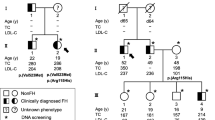
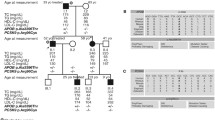
Abstract
Background
Large deletions and duplications within the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene make up approximately 10% of LDLR pathogenic variants found in Czech patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. The goal of this study was to test the hypothesis that all probands with each rearrangement share identical breakpoints inherited from a common ancestor and to determine the role of Alu repetitive elements in the generation of these rearrangements.
Methods
The breakpoint sequence was determined by PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing. To confirm the breakpoint position, an NGS analysis was performed. Haplotype analysis of common LDLR variants was performed using PCR and Sanger sequencing.
Results
The breakpoints of 8 rearrangements within the LDLR gene were analysed, including the four most common LDLR rearrangements in the Czech population (number of probands ranging from 8 to 28), and four less common rearrangements (1–4 probands). Probands with a specific rearrangement shared identical breakpoint positions and haplotypes associated with the rearrangement, suggesting a shared origin from a common ancestor. All breakpoints except for one were located inside an Alu element. In 6 out of 8 breakpoints, there was high homology (≥ 70%) between the two Alu repeats in which the break occurred.
Conclusions
The most common rearrangements of the LDLR gene in the Czech population likely arose from one mutational event. Alu elements likely played a role in the generation of the majority of rearrangements inside the LDLR gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is one of the most common autosomal dominant disorders. The worldwide prevalence of FH in the general population is around 1:300 for heterozygous FH and around 1:400,000 for homozygous FH [1, 2]. FH is characterized by elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, leading to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease [3]. Untreated males with clinically diagnosed heterozygous FH have a 50% risk of myocardial infarction by 50 years of age, whereas untreated females have a 12% chance by age 50 and a 30% chance by age 60 [4, 5].
FH can be caused by either a single variant (heterozygous FH) or two variants (homozygous FH) in FH-associated genes, with homozygous FH having a more severe phenotype [6]. The three genes most commonly associated with FH are the LDL receptor (LDLR), apolipoprotein B (APOB) or proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) (reviewed in [7]). During genetic testing of Czech patients with a clinical diagnosis of FH, a pathogenic variant in the LDLR gene was found in 22% of patients, while 11% of patients carried an APOB variant, and the rest remained without a known causal variant [8].
The LDLR gene was the first gene associated with FH, and its variants remain the most common cause of FH [8,9,10]. The LDLR gene is located on chromosome 19, spans 45 kbps and contains 18 exons. It encodes a protein that is 860 amino acids long, with the first 21 amino acids making up the signal sequence that is cleaved off during processing, giving rise to a mature protein of 839 amino acids [11]. The LDLR gene contains 98 Alu repeats, out of which 3 are located in the 3’UTR, while the rest reside inside introns [12].
Large rearrangements of the LDLR gene are a relatively common cause of FH [8], possibly due to Alu-mediated rearrangements caused by the high density of Alu elements inside LDLR introns.
Alu elements are the most common sequence elements in the human genome, numbering over one million copies and making up 11% of the human genome [13]. Alu elements are transposable elements belonging to the class of short interspersed nuclear elements (SINE). The name Alu is based on the presence of an AluI restriction site within these elements [14]. The elements were originally derived from 7SL RNA [15].
The typical structure of an Alu element is shown in Fig. 1. Alu elements can be divided into three major subfamilies: the oldest AluJ, younger AluS and the youngest AluY. The subfamilies can be distinguished based on the presence of diagnostic variants. Individual Alu elements may differ from each other both by subfamily-specific variants (which are shared by all Alu elements belonging to a specific subfamily due to common origin from the same ancestral Alu) and by random variants, which are specific to the individual element (since these variants started accumulating after the individual Alu element had integrated into the genome). Youngest Alus have the largest number of subfamily-specific variants and the lowest number of random variants (reviewed in [16]).
The structure of an Alu element. One Alu element is about 300 bps long and consists of two monomers separated by a short A-rich sequence. The left monomer contains a bipartite RNA polymerase III promoter, composed of an A and a B box. The right monomer contains an insertion, rendering it 31 bps longer than the left monomer, and ends with a poly-A tail [16]
Alu elements have been implicated in the generation of genomic rearrangements [11, 17, 18]. Recombination between two Alus can generate a new chimeric Alu element, with the breakpoint located within a microhomology region common to both Alus. In this publication, the word „breakpoint “ is used to describe the region of microhomology in which the break occurred because the exact location of the break within this microhomology region cannot be determined. Alu-mediated rearrangements were previously thought to arise mainly through non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR) or non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) [19]. Recently, other mechanisms have been suggested for the generation of Alu-mediated rearrangements, such as microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ), fork stalling and template switching/microhomology-mediated break-induced replication (FoSTeS/MMBIR), single-strand annealing (SSA), and others [20,21,22].
