Abstract
Over the past 2 decades, pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) have been shown to be on the front line of many illnesses such as autoimmune, inflammatory, and neurodegenerative diseases as well as allergies and cancer. Among PRRs, toll-like receptors (TLRs) are the most studied family. Dissecting TLRs signaling turned out to be advantageous to elaborate efficient treatments to cure autoimmune and chronic inflammatory disorders. However, a broad understanding of TLR effectors is required to propose a better range of cures. In addition to kinases and E3 ubiquitin ligases, phosphatases emerge as important regulators of TLRs signaling mediated by NF-κB, type I interferons (IFN I) and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases signaling pathways. Here, we review recent knowledge on TLRs signaling modulation by different classes and subclasses of phosphatases. Thus, it becomes more and more evident that phosphatases could represent novel therapeutic targets to control pathogenic TLRs signaling.
Graphic abstract

Video Abstract
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) belong to the Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) superfamily that recognizes Microbe-Associated Molecular Patterns (MAMPs)—not necessarily found on pathogens—, PAMPs (Pathogen) and DAMPs (Damage) [1]. There are 13 identified TLRs in mammals playing an instrumental role in the regulation of the innate immune system [2]. These receptors are highly conserved proteins also found in the phylum Cnidaria, including jellyfishes [3]. As TLRs evolved before the adaptive immune system, they constitute an indispensable first line of defense [4]. Accordingly, TLRs expression is not restricted to immune cell lineages. TLR3 and TLR5 mRNAs are detected ubiquitously within the human body, while other TLRs are mostly expressed in epithelial tissues (except TLR10, more restricted) [5]. Thus, because they constitute the first line of defense against microbes (see below), TLRs are involved in pathogenesis of various disorders. Several Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) of TLRs, their co-receptors and some adaptors are indeed associated with several diseases including infections, atherosclerosis, asthma, chronic cardiomyopathy and colorectal cancer [6, 7].
TLRs are divided into two groups: those localized at the plasma membrane and those localized at the endosomal membrane [8]. Plasma membrane-localized TLRs recognize conserved motifs on extracellular microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, protozoan and helminth parasites [9]. Yet, plasma membrane TLRs are also able to bind DAMPs. The most glaring example is TLR4 that is well-known to recognize Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a component of Gram-negative bacteria, and 28 other ligands including DAMPs [10]. This wide range of recognition is allowed by combinations between TLRs homodimers or heterodimers with co-receptors and/or accessory molecules [11]. The other plasma membrane TLRs include TLR1, TLR2 and TLR6 which bind various lipopeptides from Gram-positive bacteria and TLR5 which binds flagellin from flagellated bacteria [9].
Endosomal TLRs (TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9) are activated by nucleic acids derived from microbes. Their ectodomains undergo proteolytic cleavage in endosomes to generate functional receptors for nucleic acid structures [12]. For instance, TLR3 recognizes double stranded RNA (dsRNA), TLR7 and TLR8 recognize single stranded RNA (ssRNA) and TLR9 binds unmethylated cytidine-phosphate-guanosine (CpG) dinucleotides [13].
Notably, half of the TLRs exhibit both plasma membrane and endosomal localizations. For instance, in intestinal epithelial cells exposed to bacterial DNA, TLR9 moves from the endosomal compartment to the cytoplasmic membrane [14]. In macrophages, membrane-associated TLR4 reaches the endosomal compartment through endocytosis [15]. A similar process has been described for TLR2 which is endocytosed after its heterodimerization with TLR1 or TLR6 in myeloid cells [16].
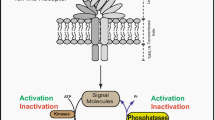
Binding of ligands to TLRs triggers the activation of several intracellular signaling pathways involving protein phosphorylation, dephosphorylation and ubiquitination. While the roles of specific protein kinases in this process have been well described [17, 18], much less is known about the implications of phosphatases, particularly tyrosine phosphatases. In this review, we summarize how specific phosphatases regulate TLRs signaling and function.
TLR signaling pathways: an overview
Rapid tyrosine phosphorylation following TLRs engagement
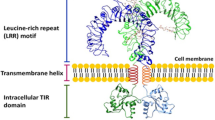
TLRs are type I membrane glycoproteins with an ectodomain consisting of Leucine-Rich Repeats (LRRs), responsible for the molecular recognition of ligands [19]. TLRs contain also a cytoplasmic domain called Toll/Interleukin-1 Receptor (TIR) domain, which recruits several adapter proteins including Myeloid Differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88), Toll/Interleukin-1 Receptor domain-containing Adapter Protein (TIRAP) or TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing Interferon-β (TRIF). Upon ligand binding, TLRs undergo conformational changes inducing homodimerization or heterodimerization which unveil TIR domains which can now recruit and bind different downstream signaling effectors regulating the host inflammatory response [20].
Notably, the TIR domain of TLR2, 3, 4, 5, 8 and 9 is rapidly phosphorylated on tyrosine upon stimulation with their respective ligands. This phosphorylation is required for the recruitment of adapter proteins and subsequent activation of the downstream signaling cascades [17, 21, 22]. Several tyrosine kinases interact with TLRs, including Src, Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK), Lyn and Syk. The Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) is also rapidly activated upon ligand binding to TLR. Indeed, FAK phosphorylation is observed in macrophages isolated from mice deficient for MyD88, one of the first adapter molecule recruited following TLR4 activation (see below), suggesting that FAK activation occurs early after TLR activation [23]. FAK is indeed required for TLR4 downstream signaling since cytokine induction in response to LPS is totally abrogated in Fak−/− cells. However, FAK does not possess TIR domains for direct interaction with MyD88 or TLR4 [24]. Instead, activated FAK phosphorylates BTK which interacts with the TIR domains of TLR4 (but also of TLR6, 8, and 9) [25]. BTK phosphorylation by FAK opens its conformation [26] allowing its phosphorylation and activation by Src kinases (Fig. 1). Once activated, BTK phosphorylates different adapter molecules such as the bridging adapter TIRAP, facilitating Myd88 recruitment to TLR4 [27]. Interestingly, BTK can also phosphorylate TLR3 and this is required for downstream signaling [28]. However, BTK does not phosphorylate TRIF, but rather facilitates TRIF interaction with effectors Since BTK expression is restricted to myeloid cells, ETK, a member of the TEC family of tyrosine kinases, is suspected to play similar functions in other cell types such as epithelial cells.
Aside from these observations, tyrosine phosphorylation of TLR3 and TLR4 also increased in response to EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor), and inhibition of EGFR (EGF Receptor) kinase activity impaired activation of their downstream signaling. In fact, the Src family kinases mediated this crosstalk between EGFR and TLRs, triggering the recruitment of adapters and other effector proteins [31, 32].
Altogether, these observations strongly suggest that a coordinated interplay should exist between tyrosine kinases and phosphatases in order to tightly regulate the activation status of TLRs intracellular signaling and cellular function. Below, we summarize the main signaling pathways activated by TLRs and we discuss how these pathways are modulated by various tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphatases.
The MyD88-dependent signaling
TLRs activate two types of pathways to control inflammatory responses: the MyD88-dependent pathway activated by all TLRs except TLR3, and the MyD88-independent but TRIF-dependent pathway activated directly by TLR3 and indirectly by other TLRs [33, 34]. Importantly, Myd88 contains a TIR domain as observed in most TLRs, but most TLRs use the bridging adapter TIRAP to recruit MyD88 [35]. Indeed, TIRAP contains a TIR domain at its C-terminus and a phosphatidylinositol-4,5 biphosphate (PIP2) binding motif at its N-terminus, required for recruitment to the plasma membrane [36]. Of note, TIRAP tyrosine phosphorylation by BTK is necessary for Myd88 recruitment to the plasma membrane (Fig. 1). Furthermore, Tirap-deficient mice revealed that TIRAP is crucial for the activation of MyD88-dependent signaling following TLR2 and TLR4 activation [37]. The N-terminus Death Domain (DD) of MyD88 recruits the Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4 (IRAK4) via DD-DD domains interaction. Consequently, mice lacking Irak-4 display an almost total irresponsiveness to LPS challenge [38]. The IRAK1/Toll-Interacting Protein (TOLLIP) complex in which TOLLIP acts as a TLR signaling inhibitor [39], is also recruited. Hyperphosphorylation of IRAK1 by IRAK4 dissociates TOLLIP and IRAK1, and IRAK1 can then recruit and activate the TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 6 (TRAF6) ubiquitin E3 ligase. TRAF6 promotes lysine (K)63-linked polyubiquitination of IRAK1, IKK-γ and TRAF6 itself. The K63-linked ubiquitin chains serve as docking sites for adapters TGF-β-Activated kinase 1-Binding 2 and 3 (TAB2, TAB3) which sequester TGFβ-Activated Kinase 1 (TAK1). Then, TAK1 auto-phosphorylates and becomes activated [40]. Hence, TAK1 activation mostly depends on TRAF6 E3 ubiquitin ligase [41]. Activated TAK1 then phosphorylates substrates such as IKKs (IκB-α kinases) and the MAPK Kinases (MAPKKs) MKK3, MKK4, MMK6 and MKK7 (Fig. 2) [42].
