Abstract
Background
We have previously shown that a combination of glucosyl hesperidin (G-hesperidin) plus caffeine reduces accumulation of body fat, whereas G-hesperidin or caffeine alone shows little effect on high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice. The aim of this study is to evaluate the anti-obesity effect of G-hesperidin plus caffeine on body fat and serum TG in healthy subjects with moderately high body mass index (BMI) and serum TG. Since we considered that there are individual differences in caffeine sensitivity, we conducted dose-finding study of caffeine combined with G-hesperidin.
Methods
Seventy-five healthy subjects with moderately high BMI (24–30 kg/m2) and serum TG (100–250 mg/dl) were divided and assigned to 12-week intervention with daily intakes of 500 mg of G-hesperidin with or without 25, 50, or 75 mg of caffeine, or placebo in a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled design .
Results
After intervention, decreases in abdominal fat area (AFA), especially subcutaneous fat area (SFA), were significantly greater in the G-hesperidin with 50-mg caffeine group (AFA:-8.4 ± 21.9 v.s. 16.3 ± 34.1 cm2; p < 0.05, SFA: -9.3 ± 17.1 v.s. 11.2 ± 18.3 cm2; p < 0.01) and in the G-hesperidin with 75-mg caffeine group (AFA:-17.0 ± 31.4 v.s. 16.3 ± 34.1 cm2; p < 0.01, SFA: -12.4 ± 18.7 v.s. 11.2 ± 18.3 cm2; p < 0.01) than in the placebo group. Fat-decreasing effects of G-hesperidin were enhanced dose-dependently by caffeine addition. BMI decreases were significantly greater in the G-hesperidin with 75-mg caffeine group than in the placebo group (-0.56 ± 0.74 v.s. -0.02 ± 0.58 kg/m2; p < 0.05). G-hesperidin with/without caffeine had no effect on serum TG (p > 0.05 v.s. placebo).
Conclusions
These data suggested that a combination of 500-mg G-hesperidin with 50- or 75-mg caffeine may be useful for the prevention or treatment of obesity.
Trial registration
UMIN Clinical Trials Registry 000019241.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Prevalence of obesity continues to increase worldwide, mainly as a result of changing lifestyles. It is known that visceral fat-type obesity induces type-2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidaemia, hypertension and increases the risk of cardiovascular disease [1–3]. Subcutaneous fat-type obesity is associated with excessive weight gain, and is thought to be the main risk factor for osteoarthritis of the knee [4–7], sleep apnoea [8], and menstrual abnormalities [9–11]. Consequently, research on the prevention and treatment of obesity has been expanded.
Glucosyl hesperidin (G-hesperidin) is synthesized by enzymatic means from hesperidin purified from oranges (Citrus aurantium) and dextrin. Its solubility in water is over 10,000-fold greater than that of hesperidin [12]. G-hesperidin has been reported to reduce serum levels of triglyceride (TG) in animals [13–15] and subjects with hypertriglyceridemia [16, 17]. The mechanism of the TG-lowering effect of G-hesperidin is thought to be down-regulation of the synthesis/secretion of very-low-density lipoprotein in hepatocytes [18], inhibition of lipogenesis, and induction of beta oxidation of fatty acids in high-fat diet-fed rats [15]. Studies have shown that daily intake of G-hesperidin (500 mg) in subjects with a moderately high BMI for 12 weeks decreases abdominal fat significantly during the period, but these decreases do not differ significantly from those of subjects taking a placebo [19]. Therefore, the anti-obesity effect of G-hesperidin is incompletely understood.
Caffeine is one of the most widely consumed dietary components (e.g., tea, coffee) with pharmacological effects and psychostimulant activity. Caffeine has been reported to induce lipolysis of adipocytes [20], fat oxidation [21], energy expenditure [22] and thermogenic responses [23] in humans. However, caffeine has not been shown to reduce body fat in humans, so its effects upon fat metabolism are, in general, considered to be insignificant [24].