In the present study, we characterized the breakpoints of eight rearrangements of the LDLR gene found in the Czech population, in some cases correcting the breakpoints published in a previous study [23]. Additionally, we characterized the breakpoints of all probands carrying the same rearrangement (duplication or deletion of the same exons as characterized by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA)) to explore the hypothesis that all Czech probands with each rearrangement share the same breakpoint inherited from a common ancestor.
Methods
Patients
Patients have been identified through the Czech MedPed project (Make Early Diagnosis to Prevent Early Deaths), which aims to identify and treat patients with FH in the Czech Republic [24]. As of 4th March 2022, there have been 8,918 patients with FH (6,753 unrelated families) in the Czech MedPed datase.
Patients included in this study carried a large rearrangement in the LDLR gene, which had been previously determined by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) analysis as part of their diagnosis [8, 23, 25]. Large deletions and duplications make up approximately 10% of LDLR pathogenic variants found in Czech patients [8]. Some of these large rearrangements number among the most common pathogenic variants found in Czech FH patients, such as deletion of exons 9–14 or duplication of exons 2–6, which have been found in 28 and 26 independent families, respectively, making them the 6th and 7th most common pathogenic variants in Czech FH patients.
For each studied rearrangement, all known Czech families carrying a specific rearrangement were analysed, apart from one proband with duplication of exons 2–6, whose DNA was not available for analysis. The numbers of analysed families can be found in Table 1. Promoter_exon2del and exon3_12del were not included in the common ancestry analysis because these rearrangements have only one known proband.
Breakpoint analysis
Breakpoint junction sequences were determined by PCR or nested PCR and subsequent Sanger sequencing. Nested PCR was used in cases where simple PCR did not yield a specific product and it was not possible to design new primers in close proximity of the presumed breakpoint due to the high density of repeats inside LDLR introns. Sequences were amplified by Taq polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific) using primers indicated in Supplementary Table S1 within Additional file 1, and sequenced using Big Dye Terminator v1.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) followed by analysis on 3130xl Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems). To determine the breakpoint location, sequences obtained by Sanger sequencing of the breakpoint region were compared to the reference sequence NG_009060.1 or analysed using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) of the NCBI [26]. The description of variants is based on the reference sequence NG_009060.1(NM_000527.4). Variants are described in accordance with the recommendations of the Human Genome Variation Society (v20.05).
Primers were designed so that only the allele with a deletion or duplication and not the WT allele gave a product. The specificity of primers was confirmed by including negative control DNA – DNA from patients that had no rearrangements of the LDLR gene according to a previous MLPA analysis [8, 23, 25]. Agarose gel electrophoresis of the control PCR products gave no product while the DNA of patients with the duplication gave one specific band on the gel. Primers were initially designed to flank the breakpoints published in a previous study [23]. In some cases, primers identical to those published in a previous study were used [23]. In the case of exon3_12del, the primer design was based on the approximate location of the breakpoint as determined by CNV analysis of NGS data.
Haplotype analysis
To determine if the rearrangements were inherited from a common ancestor, we aimed to determine the haplotype associated with a specific rearrangement in different families carrying the same rearrangement. Two strategies were used to obtain a haplotype. First, the sequences obtained during sequence analysis of the breakpoints were searched for sequence variants in close proximity of the breakpoint in all families (see Breakpoint analysis). Because the primers were designed to only amplify the allele carrying the rearrangement, all observed variants are in cis with the rearrangement.
Secondly, common variants found in the LDLR gene were genotyped in probands and their relatives (if available). Sanger sequencing was used to genotype polymorphisms commonly found within or near LDLR exons. Variants for genotyping were chosen based on their frequency in the European non-Finnish population according to gnomAD v4.0.0. The population frequency of chosen variants was between 0.063 and 0.75. A list of chosen variants and their population frequencies can be found in Table 2. Primers used for the amplification of genotyped regions can be found in Supplementary Table S2 within Additional file 1.
Together, the variants found in close proximity of breakpoints and common variants further away in the LDLR gene were used to create a haplotype.
Analysis of repeats
Repetitive sequences were identified using RepeatMasker version open-4.0.9 [27]. To determine the sequence identity of Alu elements present at both sides of the breakpoint junctions, Emboss NEEDLE was used for pairwise global alignment of the two repeats surrounding the breakpoints [28].
