Abstract
Background
Curcumin is a biomolecule that can be extracted from the Curcuma longa that has been shown to have the potential to aid skin wound healing. It has been studied for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which may help to reduce swelling and promote tissue repair. However, curcumin has low solubility in water, which can limit its absorption and bioavailability. Encapsulating it in lipid nanoparticles may help to increase its absorption, leading to improved bioavailability.
Methods
Curcumin-loaded nanostructure lipid nanocarriers (CURC-NLCs) were prepared and characterized. Also, the phenolic, flavonoid contents, antioxidant and antimicrobial efficacy against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria were investigated. Furthermore, in vivo rabbit animal model was used to test its regenerative capacity and wound-healing efficiency.
Results
The CURC-NLCs significantly increased the content of phenolic and flavonoid compounds compared to curcumin, resulting in a dramatic increase in antioxidant activity. CURC-NLCs also showed a potent inhibitory effect on Gram-positive, Gram-negative, and fungi, two times higher than curcumin. CURC-NLCs showed a higher potential to fasten the wound healing of full-thickness skin injuries as it resulted in 1.15- and 1.9-fold higher wound closure at the first week of injury compared to curcumin and control, respectively (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion
These results suggest that CURC-NLCs have an excellent potential to promote skin regeneration, which could be attributed to its antioxidant and broad-spectrum antimicrobial effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Herbal remedies have been used for centuries to aid in the healing of wounds. Many herbs have been shown to have properties that may be beneficial for wound healing, including antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. Curcumin is a natural compound found in the spice turmeric, a member of the ginger family. It is the active ingredient in turmeric and is responsible for its yellow colour. The chemical structure of curcumin consists of a cyclic diarylheptanoid, which is a type of polyphenol. It has a chemical formula of C21H20O6 and is composed of three main functional groups: a benzene ring, a hydroxyl group, and a ketone group [1]. Curcumin has been shown to have the potential to aid skin wound healing. Although the precise mechanisms underlying curcumin’s wound healing properties remain a subject of ongoing research, several studies have suggested that it may operate through a range of mechanisms. In the initial stage of wound healing, known as haemostasis, curcumin’s antiplatelet and anticoagulant properties have been proposed to play a role. By inhibiting excessive platelet aggregation and promoting normal blood clotting, curcumin could contribute to efficient haemostasis, thus controlling bleeding at the wound site [2]. Following haemostasis, the inflammatory phase begins, characterized by the influx of immune cells to the wound area. Curcumin’s well-established anti-inflammatory capabilities make it a potential candidate for modulating the inflammatory response during wound healing. It has the capacity to suppress the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and attenuate excessive inflammation [3,4,5]. During the proliferation phase, fibroblasts play a pivotal role in producing collagen, a fundamental component for tissue repair, while angiogenesis occurs. Curcumin’s ability to stimulate collagen production and promote angiogenesis has been reported, which may lead to accelerated tissue regeneration during this stage. In the final remodelling phase, the newly formed tissue undergoes further maturation and organization. Curcumin might influence this stage by promoting the alignment and remodelling of collagen fibers, which can enhance tissue strength and functionality [6, 7].
In parallel, it is crucial to recognize that delayed or defective wound healing is a complex medical issue influenced by various factors, including microbial infections. In many cases, microbial colonization of wounds can significantly impede the healing process, leading to chronic wounds or complications [8]. Consequently, addressing microbial infections within wounds assumes paramount importance in fostering effective wound healing. Remarkably, Curcumin has demonstrated its potential to inhibit the growth of certain types of bacteria [9].
However, the curcumin bioavailability, or the amount of the compound absorbed and becomes active in the body, is relatively low [10]. This is due to several factors, including its low solubility in water, its rapid metabolism and elimination from the body, and its poor absorption from the gastrointestinal tract [11]. To increase the bioavailability of curcumin, a number of strategies have been developed, including the utilization of nanoparticle technology. These approaches may help to increase the amount of curcumin that is absorbed and becomes active in the body [12]. Loading curcumin into lipid nanoparticles, or small particles composed of lipids, is a strategy developed to increase curcumin’s bioavailability. Several types of lipid nanoparticles have been used to deliver curcumin, including liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles, and nanostructured lipid carriers. These particles vary in size, composition, and properties, and each type has advantages and disadvantages [13].
Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) represent a versatile lipid nanocarrier system designed for the delivery of various compounds, including drugs, cosmetics, and nutraceuticals. NLCs are composed of a mixture of solid and liquid lipids, and they can be prepared in various shapes and sizes, depending on the specific application [14]. There are several advantages to using NLCs as a delivery system for compounds, including improved bioavailability, as NLCs may improve the bioavailability of the compounds they deliver by enhancing their solubility and increasing their absorption [15]. Notably, numerous studies have demonstrated the utility of NLCs in enhancing the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of curcumin. For instance, numerous studies have explored the use of NLCs to improve the oral bioavailability of curcumin, attributing the enhanced absorption to the NLC’s ability to protect curcumin from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract [16,17,18]. Additionally, NLCs loaded with curcumin have demonstrated enhanced skin permeation, making them promising candidates for topical applications [19,20,21]. Moreover, in-depth investigations into the formulation of CURC-NLCs have indicated that these carriers offer a sustained release of curcumin, extending its therapeutic effects [20, 22]. These findings collectively support the use of NLCs as a suitable vehicle for curcumin delivery, emphasizing their potential in enhancing curcumin’s therapeutic properties.
Beyond enhanced bioavailability, NLCs offer additional benefits. They can enhance stability by protecting the compound from degradation and increasing its stability [23,24,25]. NLCs also may release the compound in a controlled manner, which can help extend its therapeutic effect and reduce the frequency of dosing [26]. Notably, NLCs can be used to deliver a wide range of compounds, including drugs, cosmetics, and nutraceuticals [18, 27, 28]. Furthermore, NLCs can be easily prepared using simple and scalable manufacturing processes [29].
