Abstract
Background
Although type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is one of the most frequent comorbidities in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF), the effects of T2DM on the exercise capacity of CHF patients are fully unknown. Here, we tested the hypothesis that the coexistence of T2DM lowers CHF patients’ peak aerobic capacity.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed the cases of 275 Japanese CHF patients with non-reduced ejection fraction (left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF] ≥ 40%) or reduced EF (LVEF < 40%) who underwent cardiopulmonary exercise testing. We divided them into diabetic and nondiabetic groups in each CHF cohort.
Results
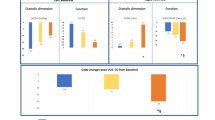
The mean peak oxygen uptake (VO2) value was 16.87 mL/kg/min in the non-reduced LVEF cohort and 15.52 mL/kg/min in the reduced LVEF cohort. The peak VO2 was lower in the diabetics versus the nondiabetics in the non-reduced LVEF cohort with the mean difference (95% confidence interval [95% CI]) of − 0.93 (− 1.82 to − 0.04) mL/kg/min and in the reduced LVEF cohort with the mean difference of − 1.05 (− 1.96 to − 0.15) mL/kg/min, after adjustment for age-squared, gender, anemia, renal function, LVEF, and log B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP). The adjusted VO2 at anaerobic threshold (AT), a submaximal aerobic capacity, was also decreased in the diabetic patients with both non-reduced and reduced LVEFs. Intriguingly, the diabetic patients had a lower adjusted peak O2 pulse than the nondiabetic patients in the reduced LVEF cohort, but not in the non-reduced LVEF cohort. A multivariate analysis showed that the presence of T2DM was an independent predictor of lowered peak VO2 in CHF patients with non-reduced LVEF and those with reduced LVEF.
Conclusions
T2DM was associated with lowered peak VO2 in CHF patients with non-reduced or reduced LVEF. The presence of T2DM has a negative impact on CHF patients’ exercise capacity, and the degree of impact is partly dependent on their LV systolic function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Exercise intolerance is one of the cardinal manifestations of chronic heart failure (CHF), and it influences the disease severity and prognosis of individuals with CHF. In particular, a lowered peak oxygen uptake (VO2) is known as a strong predictor of all-cause mortality in CHF patients [1]. We and others have demonstrated that skeletal muscle dysfunction plays a crucial role in exercise intolerance in CHF patients [2, 3]. Among the established risk factors for CHF, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is one of the most frequently observed comorbidities of CHF. The survival rate of CHF patients with T2DM is markedly reduced compared to those without type 2 diabetes [4, 5]. Intriguingly, a common phenotype of patients with T2DM is the presence of one or more skeletal muscle alterations such as impaired energy metabolism and muscle fiber-type switch [6, 7], and this phenotype is similar to that of patients with CHF. In addition, lowered aerobic capacity independently predicts the all-cause mortality of diabetic patients [8]. Accordingly, T2DM may further reduce the aerobic capacity (including the peak VO2) of CHF patients.
Several research groups have shown that T2DM has negative effects on the exercise capacity of CHF patients who have a reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF < 40%) [9, 10] or a preserved LVEF (≥ 50%) [11]. However, there was no study that comprehensively investigated effects of T2DM on the exercise capacity in CHF patients with non-reduced LVEF (≥ 40%) and those with reduced LVEF (< 40%). Herein, we examined whether T2DM is an independent predictor of lowered peak VO2 in CHF patients with either non-reduced or reduced LVEF, and whether the presence of T2DM has a differential impact on exercise capacity between CHF patients with non-reduced LVEF and those with reduced LVEF.
Methods
Patients
We retrospectively analyzed the cases of a total of 275 stable Japanese patients with CHF who underwent cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) between January 2009 and March 2016 at Hokkaido University Hospital. Before the CPET, all of the patients had a history of one or more hospital admissions due to worsening HF diagnosed on the basis of the American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF)/American Heart Association (AHA) Task Force on Practice guidelines [12]. In particular, patients who had a normal LVEF at the time of hospitalization was diagnosed as HF when they met the following criteria; (1) clinical signs or symptoms of HF; (2) evidence of abnormal LV diastolic function determined by echocardiography or cardiac catheterization; (3) exclusion of other potential noncardiac causes. All the patients were at stage C or stage D HF in the ACC/AHA guidelines. T2DM was defined as a fasting blood glucose level ≥ 126 mg/dL, a glycohemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level ≥ 6.5%, and/or the need for an oral hypoglycemic agent or insulin. Patients who were unable to perform maximal exercise due to pulmonary disease, peripheral artery disease, stroke, or orthopedic disease were excluded. We also excluded patients in whom the peak respiratory exchange ratio (RER) did not reach 1.05 in the CPET, as they might not be able to perform maximal exercise. The present investigation is a part of a large cohort study that used the database of the Exercise Testing Laboratory at Hokkaido University Hospital, and thus, some of the data are from the same patients whose data have been published in a different context [13].