NGS
To narrow down the breakpoint position, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of next-generation sequencing (NGS) data was performed. The sequencing library was prepared using the method of Hybridization Capture-Based Target Enrichment for NGS (Roche), following KAPA HyperCap Workflow v3.0. Genomic DNA was enzymatically fragmented using the KAPA HyperPlus kit (Roche), ligated to KAPA Universal Adapters (Roche). The sample library was amplified by PCR using KAPA UDI Primer Mixes (Roche) and KAPA Hifi HotStart Ready Mix (Roche), purified using KAPA HyperCapture Bead kit (Roche), and hybridized to KAPA Hyper Choice MAX 3 Mb probes (Roche), PCR amplified and purified using KAPA HyperCapture Bead kit (Roche). Enriched samples were sequenced on the NextSeq sequencer (Illumina).
Data analysis was performed in QIAGEN CLC Genomics Workbench v.21.0.5. CNV regions within NGS data were identified by applying a threshold to adjusted fold-change. The threshold used was < -1.38 fold-change (adjusted) for a deletion and > 1.29 fold-change (adjusted) for a duplication. These in-house thresholds have previously been determined by analysis of control samples by the same method. The control samples were DNA samples in which a deletion or duplication had previously been identified by MLPA analysis. Thresholds were set as the minimum/maximum fold-change (adjusted) identified in a region that has been determined to be deleted/duplicated (respectively) by MLPA.
Analysis in QIAGEN CLC Genomics Workbench only allowed for approximate determination of the breakpoint region. Next, we attempted to identify the exact location of the breakpoint by visually examining the data in Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) v.2.5.0 [29].
Results
Breakpoints of LDLR rearrangements in Czech FH patients have already been published in 2010 by Goldmann et al. [23]. The goal of this study was to analyse the breakpoints in all known families with these rearrangements available 10 years later in order to determine whether all Czech families share the same breakpoint. A secondary goal was to analyse the breakpoint region for the presence of Alu repeats to determine the role of these repetitive elements in the generation of rearrangements within the LDLR gene.
Breakpoint characterization
To determine the breakpoint position of selected rearrangements of the LDLR gene, PCR or nested PCR and Sanger sequencing were used.
The studied rearrangements included 5 deletions and 3 duplications within the LDLR gene. Among these were the four most common LDLR rearrangements in the Czech population (number of probands ranging from 8 to 28), and four less common rearrangements (1–4 probands) (Table 1). The size of analysed rearrangements ranged between 6 and 17 kbps. All of the breakpoints occurred within the introns of the LDLR gene, except for duplication of exons 16–18, which involved the 3’UTR. The breakpoint position and size of the rearrangement determined in this study is shown in Table 3, while the sequence is shown in Additional file 2. For each of the analysed rearrangements, all Czech probands with a specific rearrangement shared identical breakpoint positions. The breakpoint of an Alu-Alu rearrangement is typically found inside a microhomology region – a region with identical sequence in both Alus surrounding the breakpoint. The exact position of a breakpoint within this microhomology region cannot be determined.
Haplotype analysis
To determine if each rearrangement was inherited from a common ancestor in all patients with a specific rearrangement in the Czech population, the haplotypes associated with specific rearrangements were analysed in different families carrying the same rearrangement.
First, the sequences obtained during Sanger sequencing analysis of the breakpoints were searched for sequence variants within a few hundred bps away of the breakpoint. Two rearrangements were found in only one proband, and thus were excluded from the haplotype analysis. Six rearrangements were found in more than one family. In 5 out of these 6 rearrangements, Sanger sequencing revealed at least one sequence variant in close proximity of the breakpoint (Table 4; Additional file 2). Two of these variants were unique and specific to a certain rearrangement, while the others were common in the population. For each of these 5 rearrangements, the variants were identical in all analysed families carrying the same rearrangement.
Notably, all 28 probands with exon9_14del carried a novel, previously unreported variant NG_009060.1(NM_000527.4):c.1186+684A>C, which was situated 11 bps away from the breakpoint (11 bps from the 5’ end of the microhomology region). All probands with exon9_15del carried a rare variant c.1187-269_1187-266TG[4], which has not been reported in gnomAD v4.0.0, but it has been reported as a rare variant in 14KJPN, 8.3KJPN and Korea1K databases in Japanese and Korean population, respectively (see rs1555805065). In four rearrangements (exon2_6dup, exon5_10del, exon9_15del, exon16_18dup), all probands carried one or two identical variants, that were common in European non-Finnish population according to the gnomAD database. In both families with exon4_8dup, no variant was found in the 256 bps long analysed region around the breakpoint.
In addition to variants that were found in close proximity of breakpoints, common LDLR variants situated further away from the breakpoints were haplotyped. A list of common variants used for haplotyping can be found in Table 2.