Regulation of TLR/MyD88-dependent pathways by phosphatases. TLRs localized at the plasma membrane use the bridging adapter TIRAP to recruit MyD88 and activate the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. MyD88 then recruits IRAK4 which phosphorylates IRAK1 which activates TRAF6. TRAF6 induces K63-linked polyubiquitination of TRAF6 itself serving as a platform leading to TAK1 autophosphorylation and activation. Activated TAK1 phosphorylates IKK-α and IKK-β which induce IκBα degradation, allowing NF-κB nuclear translocation and induction of proinflammatory genes transcription. TAK1 also phosphorylates the MAPK Kinases MKK3, MKK4, MKK6 and MKK7, resulting in activation and nuclear translocation of MAP Kinases which phosphorylate several transcription factors inducing proinflammatory mediator genes transcription
Activation of the IKK complex (IKK-α, IKK-β and IKK-γ) leads to NF-κB inhibitory fragment (IκB-α) degradation. This exposes the NF-κB nuclear localization sequence and allows NF-κB translocation to the nucleus to initiate transcription of proinflammatory genes, including those encoding chemokines and cytokines. Besides, stimulation of the MAPKKs results in activation and nuclear translocation of the MAPKs ERK1/2 (Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinases 1/2), p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK), which phosphorylate several transcription factors (such as AP-1), also inducing proinflammatory mediator genes transcription (Fig. 2).
The TRIF-dependent signaling
TRIF is an adapter protein upstream of the production of type I interferons (IFN-α and IFN-β) and other proinflammatory mediators. TRIF is recruited directly to TLR3 but indirectly to TLR4 via the TRIF-Related Adapter Molecule (TRAM) [43]. In fact, TLR4 initially recruits TIRAP and MyD88 at the plasma membrane and is subsequently endocytosed to the endosomes where it recruits TRAM and TRIF. TRAM mediates the activation of TRIF which associates with TRAF3 and TRAF6. The TRAF6 complex then induces RIP-1 (Receptor-Interacting serine/threonine-Protein kinase-1) which activates the IKK-α, β, γ complex and then NF-κB [44, 45]. Furthermore, TRAF3 triggers the K63-linked ubiquitination of TANK-Binding Kinase 1 (TBK1) (47)] and IKK-ε (48)]. K63-linked ubiquitination chains act as scaffolds for kinases, inducing their catalytic activation [46,47,48]. Activated TBK1 then phosphorylates the transcription factor family IRFs (Interferon Regulatory Factors) [49], leading to homodimerization or heterodimerization, translocation into the nucleus and target genes expression, including IFNI (encoding IFN-α and IFN-β) [50] (Fig. 3).
Regulation of TLR/TRIF-dependent pathways by phosphatases. TRIF is recruited directly to TLR3 but indirectly, via TRAM adaptor, to TLR4, following stimulation. TRIF adaptor then recruits TRAF3 which induces K63-linked ubiquitination of TBK1, its autophosphorylation and then, activation. Activated TBK1 then phosphorylates the transcription factors IRF3 and IRF7, leading to homodimerization or heterodimerization, translocation into the nucleus and target genes induction, including IFNI. TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 activate the TRIF-dependent pathways via the MyD88 adaptor
Likewise, TLR3 signaling is initiated from endosomal membranes where it activates TRAF6 and TRAF3. Then, TRIF signals through TRAF3, TBK1, and IKK-ε to initiate IRF-mediated transcription. TRAF3 therefore acts as a critical component to trigger TRIF-dependent signaling pathways (Fig. 3). This is exemplified by the phenotype of Traf3-deficient myeloid and dendritic cells in which IFN production is impaired upon TLR4, TLR7 and TLR9 stimulations [51, 52]. Interestingly, analysis of gene expression profiles in dendritic cells carrying a loss of function mutation in Trif reveals that 47% of LPS-responsive genes are TRIF-dependent [53].
The human protein phosphatome
The human protein phosphatome comprises a set of genes encoding phosphatases that remove phosphate groups from proteins. Protein phosphatases were first classified according to their catalytic domain annotation [54]. Today, phosphatase families are subdivided into classes, according to their preferred substrates [55]. A simplified classification is presented in Table 1.
Classical protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs)
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B)
PTP1B is a cytoplasmic protein tyrosine phosphatase expressed in many tissues [71, 72] and which targets a wide range of substrates [73,74,75]. Notably, Ptp1b gene knockdown in mouse RAW264.7 macrophages results in increased NF-κB and IRFs activation in response to TLR3, TLR4 and TLR9 stimulation [76]. Similarly, macrophages derived from Ptp1b−/− mice exhibit accelerated IκBα degradation following TLR4 activation by LPS [77]. Elevated concentrations of inflammatory cytokines and IFN I were also found in the lungs of Ptp1b−/− mice following intranasal administration of Oligo-Deoxy-Nucleotide 1826 (ODN 1826, a TLR9 agonist) [78]. Thus, these studies suggest that PTP1B restrains TLR4 and TLR9-induced inflammatory responses. Conversely, PTP1B expression levels were significantly increased in the brain 24 h after LPS injection in mice. In addition, when overexpressed in microglial cells, PTP1B increased LPS-induced TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis Factor-α), iNOS (inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase) and IL-6 (Interleukin 6) expression as well as NO production. It has been demonstrated that PTP1B exerts such pro-inflammatory function by dephosphorylating a negative regulatory site (tyrosine 527) on Src, hence activating its kinase activity and downstream NF-κB signaling [79, 80]. These studies suggest cell type-specific roles for PTP1B in TLRs signaling.
Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 4 (PTPN4)
PTPN4 tyrosine phosphatase regulates T Cell Receptor signaling [81]. Huai et al. have reported that PTPN4 dephosphorylates TRAM adapter, hence inhibiting TRIF-dependent TLR4 signaling [82]. Additionally, Ptpn4 silencing in mouse macrophages increases IRF3 phosphorylation in response to LPS but not in response to Poly I:C, a TLR3 ligand. Ectopic expression of a catalytically inactive mutant of PTPN4 in RAW264.7 macrophages abolishes LPS-induced IFN-β secretion [82]. Biochemical and genetic analyses demonstrate that PTPN4 dephosphorylates TRAM adapter on tyrosine 167 – within the TIR domain –, thereby disrupting TRAM-TRIF direct interaction [82] (Table 2). Thus, PTPN4 is a negative regulator of TLR4/TRIF-dependent signal transduction.
Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22 (PTPN22)
PTPN22 is expressed in lymphoid tissues where it promotes type I IFNs production following TLR3 and TLR4 ligation [83]. Mechanistically, it has been shown that PTPN22 directly interacts with TRAF3, enhancing its K63-linked ubiquitination and consequently IFNs induction. In a model of IL-1β-dependent inflammatory arthritis, Ptpn22−/− mice develop severe arthritis despite Poly I:C treatment, which usually attenuates disease symptoms [84]. Notably, a single nucleotide polymorphism in PTPN22 gene, encoding a tryptophan at amino acid 620, has been described as a susceptibility locus for autoimmune diseases and infections [85]. Accordingly, patients with autoimmune Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) expressed the PTPN22 R620W variant and this was associated with impaired TLR7 and TLR8-dependent IFN-α induction [86]. These data argue for a protective role of PTPN22 against autoimmune diseases via the regulation of TRAF3-dependent signaling.
Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-1 (SHP-1)
SHP-1 belongs to the SH2-domain-containing family of non-membrane protein tyrosine phosphatases. It has been broadly studied in immune lineages as its expression is abundant in hematopoietic cells [87]. Several studies have reported that SHP-1 differentially modulates NF-κB and IRF3 activation upon TLR3 and TLR4 stimulation [88]. Indeed, in splenocytes, dendritic cells and peritoneal macrophages, SHP-1 inhibits NF-κB-dependent gene induction while it promotes IFN-β production. In fact, SHP-1 directly interacts with IRAK1 which in turn inhibits IRF3 and IRF7 activation through its kinase activity [88, 89]. Surprisingly, this regulatory function of SHP-1 is independent from its phosphatase activity since it is also observed in macrophages expressing the catalytically inactive SHP-1 mutant (C453S, Table 1, section “PTPs”). This interaction between SHP-1 and IRAK1 occurs through a ITIM-like motif found in the kinase domain of IRAK1 [90].
Notably, SHP-1 has been associated with autoinflammatory diseases and infections. Macrophages from autoimmune Multiple Sclerosis (MS) patients exhibit deficient SHP-1 gene expression in comparison to normal subjects [91]. In line with these observations, SHP-1 knockdown in normal macrophages increases LPS-mediated NF-κB responses, up to levels observed in macrophages from MS patients [91]. Aside from these observations, treatment of human macrophages with the specific SHP-1 inhibitor Sodium Stibogluconate (SS) [92] reduces LPS-induced production of IL-27 which then inhibits HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) infection in CD4 T cells [93]. These results suggest a pivotal role for SHP-1 in antiviral immunity.
Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-2 (SHP-2)
As SHP-1, SHP-2 belongs to the SH2-domain-containing family of non-membrane protein tyrosine phosphatases. SHP-2 shares 60% of sequence identity with SHP-1 [94] but in contrast to SHP-1, SHP-2 is ubiquitously expressed [95], regulating many different signaling pathways [96]. The first evidence that SHP-2 regulates TLRs signaling were provided by An et al. [97] who demonstrated that SHP-2 inhibits IFN production in response to TLR3 and TLR4 ligands. Indeed, SHP-2 deficiency significantly enhanced LPS and poly(I:C)-induced IFN-β luciferase reporter gene expression in macrophages. Interestingly, this function of SHP-2 occurs in a phosphatase activity independent manner [97]. Molecularly, SHP-2 directly interacts with the kinase domain of TBK1, inhibiting IRF3 activation and IFNs production (Fig. 3). These observations were confirmed by Xu et al. who demonstrated that Shp-2−/− macrophages secrete higher amounts of IFN-β upon TLR3, TLR4 and TLR9 activation in comparison to wild-type macrophages [98]. On the other hand, increased TRAF6 ubiquitination and NF-κB activation were observed in Shp-2−/− macrophages stimulated with LPS, suggesting that SHP-2 suppresses NF-κB pathway activation in response to LPS.
Regarding the MAPK pathways, it has been reported that conditional Shp-2 deletion in murine podocytes attenuates JNK and p38 MAPK activation in response to LPS [99]. Similar observations were reported in LPS-stimulated bronchial epithelial cells [100]. However, the molecular mechanisms involved in such regulation remain to be clarified. One could speculate that SHP-2 modulates TRAF6 ubiquitination which in turn modulates TAK1 activity. Additionally, some data suggest that SHP-2 might be involved early following TLR engagement. Indeed, conditional expression of an active SHP-2 mutant in murine endothelial cells blocks LPS-induced barrier disruption and this correlates with increased FAK phosphorylation [101].
Protein tyrosine phosphatase-PEST (PTP-PEST)
PTP-PEST is a protein tyrosine phosphatase containing a PEST motif (enrichment in P: Proline, E: Glutamate, S: Serine and T: Threonine) [102] which is associated with proteins with short half-lives [103]. Interestingly, enhanced PTP-PEST expression is observed in macrophages after long term stimulation with LPS, Poly I:C or ODN [104]. This increased expression is associated with decreased induction of proinflammatory cytokines and secretion of IFN-β. Such regulation depends on phosphatase activity of PTP-PEST, since overexpression of a catalytically inactive PTP-PEST mutant abrogates NF-κB and IRFs signaling inhibition [104]. Additional data indicate that PTP-PEST directly interacts with IKK-β and dephosphorylates two tyrosine residues (Table 2) [104]. Much more studies are needed to exactly understand how PTP-PEST modulates NF-κB and IRFs signaling following TLRs ligation.
MAPK phosphatases (MKPs)
MAPK Phosphatases (MKPs) are dual-specificity phosphatases (DUSPs) (Table 1). They dephosphorylate both threonine and tyrosine residues of MAPKs such as ERK1/2, p38α/β/γ/δ and JNK1/2/3 kinases, hence antagonizing their activation and cellular functions [107].
DUal Specificity Phosphatase 1 (DUSP1)
DUSP1 is a nuclear MKP targeting the stress-activated MAPKs p38 and JNK, and which is rapidly up-regulated in response to mitogenic and/or stress stimuli [121]. Interestingly, Dusp1 KO (Knockout) mice exhibit increased sensitivity to endotoxic shock induced by LPS [122]. Indeed, prolonged JNK and p38 MAPK activation as well as increased TNF-α and IL-6 expression are observed in Dusp1−/− cells [122]. Aside from these observations, macrophages pre-treatment with a pharmacological inhibitor of DUSP1, namely triptolide, over-activates JNK and p38 pathways following LPS [106, 107] or the TLR2 agonist peptidoglycan [108] stimulations. Since MAPK activation is necessary for the maximal production of cytokines [123], DUSP1 may act as a pivotal regulator of the innate immune response. In this regard, long-term stimulation of macrophages with peptidoglycan or LPS markedly increases DUSP1 mRNA and protein expression [124].
DUal Specificity Phosphatase (DUSP16)
DUSP16 shows greater specificity for JNK and p38, with little or no activity towards ERK1/2 [105]. Notably, macrophages from Dusp16−/− mice show enhanced JNK activation with an overproduction of IL-12 (Interleukin 12) following LPS and CpG stimulation [109]. As observed for DUSP1, long-time exposure of macrophages with TLR4 or TLR9 ligands promotes Dusp16 transcription.
DUal Specificity Phosphatase (DUSP4)
While DUSP1 and DUSP16 mostly target the stress-activated MAPKs p38 and JNK, DUSP4 inactivates all three MAPKs (p38, JNK and ERK1/2). Interestingly, Dusp4-deficient mice exhibit increased susceptibility to Leishmania mexicana infection [110], a parasite targeting TLR4 on macrophages [125]. Enhanced release of pro-inflammatory mediators (IL-6, IL-12, TNF-α and Prostaglandin E2) is indeed observed in LPS-stimulated Dups4−/− macrophages, which is associated with over-activation of MAPKs (Table 2). Additionally, increased arginase-1 expression and activity are observed in Dusp4−/− macrophages, resulting in decreased iNOS formation [110]. Mechanistically, arginase-1 hydrolyses arginine (the substrate of iNOS) to ornithine and urea [126]. Notably, arginase-1 inhibition reverses the effect of Dusp4 deficiency on Leishmania growth. Therefore, these studies indicate that DUSP4 protects against Leishmania infection mainly by controlling arginase-1 expression and iNOS production.
Serine/threonine phosphatases (PPPs)
Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1)
PP1 phosphatase is involved in many different cellular processes, including TLRs responses [127, 128]. Indeed, PP1 dephosphorylates IKK-α and IKK-β induced by LPS [111]. PP1 negatively regulates TLRs signaling by dephosphorylating TAK1 on serine 412 [112], a residue targeted by Protein Kinase A (PKA) [129]. Mutation of serine 412 on TAK1 prevents PKA-induced degradation of IκB-α and p38 MAPK phosphorylation in RAW264.7 macrophages [129]. PP1 overexpression in macrophages also abrogates NF-κB, MAPKs and proinflammatory cytokine secretion upon TLRs engagement [112]. In addition, other studies have reported that PP1 regulates the IRFs axis as well [113]. In fact, PP1 interacts with and dephosphorylates IRF3 in macrophages, hence abrogating TLR3 response [113]. Recently, IRF7 has also been shown to be dephosphorylated by PP1 (Table 2) [114]. In line with these observations, inhibition of PP1 phosphatase activity enhances IFN-α production and impairs viral replication in human U-937 macrophages infected with Newcastle Disease Virus [114].
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A)
The ubiquitously expressed serine/threonine phosphatase PP2A accounts for a large fraction of phosphatase activity in eukaryotic cells [130]. Du et al. have shown that PP2A negatively regulates IRF3 activation in macrophages and myeloid cells [117]. In vitro assays demonstrate that PP2A directly dephosphorylates IRF3 (Table 2). In mice, the myeloid-specific knockout of Ppp2a results in higher mortality in response to LPS challenge and bacterial infection [131]. Notably, increased phosphorylation of MAPKs and NF-κB (IKK-α/β, p65) signaling effectors as well as enhanced secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines were observed in BMDMs (Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages) from Ppp2a−/− mice [132]. Aside from these observations, it has been shown that PP2A dephosphorylates c-Jun, hence inhibiting its proteasomal degradation in response to LPS [115] (Table 2).
Recently, the catalytic PP2A α-subunit was recognized as a novel protective factor for LPS-induced ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome). Indeed, specific ablation of the catalytic subunit of PP2A (Ppp2ca) in alveolar macrophages enhances NF-κB and MAPKs activation and aggravates cytokine secretion in response to LPS [133]. Conversely, adoptive transfer of alveolar macrophages with activated PP2A attenuates lung inflammation. Taken together, these results indicate that PP2A tightly regulates the inflammatory responses induced by TLRs, at least TLR3 and TLR4, by limiting the activation of MAPKs and NF-κB pathways.
