Abstract
Background
Frameshift mutations in LRPAP1 are responsible for autosomal recessive high myopia in human beings but its underlying mechanism remains elusive. This study aims to investigate the effect of LRPAP1 defect on ocular refractive development and its involved mechanism.
Methods
A lrpap1 mutant zebrafish line with homozygous frameshift mutation was generated by CRISPR/Cas9 technology and confirmed by Sanger sequencing. The ocular refractive phenotype was analyzed by calculating the relative refractive error (RRE) with vivo photography and histological analysis at different development stages, together with examining ocular structure change via transmission electron microscopy. Further, RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis were performed. The potentially involved signaling pathway as well as the interacted protein were investigated in vivo.
Results
The lrpap1 homozygous mutant zebrafish line showed myopic phenotype. Specifically, the mutant lines showed larger eye axial length-to-body length in one-month old individuals and a myopic shift with an RRE that changed after two months. Collagen fibers became thinning and disordered in the sclera. Further, RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis indicated that apoptosis signaling was activated in mutant line; this was further confirmed by acridine orange and TUNEL staining. Moreover, the expression of TGF-β protein was elevated in the mutant lines. Finally, the treatment of wild-type embryos with a TGF-β agonist aggravated the degree of eyeball apoptosis; conversely, the use of a TGF-β inhibitor mitigated apoptosis in mutant embryos.
Conclusion
The study provides functional evidence of a link between lrpap1 and myopia, suggesting that lrpap1 deficiency could lead to myopia through TGF-β-induced apoptosis signaling.
Video abstract
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Myopia or nearsightedness is characterized by a mismatch between the axial length of the eye and its refractive power, leading to the projection of a defocused image on the retina. This condition is the most common cause of refractive error and has recently emerged as a global health issue [1, 2]; of note, high myopia increases the risk of retinal detachment, glaucoma, cataracts, and myopic macular degeneration [3].
Myopia is influenced by genetic and environmental factors; the contribution of the former has been estimated to be 60%–80% [4]. In fact, molecular genetic studies based on families/populations with high myopia have identified multiple loci and pathogenic genes, including low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-associated protein 1 (LRPAP1) [5,6,7,8,9]. To date, a total of three homozygous frameshift mutations in LRPAP1 have been found in fourteen patients with early-onset high myopia from nine unrelated families: c.863_864delTC (p.Ile288Argfs*118) (n = 10) [7, 8], c.605delT (p.Asn202Thrfs*8) (n = 3) [6], and c.199delC, (p.Q67sfs*8) (n = 1), as reported in our previous study [7]. Altogether, these findings indicate a relationship between frameshift mutations in LRPAP1 and autosomal recessive high myopia. However, the underlying mechanism is still unclear.
LRPAP1 functions as a chaperone of lipoprotein receptor-related proteins [10, 11]. Previous studies have shown that the main functions of LRP1 are to assist the liver in clearing plasma proteins, control the function of adipocytes and the blood–brain barrier, regulate lipid metabolism, and transport the Aβ peptide in Alzheimer’s disease [12] through platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling [13, 14]. TGF-β signaling has also been shown to be involved in myopia, particularly in the remodeling of the sclera extracellular matrix [15,16,17]; the loss of function of LRPAP1 may lead to a decrease in LRP1, which in turn activates TGF-β signaling [9]. However, whether TGF-β was interacted with LRPAP1 in regulation of myopia development remains unknown.
Zebrafish and humans have 70% sequence similarity, as well as a similar development of the visual systems; therefore, zebrafish is an appropriate model for the study of genetic and environmental eye diseases [18, 19]. Here, we analyzed the role of the lrpap1 gene, orthologous to the human LRPAP1 gene by generating a lrpap1 frameshift mutant. The mutant line with lrpap1 deficiency resulted in myopic phenotype. Our mechanistic analysis indicated that apoptosis signaling was activated in lrpap1 mutant zebrafish, in a TGF-β-dependent fashion. Altogether, our results provide new insights into the mechanisms underlying LRPAP1-related myopia.
Materials and methods
Ethics statement
All experiments involving zebrafish were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committees of Southern Medical University and the South China University of Technology.
Zebrafish lines and maintenance
The founder of zebrafish line was purchased from the China Zebrafish Resource Center (CZRC Catalog ID CZ921). A stable lrpap1 homozygous mutant line was obtained via several rounds of crossing and genotyping. Mutalyzer 2.0.34 (https://mutalyzer.nl/) was used to check variant descriptions and predict the affected protein from the variant coding sequence. Protein Homology/analogY Recognition Engine V 2.0 (Phyre2, http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2) was used to predict the protein tertiary structure [20]. All animal procedures were performed according to previously established protocols [21]; embryos were collected and staged as described by Kimmel et al. [22].
Genotyping
The tail fin tissues of zebrafish were extracted, and each zebrafish was kept in isolation until the genotype was determined. Each tail fin was immersed in 30 μL of 50 mM NaOH and incubated at 96 °C for 40 min. After the tissue was completely dissolved, 3 μL of 1 M Tris–HCl (pH 8.0) was added to the solution (Additional file 1). PCR was performed using ApexHF HS DNA Polymerase FS (Accurate Biology, China) and the primers were: lrpap1-Forward: GGATAGCGCTGCAGATGCTC/ lrpap1-Reverse: AACTTGCTTCACGTTAACTGCGAGTA. Single bands from agarose gels were sequenced (Shanghai Shenggong Bioengineering Co. Ltd).
