Abstract
Background
The C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation structure in gentamicin can prevent deactivation by aminoglycoside 3′-phosphotransferase (APH(3′)) in drug-resistant pathogens. However, the enzyme catalyzing the dideoxygenation step in the gentamicin biosynthesis pathway remains unknown.
Results
Here, we report that GenP catalyzes 3′ phosphorylation of the gentamicin biosynthesis intermediates JI-20A, JI-20Ba, and JI-20B. We further demonstrate that the pyridoxal-5′-phosphate (PLP)-dependent enzyme GenB3 uses these phosphorylated substrates to form 3′,4′-dideoxy-4′,5′-ene-6′-oxo products. The following C-6′-transamination and the GenB4-catalyzed reduction of 4′,5′-olefin lead to the formation of gentamicin C. To the best of our knowledge, GenB3 is the first PLP-dependent enzyme catalyzing dideoxygenation in aminoglycoside biosynthesis.
Conclusions
This discovery solves a long-standing puzzle in gentamicin biosynthesis and enriches our knowledge of the chemistry of PLP-dependent enzymes. Interestingly, these results demonstrate that to evade APH(3′) deactivation by pathogens, the gentamicin producers evolved a smart strategy, which utilized their own APH(3′) to activate hydroxyls as leaving groups for the 3′,4′-dideoxygenation in gentamicin biosynthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Aminoglycoside antibiotics (AGAs) have been available for clinical use since the 1940s and have been shown to exhibit broad-spectrum activities [1]. However, the spread of resistance is limiting their use in the clinic, which is primarily induced by aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes (AMEs). The amino and hydroxyl groups of AGAs are deactivation targets of AMEs [2, 3]. Because deoxygenations remove the modifiable groups of AGAs, deoxy functionalities are natural defensive strategies that can prevent deactivation by AMEs [4]. The C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation structure can prevent deactivation by APH(3′) and adenyltransferase (ANT(4′)) [5]. Some semi-synthetic antibiotics have utilized the C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation structure to increase their efficacies, such as dibekacin (3′,4′-dideoxykanamycin B) [6], arbekacin (1-N-((S)-4-amino-2-hydroxybutyryl)-3′,4′-dideoxy-kanamycin B) [7, 8], and the newly approved sisomicin derivative plazomicin, which retains antibiotic activity in the presence of most AMEs [9, 10] (Fig. 1). The C-3′-deoxygenation biosynthetic process has recently been dissected by several research groups [11,12,13]. A radical S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) enzyme, AprD4, along with AprD3, is responsible for the 3′-deoxygenation in apramycin biosynthesis [14]. The C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation biosynthetic process in gentamicin and sisomicin is still obscure.
Gentamicin is a broad-spectrum aminoglycoside bactericidal antibiotic produced by Micromonospora echinospora with a C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation moiety. As with other 2-deoxystreptamine-containing AGAs, significant progress has been made in the study of gentamicin biosynthesis [15,16,17,18,19]. The enzymatic steps that lead to the pseudotrisaccharide gentamicins JI-20A, JI-20Ba, and JI-20B have all been elucidated. They are the starting compounds of the C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation biosynthetic process. However, little detailed information of the featured C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation process is available (Fig. 2).
Genetic studies have shown that an APH(3′) GenP is involved in the aminoglycoside dideoxy process in gentamicin biosynthesis [20], and a biochemical study showed that GenP can phosphorylate C-3′ of an unnatural substrate, kanamycin B. Furthermore, kanamycin B is the synthetic precursor of dibekacin (3′,4′-dideoxy- kanamycin B) [21], so synthesis of dibekacin by C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation enzymes is a promising approach. GenP has 52% identity with ForP (GenBank No. CAF31545.1), while ForP can complement mutants in the dehydroxylation process of the fortimicin A biosynthesis pathway. Therefore, it is speculated that GenP can phosphorylate JI-20A, JI-20Ba, and JI-20B, which are the starting compounds of the C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation biosynthetic process [22].
Bioinformatic analysis showed that GenB3 is a PLP-dependent enzyme. Guo and colleagues showed that GenB3 catalyzes the 6′-transamination in the gentamicin biosynthetic pathway, although with lower activity than GenB1 and GenB2 [23] (Fig. 2). Interestingly, GenB3 has 85% identity with Sis18 (GenBank No. ACN38352.1) in the biosynthetic pathway of sisomicin, which is a 3′,4′-dideoxy-AGA too (Fig. 1). However, GenB3 has only approximately 30% identity with C-6′-aminotransferases in the biosynthetic pathway of AGAs without 3′,4′-dideoxygenation, like KanB [24] (GenBank No. CAF31586.1) from the kanamycin biosynthetic pathway (Additional file 1: Figure S1). Therefore, GenB3 may catalyze C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation in the gentamicin pathway.