For all these reasons, we have selected NLCs to encapsulate curcumin for promoting skin regeneration. In addition, we hypothesized that CUR-NLCs would provide a broad-spectrum of the antimicrobial effect, which could further promote wound healing.
Methods
Materials
Curcumin (C1386), 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), and Folin-Ciocalteau phenol reagents were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Other chemicals include ascorbic acid, capric acid, glycerol mono-stearate, lecithin, sodium carbonate, tween 80, tannic acid, Carbopol-942, triethanolamine, propylene glycol, ethanol, and methanol were purchased from EL-Gomhouria Company (Alexandria, Egypt). In addition, xyla-Ject (xylazine hydrochloride) and ketamine hydrochloride (ET13L087-11) were obtained as anaesthetic drugs for surgery from ADWIA Co. (10th of Ramadan City) and Rotexmedica (Trittau, Germany), respectively.
Preparation of CURC-NLCs
As previously described [26], the emulsion-evaporation-solidification method was used to prepare NLCs, as shown in Fig. 1, with some modifications. First, three concentrations (0.75%, 0.5%, and 0.25%, w/v) of curcumin were dissolved in 7% (w/v) glycerol mono-stearate (solid lipid), 3% (w/v) capric acid (liquid lipid), and 5% (w/v) lecithin in 15% (w/v) ethanol 70%. Next, this organic phase was heated to 70 °C, while the aqueous phase, consisting of 2% (w/v) tween 80 (surfactant) dissolved in 67.5% (w/v) distilled water, was also heated to 70 °C. Finally, under magnetic stirring, the organic phase was added to the aqueous phase dropwise at 70 °C for 3 h. The mixtures were then sonicated for 15 min at 7 kHz.
Characterization of CURC-NLCs
The size of CURC-NLCs was analysed using a JEOL JSM-IT200 InTouchScope TM Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM Inc., Japan) and a JEOL JEM-1400 plus Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM Inc., Japan). Also, CURC-NLCs samples were analysed using photon correlation spectroscopy (Zetasizer Nano ZS, Malvern Instruments, USA). The measurements were carried out after dilution with distilled water and sonication. The polydispersity index (PDI) values were obtained using polystyrene cells at 25 °C and a refractive index (RI) of 1.330 (abs = 0.01) to measure the dispersion of the lipid nanoparticles. In addition, Zeta potential (ZP) was determined using zeta-dip cells at 12 runs to measure the charge on the surface of the nanoparticles and evaluate their physical stability [30]. Furthermore, entrapment efficiency (EE) and drug loading (DL) were determined using a modified version of the method described in Elkhateeb et al. [31]. CURC-NPs dispersion (0.1 mL) was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 20 min, and the supernatant was diluted with methanol (50:50). The resulting solution was then measured using a unico-1200 spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 323 nm. The EE (%) was calculated using the following equation:
The DL (%) was calculated using the following equation:
Total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of curcumin and CURC-NLCs
The total phenolic in curcumin and CURC-NLCs at three different concentrations (25, 50 and 75 mg / 10 ml) were measured following the method described previously [31]. Furthermore, the antioxidant activity of curcumin and CURC-NLCs at the same concentrations mentioned above was measured using 2,2-Diphenyl picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity assay [32, 33].
Encapsulation of curcumin and CURC-NLCs in Carbopol gel
To encapsulate the curcumin and CURC-NLCs, Carbopol-942, at a concentration of 5% was added to 7.5% of the curcumin or CURC-NLCs solution and stirred the mix. Triethanolamine (0.5 mL) and propylene glycol (a few drops) were added to neutralize the gel and improve its plasticity.
Evaluation of the antimicrobial properties of the Carbopol encapsulated CURC-EXTR and CURC-NLCs
Carbopol-encapsulated curcumin and CURC-NLCs were tested for their microbial activity against the following bacterial strains (Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633, Escherichia coli ATCC 25,922, Salmonella spp., Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25,923, Staphylococcus epidermidis) and one fungal strain (Candida albicans EMCC 105). Strains were kindly provided by the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, USA). The experiment was performed in triplicate, and the average values were recorded. The microbial culturing technique followed the previously described method in [31]. In addition, the ability of the curcumin or CURC-NLCs loaded gel to inhibit microbial growth was evaluated based on the inhibition zone diameter (IZD). As previously described, the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) was measured using the disc diffusion method for all diluted solutions [31, 34].
Surgical animal model and treatment protocol
Eighteen male rabbits (New Zealand, weighing 1.9−2.0 kg) purchased from Faculty of Agriculture, Alexandria University. The animals used in this study were screened for any pre-existing health conditions and were acclimated for a period of 7 days prior to the start of the experiment. During this acclimation period, the animals were housed in the experimental animal facility under controlled environmental conditions of temperature and humidity, with a 12-hour light/dark cycle. The animals were provided with standard laboratory animal diet and water ad libitum and were observed daily for any signs of illness or distress. Rabbits were randomly divided into three groups carbopol alone, Curcumin @carbopol gel, and CURC-NLCs @carbopol gel, each group with six wounds. Full-thickness skin excisions with dimensions 3 × 3 cm were made on the dorsum of each rabbit. The skin excision surgeries were performed under general anaesthesia, with the animals sedated by intramuscular injection of xylazine (5 mg/kg) followed by ketamine (35 mg/kg). After surgery, the animals were injected with the analgesic drug meloxicam (0.2 mL). This surgical procedure was conducted according to the protocol approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (AU-IACUC, AU01320190130108). The animals used in this study were not euthanized but were released at the completion of the study and that was deemed compatible with the ethical guidelines for animal experimentation. Prior to release, the animals were monitored to ensure they were in good health and able to thrive.
The different treatments were applied to the wounds seven days after surgery, as previously described [31]. After that, the wounds were followed up until complete healing (21 day). During the follow-up, multiple images were taken for wounds at days 0, 7, 14 and 21 in the presence of a refence object (well-known dimensions). These images were then analyzed using Image J software (ImageJ 1.53p, Java 1.8.0_112 (64-bit), USA) [35].