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing
Each of the patients exercised on an upright cycle ergometer (Aerobike 75XLII, Combi Wellness, Tokyo, Japan) using a ramp protocol (5–25 watts/min). A respiratory gas analysis was simultaneously performed with a breath-by-breath apparatus (Aeromonitor AE300S, Minato Medical Science, Osaka, Japan) as described [14]. Peak VO2 was defined as the maximal VO2 attained during the symptom-limited incremental exercise, and the anaerobic threshold (AT) was determined by the V-slope method [15]. The RER was calculated as the ratio of carbon dioxide production (VCO2) to VO2. We calculated the ΔVO2/Δworkload as the ratio of the peak VO2 to the peak workload. The peak O2 pulse was calculated as the ratio of the peak VO2 to the peak heart rate (HR). We defined HR reserve as: HR reserve = peak HR − resting HR. The chronotropic index (CI) was defined as: CI = (peak HR − resting HR) / (predicted maximal HR − resting HR), where the predicted maximal HR was calculated as: the predicted maximal HR = 220 − age. The lowest minute ventilation (VE)/VCO2 during exercise was evaluated to assess patients’ ventilatory efficiency.
Other clinical variables and outcomes
We reviewed the patients’ medical records to collect their demographic and clinical data including age, gender, body mass index (BMI), New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class, primary cause of HF, cardiovascular risk factor(s), and medication(s). Each patient’s echocardiographic parameters and laboratory data were acquired within 30 days before or after he or she underwent the CPET. The left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD) of each patient was evaluated from the parasternal long-axis view, and the LVEF was measured by the biplane method of disks using echocardiography. To assess LV diastolic function, we measured the peak early-diastolic and atrial systolic transmitral flow velocities (E and A, respectively) and the deceleration time of the E wave using pulsed-Doppler echocardiography, and the peak early-diastolic mitral annular velocity (e′) at the septal and lateral sides of the annulus with tissue-Doppler imaging. The e′ was averaged, and then, E/e′ was calculated. Hemoglobin, plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), and the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were determined by routine in-house analyses. The eGFR was calculated from the serum creatinine values and age using the Japanese equation [16]: eGFR = 194 × (serum creatinine, mg/dL)−1.094 × (age, years)−0.287 × (0.739 if female).
Statistical analyses
Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables and as numbers (percentages) for categorical variables. We divided the CHF patients into diabetic and nondiabetic groups based on the presence/absence of T2DM. We also conducted a subgroup analysis defined by the patients’ non-reduced LVEF (LVEF ≥ 40%) or reduced LVEF (LVEF < 40%). We compared the CPET parameters between the diabetic and nondiabetic groups in each subgroup after adjustment for age-squared, gender, hemoglobin, eGFR, LVEF, and log BNP, all of which are considered confounders. We performed a multivariate analysis to determine the independent variables of peak VO2 in the CHF patients, including T2DM (treated as the presence of T2DM = 1; the absence of T2DM = 0), LVEF, log BNP, age-squared, gender, hemoglobin, and eGFR. All analyses were performed using the JMP 12.2.0 program (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). A confidence level was set at 95%. Probability (P)-values < 0.05 were considered significant.
Results
The baseline characteristics of the total CHF population
The baseline data of the total population of CHF are summarized in Table 1. Of the 275 patients with CHF, 78 patients (28%) had T2DM. The mean age of the total CHF population was 56 years (61 years in the diabetic group and 54 years in the nondiabetic group). The primary cause of HF was ischemic heart disease (21% of the total population; 28% of the diabetics and 19% of the nondiabetics), dilated cardiomyopathy (26% of the total population; 27% of the diabetics and 26% of the nondiabetics), or other causes including hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, hypertensive heart disease, and valvular heart disease. In addition, 48% of the total CHF population had a non-reduced LVEF.
