additional file 3: Figure S2.
Variants annotation workflow.
Additional file 4: Table S2.
List of all detected variants of DCM related genes.
Additional file 5: Figure S3.
Structure and domains of TTN.
Additional file 6: Table S3.
Characteristics of DCM patients, according to the presence or absence of TTNtv.
Additional file 7: Figure S4.
Structure and domains of RBM20.
Additional file 8: Figure S5.
Structure and domains of FLNC.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Xia, S., Xu, L. et al. Genetic analysis using targeted next-generation sequencing of sporadic Chinese patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Transl Med 19, 189 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-021-02832-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-021-02832-3