The % of wound healing was calculated using the following equation [36]:
Histopathological examination
Tissue samples were collected from each animal (n = 5 from each group) using 10 mm biopsy punch (Integra® Miltex) under anaesthesia. After collecting tissue samples, the animals were carefully monitored during their recovery from anaesthesia to ensure their well-being. We provided appropriate post-operative care, including pain management and monitoring for any signs of distress or discomfort. Once the animals had fully recovered and were deemed to be in good health, they were safely released into their respective housing environments. Subsequently, the collected tissues were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin solution, embedded in paraffin wax, cut into five micron-thick sections and stained with haematoxylin-eosin (H&E) for examination by light microscopy [37]. To evaluate the histopathologic parameters of wound healing during 1st, and 3rd week was described as the following (0) absence of the lesion = 0%, (+) mild = 5–25%, (++) moderate = 26–50% and (+++) severe ≥ 50% of the examined tissue sections.
Statistical analysis
In vitro and in vivo experimental data were collected from three independent experiments. The results were reported as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis was performed using 2-way ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test to compare different groups. GraphPad software version 8.0 (La Jolla, CA, USA) was used to analyze and generate a graphical representation of the data statistically. Differences were considered significant at * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001.
Results and discussion
Curcumin has been shown to have a number of potential skin health benefits, including antimicrobial, antioxidant, and wound-healing properties. Using NLCs could enhance the curcumin loading capacity and hence improve its delivery in topical applications in case of skin injuries. Herein, we have revealed the potential of NLCs to provide a protective layer around the curcumin, helping to preserve its activity and increase its stability, leading to increased skin benefits.
Characterization of CURC-NLCs
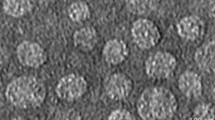
SEM images showed irregular spherical particles for CURC-NLCs, as shown in Fig. 2A. The mean particle sizes of CURC-NLCs at concentrations 25, 50 and 75 mg / 10 ml was 69.17 ± 9.17, 66.81 ± 10.93 and 59.41 ± 7.72 nm (Fig. 2A). Furthermore, TEM images in Fig. 2B illustrated the morphology of the prepared nanoparticles, which were clearly compatible with the scanning microscopy results.
Characterization of CURC-NLCs at concentrations 25, 50 and 75 mg. (A) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) Scale bar = 1 μm. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scale bar = 200 μm. Zeta Potential of CURC-NLCs. (B) Graph of particles size and Polydispersity index (PDI) of all tested concentrations. (C & D) Graphs show the Entrapment efficiency (EE), and Drug loading (DL) of CURC-NLCs formulations
Photon correlation spectroscopy results for zeta potential and PDI for CURC-NLCs ranged between − 16.1 ± 8.67 to -27.1 ± 13.1 and 0.152 to 0.4 mV (Table 1; Fig. 2C). Of particular note, the formulation with a concentration of 75 mg/10 mL exhibited the highest zeta potential, affirming its long-term stability. Furthermore, our study demonstrated that the formulations achieved low PDI values, indicative of homogeneous particle size distribution (Table 1). This uniformity in distribution, especially notable in formulations with low PDI values.
Our findings align with established literature on NLCs, which are known for their ability to encapsulate hydrophobic compounds like curcumin, resulting in the formation of nano-sized particles [38]. For instance, a study employing Stearic Acid and Caprylic/capric Triglycerides lipids in NLC preparation reported particle sizes ranging from 220 to 231 nm [39]. Another study using solid lipid glyceryl monooleate and Geleol, along with Olive oil as a liquid lipid, achieved particle sizes of 113.94 ± 11.3 nm and smaller PDI values (0.29 ± 0.05). In addition, studies employing lipids such as Precirol as a solid lipid, Capmul MCM as a liquid lipid, and Tween 80 and soya lecithin as surfactants reported a particle size of 146.8 nm with a zeta potential of -21.4 ± 1.87 [40].
Entrapment efficiency and drug loading
This study analysed the EE and DL of CURC-NLCs using spectrophotometry at an optimal wavelength of 323 nm. The EE % results of CURC-NLCs at concentrations 25, 50 and 75 mg were 96.75 ± 0.35%, 95.84 ± 0.35%, and 94.5 ± 0.38%, respectively (Table 1). However, the DL % of the same concentrations were 1.59 ± 0.010%, 3.09 ± 0.014% and 4.53 ± 0.016%, respectively (Table 1). The results confirm that CURC-NLCs with a high drug concentration had a higher drug loading but a lower encapsulation efficiency than those with a lower drug concentration. Similarly, we have demonstrated previously that the highest concentration of propolis-NLCs possessed a high EE% and low DL% [31]. This data also matches the previous report by Chen et al. [41] which showed that increasing the drug-to-lipid ratio could improve DL capacity but decrease EE.
It has been demonstrated that EE and DL in NLCs are influenced by various factors, including drug solubility in lipids, miscibility of drug and lipid melts, solid lipid selection and its drug solubility, lipid polymorphic state, solid lipid ratio, lipid concentration, and the impact of surfactants. Notably, our formulation distinguishes itself by consistently achieving an impressive EE averaging at 95%, surpassing previously tested formulations. For instance, in the study conducted by Madane and Mahajan [40] study, an EE of 90.86% was reported, while Kamel et al. [22] research recorded an EE of 82.49%.
CURC-NLCs exhibited higher total phenolics and antioxidant activity
Excess free radicals can lead to oxidative stress, causing damage to cellular components, including lipids, proteins, and DNA. This oxidative damage can impair the functionality of cells involved in wound healing, including fibroblasts and keratinocytes, thereby delaying the process [42, 43]. Moreover, oxidative stress can trigger chronic inflammation at the wound site, leading to the accumulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). This sustained inflammatory response can hinder tissue regeneration and result in non-healing or chronic wounds [44, 45]. Therefore, strategies aimed at mitigating excessive free radical production or enhancing the antioxidant defense mechanisms can be beneficial in promoting efficient wound healing.
