Abstract
Background
Patients with multiple long-term conditions requires understanding the existing care models to address their complex and multifaceted health needs. However, current literature lacks a comprehensive overview of the essential components, impacts, challenges, and facilitators of these care models, prompting this scoping review.
Methods
A scoping review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Extension for Scoping Reviews guideline. Our search encompassed articles from PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, SCOPUS, and Google Scholar. The World Health Organization’s health system framework was utilized to synthesis the findings. This framework comprises six building blocks (service delivery, health workforce, health information systems, access to essential medicines, financing, and leadership/governance) and eight key characteristics of good service delivery models (access, coverage, quality, safety, improved health, responsiveness, social and financial risk protection, and improved efficiency). Findings were synthesized qualitatively to identify components, impacts, barriers, and facilitators of care models.
Results
A care model represents various collective interventions in the healthcare delivery aimed at achieving desired outcomes. The names of these care models are derived from core activities or major responsibilities, involved healthcare teams, diseases conditions, eligible clients, purposes, and care settings. Notable care models include the Integrated, Collaborative, Integrated-Collaborative, Guided, Nurse-led, Geriatric, and Chronic care models, as well as All-inclusive Care Model for the Elderly, IMPACT clinic, and Geriatric Patient-Aligned Care Teams (GeriPACT). Other care models (include Care Management Plus, Value Stream Mapping, Preventive Home Visits, Transition Care, Self-Management, and Care Coordination) have supplemented the main ones. Care models improved quality of care (such as access, patient-centeredness, timeliness, safety, efficiency), cost of care, and quality of life for patients that were facilitated by presence of shared mission, system and function integration, availability of resources, and supportive tools.
Conclusions
Care models were implemented for the purpose of enhancing quality of care, health outcomes, cost efficiency, and patient satisfaction by considering careful recruitment of eligible clients, appropriate selection of service delivery settings, and robust organizational arrangements involving leadership roles, healthcare teams, financial support, and health information systems. The distinct team compositions and their roles in service provision processes differentiate care models.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Find the latest articles, discoveries, and news in related topics.Background
Multimorbidity refers to the coexistence of multiple diseases conditions, including chronic diseases, biopsychosocial factors, or some risk factor [1, 2]. In 2023, it was estimated that 37.2% of the adult population worldwide experienced multimorbidity [3]. Notably, this percentage surpasses 50% when considering adults aged 65 years and older [3]. The burden of multimorbidity varies across geographical regions. South America had the highest prevalence of multimorbidity at 45.7%, followed by North America (43.1%), Europe (39.2%), Asia (35%), and Africa (28.2%) [4]. The prevalence of multimorbidity also varies across populations. For instance, it was 25.4% among Chinese adults [4] while it ranged from 27 to 74% among elderly Nigerians [5]. This burden has significantly varied based on age, gender, socioeconomic status, and health status [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. To illustrate, according to a meta-analysis of primary studies from 2000 to 2021, 39.4% of adult females were diagnosed for multimorbidity compared to 32.8% of adult males [3]. There is a non-negligible prevalence of multimorbidity, ranging from 1.2 to 24.8%, among children under five years old in Sub-Saharan African countries [14]. In this continent, the prevalence of multimorbidity escalates with age, from 3.3% for those aged 18–29 years to 40.2% for those aged ≥ 80 years [4].
Multimorbidity poses significant challenges to the global health and wellbeing [15]. For individuals, it results in a host of adverse outcomes, including poor quality of life, increased loneliness, frequent hospital admissions, fragmented care, disability or daily activities impairment, polypharmacy, poor treatment adherence, and higher probability of mortality. It also places a substantial burden on health care services, affecting both costs and drug utilization [9, 16,17,18], and results in undesired health consequences [19], which are exacerbated when there is poor service integration, a lack of person-centred care, and limited healthcare professionals’ skills [20]. Moreover, the way health system is structured, and functions contributes to leaving behind clients with two or more conditions. In most situations, health professionals specialize vertically, resulting in specific areas of expertise and missed management of comorbid cases [21]. Vertical budgets and programs, along with disease-specific short-term training, medicine, and supplies, focus on addressing single diseases [22]. The challenges arose from disease specific treatment are also identified by the sixty-ninth World Health Assembly [23]. For these reasons, it is essential to reshape medical training, shifts in global governance and funding, and actualize care for whole persons. Furthermore, individuals with multimorbidity often experience a lack of holistic care and insufficient guidance from healthcare providers [21].
Individuals with multimorbidity require maintaining social connections, accessing individualized care, and receiving support [24] through convenient access to providers (telephone, internet or in person), clear communication of individualized care plans, and continuity of relationships. Additionally, they value providers who actively listen, acknowledge unique and fluctuating needs, and exhibit a caring attitude [25]. Addressing all these needs and alleviating the burden of multimorbidity call for care models that facilitate integration, linkage and collaboration [8]. The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the importance of people-centered integrated health services [23].
Reviewing the existing models of care is essential to address the multifaceted effects of multimorbidity effectively. However, current literature lacks a comprehensive overview of the essential components, impacts, challenges, and facilitators of these care models. The objective of this scoping review was to assesses multimorbidity care models, examining their components, impact, and implementation challenges and facilitators. By exploring different care models and their unique features, we can adapt and utilize them effectively in diverse contexts and countries.
Methods
Protocol and registration
A systematic search was conducted to identify literature on the Care models related to multimorbidity. A scoping review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Extension for Scoping Reviews guideline (PRISMA-ScR) [26]. Although PRISMA-ScR was utilized as a reporting tool, Arksey and O’Malley’s scoping review framework was considered from conception to evidence synthesis. The process included developing the research question, identifying relevant articles, conducting study selection, collating and summarizing data, and reporting the results. Consultations were also addressed during the weekly team meetings [27].