We have shown before that combining food ingredients involved in lipid metabolism is useful for the prevention or treatment of obesity. For example, a mixture of thiamine, L-arginine, caffeine, and citric acid has been shown to have an anti-obesity effect in obese mice and humans with a high BMI [25, 26]. We have also shown that a combination of G-hesperidin and caffeine reduces accumulation of body fat through (at least in part) inhibition of hepatic lipogenesis, whereas G-hesperidin or caffeine alone show little effect on high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice [27].
We conducted an exploratory trial to investigate the anti-obesity effects of a combination of G-hesperidin and caffeine in subjects with a BMI of 24–30 kg/m2 and serum levels of TG of 100–250 mg/dl at a potentially effective dose of G-hesperidin (500 mg) [19] with that of caffeine (25, 50, or 75 mg) [26].
Methods
Test samples
Composition of test samples is listed in Table 1. The base tablet comprised lactose, cornstarch, hard starch, and sugar ester. Lactose was substituted by G-hesperidin and caffeine. G-hesperidin was provided from Hayashibara (Okayama, Japan) and contained monoglucosyl hesperidin (>75.0 %) and non-glycosylated hesperidin (<25.0 %), which was confirmed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Caffeine (purity, >98.5 %), extracted from coffee beans, was purchased from Shiratori Pharmaceuticals (Chiba, Japan).
Subjects
A total of 160 Japanese people subjects were evaluated for eligibility. Screening led to a study cohort of 38 men and 37 women (20–65 years) with a moderately high BMI (24–30 kg/m2) and serum level of TG (100–250 mg/dL). Exclusion criteria were patients who had (i) ingested medicines and/or health-foods that might affect obesity and serum levels of TG or (ii) consumed many beverages containing caffeine (e.g. tea, green tea, coffee, and cola). From the results of a pre-questionnaire, daily caffeine consumption of each group was estimated as G-hesperidin, 112 ± 104 mg/day; G-hesperidin with 25-mg caffeine, 111 ± 76 mg/day; G-hesperidin with 50-mg caffeine, 89 ± 86 mg/day; G-hesperidin with 75-mg caffeine, 145 ± 104 mg/day; and placebo, 112 ± 84 mg/day.
Trial design
This trial was carried out from April to August 2013 on subjects at Fukuhara Clinic (Hokkaido, Japan) and complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Review Board of Miyawaki Orthopedic Clinic (Hokkaido, Japan). Procedures were explained fully to subjects. Written informed consent was obtained from each subject before study commencement.
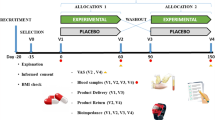
This was a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial comprising periods of pre-checking (1 week), eligibility assessment (4 weeks), intervention (12 weeks), and post-ingestion (4 weeks).
After assessment of eligibility, 75 subjects were allocated into five groups: 500-mg G-hesperidin; 500-mg G-hesperidin with 25-mg caffeine; 500-mg G-hesperidin with 50-mg caffeine; 500-mg G-hesperidin with 75-mg caffeine; placebo (Fig. 1). Allocation was by stratified randomisation based on age, sex, and waist circumference.
Intervention
Subjects ingested test samples as tablets (Table 1) every day for 12 weeks. Time of ingestion of the test sample was not dictated to patients, but was recommended to be in the morning. Ingestion of large quantities of caffeine was prohibited. Ingestion of health-foods that influence levels of TG or cholesterol, or that affect obesity, was prohibited. Use of drugs for prolonged periods and use of drugs that interact with caffeine was banned. However, if a subject had been instructed to use a drug by his/her physician, he/she reported its name, dose, period, and indication. Dieting, drinking excessive amounts of alcohol, and intake of medicines known to affect lipid metabolism was prohibited. Subjects were instructed to maintain their regular lifestyle, in particular in relation to meal size and amount of exercise.
After assessment of eligibility, subjects visited the clinic five times at 4-week intervals. Subjects were prohibited from eating and drinking except for water from 9 pm the day before their visit until all checkups had been completed.