The resulting haplotype is a combination of variants found in close proximity of the breakpoint, and frequent variants in or near LDLR exons. The haplotype was obtained in 20 out of 26 families with exon2_6dup, 2 out of 2 families with exon4_8dup, 4 out of 4 families with exon5_10del, 16 out of 28 families with exon9_14del, 8 out of 11 families with exon9_15del, and 5 out of 8 families with exon16_18dup. All the analysed families with a specific rearrangement had the same haplotype associated with the rearrangement. The obtained haplotypes are shown in Table 5.
Analysis of Alu repeats
To assess the role of Alu repeats in the generation of the rearrangements, the position of repeats within the LDLR gene was annotated using RepeatMasker. If the break had occurred in an Alu repeat on both sides of the breakpoint, the sequence identity of the two repeats in which the break occurred was determined using the global alignment tool Emboss Needle.
The characteristics of repeats present at the breakpoints are shown in Table 6 and Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of rearrangements and repetitive elements present at breakpoints. The figure shows the sizes of studied duplications (top part) and deletions (bottom part), along with the character of repeats on each side of the breakpoint. The rearrangements are shown relative to the whole LDLR gene, which is shown at the top of the figure. In the LDLR schematic, exons are denoted by a vertical line, while the horizontal line represents introns. The orientation of coloured triangles denotes the orientation of Alu repeats at breakpoints, while their colour denotes an Alu repeat subfamily (as determined by RepeatMasker)
All breakpoints were located inside an Alu element except for one. The duplication of exons 4–8 joined together an Alu element with Mer83, which is an LTR retrotransposon without sequence homology to Alu repeats. In 3 out of 8 rearrangements, the recombination was mediated by a pair of Alu elements belonging to the same subfamily.
In 6 out of 8 rearrangements (2 duplications and 4 deletions), there was high homology (≥ 70%) between the two Alu repeats in which the break occurred. In these cases, the two repeats were in the same orientation and the break occurred in a microhomology region at the same position within the two repeats, creating a new chimeric Alu element. The average percent identity between these 6 pairs of Alu repeats was 83%, ranging from 70 to 91% (Table 6).
In 2 remaining rearrangements (1 duplication and 1 deletion) there was low homology (35%) between repeats surrounding the breakpoint. In the case of exon4_8dup, the recombination occurred between an Alu element and a non-Alu repetitive element Mer83. In the case of exon5_10del, the two Alu repeats flanking the breakpoint were in opposite orientations.
In the case of deletion of exons 9–15, it was hard to compute the percent homology as the breakpoint in intron 8 is inside a partial Alu repeat that has had another Alu repeat inserted inside of it. Taking only the partial Alu surrounding the breakpoint in intron 8 and aligning it with half of the Alu surrounding the breakpoint in intron 15, the homology of these two partial Alus was 70% in a region of 142 bps. The region of (imperfect) homology was shorter than for most other rearrangements reported in this work, but the microhomology (region of perfect homology) was longer.
For all the rearrangements analysed in this publication, the length of the microhomology region present at the breakpoint junction ranged from 0 to 49 bps (Table 6), mean 19.6 bps. The longest microhomology was in the case of exon3_12del (49 bp). The breakpoint of exon16_18dup contained no microhomology.
NGS CNV analysis
To narrow down the breakpoint position or to confirm a breakpoint determined by Sanger sequencing, CNV analysis of NGS data was performed (Table 7).
In most cases, NGS CNV analysis did not allow for accurate determination of breakpoint position, due to the method’s inability to reliably sequence repetitive regions, such as Alu repeats, which are plentiful inside the introns of the LDLR gene. Thus, the NGS analysis was mostly used to narrow down the breakpoint position within the bounds of a few Alu repeats, sometimes only within a certain intron. In a few cases, the exact location of the breakpoint could be determined by visually examining the data in IGV.
For exon5_10del, it was possible to determine the exact position of the breakpoint using solely NGS analysis. The deleted region determined by NGS was identical to the deleted region determined by Sanger sequencing with the exception that the deletion according to NGS did not include the microhomology region surrounding the breakpoint.
All breakpoints determined by Sanger sequencing in this study fell within the borders determined by the NGS CNV analysis.
Discussion
Common ancestry
In the present study, the breakpoints of eight large rearrangements within the LDLR gene were characterized in the Czech population. The main goal of this work was to determine whether all Czech families with the same rearrangement carry identical breakpoints inherited from a common ancestor. Sequence analysis of all Czech families carrying exon2_6dup, exon4_8dup, exon5_10del, exon9_14del, exon9_15del, exon16_18dup was performed (with the exception of one proband of exon2_6dup, whose DNA was not available for analysis). (The remaining two rearrangements whose breakpoint was analysed in this publication, namely exon3_12del and promoter_exon2del, were found only in one proband, and thus excluded from this analysis.) For each of these 6 rearrangements, all Czech families with a specific rearrangement shared identical breakpoint positions and sequences.