Eligibility criteria
Any article on care models for chronic multimorbidity was included. Articles published in English on care models for multimorbidity and/or its elements, outcome, barriers or challenges, and facilitators or strategies were included. Articles were not excluded due to the date of publication, study design, and study settings. Reviews were excluded after checking the included articles in those reviews. If the included articles in a review article were parts of the current review, that review were excluded prevent duplication of findings from the same articles. However, few reviews were included when the objectives and main findings of the previous review were synthesised from various sources, and its included articles are not included in our review.
Information sources
Articles were searched in PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, and SCOPUS. Articles were also searched in Google Scholar. The reference lists of eligible articles were reviewed for full-text review to find relevant articles. The most recent search date in databases was 12 February 2024.
Search
Lists of key words or search terms and/or phrases were identified based on three key domains: “Care model”, “Multimorbidity”, and “Chronic”. Search strategies were developed in lined with each database’s requirements. The search strategy was built using Boolean Operators: AND, OR, quotation marks “”, parentheses (), and asterisks*. The search strategy for each database is presented in the supplementary file (Supplementary file 1: Search strategy).
Selection of sources of evidence
AE conducted a search and collected available articles. All available articles were exported into EndNote 20 for duplication removal and reference managers. Then, AE automatically removed duplicates using the “Find Duplicates” command in EndNote 20. Next, AE screened articles by title and abstract to identify eligible articles for full-text review. AE weekly reported each step and the activities to the team. Then, team members provided comments on the reported activities and discussed the way forward for the next stages. AE and YA conducted a preliminary overview of samples of articles for full-text review. Finally, AE assessed eligibility for full-text review, and it was approved by YA.
Data items and charting process
The team prepared and evaluated the data extraction format. The format emphasised the following aspects: types of care models, health care setting, country, definition of care models, multimorbid diseases, elements or components of care models, impacts or outcomes of care models, barriers or challenges of care models, and facilitators or strategies of care models. AE charted data from the included sources of evidence in duplicates. Any discrepancies were checked with YA. When discrepancies were found, AE and YA reviewed the extracted data alongside the sources and made necessary corrections.
Synthesis of results
Data synthesis was done based on the objectives. Similar or unique findings were gathered and was provided qualitative meanings in relation to the meaning of care models for individuals with multimorbidity and its elements, outcomes, barriers, and facilitators. The WHO health system framework was used to synthesise findings on elements, outcomes, barriers, and facilitators of care models. This framework has six system building blocks and eight overall goals/outcomes. The system building blocks are service delivery, health workforce, information, medical products, vaccines & technologies, financing, and leadership/governance, which guided us in framing elements, barriers, and facilitators of care models. Community engagement and multisectoral policy and action were also considered in the data extraction and synthesis. These dimensions were included because primary health care encompasses community engagement and multisectoral action as one of its aspects. The overall goals/outcomes include access, coverage, quality, safety, improved health (level and equity), responsiveness, social and financial risk protection, and improved efficiency. We used these goals/outcomes to synthesise the outcomes or impacts of care models [28]. Additionally, we considered outcomes beyond health system frameworks.
Results
Selection of sources of evidence
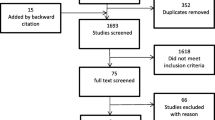
A total of 3,830 articles were collected from databases (PubMed = 555, Web of Science = 637, EMBASE = 908, and SCOPUS = 1,682) and Google Scholar (n = 48). Of these, 1,322 articles were excluded due to duplicates. After title and abstract screening, 137 articles were eligible for full text. Finally, 54 articles fulfilled the eligibility criteria for data extraction (Fig. 1).
Models of care for patients with multiple chronic health conditions
A care model represents collective interventions in the healthcare delivery process aimed at achieving desired outcomes, named based on core activities or responsibilities, involving healthcare teams, disease conditions, eligible clients, purposes, and services settings. Examples include, Integrated, Collaborative, Integrated-Collaborative, Guided, and NCMs. Geriatric Care, All-inclusive Care Model for the Elderly, and Geriatric Patient-Aligned Care (GeriPACT) Teams (based on eligible clients), the IMPACT clinic (based on the role of health workers and eligible patients). Chronic Care Model (based on disease conditions), and Care Management Plus, Value Stream Mapping, Preventive Home Visits, and Transition Care (based on the types of services provided).
Meaningful care models are developed through collective understanding of contexts (such as identifying eligible clients and selecting healthcare settings), organizing healthcare team, and providing health services. Additionally, they involve accessing community resources, arranging financial issues, utilizing health information systems, and setting measurable outcomes [29, 30].
Types of care models
Integrated Model of Care (IMC) [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51]
The IMC has been implemented across Europe, Spain, Italy, Canada, the United States, Australia, China, and Taiwan, with related initiatives like Canada’s PRISMA program. This model operates in various settings, including hospitals, community geriatric units, chronic disease clinics, and nursing homes. Essential components of the IMC include organizational arrangements, patient recruitment, multidisciplinary team collaboration, comprehensive service delivery, financial management, and the use of information communication technology-based platforms like e-health records. Specifically, teams comprise case managers, physicians, specialists, pharmacists, geriatric practitioners, general practitioners, social workers, psychologists, project managers, and occupational therapists. Service delivery involves assessments, care planning, management, follow-ups, medication reviews, care coordination, patient empowerment, self-management, and effective communication.
The impacts of the IMC are significant, leading to improved quality of care, better health outcomes, cost efficiency, and enhanced patient satisfaction. However, challenges include resource allocation, team coordination and communication, service integration, technological barriers, and policy and regulatory hurdles. Facilitators for successful implementation include strong leadership and governance, supportive policies, continuous professional training, access to community and social resources, adequate financial support, and effective use of health information systems and digital tools. These elements underscore the comprehensive nature of the IMC and highlight the coordinated efforts needed to meet the complex healthcare needs of patients with multiple long-term conditions.