As expected, the HbA1c level was higher in the diabetic patients than in the nondiabetic patients. Renal function was impaired in the diabetic patients with higher serum creatine and lower eGFR compared to the nondiabetic patients. The mean level of plasma BNP, a marker of the severity of HF, was 291.6 pg/dL in the total CHF population, 321.0 pg/dL in the diabetic patients with CHF, and 280.5 pg/dL in the nondiabetic patients with CHF. Regarding medications, 83% of the total CHF population were being treated with an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB), and 80% received β-blockers; 9% of the diabetic patients with CHF were treated with insulin.
The baseline characteristics of the CHF patients with non-reduced or reduced LVEF
We divided the total CHF population into two subgroups: the patients with non-reduced LVEF (≥ 40%; n = 131) and the patients with reduced LVEF (< 40%; n = 144). The baseline data of each subgroup are summarized in Table 2. The mean ages of the CHF patients with LVEF ≥ 40% and those with LVEF < 40% were 58 years and 54 years, and 67% and 86% of these subgroups were male, respectively. The ratio of New York Heart Association (NYHA) class I (asymptomatic)/class II (mild CHF)/class III (moderate-to-severe CHF) was 22%/68%/10% in the LVEF ≥ 40% group and 10%/61%/28% in the LVEF < 40% group. The E/e’ was higher in the diabetics compared to the nondiabetics in the non-reduced LVEF cohort, indicating impaired LV diastolic function in the diabetic patients with non-reduced LVEF. The mean level of plasma BNP was 180.0 pg/dL in the LVEF ≥ 40% and higher at 383.7 pg/dL in the LVEF < 40% group. Diabetic patients with non-reduced LVEF were more often taking ACE inhibitors or ARBs and β-blockers, while those with reduced LVEF were more often taking statins.
We further divided the non-reduced LVEF cohort into the preserved LVEF (≥ 50%; n = 73) and the mid-range LVEF cohorts (40–49%; n = 58), which is summarized in Additional file 1: Table S1. Diabetic patients with LVEF ≥ 50% had more often hypertension and atrial fibrillation, while those with LVEF 40–49% had more often hypertension and dyslipidemia. The E/e′ was higher in the diabetics in the preserved LVEF cohort.
The exercise capacity of the CHF patients with non-reduced or reduced LVEF
The CPET data of the CHF patients with non-reduced or reduced LVEF are summarized in Table 3. The mean peak VO2 value was 16.87 mL/kg/min in the LVEF ≥ 40% group and 15.52 mL/kg/min in the LVEF < 40% group. After the adjustment for age-squared, gender, anemia, renal function, LVEF, and log BNP, the peak VO2 was lower in the diabetics compared to the nondiabetics among the patients with LVEF ≥ 40%, with the mean difference (95% CI) of − 0.93 (− 1.82 to − 0.04) mL/kg/min; the peak VO2 was also lower in the diabetics compared to the nondiabetics among the patients with LVEF < 40%, with the mean difference of − 1.05 (− 1.96 to − 0.15) mL/kg/min. The O2 pulse (i.e., the O2 consumed per beat) at peak exercise was decreased in the diabetics compared to the nondiabetics only in the LVEF < 40% group. The AT VO2, a marker of the body’s submaximal aerobic capacity, was also lower in the diabetics than in the nondiabetics in the LVEF ≥ 40% group, with the adjusted mean difference of − 0.65 (− 1.18 to − 0.12) mL/kg/min, and in the LVEF < 40% group with the adjusted mean difference of − 0.66 (− 1.11 to − 0.21) mL/kg/min. In contrast, there was no difference in the lowest VE/VCO2 between the diabetics and nondiabetics in either LVEF group. When we further divided the non-reduced LVEF cohort into the preserved LVEF and the mid-range LVEF cohorts, the peak VO2 and the AT VO2 were lowered in the diabetics in the LVEF 40-49% group, but not in the LVEF ≥ 50% group, after adjustment for age-squared, gender, anemia, renal function, LVEF, and log BNP (Additional file 1: Table S2).
Predictors of lowered peak aerobic capacity in CHF patients with non-reduced or reduced LVEF
The results of the multivariate analysis revealed that after the adjustment for age-squared, gender, hemoglobin, eGFR, LVEF, and log BNP, the presence of T2DM was an independent predictor of lowered peak VO2 in the CHF patients with LVEF ≥ 40% and in those with LVEF < 40% (Table 4). The LVEF, but not log BNP, was also an independent variable to predict the peak VO2 only in the CHF patients with LVEF < 40% (Table 4). In the subgroup analysis of the LVEF ≥ 50% and LVEF 40–49% cohorts, the presence of T2DM was an independent predictor of lowered peak VO2 only in the LVEF 40-49% cohort (Additional file 1: Table S3).