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol (Accurate Biology, AG21101, Hunan, China), reverse-transcribed using random primers and reverse transcriptase (Yeasen, 11121ES60, Shanghai, China). qRT-PCR was performed on a real-time PCR system (CFX96 Connect, Bio-Rad, USA) using the qPCR SYBR Master Mix (Yeasen, 11203ES03, Shanghai, China). The expression levels were determined with the obtained threshold cycle values using the 2−△△Ct method. β-Actin was used as the housekeeping gene in this study. The primer sequences used were as follows: lrpap1-Forward: 5’-GCAACAACCAGGTGGAAT-3’; lrpap1-Reverse: 5’-TCAAGTCACTGTGTAGTTCTG-3’; β-actin-Forward: 5’-TTCTTGGGTATGGAATCTTGCGGTATC-3’; β-actin-Reverse: 5’-CAGTGTTGGCATACAGGTCCTTACG-3’.
Longitudinal measurements of the eye dimensions via in vivo imaging
Zebrafish were anesthetized with 5 mg/L tricaine (Macklin, E808894, Shanghai, China) and imaged using an Olympus stereoscopic fluorescence microscope from the side and back perspectives. Images were uploaded into Image J (version 1.51) to measure values of the following parameters: axial length (from the front of the cornea to the back of the sclera), body length (from the top of the head to the end of the trunk before the caudal fin), and lens diameter (from the anterior to the posterior surface of the lens). The time points analyzed were 7, 14, and 21 days post-fertilization, as well as one and two months post-fertilization. The relative refractive error (RRE) was calculated [23, 24]: 1 − retinal radius/(lens radius × 2.324), where retinal radius = (axial length—lens radius).
RRE measurement through the histology method
Heads were fixed in 10% neutral formalin at room temperature (RT) overnight, then placed in EDTA decalcification solution [25]. Samples were dehydrated and embedded in paraffin (Additional file 2: Table S1) to prepare sections of 4-μm thickness (Leica, RM2245, Germany). Central eye sections where the optic nerve is located (or close to) was selected for hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining (Additional file 3: Table S2). The axial length was measured from the front of the cornea to the back of the retinal pigment epithelium, and the lens diameter was measured from the anterior surface to the posterior surface.
Electron microscopy of the scleral collagen fibers
The eyeballs of three-month-old zebrafish were processed for electron microscopy as previously described [26] and imaged using a transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEM-1400 PLUS, Japan Electron Optics Laboratory). One hundred and twenty collagen fibers were selected from six different locations in each group, and the fiber diameter and cross-sectional area were measured using the ImageJ software.
Western blot analysis
Both eyes of each fish were lysed in RIPA lysis buffer (Beyotime, P0013B, Shanghai, China) containing protease inhibitors. The protein concentration was determined using the BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo, NO.23227, USA), and samples were resolved on SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were blocked in 5% nonfat milk with shaking for 1.5 h at RT, and incubated with primary antibody (1:100 dilution) at 4 °C overnight. After washing the membrane with Tris-buffered saline-Tween (Boster, AR0195, Wuhan, China) three times (10 min each), HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (1:5000, NO. BA1054, Boster, Wuhan, China) was added and incubated for two hours at RT. Finally, proteins were visualized by using an enhanced chemiluminescent detection reagent (Tannon, 180–501, Shanghai, China) and an ECL detection system (Tannon 5200, Shanghai, China). The anti- Lrpap1 primary antibody was prepared in-house via the immunization of rabbits with the peptide SKEMNEKNASDKSNN + Cys. The anti-TGF-beta 1 primary antibody was purchased from SAB (NO.48569, Signalway Antibody, USA).
RNA-seq and bioinformatics analysis
Twelve pairs of samples (eyeballs from three-month-old zebrafish, including six wild-type and six mutant) were collected. After total RNA was extracted, mRNA with a PolyA tail was enriched with oligo(dT). Then, 6G clean bases were generated by sequencing (Illumina HiSeq2500). RNA-seq reads were aligned to the zebrafish genome (Ensembl, GRCz11) using HISAT2 [27], and TPM was used to further normalize the gene expression counts [28]. Differentially expressed genes were determined using DESeq2, based on the negative binomial generalized linear model using the following cut-off values: |log2 (fold change)|> 1 and adjusted p value < 0.05.
Treatment with the TGF-β agonist or inhibitor
At 20 hpf, wild-type embryos were treated with hydrochloride (10 μM TGF-β agonist, HY-100347A, MedChemExpress, USA), whereas lrpap1 mutant embryos were treated with oxymatrine (10 μM TGF-β inhibitor, HY-NO158, MedChemExpress, USA). Fresh agonist or inhibitor solution was added once per day.
Detection of cell apoptosis
Embryos were immersed in 2 μg/mL acridine orange (AO) in E3 medium for 40 min and then rinsed four times with E3 medium. After incubation with 140 mg/L tricaine for three minutes to obtain an effective anesthesia, embryos were observed and imaged using Olympus (SZ61, Olympus, Japan) and Zeiss (SteREO Discovery, V20, Carl Zeiss AG, Germany) microscopes.