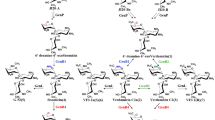
In the present study, we demonstrate that the phosphorylation catalyzed by GenP is the first step in the gentamicin C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation process. More importantly, we show that a PLP-dependent enzyme, GenB3, uses the products of GenP to catalyze the dideoxygenation, forming 3′,4′-dideoxy-4′,5′-ene-6′-oxo products. The following transamination and reduction by GenB4 finish the gentamicin biosynthesis (Fig. 2).
Results and discussion
GenP starts the C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation process in the gentamicin biosynthetic pathway
To investigate the function of GenP in gentamicin biosynthesis, the intermediate metabolites of the biosynthetic pathway, JI-20A, JI-20Ba, and JI-20B were used as substrates. They are the starting compounds for the C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation process in gentamicin biosynthesis. The results of high-performance liquid chromatography using evaporative light-scattering detection (HPLC-ELSD) are shown in Fig. 3a. GenP converted all of these substrates into new products. Products of the reactions were analyzed by mass spectrometry (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometry. The ESI–MS spectrum suggested that GenP catalyzed the formation of monophosphorylated products (Fig. 3). Additionally, 1H, 13C, HHCOSY, and 31P NMR results of compound 2 confirmed that the product had a C-3′-OH phosphorylation moiety (Additional file 1: Figure S2). Further experiments showed that GenP had broad substrate specificities. In addition to phosphorylating the other two intermediate metabolites of the gentamicin biosynthetic pathway, X2 and G418, giving phosphorylated compounds 4 and 5 (Additional file 1: Figure S3), GenP can also phosphorylate kanamycin B, as previously reported [14]. However, GenP has a higher specificity toward JI-20A and JI-20Ba (Additional file 1: Table S1).
GenB3 completes the C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation process
We then investigated the proteins with unknown function in gentamicin biosynthesis. To investigate the function of genB3, gene-disruption experiments were performed. The disruption strain, ΔgenB3, did not produce C-3′,4′-deoxygenated products, but instead it accumulated non-deoxygenated products, including JI-20Ba and JI-20B (Fig. 4a). These results demonstrate that GenB3 is involved in gentamicin C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation.
GenB3-catalyzed dideoxygenation. a HPLC-ELSD analysis of mutant- strain fermentation products, showing the (i) wild-type, (ii) genB3-disruption strain (ΔgenB3), and (iii) ΔgenB3::genB3 (complementation of the ΔgenB3 mutant). b Ultraviolet–visible absorption spectrum of GenB3-catalyzed reaction at different reaction times, where UV absorption was measured every 2 min from 300 to 500 nm. c HPLC-ELSD analysis of (i) the compound 2 standard with L-Glu, (ii) the GenB3-catalyzed reaction without L-Glu, (iii) the GenB3-catalyzed reaction with L-Glu, (iv) with NaBH4 added after the reaction, (v) the compound 3 standard with L-Glu, and (vi) the GenB3-catalyzed reaction with compound 3. d HPLC-ELSD analysis. (i) The GenB3-catalyzed reaction with compound 1 was found to produce compound 9. (ii) L-Glu was added. (iii) An L-Glu-added sisomicin standard (Sis) was used. e–h MS analysis of compounds 6, 7, 8, and 10
To further investigate the role of GenB3, the recombinant protein was expressed and purified in Escherichia coli. GenB3 did not show obvious activity on JI-20Ba and JI-20B. We suspected that C-3′-phosphorylation-JI-20Ba (2) might be the substrate of GenB3 and the phosphate group could be hydrolyzed in the experiments with the ΔgenB3 strain. Indeed, HPLC-ELSD analysis showed that GenB3 converted 2 to a new compound 6 (Fig. 4c), which was characterized to be 6′-oxo-verdamicin by MS (Fig. 4e), 1H, and 13C NMR (Additional file 1: Figure S4). The results demonstrate that GenB3 catalyzed the C-3′-dephosphation and C-4′,5′-dehydratation of compound 2. To gain more evidences on the keto group on C-6′, NaBH4 was added to the reaction mixture to reduce the keto group. HPLC-ELSD analysis showed that compound 6 disappeared after adding NaBH4, and two new peaks appeared as compounds 7 and 8 (Fig. 4c). MS analysis revealed that their molecular masses were both 462, and they were thus presumed to be C-6′-isomers of the hydroxyl group (Figs. 4f, g). In addition, JI-20Ba and JI-20B are a pair of C-6′ epimers, and GenB3 also catalyzes C-3′-phospho-JI-20B (3) to produce compound 6 (Fig. 4c).