Discussion
Our retrospective analyses of 275 patients with CHF revealed that peak VO2 and AT VO2 were lower in the presence of T2DM in the patients with non-reduced LVEF as well as in those with reduced LVEF. Notably, the multivariate analysis showed that T2DM was an independent predictor of the lowered peak VO2 in both the CHF patients with non-reduced LVEF and those with reduced LVEF after the adjustment for age-squared, gender, hemoglobin, eGFR, LVEF, and log BNP, all of which may influence exercise capacity.
Exercise intolerance is a cardinal symptom of HF regardless of the LVEF [17]. It is widely recognized that comorbidity of T2DM may induce reduced cardiorespiratory fitness as well as worse clinical outcomes in patients with CHF. It has been demonstrated that T2DM lowers the peak VO2 in the CHF patients who have a reduced LVEF (< 40%) [9, 10] or a preserved LVEF (≥ 50%) [11]. To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first to thoroughly investigate the negative effects of the presence of T2DM on the exercise capacity in CHF patients with both non-reduced and reduced LVEFs.
In the present study, the adjusted mean difference of peak VO2 between the diabetics and the non-diabetics was 0.93 mL/kg/min (approx. 6% of mean value of peak VO2 in all CHF cohort) and 1.05 mL/kg/min (approx. 7% of mean value of peak VO2 in all CHF cohort) in the patients with non-reduce LVEF and in those with reduced LVEF, respectively, and the difference of absolute value of peak VO2 between the diabetics and the nondiabetics appears to be small. However, a large clinical trial has reported that every 6% increase of peak VO2 after exercise training results in a 5% lower risk of all-cause mortality or all-cause hospitalization and an 8% lower risk of cardiovascular mortality or HF-related hospitalization in CHF patients [18]. Accordingly, a modest but significant difference of peak VO2 is clinically relevant in the prevention of HF development.
The VO2 is defined by the Fick equation: VO2 = cardiac output × arteriovenous O2 difference, where arteriovenous O2 difference is determined by peripheral factors. Low aerobic capacity may be generally caused by cardiac, vascular, or skeletal muscle dysfunction, which results in reduced O2 delivery or O2 utilization. Recent studies have shown that predominantly peripheral (i.e., noncardiac) factors contribute to reduced peak VO2 in CHF patients [19, 20]. In particular, skeletal muscle relies largely on O2 utilization for energy production during exercise, and it has been demonstrated that skeletal muscle dysfunction characterized by impaired mitochondrial oxidative capacity and fiber-type switch (i.e., a reduced ratio of slow oxidative fibers to fast glycolytic fibers) is a common feature of CHF patients with both preserved and reduced LVEFs [3, 21, 22]. Interestingly, the arteriovenous O2 difference at peak exercise is reported to be reduced in association with lowered peak VO2 in patients with T2DM [23], and a similar functional impairment of skeletal muscle is observed in patients with insulin resistance or T2DM [6, 7, 24]. Taken together, the presence of T2DM may further decrease the peak VO2 via skeletal muscle dysfunction in CHF patients with non-reduced or reduced LVEF.
On the other hand, we observed that the peak O2 pulse (a parameter that relies on the stroke volume at peak exercise) was lower in the diabetics than in the nondiabetics in the group of CHF patients with a reduced LVEF, but not in those with a non-reduced LVEF. In addition, the multivariate analysis showed that the LVEF was an independent predictor of lowered peak VO2 in the CHF patients with reduced LVEF. Accordingly, in patients with reduced LVEF, a decrease in LV systolic function (i.e., cardiac factors) may also underlie the association between T2DM and lowered peak aerobic capacity.
Another possible explanation of the lowered peak aerobic capacity in diabetic CHF patients is reduced muscle blood flow, which results in low O2 supply to skeletal muscle. Insulin resistance is associated with decreased vasodilatation and capillary recruitment [25], and a recent study revealed that peak VO2 was correlated with the muscle blood flow reserve in patients with T2DM [26]. In addition, microvascular complications of diabetes such as retinopathy and microalbuminuria are associated with a lowered peak VO2 in these patients [27]. Taken together, these findings suggest that the comorbidity of T2DM in CHF patients may have an additive effect that worsens the patients’ aerobic capacity via an impairment of endothelium-dependent vasodilatation.