For Tdt-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) immunostaining, the One Step TUNEL Apoptosis Assay Kit (Beyotime Biotechnology, Shanghai, China) was used following the manufacturer’s instructions. After treatment with the fluorescent labeling solution, the cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (Solarbio, Beijing, China) for 10 min. All samples were imaged using an inverted fluorescence microscope (model no. TI2-E, Nikon, Japan).
Statistical analysis
All data were processed, calculated, and graphed using GraphPad Prism 8. Statistical significance was determined using the Student’s t-test, Linear regression analysis or the one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction (more than two groups). The significance levels are defined as follows: ns, p > 0.05; *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001; ****p ≤ 0.0001.
Results
Characterization of the zebrafish lrpap1 homozygous mutant line
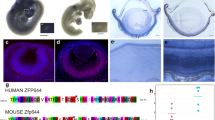
In situ hybridization showed that lrpap1 is widely expressed in wild-type embryos, 72 hpf, mainly in the kidneys and head, including in the eyeball (Fig. 1A). lrpap1 frameshift mutations were introduced by CRISPR-Cas9 technology. The CRISPR target and PAM site were in exon1 (Fig. 1B); a 5-base deletion and a 4-base insertion mutation were confirmed by Sanger sequencing (Fig. 1C, D), described as c.264_268delinsTCTC and predicted to result in an abnormal protein (p.Lys35Asnfs*3). Of note, results of qRT-PCR analysis (Fig. 1E) reveal that lrpap1 mRNA expression was slightly decreased in the lrpap1 mutant lines, although this was not statistically significant (p = 0.631). Phyre2 model with the highest confidence is shown in Fig. 1F. For wild-type zebrafish, 276 residues (83% of the sequence) were modeled with 97.4% confidence and for the mutant, 12 residues (33% of the sequence) were modeled with 93.5% confidence. Importantly, the predicted tertiary structure of the Lrpap1 protein changed greatly in the context of the lrpap1 mutation. Western blot analysis revealed that the Lrpap1 protein levels were markedly lower in lrpap1 mutant zebrafish than in the wild-type, both two- and three-months post-fertilization (Fig. 1G), with the relative quantitation result shown in Fig. 1H (p < 0.0001).
Generation of lrpap1 knockout zebrafish. A Representative image of a zebrafish embryo (72 hpf) subjected to whole-mount in situ hybridization targeting lrpap1. B The gRNA target and its corresponding position in the lrpap1 gene sequence are shown. C Agarose gel electrophoresis of the lrpap1 DNA amplified fragments. D DNA sequencing results of wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous zebrafish; the 5 bp deletion/4 bp insertion mutation (c.262_266delinsTCTC) is highlighted by the black arrows. The mutation was predicted to cause a frameshift with premature translation termination, resulting in an abnormal protein (p.Lys35Asnfs*3). E lrpap1 mRNA expression was slightly decreased in the lrpap mutant lines, although this was not statistically significant (p = 0.631). F The protein structure of wild-type and mutant Lrpap1, as predicted by Phyre2. Image colored using the rainbow colors, from the N to C terminus. G Western blot analysis of the levels of Lrpap1 in the eyes of lrpap1 mutant and wild-type zebrafish two months and three months post-fertilization. H Relative quantitative result of Lrpap1 protein revealed that the Lrpap1 protein levels were markedly lower in mutant zebrafish than in the wild-type. n = 10 for wild-type zebrafish and n = 10 for mutants. Statistical significance was determined using the Student’s t-test. ****p < 0.0001. β-Actin was used as the internal control. WT, wild-type; MU, lrpap1 homozygous mutant. hpf, hours post-fertilization; 2 m, two months; 3 m, three months
Lrpap1 deficiency leads to progressive myopia
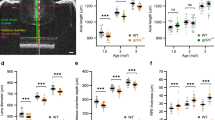
Adult zebrafish homozygous mutant line and wild type were shown under in vivo photography, and the heterozygous phenotype has not been investigated in this study (Fig. 2A). To be more specific, different ocular parameters were measured and calculated during the ocular development (Fig. 2B). The eye axis/body length ratio of mutant lines were significantly higher than that of their wild-type counterparts at both one and two months post-fertilization (Fig. 2C), indicating a mismatched development of the eye axis and trunk in mutant lines. Moreover, the eye axis length of lrpap1 mutant zebrafish was significantly shorter than that of wild-type zebrafish at one month post-fertilization (Fig. 2D), and the body length was significantly shorter in mutant than in wild-type zebrafish at both one and two months post-fertilization (Fig. 2E). In addition, RRE significantly differed between mutant and wild-type zebrafish at two months post-fertilization (− 0.159 ± 0.083 and 0.003 ± 0.049, respectively; Fig. 2F), demonstrating myopic shift was occurred in mutant line. Importantly, consistent with previous study [24], we found a strong linear correlation between the axis of the eye and body length (R2 = 0.974, p < 0.0001; R2 = 0.975, p < 0.0001, respectively, Fig. 2G), as well as between the retinal diameter and lens diameter (R2 = 0.973, p < 0.0001; R2 = 0.907, p < 0.0001, respectively, Fig. 1H).