Collaborative care model (CCM) [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60]
The CCM has been studied in various settings, including a safety net clinic for low-income Hispanic patients, primary care clinics in the USA, general practices in Australia, and Northwest England. It involves selectively engaging healthcare professionals based on their roles and contributions. For instance, social workers, psychiatrists, and primary care physicians (PCPs) are involved in managing depression and diabetes. In these cases, bilingual social work specialists and PCPs deliver problem-solving therapy and prescribe antidepressants, respectively. While social workers and PCPs play primary roles, they receive supervision from higher-level professionals, with psychiatrists providing telephone consultations for medication management. In managing diabetes and coronary heart disease, practice nurses and psychological practitioners deliver case management and low-intensity psychological treatment.
Essential components of the CCM include a well-trained health workforce, a multidisciplinary team, case management, comprehensive assessments, care planning, drug prescriptions, problem-solving therapy, and psychological therapy. It emphasizes client support, including self-care with pharmacotherapy, guideline-based drug preferences, motivational coaching, self-monitoring materials, and follow-up activities. Monthly telephone follow-ups, bi-weekly visits, outreach visits, and weekly case review meetings are integral to this model. The impacts of the model include improved patient care coordination and treatment outcomes. However, challenges such as ensuring adequate training, maintaining effective collaboration among diverse professionals, and managing communication barriers must be addressed. Facilitators for this model include strong leadership, continuous professional training, and supportive policies to ensure effective implementation. CCM improved quality of care (client satisfaction, recovery), increased recipient of treatment, reduced costs of care, and improved quality of life. In contrast, this care model was not effective on pain management among individuals with depression and musculoskeletal problems, as well as in improving depression among individuals with diabetes or cardiovascular diseases.
Integrated-collaborative care model (ICCM) [61]
The ICCM evaluated in general practices in northwestern England, aims to address the needs of individuals dealing with depression and chronic conditions like diabetes or cardiovascular disease. This model operates through two distinct intervention phases. Initially, collaborative care is provided by psychological practitioners, focusing on psychological well-being and symptom management. Subsequently, care is integrated jointly with the practice nurse, emphasizing comprehensive patient assessment, care plan development, and various symptom management techniques such as behavioral activation and cognitive restructuring. Key components also include training for psychological practitioners, collaborative care meetings involving patients, practitioners, nurses, and general practitioners for medication management, as well as rigorous monitoring and supervision by experienced psychological therapists on a weekly basis.
The model underscores the importance of follow-up care, with weekly follow-ups for clients facing more complex issues and monthly follow-ups for others. Implementations typically occur within general practice clinics or psychological therapy centers, ensuring accessibility and consistency in the treatment environment. While the Integrated CCM has shown positive impacts on patient outcomes, challenges include ensuring adequate training for practitioners, fostering effective collaboration among team members, and managing the coordination of care across different settings. Facilitators for successful implementation encompass robust training programs, effective communication strategies, supportive leadership, and patient engagement. These elements are crucial for optimizing care delivery and addressing the multifaceted needs of individuals with depression and long-term physical conditions within the Integrated CCM framework. IMC improve quality of care (client satisfaction and recovery), accessibility (increased patient’s clinical visits), patient-centredness communication between levels of care, safety (reduce medication errors and facilitate home death), efficiency (shorten hospitalization and reduced unnecessary services uses), quality of life, and foster self-management. However, this model did not yield in significant differences in quality of life, self-efficacy, disability, and social support.
Guided care mode (GCM) [62,63,64]
The GCM, implemented in primary care offices in the USA, comprises several essential components aimed at improving patient care. These elements, viewed as guiding principles, include meticulous planning, comprehensive training for healthcare providers, and thorough patient assessment primarily conducted by nurses. Collaboration among interdisciplinary team members, including nurses, physicians, patients, and caregivers, is emphasized to ensure holistic care delivery. Central to the model is the development of personalized care plans tailored to each patient’s needs, alongside disease or case management services provided by the healthcare team. Regular follow-up, monitoring, and evaluation are integral to track patient progress and adjust care plans accordingly. Additionally, the model emphasizes support for patient self-management, encompassing lifestyle modifications, as well as coordination of care among healthcare professionals and seamless transitions between care settings. Adequate allocation of resources is also highlighted to ensure the effective implementation of the model.
The GCM has significant impacts on patient outcomes, including improved quality of care, enhanced patient satisfaction, and better health outcomes. However, challenges exist, such as ensuring sufficient training for healthcare providers, fostering effective collaboration among team members, and managing the coordination of care across various healthcare settings. Facilitators for successful implementation include robust planning processes, comprehensive training programs, effective communication strategies, and access to adequate resources. Additionally, supportive policies and leadership, alongside patient and caregiver engagement, are crucial for overcoming challenges and optimizing the delivery of care within the GCM framework. GCM increased quality of care and acceptability of services.
Nurse-led care model (NCM) [65,66,67]
This model was developed with a multidisciplinary team in Australia to support continuity of care at the primary-secondary interface for people with multimorbidity. NCM, led by nursing professionals, was also evaluated in Japan, the USA, Canada, UK, Australia, Netherlands, New Zealand, and Slovenia. Elements were coordination, governance, communication, culture, health assessment, develop care process or care plan (e.g., self-management action plan), collaboration (patient and care provider), clinical best practice and interventions (psychological support), evaluation & improvement, and systems, processes and resources. Multidisciplinary involvement was also emphasised in this care model i.e., coordinated multidisciplinary intervention. NCM was acceptable to physician, patients, and caregivers and transferrable to other health care settings.
Chronic model of care (CMC)
It was implemented for multiple chronic conditions in primary care and promoting effective advance care for elders in the USA. The first step in adopting CMC is healthcare organization, involving leadership, incentives, resources, support, and area agency. Number of clinics, number of physicians, number of physicians per clinic, types of specialities, years of physician’s experiences, productivity per month, payer by clinic, intermountain health plan are part of the organization. Care delivery redesign is the second major element that includes care management encounters, face to face visits, telephone calls, coordination, and care conferences. Self -management support includes education sessions and motivation of patient. Electronic accesses and connection to external programs are involved as part of connection to community. Using protocols was part of support for evidence-based practice. Monthly information system usage used for access, best practice support, and communication by participating care managers and physicians [68]. The Promoting Effective Advance Care for Elders (PEACE) [69] model, which was evaluated in the USA, utilised CMC’s interventions.