Anemia, a determinant of lowered peak aerobic capacity, is known to be common in diabetic patients, and prevalence of anemia in diabetic patients could be doubled when they have an impaired renal function [28]. In addition, it has been shown that iron deficiency is frequently observed in diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease [29]. Since iron plays a role in O2 delivery, O2 storage, and muscle oxidative metabolism, iron deficiency can be an independent predictor of reduced peak VO2 in patients with CHF irrespective of hemoglobin levels [30]. In the present study, hemoglobin levels were comparable between the groups, but the eGFR was lower in the diabetics than in the non-diabetics in the CHF patients with non-reduced and reduced LVEFs. Although we did not measure serum ferritin levels, iron deficiency might affect lowered peak aerobic capacity in the CHF patients with T2DM.
Guazzi et al. demonstrated that the coexistence of T2DM reduces the peak VO2 in CHF patients with a reduced LVEF via an impairment of the alveolar-capillary gas transfer, possibly due to microangiopathy, which may lead to decreased O2 uptake through the lungs during exercise [9, 31]. In the present study, the lowest VE/VCO2, a parameter of ventilatory efficiency during exercise, did not differ between the CHF patients with and without T2DM, which is inconsistent with the previous report [9]. However, we did not evaluate the patients’ pulmonary function, and we therefore could not exclude the possibility of a contribution of the reduced capacity of pulmonary O2 perfusion to the depressed peak VO2 in CHF patients with T2DM.
Our analyses demonstrated that T2DM is an independent predictor of lowered peak VO2 in CHF patients with non-reduced LVEF (≥ 40%). However, in the multivariate analysis to determine the independent variables of peak VO2 after division of the non-reduced LVEF cohort into the preserved LVEF (≥ 50%) and the mid-range LVEF (40–49%) cohorts, the presence of T2DM did not reach statistical significance in the CHF patients with preserved LVEF, which is inconsistent with a previous study [11]. There are some possible reasons for it. First, in the present study, the number of CHF patients with preserved LVEF was small, and therefore, it may be insufficient to conduct multivariate analysis. Second, CHF with preserved LVEF is a complex, heterogenous syndrome involving multiple comorbidities such as hypertension and atrial fibrillation, which may weaken the impact of T2DM on the CHF patients’ exercise capacity. Accordingly, CHF patients with preserved LVEF is likely to be less susceptible to T2DM with respect to exercise capacity than those with reduced LVEF.
It has been shown that sedentary behavior and physical inactivity may induce exercise intolerance and increase risk of cardiovascular events in individuals with pre-diabetes or T2DM [32, 33] and in patients with CHF [34]. Accordingly, promotion of increased physical activity and exercise training is essential for CHF patients with T2DM to improve cardiorespiratory fitness and reduce cardiovascular or all-cause mortality. Indeed, various types of exercise training including moderate-intensity continuous training and high-intensity interval training are reported to improve cardiac function, vascular function, lipid profiles, and low-grade inflammation as well as exercise capacity in obese subjects or patients with T2DM [35,36,37,38] and in patients with CHF [39]. A large clinical trial has shown that sustained improvement of exercise capacity by intensive lifestyle intervention aiming at increased physical activity and weight loss reduces risk of incident HF in obese subjects with T2DM [40]. Because CHF patients with T2DM tend to have multiple comorbidities and optimal exercise training may vary depending on individual’s target of exercise parameters, types of exercise should be personalized [41]. For evaluation of exercise capacity, a 6-min walk test can be used as an alternative and cost-effective tool instead of CPET in CHF patients with T2DM [42].
There are some limitations in this study. First, we could not identify the causes of the lowered peak aerobic capacity in the CHF patients with T2DM, including cardiac and peripheral factors that determine the peak VO2. Second, our participants’ mean value of peak VO2 was higher than 14 mL/kg/min, a cut-off value of candidate of heart transplantation, indicating that most participants had a mild-to-moderate CHF. Third, some of the patients underwent echocardiography or blood testing on another day within 30 days before or after CPET, which might influence the data analysis, although all the participants were in stable condition. Finally, we could not eliminate patients with recovered or improved LVEF from the non-reduced LVEF cohort.
Conclusions
T2DM is an independent predictor of the lower peak VO2 in CHF patients with non-reduced LVEF and in those with reduced LVEF. The comorbidity of T2DM has a negative impact on CHF patients’ exercise capacity, and the degree of impact is partly dependent on their LV systolic function. The prevention of T2DM is important not only for the reduction of cardiovascular risks but also for the maintenance of exercise capacity in HF management.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due regulations of patient information to be released in public but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request, after anonymization.