When C-3′-phospho-JI-20A (1) was used as a substrate, GenB3 catalyzed C-3′-dephosphorylation and C-4′,5′-dehydration to form 9 (Fig. 4d). However, unlike with 6, GenB3 further catalyzed the aminotransfer of C-6′ to form sisomicin (10) (Fig. 4h). This discrepancy may have been caused by the steric hindrance from the C-6′-methyl group of compound 6. Results of UV spectrometry confirmed that PLP of GenB3 was converted to pyridoxamine 5′-phosphate (PMP) during the enzymatic reaction (Fig. 4b). Furthermore, no free ammonia was detected in the reaction solution (Additional file 1: Figure S5). In addition, addition of the amino acceptor α-ketoglutarate to the reaction mixture promoted the GenB3-catalyzed reaction (Additional file 1: Figure S6). These results indicate that the C-6′-amino group of the substrate was transferred to PMP.
All of the tested substrates of GenB3 contain amino groups at both C-2′ and C-6′. To identify which amino group is the functional group for PLP binding, we tested GenB3 activity toward substrates only containing one amino group at C-6′ and C-2′. GenB3 did not catalyze the deoxygenation of compounds containing the C-2′-amino group, but it did catalyze the deoxygenation of phosphorylated gentamicin B containing the C-6′-amino group. Therefore, the C-6′-amino group is the functional group for the GenB3-catalyzed reaction (Additional file 1: Figure S7).
GenB3 first catalyzes the C-4′,5′-dehydration in the C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation process
To further investigate the reaction mechanism of GenB3, the reaction condition was shifted from 30 to 20 °C, when C-3′-phospho-JI-20Ba (2) was used as a substrate. A small amount of compound 11 was detected in the reaction (Fig. 5a). MS results showed that it was a hydroxyl group at the 3′ position of 11 (Fig. 5c). We speculated that compound 11 was a reaction byproduct instead of an intermediate, because GenB3 did not further catalyze the 3′-hydroxyl deoxygenation of compound 11 with longer incubation times at 30 °C. We assumed that the C-4′,5′-dehydration occurred first in the dideoxygenation process, after which the C-3′-phosphate was removed. However, during unfavorable conditions for phosphate elimination, the C-3′-phosphate bond may have been hydrolyzed, which would then form compound 11. This speculative step is consistent with our in vivo results. Compound 11 was also detected in genB4-disruption strains (Fig. 5b). These results demonstrate that C-4′,5′-dehydration occurred first in the dideoxygenation process.
Plausible mechanism of GenB3
Based on these results, we proposed the following mechanism for the GenB3 catalyzed dideoxygenation reaction (Scheme 1). Like other PLP-dependent enzymes, the reaction starts with an external aldimine 12 generated from the 6′-amine of compound 2 with the internal aldimine of the enzyme with PLP [25]. The 4′-hydroxyl group of aldimine 12 may be deprotonated by a basic residue and then attacks the adjacent phosphate group on the 3′-C, forming a more stable cyclic phosphodiester. By this means, the 4′-hydroxyl was activated by the enzyme as a good leaving group, which is a prerequisite for γ-elimination. A following deprotonation would convert the external aldimine 13 to the quinonoid 14 [26]. Then a classical PLP-dependent γ-elimination can happen, giving the 4′-deoxyl-4′,5′-olefin quinonoid 16 [27,28,29]. The 3′-phosphate group facilitates the second dehydroxylation as a good leaving group to yield the aldimine 17. Protonation at 3′-C of the aldimine 17 affords ketimine 18. Hydrolysis of the ketimine 18 would give the keto product compound 6 and PMP as the cofactor. This mechanism was supported by the isolation of the 3′-hydroxyl intermediate compound 11 from the GenB3 reaction, which should be the hydrolysis product of intermediate 16.
GenB3-catalyzed products need further aminotransfer and reduction to produce components of gentamicin C. Although the intact C-6′-aminotransferases GenB1, and GenB2 existed in the genB4-disruption strain, the main product of the genB4-disruption strain was the 6′-oxo-containing compound 6 (Fig. 5b), which indicated that the C-6′-aminotransferase was inefficient for compound 6 in vivo. We have also proved that GenB4 could convert C-6′-amino-containing 6 (verdamicin C2 and verdamicin C2a) into gentamicin C2a, when GenB4 coupled with aminotransferases [23, 30]. However, when we incubated 6 with purified GenB4, the C-4′,5′-olefin reduction was undetectable via HPLC-ELSD (Additional file 1: Figure S8). These results demonstrate that the C-6′-amino group was a prerequisite for GenB4-catalyzed C-4′,5′-olefin reduction.