Longitudinal measurements of the eye dimensions using in vivo imaging. A Eye globes of wild-type and lrpap1 mutant zebrafish at three months. The scale bars refer to 500 μm. B The different ocular parameters measured and the method of calculation of the relative refractive error (RRE) used. C The eye axis to body length ratio was determined at different time points. The eye axis length (D) and body length (E) of one- and two-month-old wild-type and mutant zebrafish were also determined individually. F RRE measurements in one- and two-month-old mutant and wild-type zebrafish. G Correlation analysis of the eye axis length and body length measurements. H Correlation analysis of the retinal radius and lens radius measurements. WT, wild-type. MU, lrpap1 homozygous mutant. Statistical significance was determined using the Student’s t-test: n.s. = no significance; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. For wild-type zebrafish, n = 16, 13, 12, 36, and 12 eyes one week, two weeks, three weeks, one month, and two months post-fertilization, respectively. For the lrpap1 mutant line, n = 12, 10, 13, 24, and 14 eyes one week, two weeks, three weeks, one month, and two months post-fertilization, respectively
We next analyzed the anatomical structure of the zebrafish eyeball using HE staining and TEM. The RRE was calculated based on the anatomical structure (Fig. 3A). The significant RRE difference between mutant and wild-type line were detected from two months post-fertilization, as gradually proceeding toward myopic direction at two and three-months post-fertilization (Fig. 3B), suggesting a progressive myopia development. In line with these results, TEM showed that collagen fibers of sclera were thinner and more disordered in mutant than in wild-type lines (Fig. 3C–E).
Histological analysis via hematoxylin–eosin (HE) staining and ultrastructural analysis using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). A The method used to calculate the relative refractive error (RRE). Refractive error = 1-retinal radius/ (lens radius × 2.324). B RRE quantitative data. N = 8 and 14 eyes for 1-month-old wild-type and mutant zebrafish, respectively; n = 18 and 17 eyes for 2-month-old wild-type and mutant zebrafish, respectively; n = 10 and 21 eyes for 3-month-old wild-type and mutant zebrafish, respectively. C Electron micrographs of 3-month old zebrafish from the two groups. The yellow triangle points to disordered collagen fibers. The scale bars refer to 2 μm. D Schematic diagram of collagen fiber diameter measurement. E Quantification of the diameter of the collagen fibers; 120 fibers per group were analyzed. WT, wild-type. MU, lrpap1 homozygous mutant. Statistical significance was determined using the Student’s t-test: n.s. = no significance; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001
Bioinformatics analysis based on RNA sequencing reveals apoptosis and necroptosis in lrpap1 mutant line
To identify differentially expressed genes in the lrpap1 mutants, RNA sequencing was performed on three month-old zebrafish. Based on correlation analysis of 12 samples, expectedly, samples from the same genotype showed a high correlation (Fig. 4A) and this validates our dataset overall. In the heat map (Fig. 4B), each matrix entry represents a gene expression value. Of note, the volcano map (Fig. 4C) shows detection of 1661 differentially expressed genes between lrpap1 mutant and wild-type zebrafish samples, using the criteria p-value < 0.05 and |Log (fold change)|> 1, of which 1209 genes were upregulated and 452 were downregulated. Among them, 22 differentially expressed genes were associated with apoptosis factors, including 20 up-regulated genes and 2 down-regulated genes. We conducted gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) to examine if the genes in apoptotic signaling pathway were upregulated in the lrpap1 gene mutant. The results revealed that all the 165 genes in the differential expressed gene set related to apoptosis were enriched at the top of the list; the gene set was upregulated, with an NES score of 1.642 and a p value of 0.010 (Fig. 4D, Additional file 4: Table S3). Gene ontology (GO) (Fig. 4E) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis (Fig. 4F) were performed. In GO, molecular functions involved in the apoptotic signaling pathway and apoptotic process included endopeptidase activity, and cysteine-type endopeptidase activity (Additional file 5: Table S4). In line with these results, KEGG analysis revealed that many differentially expressed genes were closely related to apoptosis and necroptosis (Additional file 6: Table S5). Detailed results of differential gene expression analysis and the genes of interest are shown in Additional file 5: Tables S4 and Additional file 6: S5, respectively.
Results of RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis. A Correlation matrix. The darker the blue, the higher the correlation coefficient. B Heat map showing differentially expressed genes in the eyes of lrpap1 mutant versus wild-type zebrafish. The log10 (TPM expression levels + 1) value is color-coded. C Volcano plot analysis of differentially expressed genes in lrpap1-deficient versus wild-type animals at three months post-fertilization. The abscissa represents the change in gene expression multiple in different samples, and the ordinate represents the statistical significance of the change of gene expression. The orange dots represent 91 genes significantly up-regulated in the mutant group, and the green dots represent 247 down-regulated genes. The purple circles show 22 genes associated with apoptosis factors. D GSEA analysis in the context of apoptosis pathway gene sets (NES = 1.642, p value = 0.010). E, F GO and KEGG analysis of the differentially expressed (|log2(Fold Change)|> 1 and Q value < 0.05). Apoptotic-related pathways are highlighted with red boxes. WT, wild-type. MU, lrpap1 homozygous mutant
Deleting lrpap1 triggers apoptosis in the eyes of zebrafish
AO in vivo staining of embryos 24 hpf revealed many dense yellowish-green fluorescent bodies in the eyes of lrpap1 mutant zebrafish (Fig. 5A), indicating a higher degree of apoptosis than in the eyes of control animals. The same phenomenon was also observed in adult fish, at three months post-fertilization, as revealed by TUNEL staining (Fig. 5B, red dots). Of note, apoptosis occurred mainly in choroid tissues; a small amount was also detected in the sclera and iris tissues.