It is worth mentioning that herbal extracts are known for their robust antioxidant activity, a property closely linked to their phenolic and flavonoid contents [46]. These bioactive compounds have demonstrated a direct relationship with their ability to reduce oxidative stress and promote healing. Herein this study, the CURC-NLCs 75 mg had 9.26 ± 0.27 phenolic content compared to 6.33 ± 0.25 equivalent to tannic acid mg/g which was notably higher than the lower concentrations of 25 and 50 mg (p < 0.0001, Fig. 3A).
Curcumin has been shown to have antioxidant activity, which means that it can scavenge or neutralize harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can damage cells and contribute to the development of various diseases. The antioxidant activity of curcumin may be due to its ability to donate electrons to ROS, rendering them inactive and preventing them from causing harm to cells [47]. Additionally, curcumin has been reported to stimulate the production of antioxidant enzymes within cells and activation of Nrf2-Keap1 signalling pathway, further contributing to its antioxidant activity [48].
Herein, we have investigated the DPPH scavenging capacity of CURC-NLCs to confirm the antioxidant activity of curcumin and CURC-NLCs. The results revealed that the CURC-NLCs possess a potent antioxidant activity compared to ascorbic acid (18-fold, p < 0.0001) and curcumin (̴ 8.5-fold, p < 0.0001, Fig. 3B). A similar study has previously reported that CURC-NLCs can significantly enhance antioxidant ability, resulting in a remarkable 7-fold increase compared to CURC when assessed using the ABTS assay [21]. Another study conducted by Karimi et al. reported significantly higher antioxidant activity for CURC-NLCs compared to free curcumin extract using the DPPH assay [49]. Likewise, in our previous research involving the encapsulation of propolis in NLCs, we also documented significantly elevated antioxidant activity when compared to propolis extract [31, 50].
Hence, this study showed that CURC-NLCs have a stronger antioxidant effect than curcumin. This effect can be attributed to the high levels of phenolic and non-phenolic compounds entrapped in CURC-NLCs that can prevent oxidation reactions and attack free radicals. In addition, the transformation of curcumin into nanoparticles significantly improved its ability to scavenge free radicals compared to its native form.
The mechanism by which lipid nanostructures exhibit antioxidant activity may involve a combination of direct scavenging of ROS and indirect effects on the production of antioxidant enzymes within cells. For example, the presence of antioxidant lipids such as lecithin [51] and Tween 80 [52] within the nanostructures may directly scavenge ROS, while the delivery of curcumin well characterized antioxidants to cells would stimulate the production of antioxidant enzymes and enhance the overall antioxidant activity of the NLCs.
CURC-NLCs performed significantly higher antimicrobial and antifungal activities
Microbes, particularly bacteria and fungi, can significantly influence the wound healing process. Infections resulting from these microorganisms can hinder and prolong the natural course of wound healing [53]. Specific bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli, are known contributors to wound infections, producing toxins, biofilms, and inflammatory responses that disrupt the normal healing cascade [54, 55]. In this context, the antimicrobial properties of therapeutic agents become crucial in managing and expediting wound healing.
The antimicrobial activity of curcumin and CURC-NLCs against the tested microorganisms was determined by IZD and MIC, as shown in Fig. 4. The results of IZD confirms that the CURC-NLCs in carbopol gel displayed strong antimicrobial activity against Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., Staphylococcus epidermidis bacterial strains and fungal strain (Candida albicans) compared to curcumin (Fig. 4; Table 2). Herein, both curcumin and CURC-NLCs exhibited similar effects against Staphylococcus aureus with nearly identical IZD measurements of approximately 23 mm. In contrast, a recent study by Hettiarachchi et al. reported recently that curcumin nanoparticles could enhance the antibacterial activity against S. aureus as confirmed by an increase in the IZD from 24.82 ± 0.54 mm in crude curcumin to 29.91 ± 0.53 mm in nano-formula [56]. On the other hand, our CURC-NLCs exhibited a notably more pronounced effect on E. coli, as evidenced by the substantial increase in IZD from 11 ± 0.78 to 24 ± 0.99. This aligns with a previous study where IZD for E. coli increased from 19.70 ± 1.18 to 24.58 ± 1.12 mm upon the use of curcumin nanoparticles [56].
Assessment of the antibacterial and antifungal activity of Curcumin and CURC-NLCs. (A) Antibacterial activity of Curcumin and CURC-NLCs against different bacterial species as Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633, Salmonella spp, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25,923, Staphylococcus epidermis, and Escherichia coli ATCC 25,922 using inhibition zone diameter (IZD) and minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC). (B) Antifungal activity of CURC-EXTR and CURC-NLCs against Candida albicans EMCC 105. (C & D) Quantitative analysis of IZD and MIC, data was represented as mean ± SD (nsp > 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001)
It is also worth mentioning that the MIC of CURC-NLCs was significantly lower than that of curcumin, as evidenced by a reduction of almost half in the concentration needed to inhibit microbial growth in the epidermis of Bacillus and Staph (from 31.25 to 500 in curcumin to 15.6 and 250 in CURC-NLCs, respectively) (Fig. 4; Table 2).
Several studies have demonstrated that curcumin can inhibit the growth of a variety of bacteria, including Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi, and Staphylococcus aureus [57]. In addition, it may also have antimicrobial activity against other types of microorganisms, such as fungi and viruses. The curcumin’s antimicrobial properties are believed to work in two ways: it blocks cell division through perturbing of the filamenting temperature-sensitive mutant Z (FtsZ) protein functions in the Z-loop and hence damages the bacterial membrane, and it inhibits SOS-response and hinder the quorum sensing system (QS) by reducing the biofilm production and weakening of QS dependant factors [58].