At the day of the visit, subjects underwent a physical examination, and analyses of blood and urine were conducted. The diet record, walking record, and diary were submitted at this time. At week 0 and week 12, the abdominal fat area (AFA) was measured.
Measurement of AFA
Umbilical AFA was measured using a computed tomography system (CT-W450; Hitachi Medical Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) in accordance with the method described by Tokunaga et al. [28]. Total fat area (TFA), visceral fat area (VFA), and subcutaneous fat area (SFA) were computed using Fat Scan™ v3.0 (N2 systems, Osaka, Japan).
Safety assessment
Haematological assessments (counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, haemoglobin, haematocrit, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular haemoglobin, mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration), blood biochemical assessment (total protein, albumin, total bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine transaminase, lactate dehydrogenase, alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transferase, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C), TG, glucose, uric acid, urea nitrogen, creatinine, Na+, K+, Cl–, HbA1c), and urine analyses (specific gravity, pH, protein, sugar, urobilinogen, bilirubin, ketone bodies, occult blood reaction) were conducted at Daiichi-Kishimoto Clinical Laboratory (Sapporo, Japan). Anthropometric measurements were undertaken at Fukuhara Clinic.
Diet and walking surveys
During the intervention period and post-ingestion period, subjects photographed all the meals (including snacks) that they had consumed and recorded their contents in a diet questionnaire for 3 days before the checkup. A nutritionist calculated values of energy, protein, lipid, and carbohydrate using Excel Eiyokun™ v6.0 (Kenpakusha, Tokyo, Japan) from the diet questionnaires and photographs. During the same 3 days as diet recording, the number of steps was documented (using a pedometer) as the exercise volume.
Subject diaries
During the intervention period and post-ingestion period, subjects recorded the time of ingestion of the test sample and subjective symptoms in their diaries.
Statistical analyses
Values are the mean ± SD. Comparison between baseline (week 0) and each time-point in each group was done by the paired t-test with multiple corrections except for AFA. After checking the equality of variance by the Bartlett method, comparisons between groups were analysed by Dunnett’s method in the case of equal variance, and by Steel’s method in the case of unequal variance. Analyses were performed using SAS v9.3 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA), and p < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Baseline characteristics of study participants
Seventy-five subjects completed the study. However, one subject who completed the study with a major violation of the test protocol owing to bereavement was excluded from efficacy analyses. The baseline (week 0) characteristics of 74 subjects are listed in Table 2. No significant difference was observed in baseline (week 0) characteristics between groups. Safety analyses were conducted in all 75 subjects. The study flowchart is shown in Fig. 1.
Ingestion of test samples
Percentage of patients who ingested test samples in the placebo group, 500-mg G-hesperidin group, 500-mg G-hesperidin with 25-mg caffeine group, 500-mg G-hesperidin with 50-mg caffeine group, and 500-mg G-hesperidin with 75-mg caffeine group was 99.4, 99.6, 99.8, 99.8, and 99.8 %, respectively.
Energy intake and exercise volume
Energy intake and exercise volume throughout the intervention period and post-ingestion period are shown in Table 3. Occasionally, significant differences were found within groups, but there was no significant difference between groups.
Effect of a combination of G-hesperidin and caffeine upon obesity
Measurement at week 0 and week 12 as well as change from the baseline (week 0) in AFA is shown in Table 4. Furthermore, changes from baseline are also represented in Fig. 2. Decreases in TFA in the G-hesperidin with 50-mg caffeine group and in the G-hesperidin with 75-mg caffeine group were significantly greater than those in the placebo group. Degree of decrease of TFA appeared to be enhanced in a caffeine dose-dependent manner. Decreases in SFA in the G-hesperidin with 50-mg caffeine group and G-hesperidin with 75-mg caffeine group were significantly greater than those in the placebo group. However, there were no significant decreases in VFA between the placebo group and groups that ingested G-hesperidin with or without caffeine.