Several care models have been explored but are not frequently investigated. The Geriatric Care model, developed in the Netherlands, focuses on enhancing the health conditions of the elderly [70]. The Geriatric Care model did not effectively improve quality of life, functional limitations, self-rated health, psychological wellbeing, social functioning, or reduce hospitalizations [70]. In the USA, the All-inclusive Care for the Elderly (PACE) model [71], Care Coordination [60], and Care management Plus [72] were evaluated .The IMPACT clinic [73] and Value stream mapping [74] in Canada represents an innovative model of interprofessional primary care for community-dwelling seniors and patient waiting time enhancement model, respectively. The Preventive Home Visit in Japan involves the assessment of locomotion, daily activities, social contacts or relationships with other people, health conditions, and signs of abuse by community health nurses, care managers, or social workers [75]. Lastly, Transitional Care conducted in Chile involves a transition nurse who establishes a transition office, communicates via email, identifies patients, and reviewing clinical records [76]. The overview of common care models with their essential components, impacts, challenges, and facilitators are presented in Table 1.
Discussion
This review maps the available care models and their elements, impact, implementation barriers and facilitators. All available care models were from high-income countries (the USA, Netherlands, Canada, Australia, England, Japan, and Chile), and an upper-middle-income country (China). The discussion focuses on which and how the applicability and adaptability of care model are likely in the low-income country’s contexts.
The available care models have been implemented across various settings, from home to hospital levels. In high-income countries, home care is feasible due to the large elderly population and consistent support from the governments, such as Medicare [71]. For instance, in Australia, 4.2 million (16%) of the population are aged 65 years and above as of June 2020 [77]. Additionally, proactive healthcare services, such as eligibility assessments conducted at homes of elderly individuals by interdisciplinary teams that include geriatric experts, have been established in high-income countries but are largely absent in low-income countries. Notably, models like the All-inclusive Care for the Elderly [71], the ‘Geriatric Care model’ [70], and the IMPACT clinic [73] are specifically designed for community-dwelling seniors or elderly individuals in high-income countries.
However, assessing eligibility for elderly care and identifying health issues at homes of elderly individuals before they seek care at health institutions can be resource-intensive, particularly in the absence of financial support from the government or other sources. In high-income countries, such as Australia, the government provides subsidised aged care services, including residential care and home care, while also regulating the aged care sector [78]. Furthermore, the availability of well-established residences for aged care and retirement communities may be conducive to implementing multidisciplinary, elderly-focused care models [79]. Hence, such care models could be adopted in other high-income countries due to their effectiveness in reducing institution-based service utilization [71], adaptability, acceptability, and feasibility [73].
In contrast, in low-income countries, despite the presence of a non-negligible number of elderly populations (for instance, in Ethiopia, 3.0% of the population is aged 65 years and above in 2022 [80]), there was no system specifically designed for the elderly populations, no dedicated geriatric specialists, and no established financial support schemes. Instead, individuals with multimorbidity, regardless of their age and other constraints, regularly seek care in primary care settings with or without appointments. These visits occur either as frequent follow-ups or new health concerns, aligning with their specific needs in low-income countries [81]. As a result, an elderly-focused approach to care models is less likely to be effectively implemented in low-income countries. These countries require political and policy initiatives to develop strategies that address the needs of their growing aged populations.
In most care models, effective leadership, financial support, health information technologies, health workforce teams, and service delivery perspectives were essential, in addition to considering the population and overall country context. The WHO’s framework for integrated, people centred care supports the current findings, as that framework was developed to be adapted and implemented in low- or high-income countries [23]. Community engagement, governance, reorientation of the model of care, services coordination within and across sectors, and creation of an enabling environment [23]. Aligning with this WHO’s framework, selecting and adapting appropriate care models is crucial for managing chronic diseases in low-income countries. Taking Ethiopia as an example, Ethiopia has developed a national strategy to address chronic diseases [82]. Similar to people-centred care [23], strategies such as strengthening national health policy and chronic diseases governance, promoting multisectoral coordination, enhancing integrated health service delivery, developing multidisciplinary team, and improving infrastructure are included in chronic disease management strategic document [82].
The implementation of various care models critically depends on how teams are built, and roles and responsibilities are allocated. This underscores the importance of understanding how multidisciplinary teams interact to provide services for individuals with multimorbidity. When implementing care models, teams may take one or more approaches: collaborative efforts towards a common goal (interdisciplinary team) or independently work within their respective disciplines to create tailored plans to their expertise (multidisciplinary team) [83]. The Integrated, Collaborative, Guided, Nurse-led, Geriatric, PACE, and IMPACT Care models require two or more healthcare professionals. The difference lies in which specific field of study the team members come from and how they interact in delivering the services. Team composition with clearly defined roles and responsibilities may depend on the types of care, diseases nature, and level of health care (home care, primary care, secondary care, or tertiary care) that aimed at ensuring effective care delivery. For the GCM [62,63,64], only nurses and physicians were team members. In contrast, NCMs included nurses with different education levels, such as nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialist, and advanced nurse specialists [65,66,67]. In this model, the nurses took on leadership roles [66]. Ideally, involving professionals from only two disciplines (nurses and physicians) can be cost effective and feasible, especially in the absence of other professionals. However, this approach may require extensive training or task-shifting for the team to address the comprehensive needs of clients with multiple conditions. Nurses could replace physician if they received appropriate training [84].