Abbreviations
- A:
-
atrial systolic transmitral flow velocity
- ACE:
-
angiotensin converting enzyme
- ARB:
-
angiotensin receptor blocker
- AT:
-
anaerobic threshold
- BNP:
-
B-type natriuretic peptide
- CHF:
-
chronic heart failure
- CI:
-
chronotropic index
- DPP4:
-
dipeptidyl peptidase 4
- CPET:
-
cardiopulmonary exercise testing
- E:
-
peak early-diastolic transmitral flow velocity
- e′:
-
peak early-diastolic mitral annular velocity
- eGFR:
-
estimated glomerular filtration rate
- HbA1c:
-
glycohemoglobin A1c
- HR:
-
heart rate
- LVEDD:
-
left ventricular end-diastolic diameter
- LVEF:
-
left ventricular ejection fraction
- MRAs:
-
mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
- NYHA:
-
New York Heart Association
- RER:
-
respiratory exchange ratio
- SD:
-
standard deviation
- T2DM:
-
type 2 diabetes mellitus
- VCO2 :
-
carbon dioxide production
- VE:
-
minute ventilation
- VO2 :
-
oxygen uptake
- 95% CI:
-
95% confidence interval
References
Mancini DM, Eisen H, Kussmaul W, Mull R, Edmunds LH Jr, Wilson JR. Value of peak exercise oxygen consumption for optimal timing of cardiac transplantation in ambulatory patients with heart failure. Circulation. 1991;83(3):778–86.
Massie B, Conway M, Yonge R, Frostick S, Ledingham J, Sleight P, Radda G, Rajagopalan B. Skeletal muscle metabolism in patients with congestive heart failure: relation to clinical severity and blood flow. Circulation. 1987;76(5):1009–19.
Okita K, Yonezawa K, Nishijima H, Hanada A, Ohtsubo M, Kohya T, Murakami T, Kitabatake A. Skeletal muscle metabolism limits exercise capacity in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation. 1998;98(18):1886–91.
Dries DL, Sweitzer NK, Drazner MH, Stevenson LW, Gersh BJ. Prognostic impact of diabetes mellitus in patients with heart failure according to the etiology of left ventricular systolic dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;38(2):421–8.
Varela-Roman A, Grigorian Shamagian L, Barge Caballero E, Mazon Ramos P, Rigueiro Veloso P, Gonzalez-Juanatey JR. Influence of diabetes on the survival of patients hospitalized with heart failure: a 12-year study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2005;7(5):859–64.
Mogensen M, Sahlin K, Fernstrom M, Glintborg D, Vind BF, Beck-Nielsen H, Hojlund K. Mitochondrial respiration is decreased in skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2007;56(6):1592–9.
Oberbach A, Bossenz Y, Lehmann S, Niebauer J, Adams V, Paschke R, Schon MR, Bluher M, Punkt K. Altered fiber distribution and fiber-specific glycolytic and oxidative enzyme activity in skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(4):895–900.
Wei M, Gibbons LW, Kampert JB, Nichaman MZ, Blair SN. Low cardiorespiratory fitness and physical inactivity as predictors of mortality in men with type 2 diabetes. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132(8):605–11.
Guazzi M, Brambilla R, Pontone G, Agostoni P, Guazzi MD. Effect of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus on pulmonary function and exercise tolerance in chronic congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2002;89(2):191–7.
Tibb AS, Ennezat PV, Chen JA, Haider A, Gundewar S, Cotarlan V, Aggarwal VS, Talreja A, Le Jemtel TH. Diabetes lowers aerobic capacity in heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46(5):930–1.
Lindman BR, Davila-Roman VG, Mann DL, McNulty S, Semigran MJ, Lewis GD, de Fuentes L, Joseph SM, Vader J, Hernandez AF, et al. Cardiovascular phenotype in HFpEF patients with or without diabetes: a RELAX trial ancillary study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(6):541–9.
Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Drazner MH, Fonarow GC, Geraci SA, Horwich T, Januzzi JL, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(16):e147–239.
Kakutani N, Fukushima A, Yokota T, Katayama T, Nambu H, Shirakawa R, Maekawa S, Abe T, Takada S, Furihata T, et al. Impact of high respiratory exchange ratio during submaximal exercise on adverse clinical outcome in heart failure. Circ J. 2018;82(11):2753–60.