The high antimicrobial capacity of CURC-NLCs can be attributed to the loaded curcumin. Additionally, the NLCs components may have antimicrobial activity of their own, contributing to the overall effectiveness of curcumin in combating infections. For example, capric acid has been demonstrated to possess an antibacterial effect against Propionibacterium acnes [59]. Also, Lecithin was previously reported to enhance the antibacterial effect of Eugenol against E. coli [60]. Therefore, when curcumin is incorporated into NLCs, it may be more effectively delivered to the site of infection, leading to increased antimicrobial activity.
CURC-NLCs enhanced skin regeneration
CURC-NLCs-carbopol proved that treating wounds with nanoparticles promotes wound healing and reduces the epithelization period where the closure percentages were higher than the curcumin-carbopol treated wounds. They also revealed early stages of healing with 60.39 ± 0.04% wound closure on the 7th day, while curcumin-carbopol treated wounds were of 51.62 ± 0.09% closure. However, the carbopol treated wounds revealed a slow wound closure rate estimated by 31.85 ± 0.07% (Fig. 5). By day 14, CURC-NLCs-Carbopol treated wounds were significantly healing with 93.73 ± 0.04% wound closure, curcumin-carbopol and carbopol treated ones were closuring with 88.91 ± 0.03% and 65.22 ± 0.014%, respectively (Fig. 5). By day 21, there was complete closure of wounds at curcumin and CURC-NLCs groups however, control group was yet 87.49% wound closure.
Wound healing evaluation after treated with Curcumin, CURC-NLCs in comparison to control group. (A) Schematic diagram showing the in vivo skin injury experiment design clarifying different treatment groups. Created with BioRender.com. (B) Representative images show wound dimensions after induction of injury (0 day) and then after 7, 14, and 21 days. (C) Qualitative analysis of the wound healing ratio in control, curcumin, and CURC-NLCs groups at days 7, 14 and 21 normalized to initial wound size at day 0, data represented as mean ± SD (****p < 0.0001)
The notable improvement in wound healing outcomes observed in our study can be attributed to the enhanced permeation and skin retention properties of CURC-NLCs, as corroborated by previously published ex-vivo skin permeation study. This study demonstrated a remarkable increase in permeation and skin retention when utilizing the CURC-NLC gel as compared to the free curcumin gel. This substantial enhancement in skin permeation and retention strongly suggests that CURC-NLCs excel at delivering curcumin precisely to the target site, thereby enabling a more prolonged and localized therapeutic effect [20]. Furthermore, our results align with in vitro findings that underscore the potential of CURC-NLCs to enhance wound healing. Specifically, CURC-NLCs have been shown to promote the proliferation of fibroblasts [21], key players in tissue regeneration, and enhance cell migration [61].
On the contrary, previous research has indicated an antimigratory effect associated with CURC-NLCs. Specifically, CURC-NLCs were found to reduce the migration and proliferation abilities of cells after 24 h, accompanied by noticeable morphological changes in keratinocytes when compared to control groups [21]. Additionally, investigations involving curcumin loaded onto poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles have similarly revealed a potent inhibition of cellular activity in the HaCaT human keratinocyte cell line [62].
Histopathologic findings and quantitative analysis
Histopathological findings of injured rabbit skin of the control group during 1st week were scab formed by necrotic tissue remnants beside hyperaemic blood vessels in the dermis with severe haemorrhage and faint eosinophilic albuminous oedema. In addition, there was moderate acute interstitial inflammatory cell infiltration as pleomorphic nuclear eosinophilic cell and macrophage. However, in curcumin and CURC-NLCs group exhibited mild to moderate haemorrhage, proliferation fibroblastic cell and immature granulation tissues (Fig. 6A). In both the curcumin and CURC-NLCs treated groups, there was a reduction in the infiltration of macrophages and eosinophils compared to the untreated control group (Table 3). This observation is consistent with previous studies reporting the anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin and CURC-NLCs [63, 64].
(A) photomicrograph of rabbit skin during 1st week stained by haematoxylin and eosin from the control (a, d & g), Curcumin (b, e & h), and CURC-NLCs (c, f & i) group showing necrotic layers (N), and interstitial inflammatory cell infiltration (IC) as mononuclear cell (long black arrows) and pleomorphic nuclear eosinophilic cell (arrowheads) with fibroblastic cell proliferation (short black arrows) beside neovascularization (asterisks). The bar = 100 μm for (a), (b), (c) and 50 μm for (d), (e), (f), (g), (h), (i). (B) Photomicrograph of rabbit skin during 3rd week stained by haematoxylin and eosin from the control (j), Curcumin (k), and CURC-NLCs (i) group showing epithelial regeneration and granular cell layer (Gr) with rete ridges (red arrows) mature collagen (C), hair follicle (F). The bar = 100 μm
It is particularly noteworthy that the angiogenesis observed in the CURC-NLCs group was significantly more pronounced than in the other treatment groups, as indicated by a majority of samples receiving a high angiogenesis ranking (3 out of 5 ranked as +++). This heightened angiogenic response can be attributed to the potential enhancement of endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs). An intriguing study conducted by You et al. revealed that the administration of curcumin to diabetic mice resulted in a remarkable improvement in the migratory, angiogenic, and proliferative capacities of EPCs, coupled with a reduction in cellular senescence. Furthermore, this treatment was associated with a substantial upregulation in the expression of key angiogenic factors, including VEGF-A and Ang-1 [65].
The noticeable lesions during 3rd week in the control group were normal keratinized and epidermal layers covering the mature granulation tissue with mild formation of rete ridges. However, in curcumin and curcumin -NLCs group showed complete healthy epidermal regeneration in the form of thick keratin and granular epidermal layers covered with mature granulation tissue and collagen, with the wide formation of rete ridges, dermal glands structure and hair follicles (Fig. 6B). Incidence and severity of histopathological lesions of rabbit skin wound of all treatment groups were summarized in Table 3. Several in vivo studies have collectively shown that curcumin enhances cutaneous wound healing through various mechanisms. These include increased fibroblast proliferation, stimulated epithelial regeneration, facilitated tissue remodelling, promoted granulation and new tissue formation, as well as enhanced collagen deposition [66,67,68].