Collaboration of healthcare teams is crucial in all care models though there is some confusion regarding integration. For instance, the IMC and CCM often emphasize collaboration, which can cause confusion. Both models of care require effective leadership, multidisciplinary teams, financial support, and client and caregiver engagement. While integration necessitates collaboration, the reverse is not true: collaboration does not require integration as a precondition [85]. In the IMC, shared decision between teams may be required at certain intersection points. For instance, in an IMC within ambulatory care setting of a hospital in Taiwan [36], the case manager and pharmacist independently conduct comprehensive assessments and medication review, respectively, as the initial step. Next, they cooperate and jointly make recommendations. The physician then reconciles team’s decision and provides recommendation based on teams’ input and the client’s preferences. Finally, the case manager takes responsibility for follow-up care. Comparably in another study, IMC has passed some steps: intake screen by physician, care coordination screen by occupational therapists, orientation about care delivery process by nurse, multidisciplinary care appointment by multidisciplinary team, integrated care phase by team, transition phase by occupational therapist, and discharge phase by physician [39]. In contrast, the CCM requires teams work collaboratively, aligned with their expertise, towards common interests. For instance, bilingual graduate social work diabetes depression clinical specialists (DDCSs) and PCPs independently perform their roles. Meanwhile, psychiatrists supervised DDCSs and PCPs via telephone in a weekly basis [53]. Similarly, in another CCM, nurses develop care plans, follow-up clients, and provide self-care training for patients, while PCP prescribes drugs. Nurses in this model are supervised by psychiatrists, PCPs, and psychologists [54]. These implies that implementation of care models is varied and need careful understanding despite having many identical elements.
As for the implication of the review findings, care models for multimorbidity were rarely implemented and evaluated in low-income countries. However, considering the WHO’s integrated, people-centred care approach [23] and the national health plans in low-income countries (e.g., Ethiopia) [82], when we see the implications of each care model, the IMC emerges as the most suitable choice. For instance, in Ethiopia, it holds a prominent position at the Ministry of Health level, and some health facilities have already initiated integrated care for non-communicable diseases at the primary health care level. These initiatives involve practices such as task shifting, task sharing, and improving referral networks. Additionally, families are actively engaged, health care settings are reoriented and multidisciplinary teams—including general practitioners, nurses, and pharmacists—are established [81, 82]. This alignment with leadership support and the availability of functional clinics positions the IMC favourably for evaluating its implementation. Notably, challenges related to building interdisciplinary team, financial system integration (including funds, incentives, and health insurance), and resource allocation [41] may be unlikely to hinder its adoption in Ethiopia, given the national strategic plan’s endorsement.
However, the evaluation of the implementation process that requires strategical and operational plans is critical to understand the forms of integration. Integration could be organisational, professional, cultural, or technological at macro-, meso- and micro level for a whole population group or specific client group [86]. Additionally, it requires attention on how integrated care delivery is organised and provided. Horizontal integration aims to provide comprehensive services for clients by multidisciplinary team, and vertical integration focuses on improving referrals between different hierarchical care levels [87]. It is also necessitates to clearly demonstrate how care co-ordination and fully integrated teams are functions [86]. Furthermore, effective interventions may be introduced into the existing IMC. For instance, Care Coordination was initiated in the exiting IMC. There was a subspeciality-trained nurse led care coordination for patients with complex health profiles in inpatient and outpatient settings in an already available integrated health care system involving care coordinators (all nurses), social workers, and administrative support person [60].
Limitation
Articles conducted and published in English were included. However, there may be other studies conducted in languages other than English. The search strategy did not incorporate database-specific indexed terms (e.g., MeSH terms for PubMed), which is another limitation because it may result in missing relevant articles indexed under these terms. Search for articles and title screening were conducted by a sole author, even though each activity were discussed during the weekly meeting.
Conclusions
The review and analysis of various care models reveals a comprehensive approach to improving healthcare delivery across diverse settings. Each model, whether integrated, collaborative, nurse-led, or specific to chronic and geriatric care, demonstrates significant potential for enhancing quality of care, health outcomes, cost efficiency, and patient satisfaction. The success of these models hinges on addressing common challenges such as resource allocation, team coordination, and technological barriers. Key facilitators like strong leadership, supportive policies, continuous professional training, and robust communication strategies are crucial for overcoming these challenges and ensuring effective implementation. As healthcare systems worldwide continue to evolve, these models offer valuable insights and frameworks that can be adapted and scaled to meet the unique needs of different populations, ultimately leading to more integrated, efficient, and patient-centred care.
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- CCM:
-
Collaborative Care Model
- CMC:
-
Chronic Model of Care
- DDCSs:
-
Diabetes Depression Clinical Specialists
- GCM:
-
Guided Care Mode
- GeriPACT:
-
Geriatric Patient-Aligned Care Teams
- ICCM:
-
Integrated-Collaborative Care Model
- ICM:
-
Integrated Model of Care
- NCM:
-
Nurse-led Care Model
- PACE:
-
The All-inclusive Care for the Elderly
- PCPs:
-
Primary Care Physicians
- PEACE:
-
Promoting Effective Advance Care for Elders
- PRISMA-ScR:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Extension for Scoping Reviews guideline
- USA:
-
United States of America
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Le Reste JY, Nabbe P, Manceau B, Lygidakis C, Doerr C, Lingner H, et al. The European General Practice Research Network presents a comprehensive definition of multimorbidity in family medicine and long term care, following a systematic review of relevant literature. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2013;14(5):319–25.
Tan MM, Barbosa MG, Pinho PJ, Assefa E, Keinert AÁ, Hanlon C et al. Determinants of multimorbidity in low-and middle‐income countries: a systematic review of longitudinal studies and discovery of evidence gaps. Obes Rev. 2023:e13661.
Chowdhury SR, Das DC, Sunna TC, Beyene J, Hossain A. Global and regional prevalence of multimorbidity in the adult population in community settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine. 2023;57.
Hu Y, Wang Z, He H, Pan L, Tu J, Shan G. Prevalence and patterns of Multimorbidity in China during 2002–2022: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. 2023:102165.
Ahmed A, Khan HT, Lawal M. Systematic literature review of the prevalence, pattern, and determinant of multimorbidity among older adults in Nigeria. Health Serv Res Managerial Epidemiol. 2023;10:23333928231178774.