Yokota T, Kinugawa S, Okita K, Hirabayashi K, Suga T, Hattori M, Nakagawa Y, Oyama-Manabe N, Shirato H, Tsutsui H. Lower aerobic capacity was associated with abnormal intramuscular energetics in patients with metabolic syndrome. Hypertens Res. 2011;34(9):1029–34.
Beaver WL, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ. A new method for detecting anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J Appl Physiol. 1986;60(6):2020–7.
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K, Yamagata K, Tomino Y, Yokoyama H, Hishida A, et al. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53(6):982–92.
Nadruz W, West E, Sengelov M, Santos M, Groarke JD, Forman DE, Claggett B, Skali H, Shah AM. Prognostic value of cardiopulmonary exercise testing in heart failure with reduced, midrange, and preserved ejection fraction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6:11.
Swank AM, Horton J, Fleg JL, Fonarow GC, Keteyian S, Goldberg L, Wolfel G, Handberg EM, Bensimhon D, Illiou MC, et al. Modest increase in peak VO2 is related to better clinical outcomes in chronic heart failure patients: results from heart failure and a controlled trial to investigate outcomes of exercise training. Circ Heart Fail. 2012;5(5):579–85.
Dhakal BP, Malhotra R, Murphy RM, Pappagianopoulos PP, Baggish AL, Weiner RB, Houstis NE, Eisman AS, Hough SS, Lewis GD. Mechanisms of exercise intolerance in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: the role of abnormal peripheral oxygen extraction. Circ Heart Fail. 2015;8(2):286–94.
Shimiaie J, Sherez J, Aviram G, Megidish R, Viskin S, Halkin A, Ingbir M, Nesher N, Biner S, Keren G, et al. Determinants of effort intolerance in patients with heart failure: combined echocardiography and cardiopulmonary stress protocol. JACC Heart Fail. 2015;3(10):803–14.
De Sousa E, Veksler V, Bigard X, Mateo P, Ventura-Clapier R. Heart failure affects mitochondrial but not myofibrillar intrinsic properties of skeletal muscle. Circulation. 2000;102(15):1847–53.
Kitzman DW, Nicklas B, Kraus WE, Lyles MF, Eggebeen J, Morgan TM, Haykowsky M. Skeletal muscle abnormalities and exercise intolerance in older patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014;306(9):H1364–70.
Baldi JC, Aoina JL, Oxenham HC, Bagg W, Doughty RN. Reduced exercise arteriovenous O2 difference in Type 2 diabetes. J Appl Physiol. 2003;94(3):1033–8.
Yokota T, Kinugawa S, Yamato M, Hirabayashi K, Suga T, Takada S, Harada K, Morita N, Oyama-Manabe N, Kikuchi Y, et al. Systemic oxidative stress is associated with lower aerobic capacity and impaired skeletal muscle energy metabolism in patients with metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(5):1341–6.
Reusch JE, Bridenstine M, Regensteiner JG. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and exercise impairment. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2013;14(1):77–86.
Sacre JW, Jellis CL, Haluska BA, Jenkins C, Coombes JS, Marwick TH, Keske MA. Association of exercise intolerance in type 2 diabetes with skeletal muscle blood flow reserve. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;8(8):913–21.
Estacio RO, Regensteiner JG, Wolfel EE, Jeffers B, Dickenson M, Schrier RW. The association between diabetic complications and exercise capacity in NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(2):291–5.
Thomas MC, MacIsaac RJ, Tsalamandris C, Molyneaux L, Goubina I, Fulcher G, Yue D, Jerums G. The burden of anaemia in type 2 diabetes and the role of nephropathy: a cross-sectional audit. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19(7):1792–7.
Robles NR, Ramos JL, Chavez E, Gonzalez Candia B, Bayo MA, Cidoncha A, Gomez JL, Cubero JJ. Iron deficiency in chronic kidney disease patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018;12(6):933–7.
Jankowska EA, Rozentryt P, Witkowska A, Nowak J, Hartmann O, Ponikowska B, Borodulin-Nadzieja L, von Haehling S, Doehner W, Banasiak W, et al. Iron deficiency predicts impaired exercise capacity in patients with systolic chronic heart failure. J Card Fail. 2011;17(11):899–906.
Guazzi M, Brambilla R, De Vita S, Guazzi MD. Diabetes worsens pulmonary diffusion in heart failure, and insulin counteracts this effect. Am J Respir Crit Care. 2002;166(7):978–82.