Conclusions
In summary, the results presented here firmly demonstrate the functions of both GenP and GenB3 in gentamicin biosynthesis. GenB3 appears to be the first reported PLP-dependent enzyme catalyzing dideoxygenation in aminoglycoside biosynthesis. Interestingly, structurally related C-3′-deoxygenation and C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation of AGAs are catalyzed by distinct catalytic pathways. C-3′-deoxygenation is catalyzed through a radical mechanism by the radical SAM dehydratase, AprD4, along with the reductase partner, AprD3 [11,12,13,14]. Although an AprD3 homologue was identified in the gentamicin pathway, GenB3-catalyzed dehydration and 3′-phosphate elimination do not require a reductase partner. Instead, this process behaves in an “aminotransferase-like” manner, which is similar to that with dehydratase ColD from the biosynthetic pathway of l-colitose [31, 32]. PLP-dependent amino-transferases GenB1, GenB2, GenB3, and GenB4 not only have the common promiscuous activity to catalyze C-6′-aminotransfer as reported [23], but also have their unique functions in gentamicin biosynthesis, which demonstrates the diversity of PLP chemistry in enzymatic catalysis.
AMEs exist in both resistant pathogens and AGA producers [33]. It has been speculated that these enzymes may perform other metabolic functions [22]. In the present study, we have demonstrated that gentamicin producers evolved a smart strategy to evade APH(3′) deactivation by pathogens. The gentamicin biosynthetic pathway utilizes its APH(3′) to activate hydroxyls as leaving groups, and then the PLP-dependent enzyme GenB3 catalyzes dideoxygenation. The unveiling of the C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation pathway of gentamicin may pave the way for dissection of other sugar dideoxygenation pathways. As fortimicin and istamycin share the same C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation with gentamicin, and their biosynthetic gene clusters have identical enzymes with GenP and GenB3/GenB4 [34], their deoxygenation pathways may be identical with one another.
The APH(3′)-activated dideoxygenation pathway of gentamicin provides inspiration for chemical regiospecific removal of oxygen from sugars [35]. Since GenP, GenB3, and GenB4 catalyze C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation, they have the potential to be applied in combinatorial biosynthesis of C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation containing semi-synthetic antibiotics, such as dibekacin and arkekacin [36], to develop novel drugs against life-threatening pathogens and to yield an improved safety profile [37]. Because C-3′, C-4′, and C-6′ are frequently used chemical modification sites for semi-synthesis of AGAs [38,39,40], GenP, GenB3, and GenB4 may be used for combined chemical and enzymatic syntheses of promising therapeutic leads.
Methods
Strains and culture conditions
Escherichia coli Top10 was used as cloning host; E. coli ET12567 (pUZ8002) was used for E. coli–M. echinospora conjugation; E. coli BL21 (DE3) was used for protein expression. E. coli strains were grown in LB medium (tryptone 10 g/L, yeast extract 5 g/L, NaCl 10 g/L) at 37 °C via antibiotic selection (100 μg/ml ampicillin, 50 μg/ml apramycin, 25 μg/ml chloramphenicol, 50 μg/ml kanamycin). Pfu DNA polymerase was obtained from Vazyme, while GC buffer and dNTPs were obtained from Takara. T4 DNA ligase and DNA marker were purchased from Takara. M. echinospora ATCC 15,835 was used for the creation of in-frame deletion mutants and as the source of GenP (GenBank No. AGB13904.1) and GenB3 (GenBank No. AGB13905.1). The GenBank No. of the M. echinospora ATCC 15,835 genome is JQ975418.1. Gene sequencing was performed by Genewiz. M. echinospora ATCC 15,835 wild-type and mutants were grown in growth medium (soluble starch 10 g/L, wheat bran 10 g/L, MgSO4·7H2O 5 g/L, K2HPO4·3H2O 0.3 g/L, KNO3 1 g/L, NaCl 0.5 g/L, CaCO3 1 g/L, asparagine 0.02 g/L, agar 2.5 g/L) at 37 °C to obtain spores. For the collection of gentamicin, M. echinospora ATCC 15,835 wild-type and mutants were cultured in seed cultures (soluble starch 15 g/L, soybean powder 1 g/L, glucose 1 g/L, KNO3 0.5 g/L, CaCO3 23 g/L) at 34 °C for 36 h. Fermentation cultures (soluble starch 50 g/L, soybean powder 35 g/L, glucose 15 g/L, corn powder 15 g/L, peptone 15 g/L, (NH4)2SO4 0.5 g/L, KNO3 0.5 g/L, CoCl2·6H2O 0.01 g/L, CaCO3 26 g/L) were conducted for 120 h.