Knockout of lrpap1 in zebrafish leads to increased apoptosis in the eye. (A) AO was used to quantify apoptosis in the eyes of 24 hpf embryos: green fluorescence, as highlighted using white triangles. (B) TUNEL staining was also used to investigate ocular apoptosis in adult zebrafish. Apoptosis is highlighted by yellow triangles, particularly in the choroidal tissue (magnified image). The green circles highlight apoptotic cells in the sclera. The scale bars refer to 200 μm. WT, wild-type. MU, lrpap1 homozygous mutant. dpf, days post-fertilization
lrpap1 deficiency is associated with the upregulation of TGF-β
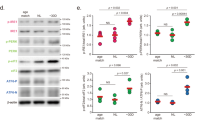
Immunoblot analysis showed that TGF-β was upregulated both at two and three months post-fertilization in mutant compared with wild-type zebrafish (Fig. 6A). Specifically, the relative quantitation result of TGF-β protein was shown in Fig. 6B (p < 0.05).
Lrpap1 deficiency is associated with the up-regulation of TGF-β. (A) Western blot analysis of TGF-β in the eyes of lrpap1 mutants and wild-type zebrafish two months and three months post-fertilization. (B) Relative quantitative result of TGF-β protein. n = 8 for wild-type zebrafish and n = 8 for mutants. Statistical significance was determined using the Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05. β-Actin was used as the internal control. WT, wild-type; MU, lrpap1 homozygous mutant; 2 m, two months; 3 m, three months
TGF-β promotes apoptosis in the eye during development
Finally, we treated wild-type and knockout zebrafish with TGF-β agonist and TGF-β antagonist, respectively, and analyzed apoptotic cells in the eyes at 3 and 5 dpf. A statistically significant increase in the number of apoptotic cells was observed in wild-type zebrafish treated with the TGF-β agonists (Fig. 7A; B), whereas there was a significant decrease in the number of apoptotic cells in wild-type and mutant zebrafish treated with the TGF-β inhibitor. We found almost no apoptotic cells in the eyes of normal wild-type embryos or embryos treated with antagonist 5 dpf; however, a few apoptotic cells existed in their counterparts treated with the agonist. After the appearance of the lrpap1 homozygous mutant phenotype, apoptosis persisted in the eyes of zebrafish at 3 and 5 dpf, and even the use of the TGF-β antagonist did not completely eliminate the occurrence of apoptosis. Additionally, at 5 dpf (Fig. 4C), the eyeball area of the agonist-treated group was larger than that of all other groups.
TGF-β promotes apoptosis in the eyes of zebrafish embryos during development. A As shown by the white triangles and yellow arrows, the bright green fluorescence from AO staining indicates the apoptosis in eyeballs in each group at 3 dpf and 5 dpf, respectively. The bright-field picture shows the side view of each group of embryos in which the eyeball is magnified in equal proportion. The scale bars refer to 200 μm. B Number of apoptotic cells at 3 dpf per eye from AO staining (n = 26, 54, 54, 45, and 39 from left to right). C Lateral area of the eyeball in each group (n = 11, 20, 21, 20, and 16 from left to right). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. β-Actin was used as the internal control. WT, wild-type. MU, lrpap1 homozygous mutant. dpf, days post-fertilization. 2 m, two months. 3 m, three months
Discussion
To investigate the role of LRPAP1 in myopia development, a zebrafish model with a homozygous frameshift mutation of lrpap1 (c.264_268delinsTCTC, p.Lys35Asnfs*3) was generated. A myopic phenotype was characterized in lrpap1 homozygous mutant line. Furthermore, RNA sequencing analysis and functional studies established a relationship among lrpap1, TGF-β, and apoptosis in the context of the development of the eyes.
Indeed, our results showed that the deficiency of the lrpap1 gene in zebrafish resulted in a myopia phenotype with a higher eye axial length-to-body length ratio, a myopic shift with RRE changes, and thinner scleral collagen fibers. In fact, null mutations of LRPAP1 play an active role in the myopization process [5,6,7,8,9]. However, thus far, no functional studies have been performed. Interestingly, we found that after lrpap1 deficiency, zebrafish developed more slowly than their wild-type siblings, as suggested by the fact that the eye axis length of lrpap1 mutants was shorter than that of wild-type fish. Of note, after adjusting for the trunk length parameters, lrpap1 mutant line had a larger eye axis length-to-body length ratio, with correlation coefficients close to 1. Therefore, our results, in line with those of previous studies [23, 24], suggest that this ratio is a good index to evaluate the myopia phenotype of zebrafish. In addition, because of the weak refractive power of the cornea in water, the matching degree of the lens size and retinal diameter can be used to evaluate the refractive state [23, 24, 29, 30]. We showed that the diameter of the retina in mutant fish does not match that of the lens; thus, the relatively longer axis of vision causes the image to fall in front of the retina, causing blurred vision. It is worth mentioning that the RRE measured using in vivo imaging and tissue sections was not consistent at one month, which may be owing to a different definition of the retinal radius. The position of the posterior pole of the eye is toward the sclera or choroid, resulting in a larger retinal radius and relative shift in diopter toward myopia. By demonstrating that homozygous mutant of lrpap1 results in a myopic phenotype in zebrafish, we have created a model with which future studies can explore the mechanism of interaction between genes and environmental factors that causes myopia.