In a recap, the mechanism by which CURC-NLCs may improve full skin healing and be involved in all the skin structures may involve a combination of the following. First, the antioxidant availability of CURC-NLCs has been shown to have antioxidant activity, which may help to scavenge harmful ROS that can damage skin cells and contribute to the development of various skin conditions [69]. Second, angiogenesis, as evidenced by histological Sect. [65], can be a pivotal factor in skin regeneration. Angiogenesis is crucial for ensuring an adequate blood supply to the wounded area, facilitating nutrient and oxygen delivery, and promoting overall tissue repair. Additionally, CURC-NLCs exhibit antimicrobial activity that can address microbial infection which may hinder the wound healing process. By inhibiting the growth of pathogenic microorganisms, CURC-NLCs help create a more favourable environment for effective wound healing.
Conclusion
CURC-NLCs were successfully prepared and characterized using SEM, TEM, ZP and various other analytical techniques, demonstrating good drug loading and drug entrapment efficiency. Our results suggest that CURC-NLCs exhibit strong potential to enhance the quality of skin healing and accelerate the healing process. This enhancement can be attributed to improved curcumin bioavailability, as well as the antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of CURC-NLCs.
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Aggarwal BB, Bhatt ID, Ichikawa H, Ahn KS, Sethi G, Sandur SK, Natarajan C, Seeram N, Shishodia S. 10 Curcumin—biological and medicinal properties. 2006.
Kim DC, Ku SK, Bae JS. Anticoagulant activities of curcumin and its derivative. BMB Rep. 2012;45(4):221–6.
Buhrmann C, Mobasheri A, Busch F, Aldinger C, Stahlmann R, Montaseri A, Shakibaei M. Curcumin modulates nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)-mediated inflammation in human tenocytes in vitro: role of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(32):28556–66.
Bonilla P, Hernandez J, Giraldo E, González-Pérez MA, Alastrue-Agudo A, Elkhenany H, Vicent MJ, Navarro X, Edel M. Moreno-Manzano, Human-induced neural and mesenchymal stem cell therapy combined with a curcumin nanoconjugate as a spinal cord injury treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5966.
Elkhenany H, Bonilla P, Giraldo E, Alastrue Agudo A, Edel MJ, Vicent MJ, Roca FG, Ramos CM, Doblado LR, Pradas MM. A Hyaluronic Acid Demilune Scaffold and Polypyrrole-Coated Fibers Carrying Embedded Human Neural Precursor Cells and Curcumin for Surface Capping of Spinal Cord Injuries Biomedicines, 2021. 9(12): p. 1928.
Qian S, Wang J, Liu Z, Mao J, Zhao B, Mao X, Zhang L, Cheng L, Zhang Y, Sun X, Cui W. Secretory fluid-aggregated Janus Electrospun Short Fiber Scaffold for Wound Healing. Small. 2022;18(36):e2200799.
Mobaraki M, Bizari D, Soltani M, Khshmohabat H, Raahemifar K, Amirdehi MA. The Effects of Curcumin Nanoparticles Incorporated into Collagen-Alginate Scaffold on Wound Healing of Skin Tissue in Trauma Patients Polymers (Basel), 2021. 13(24).
Williams H, Crompton RA, Thomason HA, Campbell L, Singh G, McBain AJ, Cruickshank SM, Hardman MJ. Cutaneous Nod2 expression regulates the skin Microbiome and Wound Healing in a murine model. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137(11):2427–36.
Moghadamtousi SZ, Kadir HA, Hassandarvish P, Tajik H, Abubakar S, Zandi K. A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin Biomed Res Int, 2014. 2014: p. 186864.
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, Aggarwal BB. Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Mol Pharm. 2007;4(6):807–18.
Tapal A, Tiku PK. Complexation of curcumin with soy protein isolate and its implications on solubility and stability of curcumin. Food Chem. 2012;130(4):960–5.
Ma Z, Wang N, He H, Tang X. Pharmaceutical strategies of improving oral systemic bioavailability of curcumin for clinical application. J Control Release. 2019;316:359–80.
Xu L, Wang X, Liu Y, Yang G, Falconer RJ, Zhao C-X. Lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery. Adv NanoBiomed Res. 2022;2(2):2100109.
Chauhan I, Yasir M, Verma M, Singh AP. Nanostructured lipid carriers: a Groundbreaking Approach for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv Pharm Bull. 2020;10(2):150–65.
Gaba B, Fazil M, Ali A, Baboota S, Sahni JK, Ali J. Nanostructured lipid (NLCs) carriers as a bioavailability enhancement tool for oral administration. Drug Delivery. 2015;22(6):691–700.
Fang M, Jin Y, Bao W, Gao H, Xu M, Wang D, Wang X, Yao P, Liu L. Vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation of nanostructured lipid curcumin carriers for intragastric administration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:5395–404.
Tian C, Asghar S, Wu Y, Chen Z, Jin X, Yin L, Huang L, Ping Q, Xiao Y. Improving intestinal absorption and oral bioavailability of curcumin via taurocholic acid-modified nanostructured lipid carriers. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:7897–911.
Hyun JE, Yi H-Y, Hong G-P, Chun J-Y. Digestion Stab curcumin-loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier LWT. 2022;162:113474.
Riaz A, Ahmed N, Khan MI, Haq I-u, Rehman Au, Khan GM. Formulation of topical NLCs to target macrophages for cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2019;54:101232.
Rapalli VK, Kaul V, Waghule T, Gorantla S, Sharma S, Roy A, Dubey SK, Singhvi G. Curcumin loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for enhanced skin retained topical delivery: optimization, scale-up, in-vitro characterization and assessment of ex-vivo skin deposition. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020;152:105438.