Kamp M, Achilonu O, Kisiangani I, Nderitu DM, Mpangase PT, Tadesse GA, et al. Multimorbidity in African ancestry populations: a scoping review. BMJ Global Health. 2023;8(12):e013509.
Tazzeo C, Zucchelli A, Vetrano DL, Demurtas J, Smith L, Schoene D et al. Risk factors for Multimorbidity in adulthood: a systematic review. Ageing Res Rev. 2023:102039.
Edeh-Asogwa OA, Quansah DY, Boakye D, Ezewuiro O, Boateng D. Prevalence, patterns, and determinants of multimorbidity among childhood and adult cancer survivors: a systematic review. Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol. 2023:104147.
Ahmad TA, Gopal DP, Chelala C, Ullah AZD, Taylor SJ. Multimorbidity in people living with and beyond cancer: a scoping review. Am J Cancer Res. 2023;13(9):4346.
Nistor P, Chang-Kit B, Nicholson K, Anderson KK, Stranges S. The relationship between sleep health and multimorbidity in community dwelling populations: systematic review and global perspectives. Sleep Med. 2023.
Kantilafti M, Giannakou K, Chrysostomou S. Multimorbidity and food insecurity in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2023;18(7):e0288063.
Zhou Y, Jin Y, Zhu Y, Fang W, Dai X, Lim C, et al. Sleep problems associate with multimorbidity: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Public Health Rev. 2023;44:1605469.
Delpino FM, dos Santos Rodrigues AP, Petarli GB, Machado KP, Flores TR, Batista SR, et al. Overweight, obesity and risk of multimorbidity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Obes Rev. 2023;24(6):e13562.
Obasohan PE, Walters SJ, Jacques R, Khatab K. Risk factors Associated with Multimorbidity among children aged under-five years in Sub-saharan African countries: a scoping review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(2):1377.
Marsland I, Sobala R, De Soyza A, Witham M. Multimorbidity in bronchiectasis: a systematic scoping review. ERJ Open Res. 2023;9(1).
Khunti K, Chudasama YV, Gregg EW, Kamkuemah M, Misra S, Suls J, et al. Diabetes and multiple long-term conditions: a review of our current Global Health Challenge. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(12):2092–101.
Hajek A, Kretzler B, König H-H. Multimorbidity, loneliness, and social isolation: a systematic review. Loneliness and Social Isolation in Old Age. 2023:150 – 69.
Stirland LE, González-Saavedra L, Mullin DS, Ritchie CW, Muniz-Terrera G, Russ TC. Measuring multimorbidity beyond counting diseases: systematic review of community and population studies and guide to index choice. BMJ. 2020;368.
Bestman PL, Kolleh EM, Moeng E, Brhane T, Nget M, Luo J. Association between multimorbidity of pregnancy and adverse birth outcomes: a systemic review and Meta-analysis. Prev Med. 2024:107872.
Bellass S, Scharf T, Errington L, Bowden Davies K, Robinson S, Runacres A, et al. Experiences of hospital care for people with multiple long-term conditions: a scoping review of qualitative research. BMC Med. 2024;22(1):25.
Van der Aa MJ, van den Broeke JR, Stronks K, Plochg T. Patients with multimorbidity and their experiences with the healthcare process: a scoping review. J Comorbidity. 2017;7(1):11–21.
De Maeseneer J, Willems S, De Sutter A, Van de Geuchte I, Billings M. Primary health care as a strategy for achieving equitable care: a literature review commissioned by the Health Systems Knowledge Network. 2007.
World Health Organization. Integrated people-centred care: World Health Organization,; [updated 2024; cited 2024 11 Jul]. https://www.who.int/health-topics/integrated-people-centered-care#tab=tab_2.
Nicholson CJ, Combes S, Mold F, King H, Green R. Addressing inequity in palliative care provision for older people living with multimorbidity. Perspectives of community-dwelling older people on their palliative care needs: a scoping review. Palliat Med. 2023;37(4):475–97.
Bayliss EA, Edwards AE, Steiner JF, Main DS. Processes of care desired by elderly patients with multimorbidities. Fam Pract. 2008;25(4):287–93.
Tricco A, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien K, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
World Health Organization. Everybody’s business -- strengthening health systems to improve health outcomes: WHO’s Framework for Action Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. 2007 [cited 2024 11 Jul]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/everybody-s-business----strengthening-health-systems-to-improve-health-outcomes.
Palmer K, Marengoni A, Forjaz MJ, Jureviciene E, Laatikainen T, Mammarella F, et al. editors. Multimorbidity care model: recommendations from the consensus meeting of the Joint Action on Chronic diseases and promoting healthy ageing across the life cycle. JA-CHRODIS). Health Policy;; 2018.
Stokes J, Man MS, Guthrie B, Mercer SW, Salisbury C, Bower P. The foundations framework for developing and reporting new models of care for multimorbidity. Ann Fam Med. 2017;15(6):570–7.
Bogner HR, de Vries HF. Integrating type 2 diabetes mellitus and depression treatment among African americans. Diabetes Educ. 2010;36(2):284–92.
Csanádi M, Kaló Z, Rutten-van Molken M, Looman W, Huic M, Ercevic D, et al. Prioritization of implementation barriers related to integrated care models in Central and Eastern European countries. Health Policy. 2022;126(11):1173–9.
Ho SB, Bräu N, Cheung R, Liu L, Sanchez C, Sklar M, et al. Integrated Care Increases Treatment and improves outcomes of patients with chronic Hepatitis C virus infection and Psychiatric illness or substance abuse. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13(11):2005–e143.
Jauregui ML, Silvestre C, Valdes P, Gaminde I. Qualitative evaluation of the implementation of an Integrated Care Delivery Model for chronic patients with Multi-morbidity in the Basque Country. Int J Integr Care. 2016;16.