Measurements during and after the intervention period as well as changes from baseline (week 0) in body weight, the BMI, and circumferences of the waist and hip are shown in Table 5. Decreases in body weight at week 8 (p = 0.045) but not at week 12 (p = 0.089) were significantly greater in the G-hesperidin with 75-mg caffeine group than in the placebo group. Decreases in the BMI in the G-hesperidin with 75-mg caffeine group were significantly greater than those in the placebo group at week 8 and week 12. The BMI-decreasing effect of G-hesperidin appeared to be enhanced dose-dependently by caffeine addition. Decreases in waist circumference were significantly greater in the G-hesperidin with 25 mg caffeine group than in the placebo group at week-8 and at week-12. Similar decreases were observed in the G-hesperidin with 75 mg caffeine group but were not significant. There were no significant differences in decreases in hip circumference between the placebo group, and groups that ingested G-hesperidin with or without caffeine.
Effect of a combination of G-hesperidin and caffeine on serum levels of lipids
Measurements during and after the intervention period as well as changes from baseline (week 0) in serum levels of TG, total cholesterol, HDL-C and LDL-C are shown in Table 6. G-hesperidin has been reported to lower the serum levels of TG in subjects with moderately high levels of TG in serum [17]. However, TG levels in the G-hesperidin-alone group did not decrease during the intervention period, and the changes from baseline (week 0) were not different from those of the placebo group. TG levels in the G-hesperidin with caffeine group also did not decrease. Occasionally, serum levels of total cholesterol, HDL-C, and LDL-C decreased in G-hesperidin with/without caffeine groups during intervention periods but changes from baseline (week 0) were not different from those in the placebo group.
Safety assessment
Twenty-nine adverse events (AEs) were recorded during the study. Of the seven AEs in the placebo group, three were symptoms of a common cold, one was a pollen allergy, one was pain, one was tinnitus, and one was sudden deafness. Of the six AEs in the G-hesperidin group, three were symptoms of a common cold, two were pain, and one was conjunctivitis. Of the five AEs in the G-hesperidin with 25 mg caffeine group, two were symptoms of a common cold, two were digestive symptoms, and one was pain. Of the eight AEs in the G-hesperidin with 50-mg caffeine group, three were digestive symptoms, one was a symptom of a common cold, one was pain, one was a pollen allergy, one was fatigue, and one was irritation. Of three AEs in the G-hesperidin with 75-mg caffeine group, one was a symptom of common cold, one was pain, and one was a pollen allergy. Of the 29 AEs, one was moderate and 28 were mild. All AEs were judged to be unrelated to the dietary intervention, in which the moderate AE of sudden deafness was considered to be a result of the stress of bereavement.
Among the safety assessments undertaken, total protein in serum at week 4 in the G-hesperidin with 25 mg caffeine group (7.24 ± 0.23 g/dl) or at week 8 in the G-hesperidin with 75 mg caffeine group (7.27 ± 0.39 g/dl) were significantly greater than in the placebo group (week 4: 6.94 ± 0.19 g/dl, week 8: 7.27 ± 0.39 g/dl), and urine gravity at week 4 in the G-hesperidin with 75 mg caffeine group (1.013 ± 0.004 g/ml) was significantly lower than in the placebo group (1.018 ± 0.006 g/ml). However, these changes were within the ranges of corresponding reference values.
Discussion
We conducted a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study to evaluate the anti-obesity effect and serum TG-lowering effect of a combination of G-hesperidin and caffeine in subjects with a moderately high BMI and moderately high serum levels of TG.
Intake of G-hesperidin with 50-mg caffeine and 75-mg caffeine showed significant decreasing effects on AFA (especially on SFA). This fat-decreasing effect seemed to be enhanced by the dose-dependent addition of caffeine. Significant decreases in body weight and the BMI were observed in the G-hesperidin with 75-mg caffeine group compared with those in the placebo group. Decreases in VFA in G-hesperidin with caffeine groups were not significant compared with those in the placebo group. Visceral adipose tissue has been proposed to mediate obesity-related unfavourable levels of insulin, glucose and lipids, but subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue has been shown to be independent risk factor for the metabolic complications of obesity [29–31]. Therefore, our observations that a combination of G-hesperidin and caffeine decreased AFA may have clinical significance.