Calderon-Jacinto R, Matricardi P, Gueguen V, Pavon-Djavid G, Pauthe E, Rodriguez-Ruiz V. Dual nanostructured lipid Carriers/Hydrogel system for delivery of Curcumin for topical skin applications. Biomolecules. 2022;12(6):780.
Kamel AE, Fadel M, Louis D. Curcumin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers prepared using Peceol™ and olive oil in photodynamic therapy: development and application in breast cancer cell line. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:5073–85.
Rincón M, Calpena AC, Fabrega M-J, Garduño-Ramírez ML, Espina M, Rodríguez-Lagunas MJ, García ML, Abrego G. Development of pranoprofen loaded nanostructured lipid carriers to improve its release and therapeutic efficacy in skin inflammatory disorders. Nanomaterials. 2018;8(12):1022.
Das S, Ng WK, Tan RB. Are nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) better than solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs): development, characterizations and comparative evaluations of clotrimazole-loaded SLNs and NLCs? Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012;47(1):139–51.
Li B, Ge ZQ. Nanostructured lipid carriers improve skin permeation and chemical stability of idebenone. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012;13(1):276–83.
Dan N. Compound release from nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs). J Food Eng. 2016;171:37–43.
Chen Y, Zhou L, Yuan L, Zhang ZH, Liu X, Wu Q. Formulation, characterization, and evaluation of in vitro skin permeation and in vivo pharmacodynamics of surface-charged tripterine-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:3023–32.
Müller RH, Radtke M, Wissing SA. Nanostructured lipid matrices for improved microencapsulation of drugs. Int J Pharm. 2002;242(1):121–8.
Akbari J, Saeedi M, Ahmadi F, Hashemi SMH, Babaei A, Yaddollahi S, Rostamkalaei SS, Asare-Addo K, Nokhodchi A. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Review of the Methods of Manufacture and Routes of Administration Pharm Dev Technol. 2022;27(5):525–44.
Lakhani P, Patil A, Taskar P, Ashour E, Majumdar S. Curcumin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for ocular drug delivery: design optimization and characterization. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2018;47:159–66.
Elkhateeb OM, Badawy ME, Noreldin AE, Abou-Ahmed HM, El-Kammar MH, Elkhenany HA. Comparative evaluation of propolis nanostructured lipid carriers and its crude extract for antioxidants, antimicrobial activity, and skin regeneration potential. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022;22(1):1–13.
El Sohaimy S, Abdelwahab A, Brennan CS, Aboul-Enein A. Phenolic content, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Egyptian date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruits 2015.
Shimada K, Fujikawa K, Yahara K, Nakamura T. Antioxidative properties of xanthan on the autoxidation of soybean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion. J Agric Food Chem. 1992;40(6):945–8.
Nichitoi MM, Josceanu AM, Isopescu RD, Isopencu GO, Geana E-I, Ciucure CT, Lavric V. Polyphenolics profile effects upon the antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of propolis extracts. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1–12.
Caruso M, Shuttle S, Amelse L, Elkhenany H, Schumacher J, Dhar MS. A pilot study to demonstrate the paracrine effect of equine, adult allogenic mesenchymal stem cells in vitro, with a potential for healing of experimentally-created, equine thoracic wounds in vivo. Front Veterinary Sci, 2022. 9.
Eldebany N, Abd Elkodous M, Tohamy H, Abdelwahed R, El-Kammar M, Abou-Ahmed H, Elkhenany H. Gelatin loaded titanium dioxide and silver oxide nanoparticles: implication for skin tissue regeneration. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021;199(10):3688–99.
Suvarna K, Layton C. The hematoxylin and eosin, connective and mesenchymal tissues with their stains, immunohistochemical techniques and transmission electron microscopy Bancroft’s theory and practice of histological techniques, Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, in Bancroft’s theory and practice of histological techniques. 2013, Churchill Livingstone Elsevier Oxford.
Müller RH, Mäder K, Gohla S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery – a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2000;50(1):161–77.
Sadati Behbahani E, Ghaedi M, Abbaspour M, Rostamizadeh K, Dashtian K. Curcumin loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: in vitro digestion and release studies. Polyhedron. 2019;164:113–22.
Madane RG, Mahajan HS. Curcumin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) for nasal administration: design, characterization, and in vivo study. Drug Delivery. 2016;23(4):1326–34.
Chen J, Dai W, He Z, Gao L, Huang X, Gong J, Xing H, Chen W. Fabrication and evaluation of curcumin-loaded nanoparticles based on solid lipid as a new type of colloidal drug delivery system. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2013;75(2):178.
Xu H, Zheng Y-W, Liu Q, Liu L-P, Luo F-L, Zhou H-C, Isoda H, Ohkohchi N, Li Y-M. Reactive oxygen species in skin repair, regeneration, aging, and inflammation Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in living cells, 2018. 8: p. 69–88.
Sampson N, Berger P, Zenzmaier C. Therapeutic Targeting of Redox Signaling in Myofibroblast Differentiation and Age-Related Fibrotic Disease Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2012. 2012: p. 458276.
Ponugoti B, Xu F, Zhang C, Tian C, Pacios S, Graves DT. FOXO1 promotes wound healing through the up-regulation of TGF-β1 and prevention of oxidative stress. J Cell Biol. 2013;203(2):327–43.
Zaw KK, Yokoyama Y, Abe M, Ishikawa O. Catalase restores the altered mRNA expression of collagen and matrix metalloproteinases by dermal fibroblasts exposed to reactive oxygen species. Eur J Dermatology. 2006;16(4):375–9.
Saeed N, Khan MR, Shabbir M. Antioxidant activity, total phenolic and total flavonoid contents of whole plant extracts Torilis leptophylla L. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012;12(1):221.
Singh U, Barik A, Singh BG, Priyadarsini KI. Reactions of reactive oxygen species (ROS) with curcumin analogues: structure–activity relationship. Free Radic Res. 2011;45(3):317–25.