Lo C, Zimbudzi E, Teede H, Cass A, Fulcher G, Gallagher M, et al. Models of care for co-morbid diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Nephrology. 2018;23(8):711–7.
Lo YT, Chen MH, Chen PH, Lu FH, Chang CM, Yang YC. Effectiveness of an Integrated Ambulatory Care Program in Health Care and Medication Use in patients with multimorbidity and polypharmacy. Qual Saf Health Care. 2024;33(1):18–28.
Mas MA, Miralles R, Heras C, Ulldemolins MJ, Bonet JM, Prat N et al. Designing a Person-Centred Integrated Care Programme for people with Complex Chronic conditions: a Case Study from Catalonia. Int J Integr Care. 2021;21(4).
Piñeiro-Fernández JC, Fernández-Rial A, Suárez-Gil R, Martínez-García M, García-Trincado B, Suárez-Piñera A, et al. Evaluation of a patient-centered integrated care program for individuals with frequent hospital readmissions and multimorbidity. Intern Emerg Med. 2022;17(3):789–97.
Sampalli T, Fox RA, Dickson R, Fox J. Proposed model of integrated care to improve health outcomes for individuals with multimorbidities. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2012;6:757–64.
Shakib S, Dundon BK, Maddison J, Thomas J, Stanners M, Caughey GE et al. Effect of a Multidisciplinary Outpatient Model of Care on Health outcomes in older patients with multimorbidity: a retrospective Case Control Study. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(8).
Wu J, Xue E, Huang S, Fu Y, Chen D, Shao J, et al. Facilitators and Barriers of Integrated Care for older adults with multimorbidity: a descriptive qualitative study. Clin Interv Aging. 2023;18:1973–83.
Bernabei R, Landi F, Gambassi G, Sgadari A, Zuccala G, Mor V, et al. Randomised trial of impact of model of integrated care and case management for older people living in the community. BMJ. 1998;316(7141):1348.
Landi F, Lattanzio F, Gambassi G, Zuccala G, Sgadari A, Panfilo M, et al. A model for integrated home care of frail older patients: the Silver Network Project. Aging Clin Exp Res. 1999;11:262–72.
Melchiorre MG, Papa R, Quattrini S, Lamura G, Barbabella F, Consortium IE. Integrated care programs for people with multimorbidity in European countries: eHealth adoption in health systems. BioMed Research International. 2020;2020.
Park G, Miller D, Tien G, Sheppard I, Bernard M. Supporting frail seniors through a family physician and Home Health integrated care model in Fraser Health. Int J Integr Care. 2014;14.
Rosenberg T. Acute hospital use, nursing home placement, and mortality in a frail community-dwelling cohort managed with Primary Integrated Interdisciplinary Elder Care at Home. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60(7):1340–6.
Mateo-Abad M, González N, Fullaondo A, Merino M, Azkargorta L, Giné A et al. Impact of the CareWell integrated care model for older patients with multimorbidity: a quasi-experimental controlled study in the Basque Country. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1).
Bird SR, Kurowski W, Dickman GK, Kronborg I. Integrated care facilitation for older patients with complex health care needs reduces hospital demand. Aust Health Rev. 2007;31(3):451–61.
Hébert R, Durand PJ, Dubuc N, Tourigny A, Group P. Frail elderly patients. New model for integrated service delivery. Can Fam Physician. 2003;49(8):992–7.
Hébert R, Raîche M, Dubois M-F, Gueye NDR, Dubuc N, Tousignant M, et al. Impact of PRISMA, a coordination-type integrated service delivery system for frail older people in Quebec (Canada): a quasi-experimental study. Journals Gerontol Ser B: Psychol Sci Social Sci. 2010;65(1):107–18.
Mesa-Melgarejo L, Carreño Moreno S, Chaparro-Diaz L, Quintero González LA, Garcia-Quintero D, Carrillo-Algarra AJ, et al. Effectiveness of a case management model for people with multimorbidity: mixed methods study. J Adv Nurs. 2022;78(11):3830–46.
Camacho EM, Ntais D, Coventry P, Bower P, Lovell K, Chew-Graham C et al. Long-term cost-effectiveness of collaborative care (vs usual care) for people with depression and comorbid diabetes or cardiovascular disease: a Markov model informed by the COINCIDE randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2016;6(10).
Ell K, Katon W, Xie B, Lee P-J, Kapetanovic S, Guterman J, et al. Collaborative care management of major depression among low-income, predominantly hispanic subjects with diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(4):706–13.
Katon WJ, Lin EH, Von Korff M, Ciechanowski P, Ludman EJ, Young B, et al. Collaborative care for patients with depression and chronic illnesses. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(27):2611–20.
Katon W, Russo J, Lin EHB, Schmittdiel J, Ciechanowski P, Ludman E, et al. Cost-effectiveness of a Multicondition Collaborative Care intervention < i > a Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69(5):506–14.
Katon WJ, Von Korff M, Lin EH, Simon G, Ludman E, Russo J, et al. The pathways study: a randomized trial of collaborative care in patients with diabetesand depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61(10):1042–9.
Lin EH, Von Korff M, Peterson D, Ludman EJ, Ciechanowski P, Katon W. Population targeting and durability of multimorbidity collaborative care management. Am J Manag Care. 2014;20(11):887.
Morgan MA, Coates MJ, Dunbar JA. Using care plans to better manage multimorbidity. Australasian Med J. 2015;8(6):208.
Hamberger LK, Hindman M. Collaborative care of a patient with multiple, chronic physical and emotional health problems. Clin Case Stud. 2005;4(2):139–59.
Berry LL, Rock BL, Houskamp BS, Brueggeman J, Tucker L, editors. Care coordination for patients with complex health profiles in inpatient and outpatient settings. Mayo Clinic Proceedings; 2013: Elsevier.
Coventry P, Lovell K, Dickens C, Bower P, Chew-Graham C, McElvenny D et al. Integrated primary care for patients with mental and physical multimorbidity: cluster randomised controlled trial of collaborative care for patients with depression comorbid with diabetes or cardiovascular disease. BMJ. 2015;350.