There are two possible reasons why the breakpoint was identical in all families with the same rearrangement. This could be the result of either a founder mutation in the Czech population or a recurrent rearrangement mediated by the same microhomology region within the same pair of Alu repeats in each family. However, the possibility of a recurrent rearrangement seems less likely. Even though recurrent rearrangements mediated by the same pair of Alu repeats have been reported by Vocke et al. [30], the breakpoint was not the same in all families with the recurrent Alu-mediated rearrangement. Vocke et al. [30] described several recurrent rearrangements occurring in the same pairs of Alu repeats in the VHL gene. Firstly, they described a “hotspot” Alu repeat‐based deletion of exon 3 of the VHL gene. Among 12 families with recombination occurring between the same pair of Alu-repeats, there were 4 distinct (distinguishable) breakpoints. In addition, they described four families with a deletion of exon 2, in which case all four families had a deletion occurring between the same pair of Alu repeats, but different breakpoint positions within these repeats. Three other VHL deletions were each found in two families, with the rearrangement occurring in the same pair of Alu repeats in both families, but with a different breakpoint.
In contrast, among our patients, there were relatively large sets of families with the same breakpoint. Whereas 12 families described in Vocke et al. [30] had four different breakpoints within the same pair of Alu repeats, the current study included as many as 28 families with exon9_14dup and 26 families with exon2_6dup that shared exactly the same breakpoint. If this was a case of a recurrent rearrangement, it seems likely that at least some of these families would have a different breakpoint.
To obtain further evidence for the common origin of these rearrangements in the Czech population, haplotypes associated with the rearrangements in multiple families carrying the same rearrangement were determined, and the results showed that families with the same rearrangement shared the same haplotype.
Based on these findings, it is likely that in all Czech families with duplication of exons 2–6, exons 4–8 and exons 16–18, and the deletion of exons 5–10, 9–14 and 9–15, the rearrangement comes from a common ancestor.
There is also a concerning possibility that a PCR artefact could have arisen during our analysis. This could potentially explain why the resulting breakpoint was the same in all probands with the same rearrangement. However, the fact that all analysed families also had the same haplotype associated with the rearrangement makes this option less likely.
The role of Alu repeats in the generation of rearrangements
For 7 out of 8 breakpoints, the rearrangement occurred between two Alu repeats. To determine the role of Alu repeats in the generation of these rearrangements, the percent identity of the two Alu repeats was taken into account, as well as the fact whether the break has occurred in the same position in the two repeats or not.
In 6 out of 8 rearrangements (2 duplications and 4 deletions), there was high homology (≥ 70%) between the two Alu repeats in which the break occurred. In these cases, the two repeats were in the same orientation and the break occurred in a microhomology region at the same position within the two repeats, creating a new chimeric Alu element. Based on these observations, Alu elements likely played a role in the generation of these 6 rearrangements. In 3 out of these 6 rearrangements, the recombination was mediated by a pair of Alu elements belonging to the same subfamily.
In the remaining 2 out of 8 rearrangements, there was low homology (35%) between repeats surrounding the breakpoint. The role of Alu repeats in the generation of these rearrangements is uncertain.
Only in one out of 8 rearrangements, the break did not occur in two Alu repeats. In the case of exon4_8dup, one break occurred within an AluSx repeat inside intron 3, and the other one occurred within a short fragment of Mer83 inside intron 8. Mer83 belongs to the class of LTR retrotransposons without sequence homology to Alu repeats. This Mer83 fragment was located between an AluSx repeat and a Tigger4a repetitive element, as identified by RepeatMasker version open-4.0.9. Although the sequence homology of the two repeats in which the break occurred (AluSx and Mer83) was quite low (35%), there was another AluSx element 53 bp upstream of the breakpoint, which was 75.3% identical to the breakpoint Alu in intron 3. There is a possibility that these two Alus could have aligned, contributing to the generation of the rearrangement. The rearrangement could have been initiated by the pairing of two Alu repeats, even if the resulting break occurred elsewhere [22]. Alternatively, the break could have been generated in an Alu-independent manner, and the position of one of the breaks within an Alu element could have been a coincidence due to the high density of Alu repeats within the introns of the LDLR gene.