We have developed anti-obesity agents containing dietary components that affect lipid metabolism. Their effectiveness has been evaluated in non-insulin-dependent diabetic KK mice induced to develop obesity by feeding with a high-fat diet. Among the agents examined in this model, a mixture of thiamine, arginine, caffeine, and citric acid, as well as a mixture of arginine, caffeine, soy isoflavones and carnitine, have shown prominent anti-obesity effects [25, 32]. Recently, we have shown that a combination of G-hesperidin and caffeine decreased weights of subcutaneous fat and visceral fat effectively in high-fat diet-induced obese mice [27]. We consider the mechanism of its anti-obesity effect is partially through the inhibition of hepatic lipogenesis (Fig. 3) [27]. In addition to the effectiveness of a mixture of thiamine, arginine, caffeine and citric acid in the treatment of obesity in humans [26], we showed an anti-obesity effect of a combination of G-hesperidin and caffeine in moderately obese subjects in the present study. Therefore, the effectiveness of anti-obesity agents comprising dietary components observed in obese KK mice can be expected to have a similar effect in humans.
Reports have shown that 12-week intake of G-hesperidin (500 mg) lowers serum levels of TG in subjects with moderately high levels of TG in serum [17]. In contrast to those observations, intake of G-hesperidin with or without caffeine had no effect on serum levels of TG in subjects with moderately high levels of TG. Unlike previous studies, we recruited subjects with a moderately high BMI in addition to a moderately high level of TG. It has been reported that plasma levels of TG in obese subjects do not decrease efficiently in response to insulin, are overproduced, or are resistant to clearance [33]. Such changes in TG metabolism in obese subjects may affect the action of G-hesperidin, leading to the slight effect of G-hesperidin on serum levels of TG in obese subjects.
In the present study, mean daily consumption of caffeine other than during intervention was about 100 mg in subjects of each group. Nevertheless, a dose–response of caffeine from 25 mg to 75 mg was observed in the anti-obesity effects of this combination. Hence, concomitant (but not habitual) intake of caffeine with G-hesperidin might be important for the anti-obesity activity of this combination. Indeed, in studies demonstrating the anti-obesity effect of caffeine-containing components, caffeine was taken concomitantly with other ingredients [34, 35]. If concomitant intake is important, then whether single intake of such a low dose of caffeine has physiological relevance is of particular importance. It has been reported that a single dose of 12.5 mg caffeine affects cognitive performance [36] and that 32-mg caffeine improves auditory vigilance and visual reaction time [37]. Therefore, concomitant intake of caffeine may have physiological activity and synergize with G-hesperidin. Further investigations are required to clarify the importance of concomitant intake of caffeine and G-hesperidin.
Conclusions
Our results showed that intake of a combination of 500-mg G-hesperidin and 75-mg caffeine for 12 weeks significantly reduced abdominal fat (especially subcutaneous fat), body weight and the BMI in subjects with a moderately high BMI. Therefore, a combination of G-hesperidin and caffeine may be useful for the prevention or treatment of obesity.
Abbreviations
- AFA:
-
abdominal fat area
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- G-hesperidin:
-
glucosyl hesperidin
- TG:
-
triglyceride
References
Hunt KJ, Resendez RG, Williams K, Haffner SM, Stern MP, San Antonio Heart S. National cholesterol education program versus World Health Organization metabolic syndrome in relation to all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the San Antonio Heart Study. Circulation. 2004;110:1251–7.
Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, Niskanen LK, Kumpusalo E, Tuomilehto J, et al. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA. 2002;288:2709–16.
Ninomiya T, Kubo M, Doi Y, Yonemoto K, Tanizaki Y, Rahman M, et al. Impact of metabolic syndrome on the development of cardiovascular disease in a general Japanese population: the Hisayama study. Stroke. 2007;38:2063–9.