Lin X, Bai D, Wei Z, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Deng H, Huang X. Curcumin attenuates oxidative stress in RAW264.7 cells by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes and activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(5):e0216711.
Karimi N, Ghanbarzadeh B, Hamishehkar H, Mehramuz B, Kafil HS. Antioxidant, antimicrobial and physicochemical properties of turmeric extract-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC). Colloid and Interface Science Communications. 2018;22:18–24.
Elkhateeb OM, Badawy MEI, Noreldin AE, Abou-Ahmed HM, El-Kammar MH, Elkhenany HA. Comparative evaluation of propolis nanostructured lipid carriers and its crude extract for antioxidants, antimicrobial activity, and skin regeneration potential. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022;22(1):256.
Pan Y, Tikekar RV, Nitin N. Effect of antioxidant properties of lecithin emulsifier on oxidative stability of encapsulated bioactive compounds. Int J Pharm. 2013;450(1):129–37.
Pérez-Rosés R, Risco E, Vila R, Peñalver P, Cañigueral S. Antioxidant activity of Tween-20 and Tween-80 evaluated through different in-vitro tests. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015;67(5):666–72.
Robson MC. Wound infection. A failure of wound healing caused by an imbalance of bacteria. Surg Clin North Am. 1997;77(3):637–50.
Watters C, Yuan TT, Rumbaugh KP. Beneficial and deleterious bacterial–host interactions in chronic wound pathophysiology. Chronic Wound Care Management and Research, 2015: p. 53–62.
Qin S, Xiao W, Zhou C, Pu Q, Deng X, Lan L, Liang H, Song X, Wu M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Therapy. 2022;7(1):199.
Hettiarachchi SS, Perera Y, Dunuweera SP, Dunuweera AN, Rajapakse S, Rajapakse RMG. Comparison of Antibacterial Activity of Nanocurcumin with Bulk Curcumin. ACS Omega. 2022;7(50):46494–500.
Adamczak A, Ożarowski M, Karpiński TM. Curcumin, a natural Antimicrobial Agent with strain-specific activity. Pharmaceuticals (Basel), 2020. 13(7).
Rai D, Singh JK, Roy N, Panda D. Curcumin inhibits FtsZ assembly: an attractive mechanism for its antibacterial activity. Biochem J. 2008;410(1):147–55.
Huang W-C, Tsai T-H, Chuang L-T, Li Y-Y, Zouboulis CC, Tsai P-J. Anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory properties of capric acid against Propionibacterium acnes: a comparative study with lauric acid. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;73(3):232–40.
Zhang H, Dudley EG, Davidson PM, Harte F. Critical concentration of Lecithin enhances the antimicrobial activity of Eugenol against Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2017. 83(8).
Liakopoulou A, Mourelatou E, Hatziantoniou S. Exploitation of traditional healing properties, using the nanotechnology’s advantages: the case of curcumin. Toxicol Rep. 2021;8:1143–55.
Sun L, Liu Z, Wang L, Cun D, Tong HH, Yan R, Chen X, Wang R, Zheng Y. Enhanced topical penetration, system exposure and anti-psoriasis activity of two particle-sized, curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles in hydrogel. J Controlled Release. 2017;254:44–54.
Chen P, Zhang H, Cheng S, Zhai G, Shen C. Development of curcumin loaded nanostructured lipid carrier based thermosensitive in situ gel for dermal delivery. Colloids Surf a. 2016;506:356–62.
Sinjari B, Pizzicannella J, D’Aurora M, Zappacosta R, Gatta V, Fontana A, Trubiani O, Diomede F. Curcumin/Liposome nanotechnology as delivery platform for anti-inflammatory activities via NFkB/ERK/pERK pathway in Human Dental pulp treated with 2-HydroxyEthyl MethAcrylate (HEMA). Front Physiol. 2019;10:633.
You J, Sun J, Ma T, Yang Z, Wang X, Zhang Z, Li J, Wang L, Ii M, Yang J, Shen Z. Curcumin induces therapeutic angiogenesis in a diabetic mouse hindlimb ischemia model via modulating the function of endothelial progenitor cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):182.
Sidhu GS, Mani H, Gaddipati JP, Singh AK, Seth P, Banaudha KK, Patnaik GK, Maheshwari RK. Curcumin enhances wound healing in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats and genetically diabetic mice. Wound Repair and Regeneration. 1999;7(5):362–74.
Mohanty C, Das M, Sahoo SK. Sustained wound healing activity of curcumin loaded oleic acid based polymeric bandage in a rat model. Mol Pharm. 2012;9(10):2801–11.
Dai M, Zheng X, Xu X, Kong X, Li X, Guo G, Luo F, Zhao X, Wei YQ, Qian Z. Chitosan-alginate sponge: preparation and application in curcumin delivery for dermal wound healing in rat BioMed Research International, 2009. 2009.
Fitzmaurice S, Sivamani RK, Isseroff RR. Antioxidant therapies for wound healing: a clinical guide to currently commercially available products. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2011;24(3):113–26.
Funding
Funding for open access was provided by Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) in partnership with the Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB).
Open access funding provided by The Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) in cooperation with The Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
O.E. conducted the research, performed the analysis, and contributed to the writing of the manuscript. M.B. designed the study, supervised the research, and reviewed and edited the manuscript. H.G. performed the histopathological analysis. H.A. and M.E. supervised the research and reviewed the manuscript. H.E. contributed to the conceptualization and supervision of the study, drafted the manuscript, performed data analysis, and prepared the figures. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental animal processes were carried out in accordance the Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Alexandria University (Ref no: AU01320190130108).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Elkhateeb, O., Badawy, M.E.I., Tohamy, H.G. et al. Curcumin-infused nanostructured lipid carriers: a promising strategy for enhancing skin regeneration and combating microbial infection. BMC Vet Res 19, 206 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-023-03774-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-023-03774-2