It is intriguing to consider that the loss of lrpap1 function is associated with the upregulation of TGF-β expression, previously reported as an important molecular change in the process of myopia [16, 31,32,33]. LRPAP1 has a specific functional domain that binds to the ligand-binding site of LRP1, thereby protecting the LRP1 protein from degradation during folding, maturation, and transportation in cells [34, 35]. Interestingly, a decrease in LRP1 can over-activate the release of TGF-β from extracellular matrix (ECM) sources [36]. In addition, LRP1 regulates the proliferation and migration of human hepatic stellate cells via the modulation of the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and of the TGF-β extracellular levels [37]. Here, we found that lrpap1 deficiency led to the upregulation of TGF-β expression. TGF-β plays a role in regulating the ECM and acts in many diseases, including myopia [38,39,40]. Previous studies have shown that TGF-β is downregulated in the context of scleral tissues with myopia and associated with ECM degradation and fibroblast transformation via the increase in levels of MMP2 or α-SMA [41,42,43]. However, bFGF and TGF-β were reported to jointly regulate ocular development in a chick model; TGF-β may be an inhibitor of bFGF, leading to axial elongation and diopter change [44]. In our embryo study, treatment of wild-type animals with a TGF-β agonist resulted in faster eye development, which manifested as a larger eyeball area. Zebrafish are a good model for studying the effects of drugs on development; therefore, future studies should explore the effects of drugs or factors on eyeball development [45].
An important question is whether the functions and regulatory mechanism of TGF-β in ocular enlargement identified in this study are related to the activation of apoptosis. TGF-β was found to induce apoptosis in mouse mammary epithelial cells; this could be inhibited by transcriptional co-regulators [46]. Similarly, some studies on TGF-β-induced apoptosis in the context of other cell types have been reported [47]. Here, we discovered that TGF-β increased levels of apoptosis in the eyes and accelerated ocular development in early juvenile zebrafish, suggesting that the nearsightedness phenotype caused by lrpap1 deficiency may be related to TGF-β-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, we observed sustained apoptosis in lrpap1 mutant line, unless TGF-β-signaling was inhibited. Of note, myopia in mutant line appeared about one month after birth and became progressively worse, and apoptosis was observed as early as in the embryonic stage, suggesting that continuous apoptosis is the cause rather than just the result of myopia. This being said, we did not explore in depth the specific apoptosis-related molecular changes influenced by TGF-β, and we plan to follow these approaches in a subsequent study.
We hypothesized that the occurrence of apoptosis might interfere with the refractive state, through impact on the choroidal tissue. Recent studies have highlighted the role of the choroid in scleral remodeling and myopia [48]. Some studies have shown that choroidal thickness is negatively correlated with diopter measurements, and the thicker the choroid, the shorter the ocular axis [49, 50]. In this study, TUNEL immunofluorescence showed that apoptosis mainly occurred in the choroid tissue, with lower levels in the sclera and iris. It is possible that apoptosis occurring in the choroid affects the focus of refraction through histomorphological changes or that the activation of the apoptosis pathway indirectly regulates scleral growth remodeling by interfering with the molecular network of growth factors normally secreted by the choroid. All in all, TGF-β-induced apoptosis is a good entry point for future in-depth exploration of retino-choroidal scleral axis signaling network regulating refractive development, thus elucidating the underlying signaling pathways and mechanisms is essential to promote the development of novel therapeutic approaches for myopia based on the modulation of the choroidal function.
Conclusion
In this study, we found that lrpap1 gene deficiency leads to the development of a myopic phenotype in zebrafish, which may be related to apoptosis induced by the upregulation of TGF-β.
Data availability
All data are included in the article or available on request by contacting the corresponding author: ljli@mail2.sysu.edu.cn. The RNA-seq data have been deposited at the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), and are accessible under the GEO Series accession number GSE186889.
References
Dolgin E. The myopia boom. Nature. 2015;519:276–8.
Holden BA, Fricke TR, Wilson DA, Jong M, Naidoo KS, Sankaridurg P, Wong TY, Naduvilath TJ, Resnikoff S. Global prevalence of myopia and high myopia and temporal trends from 2000 through 2050. Ophthalmology. 2016;123:1036–42.
Cooper J, Tkatchenko AV. A review of current concepts of the etiology and treatment of myopia. Eye Contact Lens. 2018;44:231–47.
Tedja MS, Haarman AEG, Meester-Smoor MA, Kaprio J, Mackey DA, Guggenheim JA, Hammond CJ. IMI—myopia genetics report. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019;60:M89–105.
Khan AO, AlAbdi L, Patel N, Helaby R, Hashem M, Abdulwahab F, AlBadr FB, Alkuraya FS. Genetic testing results of children suspected to have Stickler syndrome type collagenopathy after ocular examination. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021;9: e1628.
Magliyah MS, Alsulaiman SM, Nowilaty SR, Alkuraya FS, Schatz P. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in nonsyndromic high myopia associated with recessive mutations in LRPAP1. Ophthalmol Retina. 2020;4:77–83.
Jiang D, Li J, Xiao X, Li S, Jia X, Sun W, Guo X, Zhang Q. Detection of mutations in LRPAP1, CTSH, LEPREL1, ZNF644, SLC39A5, and SCO2 in 298 families with early-onset high myopia by exome sequencing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;56:339–45.