Davis MA, Ettinger WH, Neuhaus JM, Hauck WW. Sex differences in osteoarthritis of the knee. The role of obesity. Am J Epidemiol. 1988;127:1019–30.
Anderson JJ, Felson DT. Factors associated with osteoarthritis of the knee in the first national Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (HANES I). Evidence for an association with overweight, race, and physical demands of work. Am J Epidemiol. 1988;128:179–89.
Hart DJ, Spector TD. The relationship of obesity, fat distribution and osteoarthritis in women in the general population: the Chingford Study. J Rheumatol. 1993;20:331–5.
Manek NJ, Hart D, Spector TD, MacGregor AJ. The association of body mass index and osteoarthritis of the knee joint: an examination of genetic and environmental influences. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:1024–9.
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1230–5.
Correa H, Jacoby J. Nutrition and fertility: some iconoclastic results. Am J Clin Nutr. 1978;31:1431–6.
Rowland AS, Baird DD, Long S, Wegienka G, Harlow SD, Alavanja M, et al. Influence of medical conditions and lifestyle factors on the menstrual cycle. Epidemiology. 2002;13:668–74.
Mitchell Jr GW, Rogers J. The influence of weight reduction on amenorrhea in obese women. N Engl J Med. 1953;249:835–7.
Hijiya H, Miyake T. European Patent 0402049A2. 1991.
Akiyama S, Katsumata S, Suzuki K, Nakaya Y, Ishimi Y, Uehara M. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of hesperidin and cyclodextrin-clathrated hesperetin in Goto-Kakizaki rats with type 2 diabetes. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2009;73:2779–82.
Chiba H, Uehara M, Wu J, Wang X, Masuyama R, Suzuki K, et al. Hesperidin, a citrus flavonoid, inhibits bone loss and decreases serum and hepatic lipids in ovariectomized mice. J Nutr. 2003;133:1892–7.
Mitsuzumi HY-YA, Arai N, Sadakiyo T, Kubota M. Glucosyl hesperidin lowers serum triglyceride level in the rats Fed a high-fat diet through the reduction of hepatic triglyceride and cholesteryl ester. Jpn Pharmacol Ther (in Japanese). 2011;39:727–40.
Miwa Y, Yamada M, Sunayama T, Mitsuzumi H, Tsuzaki Y, Chaen H, et al. Effects of glucosyl hesperidin on serum lipids in hyperlipidemic subjects: preferential reduction in elevated serum triglyceride level. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2004;50:211–8.
Miwa Y, Mitsuzumi H, Sunayama T, Yamada M, Okada K, Kubota M, et al. Glucosyl hesperidin lowers serum triglyceride level in hypertriglyceridemic subjects through the improvement of very low-density lipoprotein metabolic abnormality. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2005;51:460–70.
Miwa Y, Mitsuzumi H, Yamada M, Arai N, Tanabe F, Okada K, et al. Suppression of apolipoprotein B secretion from HepG2 cells by glucosyl hesperidin. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2006;52:223–31.
Hanawa M, Morimoto Y, Yokomizo A, Akaogi A, Mafune E, Tsunoda K, et al. Effect of long-term intake of the tablet containing glucosyl hesperidin on body weight and body fat. J Nutr Food. 2008;11:1–17.
Leijten PA, van Breemen C. The effects of caffeine on the noradrenaline-sensitive calcium store in rabbit aorta. J Physiol. 1984;357:327–39.
Costill DL, Dalsky GP, Fink WJ. Effects of caffeine ingestion on metabolism and exercise performance. Med Sci Sports. 1978;10:155–8.
Astrup A, Buemann B, Christensen NJ, Toubro S, Thorbek G, Victor OJ, et al. The effect of ephedrine/caffeine mixture on energy expenditure and body composition in obese women. Metabolism. 1992;41:686–8.
Astrup A, Toubro S, Cannon S, Hein P, Breum L, Madsen J. Caffeine: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study of its thermogenic, metabolic, and cardiovascular effects in healthy volunteers. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990;51:759–67.