Protein phosphatase 4 (PP4)
Protein Phosphatase 4 (PP4) is a PP2A-like phosphatase [134] regulating many cellular processes including DNA damage responses or the cell cycle [135, 136]. Notably, PP4 physically interacts with the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF6 [137]. Silencing PP4 in RAW264.7 macrophages increases NF-κB luciferase activity following TLR4 stimulation [137]. PP4 may also negatively modulate the NF-κB pathway downstream of TLR4, in part by inhibiting TRAF6 ubiquitination in response to LPS. Interestingly, PP4 expression is significantly upregulated in macrophages after long-time treatment with LPS [137]. Recently, PP4 has been shown to suppress IFN I production upon TLR3 and TLR4 stimulations in a phosphatase-dependent manner [118]. Indeed, siRNA-mediated reduction of the expression of the PP4 catalytic subunit in mouse peritoneal macrophages in vivo resulted in increased IFN I expression after viral infection. In addition, it was shown that PP4 direct interaction with the kinase TBK1 leads to dephosphorylation of serine 172 (Table 2) [118] which is located in the TBK1 activation loop, necessary for kinase activity and downstream IRF3 phosphorylation [138]. Thus, PP4 also acts as a potent negative regulator of TLR-mediated antiviral immunity.
Wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 (WIP1)
WIP1 is a member of the serine/threonine protein phosphatase PP2C family. WIP1 dephosphorylates the NF-κB subunit p65 on serine 536 within its transactivation domain [139] in response to LPS [119] (Table 2). Mice lacking Wip1 exhibit increased p65 phosphorylation and expression of target genes following LPS injection. Recently, a negative feedback loop between WIP1 and NF-κB in LPS-induced astrocytes was discovered [120]. Primary astrocytes LPS-stimulated increases Wip1 transcription and WIP1 protein nuclear colocalization with p65. Conversely, Wip1 silencing in primary astrocytes results in reduced p65 phosphorylation and cytokine transcription following TLR4 activation [120]. Collectively, these results suggest that WIP1 may provide a potent therapeutic target for neuroinflammation, and more generally for chronic inflammatory disorders (Table 3).
Intestinal alkaline phosphatase (IAP)
IAP is expressed in the brush border of enterocytes where it plays a key role in gut defense [140]. Interestingly, this phosphatase can also be secreted in both the intestinal lumen and bloodstream [141, 142]. In contrast to other phosphatases, IAP does not dephosphorylate proteins. Instead, its reported substrates include bacterial products such as LPS, flagellin and CpG. Hence, IAP plays a crucial role in the regulation of gut microbiota function [143]. For example, by removing phosphates present on the lipid A moiety (which allows LPS to bind TLR4), IAP reduces LPS toxicity [144]. Accordingly, ectopic IAP expression in intestinal epithelial cells and colon cancer cells markedly reduces LPS-induced NF-κB responses [145]. Likewise, oral IAP administration impairs colitis induction in response to Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS) in wild-type mice but not in Tlr4−/− mice [146]. Therefore, IAP protects against colitis by reducing TLR4 pathways activation. Interestingly, the gut expresses three isozymes for IAP: Akp3, Akp5 and Akp6. Akp3 (coding for IAP3) KO mice exhibit normal basal intestinal MyD88-inflammatory cytokines levels and similar susceptibilities to Gram- Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection when compared to control mice. However, adult Akp3−/− mice are immune tolerant to low intestinal dose of LPS. Such endotoxin tolerance, acquired post-weaning, may result from higher TLR4 stimulation during development [141]. This suggests IAP’s LPS detoxifying activity is involved in immune education [147].
Clinical relevance
As TLRs and some adaptors are involved in many human disorders such as atherosclerosis [6], phosphatases regulating TLR signaling may also be implicated. For example, it has been suggested that DUSP1 is athero-protective, as DUSP1 induction is necessary for the anti-inflammatory effects of shear stress in endothelial cells [148]. In addition, Khadir et al. identified circulating DUSP1 as a potential biomarker for chronic inflammation in patients with cardiovascular diseases associated with atherosclerosis [149]. Cheng et al. have shown that Geniposide, an emerging immunomodulator [150], is anti-inflammatory in part by upregulating Dusp1 expression in response to LPS [151]. Geniposide reduces atherosclerotic inflammatory injuries in ApoE−/− mice which are prone to atherosclerosis [152]. To date, no treatment against rheumatoid arthritis achieved to target its triggering events. However, it has recently been proposed to screen for PTPN22 gene signatures, in order to predict patient responses to autoimmune rheumatoid arthritis targeted therapies [153]. PTPN22 has also been recommended as a novel rheumatoid arthritis therapeutic target [154], as well as PP2A for neuroinflammatory disorders [155]. Finally, daily administration of Alkaline Phosphatase has been shown to significantly improve patients ulcerative colitis scores, with clinical effects observed within 21 days [156]. Thus, phosphatases may be directly involved in the regulation of human disorders such as atherosclerosis and are currently recognized as pharmacological targets.
Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19)
Recent data suggest a role of TLR signaling and phosphatases in patient responses to Coronavirus infection. For example, Mizutani et al. observed that p38 phosphorylation was significantly elevated in SARS-Coronavirus (SARS-CoV)-infected cells [157]. Inhibition of p38 phosphorylation almost abolished IL-6 and IL-8 induction. These first results are especially promising for targeting phosphatases to treat SARS. In 2011, an evasion strategy for the IBV (Infectious Bronchitis Virus) coronavirus (IBV) was revealed [158]. Indeed, IBV induces DUSP1 expression, correlating with reduced IL-6 and IL-8 secretion. IL-6 and IL-8 releases are part of the cytokine storm, responsible for the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS). COVID-19 is the most recent coronavirus-mediated acute respiratory illness generating severe symptoms. TLR4 has been identified as a potential receptor for the outer protein spike of SARS-CoV-2 [159]. It has been reported that COVID-19 patients upregulate TLR4-mediated signaling, which exacerbates SARS [160]. The more critically ill patients present highly increased S100 calcium-binding protein A9 (S100A9) blood levels, a TLR4-recognized DAMP. In addition, neutralizing autoantibodies against IFN I were detected in patients with life-threatening COVID-19 [161]. Rare putative loss-of-function variants of X-chromosomal TLR7 are associated with impaired type I IFN in young men with severe COVID-19 [162]. Knowing that both TLR4 and TLR7 trigger NF-κB/MAPK activation and antiviral IFN I, and that these pathways may be involved in SARS-related infections, il would be relevant to consider a role for phosphatases in TLRs signaling during COVID-19 infections.
Conclusion
This review highlights that phosphatases are key players in TLRs signaling. Interestingly, downregulation of most phosphatases markedly decreased or completely abolished LPS tolerance, highlighting the importance of phosphatases in endotoxin tolerization. In this regard, increased expression and activity of PP2A, PTPN22, PTP1B and MKP1 are observed in LPS-tolerized monocytes and macrophages [124]. One could speculate that phosphatases represent attractive targets to control TLRs-induced inflammatory responses. However, unlike kinases, phosphatases are challenging targets against which to develop specific inhibitors or inducers [163]. Their catalytic sites are permissive, rather shallow and greatly polar, making them hard to target. Recent progress in allosteric or oligomerization inhibitors design reveals new chemical tools that will set future therapies [164]. That being said, there are still numerous outstanding questions at the molecular level that remain to be addressed before considering phosphatases as good therapeutic targets to control TLRs functions. For instance, which PTPs dephosphorylate tyrosine phosphorylated TLRs? How exactly TLRs control the activity of regulatory phosphatases to ensure timely proinflammatory responses? Is that modulation cell type-dependent? Further studies are warranted to dissect the kinase-phosphatase network regulating TLRs signaling pathways.