Khan AO, Aldahmesh MA, Alkuraya FS. Clinical characterization of LRPAP1-related pediatric high myopia. Ophthalmology. 2016;123:434–5.
Aldahmesh MA, Khan A, Alkuraya H, Adly N, Anazi S, Al-Saleh AA, Mohamed JY, Hijazi H, Prabakaran S, Tacke M, et al. Mutations in LRPAP1 are associated with severe myopia in humans. Am J Hum Genet. 2013;93:313–20.
Van Leuven F, Hilliker C, Serneels L, Umans L, Overbergh L, De Strooper B, Fryns JP, Van den Berghe H, et al. Cloning, characterization, and chromosomal localization to 4p16 of the human gene (LRPAP1) coding for the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor-associated protein and structural comparison with the murine gene coding for the 44-kDa heparin-binding protein. Genomics. 1995;25:492–500.
Bu G, Geuze H, Strous GJ, Schwartz AL. 39 kDa receptor-associated protein is an ER resident protein and molecular chaperone for LDL receptor-related protein. EMBO J. 1995;14:2269–80.
Carter CJ. Convergence of genes implicated in Alzheimer’s disease on the cerebral cholesterol shuttle: APP, cholesterol, lipoproteins, and atherosclerosis. Neurochem Int. 2007;50:12–38.
Cooper JM, Lathuiliere A, Migliorini M, Arai AL, Wani MM, Dujardin S, Muratoglu SC, Hyman BT, Strickland DK. Regulation of tau internalization, degradation, and seeding by LRP1 reveals multiple pathways for tau catabolism. J Biol Chem. 2021;296: 100715.
Muratoglu SC, Belgrave S, Lillis AP, Migliorini M, Robinson S, Smith E, Zhang L, Strickland DK. Macrophage LRP1 suppresses neo-intima formation during vascular remodeling by modulating the TGF-β signaling pathway. PLoS ONE. 2011;6: e28846.
Xie Y, Ouyang X, Wang G. Mechanical strain affects collagen metabolism-related gene expression in scleral fibroblasts. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;126: 110095.
Jobling AI, Gentle A, Metlapally R, McGowan BJ, McBrien NA. Regulation of scleral cell contraction by transforming growth factor-beta and stress: competing roles in myopic eye growth. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:2072–9.
Jobling AI, Nguyen M, Gentle A, McBrien NA. Isoform-specific changes in scleral transforming growth factor-beta expression and the regulation of collagen synthesis during myopia progression. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:18121–6.
Link BA, Collery RF. Zebrafish Models of Retinal Disease. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2015;1:125–53.
Noel NCL, MacDonald IM, Allison WT. Zebrafish models of photoreceptor dysfunction and degeneration. Biomolecules. 2021;11:78.
Kelley LA, Mezulis S, Yates CM, Wass MN, Sternberg MJE. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat Protoc. 2015;10:845–58.
M W. The zebrafish book: a guide for the laboratory use of zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Eugene, University of Oregon Press. 2007.
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn. 1995;203:253–310.
Veth KN, Willer JR, Collery RF, Gray MP, Willer GB, Wagner DS, Mullins MC, Udvadia AJ, Smith RS, John SW, et al. Mutations in zebrafish lrp2 result in adult-onset ocular pathogenesis that models myopia and other risk factors for glaucoma. PLoS Genet. 2011;7: e1001310.
Collery RF, Veth KN, Dubis AM, Carroll J, Link BA. Rapid, accurate, and non-invasive measurement of zebrafish axial length and other eye dimensions using SD-OCT allows longitudinal analysis of myopia and emmetropization. PLoS ONE. 2014;9: e110699.
Copper JE, Budgeon LR, Foutz CA, van Rossum DB, Vanselow DJ, Hubley MJ, Clark DP, Mandrell DT, Cheng KC. Comparative analysis of fixation and embedding techniques for optimized histological preparation of zebrafish. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2018;208:38–46.
Toms M, Dubis AM, de Vrieze E, Tracey-White D, Mitsios A, Hayes M, Broekman S, Baxendale S, Utoomprurkporn N, Bamiou D, et al. Clinical and preclinical therapeutic outcome metrics for USH2A-related disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2020;29:1882–99.
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT, Salzberg SL. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat Protoc. 2016;11:1650–67.
Mortazavi A, Williams B, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 2008;5:621–8.
Greiling TM, Clark JI. The transparent lens and cornea in the mouse and zebra fish eye. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008;19:94–9.
Jonasova K, Kozmik Z. Eye evolution: lens and cornea as an upgrade of animal visual system. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008;19:71–81.
Zhu X, Du Y, Li D, Xu J, Wu Q, He W, Zhang K, Zhu J, Guo L, Qi M, et al. Aberrant TGF-β1 signaling activation by MAF underlies pathological lens growth in high myopia. Nat Commun. 2012;12:2102.
Jobling AI, Wan R, Gentle A, Bui BV, McBrien NA. Retinal and choroidal TGF-beta in the tree shrew model of myopia: isoform expression, activation and effects on function. Exp Eye Res. 2009;88:458–66.
Li M, Yuan Y, Chen Q, Me R, Gu Q, Yu Y, Sheng M, Ke B. Expression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and its regulatory role in type i collagen with TGF-β1 in scleral fibroblasts from an experimentally induced myopia guinea pig model. J Ophthalmol. 2016;2016:5126560.