Construction of gene-disruption plasmids
For gene disruption, about 2000 bp upstream and downstream of the gene were amplified from the genomic sequence (see list of primers used in the Supplemental Information). PCR products (94 °C for 5 min; 30 cycles of 94 °C for 1 min, 60 °C for 45 s, and 72 °C for 2 min; 72 °C for 10 min) were cloned into the E. coli–M. echinospora vector pKC1139 or pD2925 (a plasmid derived from pIJ2925) to obtain the gene-disruption plasmids pKCP (genP) and pDB3 (genB3). All of the plasmids were verified by sequencing (plasmids are shown in Additional file 1: Table S3).
Gene disruption of genP and genB3 genes
To obtain the mutant strains of ΔgenP and ΔgenB3, the gene-disruption plasmids pKCP and pDB3 were introduced into the wild-type strain by conjugation from E. coli ET12567 (pUZ8002, the gene disruption plasmid) to M. echinospora. Apramycin-resistant (AprR) colonies were screened and confirmed by PCR amplification. The AprS colonies were selected from the initial AprR colonies and confirmed by PCR amplification (Additional file 1: Figure S9).
Gene complementation of ΔgenP and ΔgenB3
Complementation plasmids contained the complete fragment of the gene under the control of the PhrdB promoter. The complementation plasmids were prepared by cloning genP and genB3 into pEAP1 (a plasmid derived from pSET152) under the control of the PhrdB promoter. The complementation plasmid was introduced individually into the mutant strain by conjugation. Complemented strains were based on erythromycin resistance (100 μg/ml) and were confirmed by PCR amplification.
Extraction, isolation, and purification of gentamicin C complexes and intermediates
Fermentation products of wild-type and mutant strains were adjusted to a pH of 2.0 with H2SO4. After centrifugation (5,000 rpm, 10 min, room temperature), the supernatant was adjusted to a pH of 7.0 with NaOH. The fermentation broth was centrifuged again, and the supernatant was adsorbed by cationic resin D152 adsorption at 37 °C for 3 h. The adsorbed resin was packed into a column. The column was washed with 10 times the column volume of 0.01 mM to 0.2 M NH3·H2O. The eluate was freeze-dried, re-dissolved in 1 ml of water, and filtered through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane before subjection to HPLC-ELSD analysis.
Construction of gene-expression plasmids in E. coli
genP and genB3 genes were amplified from the DNA of M. echinospora by PCR amplification (see the list of primers used in Additional file 1: Table S2). The PCR products were digested with NdeI and HindIII and were inserted into pET28a(+) to obtain gene-expression strains. Each plasmid was transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3). The expression plasmids were verified by DNA sequencing.
Expression and purification of GenP and GenB3
E. coli BL21 (DE3) containing the expression plasmid was cultured in LB (50 μg/ml kanamycin) at 37 °C to an OD600 of 0.6–0.8 and gene expression was induced by isopropylthiogalactoside (IPTG, 0.1 mM) at 16 °C for 20 h. The cells were collected by centrifugation and resuspended in 20 ml of binding buffer (0.5 M NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl at a pH of 8.0). The recombinant protein was obtained by sonication for 20 min (3 s on, 5 s off), and the supernatant was obtained by centrifugation at 4 °C for 20 min. The recombinant protein was purified by Ni2+-charged His-Bind resin (GE Healthcare). Impurities were eluted by washing buffer A (0.5 M NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl, 20 mM imidazole), washing buffer B (0.5 M NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl, 40 mM imidazole), and washing buffer C (0.5 M NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl, 60 mM imidazole). The recombinant proteins were eluted by elution buffer (0.5 M NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl, 200 mM imidazole). Imidazole in the eluted proteins was removed by dialysis. The purified proteins were stored at − 30 °C.
Preparation of substrates for in vitro catalytic reactions
Different reaction substrates were obtained by fermentation of different mutant strains. Gentamicin X2 was obtained from the fermentation broth of the M. echinospora ΔgenKΔgenQ mutant strain. G418 was purchased from Sigma. JI-20A was isolated from the fermentation broth of ΔgenKΔgenP. JI-20Ba and JI-20B were isolated from the fermentation broth of M. echinospora ΔgenB1ΔgenP. Ver C2a was isolated from the fermentation broth of M. echinospora ΔgenB4. For the separation of these compounds, refer to Method 5.