Availability of supporting data
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ApoE− / − mice:
-
Atherosclerosis-prone apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- BMMs:
-
Bone marrow-derived macrophages
- Btk:
-
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase
- C:
-
Cysteine
- C57BL/6:
-
C57 black 6 mouse genetic background
- Cdc25:
-
Cell division cycle 25
- CoV:
-
Coronavirus
- COVID-19:
-
Coronavirus disease-2019
- CpG:
-
Cytidine-phosphate-guanosine oligonucleotides
- CREB:
-
C-AMP response element-binding protein
- D:
-
Aspartate
- DD:
-
Death domain
- DAMPs:
-
Damage-associated molecular patterns
- DSPs/DUSPs:
-
Dual-specificity phosphatases
- DSS:
-
Dextran sulfate sodium
- E. coli :
-
Escherichia coli
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
EGF receptor
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinases
- FAK:
-
Focal adhesion kinase
- FCP1:
-
F-cell production 1
- HADs:
-
Holo-acid dehalogenases
- HIV:
-
Human immunodeficiency virus
- IAP:
-
Intestinal alkaline phosphatase
- IBV:
-
Infectious bronchitis virus
- IFN-α/β/γ:
-
Interferon α/β/γ
- IFN I:
-
Interferon type I
- IKK-α/β/γ/ε:
-
IκB kinase-α/β/γ/ε
- IL-1β/6/12/27:
-
Interleukin-1β/6/12/27
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- IRAK1/4:
-
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated Kinase ¼
- IRF3/7:
-
Interferon regulatory factor 3/7
- JNK:
-
C-Jun N-terminal kinase
- LCM Virus:
-
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus
- LMW-PTP:
-
Low molecular weight-protein tyrosine phosphatases
- LPA:
-
Lysophosphatidic acid
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharides
- LRRs:
-
Leucine-rich repeats
- MAMPs:
-
Microbe-associated molecular patterns
- MAPKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- MAPKKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases
- MEFs:
-
Mouse embryonic fibroblasts
- MKPs:
-
MAPK phosphatases
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- MyD88:
-
Myeloid differentiation primary response 88
- ODN:
-
Oligodinucleotide
- PAMPs:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- PDH:
-
Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- Poly I:C:
-
Poly-inosinic:poly-cytidylic acid
- PP1/2A2B/2C/4:
-
Protein phosphatase 1/2A/2B/2C/4
- PPMs:
-
Metal-dependent protein phosphatase
- PRRs:
-
Pattern recognition receptors
- PPPs:
-
Phospho-protein phosphatases
- pS/T/Y:
-
Phospho-serine/threonine/tyrosine
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and TENsin homolog
- PTPs:
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatases
- PTP1B:
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
- PTPN:
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type
- PTP-PEST:
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase-PEST
- RIP-1:
-
Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase-1
- RTPs:
-
Receptor tyrosine phosphatases
- S100A9:
-
S100 calcium-binding protein A9
- SARS:
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome
- SCP:
-
Small carboxy-terminal domain phosphatase
- SHP-1/2:
-
Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-1/2
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- SNP:
-
Several single nucleotide polymorphism
- SS:
-
Sodium stibogluconate
- TAK1:
-
Transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1
- TAB2/3:
-
TGF-β-activated kinase 1-binding 2/3
- TANK:
-
TRAF family member-associated NF-κB activator
- TBK1:
-
TANK-binding kinase 1
- TIR:
-
Toll/interleukin-1 receptor
- TIRAP:
-
Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor adapter protein
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TOLLIP:
-
Toll-interacting protein
- TRAF3/6:
-
TNF receptor-associated factor 3/6
- TRAM:
-
TRIF-related adaptor molecule
- TRIF:
-
TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β
- WIP1:
-
Wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1
- Y:
-
Tyrosine
References
Beutler B, Jiang Z, Georgel P, Crozat K, Croker B, Rutschmann S, et al. Genetic analysis of host resistance: toll-like receptor signaling and immunity at large. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:353–89.
Du X, Poltorak A, Wei Y, Beutler B. Three novel mammalian toll-like receptors: gene structure, expression, and evolution. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000;11(3):362–71.
Franzenburg S, Fraune S, Kunzel S, Baines JF, Domazet-Loso T, Bosch TCG. MyD88-deficient Hydra reveal an ancient function of TLR signaling in sensing bacterial colonizers. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012;109(47):19374–9.
Gorvel J-P. Intracellular pathogens in membrane interactions and vacuole biogenesis. Berlin: Springer; 2004.
Zarember KA, Godowski PJ. Tissue expression of human toll-like receptors and differential regulation of toll-like receptor mRNAs in leukocytes in response to microbes, their products, and cytokines. J Immunol. 2002;168(2):554–61.
Lin Y-T, Verma A, Hodgkinson CP. Toll-like receptors and human disease: lessons from single nucleotide polymorphisms. Curr Genom. 2012;13(8):633–45.
Ramasawmy R, Cunha-Neto E, Fae KC, Borba SCP, Teixeira PC, Ferreira SCP, et al. Heterozygosity for the S180L variant of MAL/TIRAP, a gene expressing an adaptor protein in the toll-like receptor pathway, is associated with lower risk of developing chronic Chagas cardiomyopathy. J Infect Dis. 2009;199(12):1838–45.
Krishnan J, Selvarajoo K, Tsuchiya M, Lee G, Choi S. Toll-like receptor signal transduction. Exp Mol Med. 2007;39(4):421–38.
Mukherjee S, Karmakar S, Babu SPS. TLR2 and TLR4 mediated host immune responses in major infectious diseases: a review. Braz J Infect Dis. 2016;20(2):193–204.
Maru Y. Inflammation and metastasis. Tokyo: Springer; 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-56024-1.
Piccinini AM, Midwood KS. DAMPening inflammation by modulating TLR signalling. Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:1–21.
Lee BL, Moon JE, Shu JH, Yuan L, Newman ZR, Schekman R, et al. UNC93B1 mediates differential trafficking of endosomal TLRs. Elife. 2013;2:e00291.
Lombardi G, Riffo-Vasquez Y, editors. Dendritic cells (handbook of experimental pharmacology). Berlin: Springer; 2009.
Ewaschuk JB, Backer JL, Churchill TA, Obermeier F, Krause DO, Madsen KL. Surface expression of toll-like receptor 9 is upregulated on intestinal epithelial cells in response to pathogenic bacterial DNA. Infect Immun. 2007;75(5):2572–9.
Kagan JC, Su T, Horng T, Chow A, Akira S, Medzhitov R. TRAM couples endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4 to the induction of interferon-β. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(4):361–8.
Dietrich N, Lienenklaus S, Weiss S, Gekara NO. Murine toll-like receptor 2 activation induces type I interferon responses from endolysosomal compartments. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(4):e10250.
Chattopadhyay S, Sen GC. Tyrosine phosphorylation in toll-like receptor signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014;25(5):533–41.
Leifer CA, Medvedev AE. Molecular mechanisms of regulation of toll-like receptor signaling. J Leukoc Biol. 2016;100(5):927–41.
Matsushima N, Tanaka T, Enkhbayar P, Mikami T, Taga M, Yamada K, et al. Comparative sequence analysis of leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) within vertebrate toll-like receptors. BMC Genom. 2007;8:124.
Jang T, Park HH. Crystal structure of TIR domain of TLR6 reveals novel dimeric interface of TIR–TIR interaction for toll-like receptor signaling pathway. J Mol Biol. 2014;426(19):3305–13.
Johnson P, Cross JL. Tyrosine phosphorylation in immune cells: direct and indirect effects on toll-like receptor-induced proinflammatory cytokine production. Crit Rev Immunol. 2009;29(4):347–67.
Medvedev AE, Piao W, Shoenfelt J, Rhee SH, Chen H, Basu S, et al. Role of TLR4 tyrosine phosphorylation in signal transduction and endotoxin tolerance. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(22):16042–53.
Zeisel MB, Druet VA, Sibilia J, Klein J-P, Quesniaux V, Wachsmann D. Cross talk between MyD88 and focal adhesion kinase pathways. J Immunol. 2005;174(11):7393–7.
Jefferies CA, O’Neill LAJ. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk)—the critical tyrosine kinase in LPS signalling? Immunol Lett. 2004;92(1):15–22.
Jefferies CA, Doyle S, Brunner C, Dunne A, Brint E, Wietek C, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is a toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-binding protein that participates in nuclear factor kappaB activation by toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(28):26258–64.
Semaan N, Alsaleh G, Gottenberg J-E, Wachsmann D, Sibilia J. Etk/BMX, a Btk family tyrosine kinase, and mal contribute to the cross-talk between MyD88 and FAK pathways. J Immunol. 2008;180(5):3485–91.
Gray P, Dunne A, Brikos C, Jefferies CA, Doyle SL, O’Neill LAJ. MyD88 adapter-like (Mal) is phosphorylated by Bruton’s tyrosine kinase during TLR2 and TLR4 signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(15):10489–95.
Lee K-G, Xu S, Kang ZH, Huo J, Huang M, Liu D, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase phosphorylates toll-like receptor 3 to initiate antiviral response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:5791–6.
Gianni T, Campadelli-Fiume G. The epithelial αvβ3-integrin boosts the MYD88-dependent TLR2 signaling in response to viral and bacterial components. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10(11):e1004477.
Chen H-Y, Lin M-H, Chen C-C, Shu J-C. The expression of fibronectin is significantly suppressed in macrophages to exert a protective effect against Staphylococcus aureus infection. BMC Microbiol. 2017;17(1):92.
De S, Zhou H, DeSantis D, Croniger CM, Li X, Stark GR. Erlotinib protects against LPS-induced endotoxicity because TLR4 needs EGFR to signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(31):9680–5.
Sarkar SN, Smith HL, Rowe TM, Sen GC. Double-stranded RNA signaling by toll-like receptor 3 requires specific tyrosine residues in its cytoplasmic domain. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(7):4393–6.
Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13(5):816–25.
Lord KA, Hoffman-Liebermann B, Liebermann DA. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a cDNA encoding MyD88, a novel myeloid differentiation primary response gene induced by IL6. Oncogene. 1990;5(7):1095–7.
Kagan JC, Medzhitov R. Phosphoinositide-mediated adaptor recruitment controls Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell. 2006;125(5):943–55.
Zhao X, Xiong W, Xiao S, Tang T-X, Ellena JF, Armstrong GS, et al. Membrane targeting of TIRAP is negatively regulated by phosphorylation in its phosphoinositide-binding motif. Sci Rep. 2017;7:43043.