In the case of exon5_10del, the break occurred at the 3’ end of two Alu repeats, which were oriented in opposite directions. The homology of the two repeats in this orientation was only 35%. If one of the repeats is reverse-complemented, the homology is 62%, which is still lower than other Alu pairs in this study. Directly upstream of the breakpoint-Alu in intron 4 is another Alu repeat, which could potentially pair with the breakpoint-Alu in intron 11. However, the homology between these two repeats is only 33%. In conclusion, there does not seem to be any significant homology in the close vicinity of this breakpoint. This deletion probably occurred independently of Alu repeats.
In conclusion, Alu elements likely played a role in the generation of the majority of rearrangements within the LDLR gene, but not necessarily all of them.
Correction of a previous study
The breakpoints of these rearrangements have already been analysed on a smaller number of Czech probands by Goldmann et al. [23]. In the current study, we analysed the breakpoints of these rearrangements with a larger number of probands from the Czech population. We have also made the breakpoints characterised in Goldmann et al. [23] more accurate (Table 3). In 3 cases, the position of the breakpoint differed from that published by Goldmann et al. by several hundred bps (656, 790 and 1044 bps in exon16_18dup, exon3_12del and exon2_6dup, respectively). In one case, the breakpoint position determined in this study differed from the previous study by only a few bps (exon4_8 dup). For exon16_18 dup, the new breakpoint position determined in the current study was also supported by our CNV analysis of NGS data. NGS analysis could narrow down the breakpoint position to a region of 465 bps. This region included the new breakpoint position, but not the previous one. The possible causes of the discrepancies between this study and the previous study are discussed in Additional file 3.
Strengths and limitations
The strength of this study lies in having access to DNA samples from all the Czech FH patients thanks to the MedPed project. This allowed us to analyse each rearrangement in all the known probands in the Czech population in order to gain new insights into the spread and maintenance of aberrant alleles in the population.
The main limitation of the breakpoint characterization was the inability to explain why the breakpoint of exon2_6dup was different from the previous study [23]. Although other differences in breakpoint placement between these two studies could be explained (see Additional file 3), the source of the discrepancy in the breakpoint placement for exon2_6dup remains elusive. We hypothesised that this discrepancy could have been caused by a PCR artefact but we were unfortunately unable to provide experimental evidence of this artefact.
The haplotype analysis had several limitations. For some rearrangements, the haplotype analysis could not be completed in all families because some probands had no relatives available for analysis. However, a partial haplotype was obtained for families without a full haplotype, and the partial haplotype was consistent with the haplotype determined in other families with the same rearrangement. Table 4 shows a list of variants that were found in cis in close proximity of the breakpoint, and those variants were identical in all probands with the same rearrangement.
Another limitation is the fact that the haplotype analysis included a relatively low number of variants, some of which had low allele frequency in the European non-Finnish population, notably c.190+56G>A with a frequency of 0.06341 (Table 2). The conclusions of the study could be strengthened by including more variants in the haplotype analysis.
Conclusions
The goal of the present study was to analyse the breakpoints of several large rearrangements inside the LDLR gene. Sequencing the breakpoints in all Czech probands with each rearrangement has shown that the breakpoint of each rearrangement was the same in all Czech families. In addition, families with a certain rearrangement also had the same haplotype associated with the rearrangement. This result points to the likelihood that these rearrangements originate from a common ancestor, giving us a deeper insight into the genetics of FH in the Czech population.
The finding that Czech patients with a specific LDLR rearrangement typically have a specific breakpoint could streamline cascade testing in families of Czech FH patients. Nowadays, the primary method used for detecting large rearrangements in the LDLR gene is an NGS analysis or MLPA. However, the use of such cost-intensive methods may not be necessary to confirm the presence of the rearrangement in relatives of patients carrying a known rearrangement. This study opens up an opportunity to use PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing of breakpoints as a time- and cost-effective alternative to NGS or MLPA for confirmation of a specific rearrangement in the Czech population. Primers supplemented in this study can be readily used for this purpose.
Additionally, the breakpoint sequences were analysed for the presence of Alu repeats, revealing that most rearrangements had homologous Alu repeats flanking the breakpoint. In conclusion, Alu repeats could have had a role in the generation of most of these rearrangements.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files, with the exception of raw NGS data, which contain patients’ genomic data with unique variants, for which it may not be possible to guarantee complete anonymity. The sequences surrounding breakpoints that were obtained by Sanger sequencing are included in Additional file 2.