GenP-catalyzed reaction with JI-20A, JI-20Ba, and JI-20B
The GenP activity assays were conducted using mixtures containing substrate (200 μM), GenP (15.8 μM), ATP (10 mM), and MgCl2 (10 mM) in 500 μl Tris–HCl buffer (50 mM, pH 8.0). Incubations were at 37 °C for 1 h and were quenched by addition of chloroform (500 μl), followed by centrifugation to remove proteins. The supernatants were filtered through 0.22 μm microporous membranes before subjection to HPLC-ELSD analysis.
Separation and purification of compounds 1 and 2
In order to obtain large amounts of compounds 1 and 2, the volume of the GenP-catalyzed reaction was expanded to 10 mL, including substrates (JI-20A or JI-20Ba, 4 mM), GenP (25 μM), ATP (100 mM), MgCl2 (50 mM), and Tris–HCl buffer (50 mM, pH 8.0). Samples were incubated at 30 °C overnight. The reaction was ended in a boiling water bath and samples were centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was then passed through a column of D152 (5 ml) at a flow rate of 0.2 ml/min and unbound compounds were discarded. The compound-bound column was washed with water (100 ml) followed by gradient elution from 0.01 M to 0.06 mM (50 ml). Every fraction was checked by HPLC-ELSD. Then, the eluates of compound 1 or 2 with higher purity were combined and lyophilized.
GenB3-catalyzed reaction with compounds 1 and 2
The GenB3 activity assays were conducted using mixtures containing substrate (200 μM), GenB3 (25 μM), amino donor (l-Glu, 10 mM), and PLP (1 mM) in 500 μl KPi buffer (50 mM KOH, pH 8.0). Samples were incubated at 30 °C overnight and were quenched by addition of chloroform (500 μl), followed by centrifugation to remove proteins. The supernatants were filtered through 0.22 μm microporous membranes before subjection to HPLC-ELSD analysis.
GenP and GenB3 catalyze dideoxygenation with JI-20Ba
Enzymatic assays were conducted using 500 μl reaction mixtures containing substrate (JI-20Ba, 200 μM), GenP (15.8 μM), GenB3 (12.5 μM), ATP (10 mM), MgCl2 (10 mM), PLP (1 mM), α-ketoglutarate (10 mM), and Tris–HCl buffer (50 mM, pH 8.0). Samples were incubated at 30 °C overnight and were quenched by addition of chloroform (500 μl), followed by centrifugation to remove proteins. The supernatants were filtered through 0.22 μm microporous membranes before subjection to HPLC-ELSD analysis.
HPLC-ELSD analysis of gentamicin C complexes and related intermediates
HPLC-ELSD analysis of mixtures was performed with a Welch C18 column (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 μm) connected to a SofTA Model 300 s ELSD. In the GenP-catalyzed reaction, X2, G418, JI-20A, JI-20Ba, JI-20B, and gentamicin B1 were used as substrates, and the mobile phase was 0.2 M TFA (1 ml/min). In the GenB3-catalyzed reaction, compounds 1 and 2 were used as substrates, and the mobile phase was a 92:8 mixture of 0.2 M TFA:methanol (0.8 ml/min). In the GenB4-catalyzed reaction, Ver C2a and compound 6 were used as substrates, and the mobile phase was a 92:8 mixture of 0.2 M TFA:methanol (0.8 ml/min). The mobile phase analysis of the fermentation of the strains was performed using a 98:2 mixture of 0.2 M TFA:methanol (0.8 ml/min).
Mass spectrometry, 1H, and 13C NMR analyses
MS analysis of the molecular formulas of compounds was performed using a micrOTOF-Q operator. 1H and 13C NMR analyses of compounds were performed using a Bucker 600 MHz. Compounds were purified to 5–10 mg through the cationic resin D152 and were dissolved in 500 μl of D2O.
31P NMR analyses
31P NMR analysis of compound 2 was performed using a Bucker 400 MHz. Compound 2 was purified to 3 mg through the cationic resin D152 and was dissolved in 500 μl of D2O.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets and strains materials generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author H. X. upon request.
References
Dozzo P, Moser HE. New aminoglycoside antibiotics. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2010;20:1321–41.
McKay GA, Thompson PR, Wright GD. Broad spectrum aminoglycoside phosphotransferase type III from Enterococcus: overexpression, purification, and substrate specificity. Biochem. 1994;33:6936–44.
Ramirez MS, Tolmasky ME. Aminoglycoside modifying enzymes. Drug Resist Updates. 2010;3:151–71.
Garneau-Tsodikova S, Labby KJ. Mechanisms of resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics: overview and perspectives. Med Chem Commun. 2016;7:11–27.
Livermore DM, Mushtaq S, Warner M, Zhang JC, Maharjan S, Doumith M, Woodford N. Activity of aminoglycosides, including ACHN-490, against carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:48–53.