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, Sanjo H, Uematsu S, Kaisho T, et al. Essential role for TIRAP in activation of the signalling cascade shared by TLR2 and TLR4. Nature. 2002;420(6913):324–9.
Suzuki N, Suzuki S, Duncan GS, Millar DG, Wada T, Mirtsos C, et al. Severe impairment of interleukin-1 and toll-like receptor signalling in mice lacking IRAK-4. Nature. 2002;416(6882):750–6.
Bulut Y, Faure E, Thomas L, Equils O, Arditi M. Cooperation of toll-like receptor 2 and 6 for cellular activation by soluble tuberculosis factor and Borrelia burgdorferi outer surface protein A lipoprotein: role of toll-interacting protein and IL-1 receptor signaling molecules in toll-like receptor 2 signaling. J Immunol. 2001;167(2):987–94.
Cheung PCF, Nebreda AR, Cohen P. TAB3, a new binding partner of the protein kinase TAK1. Biochem J. 2004;378(Pt 1):27–34.
Wang C, Deng L, Hong M, Akkaraju GR, Inoue J, Chen ZJ. TAK1 is a ubiquitin-dependent kinase of MKK and IKK. Nature. 2001;412(6844):346–51.
Chen I-T, Hsu P-H, Hsu W-C, Chen N-J, Tseng P-H. Polyubiquitination of transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) at lysine 562 residue regulates TLR4-mediated JNK and p38 MAPK activation. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12300.
Tanimura N, Saitoh S, Matsumoto F, Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K. Roles for LPS-dependent interaction and relocation of TLR4 and TRAM in TRIF-signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;368(1):94–9.
Cusson-Hermance N, Khurana S, Lee TH, Fitzgerald KA, Kelliher MA. Rip1 mediates the Trif-dependent toll-like receptor 3- and 4-induced NF-{kappa}B activation but does not contribute to interferon regulatory factor 3 activation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(44):36560–6.
Bertrand MJM, Vandenabeele P. The ripoptosome: death decision in the cytosol. Mol Cell. 2011;43(3):323–5.
Shimada T, Kawai T, Takeda K, Matsumoto M, Inoue J, Tatsumi Y, et al. IKK-i, a novel lipopolysaccharide-inducible kinase that is related to IkappaB kinases. Int Immunol. 1999;11(8):1357–62.
Goncalves A, Bürckstümmer T, Dixit E, Scheicher R, Górna MW, Karayel E, et al. Functional dissection of the TBK1 molecular network. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(9):e23971.
Shu C, Sankaran B, Chaton CT, Herr AB, Mishra A, Peng J, et al. Structural insights into the functions of TBK1 in innate antimicrobial immunity. Structure. 2013;21(7):1137–48.
Caillaud A, Hovanessian AG, Levy DE, Marié IJ. Regulatory serine residues mediate phosphorylation-dependent and phosphorylation-independent activation of interferon regulatory factor 7. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(18):17671–7.
Lin R, Heylbroeck C, Pitha PM, Hiscott J. Virus-dependent phosphorylation of the IRF-3 transcription factor regulates nuclear translocation, transactivation potential, and proteasome-mediated degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18(5):2986–96.
Oganesyan G, Saha SK, Guo B, He JQ, Shahangian A, Zarnegar B, et al. Critical role of TRAF3 in the toll-like receptor-dependent and -independent antiviral response. Nature. 2006;439(7073):208–11.
Häcker H, Redecke V, Blagoev B, Kratchmarova I, Hsu L-C, Wang GG, et al. Specificity in toll-like receptor signalling through distinct effector functions of TRAF3 and TRAF6. Nature. 2006;439(7073):204–7.
Weighardt H, Jusek G, Mages J, Lang R, Hoebe K, Beutler B, et al. Identification of a TLR4- and TRIF-dependent activation program of dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34(2):558–64.
Mann M, Jensen ON. Proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(3):255–61.
Graves JD, Krebs EG. Protein phosphorylation and signal transduction. Pharmacol Ther. 1999;82(2):111–21.
Miki H, Funato Y. Regulation of intracellular signalling through cysteine oxidation by reactive oxygen species. J Biochem. 2012;151(3):255–61.
Wang W-Q, Sun J-P, Zhang Z-Y. An overview of the protein tyrosine phosphatase superfamily. Curr Top Med Chem. 2003;3(7):739–48.
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science. 2002;298(5600):1912–34.
Dudek RW. High-yield cell and molecular biology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007.
Denu JM, Dixon JE. A catalytic mechanism for the dual-specific phosphatases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92(13):5910–4.
Patterson KI, Brummer T, O’Brien PM, Daly RJ. Dual-specificity phosphatases: critical regulators with diverse cellular targets. Biochem J. 2009;418(3):475–89.
Caselli A, Paoli P, Santi A, Mugnaioni C, Toti A, Camici G, et al. Low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatase: multifaceted functions of an evolutionarily conserved enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2016;1864(10):1339–55.
Raugei G, Ramponi G, Chiarugi P. Low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatases: small, but smart. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002;59(6):941–9.
Strausfeld U, Labbé JC, Fesquet D, Cavadore JC, Picard A, Sadhu K, et al. Dephosphorylation and activation of a p34cdc2/cyclin B complex in vitro by human CDC25 protein. Nature. 1991;351(6323):242–5.
Crosby ME. Cell cycle: principles of control. Yale J Biol Med. 2007;80(3):141–2.
Barford D. Molecular mechanisms of the protein serine/threonine phosphatases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996;21(11):407–12.
Moorhead GBG, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Ulke-Lemée A. Emerging roles of nuclear protein phosphatases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(3):234–44.
Fiscella M, Zhang H, Fan S, Sakaguchi K, Shen S, Mercer WE, et al. Wip1, a novel human protein phosphatase that is induced in response to ionizing radiation in a p53-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94(12):6048–53.
Seifried A, Schultz J, Gohla A. Human HAD phosphatases: structure, mechanism, and roles in health and disease. FEBS J. 2013;280(2):549–71.
Zhou H, Zhang L, Vartuli RL, Ford HL, Zhao R. The Eya phosphatase: its unique role in cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;96:165–70.
Balsamo J, Arregui C, Leung T, Lilien J. The nonreceptor protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B binds to the cytoplasmic domain of N-cadherin and regulates the cadherin-actin linkage. J Cell Biol. 1998;143(2):523–32.
Chernoff J, Schievella AR, Jost CA, Erikson RL, Neel BG. Cloning of a cDNA for a major human protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. PNAS. 1990;87(7):2735–9.
Flint AJ, Tiganis T, Barford D, Tonks NK. Development of “substrate-trapping” mutants to identify physiological substrates of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94(5):1680–5.
Buckley DA, Cheng A, Kiely PA, Tremblay ML, O’Connor R. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor type I (IGF-I) receptor kinase activity by protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP-1B) and enhanced IGF-I-mediated suppression of apoptosis and motility in PTP-1B-deficient fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(7):1998–2010.
Heinonen KM, Dubé N, Bourdeau A, Lapp WS, Tremblay ML. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B negatively regulates macrophage development through CSF-1 signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(8):2776–81.
Xu H, An H, Hou J, Han C, Wang P, Yu Y, et al. Phosphatase PTP1B negatively regulates MyD88- and TRIF-dependent proinflammatory cytokine and type I interferon production in TLR-triggered macrophages. Mol Immunol. 2008;45(13):3545–52.
Través PG, Pardo V, Pimentel-Santillana M, González-Rodríguez Á, Mojena M, Rico D, et al. Pivotal role of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) in the macrophage response to pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory challenge. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1125.
Foronjy RF, Salathe MA, Dabo AJ, Baumlin N, Cummins N, Eden E, et al. TLR9 expression is required for the development of cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016;311(1):L154-166.
Song GJ, Jung M, Kim J-H, Park H, Rahman MH, Zhang S, et al. A novel role for protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B as a positive regulator of neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflamm. 2016;13(1):86.
Lyu J, Zheng G, Chen Z, Wang B, Tao S, Xiang D, et al. Sepsis-induced brain mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with altered mitochondrial Src and PTP1B levels. Brain Res. 2015;1620:130–8.
Young JA, Becker AM, Medeiros JJ, Shapiro VS, Wang A, Farrar JD, et al. The protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN4/PTP-MEG1, an enzyme capable of dephosphorylating the TCR ITAMs and regulating NF-kappaB, is dispensable for T cell development and/or T cell effector functions. Mol Immunol. 2008;45(14):3756–66.
Huai W, Song H, Wang L, Li B, Zhao J, Han L, et al. Phosphatase PTPN4 preferentially inhibits TRIF-dependent TLR4 pathway by dephosphorylating TRAM. J Immunol. 2015;194(9):4458–65.
Cohen S, Dadi H, Shaoul E, Sharfe N, Roifman CM. Cloning and characterization of a lymphoid-specific, inducible human protein tyrosine phosphatase. Lyp Blood. 1999;93(6):2013–24.