Boyd CM, Boult C, Shadmi E, Leff B, Brager R, Dunbar L, et al. Guided care for multimorbid older adults. Gerontologist. 2007;47(5):697–704.
Boult C, Reider L, Frey K, Leff B, Boyd CM, Wolff JL, et al. Early effects of guided care on the quality of health care for multimorbid older persons: a cluster-randomized controlled trial. J Gerontol Biol Sci Med Sci. 2008;63(3):321–7.
Boyd CM, Shadmi E, Conwell LJ, Griswold M, Leff B, Brager R, et al. A pilot test of the effect of guided care on the quality of primary care experiences for multimorbid older adults. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23:536–42.
Davis KM, Eckert MC, Hutchinson A, Harmon J, Sharplin G, Shakib S, et al. Continuity of care for people with multimorbidity: the development of a model for a nurse-led care coordination service. Australian J Adv Nurs. 2020;37(4):7–19.
Kazawa K, Moriyama M. Community-based Advanced Case Management for patients with Complex Multimorbidity and High Medical Dependence: a longitudinal study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(13).
Gordon K, Delacy J, Gray CS, Seto E, Dainty KN. Nurse-led models of care for patients with Complex Chronic conditions: a scoping review. Nurs Leadersh. 2019;32(3):57–76.
Dorr DA, Wilcox A, Burns L, Brunker CP, Narus SP, Clayton PD. Implementing a multidisease chronic care model in primary care using people and technology. Dis Manag. 2006;9(1):1–15.
Allen KR, Hazelett SE, Radwany S, Ertle D, Fosnight SM, Moore PS. The promoting effective Advance Care for elders (PEACE) randomized pilot study: theoretical framework and study design. Popul Health Manage. 2012;15(2):71–7.
Hoogendijk EO, Van Der Horst HE, Van De Ven PM, Twisk JW, Deeg DJ, Frijters DH, et al. Effectiveness of a geriatric care model for frail older adults in primary care: results from a stepped wedge cluster randomized trial. Eur J Intern Med. 2016;28:43–51.
Eng C, Pedulla J, Eleazer GP, McCann R, Fox N. Program of all-inclusive care for the Elderly (PACE): an innovative model of integrated geriatric care and financing. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997;45(2):223–32.
Dorr DA, Wilcox AB, Brunker CP, Burdon RE, Donnelly SM. The Effect of Technology-Supported, Multidisease Care Management on the mortality and hospitalization of seniors. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(12):2195–202.
Tracy CS, Bell SH, Nickell LA, Charles J, Upshur RE. The IMPACT clinic: innovative model of interprofessional primary care for elderly patients with complex health care needs. Can Fam Physician. 2013;59(3):e148–55.
Sampalli T, Desy M, Dhir M, Edwards L, Dickson R, Blackmore G. Improving wait times to care for individuals with multimorbidities and complex conditions using value stream mapping. Int J Health Policy Manage. 2015;4(7):459.
Kono A, Kanaya Y, Fujita T, Tsumura C, Kondo T, Kushiyama K, et al. Effects of a preventive home visit program in ambulatory frail older people: a randomized controlled trial. Journals Gerontol Ser A: Biomedical Sci Med Sci. 2012;67(3):302–9.
Varela T, Zamorano P, Muñoz P, Espinoza M, Tellez A, Irazoqui E, et al. Evaluation of a transitional care strategy implemented in adults with high-risk and multimorbidity in Chile. Value Health Reg Issues. 2023;38:85–92.
Welfare AGAIoHa. Older Australians Australia [updated 28 June 2023. https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/older-people/older-australians/contents/demographic-profile.
Australian Government: Department of Health and Aged Care. The Australian health system 2019 [updated 19 June 2019. https://www.health.gov.au/about-us/the-australian-health-system.
Queensland Government. Housing and aged care 2024 [ https://www.qld.gov.au/seniors/home-support-housing/housing-aged-care.
The World Bank. Population ages 65 and above (% of total population) - Ethiopia 2022 [ https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.65UP.TO.ZS?locations=ET.
Organization WH, Ethiopia. Transforming Chronic Disease Care: WHO Regional Office for Africa; 2023 [ https://www.afro.who.int/countries/ethiopia/news/transforming-chronic-disease-care.
Ministry of Health Ethiopia. Strategy on Prevention and Control of Cardiovascular Diseases, Diabetes Mellitus, chronic kidney diseases and Chronic Respiratory diseases. July 2020 Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Choi BC, Pak AW. Multidisciplinarity, interdisciplinarity and transdisciplinarity in health research, services, education and policy: 1. Definitions, objectives, and evidence of effectiveness. Clin Invest Med. 2006;29(6).
Martínez-González NA, Tandjung R, Djalali S, Rosemann T. The impact of physician–nurse task shifting in primary care on the course of disease: a systematic review. Hum Resour Health. 2015;13:1–14.
Boon HS, Mior SA, Barnsley J, Ashbury FD, Haig R. The difference between integration and collaboration in patient care: results from key informant interviews working in multiprofessional health care teams. J Manip Physiol Ther. 2009;32(9):715–22.
Armitage GD, Suter E, Oelke ND, Adair CE. Health systems integration: state of the evidence. Int J Integr care. 2009;9.
Leutz WN. Five laws for integrating medical and social services: lessons from the United States and the United Kingdom. Milbank Q. 1999;77(1):77–110.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Authors have no received fund to conduct this specific review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YA and AE conceptualised the project. AE extracted data, write the first draft and subsequent revision. YA supervised the whole research process, checked extracted data and edit the manuscript. AZ and EW revised the manuscript. All the authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable because the review was dependent on secondary resources from published articles and did not collect data from human participants.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Endalamaw, A., Zewdie, A., Wolka, E. et al. Care models for individuals with chronic multimorbidity: lessons for low- and middle-income countries. BMC Health Serv Res 24, 895 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11351-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11351-y