Umezawa H, Umezawa S, Tsuchiya T, Okazaki Y. 3’,4’-Dideoxy-kanamycin B active against kanamycin-resistant Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot. 1971;24:485–7.
Hotta K, Kondo S. Kanamycin and its derivative, arbekacin: significance and impact. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2018;71:417–24.
Kondo S, Iinuma K, Yamamoto H, Maeda K, Umezawa H. Syntheses of 1-N-{(S)-4-amino-2-hydroxybutyryl}-kanamycin B and-3’,4’-dideoxykanamycin B active against kanamycin-resistant bacteria. J Antibiot. 1973;26:412–5.
Cox G, Ejim L, Stogios PJ, Koteva K, Bordeleau E, Evdokimova E, Sieron AO, Savchenko A, Serio AW, Krause KM, Wright GD. Plazomicin retains antibiotic activity against most aminoglycoside modifying enzymes. ACS Infect Dis. 2018;4:980–7.
Saravolatz LD, Stein GE. Plazomicin: a new aminoglycoside. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;70:704–70.
Kim HJ, LeVieux J, Yeh YC, Liu HW. C3’-deoxygenation of paromamine catalyzed by a radical S-adenosylmethionine enzyme: characterization of the enzyme AprD4 and its reductase partner AprD3. Angew Chem. 2016;55:3724–8.
Lv M, Ji X, Zhao J, Li Y, Zhang C, Su L, Ding W, Deng Z, Yu Y, Zhang Q. Characterization of a C3 deoxygenation pathway reveals a key branch point in aminoglycoside biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138:6427–35.
Kudo F, Tokumitsu T, Eguchi T. Substrate specificity of radical S-adenosyl-l-methionine dehydratase AprD4 and its partner reductase AprD3 in the C3’-deoxygenation of aminoglycoside antibiotics. J Antibiot. 2017;70:423–8.
Liu WQ, Amara P, Mouesca JM, Ji X, Renoux O, Martin L, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Nicolet Y. 1,2-Diol dehydration by the radical SAM enzyme AprD4: a matter of proton circulation and substrate flexibility. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140:1365–71.
Yokoyama K, Numakura M, Kudo F, Ohmori D, Eguchi T. Characterization and mechanistic study of a radical SAM dehydrogenase in the biosynthesis of butirosin. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:15147–55.
Park JW, Hong JS, Parajuli N, Jung WS, Park SR, Lim SK, Sohng JK, Yoon YJ. Genetic dissection of the biosynthetic route to gentamicin A2 by heterologous expression of its minimal gene set. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:8399–404.
Kim HJ, Liu YN, McCarty RM, Liu HW. Reaction catalyzed by GenK, a cobalamin-dependent radical S-Adenosyl-l-methionine methyltransferase in the biosynthetic pathway of gentamicin, proceeds with retention of configuration. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139:16084–7.
Li S, Guo J, Reva A, Huang F, Xiong B, Liu Y, Deng Z, Leadlay PF, Sun Y. Methyltransferases of gentamicin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:1340–5.
de Araujo NC, Bury PDS, Tavares MT, Huang F, Parise-Filho R, Leadlay P, Dias MVB. Crystal structure of GenD2, an NAD-dependent oxidoreductase involved in the biosynthesis of gentamicin. ACS Chem Biol. 2019;14:925–33.
Gu Y, Ni X, Ren J, Gao H, Wang D, Xia H. Biosynthesis of Epimers C2 and C2a in the Gentamicin C Complex. ChemBioChem. 2015;16:1933–42.
Shao L, Chen J, Wang C, Li JA, Tang Y, Chen D, Liu W. Characterization of a key aminoglycoside phosphotransferase in gentamicin biosynthesis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013;23:1438–41.
Huong NL, Lee NJ, Hwang HH, Son HB, Kim HJ, Seo EG, Hoang NH, Park JW. In vivo characterization of phosphotransferase-encoding genes istP and forP as interchangeable launchers of the C3’,4’-dideoxygenation biosynthetic pathway of 1,4-diaminocyclitol antibiotics. J Microbiol Biotechn. 2019;29:367–72.
Guo J, Huang F, Huang C, Duan X, Jian X, Leeper F, Deng Z, Leadlay PF, Sun Y. Specificity and promiscuity at the branch point in gentamicin biosynthesis. Chem Biol. 2014;21:608–18.
Jnawali HN, Subba B, Liou K, Sohng JK. Functional characterization of kanB by complementing in engineered Streptomyces fradiae Deltaneo6::tsr. Biotechnol Lett. 2009;31:869–75.
Eliot AC, Kirsch JF. Pyridoxal phosphate enzymes: mechanistic, structural, and evolutionary considerations. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:383–415.