Amadid H, Johansen NB, Bjerregaard AL, Brage S, Faerch K, Lauritzen T, Witte DR, Sandbaek A, Jorgensen ME, Vistisen D. The role of physical activity in the development of first cardiovascular disease event: a tree-structured survival analysis of the Danish ADDITION-PRO cohort. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17(1):126.
Roberts TJ, Burns AT, MacIsaac RJ, MacIsaac AI, Prior DL, La Gerche A. Exercise capacity in diabetes mellitus is predicted by activity status and cardiac size rather than cardiac function: a case control study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17(1):44.
Lavie CJ, Ozemek C, Carbone S, Katzmarzyk PT, Blair SN. Sedentary behavior, exercise, and cardiovascular health. Circ Res. 2019;124(5):799–815.
Anand V, Garg S, Garg J, Bano S, Pritzker M. Impact of exercise training on cardiac function among patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2018;38(6):358–65.
Magalhaes JP, Melo X, Correia IR, Ribeiro RT, Raposo J, Dores H, Bicho M, Sardinha LB. Effects of combined training with different intensities on vascular health in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 1-year randomized controlled trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18(1):34.
Pedersen LR, Olsen RH, Anholm C, Astrup A, Eugen-Olsen J, Fenger M, Simonsen L, Walzem RL, Haugaard SB, Prescott E. Effects of 1 year of exercise training versus combined exercise training and weight loss on body composition, low-grade inflammation and lipids in overweight patients with coronary artery disease: a randomized trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18(1):127.
Qiu S, Cai X, Yin H, Sun Z, Zugel M, Steinacker JM, Schumann U. Exercise training and endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17(1):64.
Wisloff U, Stoylen A, Loennechen JP, Bruvold M, Rognmo O, Haram PM, Tjonna AE, Helgerud J, Slordahl SA, Lee SJ, et al. Superior cardiovascular effect of aerobic interval training versus moderate continuous training in heart failure patients: a randomized study. Circulation. 2007;115(24):3086–94.
Pandey A, Patel KV, Bahnson JL, Gaussoin SA, Martin CK, Balasubramanyam A, Johnson KC, McGuire DK, Bertoni AG, Kitzman D, et al. Association of intensive lifestyle intervention, fitness, and body mass index with risk of heart failure in overweight or obese adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an analysis from the Look AHEAD Trial. Circulation. 2020;141(16):1295–306.
Kemps H, Krankel N, Dorr M, Moholdt T, Wilhelm M, Paneni F, Serratosa L, Ekker Solberg E, Hansen D, Halle M, et al. Exercise training for patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: What to pursue and how to do it. A Position paper of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC). Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2019;26(7):709–27.
Nolen-Doerr E, Crick K, Saha C, de Groot M, Pillay Y, Shubrook JH, Donley D, Hornsby WG Jr. Six-minute walk test as a predictive measure of exercise capacity in adults with type 2 diabetes. Cardiopulm Phys Ther J. 2018;29(3):124–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the participants in the present study.
Funding
This work was partly supported by grants from the Center of Innovation Program from the Japan Science and Technology Agency (#JPMJCE1301 to TY) and a KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (18K08022 to TY).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TAb wrote the manuscript and analyzed data. TY designed the study and wrote the manuscript. NK, TK, RS, SM, HN, YO, KY, IN, and ST researched data and contributed to the discussion. IY contributed to the data analysis and reviewed/edited the manuscript. AF, KO, and SK designed the study, contributed to the discussion, and reviewed/edited the manuscript. TAn contributed to the discussion and reviewed/edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Hokkaido University Hospital in accordance with the ethical principles described in the latest version of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
All the authors listed have approved the manuscript for publication.
Competing interests
IY received a speaking fee from Japan Tobacco, Inc. (Pharmaceutical Division). The other authors declare no competing interest relevant to this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1. Table S1.
Baseline characteristics of the CHF patients with preserved LVEF (≥50%) or mid-range LVEF (40-49%). Table S2. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing parameters of the CHF patients with preserved LVEF (≥50%) or mid-range LVEF (40-49%). Table S3. Multivariable analysis for peak VO2 in the CHF patients with preserved LVEF (≥50%) or mid-range LVEF (40-49%).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Abe, T., Yokota, T., Fukushima, A. et al. Type 2 diabetes is an independent predictor of lowered peak aerobic capacity in heart failure patients with non-reduced or reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. Cardiovasc Diabetol 19, 142 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-020-01114-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-020-01114-4