Jeukendrup AE, Randell R. Fat burners: nutrition supplements that increase fat metabolism. Obes Rev. 2011;12:841–51.
Muroyama K, Murosaki S, Yamamoto Y, Odaka H, Chung HC, Miyoshi M. Anti-obesity effects of a mixture of thiamin, arginine, caffeine, and citric acid in non-insulin dependent diabetic KK mice. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2003;49:56–63.
Muroyama K, Murosaki S, Yamamoto Y, Ishijima A, Toh Y. Effects of intake of a mixture of thiamin, arginine, caffeine, and citric acid on adiposity in healthy subjects with high percent body fat. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2003;67:2325–33.
Ohara T, Muroyama K, Yamamoto Y, Murosaki S. A combination of glucosyl hesperidin and caffeine exhibits an anti-obesity effect by inhibition of hepatic lipogenesis in mice. Phytother Res. 2015;29:310–6.
Tokunaga K, Matsuzawa Y, Ishikawa K, Tarui S. A novel technique for the determination of body fat by computed tomography. Int J Obes. 1983;7:437–45.
Smith SR, Lovejoy JC, Greenway F, Ryan D, de Jonge L, de la Bretonne J, et al. Contributions of total body fat, abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments, and visceral adipose tissue to the metabolic complications of obesity. Metabolism. 2001;50:425–35.
Gormsen LC, Nellemann B, Sorensen LP, Jensen MD, Christiansen JS, Nielsen S. Impact of body composition on very-low-density lipoprotein-triglycerides kinetics. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009;296:E165–73.
Bissonnette S, Salem H, Wassef H, Saint-Pierre N, Tardif A, Baass A, et al. Low density lipoprotein delays clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein by human subcutaneous adipose tissue. J Lipid Res. 2013;54:1466–76.
Murosaki S, Lee TR, Muroyama K, Shin ES, Cho SY, Yamamoto Y, et al. A combination of caffeine, arginine, soy isoflavones, and L-carnitine enhances both lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation in 3 T3-L1 and HepG2 cells in vitro and in KK mice in vivo. J Nutr. 2007;137:2252–7.
Lewis GF, Uffelman KD, Szeto LW, Steiner G. Effects of acute hyperinsulinemia on VLDL triglyceride and VLDL apoB production in normal weight and obese individuals. Diabetes. 1993;42:833–42.
Diepvens K, Westerterp KR, Westerterp-Plantenga MS. Obesity and thermogenesis related to the consumption of caffeine, ephedrine, capsaicin, and green tea. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292:R77–85.
Phung OJ, Baker WL, Matthews LJ, Lanosa M, Thorne A, Coleman CI. Effect of green tea catechins with or without caffeine on anthropometric measures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91:73–81.
Smit HJ, Rogers PJ. Effects of low doses of caffeine on cognitive performance, mood and thirst in low and higher caffeine consumers. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2000;152:167–73.
Lieberman HR, Wurtman RJ, Emde GG, Roberts C, Coviella IL. The effects of low doses of caffeine on human performance and mood. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1987;92:308–12.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Naoyuki Takayama from House Wellness Foods Corporation for preparing test samples. We are also very grateful to all study participants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
This study was supported by House Wellness Foods Corporation. All authors belong to House Wellness Foods Corporation. All authors are named as inventors of a patent (JP5564330B2) or patent pending (PCT/JP2011/050495) held by the House Wellness Foods Corporation on the composition for the prevention, amelioration or treatment of the metabolic syndrome.
Authors’ contributions
All authors designed the study. TO and KM conducted the study. TO analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. YY is the principal investigator of this study. SM had primary responsibility for the final content of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12937-017-0253-6.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Ohara, T., Muroyama, K., Yamamoto, Y. et al. Oral intake of a combination of glucosyl hesperidin and caffeine elicits an anti-obesity effect in healthy, moderately obese subjects: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Nutr J 15, 6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-016-0123-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-016-0123-7