Oliveira EF, Cerqueira NM, Fernandes PA, Ramos MJ. Mechanism of formation of the internal aldimine in pyridoxal 5’-phosphate-dependent enzymes. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:15496–505.
Toney MD. Reaction specificity in pyridoxal phosphate enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005;433:279–87.
Inoue H, Inagaki K, Adachi N, Tamura T, Esaki N, Soda K, Tanaka H. Role of tyrosine 114 of L-methionine gamma-lyase from Pseudomonas putida. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2000;64:2336–43.
Sato D, Nozaki T. Methionine gamma-lyase: the unique reaction mechanism, physiological roles, and therapeutic applications against infectious diseases and cancers. IUBMB Life. 2009;61:1019–28.
Chen X, Zhang H, Zhou S. The Bifunctional Enzyme, GenB4, catalyzes the last step of gentamicin 3’,4’-di-deoxygenation via reduction and transamination activities. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01317-0.
Beyer N, Alam J, Hallis TM, Guo Z, Liu HW. The biosynthesis of GDP-L-colitose: C-3 deoxygenation is catalyzed by a unique coenzyme B6-dependent enzyme. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:5584–5.
Hong L, Zhao Z, Liu HW. Characterization of SpnQ from the spinosyn biosynthetic pathway of Saccharopolyspora spinosa: mechanistic and evolutionary implications for C-3 deoxygenation in deoxysugar biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:14262–3.
Peterson E, Kaur P. Antibiotic resistance mechanisms in bacteria: Relationships between resistance determinants of antibiotic producers, environmental bacteria, and clinical pathogens. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:794.
Kudo F, Eguchi T. Biosynthetic genes for aminoglycoside antibiotics. J Antibiot. 2009;62:471–81.
Hanessian S, Maianti JP, Matias RD, Feeney LA, Armstrong ES. Hybrid aminoglycoside antibiotics via Tsuji palladium-catalyzed allylic deoxygenation. Org Lett. 2011;13:6476–9.
Ban YH, Song MC, Park JW, Yoon YJ. Minor components of aminoglycosides: recent advances in their biosynthesis and therapeutic potential. Nat Prod Rep. 2020;37:301–11.
Pawlowski AC, Johnson JW, Wright GD. Evolving medicinal chemistry strategies in antibiotic discovery. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2016;42:108–17.
Maianti JP, Hanessian S. Structural hybridization of three aminoglycoside antibiotics yields a potent broad-spectrum bactericide that eludes bacterial resistance enzymes. MedChemComm. 2016;7:170–6.
Hanessian S, Saavedra OM, Vilchis-Reyes MA, Maianti JP, Kanazawa H, Dozzo P, Matias RD, Serio A, Kondo J. Synthesis, broad spectrum antibacterial activity, and X-ray co-crystal structure of the decoding bacterial ribosomal A-site with 4’-deoxy-4’-fluoro neomycin analogs. Chem Sci. 2014;5:4621–32.
Hanessian S, Giguere A, Grzyb J, Maianti JP, Saavedra OM, Aggen JB, Linsell MS, Goldblum AA, Hildebrandt DJ, Kane TR. Toward overcoming Staphylococcus aureus aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms with a functionally designed neomycin analogue. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2011;2:924–8.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81773613, 81502965), and the Scientific Research Fund of Liaoning Provincial Education Department (2017LZD05, 2019LZD03). We thank LetPub (www. letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XN and HZ designed research; SZ, XC, YL, HZ, and XN performed research; SZ, XC, YL, HZ, XN, and HZ analyzed data; XN, MD and SZ wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Sequence alignment of GenB3 with its homologs in other aminoglycoside pathways. Figure S2. Structure identification of compound 2. Figure S3. HPLC-ELSD analysis of GenP reactions with gentamicin X2 and G418. Figure S4. 1H and 13C NMR of compound 6. Figure S5. Ammonia analysis of GenB3-catalyzed reaction with compound 4. Figure S6. GenP and GenB3 catalyze dideoxygenation. Figure S7. Identification of PLP-binding sites in GenB3-catalyzed reactions. Figure S8. Dissection of the C-4',5' reduction process catalyzed by GenB4. Figure S9. Schematic representation and confirmation by PCR amplification of in-frame deletions of genP and genB3 genes. Table S1. Kinetic constants of GenP catalyzing phosphorylation of different substrates. Table S2. List of primers used in this study. Table S3. List of strains and plasmids used in this study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, S., Chen, X., Ni, X. et al. Pyridoxal-5′-phosphate-dependent enzyme GenB3 Catalyzes C-3′,4′-dideoxygenation in gentamicin biosynthesis. Microb Cell Fact 20, 65 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01558-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01558-7