Wang Y, Shaked I, Stanford SM, Zhou W, Curtsinger JM, Mikulski Z, et al. The autoimmunity-associated gene PTPN22 potentiates toll-like receptor-driven, type 1 interferon-dependent immunity. Immunity. 2013;39(1):111–22.
Gregersen PK, Lee H-S, Batliwalla F, Begovich AB. PTPN22: setting thresholds for autoimmunity. Semin Immunol. 2006;18(4):214–23.
Chang H-H, Tseng W, Cui J, Costenbader K, Ho I-C. Altered expression of protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 22 isoforms in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(1):R14.
Hematopoietic cell phosphatase. SHP-1, is constitutively associated with the SH2 domain-containing leukocyte protein, SLP-76, in B cells. J Exp Med. 1996;184(2):457–63.
An H, Hou J, Zhou J, Zhao W, Xu H, Zheng Y, et al. Phosphatase SHP-1 promotes TLR- and RIG-I-activated production of type I interferon by inhibiting the kinase IRAK1. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(5):542–50.
Bruni D, Sebastia J, Dunne S, Schröder M, Butler MP. A novel IRAK1–IKKε signaling axis limits the activation of TAK1–IKKβ downstream of TLR3. J Immunol. 2013;190(6):2844–56.
Abu-Dayyeh I, Shio MT, Sato S, Akira S, Cousineau B, Olivier M. Leishmania-induced IRAK-1 inactivation is mediated by SHP-1 interacting with an evolutionarily conserved KTIM motif. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2008;2(12):e305.
Christophi GP, Panos M, Hudson CA, Christophi RL, Gruber RC, Mersich AT, et al. Macrophages of multiple sclerosis patients display deficient SHP-1 expression and enhanced inflammatory phenotype. Lab Investig. 2009;89(7):742–59.
Pathak MK, Yi T. Sodium stibogluconate is a potent inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases and augments cytokine responses in hemopoietic cell lines. J Immunol. 2001;167(6):3391–7.
Greenwell-Wild T, Vázquez N, Jin W, Rangel Z, Munson PJ, Wahl SM. Interleukin-27 inhibition of HIV-1 involves an intermediate induction of type I interferon. Blood. 2009;114(9):1864–74.
Stein-Gerlach M, Wallasch C, Ullrich A. SHP-2, SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1998;30(5):559–66.
Tauchi T, Feng GS, Marshall MS, Shen R, Mantel C, Pawson T, et al. The ubiquitously expressed Syp phosphatase interacts with c-kit and Grb2 in hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(40):25206–11.
Feng G-S. Shp-2 tyrosine phosphatase: signaling one cell or many. Exp Cell Res. 1999;253(1):47–54.
An H, Zhao W, Hou J, Zhang Y, Xie Y, Zheng Y, et al. SHP-2 phosphatase negatively regulates the TRIF adaptor protein-dependent type I interferon and proinflammatory cytokine production. Immunity. 2006;25(6):919–28.
Xu S, Liu X, Bao Y, Zhu X, Han C, Zhang P, et al. Constitutive MHC class I molecules negatively regulate TLR-triggered inflammatory responses via the Fps-SHP-2 pathway. Nat Immunol. 2012;13(6):551–9.
Hsu M-F, Bettaieb A, Ito Y, Graham J, Havel PJ, Haj FG. Protein tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 deficiency in podocytes attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced proteinuria. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):461.
Qiu Z, Zhou J, Liu F, Qin X, Dai Y, Ke Y, et al. Deletion of Shp2 in bronchial epithelial cells impairs IL-25 production in vitro, but has minor influence on asthmatic inflammation in vivo. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(5):e0177334.
Chichger H, Braza J, Duong H, Harrington EO. SH2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 2 and focal adhesion kinase protein interactions regulate pulmonary endothelium barrier function. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015;52(6):695–707.
Côté JF, Charest A, Wagner J, Tremblay ML. Combination of gene targeting and substrate trapping to identify substrates of protein tyrosine phosphatases using PTP-PEST as a model. Biochemistry. 1998;37(38):13128–37.
Rogers S, Wells R, Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986;234(4774):364–8.
Zhang P, Liu X, Li Y, Zhu X, Zhan Z, Meng J, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase with proline-glutamine-serine-threonine-rich motifs negatively regulates TLR-triggered innate responses by selectively inhibiting IκB kinase β/NF-κB activation. J Immunol. 2013;190(4):1685–94.
Kondoh K, Nishida E. Regulation of MAP kinases by MAP kinase phosphatases. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Mol Cell Res. 2007;1773(8):1227–37.
Chen P, Li J, Barnes J, Kokkonen GC, Lee JC, Liu Y. Restraint of proinflammatory cytokine biosynthesis by mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. J Immunol. 2002;169(11):6408–16.
Zhao Q, Shepherd EG, Manson ME, Nelin LD, Sorokin A, Liu Y. The role of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in the response of alveolar macrophages to lipopolysaccharide: attenuation of proinflammatory cytokine biosynthesis via feedback control of p38. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(9):8101–8.
Shepherd EG, Zhao Q, Welty SE, Hansen TN, Smith CV, Liu Y. The function of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in peptidoglycan-stimulated macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(52):54023–31.
Niedzielska M, Bodendorfer B, Münch S, Eichner A, Derigs M, da Costa O, et al. Gene trap mice reveal an essential function of dual specificity phosphatase Dusp16/MKP-7 in perinatal survival and regulation of toll-like receptor (TLR)-induced cytokine production. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(4):2112–26.
Al-Mutairi MS, Cadalbert LC, McGachy HA, Shweash M, Schroeder J, Kurnik M, et al. MAP kinase phosphatase-2 plays a critical role in response to infection by Leishmania mexicana. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6(11):e1001192.
Li H-Y, Liu H, Wang C-H, Zhang J-Y, Man J-H, Gao Y-F, et al. Deactivation of the kinase IKK by CUEDC2 through recruitment of the phosphatase PP1. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(5):533–41.
Gu M, Ouyang C, Lin W, Zhang T, Cao X, Xia Z, et al. Phosphatase holoenzyme PP1/GADD34 negatively regulates TLR response by inhibiting TAK1 serine 412 phosphorylation. J Immunol. 2014;192(6):2846–56.
Gu M, Zhang T, Lin W, Liu Z, Lai R, Xia D, et al. Protein phosphatase PP1 negatively regulates the toll-like receptor- and RIG-I-like receptor-triggered production of type I interferon by inhibiting IRF3 phosphorylation at serines 396 and 385 in macrophage. Cell Signal. 2014;26(12):2930–9.
Wang L, Zhao J, Ren J, Hall KH, Moorman JP, Yao ZQ, et al. Protein phosphatase 1 abrogates IRF7-mediated type I IFN response in antiviral immunity. Eur J Immunol. 2016;46(10):2409–19.
Shi Q, Xiong B, Zhong J, Wang H, Ma D, Miao C. MFHAS1 suppresses TLR4 signaling pathway via induction of PP2A C subunit cytoplasm translocation and inhibition of c-Jun dephosphorylation at Thr239. Mol Immunol. 2017;88:79–88.
Wei W, Jin J, Schlisio S, Harper JW, Kaelin WG. The v-Jun point mutation allows c-Jun to escape GSK3-dependent recognition and destruction by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase. Cancer Cell. 2005;8(1):25–33.
Du M, Liu J, Chen X, Xie Y, Yuan C, Xiang Y, et al. Casein kinase II controls TBK1/IRF3 activation in IFN response against viral infection. J Immunol. 2015;194(9):4477–88.
Zhan Z, Cao H, Xie X, Yang L, Zhang P, Chen Y, et al. Phosphatase PP4 negatively regulates type I IFN production and antiviral innate immunity by dephosphorylating and deactivating TBK1. J Immunol. 2015;195(8):3849–57.
Chew J, Biswas S, Shreeram S, Humaidi M, Wong ET, Dhillion MK, et al. WIP1 phosphatase is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(5):659–66.
Xu F, Chen L, Zhao X, Zhong H, Cui L, Jiang L, et al. Interaction of Wip1 and NF-κB regulates neuroinflammatory response in astrocytes. Inflamm Res. 2017;66(11):1011–9.
Wang J, Yin DP, Liu Y-X, Baer R, Yin Y. Dual specificity phosphatase 1/CL100 is a direct transcriptional target of E2F–1 in the apoptotic response to oxidative stress. Cancer Res. 2007;67(14):6737–44.
Zhao Q, Wang X, Nelin LD, Yao Y, Matta R, Manson ME, et al. MAP kinase phosphatase 1 controls innate immune responses and suppresses endotoxic shock. J Exp Med. 2006;203(1):131–40.
Carter AB, Monick MM, Hunninghake GW. Both Erk and p38 kinases are necessary for cytokine gene transcription. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999;20(4):751–8.