Abbreviations
- APOB:
-
Apolipoprotein B
- BLAST:
-
Basic local alignment search tool
- CNV:
-
Copy number variation
- FH:
-
Familial hypercholesterolemia
- IGV:
-
Integrative Genomics Viewer
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- LDLR:
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor
- MLPA:
-
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification
- NAHR:
-
Non-allelic homologous recombination
- NGS:
-
Next-generation sequencing
- NHEJ:
-
Non-homologous end joining
- PCSK9:
-
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9
- SINE:
-
Short interspersed nuclear elements
- MedPed project:
-
Make Early Diagnosis to Prevent Early Deaths
References
Beheshti SO, Madsen CM, Varbo A, Nordestgaard BG. Worldwide Prevalence of Familial Hypercholesterolemia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75(20):2553–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2020.03.057.
Hu P, Dharmayat KI, Stevens CAT, Sharabiani MTA, Jones RS, Watts GF, Genest J, Ray KK, Vallejo-Vaz AJ. Prevalence of Familial Hypercholesterolemia Among the General Population and Patients With Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Circulation. 2020;141(22):1742–59. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044795.
Yu Y, Chen L, Zhang H, Fu Z, Liu Q, Zhao H, Liu Y, Chen Y. Association Between Familial Hypercholesterolemia and Risk of Cardiovascular Events and Death in Different Cohorts A Meta-Analysis of 1.1 Million Subjects Front Cardiovasc Med. 20229860196 doi https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.860196
Slack J. Risks of ischaemic heart-disease in familial hyperlipoproteinaemic states. Lancet. 1969;2(7635):1380–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90930-1. (PMID: 4188273).
Stone NJ, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS, Verter J. Coronary artery disease in 116 kindred with familial type II hyperlipoproteinemia. Circulation. 1974;49(3):476–88. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.49.3.476.
Cuchel M, Raal FJ, Hegele RA, Al-Rasadi K, Arca M, Averna M, et al. 2023 Update on European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Statement on Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolaemia: new treatments and clinical guidance. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(25):2277–91. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehad197.
McGowan MP, Hosseini Dehkordi SH, Moriarty PM, Duell PB. Diagnosis and Treatment of Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8(24):e013225. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.119.013225.
Tichý L, Fajkusová L, Zapletalová P, Schwarzová L, Vrablík M, Freiberger T. Molecular genetic background of an autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia in the Czech Republic. Physiol Res. 2017;66(Suppl 1):S47–54. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.933587.
Bertolini S, Pisciotta L, Rabacchi C, Cefalù AB, Noto D, Fasano T, Signori A, Fresa R, Averna M, Calandra S. Spectrum of mutations and phenotypic expression in patients with autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia identified in Italy. Atherosclerosis. 2013;227(2):342–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.01.007.
van der Graaf A, Avis HJ, Kusters DM, Vissers MN, Hutten BA, Defesche JC, Huijgen R, Fouchier SW, Wijburg FA, Kastelein JJ, Wiegman A. Molecular basis of autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia: assessment in a large cohort of hypercholesterolemic children. Circulation. 2011;123(11):1167–73. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.979450.
Hobbs HH, Russell DW, Brown MS, Goldstein JL. The LDL receptor locus in familial hypercholesterolemia: mutational analysis of a membrane protein. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:133–70. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001025.
Amsellem S, Briffaut D, Carrié A, Rabès JP, Girardet JP, Fredenrich A, Moulin P, Krempf M, Reznik Y, Vialettes B, de Gennes JL, Brukert E, Benlian P. Intronic mutations outside of Alu-repeat-rich domains of the LDL receptor gene are a cause of familial hypercholesterolemia. Hum Genet. 2002;111(6):501–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-002-0813-4.
Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, et al. International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409(6846):860–921. https://doi.org/10.1038/35057062. Erratum in: Nature 2001;412(6846):565. Erratum in: Nature 2001;411(6838):720. Szustakowki, J [corrected to Szustakowski, J].
Houck CM, Rinehart FP, Schmid CW. A ubiquitous family of repeated DNA sequences in the human genome. J Mol Biol. 1979;132(3):289–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(79)90261-4.
Ullu E, Tschudi C. Alu sequences are processed 7SL RNA genes. Nature. 1984;312(5990):171–2. https://doi.org/10.1038/312171a0.
Batzer MA, Deininger PL. Alu repeats and human genomic diversity. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3(5):370–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg798.
Lehrman MA, Schneider WJ, Südhof TC, Brown MS, Goldstein JL, Russell DW. Mutation in LDL receptor: Alu-Alu recombination deletes exons encoding transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Science. 1985;227(4683):140–6. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3155573.
Gu W, Zhang F, Lupski JR. Mechanisms for human genomic rearrangements. Pathogenetics. 2008;1(1):4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-8417-1-4.
de Smith AJ, Walters RG, Coin LJ, Steinfeld I, Yakhini Z, Sladek R, Froguel P, Blakemore AI. Small deletion variants have stable breakpoints commonly associated with alu elements. PLoS ONE. 2008;3(8):e3104. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003104.