Korenberg JR, Argraves KM, Chen XN, Tran H, Strickland DK, Argraves WS. Chromosomal localization of human genes for the LDL receptor family member glycoprotein 330 (LRP2) and its associated protein RAP (LRPAP1). Genomics. 1994;22:88–93.
Williams SE, Ashcom JD, Argraves WS, Strickland DK. A novel mechanism for controlling the activity of alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. Multiple regulatory sites for 39-kDa receptor-associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:9035–40.
Schnieder J, Mamazhakypov A, Birnhuber A, Wilhelm J, Kwapiszewska G, Ruppert C, Markart P, Wujak L, Rubio K, Barreto G, et al. Loss of LRP1 promotes acquisition of contractile-myofibroblast phenotype and release of active TGF-β1 from ECM stores. Matrix Biol. 2020;88:69–88.
Llorente-Cortes V, Barbarigo V, Badimon L. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 modulates the proliferation and migration of human hepatic stellate cells. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227:3528–33.
Meng XM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Lan HY. TGF-β: the master regulator of fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12:325–38.
Morikawa M, Derynck R, Miyazono K. TGF-β and the TGF-β family: context-dependent roles in cell and tissue physiology. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016;8: a021873.
Nickel J, Ten Dijke P, Mueller TD. TGF-β family co-receptor function and signaling. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2018;50:12–36.
McBrien NA. Regulation of scleral metabolism in myopia and the role of transforming growth factor-beta. Exp Eye Res. 2013;114:128–40.
Guo H, Jin X, Zhu T, Wang T, Tong P, Tian L, Peng Y, Sun L, Wan A, Chen J, et al. SLC39A5 mutations interfering with the BMP/TGF-β pathway in non-syndromic high myopia. J Med Genet. 2014;51:518–25.
Dong S, Tian Q, Zhu T, Wang K, Lei G, Liu Y, Xiong H, Shen L, Wang M, Zhao R, et al. SLC39A5 dysfunction impairs extracellular matrix synthesis in high myopia pathogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:8432–41.
Rohrer B, Stell WK. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) act as stop and go signals to modulate postnatal ocular growth in the chick. Exp Eye Res. 1994;58:553–61.
Lin MY, Lin IT, Wu YC, Wang IJ. Stepwise candidate drug screening for myopia control by using zebrafish, mouse, and Golden Syrian Hamster myopia models. EBioMedicine. 2021;65: 103263.
Liu Y, He K, Hu Y, Guo X, Wang D, Shi W, Li J, Song J. YAP modulates TGF-β1-induced simultaneous apoptosis and EMT through upregulation of the EGF receptor. Sci Rep. 2017;7:45523.
Lv X, Wang L, Zhu T. MiR-20a-5p suppressed TGF-β1-triggered apoptosis of human bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells by targeting STAT3. Mol Cell Probes. 2020;50: 101499.
Zhang Y, Wildsoet CF. RPE and choroid mechanisms underlying ocular growth and myopia. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;134:221–40.
Prousali E, Dastiridou A, Ziakas N, Androudi S, Mataftsi A. Choroidal thickness and ocular growth in childhood. Surv Ophthalmol. 2021;66:261–75.
Zhang S, Zhang G, Zhou X, Xu R, Wang S, Guan Z, Lu J, Srinivasalu N, Shen M, Jin Z, et al. Changes in choroidal thickness and choroidal blood perfusion in guinea pig myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019;60:3074–83.
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the South China University of Technology for providing zebrafish, breeding zebrafish, and supplying an experimental platform. We thank the National Zebrafish Center for providing zebrafish embryos with the lrpap1 heterozygous mutation (strain AB).
Funding
This study was funded by research grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81800871 to Jiali Li).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Funding acquisition, Writing-Review & Editing, Supervision. SL: Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data Curation, Writing-Original Draft. TC: Software, Investigation, Methodology. BC: Writing-Review & Editing, Software. YL: Resources, Data Curation. XL: Supervision, Project administration, Resources. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1
. Figure S1. Immunohistochemical (IHC) results of LRPAP1 in 3-month-old zebrafish. (A) Negative control. (B) IHC targeting LRPAP1 for wild-type zebrafish. Figure S2. Western blot analysis of LRPAP1 in the eyes of lrpap1 mutants and wild-type zebrafish two months and three months post-fertilization. WT, wild-type; MU, lrpap1 homozygous mutant. Figure S3. Western blot analysis of TGF-β in the eyes of lrpap1 mutants and wild-type zebrafish two months and three months post-fertilization. WT, wild-type; MU, lrpap1 homozygous mutant.
Additional file 2
. Supplementary Table S1. Tissue gradient dehydration procedure before paraffin section.
Additional file 3
. Supplementary Table S2. Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) staining procedure.
Additional file 4
. Supplementary Table S3. Information of 165 apoptosis pathway related genes in GSEA analysis.
Additional file 5
. Supplementary Table S4. Gene information of GO analysis.
Additional file 6
. Supplementary Table S5. Gene information of KEGG analysis.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Chen, T., Chen, B. et al. Lrpap1 deficiency leads to myopia through TGF-β-induced apoptosis in zebrafish. Cell Commun Signal 20, 162 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-022-00970-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-022-00970-9