Xiong Y, Murphy M, Manavalan TT, Pattabiraman G, Qiu F, Chang H-H, et al. Endotoxin tolerance inhibits Lyn and c-Src phosphorylation and association with toll-like receptor 4 but increases expression and activity of protein phosphatases. J Innate Immun. 2016;8(2):171–84.
Podinovskaia M, Descoteaux A. Leishmania and the macrophage: a multifaceted interaction. Future Microbiol. 2015;10(1):111–29.
Naderer T, McConville MJ. The Leishmania-macrophage interaction: a metabolic perspective. Cell Microbiol. 2008;10(2):301–8.
Tournebize R, Andersen SS, Verde F, Dorée M, Karsenti E, Hyman AA. Distinct roles of PP1 and PP2A-like phosphatases in control of microtubule dynamics during mitosis. EMBO J. 1997;16(18):5537–49.
Fong NM, Jensen TC, Shah AS, Parekh NN, Saltiel AR, Brady MJ. Identification of binding sites on protein targeting to glycogen for enzymes of glycogen metabolism. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(45):35034–9.
Kobayashi Y, Mizoguchi T, Take I, Kurihara S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N. Prostaglandin E2 enhances osteoclastic differentiation of precursor cells through protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation of TAK1. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(12):11395–403.
Mumby M. PP2A: unveiling a reluctant tumor suppressor. Cell. 2007;130(1):21–4.
Sun L, Pham TT, Cornell TT, McDonough KL, McHugh WM, Blatt NB, et al. Myeloid-specific gene deletion of protein phosphatase 2A magnifies MyD88- and TRIF-dependent inflammation following endotoxin challenge. J Immunol. 2017;198(1):404–16.
GEO Accession viewer. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE83517. Cited 12 Apr 2020.
He Z, Du L, Ke Y, Wen C, Zhang Y. PP2ACα of alveolar macrophages is a novel protective factor for LPS-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Inflammation. 2019;42(3):1004–14.
Zhao H, Huang X, Jiao J, Zhang H, Liu J, Qin W, et al. Protein phosphatase 4 (PP4) functions as a critical regulator in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced hepatic insulin resistance. Sci Rep. 2015;5:18093.
Liu J, Xu L, Zhong J, Liao J, Li J, Xu X. Protein phosphatase PP4 is involved in NHEJ-mediated repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Cell Cycle. 2012;11(14):2643–9.
Zhuang X, Semenova E, Maric D, Craigie R. Dephosphorylation of barrier-to-autointegration factor by protein phosphatase 4 and its role in cell mitosis. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(2):1119–27.
Chen L, Dong W, Zou T, Ouyang L, He G, Liu Y, et al. Protein phosphatase 4 negatively regulates LPS cascade by inhibiting ubiquitination of TRAF6. FEBS Lett. 2008;582(19):2843–9.
Kishore N, Huynh QK, Mathialagan S, Hall T, Rouw S, Creely D, et al. IKK-i and TBK-1 are enzymatically distinct from the homologous enzyme IKK-2: comparative analysis of recombinant human IKK-i, TBK-1, and IKK-2. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(16):13840–7.
Christian F, Smith EL, Carmody RJ. The regulation of NF-κB subunits by phosphorylation. Cells. 2016;5(1):12.
Alam SN, Yammine H, Moaven O, Ahmed R, Moss AK, Biswas B, et al. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase prevents antibiotic-induced susceptibility to enteric pathogens. Ann Surg. 2014;259(4):715–22.
Alpers DH, Zhang Y, Ahnen DJ. Synthesis and parallel secretion of rat intestinal alkaline phosphatase and a surfactant-like particle protein. Am J Physiol. 1995;268(6 Pt 1):E1205-1214.
Bilski J, Mazur-Bialy A, Wojcik D, Zahradnik-Bilska J, Brzozowski B, Magierowski M, et al. The role of intestinal alkaline phosphatase in inflammatory disorders of gastrointestinal tract. Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:9074601.
Chen KT, Malo MS, Moss AK, Zeller S, Johnson P, Ebrahimi F, et al. Identification of specific targets for the gut mucosal defense factor intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010;299(2):G467-475.
Bentala H, Verweij WR, Huizinga-Van der Vlag A, van Loenen-Weemaes AM, Meijer DKF, Poelstra K. Removal of phosphate from lipid A as a strategy to detoxify lipopolysaccharide. Shock. 2002;18(6):561–6.
Goldberg RF, Austen WG, Zhang X, Munene G, Mostafa G, Biswas S, et al. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase is a gut mucosal defense factor maintained by enteral nutrition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(9):3551–6.
Hwang SW, Kim JH, Lee C, Im JP, Kim JS. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase ameliorates experimental colitis via toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;820:156–66.
Yang Y, Millán JL, Mecsas J, Guillemin K. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase deficiency leads to lipopolysaccharide desensitization and faster weight gain. Infect Immun. 2015;83(1):247–58.
Zakkar M, Chaudhury H, Sandvik G, Enesa K, Luong LA, Cuhlmann S, et al. Increased endothelial mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 expression suppresses proinflammatory activation at sites that are resistant to atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2008;103(7):726–32.
Khadir A, Kavalakatt S, Dehbi M, Alarouj M, Bennakhi A, Tiss A, et al. DUSP1 is a potential marker of chronic inflammation in Arabs with cardiovascular diseases. Dis Markers. 2018;2018:9529621.
Song X, Zhang W, Wang T, Jiang H, Zhang Z, Fu Y, et al. Geniposide plays an anti-inflammatory role via regulating TLR4 and downstream signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis in mice. Inflammation. 2014;37(5):1588–98.
Cheng S, Zhou F, Xu Y, Liu X, Zhang Y, Gu M, et al. Geniposide regulates the miR-101/MKP-1/p38 pathway and alleviates atherosclerosis inflammatory injury in ApoE-/- mice. Immunobiology. 2019;224(2):296–306.
Lo Sasso G, Schlage WK, Boué S, Veljkovic E, Peitsch MC, Hoeng J. The Apoe(-/-) mouse model: a suitable model to study cardiovascular and respiratory diseases in the context of cigarette smoke exposure and harm reduction. J Transl Med. 2016;14(1):146.
Chang H-H, Ho C-H, Tomita B, Silva AA, Sparks JA, Karlson EW, et al. Utilizing a PTPN22 gene signature to predict response to targeted therapies in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2019;101:121–30.
Carmona FD, Martín J. The potential of PTPN22 as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018;22(10):879–91.
Clark AR, Ohlmeyer M. Protein phosphatase 2A as a therapeutic target in inflammation and neurodegeneration. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;201:181–201.
Lukas M, Drastich P, Konecny M, Gionchetti P, Urban O, Cantoni F, et al. Exogenous alkaline phosphatase for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010;16(7):1180–6.
Mizutani T, Fukushi S, Saijo M, Kurane I, Morikawa S. Phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and its downstream targets in SARS coronavirus-infected cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;319(4):1228–34.
Liao Y, Wang X, Huang M, Tam JP, Liu DX. Regulation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and dual-specificity phosphatase 1 feedback loop modulates the induction of interleukin 6 and 8 in cells infected with coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Virology. 2011;420(2):106–16.
Astuti I, Ysrafil. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): an overview of viral structure and host response. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020;14(4):407–12.
Sohn KM, Lee SG, Kim HJ, Cheon S, Jeong H, Lee J, et al. COVID-19 patients upregulate toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammatory signaling that mimics bacterial sepsis. J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(38):e343.
Bastard P, Rosen LB, Zhang Q, Michailidis E, Hoffmann H-H, Zhang Y, et al. Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science. 2020;370(6515):eabd4585.
van der Made CI, Simons A, Schuurs-Hoeijmakers J, van den Heuvel G, Mantere T, Kersten S, et al. Presence of genetic variants among young men with severe COVID-19. JAMA. 2020;324:663–73.
Lazo JS, McQueeney KE, Sharlow ER. New approaches to difficult drug targets: the phosphatase story. SLAS Discov. 2017;1:2472555217721142.
Stanford SM, Bottini N. Targeting tyrosine phosphatases: time to end the stigma. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017;38(6):524–40.
Acknowledgements
We apologize to our colleagues whose relevant work could not be cited because of space constraints. The figures have been created with Biorender.com.
Funding
Nathalie Rivard and Claude Asselin are members of the FRQS-Funded Centre de Recherche du CHUS. Nathalie Rivard is a recipient of a Canadian Research Chair in colorectal cancer and inflammatory cell signaling. This research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Grant to Nathalie Rivard (MOP 119593).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, V.L.; writing—review and editing, V.L., C.A. and N.R.; figures, A.C.-B.; supervision and planning, N.R. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All the authors make the statement that there is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Lannoy, V., Côté-Biron, A., Asselin, C. et al. Phosphatases in toll-like receptors signaling: the unfairly-forgotten. Cell Commun Signal 19, 10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-020-00693-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-020-00693-9