Boone PM, Yuan B, Campbell IM, Scull JC, Withers MA, Baggett BC, Beck CR, Shaw CJ, Stankiewicz P, Moretti P, Goodwin WE, Hein N, Fink JK, Seong MW, Seo SH, Park SS, Karbassi ID, Batish SD, Ordóñez-Ugalde A, Quintáns B, Sobrido MJ, Stemmler S, Lupski JR. The Alu-rich genomic architecture of SPAST predisposes to diverse and functionally distinct disease-associated CNV alleles. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;95(2):143–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.06.014.
Gu S, Yuan B, Campbell IM, Beck CR, Carvalho CM, Nagamani SC, Erez A, Patel A, Bacino CA, Shaw CA, Stankiewicz P, Cheung SW, Bi W, Lupski JR. Alu-mediated diverse and complex pathogenic copy-number variants within human chromosome 17 at p13.3. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(14):4061–77. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddv146
Morales ME, White TB, Streva VA, DeFreece CB, Hedges DJ, Deininger PL. The contribution of alu elements to mutagenic DNA double-strand break repair. PLoS Genet. 2015;11(3):e1005016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005016.
Goldmann R, Tichý L, Freiberger T, Zapletalová P, Letocha O, Soska V, Fajkus J, Fajkusová L. Genomic characterization of large rearrangements of the LDLR gene in Czech patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. BMC Med Genet. 2010;11:115. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-11-115.
Vrablík M, Vaclová M, Tichý L, Soška V, Bláha V, Fajkusová L, Češka R, Šatný M, Freiberger T. Familial hypercholesterolemia in the Czech Republic: more than 17 years of systematic screening within the MedPed project. Physiol Res. 2017;66(Suppl 1):S1–9. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.933600.
Tichý L, Freiberger T, Zapletalová P, Soška V, Ravčuková B, Fajkusová L. The molecular basis of familial hypercholesterolemia in the Czech Republic: spectrum of LDLR mutations and genotype-phenotype correlations. Atherosclerosis. 2012;223(2):401–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.05.014.
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215(3):403–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2.
Smit AFA, Hubley R, Green P. RepeatMasker. https://www.repeatmasker.org/cgi-bin/WEBRepeatMasker [Accessed 25 October2020]
Madeira F, Park YM, Lee J, Buso N, Gur T, Madhusoodanan N, Basutkar P, Tivey ARN, Potter SC, Finn RD, Lopez R. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W636–41. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz268.
Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdóttir H, Winckler W, Guttman M, Lander ES, Getz G, Mesirov JP. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(1):24–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1754.
Vocke CD, Ricketts CJ, Schmidt LS, Ball MW, Middelton LA, Zbar B, Linehan WM. Comprehensive characterization of Alu-mediated breakpoints in germline VHL gene deletions and rearrangements in patients from 71 VHL families. Hum Mutat. 2021;42(5):520–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.2419431.
Konečná K, Tichý L, Freiberger T. Common rearrangements of the LDLR gene in the Czech population likely arise from one mutational event. Poster session presented at European Human Genetics Conference; June 11–14 2022; Vienna, Austria. Abstracts from the 55th European Society of Human Genetics (ESHG) Conference: Hybrid Posters. Eur J Hum Genet. 2023;31:412–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-023-01338-4.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank physicians participating in the Czech MedPed project for providing us with their patients’ blood samples and clinical and laboratory data. A preliminary version of these results has been presented as a poster at the European Human Genetics Conference 2022 [31] .
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Health, Czech Republic [grant number NU20-02–00261], and by the project National Institute for Research of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases, Programme EXCELES [ID Project No. LX22NPO5104] funded by the European Union – Next Generation EU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.K. performed Sanger sequencing analysis and wrote the manuscript. L.T. contributed to the conception and design of the study. T.F. coordinated collection of patients’ data and cascade testing in families. P.Z. performed NGS analysis. L.T. and T.F. contributed to revisions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All patients provided written informed consent with their participation in the study. The study was approved by the ethics committee of The University Hospital Brno (reference number 09–120619/EK).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
Primers – Primers used for amplification and Sanger sequencing.
Additional file 2
. Sequences – Sequences obtained by sequencing the breakpoint region of large rearrangements of the LDLR gene.
Additional file 3
. This file includes a more detailed discussion concerning the discrepancies between the breakpoint positions reported in this study and a previous study [23].
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Konečná, K., Zapletalová, P., Freiberger, T. et al. LDLR gene rearrangements in Czech FH patients likely arise from one mutational event. Lipids Health Dis 23, 36 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-024-02013-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-024-02013-3